DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.08.001
耐受全氟辛酸细菌的筛选及其对胁迫的生理响应
易浪波1, 2,柴立元1,彭清忠2,唐崇俭1,周璐璐2
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院, 湖南 长沙, 410083;
2. 吉首大学 生物资源与环境科学学院, 湖南 吉首, 416000)
摘要:为探究微生物对全氟辛酸(PFOA)胁迫的耐受性和生理响应,采用梯度压力驯化法,获得4株能以PFOA为唯一碳源生长的细菌,基于形态学、生理生化特性和16S rRNA基因序列分析,初步鉴定菌株YAB-1为类黄色假单胞菌(Pseudomonas parafulva),YAB-2,YAB-3和YAB-4分属于葡萄球菌属(Staphylococcus sp.)、假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas sp.)和苍白杆菌属(Ochrobactrum sp.)。4株细菌耐受PFOA能力不同,其中菌株YAB-1表现出最强的耐受性能,在1 200 mg/L PFOA胁迫下仍能良好生长。研究优势菌对PFOA胁迫的生理响应发现,菌株YAB-1的丙二醛(MDA)质量摩尔浓度随着PFOA胁迫质量浓度的升高而增加,高质量浓度PFOA长期胁迫可致MDA质量摩尔浓度显著降低。当PFOA质量浓度为1 200 mg/L时,膜上Na+ K+-ATP 酶活性与Ca2+ Mg2+-ATP 酶活性显著降低。菌株YAB-1的超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和谷胱甘肽转移酶(GST)活性也表现出明显的剂量—效应关系,低质量浓度和中等质量浓度PFOA胁迫可致3种抗活性显著高于对照组,而高质量浓度PFOA胁迫会导致酶活性显著降低。菌株YAB-1能耐受并适应较高质量浓度的PFOA胁迫,推测是一株优良的降解PFOA的微生物菌株。
关键词:全氟辛酸(PFOA);耐受菌;耐受性;生理毒性
中图分类号:X592 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2019)08-1759-09
Screening of PFOA-resisting bacteria and their physiological response to stress
YI Langbo1, 2, CHAI Liyuan1, PENG Qingzhong2, TANG Chongjian1, ZHOU Lulu2
(1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. College of Biology and Environmental Sciences, Jishou University, Jishou 416000, China)
Abstract: In order to investigate the tolerance and physiological response of microorganisms under perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) stress, four PFOA-degrading bacterza were acquirecd through gradient pressure domestication and enrichment culture, which can use PFOA as the sole carbon source. Based on colony morphology, physiological and biochemical features, and 16S rRNA gene sequencing, strain YAB-1 was preliminarily identified as Pseudomonas parafulva, and YAB-2, YAB-3 and YAB-4 belonged to Staphylococcus sp., Pseudomonas sp., Ochrobactrum sp., respectively . The results show that there are difference on the maximum tolerable capacity of PFOA, and YAB-1 shows the strongest tolerance to PFOA and maintaines normal growth under 1 200 mg/L PFOA stress. Subsequently the physiological response of dominant strain YAB-1 to PFOA stress was investigated, and it is found that the malondialdehyde (MDA) content of strain YAB-1 increases with the increase of PFOA stress mass concentration. High stress mass concentration and long-term stress of PFOA can cause a MDA concentration significant decrease. When the mass concentration of PFOA is 1 200 mg/L, the activities of Na+K+-ATPase and Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase in the membrane of strain YAB-1 significantly decrease. The superoxide dismutase(SOD), catalase(CAT), and glutathione transferase(GST) activities of strain YAB-1 also show a significant dose-effect relationship. Low and medium mass concentrations of PFOA stress cause three antioxidant enzymes to be significantly higher activities than that of the control group, while high mass concentration of PFOA stress leads to a significant decrease in these enzyme activities of strain YAB-1. Strain YAB-1 can tolerate and adapt to the higher mass concentration of PFOA stress, and is presumed to be a better PFOA-degrading microorganism.
