凝聚电子相与Wagner模型在低钛渣下钛的分配行为中的应用
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第5期
论文作者:王振阳 张建良 邢相栋 刘征建
文章页码:1640 - 1647
关键词:钛;分配行为;活度系数模型;护炉;钛负荷
Key words:titanium; distribution behavior; activity coefficient model; hearth protection; titanium load
摘 要:为研究铁水中钛元素碳热还原反应规律,提供高炉护炉理论依据,利用高温熔炼、急速淬火、化学分析以及热力学模型计算等方法,在实验室条件下利用分析纯试剂研究在1350~1600 °C间钛在低钛渣系CaO-SiO2-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2与铁水间的分配行为。研究结果表明,随着反应温度的增加,钛的分配比L(Ti)增加,但系统活度系数γsys降低,从而导致反应平衡常数升高。结合Wagner与凝聚电子相模型,通过对实验数据进行拟合,得到钛碳热还原反应的吉布斯自由能公式。最后,结合实验所得结果,给出了高炉铁水中w(Si)与w(Ti)含量的关系以及可以达到护炉效果的最小入炉钛负荷。
Abstract: For studying the carbon thermal reduction rules of titanium in hot metal and providing a theoretical basis for the blast furnace (BF) hearth protection, the distribution behavior of titanium between low-titanium slag system of CaO-SiO2- MgO-Al2O3-TiO2 and hot metal was studied using analytical reagents in a temperature range from 1350 °C to 1600 °C. Through high temperature melting, rapid quenching, chemical analysis and thermodynamic model calculating, the results showed that the increase of reaction temperature, which improved the titanium distribution L(Ti) and lowered the system activity coefficient γsys, leads to the rise of equilibrium constant. Combined with Wagner and congregated electron phase models, the data obtained in distribution experiments were used to fit out the Gibbs free energy formula of titanium carbothermic reduction. Finally, the relations between the contents of Si and Ti in hot metal and the titanium load to reach the minimum w(Ti) for the formation of TiC were given.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 1640-1647
Zhen-yang WANG, Jian-liang ZHANG, Xiang-dong XING, Zheng-jian LIU
School of Metallurgical and Ecological Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
Received 28 April 2014; accepted 30 January 2015
Abstract: For studying the carbon thermal reduction rules of titanium in hot metal and providing a theoretical basis for the blast furnace (BF) hearth protection, the distribution behavior of titanium between low-titanium slag system of CaO-SiO2- MgO-Al2O3-TiO2 and hot metal was studied using analytical reagents in a temperature range from 1350 °C to 1600 °C. Through high temperature melting, rapid quenching, chemical analysis and thermodynamic model calculating, the results showed that the increase of reaction temperature, which improved the titanium distribution L(Ti) and lowered the system activity coefficient γsys, leads to the rise of equilibrium constant. Combined with Wagner and congregated electron phase models, the data obtained in distribution experiments were used to fit out the Gibbs free energy formula of titanium carbothermic reduction. Finally, the relations between the contents of Si and Ti in hot metal and the titanium load to reach the minimum w(Ti) for the formation of TiC were given.
Key words: titanium; distribution behavior; activity coefficient model; hearth protection; titanium load
1 Introduction
The premature erosion of hearth refractories in blast furnace (BF) has become one of the main factors limiting the campaign life [1]. At present, measures to extend the hearth life include intensifying hearth wall cooling, plugging tuyeres, decreasing production, and adding titanium-rich materials [2,3]. The so-called “titanium bear”, which is a precipitate of carbide, nitride and carbonitride of titanium, may form in the BF hearth area if TiO2 presents in the feed [4]. It can minimize the hearth wall erosion and extend the BF campaign life.
