Co-TiO2纳米复合薄膜中化学状态和磁电阻的基底温度依赖性
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2020年第9期
论文作者:陈浩禹 张亦文 吴忠 秦真波 吴珊珊 胡文彬
文章页码:2502 - 2509
关键词:Co;TiO2;纳米复合薄膜;铁磁性能;超顺磁性能;磁电阻
Key words:Co; TiO2; nanocomposite films; ferromagnetic property; superparamagnetic property; magnetoresistance
摘 要:采用磁控溅射法在不同基底温度下制备Co-TiO2纳米复合薄膜。所合成的纳米复合薄膜由TiO2非晶基体和分散其中的Co颗粒组成,呈铁磁和超顺磁共存的特性。随着基底温度从室温升高到400 °C,Co颗粒尺寸逐渐增大,氧化程度明显降低。因此,在Co含量相同的情况下,随着基底温度的升高(从室温升高至400 °C),饱和磁化强度从0.13增加到0.43 T。在高基底温度下,一部分Co颗粒聚集形成导电路径,导致电阻率从1600快速下降至76 μΩ·m。即使在电阻率低至76 μΩ·m的情况下,依然能获得Co-TiO2的磁电阻性能。结果表明,纳米复合薄膜在室温下具有低Co氧化、高磁化强度和磁阻特性。
Abstract: Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films were prepared via magnetron sputtering at various substrate temperatures. The films comprise Co particles dispersed in an amorphous TiO2 matrix and exhibit coexisting ferromagnetic and superparamagnetic properties. When the substrate temperature increases from room temperature to 400 °C, Co particles gradually grow, and the degree of Co oxidation significantly decreases. Consequently, the saturation magnetization increases from 0.13 to 0.43 T at the same Co content by increasing the substrate temperature from room temperature to 400 °C. At a high substrate temperature, conductive pathways form among some of the clustered Co particles. Thus, resistivity rapidly declines from 1600 to 76 μΩ·m. The magnetoresistive characteristic of Co-TiO2 films is achieved even at resistivity of as low as 76 μΩ·m. These results reveal that the obtained nanocomposite films have low Co oxidation, high magnetization and magnetoresistance at room temperature.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 30(2020) 2502-2509
Hao-yu CHEN1,2, Yi-wen ZHANG1,2, Zhong WU2, Zhen-bo QIN2, Shan-shan WU1,2, Wen-bin HU1,2
1. Key Laboratory for Advanced Ceramics and Machining Technology, Ministry of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Received 9 January 2020; accepted 9 June 2020
Abstract: Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films were prepared via magnetron sputtering at various substrate temperatures. The films comprise Co particles dispersed in an amorphous TiO2 matrix and exhibit coexisting ferromagnetic and superparamagnetic properties. When the substrate temperature increases from room temperature to 400 °C, Co particles gradually grow, and the degree of Co oxidation significantly decreases. Consequently, the saturation magnetization increases from 0.13 to 0.43 T at the same Co content by increasing the substrate temperature from room temperature to 400 °C. At a high substrate temperature, conductive pathways form among some of the clustered Co particles. Thus, resistivity rapidly declines from 1600 to 76 μΩ·m. The magnetoresistive characteristic of Co-TiO2 films is achieved even at resistivity of as low as 76 μΩ·m. These results reveal that the obtained nanocomposite films have low Co oxidation, high magnetization and magnetoresistance at room temperature.
Key words: Co; TiO2; nanocomposite films; ferromagnetic property; superparamagnetic property; magnetoresistance
1 Introduction
With the miniaturization and integration of magnetic electronic components, two-dimensional materials have been widely explored [1]. Among them, nanocomposite films comprising magnetic particles in a ceramic matrix have shown various novel properties [2,3], such as the magneto-resistance [4], the high-frequency soft magnetic characteristics [5] and the magneto-optical characteristics [6]. However, most nanocomposite films used in magnetoresistance studies are made of fluoride or nitride materials [7-9], which are costly in terms of preparation and have poor biological compatibility. On the contrary, Co-TiO2 nano- composite films are promising materials with high chemical stability and biological affinity [10].