Key words: perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA); PFOA-resisting bacterium; tolerance; biological toxicity
全氟化合物(perfluorinated compounds,PFCs)指氢原子全部被氟取代的卤代有机化合物,具备优良的稳定性、表面活性和疏水疏油等特性[1-2]。全氟辛酸(perfluorooctane acid, PFOA)作为PFCs的典型代表之一,过去几十年广泛应用于机械、纺织、石化、电子、轻工、汽车、航空航天等行业[3-5]。随着其大量使用,近些年在多种环境介质、生物体和人体中不断被检测出,从人群密集的城市到少有人类活动的极地区域,呈现出全球分布态势[6]。由于PFOA污染广、性质极其稳定、生物蓄积性强、毒性高,已经严重威胁到人类健康和整个生态环境的安全[7],成为继多氯联苯和二噁英之后日益引起人们重视的新型持久性有机污染物(POPs)。近年来,国内外学者陆续开展微生物降解PFOA的研究工作,如薛学佳等[8]通过驯化筛选得到可利用氟代有机化合物为唯一碳源生长的细菌Z1和Z3,经LG-MS检测分析发现全氟辛酸分子中与羧基相邻碳的1个氟被氢取代。何海涛等[9]通过富集筛选获得降解PFOA的克雷白氏杆菌(Klebsiella sp.)。SCHR DER等[10-11]证明在严格限定氧的条件下活性污泥能降解PFOA。但这些微生物降解PFOA效率低,除了PFOA具有优良的稳定性,其强的生物毒性抑制微生物生长也是重要原因。因此,筛选耐受PFOA能力强的降解菌是生物修复技术应用的前提。微生物在生态系统中扮演重要角色,其生物特性与生态系统的功能密切相关[12]。微生物在受到PFOA等不利环境胁迫时,会产生活性氧自由基(ROS),诱导体内脂质过氧化反应,引起微生物的损伤甚至凋亡。生物体内的抗氧化应激系统对氧化胁迫极为敏感,其活性可以间接反映机体细胞中ROS的浓度,因此,测试表征ROS水平的指标,如丙二醛(MDA)质量摩尔浓度、ATP酶、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和谷胱甘肽转移酶(GST)等的活性变化能监测微生物对PFOA胁迫的生理响应,理解微生物对PFOA胁迫的适应性和耐受机制。本研究从长期受氟化物污染的环境中筛选能以PFOA为唯一碳源生长的优良菌株,研究其在PFOA胁迫下的耐受能力和生理响应及其耐受机制。
DER等[10-11]证明在严格限定氧的条件下活性污泥能降解PFOA。但这些微生物降解PFOA效率低,除了PFOA具有优良的稳定性,其强的生物毒性抑制微生物生长也是重要原因。因此,筛选耐受PFOA能力强的降解菌是生物修复技术应用的前提。微生物在生态系统中扮演重要角色,其生物特性与生态系统的功能密切相关[12]。微生物在受到PFOA等不利环境胁迫时,会产生活性氧自由基(ROS),诱导体内脂质过氧化反应,引起微生物的损伤甚至凋亡。生物体内的抗氧化应激系统对氧化胁迫极为敏感,其活性可以间接反映机体细胞中ROS的浓度,因此,测试表征ROS水平的指标,如丙二醛(MDA)质量摩尔浓度、ATP酶、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和谷胱甘肽转移酶(GST)等的活性变化能监测微生物对PFOA胁迫的生理响应,理解微生物对PFOA胁迫的适应性和耐受机制。本研究从长期受氟化物污染的环境中筛选能以PFOA为唯一碳源生长的优良菌株,研究其在PFOA胁迫下的耐受能力和生理响应及其耐受机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 样品
采集武汉某氟化物工厂污水处理中心的活性污泥,共6份,分别装入无菌塑料袋,低温运至实验室。
1.1.2 培养基
富集培养基各种组分的质量浓度如下:NaCl为2 g/L,KH2PO4 为1 g/L,NH4NO3为5 g/L, K2HPO4 为1 g/L,CaCl2·2H2O为0.05 g/L,MgSO4·7H2O为0.5 g/L,酵母膏为1 g/L;根据需要添加不同质量的PFOA。pH为7.0,实验压力为1.01×105 Pa,并在120 ℃条件下灭菌20 min。
筛选培养基(改良的无机盐离子培养基)的质量浓度如下:NaCl为2 g/L,KH2PO4 为1 g/L,NH4NO3为5 g/L,K2HPO4为1 g/L,CaCl2·2H2O为0.05 g/L,MgSO4·7H2O为0.5 g/L,PFOA为500 mg/L;pH为7.0,实验压力为1.01×105 Pa,并在120 ℃条件下灭菌20 min。配制固体培养基时加琼脂粉15 g/L。
鉴定培养基(改良的牛肉膏蛋白胨培养基)的质量浓度如下:酵母膏为5 g/L,蛋白胨为10 g/L,NaCl为10 g/L,PFOA为500 mg/L;pH为7.0,实验压力为1.01×105 Pa,在120 ℃条件下灭菌20 min,配制固体培养基时加琼脂粉15 g/L。
