Calculations of stability of alloyed cementite from valance electron structure
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2017年第2期
论文作者:刘宏玉 王红军 刘礼 曾晓宇 卢建夺 林冲 徐红兵
文章页码:259 - 269
Key words:valence electron structure; alloyed cementite; stability; density of lattice electrons; symmetry of bonds; bond energy
Abstract: Based on the empirical electronic theory of solids and molecules (EET), the actual model for unit cell of cementite (θ-Fe3C) was built and the valence electron structures (VES) of cementite with specified site and a number of Fe atoms substituted by alloying atoms of M ( M=Cr, V, W, Mo, Mn ) were computed by statistical method. By defining P as the stability factor, the stability of alloyed cementite with different numbers and sites of Fe atoms substituted by M was calculated. Calculation results show that the density of lattice electrons, the symmetry of distribution of covalent electron pairs and bond energy have huge influence on the stability of alloyed cementite. It is more stable as M substitutes for Fe2 than for Fe1. The alloyed cementite is the most stable when Cr, Mo, W and V substitute for 2 atoms of Fe2 at the sites of Nos. 2 and 3 (or No. 6 and No. 7). The stability of alloyed cementite decreases gradually as being substitutional doped by W, Cr, V, Mo and Mn.
Cite this article as: WANG Hong-jun, LIU Hong-yu, LIU Li, ZENG Xiao-yu, LU Jian-duo, LIN Chong, XU Hong-bing. Calculations of stability of alloyed cementite from valance electron structure [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(2): 259-269. DOI: 10.1007/s11171-017-3426-3.
J. Cent. South Univ. (2017) 24: 259-269
DOI: 10.1007/s11171-017-3426-3

WANG Hong-jun(王红军)1, LIU Hong-yu(刘宏玉)1, 2, LIU Li(刘礼)3, ZENG Xiao-yu(曾晓宇)4,
LU Jian-duo(卢建夺)1, LIN Chong(林冲)1, XU Hong-bing(徐红兵)1
1. Department of Physics, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430065, China;
2. Hubei Province Key Laboratory of Systems Science in Metallurgical Process, Wuhan 430065, China;
3. School of Remote Sensing and Information Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430079, China;
4. Department of Physics and Astronomy, Clemson University, Clemson, SC 29634, USA
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2017
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2017
Abstract: Based on the empirical electronic theory of solids and molecules (EET), the actual model for unit cell of cementite(θ-Fe3C) was built and the valence electron structures (VES) of cementite with specified site and a number of Fe atoms substituted by alloying atoms of M ( M=Cr, V, W, Mo, Mn ) were computed by statistical method. By defining P as the stability factor, the stability of alloyed cementite with different numbers and sites of Fe atoms substituted by M was calculated. Calculation results show that the density of lattice electrons, the symmetry of distribution of covalent electron pairs and bond energy have huge influence on the stability of alloyed cementite. It is more stable as M substitutes for Fe2 than for Fe1. The alloyed cementite is the most stable when Cr, Mo, W and V substitute for 2 atoms of Fe2 at the sites of Nos. 2 and 3 (or No. 6 and No. 7). The stability of alloyed cementite decreases gradually as being substitutional doped by W, Cr, V, Mo and Mn.
Key words: valence electron structure; alloyed cementite; stability; density of lattice electrons; symmetry of bonds; bond energy
1 Introduction
Cementite (θ-Fe3C), as an important phase that is also in the form of alloyed cementite in alloyed steels, affects steel properties since its stability would influence microstructures of alloyed steels. For example, cold working decreased the stability of cementite [1–3] and changed mechanical properties of alloyed steels, thus it is necessary to study the stability of alloyed cementite.
The investigation of cementite has been down to the atomic or even the electronic scale [4–8], and there are many reports about the valence electron structure (VES) of cementite. Based on the empirical electronic theory of solids and molecules (EET) [9], YU et al [10] calculated the VES of cementite and the calculation indicated that the bond strength of cementite is discontinuous along crystal axis b. It is this discontinuity that leads to the obvious brittleness. YE et al [11] then reported that structure along axis b in θ-Fe3C can be divided into strong and weak bond layers and the strength of the bonds connecting strong and weak layers has huge influence on the shape of alloyed θ-Fe3C during solidifying. HUANG et al [12] agreed that the bond energy of the strongest bond can be used to testify stability of a phase by calculating binding energy [13], but unfortunately they did not consider the bond energy in different directions. LIU et al [14] calculated the VES of θ-Fe3C and θ-(Fe, M)3C by EET, and found that the strength of θ-Fe3C was increased as Mn, V and Cr atoms substituted for Fe atoms at sites of 4c; however, the direction and variety of Fe atoms still are neglected in the report. MIN et al [15] discovered that the bond network of Al2Ca has high bond energy and the differences of the bond strength between different crystal directions are not remarkable, which leads to the highest stability among the three structures studied. Above indicates that the stability of cementite is not dependent only on VES and the strongest bond energy, but also on the bond energy gap in different directions.
In addition to EET, there are many calculations on cementite structure and stability by first principle, in which the types of Fe substituted by alloy atoms are divided into Fe1 and Fe2. LV et al [16] analyzed the stability of θ-Fe3C with 4 atoms of Fe1 and 8 atoms of Fe2 substituted by Cr or Mn atoms using first principle. The results indicated that Cr and Mn can enhance the strength of alloyed θ-Fe3C. GAO et al [17] found the alloyed θ-Fe3C with Cr substituting for Fe atoms at the site of 4c is more stable than that at the site of 8d. The stability of cementite doped with Co and Ni [18, 19], Ti and V [20] has been calculated, but they did not consider the influence of specified sites and numbers of Fe substituted by alloy atoms on the stability of cementite.
