氮元素对CrFeMnVTi6高熵合金显微组织和力学性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第8期
论文作者:张琳 宋若康 屈国欣 路通
文章页码:2415 - 2427
关键词:高熵合金;氮元素;力学性能;间隙固溶强化
Key words:high entropy alloy; nitrogen element; mechanical properties; interstitial strengthening
摘 要:为了评估氮元素的间隙固溶强化机制对高熵合金性能的影响,采用机械冶金化和放电等离子体烧结工艺制备N掺杂CrFeMnVTi6高熵合金,并利用XRD、SEM、TEM和FIB检测手段对合金的相组成及显微组织进行表征。实验结果显示,CrMnFeVTi6合金组织由TiNx、BCC、Laves相和B2有序相组成。因此,合金在低温区域(<380 °C)具有极高的强度(>2729 MPa)和硬度。针对该高熵合金的BBC基体进行不同强化机制的定量计算,结果表明,氮元素引起的间隙固溶强化效果为~634 MPa/at.%,远好于其他合金中的碳或硼元素,这表明,在高熵合金里添加氮元素能够有效提高合金强度。
Abstract: In order to evaluate interstitial strengthening effect on the properties of high entropy alloy (HEA), a nitrogen-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA was fabricated by mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). XRD, SEM, TEM and FIB were used to characterize the phase composition and microstructure of this material. The sintered bulk HEA exhibits a microstructure comprising TiNx, BCC, Laves and B2 phases. The HEA exhibits high yield strength (>2729 MPa) and hardness in lower temperature range of <380 °C. Quantitative calculations of the contributions from each strengthening mechanism in the BCC phase indicate that the interstitial strengthening by nitrogen is the dominant mechanism. Nitrogen additions in the BCC phase can produce a yield strength increase of ~634 MPa/at.%, which is much higher than the strengthening effects of carbon or boron additions in other alloys. This demonstrates that adding nitrogen is a viable approach for enhancing the strength of HEAs.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 2415-2427
Lin ZHANG1, Ruo-kang SONG2, Guo-xin QU2, Tong LU3
1. Bgrimm MTC Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 102628, China;
2. Beijing System Design Institute of Electro Mechanic Engineering, Beijing 100854, China;
3. The Fourth Academy of CASIC, Beijing 100028, China
Received 1 September 2020; accepted 28 June 2021
Abstract: In order to evaluate interstitial strengthening effect on the properties of high entropy alloy (HEA), a nitrogen-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA was fabricated by mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). XRD, SEM, TEM and FIB were used to characterize the phase composition and microstructure of this material. The sintered bulk HEA exhibits a microstructure comprising TiNx, BCC, Laves and B2 phases. The HEA exhibits high yield strength (>2729 MPa) and hardness in lower temperature range of <380 °C. Quantitative calculations of the contributions from each strengthening mechanism in the BCC phase indicate that the interstitial strengthening by nitrogen is the dominant mechanism. Nitrogen additions in the BCC phase can produce a yield strength increase of ~634 MPa/at.%, which is much higher than the strengthening effects of carbon or boron additions in other alloys. This demonstrates that adding nitrogen is a viable approach for enhancing the strength of HEAs.
Key words: high entropy alloy; nitrogen element; mechanical properties; interstitial strengthening
1 Introduction
In recent years, the high entropy alloys (HEAs) have attracted tremendous research interest in the field of materials science and metallurgical engineering, due to their unique alloy design concept [1-5]. The term ‘‘high entropy alloys’’ was first introduced, based on the hypothesis that the high configurational entropies of these alloys would stabilize the solid-solution phases and inhibit the formation of intermetallic compounds [6]. Conventionally, HEAs comprise more than five principal elements mixed in an equiatomic or near-equiatomic fraction. However, the criterion for HEA design has now been extended significantly [2]. It has been found that HEAs with non-equiatomic compositions also exhibit stable solid solutions despite their somewhat lower entropies of mixing [7,8]. In our previous work [9], phase formation and strengthening mechanisms of a dual-phase nanocrystalline CrMnFeVTi HEA were investigated. It is found that CrMnFeVTi HEA exhibits high compressive strength and hardness, and the solid solution strengthening effect in this HEA is mainly resulted from Ti because of its large atomic radius. It can be seen that increasing the concentration of Ti may further improve the hardness and compressive strength of the above HEA. So, a non-equiatomic CrMnFeVTi6 HEA was designed in this work.
In order to develop successful engineering alloys, various strengthening mechanisms, such as solid solution and precipitate strengthening, have been explored to further improve the strength of HEAs [1,2]. Substitutional solid solution strengthening in metals is usually considered to arise from the lattice distortions owing to different atomic radii and moduli of the constituent elements [10]. Elements with large atomic size misfit are expected to cause severe lattice distortions and high solid solution strengthening effects. TSAO et al [11] introduced a high concentration of Ti in a Co0.5FeNiCrTi0.5 HEA, and achieved high yield strength (2.65 GPa) and Vickers hardness (8.46 GPa) due to solid solution strengthening by the Ti atoms. However, owing to the small atomic size difference (△) for solid- solution phase formation (△≤6.6%, as proposed by ZHANG et al [2]), the substitutional strengthening effects are limited in most HEA systems. In addition, the substantial use of expensive metallic elements restricts applications of HEAs. Interstitial strengthening is an alternate approach to improve the mechanical properties of engineering alloys. WANG et al [12] dissolved 1.1 at.% carbon in a FCC FeNiMnAlCr HEA, which not only increased both the yield strength (159 to 355 MPa) and ultimate tensile strength remarkably, but also produced a sharp improvement in tensile elongation (41% to 50%). WU et al [13] dissolved 0.5 at.% carbon in an FeNiCoCrMn HEA, and this increased both the yield strength and the ultimate tensile strength, but decreased the ductility. Although interstitial strengthening shows significant potential as a route for improving the properties of HEAs, it has received little attention because of the extremely low solubility of most interstitials in metals, especially in FCC structures.