葡萄糖无机盐离子培养基的质量浓度如下:NaCl为2 g/L,KH2PO4为1 g/L,NH4NO3为5 g/L,K2HPO4为1 g/L,CaCl2·2H2O为0.05 g/L,MgSO4·7H2O为0.5 g/L,PFOA为500 mg/L,葡萄糖2为g/L;pH为7.0,实验压力为1.01×105 Pa,在115 ℃条件下灭菌20 min。
1.1.3 仪器与试剂
提取细菌基因组DNA,PCR扩增所用酶和试剂均购自宝生物工程(大连)有限公司,PFOA(纯度98%)购自Sigma公司,MDA,ATP,SOD,CAT和GST等酶试剂盒购自南京建成生物工程研究所,其他分析纯化学试剂购自湖南科化工贸有限公司。配置PFOA溶液和振荡实验所用器皿均为聚丙烯容器。
实验仪器:J810R型台式冷冻离心机(德国艾本德股份公司);ABI-2720 PCR扩增仪(美国ABI公司),Tanon 1600R全自动数码凝胶成像分析系统(上海天能科技有限公司);JY98-iiin超声波细胞粉碎机(新芝生物科技股份有限公司);UV-2600紫外可见分光光度计(日本岛津仪器公司);FC酶标仪(美国热电);125 mL和500 mL聚丙烯锥形瓶(美国乐基因)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 PFOA耐受细菌的分离
将6份样品混合均匀,随机称取5 g样品接种于95 mL PFOA质量浓度为150 mg/L的富集培养基中,于30 ℃、转速160 r/min下振荡培养,每7 d以5%的接种量转接至新鲜富集培养基中,每转接2次,PFOA的质量浓度增加50 mg/L,当PFOA质量浓度增至500 mg/L时,继续传代培养4周,菌株驯化结束。取经驯化的菌液5 mL转入95 mL筛选培养基中,于30 ℃,转速160 r/min下振荡培养7 d,连续转接培养3次。取1 mL菌液按梯度稀释至10-6,吸取0.1 mL稀释液涂布于筛选培养基平板上,于30 ℃倒置培养7 d,观察菌株生长情况。挑取生长状态良好的菌落进行传代纯化。纯化后的菌株用15%的甘油于-70 ℃保存。
1.2.2 菌株鉴定
1) 菌株的形态及生理生化特性。将富集纯化的菌株接种于鉴定培养基上,于35 ℃培养96 h,观察菌落形态特征。各细菌菌株生理生化特性检测按文献[13]方法进行。
2) 16S rRNA基因序列测定及系统发育分析。采用CTAB法提取细菌总DNA,以其为模板,利用16S rRNA基因通用引物PA:5′-AGAGTTTGA TCCTGGCTCAG-3′和PB:5′-TTAAGGTGAT CCAGCCGCA-3′进行PCR扩增。反应程序如下:于95 ℃预变性5 min,于95 ℃变性30 s,于55 ℃退火30 s,于72 ℃延伸80 s,经过30个循环,最后于72 ℃延伸10 min。经电泳检测PCR产物合格后送生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司测序。
将测序所得16S rRNA基因序列用BLAST软件在GenBank数据库进行检索,下载相似性较高的16S rRNA基因序列,采用CLUSTAL-X软件多重比对序列,系统进化距离矩阵根据Kimura模型估算,用MEGA 4. 0软件进行聚类分析和系统进化树构建。
1.2.3 菌株对PFOA的耐受性测定
从平板上挑取单菌落接种至牛肉膏蛋白胨液体培养基中,于30 ℃、转速160 r/min振荡培养,取对数生长中期的菌液10 mL,在转速6 000 r/min下离心5 min,弃上清,加无菌水10 mL混匀水洗,如此重复3次,制备在600 nm下吸光度(OD600)为2.0的菌悬液。
配置PFOA甲醇母液,经滤膜过滤除菌,分别加入至300 mL 牛肉膏蛋白胨培养基中,使PFOA质量浓度分别为0,300,600,900,1 200和1 500 mg/L。培养基振荡30 min脱除甲醇后,接入0.3 mL菌悬液,于30 ℃、转速为160 r/min条件下培养,定期取样测定菌液OD600,考察菌株对PFOA的耐受性。
1.2.4 PFOA质量浓度对菌株酶活的影响
根据菌株对PFOA的耐受程度,分别设置对照 (0 mg/L)和低(600 mg/L)、中(900 mg/L)、高(1 200 mg/L)共4个PFOA处理质量浓度组,按1%的接菌量将菌株接种至LB液体培养基中振荡培养(30 ℃,160 r/min),每24 h取样60 mL,于6 000 r/min离心10 min,弃上清,用PBS缓冲液洗2次,并重悬,于冰浴超声破碎(功率300 W,开3 s,停5 s)10 min,然后将样品分成3份:第1份于1 000 r/min 离心5 min后,取上清液2 mL测定ATP酶活性;第2份在4 ℃、转速3 000 r/min下离心10 min,取上清测定蛋白质,SOD,CAT和GST酶活性;第3份在10 000 r/min下离心10 min,取上清液测定MDA浓度。MDA质量摩尔浓度,ATP酶,SOD酶、CAT活性和还原性GSH酶均采用可见分光光度法测定,测定方法按照试剂盒的说明。每组实验重复3次。