Cr, Mn, Mo, W and V are commonly used alloying elements in steel and they are doping preferable in cementite [21–23] and make cementite stable [24]. There are 4 atoms of Fe1 (site of 4c) and 8 atoms of Fe2 (site of 8d) in an unit cell of cementite; therefore, the type, number and site of the Fe atoms must be taken into consideration when substitutional alloying elements are added in cementite. However, up to now, the study on stability of cementite with specified number and site of Fe atoms replaced by alloying elements by VES calculations has not been found, which is essential for selecting the type and amount of alloying atoms.
In this work, the type (Fe1, Fe2), number (1-4 or 1-8) and site (4c, 8d) of the Fe atoms are considered in calculation. Based on EET and parameter statistical method for VES [25], built the actual model for unit cell of cementite (AMUCC). The method of “statistics” is proposed to calculate VES of M (Cr, Mn, Mo, W, V) doped cementite. The AMUCC we built is easier than “average atom model” [9, 26, 27] to calculate the interaction between different atoms when Fe substituted by M. By analyzing crystal structure and bond energy calculation for cementite, a factor of P, which is used to judge the stability, is proposed. Variation law in stability of cementite with different types, numbers, sites of Fe substituted by M was analyzed and the mechanism of stability of cementite was interpreted.
2 Calculation method
The VES of cementite was computed according to the bond length difference (BLD) method [9] by MATLAB. The theoretical bond length,  the number of covalent electron pairs, nα, the BLD, △Dα=
the number of covalent electron pairs, nα, the BLD, △Dα=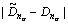 and bond energy, Eα, of covalent bonds that
and bond energy, Eα, of covalent bonds that
cannot be neglected were calculated. When △Dα≤ 0.005 nm, the theoretical bond length agrees with the experimental one in first order approximation; therefore, the chosen hybridization states of the atoms in alloyed cementite are their actual existing states. Lattice parameters of cementite (θ-Fe3C) were selected to calculate the VES of alloyed cementite (θ-(M, Fe)3C, M=Cr, V, W, Mo and Mn) and the variation of lattice parameters was realized by changing hybridization states of atoms in alloyed cementite.
For the multi-solutions of BLD method by EET, statistical method was suggested to determine the number of covalent electron pairs nα, i.e.,
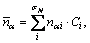
 (1)
(1)
where 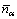 is the statistical value of bond α; σN is the number of probable states that meet △Dα≤0.005 nm. Then, the hybridization state whose VES is the closest to the statistical value was selected as the actual state of atoms in alloyed cementite, and the bond energy and density of lattice electrons were calculated out.
is the statistical value of bond α; σN is the number of probable states that meet △Dα≤0.005 nm. Then, the hybridization state whose VES is the closest to the statistical value was selected as the actual state of atoms in alloyed cementite, and the bond energy and density of lattice electrons were calculated out.
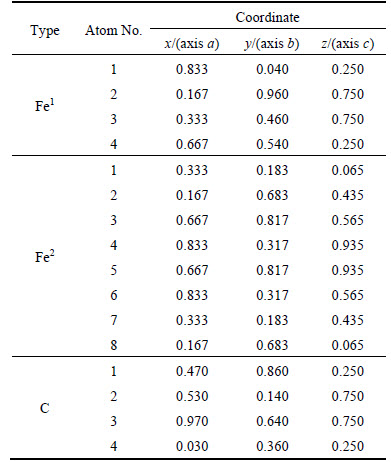
The space group of cementite (θ-Fe3C) is Pnma (No.62) with orthorhombic structure. A unit cell of cementite (UCC) shown in Fig. 1 has 4 molecules of Fe3C, where 8 and 4 atoms of Fe are located at the sites of 8d and 4c, marked as Fe2 and Fe1, respectively and 4 atoms of C are in the interstices of UCC. The lattice parameters of UCC are a=0.45144 nm, b=0.50787 nm, c=0.67297 nm [14]. In calculation, the center UCC and 26 unit cells around it were considered. All atoms in the 27 unit cells have been numbered. The number of atoms in center UCC is shown in Table 1.
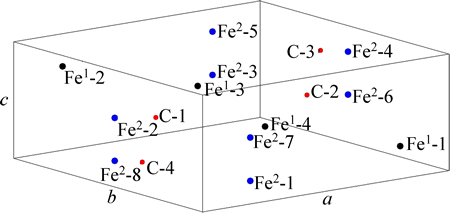
Fig. 1 Unit cell of θ-Fe3C with all atoms numbered and positioned
The sites of bonding atoms can be shown by the designated numbers. Numbers 1 to 8 represent the atoms in the center UCC; numbers greater than 8 refer to atoms outside of the center UCC. For example, atom sites “2-3” and “6-7” mean that the two bonding atoms are inside the center UCC; “1-52” means that one atom is located at the site of 1 in the center UCC and the other atom is at the site of 52 inside the unit cells surrounding the center UCC. The atom sites of the top 12 bonds in UCC are illustrated in Table 2.
According to the number of covalent electron pairs nα, the top 7 bond structures of cementite were drawn schematically in Fig. 2. Figure 2 shows that the structure along c direction in cementite can be divided into strong (C—Fe1) and weak (Fe2—Fe2) bond layers. The numbers of covalent electron pairs are n(c—Fe1) =0.967131 and n(Fe2—Fe2)=0.202053, respectively.