Recently, the researches have mainly focused on the characteristics of high titanium slag (w(TiO2)>10%) when vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite as a main ore is charged into BF [5]. The low-titanium slag (w(TiO2)<5%), which is formed in the condition of titanium ball or iron sand as a protection hearth agent presented slightly in the BF feed, was less studied. LI et al [6] pointed out that the effective titanium charging content for carbonitride formation is 3.6-5.2 kg/t. HE et al [7] studied the phase transition process of TiO2 carbothermal reduction, which is TiO2→ TinO2n-1(n≥4)→Ti3O5→Ti(N,O)→Ti(C,N,O)→Ti(C,N).However, the research related to carbothermal reduction behavior of low titanium slag using the thermodynamic model mentioned below was limited.
Through simulating the composition of low titanium slag and hot metal, the distribution behavior of Ti under the condition of low-titanium slag was studied using the model of WAGNER [8] and congregated electron phase. A series of thermodynamics parameters and formulas were received, which provided a theoretical basis for the BF hearth protection.
2 Experimental
2.1 Experimental materials
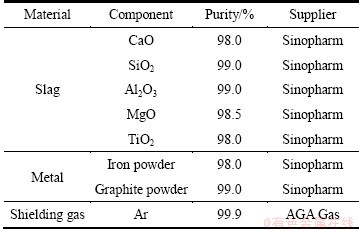
The materials used in the experiment were analytical reagent grade powders. The species and purities are shown in Table 1.
The experimental reagents of CaO, SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, and TiO2 were roasted at 1000 °C in argon atmosphere for 2 h. The carbonate and hydroxide in the reagents were decomposed during the heating, which purified raw materials and reduced experimental error through the removing of CO2 and H2O. When roasting finished, the reagents were cooled down to room temperature for the next premelting experiments.
Table 1 Experimental materials and their purity
2.2 Premelting experiment
Slag and iron were mixed up with composition shown in Table 2 and ground in a agate mortar for 40 min to ensure the composition uniformity. Then, the homogeneous slag and iron were respectively put into high purity graphite crucible and heated to 1450 °C for 2 h in argon atmosphere, which can guarantee the adequate slag crystallization and complete iron carburization through. The compositions of premelting samples through chemical analysis are listed in Table 2.
2.3 Carbothermic reduction
Under the present condition of BF in China, the slag quantity is usually about 300 kg/t. Thus, 30 g premelting slag and 100 g carbon-containing iron were put into a high purity graphite crucible as shown in Fig. 1. The crucible, whose dimension was 40 mm in diameter and 100 mm in depth, was fitted with a molybdenum basket and inserted into the constant temperature zone of the tubular resistance furnace. The samples were then heated up to a target temperature at the rate of 5 °C/min and kept for 4 h [9]. The whole heating process was under Ar atmosphere in flow of 3 L/min which can provide protection atmosphere for titanium reduction and prevent the oxidation of molybdenum wire. Finally, the molybdenum basket with samples was taken out from the furnace and quickly quenched into the ice water. The heat treatment pattern is shown in Fig. 2.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Reaction mechanism and distribution ratio
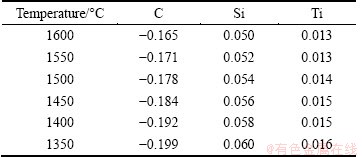
Carbon and silicon have a great influence on the activity coefficient of titanium in hot metal, so the contents of C and Si in iron were also tested. The compositions of iron and slag after reduction are shown in Table 3.
According to BERGSMA and RICHARD’s results [10], the mechanism of Ti carbothermic reduction in hot metal can be described by the following steps: 1) dissolution of TiO2 in slag phase, 2) reduction of TiO2, 3) dissolution of Ti into hot metal and emitting of CO out of slag, and 4) formation of solid particle TiC because of solubility. The reaction mechanism can be shown as Fig. 3.