1.2.5 数据统计分析
实验数据采用3次平均值加减标准差表示,利用SPSS19.0统计软件对实验数据进行方差分析和显著性检验,并采用origin8.5绘制图表。
2 结果与分析
2.1 菌株的分离、形态及生理生化特性
经长期梯度压力驯化和富集筛选,分离获得4株细菌,分别编号为YAB-1,YAB-2,YAB-3和YAB-4。根据驯化的最终质量浓度可知这4株细菌至少能耐受500 mg/L的PFOA,且能在PFOA为唯一碳源的筛选培养基中生长,表明其能转化利用PFOA。将4株菌分别接种至LB培养基平板培养3 d后,菌落形态如图1所示。
由图1可见:YAB-1菌落直径为1.5~2.5 mm,呈金黄色,表面湿润,边缘整齐,圆形隆起;YAB-2菌落直径0.5~1.0 mm,呈淡黄色,表面湿润,边缘整齐,圆形隆起;YAB-3菌落呈乳白色,表面较干燥,边缘不整齐,扁平难挑起;YAB-4菌落直径1.0~2.0 mm,半透明乳白色,表面湿润,边缘整齐,圆形隆起。
分离菌株的革兰氏染色检测发现:菌株YAB-2为革兰氏阳性菌,其他3株细菌为革兰氏阴性菌。部分生理生化反应检测结果如表1所示。
2.2 16S rRNA基因序列测定及系统发育分析
以4株细菌基因组DNA为模板,利用PCR成功扩增出16S rRNA基因片段,PCR产物经测序、序列校对后与公共数据库中相似度较高的同源序列进行多重比对和构建系统进化树(见图2)。结果表明:菌株YAB-1以99.86%的相似值与Pseudomonas parafulva(NR 040859)聚为一支;菌株YAB-2与Staphylococcus aureus(MH496642)序列同源性为99%;菌株YAB-3与Pseudomonas sp.(JX416381)聚在一起,16S rRNA基因序列同源性达99%;YAB-4与苍白杆菌属菌株处于同一分支,与Ochrobactrum anthropi(KM8994186)的同源性达99%;结合其菌落形态和生理生化特性,鉴定菌株YAB-1,YAB-2,YAB-3和YAB-4分属于类黄色假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas sp.),葡萄球菌属 (Staphylococcus sp.),假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas sp.)和苍白杆菌属(Ochrobactrum sp.)。
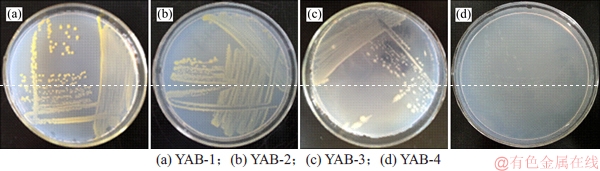
图1 细菌菌落形态
Fig. 1 Colony morphological characters of isolates
表1 菌株的生理生化实验结果
Table 1 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of the isolates
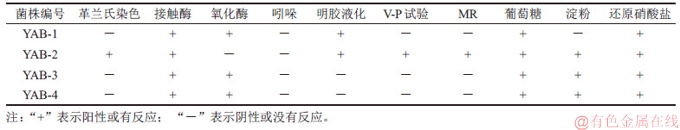
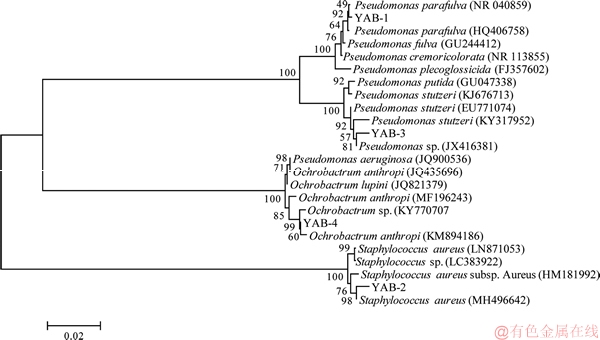
图2 基于16S rRNA基因序列构建的菌株与其相似性较高典型菌株的系统发育树
Fig. 2 Neighbor-Joining tree constructed based on 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showing phylogenetic relationships among strains and other related taxa
2.3 菌株对PFOA的耐受能力
根据预实验结果,按1%的接菌量接种测试菌至低、中、高这3种PFOA质量浓度的牛肉膏蛋白胨培养基中考察各细菌对PFOA的耐受情况,图3所示为不同质量浓度PFOA处理下菌株的生长曲线。
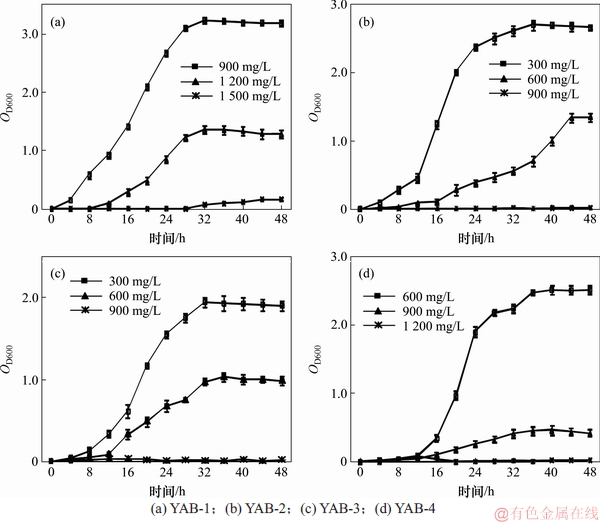
图3 PFOA处理下菌株的生长曲线
Fig. 3 Growth curves of the isolates in presence of PFOA
由图3(a)可知:当菌株YAB-1在PFOA质量浓度为900 mg/L和1 200 mg/L时,其生长规律符合微生物典型的生长曲线,而当PFOA质量浓度为1 500 mg/L时,菌株YAB-1不能生长。菌株YAB-1在900 mg/L PFOA胁迫下能较好生长,最大吸光度OD600可达3.238 3。当PFOA质量浓度为1 200 mg/L时,菌体生长相对缓慢,生物量显著降低,最大OD600仅为1.369 0。当PFOA质量浓度为1 500 mg/L时,PFOA对菌株毒害作用显著,菌体几乎不增长,菌液OD600接近0。
由图3(b)可知:当PFOA质量浓度为300 mg/L时菌株YAB-2生长良好(最大OD600为2.705 5);当PFOA质量浓度为600 mg/L时,菌株生长受到一定程度抑制;当受到900 mg/L PFOA胁迫时,菌株YAB-2不生长。