According to EET, the bond energy can be calculated through Eq. (2) for two identical atoms bondings:
Table 1 Coordinates and number of atoms in center unit cell of θ-Fe3C
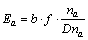 (2)
(2)
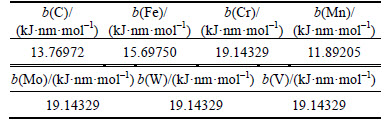
where b is the shielding factor of the electron to nuclear charge [9, 25] and its value was listed in Table 3; α is the bond order; nα is the number of covalent electron pairs of bond α; f is the bond-forming ability of covalent electrons for bond α and can be calculated by
 (3)
(3)
where g represents the contribution of spin orbit coupling effect of d electron to the bonding ability and it equals 1, 1.35 and 1.70 [9, 12] for elements in the 4th, 5th and 6th periods of the periodic table, respectively; αs, βp, γd are given as
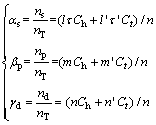 (4)
(4)
where ns, np and nd represent the valence electrons of s, p, d orbits, respectively; l, m, n, l′, m′, n′ denote the valence electron numbers of s, p, d orbits for h and t state, respectively.
τ(τ′)=1 while the valence electrons of s orbit for h(t) state are covalent electrons; otherwise, τ(τ′)=0. Chσ and Ctσ represent the components of h and t states at hybrid level, respectively. The value of Chσ and Ctσ can be calculated with the use of k formula in EET [9]. nT represents the total valence electron number, which can be calculated as
 (5)
(5)
where denotes the theoretical bond length of the αth type of covalent bond, which can be calculated as
denotes the theoretical bond length of the αth type of covalent bond, which can be calculated as
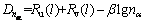 (6)
(6)
where Ru(l) and Rv(l) represent the single-bond radius of u and v atoms.
When the two atoms of the bond consisted are not the same, the bond energy can be calculated as
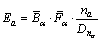 (7)
(7)
The 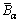 and
and 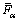 can be calculated as
can be calculated as
 (8)
(8)
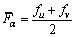 (9)
(9)
In EET, the “average atom model” is usually used to solve solid solution problem. This model considers the atoms in a crystal doped with alloy atoms the “mixed atoms”, i.e. linearly fixed atoms by the original crystal atoms and alloying atoms. This model cannot distinguish the relative sites of atoms in a crystal. In actual crystal units of alloyed cementite, the properties of alloyed cementite would be different as M substitutes Fe atoms at different sites. For example, there are 28 situations according to permutation and combination when M substitutes 2 atoms of Fe2 since there are 8 atoms of Fe2 in cementite crystal units. The “average atom model” regard the 28 kinds of structures the same, that’s to say, the ‘average atom model’ neglected the influence of the replaced sites by M in alloyed cementite. In order to clearly understand the properties of cementite with different sites, types and numbers of Fe substituted by M, the ‘actual crystal model’ is proposed, considering the environment change around every atom. In this calculation, the VES of cementite with different sites, types and numbers of Fe substituted by M was calculated, by which the stability of alloyed cementite was determined.
Table 2 Sites of atoms in unit cell of θ-Fe3C
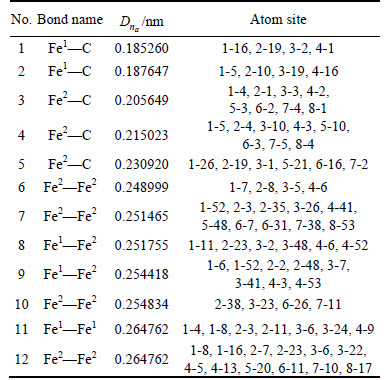
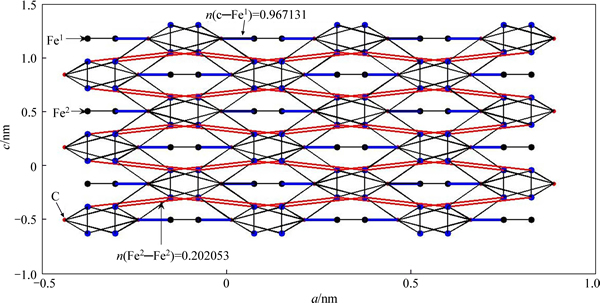
Fig. 2 Main bonds of θ-Fe3C on ac plane
Table 3 Shielding factor of electron to nuclear charge
3 Calculation results
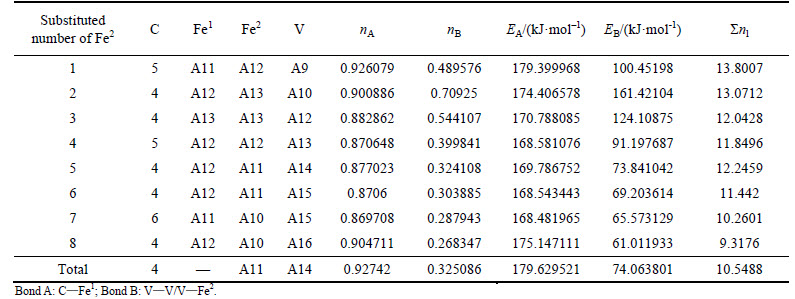
The difference in VES of alloyed cementite is not remarkable when one Fe1 or Fe2 is substituted by M at different sites, but this could be obvious when two or more Fe atoms are substituted by M since the relative location of Fe has great influence on VES. For example, the designated numbers of the bonding atoms forming Fe2—Fe2 whose bond length is 0.251465 nm are shown in Table 2. When 2 atoms of Fe2 located at the sites of Nos. 2 and 3 (or Nos. 6 and 7) in center UCC are replaced, there will form the bond of M—M, which is much stronger than Fe2—Fe2. The bond energy values of M—M, Fe2—M and Fe2—Fe2 decrease in turn. As for Mn, the bond energy decreases in order of Fe2—Mn, Mn—Mn and Fe2—Fe2 since the shielding factor of the electron to nuclear charge is smaller (Table 3). If the 2 atoms of Fe2 substituted by M are not located at the sites of Nos. 2 and 3 (or Nos. 6 and 7) at the same time, it would form the bond of Fe2—M. Therefore, the relative locations of Fe substituted by M must be considered in alloyed cementite.