In view of the above findings, we have proposed that nitrogen, which has a similar atomic size to carbon (or boron), could be expected to produce a high strengthening effect in HEAs. Therefore, in the present study, we fabricated a non-equiatomic CrMnFeVTi6 HEA doped with nitrogen using mechanical alloying (MA) followed by spark plasma sintering (SPS). The effects of nitrogen addition on the microstructure, phase constitution, and mechanical properties of the CrMnFeVTi6 HEA were investigated systematically. Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) techniques were employed to determine the phase formation and elemental distribution in the HEA. The high temperature strength of the HEA was simulated by CALPHAD modeling, and the strength variation was correlated with the phase evolution. In addition, the yield strength of the HEA was evaluated based on microstructure-related models to reveal the quantitative contributions from different underlying strengthening mechanisms.
2 Experimental
Elemental powders of chromium, manganese, iron, vanadium, and titanium with high purity (>99.9 wt.%) and particle sizes ≤45 mm were used as raw materials for fabricating non-equimolar CrMnFeVTi6 HEA samples. The mechanical alloying (MA) was performed using a planetary high-energy ball mill (BM4) operated at 260 r/min for 60 h in a mixed atmosphere of argon (Ar) and nitrogen (N2). Ethanol was used as a process- controlling agent. Tungsten carbide balls and tungsten carbide vials were used for MA, and the ball-to-powder mass ratio was 15:1. Powder samples were taken at a regular interval of 20 h in order to study the alloying behavior during the milling. The powder after 60 h milling was consolidated by SPS (SPS1050, Sumitomo Coal Mining Co., Ltd., Japan) in a 20 mm-inner- diameter graphite die at 1050 °C for 5 min. The sintering was performed under vacuum with a constant compression pressure of 40 MPa. Thin graphite foils were placed between the powders and the graphite die to ensure easy removal of the sintered compact and to promote temperature uniformity during sintering.
The phases formed in the milled powders and in the sintered bulk alloy were characterized using a D/MAX-2500 X-ray diffractometer (XRD) with Cu Kα radiation. The bulk sintered HEA samples were etched using a solution of dilute aqua regia after polishing. The morphology and microstructure of the samples were characterized using an FEI Teneo low-vacuum scanning electron microscope (LVSEM) and an FEI Talos F200X STEM equipped with a Super-X silicon drift detector (SDD) energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDXS) system. Thin-foil TEM specimens were prepared by focused ion beam (FIB) lift-out techniques using an FEI Helios Nanolab 460F1 dual beam FIB-SEM. This instrument was equipped with a flip-stage and a STEM detector for final thinning. STEM-EDXS analyses were performed to measure the chemical compositions and to reveal the elemental distribution of different phases in the HEA. The chemical compositions are the average values of measurements taken at several randomly selected points. A Vickers micro-hardness tester FM-800 was employed to measure the hardness of the bulk HEA, with a load of 9.8 N for 15 s. The average hardness was obtained from 10 measurements taken on a circular section of the sample. The hardness of the individual phases at room temperature was measured twice using a Bruker UMT-2 nano- indentation apparatus. In order to constrain the indentation to each phase, a Berkovich indenter was used with a very small load of 20 mN.
3 Results
3.1 Crystal structures
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns obtained from mechanically alloyed samples of the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA powders after milling time of 0-60 h, and after subsequent consolidation by SPS. In the XRD pattern of the 0 h-milled (as-blended) powders, peaks corresponding to all of the elemental components are evident as expected. As the MA process proceeds, the intensities of the elemental constituent peaks decrease rapidly, suggesting the onset of alloying. The peaks corresponding to Cr essentially disappear after 20 h of milling, suggesting that Cr exhibits the highest alloying rate in this quinary HEA system. As the milling time increases to 40 h, the intensities of peaks corresponding to Mn, V, and Ti decrease significantly, and some peaks have shifted evidently. After 60 h of milling, most of the peaks corresponding to the constituent elements have disappeared, and peaks corresponding to a BCC phase, an FCC phase and an ordered BCC phase are observed. In addition, peak broadening is evident as milling time increases due to crystal size refinement, high lattice strain, and decreased crystallinity caused by severe plastic deformation.
The 60 h-milled powder was consolidated by SPS to obtain the sintered bulk N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA. As shown in Fig. 1, the bulk HEA consists of an FCC phase (a=0.421 nm), a BCC phase (a=0.291 nm), and a hexagonal Laves phase (a=0.477 nm, c=0.795 nm), which was subsequently confirmed by STEM. The lattice parameters were determined using an extrapolation technique from the XRD data. A comparison of the patterns from the 60 h-milled powder and the sintered bulk HEA suggests that the hexagonal Laves phase is a transformation product from the ordered BCC phase during SPS, due to the metastable state of the solid solution caused by MA. It is worth mentioning that, based on the microstructural observations presented in the next section, the ordered BCC phase in the bulk HEA has not been consumed fully by the phase transformation. However, the peaks of this ordered BCC phase are hard to detect because of its low fraction and the effects of peak broadening.
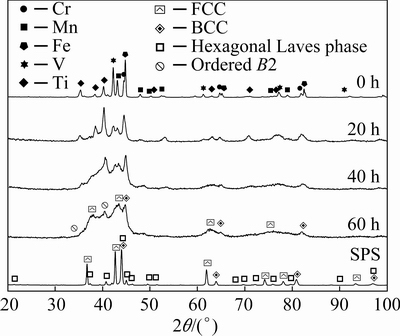
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of mechanically alloyed powders as function of milling time, together with XRD pattern of sintered sample
3.2 Microstructure and elemental distribution of sintered bulk HEA
Figures 2(a-c) show backscattered-electron (BSE) SEM micrographs of the bulk N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA, and Fig. 2(d) shows the corresponding EDXS spectrum obtained from the region shown in Fig. 2(a). As shown in Fig. 2(a), the HEA has an inhomogeneous phase distribution with a large number of particles with different sizes present in the matrix. The bulk HEA consists of at least four phases, designated the dark phase, bright phase, large particle phase, and interface layer; examples of each of these are labeled in Fig. 2(a). The enlarged micrograph in Fig. 2(b) shows that the interface layer is formed at the boundaries between the large particles and the dark phase, and some large particles are almost fully consumed by the interface layer (Fig. 2(c)). During the SPS process, the large particle phase is decomposed into the interface layer and dark phase, and this phase decomposition is not yet complete.
SEM-EDXS analysis was carried out to measure the composition of the sintered bulk HEA. The measured contents of N, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, and Fe elements are approximately 9.56, 54.30, 9.05, 9.01, 8.97, and 9.11 at.%, respectively. We note that the Ti:V:Cr:Mn:V molar ratio is generally consistent with the target composition of 6:1:1:1:1.