由图3(c)可知:菌株YAB-3在PFOA质量浓度梯度设置与YAB-2相同的条件下,生长规律也类似。菌株YAB-4对PFOA的耐受情况如图3(d)所示,在600 mg/L PFOA胁迫下生长良好,在900 mg/L PFOA胁迫下菌株生长显著降低,菌液最大OD600仅为0.465 9;当PFOA为1 200 mg/L时,菌株YAB-4无法生长。
PFOA对菌株有一定的毒害作用,高质量浓度的PFOA会显著抑制菌体增值,但4株菌仍表现出较强的耐受性和生长适应性,这可能与其筛选于长期受PFOA污染的样品有关。比较4株菌对PFOA的耐受性发现,不同菌株的耐受能力不同,所能承受的PFOA胁迫质量浓度也不一样,菌株YAB-1对PFOA的耐受性最强,其次是YAB-4,而菌株YAB-2和YAB-3的耐受能力较弱。
2.4 PFOA对菌株YAB-1的生理毒性
2.4.1 MDA质量摩尔浓度
生物细胞内浓度过高的活性氧会攻击细胞膜中不饱和脂肪酸,进而影响膜的流动性与稳定性。MDA是膜脂过氧化的主要产物之一,是评价膜脂过氧化和细胞受胁迫程度的一项重要指标[14]。图4所示为PFOA对菌株YAB-1细胞MDA质量摩尔浓度的影响。由图4可见:培养基中不添加PFOA的对照组,菌体MDA质量摩尔浓度无明显变化;当菌株YAB-1被胁迫24 h时,PFOA质量浓度越高,MDA质量摩尔浓度越高;当PFOA质量浓度为1 200 mg/L时MDA质量摩尔浓度达最高值,为19.2 nmol/g;当胁迫32 h时,MDA质量摩尔浓度变化随PFOA质量浓度提高而逐步升高,但在高质量浓度PFOA胁迫下MDA质量摩尔浓度较胁迫24 h已显著降低。当胁迫48 h时,低质量浓度和中等质量浓度PFOA胁迫能引起MDA质量摩尔浓度增加,高质量浓度PFOA胁迫会使MDA质量摩尔浓度显著降低。以上结果表明:低质量浓度PFOA短期胁迫菌株YAB-1细胞的MDA质量摩尔浓度无显著变化,长期胁迫会使MDA质量摩尔浓度显著上升;高质量浓度PFOA短期胁迫则使MDA质量摩尔浓度显著升高,长期胁迫可使菌体MDA质量摩尔浓度显著降低。
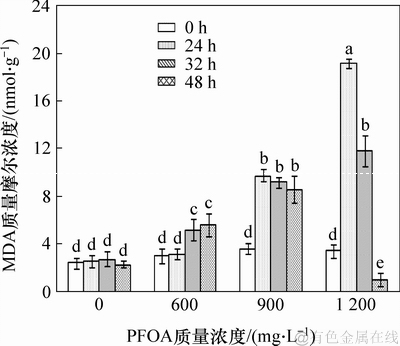
图4 PFOA 对菌株YAB-1细胞MDA 浓度的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of different time and PFOA concentrations on MDA of strain YAB-1
2.4.2 ATP酶活性
在PFOA胁迫下,菌株YAB-1细胞膜Na+K+-ATPase和Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase酶活性变化规律如图5所示。菌株YAB-1在没有PFOA胁迫下,Na+K+-ATPase和Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase酶活性无显著变化;低质量浓度PFOA胁迫能引起Na+K+-ATPase酶活性持续显著升高,而Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase酶活性自24 h显著升高后维持稳定。中等质量浓度PFOA胁迫能诱导Na+K+-ATPase和Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase酶活性出现相似的变化规律,即24 h时酶活性显著升高,随后酶活显著降低。高质量浓度PFOA胁迫菌株致使2种ATPase的活性与对照相比均显著降低。
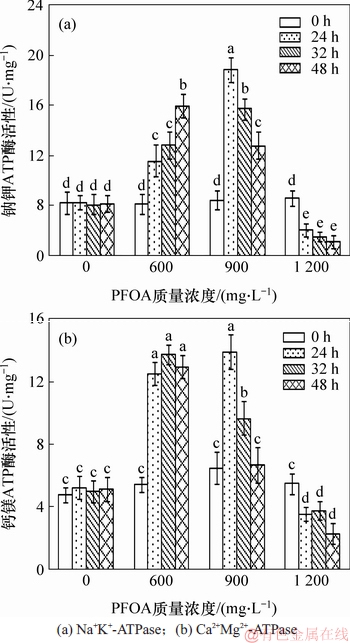
图5 PFOA对菌株YAB-1细胞ATP酶活性的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of different time and PFOA concentrations on ATPase activitres of strain YAB-1
2.4.3 SOD酶活性
机体遭受逆境胁迫时,会形成大量的活性氧自由基,从而造成氧化损伤。而抗氧化酶的存在可以降低活性氧自由基,抑制膜脂过氧化,维持细胞正常的生理功能。图6所示为菌株YAB-1遭受不同剂量PFOA胁迫时,SOD抗氧化酶活性随反应时间的变化情况。由图6可知:低质量浓度PFOA胁迫能够引起菌体SOD酶活显著升高;中等质量浓度PFOA能够刺激机体产生大量SOD,被胁迫32 h时,机体产生的SOD酶活性达最大值,为0.399 2 U/mg;高质量浓度PFOA胁迫菌株会抑制机体产生SOD,致使SOD活性显著下降。
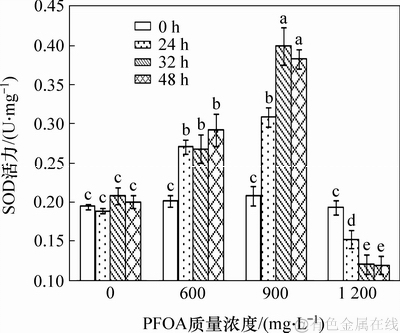
图6 PFOA对菌株YAB-1细胞SOD酶活力的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of PFOA on SOD activity of strain YAB-1