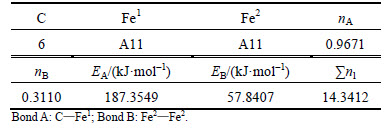
When 2 atoms of Fe2 located at the sites of Nos. 2 and 3 (or Nos. 6 and 7 ) in center UCC are substituted by M, the differences between strong and weak bond layers reach the minimum. The VES values of alloyed cementite with different numbers of Fe substituted are listed in Tables 4-14. The “total” in tables means the atoms of Fe1 or Fe2 in 27 UCCs (1 center UCC plus 26 UCCs surrounding the center one) are completely substituted by M. Bonds A and B represent the strongest bonds in strong and weak bond layers, respectively. Bond B is the bond of Fe2—M when one atom of Fe2 is substituted by M (M=Cr, Mn, Mo and W), the rest of bond B is M—M. As for M=Mn element, the bond B is the bond of Fe2—Mn.
Table 4 VES of cementite
4 Results discussion
According to EET, lattice electrons can move through the interstitials of a crystal unconstrainedly. When crystals were subjected to forces, lattice electrons move to the weak zones in crystal and help atoms bond
together temporarily so as to adjust the uniformity of VES here and enable crystals to deform successively. Thus, the lattice electrons stand for metallicity for intermetallic compounds and can be related to plasticity [9, 28, 29]. The crystal with good plasticity can keep the original structure easily when external environment changed, that is tosay, it is beneficial to self-stability. The density of lattice electron 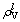 [28, 29] is:
[28, 29] is:
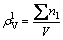 (10)
(10)
where ∑nl represents the sum of all lattice electrons in a crystal structure; V is the volume of crystal unit cell.
The symmetry of bond strength has influence on the stability of crystal [28]. The symmetry of bond strength S can be expressed by
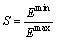 (11)
(11)
where Emin and Emax represent the bond energy of the weakest and strongest bonds in crystal, respectively. When the crystal has good symmetry, its deformation would be more uniform as being subjected to external forces. Otherwise, defects will be formed in the weak zones and lead to instability of crystal. Because of the remarkable discontinuity along c axis of cementite, the factor S is equal to the ratio of the strongest energy bond from the weak and strong bonds (Fig. 2) in this calculation.