As shown in Fig. 3, TEM specimen was extracted from the cross-section perpendicular to the SEM observation surface using the FIB “lift-out” technique. A FIB TEM foil (Fig. 3(b)) for TEM observation was milled from the rectangular region shown in Fig. 3(a). The bright field (BF) TEM images in Figs. 4(a) and (b) show the sub-micron grain microstructure of the HEA. The diameters for most of the grains in the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA are in the range of 0.2-1.1 mm, as determined by the linear intercept method. The elemental distribution and chemical compositions of the four phases (Table 1) were examined using STEM-EDXS. The high-angle annular dark field (HAADF) STEM images (Figs. 4(c) and (d)) reveal four phases in the HEA with distinct levels of composition contrast, and the corresponding EDXS elemental maps reveal the phase distribution and phase compositions in the HEA explicitly. Based on the EDXS maps, the four phases can be designated: (1) the bright phase as a Ti-depleted CrVMnFe solid-solution phase, (2) the dark phase as a TiNx compound, (3) the large particle as a TiFe-rich solid-solution phase, and (4) the interface layer as a solid-solution phase rich in MnFe. It is important to note that solubilities of nitrogen in four phases are higher than that of carbon in previously reported FCC HEAs [12,13].
The structures of the phases in the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA were further investigated by selected area electron diffraction (SAED) technique.
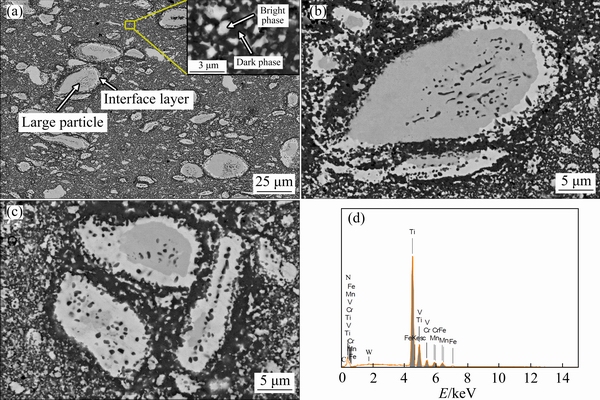
Fig. 2 SEM image of bulk N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA (a), enlarged views (b, c) of large particle phase in (a), showing partial phase transformation, and EDXS spectrum (d) corresponding to (a)
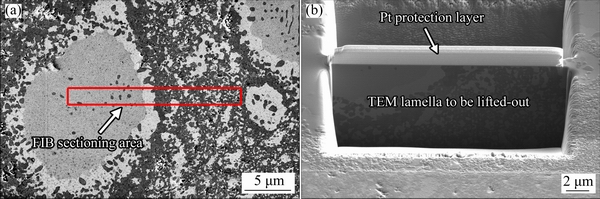
Fig. 3 SEM image showing rectangular area chosen for FIB sectioning (a) and FIB lamella defined by two trenches to lift-out for TEM observation (b)
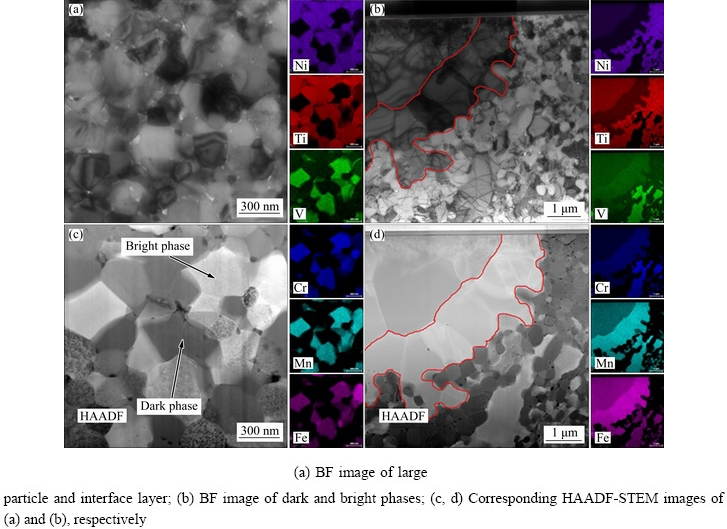
Fig. 4 TEM micrographs of HEA and corresponding quantified STEM-EDXS elemental maps
Table 1 Chemical compositions of phases in N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA, determined by SEM- and STEM-EDXS analyses (contents are average values taken from several measurements)
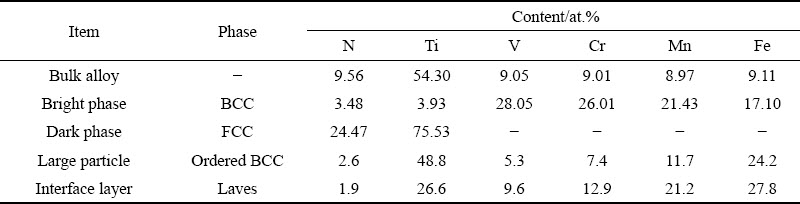
Representative HAADF STEM images and the corresponding SAED patterns of different phases in the HEA are shown in Fig. 5. The SAED patterns of Grains A and B in Fig. 5(a) along the [111] and [110] zone axes are presented in Figs. 5(c) and (d), respectively, which confirm a BCC structure of the bright phase with a lattice parameter of 0.286 nm and an FCC structure of the dark phase with a lattice parameter of 0.424 nm. As shown in Table 1, the ratio between the Ti and N contents in the dark phase is around 3:1, indicating that the dark phase is probably a NaCl-type TiNx vacancy solid solution (B1), with Ti atoms in an FCC configuration and nitrogen atoms occupying a proportion of the octahedral interstices. The diffraction pattern (Fig. 5(e)) of Grain C along [100] zone axis exhibits the superlattice reflections that one would expect for an ordered BCC phase (B2, a=0.381 nm), confirming the B2 structure of the large particle phase. SAED patterns (Figs. 5(f-h)) of Grain D along 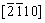 ,
, 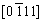 , and
, and 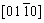 zone axes demonstrate that the interface layer has a hexagonal structure (C14, MgZn2-type Laves phase, a=0.469 nm, c=0.787 nm), which is in a good agreement with the XRD results in Fig. 1. Compared to other three phases, the FCC phase contains higher contents of Ti and N, which might be caused by the following two aspects: low solubilities of Ti in other constituent elements due to its large atomic radius; higher bonding energy of Ti-N than that of Cr-N, V-N, Mn-N, and Fe-N [14,15].
zone axes demonstrate that the interface layer has a hexagonal structure (C14, MgZn2-type Laves phase, a=0.469 nm, c=0.787 nm), which is in a good agreement with the XRD results in Fig. 1. Compared to other three phases, the FCC phase contains higher contents of Ti and N, which might be caused by the following two aspects: low solubilities of Ti in other constituent elements due to its large atomic radius; higher bonding energy of Ti-N than that of Cr-N, V-N, Mn-N, and Fe-N [14,15].