In preparing Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films, magnetic Co is exposed to an oxidizing atmosphere and becomes prone to oxidation [11-13]. The generated cobalt oxide with antiferromagnetism can reduce the magnetization and magnetoresistance of films [14]. Therefore, decreasing the degree of Co oxidation in films has been extensively investigated. CHO et al [15] observed that the state of metal clusters can be changed by regulating the annealing temperature, thereby reducing the oxidation degree of Co. WAN et al [16] prepared low-oxidized Co-TiO films via reactive cosputtering and observed that a large particle size distribution helps increase the metal state of films. IKEMIYA et al [17] also revealed that a large particle size is helpful for inhibiting metal oxidation.
A low Co content in Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films should be maintained to obtain the desirable magnetoresistive characteristics [18]. A low Co content leads to a small particle size, which causes Co to oxidize easily. ZHU et al [19] claimed that the particle size can be controlled by adjusting substrate temperatures with the same composition.
In this study, the effects of a high substrate temperature (Ts) on Co particle size, chemical state and magnetoresistive characteristics were investigated. In addition, the schematic of particle assembly was creatively proposed to explain the relationship between the microstructure and properties of materials.
2 Experimental
Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films were deposited on Si(100) and quartz substrates via direct current (DC) and radio frequency magnetron sputtering. The flow rate of Ar was maintained at 20 mL/min. Pre-sputtering was performed for a few minutes to remove the oxide on the surface of targets, and the pressure on the chamber was maintained at 2.2 Pa. The deposition of Co and TiO2 targets was respectively conducted at 50 and 150 W, respectively, a substrate rotation speed of 4 r/min and substrate temperatures Ts of RT, 150, 300 and 400 °C for 1 h, respectively. The average thickness of the resultant films was ~160 nm.
The microstructure of the films was measured through transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). The surface morphology of the films was characterized via field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The elemental compositions of the films were analyzed via X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The crystal structure of the films was examined through X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Cu Kα radiation. The static magnetic properties of the films were measured using a superconducting quantum interference device. The electrical and magnetoresistance properties of the films were evaluated using a physical property measurement system.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Structural and morphological characterization
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of Co-TiO2 films deposited at various Ts ranging from RT to 400 °C. After Ts increases, the Co (002) peak narrows, and its intensity increases, indicating that crystallinity can be enhanced at high Ts. The (311) peak of cobalt oxide Co3O4 appears at 300 °C or above, and the intensity of the diffraction peak gradually increases as Ts increases. This result suggests that the crystallinity of cobalt oxide increases with an increase in Ts. No peaks related to titanium oxides are observed, implying that the deposited material may contain Co nanograins embedded in an amorphous TiO2 matrix.

Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Co-TiO2 films deposited at Ts ranging from RT to 400 °C
Figure 2(a) shows a TEM image of a Co–TiO2 nanocomposite film deposited at RT, and Fig. 2(b) illustrates the corresponding HRTEM image. In Fig. 2(a), black particles mainly correspond to magnetic Co, and the bright part of the surrounding coating indicates amorphous titanium oxide. The TEM images reveal that the film comprises spherical nanosized particles with sizes ranging from 4 to 7 nm, and the average particle size likely increases as Ts increases. The HRTEM image presents clear lattice fringes with a d-spacing of 0.202 nm, which corresponds to the (002) plane of HCP Co. The area without lattice fringes around the cobalt particle denotes the amorphous TiO2 matrix. These results further indicate that most of the crystalline Co particles in the film are coated with an amorphous TiO2 host matrix.
Figure 3 shows SEM images of the films deposited at various Ts. The cluster size present in the films can be observed clearly. In particular, the cluster size on the film surface increases gradually as Ts increases possibly because of the thermal effects on grain size [20].