The grater the bond-forming ability, the harder the damaging to the crystal is, and the more stable the crystal structure is. Bond-forming ability of unit volume crystal FV [28–30] is expressed by
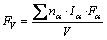 (12)
(12)
where V is the volume of crystal cell for cementite; Fα is the bond-forming ability of electron in bond α; Iα and nα are the equivalent bond number and the number of covalent electron pairs of bond α, respectively. Because of remarkable difference of cementite in strong and weak bond layers, the geometrical mean Q [31] of the strongest bond energy in strong and weak bond layers was selected to describe the stability of bond strength for cementite with Fe1and Fe2 replaced by M. Considering the formula of bond energy including nα and Fα factors, Q is define as
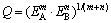 (13)
(13)
where m and n represent the numbers of bonds A and B in crystal cell for cementite, respectively; EA and EB are bond energy of the strongest bonds in strong and weak bond layers, respectively.
Table 5 VES of cementite with Fe1 substituted by Cr
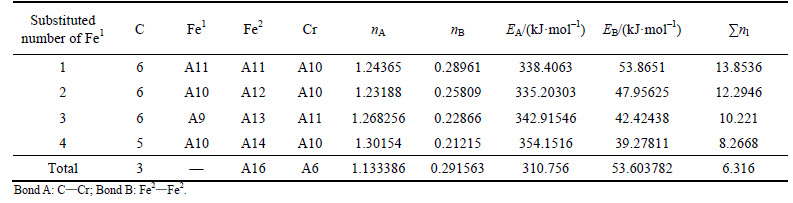
Table 6 VES of cementite with Fe2 substituted by Cr
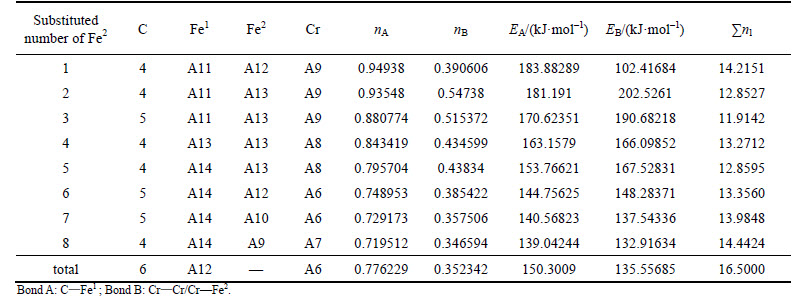
Table 7 VES of cementite with Fe1 substituted by Mn
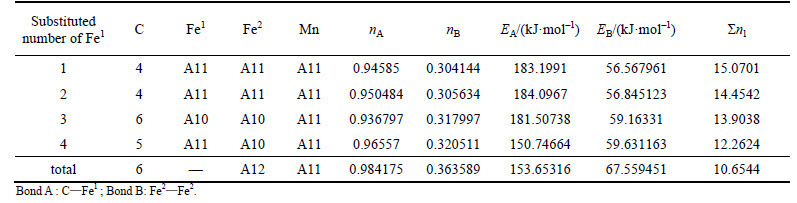
Table 8 VES of cementite with Fe2 substituted by Mn
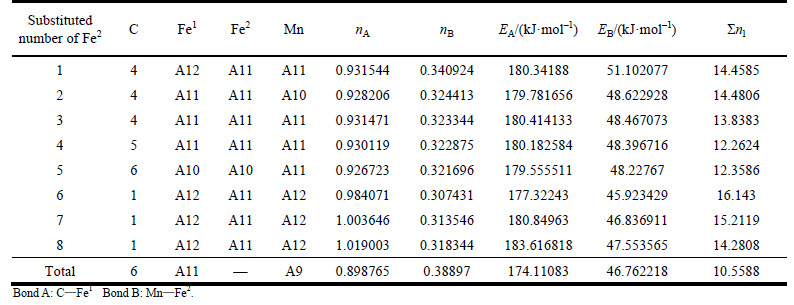
Table 9 VES of cementite with Fe1 substituted by Mo

Table 10 VES of cementite with Fe2 substituted by Mo

Table 11 VES of cementite with Fe1 substituted by W
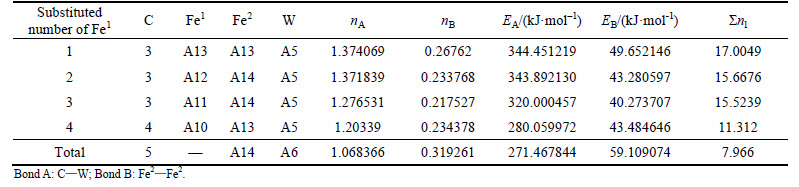
Table 12 VES of cementite with Fe2 substituted by W
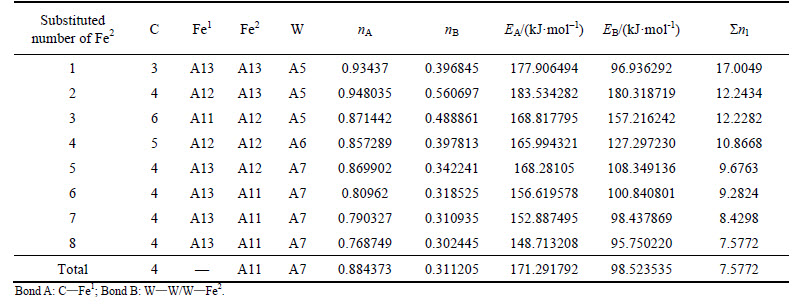
Table 13 VES of cementite with Fe1 substituted by V
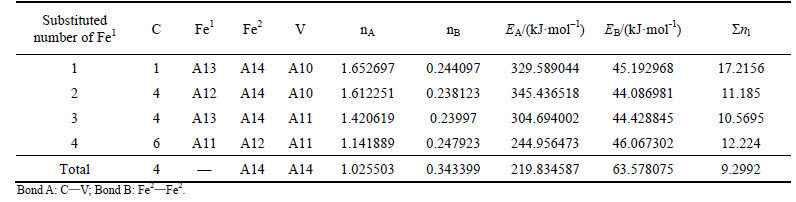
Table 14 VES of cementite with Fe2 substituted by V
Taking density of lattice, symmetry of bond strength and bond energy into consideration, the factor of stability, P, can be defined as
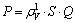 (14)
(14)
Calculation results of density of lattice electron, Q and S factors are listed in Tables 15 and 16.
For θ-Fe3C, the ∑nl=14.3412, Q=73.1678 kJ/mol and S=EB/EA=0.3087. What should be noted particularly is that S=EA/EB when 2-6 atoms of Fe2 are substituted by Cr; in other cases, S=EB/EA. Calculation results of P, the stability factor of alloyed cementite, are shown in Figs. 3 and Fig. 4.