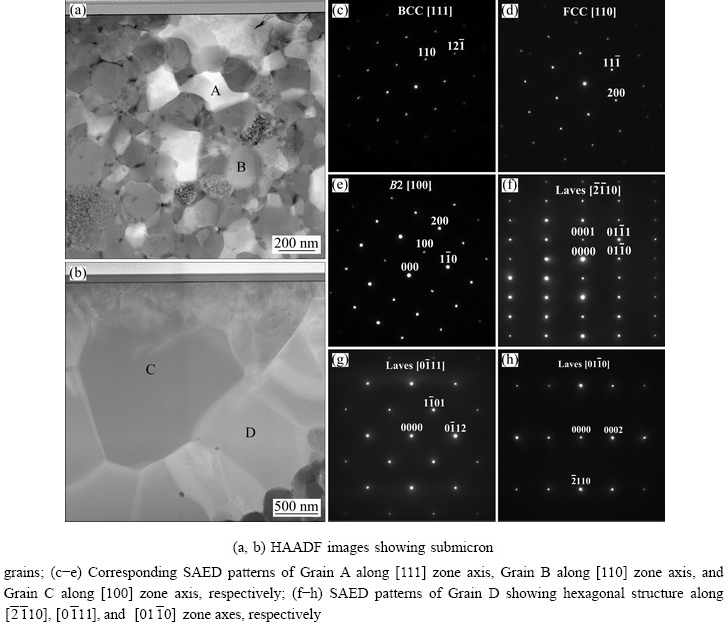
Fig. 5 STEM images and SAED patterns of N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA
3.3 Mechanical properties
Figure 6 shows the true compressive stress-strain curve of the bulk CrMnFeVTi6 HEA. Obviously, the HEA fractured in the elastic deformation stage with a high compressive strength of 2667 MPa, and low plastic deformability. Nano-indentation measurements were carried out for each phase in the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA, as shown in Fig. 7. The load-displacement curves (Fig. 7(a)) illustrate the response of the phase during loading and unloading. The initial linear part of the unloading curve represents the elastic behavior of the HEA as it measures linear recovery during removal of the indenter tip. The elastic modulus is evaluated based on Schwarm’s research [16], where Poisson ratio ν is assumed to be 0.30 for the phases in the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA. As shown in Fig. 7(b), the values of the hardness and elastic modulus for each phase demonstrate that the TiNx has the highest hardness (17.18 GPa) and elastic modulus (294.55 GPa) owing to its semi-ionic bond between Ti and N atoms, and the other three solid-solution phases have similar elastic moduli and relatively low hardness. The softest BCC phase still has a hardness of 9.81 GPa, which might be attributed to strengthening effect of the interstitial nitrogen.
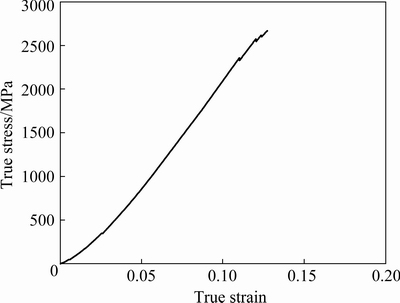
Fig. 6 True compressive stress-strain curve of bulk CrMnFeVTi6 HEA
The Vickers hardness of the HEA is measured to be 12.0 GPa. Figure 8(a) presents the indentation morphology produced by the Vickers indenter. When the square pyramidal indenter penetrates into the specimen, materials near the edges are deformed by both normal stress and shear driven by the shear stress, but materials near the corners are mainly deformed under the normal stress, which could induce the corner cracking behaviors [17]. According to the classification of indentation geometries by ZHANG et al [17], the indentation morphology in Fig. 8(a) corresponds to the third type of “crack” morphology, which is illustrated schematically in Fig. 8(b). Thus, the HEA exhibits very low plastic deformability, and the extrusion behaviors under the penetration of indenter are greatly limited. The hardness of the HEA is related to its fracture strength. Figure 9 illustrates the hardness of a variety of HEAs and metals [2,15,17,18-22] compared with our HEA. The N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA exhibits the highest hardness among the previous reported HEAs, and even close to the hardness of tungsten cemented carbide alloy, making it promising for applications including wear-resistant coatings [6,23], as well as bulk products such as cutting tools and high temperature structural components [1].