Fig. 2 TEM (a) and HRTEM (b) images of Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films deposited at RT
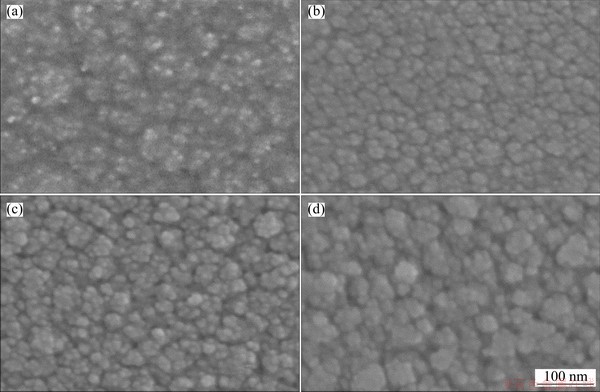
Fig. 3 SEM images of Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films deposited at RT (a), 150 °C (b), 300 °C (c) and 400 °C (d)
Figure 4 shows the AFM images of Co-TiO2 films deposited at RT, 150, 300 and 400 °C and their surface morphologies. The root mean square roughness (RMS(Sq)) does not change significantly below 150 °C, but it increases from 0.50 to 0.67 nm at Ts from 150 to 400 °C. At high temperatures, the surface roughness of the films increases with increasing Ts because of the growth of the particles. This finding is consistent with those shown in the SEM images.
3.2 Elemental composition analysis
EDS analysis reveals that the Co content in the films is almost 40 at.%, and it does not change significantly as Ts varies. Figure 5 shows the XPS spectra of the Co-TiO2 films deposited at different Ts. Figure 5(a) presents the high-resolution XPS spectrum in the Co 2p region obtained from the surface of the film prepared at RT. The main doublet peaks at 777.3 and 792.3 eV belong to Co 2p3/2 and Co 2p1/2 in Co metal, respectively [21]. Two other Co 2p XPS doublet peaks appear at 780.1 and 786.0 eV for Co 2p3/2, and doublet peaks at 796.0 and 802.2 eV attributed Co 2p1/2 are observed; these results indicate that Co is partly oxidized during sputtering [22]. The spectrum of Co can be decomposed into two characteristic peaks at 779.1 and 781.7 eV, which belong to Co3+ and Co2+, respectively [12]. Figure 5(b) illustrates the XPS spectra in the Co 2p region of the films deposited at various Ts. The peaks due to Co—Co bonds (blue- shaded areas) and Co—O bonds (red-shaded areas) occur at all Ts likely because of oxidation during sputtering. When Ts increases, the intensity of the Co peaks increases possibly because of the agglo- meration of Co grains at high Ts. The agglomeration of metal particles decreases the particle interface area between Co and TiO2, leading to the reduced oxidation of Co. Figure 5(c) displays the high- resolution XPS spectrum in the Ti 2p region acquired from the surface of a film prepared at RT. The Ti 2p XPS peaks can be fitted with a doublet of peaks at 459.0 and 464.7 eV, which are related to Ti 2p3/2 and Ti 2p1/2 in TiO2 [23], respectively. Figure 5(d) exhibits the XPS spectra in the Ti 2p region of the films prepared at various Ts. Ts slightly affects the valence state of Ti. Consistent with XRD and TEM results, this finding implies that Co particles are coated with a layer of amorphous titanium oxide.
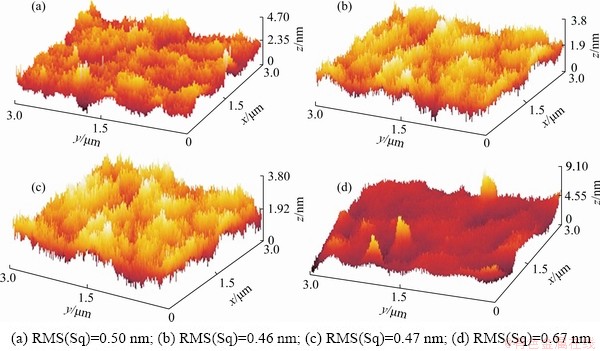
Fig. 4 AFM images of Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films deposited at RT (a), 150 °C (b), 300 °C (c) and 400 °C (d)

Fig. 5 High-resolution XPS spectrum of Co 2p region from surface of film deposited at RT (a), XPS spectra in Co 2p region of films deposited at various Ts (b), high-resolution XPS spectrum of in Ti 2p region from surface of film deposited at RT (c) and XPS spectra in Ti 2p region of films deposited at various Ts (d)
3.3 Magnetic and electrical properties
Figure 6(a) presents the magnetic hysteresis loops of the films prepared at different Ts. Figure 6(b) shows the dependence of metal content on Ts and the corresponding magnetic property data. As Ts increases from 25 to 400 °C, the saturation magnetization (Ms) increases from 0.13 to 0.43 T, and the Co content does not obviously change. Few reports have described this significant increase in saturation magnetization because of an increase in Ts, which may be explained by an increase in particle size and improved crystallinity [24-26]. The remanence ratio (Mr/Ms), an important magnetic parameter, is expressed as the ratio of residual magnetization (Mr) and saturation magnetization. As shown in Fig. 6(b), Mr/Ms increases rapidly as Ts increases.