Table 15 Q and S factors of alloyed cementite with Fe1 substituted by M
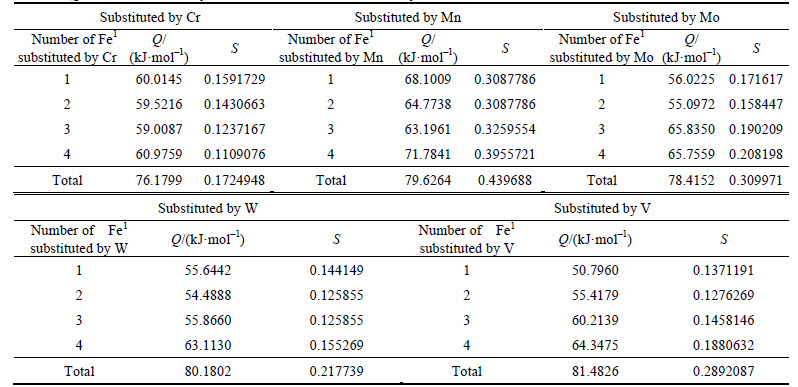
Table 16 Q and S factors of alloyed cementite with Fe2 substituted by M
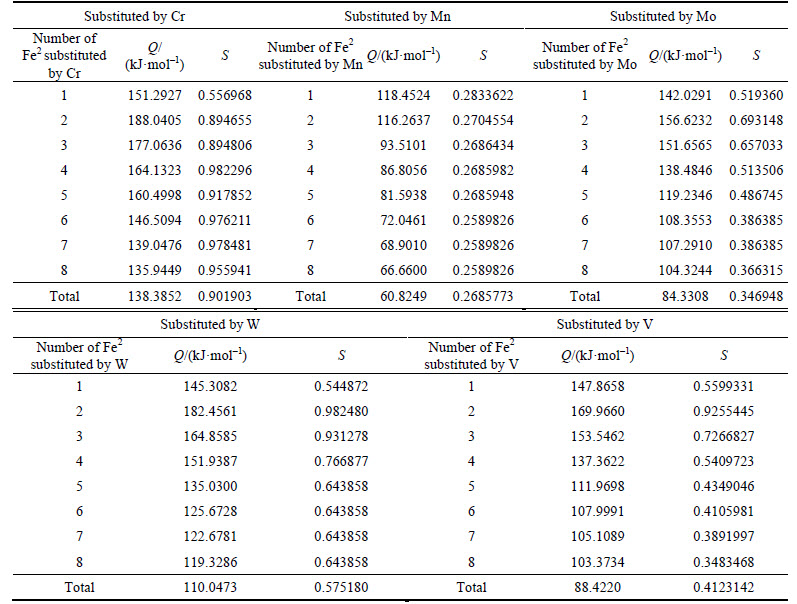
Comparison of Figs. 3 and 4 shows that factor P of alloyed cementite with Fe2 substituted by M is one order of magnitude larger than cementite with Fe1 substituted and it is also larger than that of θ-Fe3C. This means that M will substitute for Fe2 when it is doped in cementite, which is in agreement with the results calculated by first principle [16, 20, 32]. The alloyed cementite is most stable when 2 atoms of Fe2 (located at the sites of Nos. 2 and 3 or Nos. 6 and 7) are substituted by M, and the stability of alloyed cementite decreases in order of W, Cr, V, Mo, Mn.
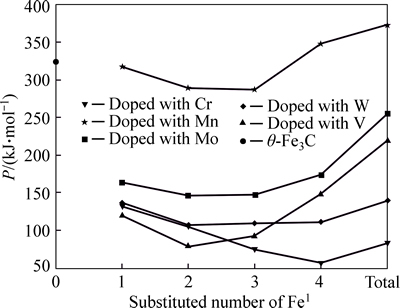
Fig. 3 Factor P of alloyed cementite with Fe1 substituted by M
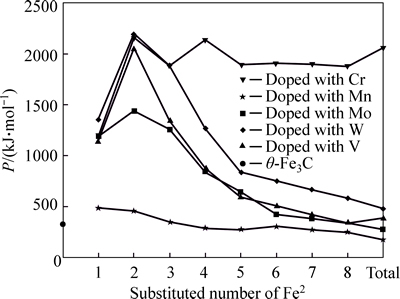
Fig. 4 Factor P of alloyed cementite with Fe2 substituted by M
With the number of substituted atoms increasing, the density of lattice electrons of alloyed cementite with Fe1 substituted by V, Mo, W increases first and then decreases. The density of lattice electron gradually decreases when cementite is doped with Cr. Compared with θ-Fe3C, factor S decreases by about 50% when one atom of Fe1 is substituted by V, Mo, W and Cr, and S increases with increasing substituted atoms but not greater than that of θ-Fe3C. This means that the addition of alloyed elements increases the difference between strong and weak bond layers, meanwhile, the Q is smaller than that of θ-Fe3C, thus factor P is not greater than that of θ-Fe3C, namely the stability of alloyed cementite decreases when V, Mo, W and Cr substitute Fe1. The density of lattice electron of alloyed cementite with Fe1 substituted by Mn decreases gradually; S and Q are close to that of θ-Fe3C and they slightly increase with increment of substituted atoms number. The variation of stability is not remarkable when Fe1 is substituted by Mn.
The S significantly increases when Fe2 is substituted by Cr, V, Mo and W, which means that the difference between strong and weak bond layers decreases and S and Q reach the maximum when 2 atoms of Fe2 are substituted. Though the density of lattice electron decreases, the favorable bond strength and symmetry lead to signification improvement of P and result in enhancement of stability of alloyed cementite. As Fe2 is substituted by Mn, the P decreases slightly with increasing substituted atoms, thus the stability of alloyed cementite decreases gradually when 2 atoms of Fe2 are substituted with W, Cr, V, Mo and Mn. On the other hand, the density of lattice electron and symmetry of bond strength are related to plasticity, so the plasticity of alloyed cementite would be better than that of θ-Fe3C when 2 atoms of Fe2 are substituted by Cr, V, W and Mo, and decreases in order of V, W, Cr, Mo, Mn. The stress-strain curves of alloyed cementite doped with Cr and Mn, measured by UMEMOTO [33, 34], showed that the plasticity values of (Fe0.8Cr0.2)3C and (Fe0.8Mn0.2)3C were both greater than that of θ-Fe3C, which is in agreement with our calculations. Calculations in this work indicate that the most probable chemical formula of alloyed cementite is θ-(Fe2.5M0.5)C. According to the stability variation of cementite doped with Cr and Mn, the Cr and Mn could have a larger solid solubility than other alloyed elements.