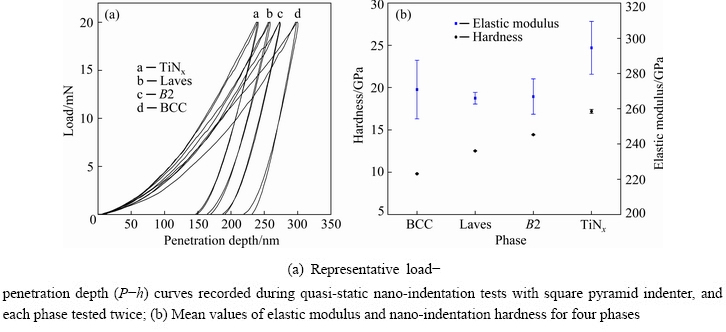
Fig. 7 Nano-indentation measurement results for phases in N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA
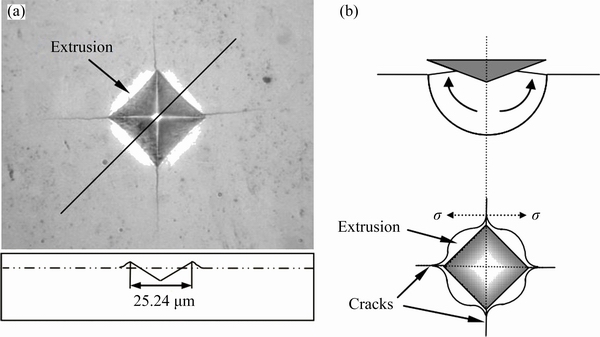
Fig. 8 Micro-indentation morphology of Vickers indenter for N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA (a) and schematic illustration of deformation and stress state near indentation (b)
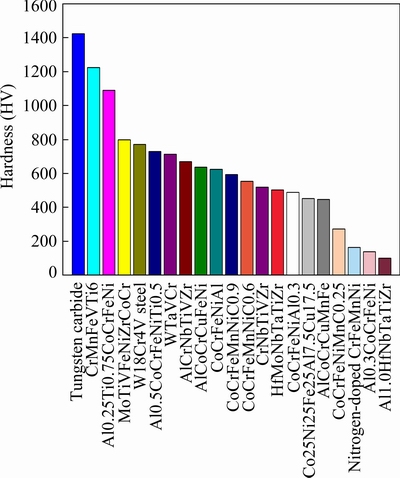
Fig. 9 Comparison of hardness of N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 with other reported HEAs, tungsten cemented carbide alloy and W18Cr4V steel
4 Discussion
4.1 Effect of nitrogen on phase formation
As described in Section 3.2, the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA contains two random solid solutions (the BCC and hexagonal phases), an FCC structured TiNx, and a B2 ordered solid solution. The multiphase structure of the HEA is different from general HEAs that form simple FCC and/or BCC solid solutions [1,2]. The formation of TiNx and B2 phases in the bulk N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA suggests that not all elements are randomly distributed in the crystal lattice, though the HEA possesses a high value of mixing entropy (△Smix= 11.85 J/(K·mol)). This suggests that the high entropy of mixing might be insufficient to dominate the formation of phases in this HEA system. To explore the characteristics of phase selection in HEAs, two parameters, atomic size misfit △ and the enthalpy of mixing △Hmix, were proposed by ZHANG et al [2]. When the two empirical parameters satisfy the condition of -15 kJ/mol < △Hmix <5 kJ/mol and △≤5%, stable solid-solution phases are formed in multi-component HEA systems. These two parameters are defined by the following equations [2,15]:
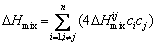 (1)
(1)
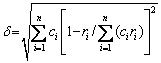 (2)
(2)
where ci and cj are the molar fractions of the ith and jth elements, respectively, ri is the atomic radius of the ith element, R (=8.314 J/(K·mol)) is the mole gas constant, and △H ij mix is the enthalpy of mixing for the atomic pairs between the i and j elements. The values of △H ij mix and ri for the constituent elements are listed in Table 2 [15].
Table 2 Atomic radius and mixing enthalpies of unlike atomic pairs [15]
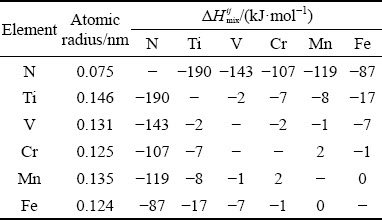
According to Eqs. (1) and (2), the values of △ and △Hmix for the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA were calculated to be △=15.5% and △Hmix=-62.2 kJ/mol. The values of △ and △Hmix both break the solid- solution formation rules for the HEAs. Firstly, enthalpy of mixing in alloys indicates the tendency for ordering or clustering, thus a more negative value of enthalpy of mixing can promote the formation of intermetallic compounds and ordered phases [24,25]. Secondly, the large value of △ could increase the strain energy and lower the stability of the solid solution. This phenomenon indicates that the formation of TiNx and ordered B2 phases is reasonable in this HEA, and it well conforms to the principles laid out by ZHANG et al [2]. In addition, the solubilities of interstitial nitrogen in solid- solution phases are quite limited, and therefore nitrogen has a strong tendency to form nitride in the HEA. The mixing enthalpies of Ti-N, V-N, Cr-N, Mn-N, and Fe-N are -190, -143, -107, -119, and -87 kJ/mol, respectively [15]. More negative enthalpies of mixing values correspond to larger binding forces between the elements. The binding force between Ti and N is the largest, which promotes the formation of TiNx nitride instead of other nitrides in the HEA.
The phase stability of the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA was evaluated by CALPHAD method. In previous study [26], CALPHAD-based phase diagram calculation has been proved to be a feasible and reliable tool to evaluate the phase stability of multicomponent alloy systems. As exhibited in Fig. 10(a), three equilibrium phases coexist in the HEA in a temperature range from 1050 to 100 °C, including TiNx, BCC, and Laves phases. As the temperature drops from the XPS temperature of 1050 °C, some of the BCC phase will gradually transform into Laves and TiNx phases. However, in the present work, it is the ordered BCC phase (B2) that transformed into the Laves and TiNx phases during SPS (Fig. 2(b)). As explained by MIRACLE et al [27], the discrepancy between the theoretical prediction and experimental results arises from the non-equilibrium fabrication process of the milled powder. During the MA process, higher energy is introduced into the alloy than that during traditional casting, and the alloying procedure induces a non-equilibrium state. Thus, the metastable B2 phase should be classified into the BCC phase, regarding the BCC phase as a partially ordered phase. High Ti and N contents (47.8 at.% Ti and 2.1 at.% N) in the B2 phase lead to large value of △ (=10.2%) and △Hmix (=-26.38 kJ/mol), which results in the phase transformation. As illustrated in Fig. 10(b), the equilibrium phases at 1050 °C are BCC, Laves, and TiNx. Thus, the B2 phase in the milled powder should transform into Laves phase and TiNx during SPS.

Fig. 10 Mass fraction of equilibrium phases as function of temperature (a) and at isothermal temperature of 1050 °C (b) calculated using JMatPro software with titanium alloy database
4.2 Effect of nitrogen on mechanical properties
4.2.1 High temperature strength of bulk HEA
According to the equilibrium phases predicted by CALPHAD (Fig. 10(a)), the evaluation of flow stress and high temperature strength (25-540 °C) for the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA was carried out using the titanium alloy database, as shown in Fig. 11. It is important to note that the flow strain in Fig. 11(a) is obtained by the extrapolation method, which cannot be taken as the real strain under tensile stress. Engineering tensile stress-strain curves (Fig. 11(a)) indicate that the stress of the HEA decreases rapidly after elastic deformation. Thus, the HEA has almost no plastic deformation and strain hardening ability, which might be ascribed to the high solubility of interstitial nitrogen in the HEA, leading to the formation of brittle TiNx and solid-solution phases with high hardness.