2.4.4 CAT酶活性
CAT酶是抗氧化防御系统中一类重要的酶,能将SOD酶歧化产生的H2O2分解成为H2O和O2,从而消除细胞内过剩的活性氧自由基,保护细胞稳定的内环境及细胞的正常代谢。图7所示为PFOA对菌株YAB-1细胞CAT酶活力的影响。由图7可知:低质量浓度PFOA胁迫诱导菌株YAB-1细胞CAT酶升高,胁迫32 h时CAT活性达最大为0.361 9 U/mg;中等质量浓度PFOA会诱导菌株CAT活性缓慢升高,之后趋于平缓,48 h后CAT活性达最高为0.294 3 U/mg。采用高质量浓度PFOA处理菌株,CAT活性与处理时间呈负相关,培养至48 h时,菌体CAT活性仅为0.115 4 U/mg,显著低于对照组。
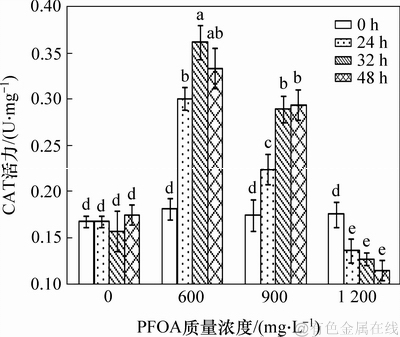
图7 PFOA对菌株YAB-1细胞CAT酶活力的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of different time and PFOA concentrations on CAT activity of strain YAB-1
2.4.5 GST酶活性
作为非酶抗氧化系统一类重要的物质GST,也是活性氧自由基重要的清除剂,能保护细胞膜中含巯基的蛋白质和酶不被氧化变性,从而维持细胞体内活性氧自由基的动态平衡。图8所示为菌株YAB-1细胞从图8可见:GST在不同质量浓度PFOA胁迫下的变化关系曲线。低质量浓度PFOA胁迫能引起菌株YAB-1随时间延长而GST活性大幅增长,48 h时达到最大值,GST活性为0.077 8 U/mg;中等质量浓度PFOA能诱导菌株GST活性随时间延长而小幅增长,48 h时达最大值,GST活性为0.047 3 U/mg。高质量浓度PFOA胁迫不能诱导GST活性显著变化。
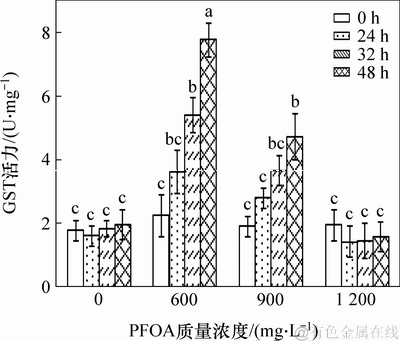
图8 PFOA 对菌株YAB-1细胞GST 酶活力的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of different time and PFOA concentrations on GSH of strain YAB-1
3 讨论
3.1 分离株耐受PFOA能力
本研究采用梯度压力驯化和以PFOA为唯一碳源富集培养,筛选获得4株耐受力较强的细菌。其中,菌株YAB-1表现出突出的耐受优势,在1 200 mg/L PFOA胁迫下仍能生长。总体来看,4株菌对PFOA的耐受性相比薛学佳等[8]分离的降解菌Z1和Z3更强,也远优于符安等[15]报道的酿酒酵母耐受PFOA的能力(<100 mg/L)。推测分离菌株来自受氟化物污染的环境,长期的选择压力导致部分细菌发生突变以适应新的环境,耐受能力显著提高。同时,开展这些菌株对PFOA降解效率的研究,发现4株细菌在优化培养条件下PFOA降解率达到25%~35%,其中菌株YAB-1的最大降解率为32.4%[16]。
3.2 PFOA胁迫对耐受菌的细胞毒性
微生物受到外界胁迫时,会引发细胞内ROS含量升高,过量的ROS会导致细胞质膜的过氧化而引起膜氧化损伤。MDA是细胞膜脂过氧化作用的产物之一,可用来表征细胞膜脂过氧化作用能力,揭示细胞膜损伤程度。本研究中,菌株YAB-1细胞内的MDA质量摩尔浓度随PFOA质量浓度的增加而显著升高。当PFOA质量浓度升高到1 200 mg/L时,随着胁迫时间的延长,菌体内MDA浓度呈现出先升高后降低的变化趋势,这表明污染物胁迫可以增加细胞内活性氧的积累,引起菌体细胞膜脂质化,MDA浓度升高。MDA浓度越高说明细胞膜损伤越严重,当长时间高质量浓度胁迫后,细胞膜损伤,可致菌体破裂解体,MDA释放至溶液中,膜上MDA相对浓度降低。邓庭进等研究微囊藻毒素对细菌中MDA浓度影响时也证实了该变化规律[17]。重金属胁迫也会造成MDA在微生物细胞质膜上积累,从而降低质膜的流动性,损伤细胞[18]。
Na+K+-ATPase和Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase等ATP酶广泛存在于细胞膜及细胞器膜上,对维持细胞能量代谢和细胞内外渗透压平衡、离子运输和细胞膜完整性起着重要作用。当中等质量浓度PFOA胁迫时,能诱发菌株YAB-1细胞膜上Na+K+-ATPase和Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase酶活性显著升高,在高质量浓度PFOA胁迫下,这2种ATP酶活性显著降低。胁迫初期菌体通过提高酶的活性来维持细胞膜两侧的膜电位,维持细胞内外渗透压平衡,当ROS积累过量时,膜系统完整性受损严重,膜上的ATP酶也受到攻击,ATP酶活下降,物质运输受阻,进而使得细胞凋亡。不同种类的菌株对PFOA的响应情况不同,杨蒙等[19]研究PFOA对大肠杆菌细胞膜上的Na+K+-ATPase和Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase活性发现,10 mg/L的PFOA胁迫36 h即能诱导ATP酶活力下降,符安等[15]通过研究PFOA对酵母菌细胞膜上ATP酶活性影响得出,100 mg/L PFOA 对酿酒酵母具有即时毒性,能使ATP酶活性降低,致使细胞凋亡,本实验室筛选的菌株YAB-1较之有突出的耐受优势,这与菌株来源于受PFOA长期胁迫的环境有关。