Fig. 2 Experimental heat treatment pattern
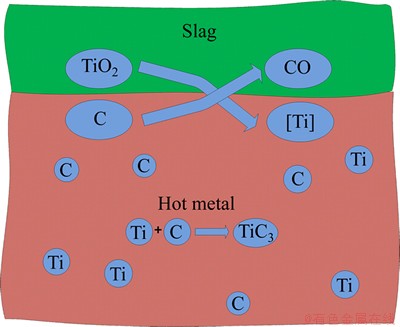
Fig. 3 Model of titanium reaction between liquid slag and hot metal
The main reactions of titanium between iron and slag are as follows:
TiO2+2[C]=[Ti]+2CO
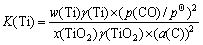 (1)
(1)
[Ti]+[C]=TiC(s)
 (2)
(2)
where K(Ti) and K(TiC) represent equilibrium constants of Reaction (1) and (2), w(Ti) and x(TiO2) are the mass fraction of Ti in metal phase and mole fraction of TiO2 in slag phase respectively, γ(Ti) and γ(TiO2) indicate the activity coefficients of Ti and TiO2, respectively. The equilibrium partial pressure of carbon monoxide is given by p(CO).
According to Raoult’s law, taking the purity as a standard, the activities of carbon approximates to 1 if carbon is at a saturated state dissolved in hot metal. While the other components use 1% solution as standard state. Since the reaction happened in an open system, the p(CO)/pΘ can be considered as 1. As the form of pure solid particles existing in hot metal, the activity of titanium carbide a(TiC) is equal to 1 [11,12]. Thus, Eqs. (1) and (2) can be simplified as
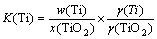 (3)
(3)
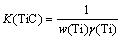 (4)
(4)
In Eq. (3), the group containing the content of titanium in hot metal and slag can be termed as the “distribution ratio,” L(Ti), and the activity coefficients group can be defined as the “system activity coefficient”, γsys, which are given as
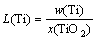 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
Thus, Eq. (3) can be written to express the equilibrium constant as a function of distribution ratio and system activity coefficient:
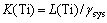 (7)
(7)
The equilibrium constant K(Ti) will remain the same under certain conditions of temperature and pressure. Thus, the titanium distribution ratio L(Ti) between slag and hot metal is only related to the system activity coefficient γsys when temperature and pressure keep unchanged. The reduction degree of titanium from slag phase migrating to hot metal can be expressed as L(Ti). While the γsys, which is the activity coefficients ratio of reactants and products, represents the titanium reduction potential between liquid slag and hot metal. As shown in Eq. (7), L(Ti) and γsys are positive correlation.
Table 3 Slag and iron compositions after reduction
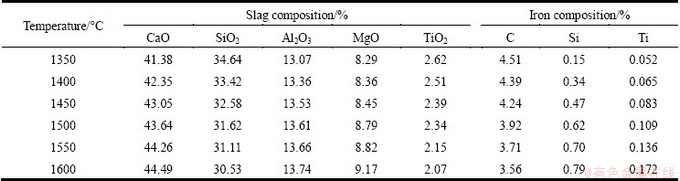
In titanium balanced system of liquid slag and hot metal, when a parameter, such as a component content, has changed, it will cause a variation of titanium reduction potential, which leads to a change of L(Ti) between liquid slag and hot metal. This process can be quantificationally described as Eqs. (5)-(7). That is, the changed conditions of titanium balanced system will influence the activity coefficient of titanium in the liquid slag and hot metal phase and finally the system activity coefficient γsys. As a result, the titanium distribution ratio, LTi, will change.
The TiO2 mass fraction in Table 3 can be converted to mole fraction through Eq. (8). Combined the data in Table 3 with Eq. (5), the relationship between distribution ratio L(Ti) and temperature is obtained, as shown in Fig. 4.
 (8)
(8)
where i means slag components of CaO, SiO2, MgO, Al2O3, TiO2 and M(i) is the relative molecular mass of component i.