Figure 11(b) shows the yield strength of the HEA versus temperature. In the low-temperature range of 25-380 °C, the alloy exhibits high yield strength (over 2729 MPa), and the yield strength slowly decreases with increase of the temperature. However, when temperature is higher than 380 °C, the yield strength drops steeply with increase of the temperature. It can be seen from Fig. 10(a) that when temperature rises from 380 °C, the mass fraction of the BCC phase increases rapidly and the mass fractions of the harder TiNx and Laves phases are reduced, implying that the TiNx and Laves phases are partially transformed into the softer BCC phase. Therefore, it can be considered that the high yield strength of the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA is primarily attributed to the TiNx and Laves phases, and that the BCC phase will limit the high temperature strength (>380 °C) of this HEA.
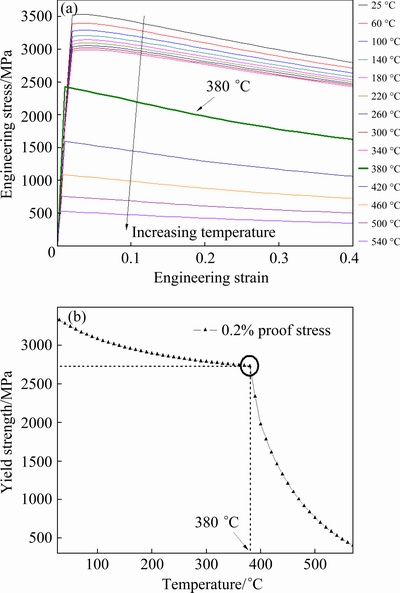
Fig. 11 Engineering stress-strain curves (a) and corresponding high temperature yield strength (b) of N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA, calculated using titanium alloy database
The newly developed N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA does exhibit excellent strength and hardness, whereas the volume fraction of the BCC phase should be controlled when this HEA is used as an alternative for high-temperature applications. The mechanical performance of the N-doped CrMnFe- VTi6 HEA might be further improved by carefully adjusting the alloy composition or introducing heat-treatment [26]. The feasible approaches include improving the mechanical properties of the BCC phase or decreasing its volume fraction. In the following section, quantitative contributions to strength of the BCC phase were analyzed to reveal the underlying strengthening mechanisms and to seek approaches to improve the performance of this phase as well as the HEA.
4.2.2 Strengthening mechanisms in BCC phase
Nano-indentation measurements (Fig. 7) show that the four phases in the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA have superior high hardness, and that even the softest BCC phase still has a hardness of 9.81 GPa. However, it is difficult to evaluate quan-titative contributions from different strengthening mechanisms in the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA because of its complex phase composition and the inclusion of non-metallic nitrogen. As discussed in Section 4.2.1, the BCC phase with lower hardness limits the high temperature application of the HEA. In order to understand the interstitial strengthening of nitrogen and seek approaches to improve strength of the BCC phase, the strengthening mechanisms in the BCC phase were analyzed, and the respective quantitative contribution of each strengthening mechanism was estimated.
The relationship between hardness and yield strength of alloys represents their plastic deformation ability, which is determined by the hardness and strain hardening ability of the alloys. ZHANG et al [17] discovered that alloys that display typical brittle fracture behavior often have a relationship of HV>3σy, where HV is the hardness and σy is the yield strength of the material, e.g., the ratios of hardness to strength for Zr-, Fe-, and Cu-based BMGs were measured in the range of 3.06 to 4.16. The N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA exhibits a yield strength of 3350 MPa and a hardness of 12 GPa (HV 1225) at room temperature. The value of HV/σy for the HEA is calculated to be 3.58, which is consistent with its brittle fracture behavior. Therefore, the yield strength of the BCC phase is estimated to be 2737 MPa under assumption of HV/σy of 3.58.
In the absence of precipitates and considerable density of dislocations (Fig. 4(a)), the yield strength for the BCC phase can be described by [17,18].
σy=σfr+σis+σss+σgb (3)
where σfr is the lattice friction stress, σss and σis are the strengthening contributions from substitutional and interstitial solid solution strengthening, respectively. Since the grain sizes in the HEA are quite large (0.2-1.1 mm), the grain boundary strengthening effect is negligible [18,19]. Thus, the increase in yield strength mainly results from the interstitial strengthening of nitrogen and sub- stitutional strengthening of the metallic elements.
Inspection of the HEA researches reveals that there is a c2/3 (c is the atomic fraction of a solute) relationship for the interstitial solid solution strengthening of nitrogen [13,28], as given by Eqs. (4) and (5), whereas the Friedel model [29] predicts that the strengthening effect of nitrogen has a square root relation c1/2. The 2/3 relation showed good agreement for strengthening contributions to tensile strength, while the square root relation showed good agreement for yield strength [28].
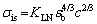 (4)
(4)
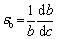 (5)
(5)
where KLN is 23500 MPa [28], εb is the lattice strain (or fractional increase in lattice parameter) per atom fraction of solute atoms, and b is the Burgers vector component. It is difficult to determine the value of εb,nitrogen for the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA. WANG and BAKER [30] found that the increase in the lattice parameter per change in at.% carbon (△a/△c) for Fe40.4Ni11.3Mn34.8Al7.5Cr6 was measured to be 2.74 pm/at.%, producing a value of the lattice strain εb,carbon of 0.78/at.%. Assuming that the △a/△c for the interstitial elements changes linearly with the atomic size and is not affected by the atom types [19,30], △a/△c for nitrogen can be estimated to be 2.55 pm/at.%, resulting in εb,nitrogen= 0.91/at.%. The strengthening contribution from interstitial nitrogen is estimated to be 2209 MPa.