逆境胁迫诱发生物体产生的ROS和SOD是细胞对抗ROS的第一道防线,能将细胞内过量的O2-歧化为H2O2和H2O,而CAT则能有效地把H2O2转化成H2O和O2,降低氧自由基的毒性,增强细菌的耐受性和适应性。在本研究中,菌株YAB-1细胞SOD和CAT活性在遭受到低质量浓度PFOA胁迫时与对照相比显著增加,在高质量浓度PFOA胁迫时,SOD和CAT酶活性均显著降低。低质量浓度PFOA能引发机体产生活性氧,从而诱导抗氧化酶浓度升高,高质量浓度PFOA长时间胁迫会引起机体ROS大量积累,机体不能及时清除造成氧化损伤,导致酶活性降低。这与王志刚等[20]研究邻苯二甲酸二甲酯对典型细菌Bacillus subtilis B19和Escherichia coli K12的氧化损伤所得结果一致。
机体内GST易与有害物质亲电结合,具有解毒作用。菌株YAB-1在小于900 mg/LPFOA处理下,刺激机体产生大量的GST与PFOA或其他中间代谢物结合,阻止外源化合物与细胞内其他生物大分子结合,从而实现减毒效应,增强机体对毒物的耐受性能。随着PFOA浓度升高,氧化损伤加剧,细胞受损甚至凋亡,导致GST活性降低。
4 结论
1) 筛选到4株以PFOA为唯一碳源生长的细菌,鉴定YAB-1为类黄色假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas parafulva),YAB-2,YAB-3和YAB-4分别属于葡萄球菌属(Staphylococcus sp.),假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas sp.)和苍白杆菌属(Ochrobactrum sp.)。
2) 对分离株进行PFOA耐受胁迫分析,发现低质量浓度PFOA胁迫细菌生长速度快,在中等质量浓度PFOA胁迫下生长相对较慢,生物量较低;高质量浓度PFOA抑制菌株增值。菌株YAB-1表现出较强的PFOA耐受性。
3) 优势耐受菌YAB-1受低质量浓度PFOA短期胁迫后,引起细胞内MDA相对质量摩尔浓度显著升高,膜上Na+ K+-ATP 酶活性与Ca2+ Mg2+-ATP 酶活性显著升高,胞内SOD,CAT和GST酶活性显著升高。当高质量浓度长时胁迫时,细胞内MDA浓度显著降低,膜上Na+ K+-ATP 酶活性与Ca2+ Mg2+-ATP 酶活性显著降低,胞内SOD和CAT 酶活性显著降低。
参考文献:
[1] ARVANITI O S, STASINAKIS A S. Review on the occurrence, fate and removal of perfluorinated compounds during wastewater treatment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 524/525: 81-92.
[2] PRAMANIK B K, PRAMANIK S K, SARKER D C, et al. Removal of emerging perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate contaminants from lake water[J]. Environmental Technology, 2017, 38(15): 1937-1942.
[3] LI Qifeng, WANG Tieyu, ZHU Zhaoyun, et al. Using hydrodynamic model to predict PFOS and PFOA transport in the daling river and its tributary, a heavily polluted river into the bohai sea, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 167: 344-352.
[4] TEAF C M, GARBER M M, COVERT D J, et al. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA): environmental sources, chemistry, toxicology, and potential risks[J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination: an International Journal, 2019, 28(3): 258-273.