Figure 6(b) illustrates the coercivity (Hc) evaluated from the hysteresis loops of the films. When Ts increases, Hc initially remains unchanged at about 10 kA/m from RT to 150 °C and then increases to 13 kA/m at 400 °C. An increase in Hc can be explained well by random anisotropy model [27,28]. This model describes the magnetic properties of particles with sizes below exchange length (50 nm), and coercivity is positively correlated with particle size. As Ts increases, particle size increases, thereby causing Hc to increase. In a material system, the relative content of ferromagnetic states can be qualitatively expressed by Mr/Ms. When Mr/Ms is 1, the films exhibit ferromagnetic characteristics. When Mr/Ms is 0, the films exhibit super-paramagnetic characteristics. The Langevin equation can also be fitted with the data to determine whether the sample is in a super-paramagnetic state [18]. Mr/Ms of the sample at RT is close to 0, which indicates that the sample is in a superparamagnetic state at a low temperature. In Fig. 6(b), Mr/Ms and coercivity increase as Ts increases, and the state of the film changes from superparamagnetic to ferromagnetic. However, some of the superparamagnetic structures are still preserved at high Ts. In Fig. 6(c), the magnetization curve of the sample prepared at RT is well fitted with the Langevin equation.
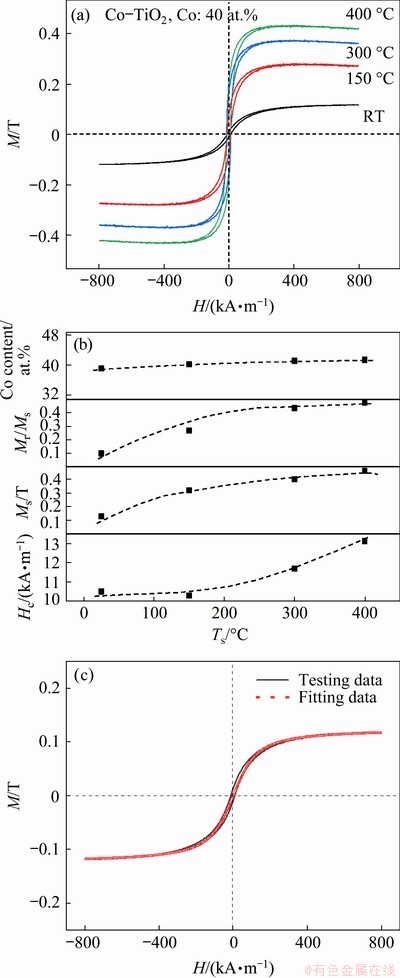
Fig. 6 Magnetic hysteresis loops of Co-TiO2 nano- composite films deposited at various Ts (a), plots of Co content, remanence ratio, saturation magnetization and coercivity as function of Ts (b), and representative fit of Langevin equation to magnetization curve of sample prepared at RT (c)
Figure 7(a) shows the dependence of resistivity (ρ) and magnetoresistance on Ts. As Ts increases from RT to 400 °C, resistivity decreases rapidly from 1600 to 76 μΩ·m. Magnetoresistance also decreases. Resistivity varies because of the following reasons. As Ts increases, the magnetic particles in the film form agglomerates, creating local conductive channels. The mechanism of electronic transport changes gradually from tunnelling to conduction [29,30]. Variations in magnetoresistance are likely related to the change in electronic transport mechanism in the films. Figure 7(b) illustrates the magnetoresistance ratio curves and the normalized magnetization -(M/Ms)2 curve fitting. As suggested by the Inoue–Maekawa model [31], the dependence of the magnetoresistance ratio on the normalized magnetization -(M/Ms)2 indicates a spin-dependent tunnelling transport. The magnetoresistance ratio corresponds well with a portion of the -(M/Ms)2 curve after the ferromagnetic component is subtracted; this observation is consistent with the films comprising a mixture of superparamagnetic and ferromagnetic states [32]. The inset of Fig. 7(b) presents a schematic of the proposed particle assembly. The grey particles represent Co metal particles dispersed in an amorphous TiO2 matrix. At low Ts, metal particles are small, isolated from one another and mainly in the superparamagnetic state. Electronic transport between metal particles is mainly accomplished through electron tunnelling, leading to high resistivity. As Ts increases, the size of metal particles increases, and