Equation (4) is not applicable for calculation of the substitutional solid solution strengthening because the values of εb for metallic elements are unavailable in the literatures. The substitutional strengthening change △σss is calculated using the following equation [21,27]:
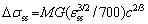 (6)
(6)
where cTi=3.93 at.%, cV=28.05 at.%, cCr=26.01 at.%, and cMn=21.43 at.%, as shown in Table 1. It is important to note that Fe is taken as solvent in the BCC phase, because the BCC phase (0.291 nm) has a similar lattice parameter to Fe (0.286 nm), as shown in Fig. 1. εss is a parameter related to εb [21], M(=3.0) is the mean orientation factor for the BCC polycrystalline phase [17,21], G is the shear modulus, G=E/[2(1+n)]=104.2 GPa. Calculation of  for Ti, V, Cr, and Mn is infeasible for lack of data. Due to similarity of the atomic radii, the value of
for Ti, V, Cr, and Mn is infeasible for lack of data. Due to similarity of the atomic radii, the value of  =3.2×10-5 for Fe was used for estimation of strengthening effect of V, Cr, and Mn, and
=3.2×10-5 for Fe was used for estimation of strengthening effect of V, Cr, and Mn, and  =1.3×10-3 for Al was used for calculation of strengthening effect of Ti [21]. Therefore, the substitutional strengthening effect is estimated to be △σss=(46.9+4.3+4.2+3.6) MPa= 59 MPa. Owing to the small atomic size difference of metallic elements, the substitutional solid solution strengthening effect is very low, and similar results can be found in Refs. [15-17].
=1.3×10-3 for Al was used for calculation of strengthening effect of Ti [21]. Therefore, the substitutional strengthening effect is estimated to be △σss=(46.9+4.3+4.2+3.6) MPa= 59 MPa. Owing to the small atomic size difference of metallic elements, the substitutional solid solution strengthening effect is very low, and similar results can be found in Refs. [15-17].
In the BCC phase, the calculated values of the quantitative contributions from interstitial and substitutional solid solution strengthening are 2209 and 59 MPa, respectively. Evidently, the high strength of the BCC phase is primarily ascribed to interstitial solid solution strengthening of nitrogen. We applied rule of mixture of friction stress for constituent elements [16,31] to obtain the corresponding value for the BCC phase, σfr= 235 MPa. The σy is 2503 MPa, which is in a good agreement with the experimental value. The increase in yield strength (σy) per at.% nitrogen (△c) in the BCC phase (σy/△c=634 MPa/at.% nitrogen) is significantly higher than carbon strengthening in TWIP steels (26-42 MPa/at.% carbon) [23,32] and Fe40.4Ni11.3Mn34.8Al7.5Cr6 HEA (184 MPa/ at.% carbon) [19], and is even higher than the boron strengthening effect in Ni3Al alloy (387-420 MPa/at.% boron) [33,34]. Thus, the strength improvement for the BCC phase, which is related to high temperature strength of the N-doped CrMnFeVTi6 HEA, can be achieved through increasing the solubility of nitrogen, e.g. increasing the atomic size difference of the metallic elements to produce more sites for interstitial nitrogen atoms to reside.
5 Conclusions
(1) Four phases, including TiNx, BCC, Laves phase, and ordered B2 phase, are formed in the sintered bulk HEA, and phase decomposition of B2 during SPS process can be ascribed to its high Ti and nitrogen contents that reduce the phase stability.
(2) The HEA exhibits high strength at lower temperatures (<380 °C), and partial phase trans- formation from TiNx and Laves phase to BCC phase at higher temperatures (>380 °C) can result in steep drop of strength.
(3) The calculated values of the quantitative contributions from interstitial and substitutional solid solution strengthening in the BCC phase are 2209 and 59 MPa, respectively, demonstrating that interstitial strengthening of nitrogen is the dominant strengthening mechanism, and the same conclusion can also be applied to the Laves phase and B2 phase due to their high nitrogen contents.
(4) Nitrogen additions can induce a yield strength increase of ~634 MPa/at.% nitrogen, which is significantly higher than for carbon or boron additions. Increasing the solubility of nitrogen in the BCC phase should be an efficient way to enhance its strength, as well as high temperature strength of the HEA.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the support for experiments provided by both Beihang University (China) and the University of Connecticut (USA).
References
[1] YE Y F, WANG Q, LU J, LIU C T, YANG Y. High-entropy alloy: Challenges and prospects [J]. Materials Today, 2016, 19(6): 349-362.
[2] ZHANG Y, ZUO T T, TANG Z, GAO M C, DAHMEN K A, LIAW P K, LU Z P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2014, 61(8): 1-93.
[3] QIN Gang, WANG Shu, CHEN Rui-run, GONG Xue, WANG Liang, SU Yan-qing, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Nb-alloyed CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018, 34: 365-369.
[4] PENG Jian, LI Zi-yong, JI Xin-bo, SUN Yan-le, FU Li-ming, SHAN Ai-dang. Decomposition kinetics of carbon-doped FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloy at intermediate temperature [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(7): 1884-1894.
[5] JIANG Hui, JIANG Li, QIAO Dong-xu, LU Yi-ping, WANG Tong-min, CAO Zhi-qiang, LI Ting-ju. Effect of niobium on microstructure and properties of the CoCrFeNbxNi high entropy alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2017, 33(7): 712-717.
[6] XU Jun, CAO Cheng-ming, GU Ping, PENG Liang-ming. Microstructures, tensile properties and serrated flow of Al CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(3): 746-755.
[7] ZHOU Shang-cheng, ZHANG Peng, XUE Yun-fei, WANG Fu-chi, WANG Lu, CAO Tang-qing, TAN Zhen, CHENG Bao-yuan, WANG Ben-peng. Microstructure evolution of Al0.6CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy powder prepared by high pressure gas atomization [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(5): 939-945.
[8] FU Jian-xin, CAO Cheng-ming, TONG Wei, PENG Liang-ming. A TRIP-assisted dual-phase high-entropy alloy: Grain size and phase fraction effects on deformation behavior [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 131: 323-335.
[9] SONG Ruo-kang, WEI Li-jun. Phase formation and strengthening mechanisms in a dual-phase nanocrystalline CrMnFeVTi high-entropy alloy with ultrahigh hardness [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 744: 552-560.
[10] VARVENNE C, LEYON G P M, GHAZISAEIDI M, CURTIN W A. Solute strengthening in random alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 124: 660-683.