[5] SHAFIQUE U, SCHULZE S, SLAWIK C, et al. Perfluoroalkyl acids in aqueous samples from Germany and Kenya[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(12): 11031-11043.
[6] VEDAGIRI U K, ANDERSON R H, LOSO H M, et al. Ambient levels of PFOS and PFOA in multiple environmental media[J]. Remediation Journal, 2018, 28(2): 9-51.
[7] RAINIERI S, CONLLEDO N, LANGERHOLC T, et al. Toxic effects of perfluorinated compounds at human cellular level and on a model vertebrate[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2017, 104: 14-25.
[8] 薛学佳, 周钰明, 吴敏, 等. 含氟有机化合物优势降解菌的筛选[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2004, 27(1): 11-12, 110-111.
XUE Xuejia, ZHOU Yuming, WU Min, et al. Screening of dominant strains of degrading organo-fluorine compounds[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2004, 27(1): 11-12, 110-111.
[9] 何海涛, 马中良, 罗会华, 等. 全氟化合物的微生物降解研究[C]// 中国化学会第十二届全国氟化学会. 论文摘要集. 南昌: 江西师范大学出版社, 2012: 64.
HE Haitao, MA Zhongliang. LUO Huihua, et al. Biodegradation of perfluorinated compounds[C]// The Twelvth Chinese Chemical Society National Conference on Fluoride Chemistry. Nanchang: Jiang Normal University Press, 2012: 64.
[10] SCHR DER H F. Determination of fluorinated surfactants and their metabolites in sewage sludge samples by liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry after pressurised liquid extraction and separation on fluorine-modified reversed-phase sorbents[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2003, 1020(1): 131-151.
DER H F. Determination of fluorinated surfactants and their metabolites in sewage sludge samples by liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry after pressurised liquid extraction and separation on fluorine-modified reversed-phase sorbents[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2003, 1020(1): 131-151.
[11] MEESTERS R J W, SCHR DER H F. Perfluorooctane sulfonate - a quite mobile anionic anthropogenic surfactant, ubiquitously found in the environment[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 50(5): 235-242.
DER H F. Perfluorooctane sulfonate - a quite mobile anionic anthropogenic surfactant, ubiquitously found in the environment[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 50(5): 235-242.
[12] GRAHAM E B, WIEDER W R, LEFF J W, et al. Do we need to understand microbial communities to predict ecosystem function? A comparison of statistical models of nitrogen cycling processes[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 68: 279-282.
[13] 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 128-244.
DONG Xiuzhu, CAI Miaoying. Manual of determinative bacteriology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 128-244.
[14] 李延, 刘丽君, 梁文艳. 儿茶酚胁迫下铜绿微囊藻的生理生化响应[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(6): 2781-2785.
LI Yan, LIU Lijun, LIANG Wenyan. Physiological and biochemical responses of Microcystis aeruginosa to catechol stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(6): 2781-2785.
[15] 符安, 杨蒙, 叶锦韶, 等. 全氟辛酸对酿酒酵母细胞毒性作用[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(4): 1486-1492.
FU An, YANG Meng, YE Jinshao, et al. Cytotoxicity of pentadecafluorooctanoic acid on saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(4): 1486-1492.
[16] YI Langbo, CHAI Liyuan, XIE Yu, et al. Isolation, identification, and degradation performance of a PFOA-degrading strain. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2016, 15(2), 1-12.
[17] 邓庭进, 尹华, 叶锦韶, 等. Pseudomonas putida细胞对微囊藻毒素-LR的胁迫响应[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(2): 603-609.
DENG Tingjin, YIN Hua, YE Jinshao, et al. Response of Pseudomonas putida cells to MC-LR stress[J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(2): 603-609.
[18] 杨钰昆, 杨文飞, 常媛媛, 等. 硒对镉胁迫下酿酒酵母抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品科学, 2018, 39(22): 129-134.
YANG Yukun, YANG Wenfei, CHANG Yuanyuan, et al. Effects of selenium on antioxidant activity of saccharomyces cerevisiae under cadmium stress[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(22): 129-134.
[19] 杨蒙, 李祎, 叶锦韶, 等. 全氟辛酸对大肠杆菌的氧化胁迫和膜损伤[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(3): 1167-1172.
YANG Meng, LI Yi, YE Jinshao, et al. Effect of PFOA on oxidative stress and membrane damage of escherichia coli[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(3): 1167-1172.
[20] 王志刚, 胡影, 崔竞文. 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯对典型细菌生长和氧化应激酶系的影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(3): 297-303.
WANG Zhigang, HU Ying, CUI Jingwen. Impact of dimethyl phthalate on the activities of oxidative stress enzymes and growth of typical Bacteria[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(3): 297-303.
(编辑 秦明阳)
收稿日期: 2019 -03 -01; 修回日期: 2019 -05 -10
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(31760033);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(2018JJ3414);湖南省教育厅优秀青年项目(17B217)(Project(31760033) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2018JJ3414) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province; Project(17B217) supported by the Educational Commission of Hunan Province)
通讯作者:柴立元,博士,教授,从事有色冶金、环境工程领域研究,E-mail:lychai@mail.csu.edu.cn