particles aggregate into clusters. These clusters are mainly in a ferromagnetic state, and the state of the films gradually changes from superparamagnetic to ferromagnetic as aggregation increases. Some clusters of metal particles may form conductive channels, and the mechanism of electronic transport varies from electron tunnelling to traditional metallic conduction. In the film prepared at Ts of 400 °C, many clusters are produced in most parts of the films. However, the films still exhibit a partial superparamagnetic behaviour, which is likely caused by a small number of metal particles isolated from one another. Consequently, both superparamagnetic and ferromagnetic states coexist in the films and exhibit a low resistivity of 76 μΩ·m. These Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films still manifest an obvious RT magnetoresistance behavior.
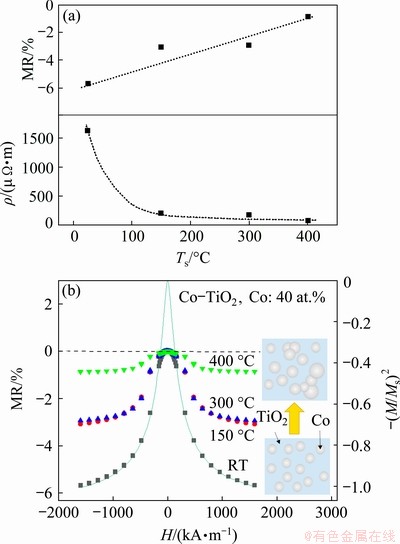
Fig. 7 Dependence of magnetoresistance ratio (MR) and resistivity of Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films on Ts (a) and dependence of MR and -(M/Ms)2 on external magnetic field H at various Ts (Solid curve shows normalized magnetization required to fit magnetoresistance response of sample prepared at RT, and inset presents the proposed structural model of Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films) (b)
4 Conclusions
(1) The Co-TiO2 nanocomposite films comprise Co nanoparticles with HCP structure embedded in an amorphous TiO2 matrix. A high substrate temperature can inhibit Co oxidation by increasing the particle size of Co.
(2) As Ts increases, Co particles grow and form clusters. Consequently, the state of the films changes from superparamagnetic to ferromagnetic. The elemental composition of the films is almost the same even when Ts varies, and saturation magnetization increases to almost 230%. Moreover, conductive paths form between particle clusters, which induce a decrease in resistivity from 1600 to 76 μΩ·m.
(3) The prepared Co-TiO2 films retain their magnetoresistive character at room temperature even at low resistivity because of the existence of the superparamagnetic state.
(4) The relationship between the micro- structure and properties of materials is illustrated in the schematic of particle assembly, which helps further elucidate the magnetoresistance characteristics of films.
References
[1] DAI Ming-jiang, WEI Chun-bei, ZHOU Ke-song, ZHU Min, HOU Hui-jun, LIN Song-sheng, TONG Xin. Properties of W/DLC/W-S-C composite films fabricated by magnetron sputtering [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(9): 3002-3011.
[2] NGUYEN T, SHIRATSUCHI Y, NAKATANI R. Pulse- voltage-driven dynamical switching of perpendicular exchange bias in Pt/Co/Au/Cr2O3/Pt thin film [J]. Applied Physics Express, 2017, 10(8): 083002.
[3] ABE S, OHNUMA M, PING D H, OHNUMA S. Anatase- dominant matrix in Ge/TiO2 thin films prepared by RF sputtering method [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 1: 095001.
[4] SOCOLOVSKY L, OLIVEIRA C, DENARDIN J, KNOBEL M, TORRIANI I. Nanostructure of granular Co-SiO2 thin films modified by thermal treatment and its relationship with the giant hall effect [J]. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter, 2019, 72: 184423.