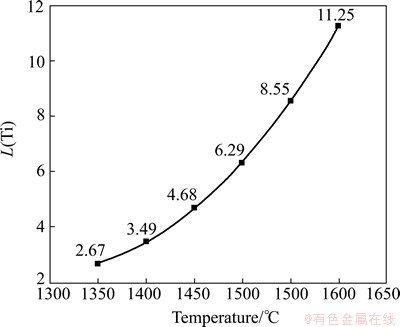
Fig. 4 Titanium distribution L(Ti) along with change of temperature
Indicates that the titanium distribution ratio increases with carbothermic reduction temperature increasing. L(Ti) will be enhanced from 2.67 at 1350 °C up to 11.25 at 1600 °C. The increase of reaction temperature can result in a significant increase in titanium recovery, which is beneficial to improving the content of Ti in hot metal.
3.2 Activity coefficient of titanium in metal and slag phase
Wagner model can be used to obtain activity coefficient of titanium in multicomponent metal phase. The activity interaction coefficients of titanium in hot metal at a certain temperature range from 1350 °C to 1600 °C are shown in Table 4 [13]. The activity coefficient of titanium under a specific composition can be received from Eq. (9).
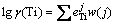 (9)
(9)
where j represents the elements of C, Si and Ti in hot metal.
Table 4 Activity interaction coefficients  of elements in hot metal at different temperatures
of elements in hot metal at different temperatures
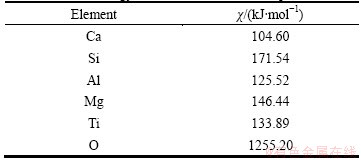
The activity coefficients of TiO2 in slag phase can be obtained by the model of congregated electron phase [14], which are expressed as Eqs. (10) to (13). The atomic energy scalar χ will be used in the calculation process, as seen in Table 5 [13].
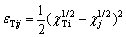 (10)
(10)
 (11)
(11)
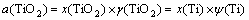 (12)
(12)
 (13)
(13)
where ε represents the exchanging position energy of adjacent atom. ψ(Ti) and x(Ti) respectively mean activity coefficient and mole fraction of titanium atom in slag.
Table 5 Atomic energy scalar used in calculation process
The activity coefficient of Ti in hot metal γ(Ti), the activity coefficient of TiO2 in slag phase γ(TiO2) and the system activity coefficient γsys at different reaction temperature are shown in Fig. 5.
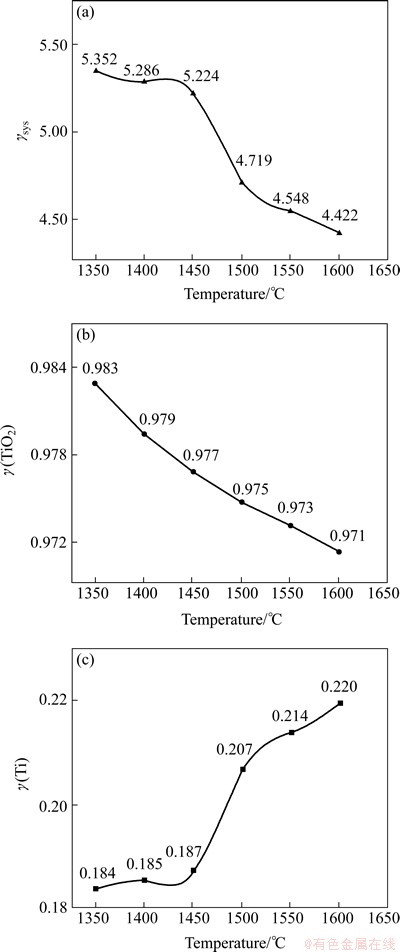
Fig. 5 Change of activity coefficient with temperature
As seen in Fig. 5, when the reaction temperature goes up from 1350 °C to 1600 °C, γ(Ti) increases gradually, from 0.184 to 0.220, while γ(TiO2) shows a trend of decrease, from 0.983 down to 0.971. Since the system activity coefficients γsys are correlated with γ(TiO2) positively and γ(Ti) negatively, γsys declines from 5.352 to 4.422. It is apparent that the titanium reduction potential between liquid slag and hot metal decreases with the temperature going up. However, the distribution ratio of titanium rises instead. These opposite variation trends of γsys and L(Ti) indicate that the equilibrium constant of titanium reduction increases following the temperature. Combined L(Ti) with γsys, a series of thermodynamic parameters and formulas can be received.