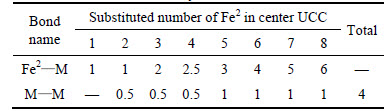
Based on EET, the variation of P can be explained from the perspective of electron. The bond of Fe2—M forms when one Fe2 is substituted by M and the electron number on this bond is greater than that of the original bond of Fe2—Fe2 in cementite, so the bond energy of Fe2—M is greater than that of Fe2—Fe2, strengthening the weak bond layers in cementite. The bonds of Fe2—M and M—M gradually form when the number of M is increased. For elements Cr, V, W and Mo, the bond energy of M—M is greater than that of Fe2—M except for Mn, namely the bond energy of Fe2-M is greater than M—M. The variation of equivalent bond number of M—M and Fe2—M is different when the number of alloyed atoms increasing. Table 17 shows that the increasement of equivalent bond number of Fe2—M is faster. The ratio of equivalent bond number of M—M to Fe2—M reaches the maximum when 2 atoms of Fe2 located at the sites of No. 2 and No. 3 (or No. 6 and No. 7) are substituted by M, the number of covalent electron pairs on M—M bond reaches the maximum and factors S and Q reach the maximum, thus P reaches the maximum when cementite is doped with Cr, V, Mo and W. Further increasing the number of M, the number of Fe2—M increases quickly, which leads to the reduction of covalent electron pairs on the M—M, bond energy decreasing, hybridization states varying, lattice electrons decreasing, factors S and Q decreasing; therefore, the stability of alloyed cementite decreases.
Table 17 Variation in equivalent bond number of M—M and Fe2—M with Fe2 substituted by M
After Cr and Mn are doped in cementite, the variation of P is different from that after Mo, W and V are doped (Fig. 4). Alloyed cementite still has high stability even more atoms of Fe2 are substituted by Cr atoms due to the strong strengthening effect of Cr. The strength of Cr-doped weak bond layers is greater than the original strong bond layers, i.e. EB>EA. Even though the covalent electron number on bond Cr—Cr decreases which leads to decrease of factor Q, the factor S increases, so factor P still maintains a high value and keeps high stability of alloyed cementite. Because the shielding factor of the electron to nuclear charge of Mn element is smaller than other alloyed elements, the strongest bond on weak bond layer is Fe2—Mn. With increasing number of Mn in cementite, the number of covalent electron pairs on Fe2—Mn decreases and bond energy decreasing results in less strengthening effect on weak bond layers. The decrease in S and P leads to the low stability of alloyed cementite doped with Mn. The stability increases slightly when the substituted numbers of Mn is 6, 7 and 8 due to the increase of the lattice electron number.
5 Conclusions
1) The VES has huge influence on stability of alloyed cementite. The higher the symmetry distribution of covalent electron pairs, the larger the number of lattice electron and the greater the bond energy, the more stable the alloyed cementite.
2) The stability of alloyed cementite with Fe2 substituted is higher than that with Fe1 substituted from VES calculation. The alloyed cementite is the most stable as Cr, V, W and Mo substitute 2 atoms of Fe2 at the sites of Nos. 2 and 3 (or Nos. 6 and 7). The stability of alloyed cementite decreases in order of W, Cr, V, Mo and Mn.
3) The VES values of the alloyed cementite with Cr, V, W and Mo becomes homogeneous after Fe2 atoms are substituted, and stability of alloyed cementite is strengthened due to the enhancement of weak bond layers. The effect of Mn on the stability of alloyed cementite is not obvious after atoms of Fe2 are substituted.
4) The most probable chemical formula of alloyed cementite is θ-(Fe2.5M0.5)C since the stability of alloyed cementite is the most stable as atoms of M replace 2 atoms of Fe2 at the site of 8d . Cr and Mn could have a larger solid solubility than other alloyed elements.
References
[1] WONG J N, CHUL M B, SEI J O, KWON S J. Effect of interlamellar spacing on cementite dissolution during wire drawing of pearlitic steel wires [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 42(5): 457–463.
[2] HONO K, OHNUMA M, MUEAYAMA M, NISHDA S, YOSHIE A, TAKAHASHI T. Cementite decomposition in heavily drawn pearlite steel wire [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 44(6): 977–983.
[3] CHAE J Y , JANG J H, ZHANG G H, KIM K H, LEE J S, BHADESHIA H K D H, SUH D W. Dilatometric analysis of cementite dissolution in hypereutectoid steels containing Cr [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65(3): 245–248.
[4] LANGUILLAUME J, KAPELSKI G, BAUDELET B. Cementite dissolution in heavily cold drawn pearlitic steel wires [J]. Acta Materialia, 1997, 45(3): 1201–1212.
[5] DANOIX F, JULIEN D, SAUVAGE X, COPREAUX J. Direct evidence of cementite dissolution in drawn pearlitic steels observed by tomographic atom probe [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 250(1): 8–13.
[6] ZHOU C T, XIAO B, FENG J, XING J D, XIE X J, CHEN Y H, ZHOU R. First principles study on the elastic properties and electronic structures of (Fe, Cr)3C [J] Computational Materials Science, 2009, 45(4): 986–992.
[7] LI Zhi-lin, LIU Zhi-lin, LIU Wei-dong. Valence electron structure of cementite phase and its interface and the tempering phenomenon [J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2002, 45(3): 282–289.
[8] WUN C C J, EMILY A C. Structure and stability of Fe3C-cementite surfaces from first principles [J]. Surface Science, 2003, 530(1): 88–100.