[11] TSAO L C, CHANG S Y, YU Y C. Direct active soldering of Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 high entropy alloy to 6061Al using Sn-Ag-Ti active solder [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(4): 748-756.
[12] WANG Zhang-wei, BAKER I, CAI Zhong-hou, CHEN Si, POPLAWSKY J D, GUO Wei. The effect of interstitial carbon on the mechanical properties and dislocation substructure evolution in Fe40.4Ni11.3Mn34.8Al7.5Cr6 high entropy alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 120: 228-239.
[13] WU Z, PARISH C M, BEI H. Nano-twin mediated plasticity in carbon-containing FeNiCoCrMn high entropy alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 647: 815-822.
[14] YAND E E. The effect of carbon content on the mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of Fe22MnC TWIP/TRIP steels [J]. Iron & Steel, 2010, 45(6): 74-78.
[15] TAKEUCHI A, INOUE A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element [J]. Materials Transactions, 2005, 46(12): 2817-2829.
[16] SCHWARM S C, KOLLI R P, AYDOGAN E, MBURU S, ANKEM S. Characterization of phase properties and deformation in ferritic-austenitic duplex stainless steels by nanoindentation and finite element method [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 680: 359-367.
[17] ZHANG P, LI S X, ZHANG Z F. General relationship between strength and hardness [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 529(1): 62-73.
[18] GWALANI B, AYYAGARI A, CHOUDHURI D, SCHARF T, MUKHERJEE S, GIBSON M, BANERJEE R. Microstructure and wear resistance of an intermetallic-based Al0.25Ti0.75CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy [J]. Materials Chemistry & Physics, 2018, 210: 197-206.
[19] TRANVERSIER M, MESTRE-RINN P, PEILLON N. Nitrogen-induced hardening in an austenitic CrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 804: 140725.
[20] YURCHENKO N Y, STEPANOV N D, SHAYSULTANOV D G, TIJHNONVSKY M A. SALISHCHEV G A. Effect of Al content on structure and mechanical properties of the AlxCrNbTiVZr (x=0.25; 0.5; 1) high-entropy alloys [J]. Materials Characterization, 2016, 121: 125-134.
[21] XIAO Jin-kun, TAN Hong, CHEN Juan, ZHANG Chao. Effect of carbon content on microstructure, hardness and wear resistance of CoCrFeMnNiCx high-entropy alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 847: 156533.
[22] FU Zhi-qiang, CHEN Wei-ping, WEN Hai-ming, CHEN Zhen, LAVERNIA E J. Effects of Co and sintering method on microstructure and mechanical behavior of a high-entropy Al0.6NiFeCrCo alloy prepared by powder metallurgy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 646(18): 175-182.
[23] HUANG Ping-kang, YEH Jien-wei. Inhibition of grain coarsening up to 1000°C in (AlCrNbSiTiV)N superhard coatings [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 62(2): 105-108.
[24] MA D, GRABOWSKI B, KORMANN F, NEUGEBAUER J, RAABE D. Ab initio thermodynamics of the CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy: Importance of entropy contributions beyond the configurational one [J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 100: 90-97.
[25] FANG Si-cong, CHEN Wei-ping, FU Zhi-qiang. Microstructure and mechanical properties of twinned Al0.5CrFeNiCo0.3C0.2 high entropy alloy processed by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering [J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 54(2): 973-979.
[26] SHAYSULTANOV D G, SALISHCHEV G A, IVANISENKO Y V, ZHEREBTSOV S V, TIKHONOVSKY M A, STEPANOV N D. Novel Fe36Mn21Cr18Ni15Al10 high entropy alloy with bcc/B2 dual-phase structure [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 705: 756-763.
[27] MIRACLE D, MILLER J, SENKOV O, WOODWARD C. Exploration and development of high entropy alloys for structural applications [J]. Entropy, 2014, 16(1): 494-525.
[28] SIEURIN H, ZANDER J, SANDSTROM R. Modelling solid solution hardening in stainless steels [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 415(1): 66-71.
[29] BYRNES M L G, GRUJICIC M, OWEN W S. Nitrogen strengthening of a stable austenitic stainless steel [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1987, 35(7): 1853-1862.
[30] WANG Z W, BAKER I. Interstitial strengthening of a fcc FeNiMnAlCr high entropy alloy [J]. Materials Letters, 2016, 180: 153-156.
[31] CORDERO Z C, KNIGHT B E, SCHUH C A. Six decades of the Hall–Petch effect—A survey of grain-size strengthening studies on pure metals [J]. International Materials Reviews, 2016, 61(8): 1-18.
[32] BOUAZIZ O, ZUROB H, CHEHAB B, EMBURY J D, ALLAIN S, HUANG M. Effect of chemical composition on work hardening of Fe-Mn-C TWIP steels [J]. Metal Science Journal, 2011, 27(3): 707-709.
[33] BAKER I, HUANG B, SCHULSON E M. The effect of boron on the lattice properties of Ni3Al [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1988, 36(3): 493-499.
[34] WEIHS T P, ZINOVIEV V, VINENS D V, SCHULSON E M. The strength, hardness and ductility of Ni3Al with and without boron [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1987, 35(5): 1109-1118.
张 琳1,宋若康2,屈国欣2,路 通3
1. 北矿检测技术有限公司,北京 102628;
2. 北京机电工程总体设计部,北京100854;
3. 中国航天科工集团 第四研究院,北京 100028
摘 要:为了评估氮元素的间隙固溶强化机制对高熵合金性能的影响,采用机械冶金化和放电等离子体烧结工艺制备N掺杂CrFeMnVTi6高熵合金,并利用XRD、SEM、TEM和FIB检测手段对合金的相组成及显微组织进行表征。实验结果显示,CrMnFeVTi6合金组织由TiNx、BCC、Laves相和B2有序相组成。因此,合金在低温区域(<380 °C)具有极高的强度(>2729 MPa)和硬度。针对该高熵合金的BBC基体进行不同强化机制的定量计算,结果表明,氮元素引起的间隙固溶强化效果为~634 MPa/at.%,远好于其他合金中的碳或硼元素,这表明,在高熵合金里添加氮元素能够有效提高合金强度。
关键词:高熵合金;氮元素;力学性能;间隙固溶强化
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: Lin ZHANG, Tel: +86-10-59069642, E-mail: zhanglin_1012@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65663-7
1003-6326/  2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