3.3 Thermodynamics calculation of titanium carbothermic reduction
The standard Gibbs free energy change for Reactions (14) and (15) can be calculated from the data of WANG [15] and LI et al [6], which were applicable over the temperature range from 1300 °C to 1700 °C, as seen in Eqs. (14) and (15).
TiO2+2[C]=[Ti]+2CO
 /(J·mol-1)=164060-95.05T (14)
/(J·mol-1)=164060-95.05T (14)
[Ti]+[C]=TiCs
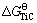 /(J·mol-1)=-153700+57.53T (15)
/(J·mol-1)=-153700+57.53T (15)
Based on the system activity coefficients and distribution ratios of titanium obtained above, the equilibrium constant K and Gibbs free energy curve can be received using Eqs. (4), (7) and Eqs. (14), (15). The data from experiments of WANG [15] and LI et al [6] are demonstrated in Fig. 6.
From Fig. 6(a), with the increase of reaction temperature, the equilibrium constant K(Ti) goes up gradually, which promotes the course of titanium carbothermal reduction reaction. The K(Ti) of present study is slightly larger than the data from WANG [15]. It can come down to the product of TiC in the hot metal, which accelerates the reduction reaction. K(Ti) of the present study is a little higher. The equilibrium constant K(TiC) based on both of the present study and LI [6] are plotted against the reaction temperature in Fig. 6(c). It shows that K(TiC) decreases obviously when the temperature varies from 1350 °C to 1600 °C. This tendency also verifies the formation of TiC in the hearth refractory breakage because of cooling. From Figs. 6(b) and (d), the Gibbs free energy change formulas of titanium carbothermal reduction based on experiments are fitted, which are  /(J·mol-1)=169251-97.93T and
/(J·mol-1)=169251-97.93T and  /(J·mol-1)=-143370+49.18T.
/(J·mol-1)=-143370+49.18T.
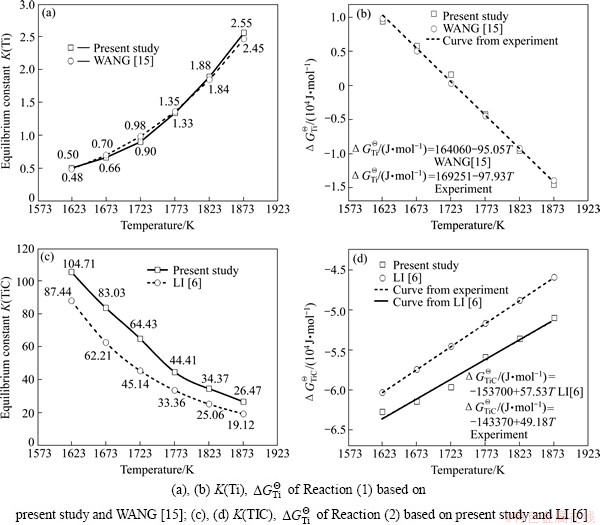
Fig. 6 Equilibrium constant K and ΔGΘ of titanium reduction along with temperature
3.4 Volume of titanium-bearing feed to protect BF hearth refractory
The content of silicon is a common evaluation standard to hot metal. Since the reduction of silicon is closely associated with hearth temperature, silicon is commonly used to represent the chemical heat of hot metal. To obtain a more utility parameter for actual production, the relationship between distribution ratio of titanium and silicon is fitted based on the experimental data obtained above, as shown in Eq. (16) and Fig. 7.
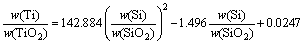 (16)
(16)
Since high hearth temperature is beneficial to the reduction of silicon, the distribution ratios of silicon and titanium have the positive correlation. Taking 35% as a typical content of SiO2 in slag and 5-20 kg/t as a TiO2 load into BF, the content of titanium in hot metal as a function of silicon and TiO2 load can be plotted using Eq. (16), as shown in Fig. 8. Thus, w(Ti) can be estimated directly based on the quantity of effective charging TiO2 and w(Si).