[5] ZHANG Y W, OHNUMA S, MASUMOTO H. Soft magnetic Co-(TiN) composite films realized within a wide-range of cobalt content [J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2011, 47(10): 3795-3798.
[6] ZHAO Xue-ping, ZHANG Ming, BAI Pu-cun, HOU Xiao-hu, LIU Fei, YAN Hui. Effect of substrate temperature on structural and optoelectronic properties of CuCrO2 thin films [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(2): 255-261.
[7] CAO Y, UMETSU A, KOBAYASHI N, OHNUMA S, MASUMOTO H. Tunable frequency response of tunnel-type magneto-dielectric effect in Co-MgF2 granular films with different content of Co [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(12): 122901.
[8] CAO Y, ZHANG Y W, OHNUMA S, KOBAYASHI N, MASUMOTO H. Magnetic properties and thermal stability of Co/HfN multilayer films for high-frequency application [J]. AIP Advances, 2017, 7: 065202.
[9] ZHANG Y W, KIJIMA H, KOBAYASHI N, OHNUMA S, MASUMOTO H. Structure and high-frequency soft- magnetic properties of Co-TiN nano-composite films [J]. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2013, 121(1409): 36-39.
[10] ZHANG Shai-lin, SUN Jun-ying, XU Ying, QIAN Shi, WANG Bing, LIU Fei, LIU Xuan-yong. Biological behavior of osteoblast-like cells on titania and zirconia films deposited by cathodic arc deposition [J]. Biointerphases, 2012, 7: 60.
[11] SONG Hong-qiang, MEI Liang-mo, YAN Shi-shen. Microstructure, ferromagnetism, and magnetic transport of Ti(1-x)CoxO2 amorphous magnetic semiconductor [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 99: 123903.
[12] WANG Li-dong, QI Tie-yue, WANG Juan, ZHANG Shi-han, XIAO Hui-ning, MA Yong-liang. Uniform dispersion of cobalt nanoparticles over nonporous TiO2 with low activation energy for magnesium sulfate recovery in a novel magnesia-based desulfurization process [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 342: 579-588.
[13] HAN G, LUO P, GUO Z, NAHAR F, TAY M, WU Y, WANG S. Co-doped TiO2 epitaxial thin films grown by sputtering [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 505: 137-140.
[14] CORTIE D, KHAYDUKOV Y, KELLER T, SPROUSTER D, HUGHES J, SULLIVAN J, WANG X L, BRUN A, BERTINSHAW J, CALLORI S, AUGHTERSON R, JAMES M, EVANS P, TRIANI G, KLOSE F. Enhanced magnetization of cobalt defect clusters embedded in TiO2-delta films [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(10): 8783-8795.
[15] CHO C, KIM J, HWANG J, JEONG S, JOH Y, KIM D. High resolution elemental and magnetic distribution mapping and chemical bonding states of Co:TiO2 films: A SAM, MFM and XPS study[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2004, 43(10B): L1323-L1326.
[16] WAN F X, AN H Y, HARUMOTO T, NAKAMURA Y, SHI J. Temperature-dependent magnetotransport of Co-Ti-O nanocomposite films [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2019, 52(13): 135302.
[17] IKEMIYA K, HIROSE Y, HASEGAWA T. Fabrication and magnetic properties of fcc-Co nanorods embedded in epitaxial thin films of anatase TiO2 as a transparent matrix [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(5): 1776-1779.
[18] KUMAR H, GHOSH S, BURGER D, LI L, ZHOU S Q, KABIRAJ D, AVASTHI D, GROTZSCHEL R, SCHMIDT H. Role of coulomb blockade and spin-flip scattering in tunneling magnetoresistance of FeCo-Si-O nanogranular films [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109: 073914.
[19] ZHU Zeng-tai, WEI Jin-wu, FENG Hong-mei, DU Jin-lu, LIU Qing-fang, WANG Jian-bo. Influence of substrate temperature on static and dynamic magnetic properties of FeNiN films [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2017, 50(1-4): 045002.
[20] ZIELINSKI E, VINCI R, BRAVMAN J. Effects of barrier layer and annealing on abnormal grain growth in copper thin films [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1994, 76: 4516.