[9] ZHANG Rui-lin. The empirical electron theory of solids and molecules [M]. Changchun: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1993: 287–290. (in Chinese)
[10] YU Rui-huang, ZHANG Rui-lin, ZHENG Wei-tao, HU An-guang. Valence structure and properity of cementite [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1993, 38(7): 665–667. (in Chinese)
[11] YE Yi-fu, FAN Tong-xiang, SHANG Yu-xia, CHEN Zong-min. The different coefficient of bonding force between intrastratal and interlamination of M3C type cementite [J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 1997, 27(4): 300–303. (in Chinese)
[12] HUANG Lian, GAO Kun-yuan, WEN Sen-ping, HUANG hui, WANG Wei, NIE Zuo-ren. Valance electron structure analysis of equilibrium and metastable phases of Al3M(M=Ti, Zr, Hf) [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(4): 492–501. (in Chinese)
[13] XU Wan-dong, ZHANG Rui-lin, YU Rui-huang. The bonding energy caculation of transition metal compound [J]. Science in China Series A: Mathematics, 1988(3): 323–330. (in Chinese)
[14] LIU Zhi-lin, LI Zhi-lin, LIU Wan-dong. Calculation of the valence electron structures of alloying cementite and its biphase interface [J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2001, 44(5): 542–552.
[15] MIN Xue-guang, SUN Yang-shan, XUE Feng, DU Wen-wen, WU Deng-yun. Analysis of valence electron structures (VES) of intermetallic compounds containing calcium in Mg–Al-based alloys [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 78(1): 88–93.
[16] LV Z Q , FU W T , SUN S H , BAI X H , GAO Y , WANG Z H. First-principles study on the electronic structure, magnetic properties and phase stability of alloyed cementite with Cr or Mn [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2011, 33: 915–919.
[17] GAO Y , LV Z Q , SUN S H ,QU M G , SHI Z P , ZHANG R H , FU W T. First principles study on surface structure and stability of alloyed cementite doped with Cr [J]. Materials Letters, 2013, 100: 170–172.
[18] WANG C X, LV Z Q, FU W T, LI Y, SUN S H, WANG B. Electronic properties, magnetic properties and phase stability of alloyed cementite (Fe,M)3C (M=Co,Ni) from density-functional theory calculations [J]. Solid State Sciences, 2011, 13: 1658–1663.
[19] GAO Y , WANG B , GUO M W, LV Z Q , SUN S H , ZHANG R H, FU W T. First-principles study on surface structural, magnetic and electronic properties of alloyed cementite with Co or Ni [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2014, 85: 154–158.
[20] WANG B W, XIE Y P, ZHAO S J, LI J, HU L J. Density functional theory study of the influence of Ti and V partitioning to cementite in ferritic steels [J]. Physica Status Solidi B: Basic Solid State Physics, 2014, 251: 950–957.
[21] UMEMOTO M, LIU Z G, MASUYAMA K, TSUCHIYA K. Influence of alloy additions on production and properties of bulk cementite [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 45(3): 391–397.
[22] LIU Qing-dong, CHU Yu-liang, WANG Ze-min, LIU Wen-qin, ZHOU Bang-xing. 3D atom probe characterization of alloying elements partitioning cementite of Nb-V Microalloying steel [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008, 44(11): 1281–1285.
[23] DUNLOP G L, CARLSSON C J, FRIMODIG G. Precipitation of VC in ferrite and pearlite during direct transformation of a medium carbon microalloyed steel [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 1978, 9(2): 261–266.
[24] SHEIN I R, MEDVEDEVA N I, IVANOVSKII A L. Electronic structure and magnetic properties of Fe3C with 3d and 4d impurities [J]. Physica Status Solidi B: Basic Solid State Physics, 2007, 244(6): 1971–1981.
[25] LIU Zhi-lin, LIN Cheng. Statistics of alloy electronic structure parameter and calculation of mechanics performance [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press. 2008: 20–22. (in Chinese)
[26] LI Jing-ping, MENG Song-he, HAN Jie-cai, ZHANG Xin-hong, LUO Xiao-guang. Valence electron structure and properties of the ZrC1-xNx solid solution [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(6): 980–983. (in Chinese)
[27] PENG Ke, YI Mao-zhong, RAN Li-ping, GE Yi-cheng. Valence electron structure and properties of (Mo1-x,Wx)Si2 solid solutions [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(3): 414–416. (in Chinese)
[28] JIANG Shu-ying, LI Shi-chun. Valence electron structures and properties of Al-Ce compounds [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(S2): 397–400. (in Chinese)
[29] JIANG Shu-ying, LI Shi-chun. Effect of valance electron structure of La-Al compounds on aluminum alloy properties [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013, 34(7): 31–35. (in Chinese)
[30] SU Juan-hua, JIANG Tao, REN Feng-zhang. Effect of Cr on electron structure and properties of copper [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2012, 33(4): 152–155. (in Chinese)
[31] LUO Xiao-guang, LI Jing-ping, HU Ping, DONG Shan-liang. Empirical electron theory model for calculating hardness of Covalent crystals [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(19): 1957–1962. (in Chinese)
[32] CHAITANYA K A, MARCEL H F S. First-principles prediction of partitioning of alloying elements between cementite and ferrite [J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(19): 6276–6281.
[33] UMEMOTO M, LIU Z G, MASUYAMA K, TSUCHIYA K. Influence of alloy additions on production and properties of bulk cementite [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 45(4): 391–397.
[34] UMEMOTO M, TODAKA Y, TAKAHASHI T, LI P, TOKUMIYA R, TSUCHIYA K. Characterization of bulk cementite produced by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials, 2003, 15: 607–614.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Cite this article as: WANG Hong-jun, LIU Hong-yu, LIU Li, ZENG Xiao-yu, LU Jian-duo, LIN Chong, XU Hong-bing. Calculations of stability of alloyed cementite from valance electron structure [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(2): 259-269. DOI: 10.1007/s11171-017-3426-3.
Foundation item: Project(2014CFB801) supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China; Project(11304236) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2015-09-24; Accepted date: 2016-03-22
Corresponding author: LIU Hong-yu, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86–27–68893335; E-mail: liuhongyu@wust.edu.cn