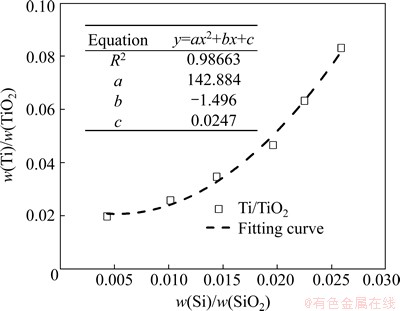
Fig. 7 Relationship of mass distribution ratio between titanium and silicon
ZHANG [16] showed that when the content of titanium in hot metal reached 0.1%-0.18%, it can effectively protect the BF hearth refractories and keep a smooth operation at same time. Based on the titanium distribution ratio obtained above, the minimum titanium load for a typical BF slag amount of 300 kg/t is shown in Fig. 9.
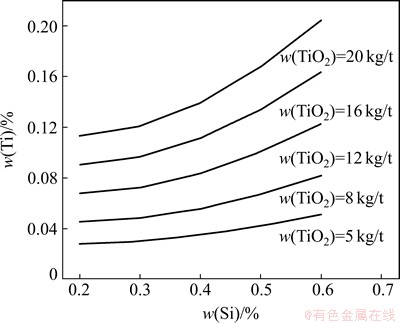
Fig. 8 Content of titanium in hot metal as function of silicon and TiO2 load
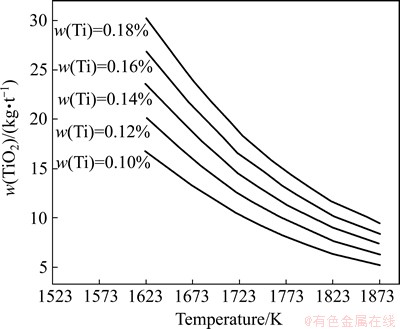
Fig. 9 Predicted minimum titanium load required for protection of hearth in BF
From Fig. 9, since L(Ti) and reduction potential increase with the hearth temperature going up, the volume of TiO2 load required for protecting refractories decreases gradually. For a representative hearth temperature of 1773 K, the load of TiO2 in BF feed is in the range of 8.11-14.59 kg/t, which indicates that the prediction according to experiment data agree well with that used in BF practical operation.
4 Conclusions
1) Through defining the distribution ratio of titanium L(Ti) and system activity coefficient γsys, the equilibrium constant of titanium carbothermal reduction reaction K(Ti) can be expressed as the ratio of L(Ti) and γsys. System activity coefficient γsys can be used to represent Ti reduction potential.
2) Activity coefficient of titanium in metal phase goes up gradually along with the increase of reduction temperature, while the activity coefficient of titanium dioxide in slag phase shows a trend of decrease, which leads to the decrease of system activity coefficient. Since L(Ti) is correlated with temperature positively, the K(Ti) increases with the rise of temperature. K(Ti) of the present study is a little higher than the published, which can come down to the appearance of TiC.
3) Based on the model of Wagner and congregated electron phase, the Gibbs free energy change formulas of titanium carbothermal reduction are fitted, which are  /(J·mol-1)=169251-97.93T and
/(J·mol-1)=169251-97.93T and 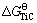 /(J·mol-1)= -143370+49.18T.
/(J·mol-1)= -143370+49.18T.
4) Through the fitted formula between silicon and titanium distribution ratio, the relation of w(Si) and w(Ti) is received at different titanium loads, which is beneficial to making a quick judgment in practical operation. Finally, the predicted titanium load to reach the minimum w(Ti) for BF hearth protection is given.
References
[1] NAM S J, KANG Y B, JUNG S M, YASUSHI S. Feasibility of BF hearth protection using spinel formation by slag composition control [J]. ISIJ International, 2013, 53(10): 1779-1785.