[21] ANUPAMA C, KUMARMANI R, VASUNDHARA M, JOSHIC S, SINGH J. Structural and magnetic study of undoped and cobalt doped TiO2 nanoparticles [J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8: 10939-10947.
[22] LI J H, WANG J X, WANG D H, GUO G Y, YEUNG K, ZHANG X L, LIU X Y. Band gap engineering of titania film through cobalt regulation for oxidative damage of bacterial respiration and viability [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(33): 27475-27490.
[23] KOLLBEKA K, SIKORAA M, KAPUSTAA C, SZLACHETKOB J, ZAKRZEWSKAD K, KOWALSKIE K, RADECKAF M. X-ray spectroscopic methods in the studies of nonstoichiometric TiO2-x thin films [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 281: 100-104.
[24] QIAN Z H, WANG G, SIVERTSEN J, JUDY J. NiZn ferrite thin films prepared by facing target sputtering [J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1997, 33(5): 3748-3750.
[25] WANG Li, SUN Hong-fang, ZHOU Hui-hua, ZHU Jing. Self-assembly growth and size control of silver nanocrystals for nonvolatile memory applications [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2009, 610-613: 585-590.
[26] WANG Xiang-qian, ZHU Zeng-tai, MA Lei, FENG Hong-mei, XIE Hong-kang, WANG Jian-bo, LIU Qing-fang, HAN Gen-liang. Influence of deposition cycle and magnetic annealing on high-frequency magnetic properties of the (Co90Fe10/Ta)n multilayer thin films [J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2018, 54(8): 1-7.
[27] HERZER G. Modern soft magnets: Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(3): 718-734.
[28] HERZER G. Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 1996, 157-158: 133-136.
[29] ABELES B, PINCH H L, GITTLEMAN J. Percolation conductivity in W-Al2O3 granular metal films [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1975, 35(4): 247-250.
[30] KULKARNI A, CHAKRAVADHANULA V, DUPPEL V, MEYNERS D, ZAPOROJTCHENKO V, STRUNSKUS T, KIENLE L, QUANDT E, FAUPEL F. Morphological and magnetic properties of TiO2 /Fe50Co50 composite films [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2011, 46(13): 4638-4645.
[31] INOUE J, MAEKAWA S. Theory of tunneling magnetoresistance in granular magnetic films [J]. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter, 1996, 53(18): R11927- R11929.
[32] CAO Y, KOBAYASHI N, ZHANG Y W, OHNUMA S, MASUMOTO H. Enhancement of low-field magneto- dielectric response in two-dimensional Co/AlF granular films [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(7): 072902.
陈浩禹1,2,张亦文1,2,吴 忠2,秦真波2,吴珊珊1,2,胡文彬1,2
1. 天津大学 先进陶瓷与加工技术教育部重点实验室,天津 300072;
2. 天津大学 材料科学与工程学院,天津 300072
摘 要:采用磁控溅射法在不同基底温度下制备Co-TiO2纳米复合薄膜。所合成的纳米复合薄膜由TiO2非晶基体和分散其中的Co颗粒组成,呈铁磁和超顺磁共存的特性。随着基底温度从室温升高到400 °C,Co颗粒尺寸逐渐增大,氧化程度明显降低。因此,在Co含量相同的情况下,随着基底温度的升高(从室温升高至400 °C),饱和磁化强度从0.13增加到0.43 T。在高基底温度下,一部分Co颗粒聚集形成导电路径,导致电阻率从1600快速下降至76 μΩ·m。即使在电阻率低至76 μΩ·m的情况下,依然能获得Co-TiO2的磁电阻性能。结果表明,纳米复合薄膜在室温下具有低Co氧化、高磁化强度和磁阻特性。
关键词:Co;TiO2;纳米复合薄膜;铁磁性能;超顺磁性能;磁电阻
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (2016YFE0205700) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; Project (18JCYBJC18000) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City, China
Corresponding author: Yi-wen ZHANG, Tel: +86-17822008898, E-mail: ywzsci@tju.edu.cn;
Zhong WU, Tel: +86-13664537723, E-mail: wuzhong2319@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65396-1