[2] GUO Bao-yu, PAUL Z, DANIEL M, YU Ai-bing. A model to simulate titanium behavior in the iron blast furnace hearth [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2010, 41(4): 876-885.
[3] WAN He-li, XU Bao-qiang, DAI Yong-nian, YANG Bin, LIU Da-chun, SEN Wei. Preparation of titanium powders by calciothermic reduction of titanium dioxide [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(9): 2434-2439.
[4] LI Y, RICHARD J F. Thermodynamics of TiCN and TiC in Fe-Csat melts [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2001, 30(6): 1203-1205.
[5] HOU Ya-li, QING Shan, WANG Hua, SHI Zhe, LI Hui-bin. Mixture of ilmenite and high phosphorus iron ore smelted by oxygen- enriched top-blown smelting reduction [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(10): 2760-2767.
[6] LI Y, LI Y Q, RICHARD J F. Formation of titanium carbonitride from hot metal [J]. ISIJ International, 2001, 41(12): 1417-1422.
[7] HE X, YE J W, LIU Y, CHEN B Q, JIANG Z T, ZOU H W, DENG L, TU M J. Phase transition and microstructure evolution during the carbothermal preparation of Ti(C,N) powders in an open system [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2010, 21(4): 448-451.
[8] HAN C, YANG H, XUE X X. Effects of Fe content on photocatalytic activity of CaTiO3-Fex [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(10): 3215-3220.
[9] XUN Shi-wei, WANF Da-guang, XUAN De-mao. The research on smelting reduction between vanadium-titanium slag system and carbon saturated hot metal [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1989, 10(2): 44-50. (in Chinese)
[10] BERGSMA D, RICHARD J F. Fundamentals of titanium-rich scaffold formation in the blast-furnace hearth [C]// Proceedings of 60th Ironmaking Conference. Baltimore: Iron & Steel society, 2001: 297-312.
[11] MORIZANE Y, OZTURK B, RICHARD J F. Thermodynamics of TiOx in blast furnace-type slag [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1999, 30(1): 29-43.
[12] DU Q, LI Y J. Effect modeling of Cr and Zn on microstructure evolution during homogenization heat treatment of AA3xxx alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 2145-2149.
[13] HUANG Xi-hu. Iron and steel metallurgy principle [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 270-271. (in Chinese)
[14] PONOMARENKO A G. Questions in the thermodynamics of phases of variable composition with a collective electronic system [J]. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1974, 48(7): 1668-1674. (in Russian)
[15] WANG Qing-xi. Vanadium titanium magnetite smelt in blast furnace [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1994: 100-101. (in Chinese)
[16] ZHANG Yu-cai. Overview of BF protection technology with Ti-bearing materials for blast furnace [J]. Baosteel Meishan, 2006, 26(2): 56-59. (in Chinese).
王振阳,张建良,邢相栋,刘征建
北京科技大学 冶金与生态工程学院 北京 100083
摘 要:为研究铁水中钛元素碳热还原反应规律,提供高炉护炉理论依据,利用高温熔炼、急速淬火、化学分析以及热力学模型计算等方法,在实验室条件下利用分析纯试剂研究在1350~1600 °C间钛在低钛渣系CaO-SiO2-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2与铁水间的分配行为。研究结果表明,随着反应温度的增加,钛的分配比L(Ti)增加,但系统活度系数γsys降低,从而导致反应平衡常数升高。结合Wagner与凝聚电子相模型,通过对实验数据进行拟合,得到钛碳热还原反应的吉布斯自由能公式。最后,结合实验所得结果,给出了高炉铁水中w(Si)与w(Ti)含量的关系以及可以达到护炉效果的最小入炉钛负荷。
关键词:钛;分配行为;活度系数模型;护炉;钛负荷
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (2012CB720401) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (2011BAC01B02) supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China
Corresponding author: Zhen-yang Wang; Tel: +86-10-62332550; E-mail: wangzheny@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63769-4

