文章编号:1004-0609(2014)03-0577-07
压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的腐蚀和腐蚀疲劳行为
胡祖麒,万 里,吴树森,朱 鹏
(华中科技大学 材料成形与模具国家重点实验室,武汉 430074)
摘 要:研究压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的电化学腐蚀、晶间腐蚀和腐蚀疲劳机理。结果表明:合金的自腐蚀电位和点蚀电位分别为-1220和-690 mV,钝化区间约为530 mV,说明合金的耐腐蚀性能良好。合金的晶间腐蚀倾向明显,这主要是由于Mg2Si相自腐蚀电位较低,且(Al+Mg2Si)共晶区的体积分数较大(29.6%)。电化学腐蚀反应和Mg2Si自身溶解产生的氢元素导致疲劳试样表面发生阳极溶解,加速了疲劳裂纹的萌生,从而显著降低了合金的疲劳寿命。腐蚀疲劳试样的裂纹主要是沿晶界扩展。氢元素也导致合金塑性下降,造成应力腐蚀开裂。
关键词:铝合金;压力铸造;腐蚀疲劳;极化;断口形貌
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Corrosion and corrosion-fatigue behavior of die cast AlMg5Si2Mn alloy
HU Zu-qi, WAN Li, WU Shu-sen, ZHU Peng
(State Key Laboratory of Materials Processing and Die & Mould Technology,
Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China)
Abstract: The electrochemical corrosion, intergranular corrosion and corrosion-fatigue mechanisms of die cast AlMg5Si2Mn alloy were studied. The results indicate that the self-corrosion potential and pitting potential are -1220 and -690 mV, respectively. The wide domain of passivity (of about 530 mV) indicates good corrosion resistance of the alloy. The poor intergranular corrosion resistance of the alloy is attributed to the low corrosion potential and high volume fraction (29.6%) of (Al+Mg2Si) eutectic region. Considerable hydrogen concentration, which is created by the electrochemical reaction and the dissolution of Mg2Si dendrite, results in the anodic dissolution on the surface of fatigue specimens and accelerates the premature crack initiation, thus obviously decreasing the fatigue life of the alloy. Fatigue cracks of the corroded fatigue specimens mainly propagate along grain boundaries. In addition, hydrogen reduces the ductility of the alloy and leads to stress corrosion cracking.
Key words: aluminum alloy; high pressure die cast; corrosion fatigue; polarization; fractograph
压力铸造(HPDC)是一种生产效率高、尺寸精度良好的近净成形技术,在通讯、机电和汽车零件制造等多个领域具有广泛的应用前景。然而,在压铸过程中金属液在高速高压下充型,导致型腔内部气体无法排出最终在铸件内部形成大量的气孔,从而严重降低铸件的韧性。为了提高压铸件的韧性,扩大压铸件在关键受力结构件领域的应用,高强韧压铸铝合金的开发受到了国内外的广泛关注[1-4]。
由德国Aluminum Rheinfelden公司开发的3种低Fe含量(<0.2%,质量分数)的高强韧压铸铝合金分别为Magsimal-59 (AlMg5Si2Mn)、Silafont-36
(AlMg5Si2Mn)、Silafont-36 (AlSi9Mg)和Castasil-37
(AlSi9Mg)和Castasil-37 (AlSi9)合金,与其他压铸铝合金相比,AlMg5Si2Mn主要具有以下特点[5]:1) 具有较高的伸长率(13%~17%),无需热处理即可获得良好的力学性能,缩短零件制造周期;2) 由于含有5%(质量分数)的Mg元素,合金具有良好的耐腐蚀性能,可以应用于腐蚀性环境中;3) 加入0.8%的Mn元素,减缓了由于Fe含量降低导致的粘模现象。因此,深入研究该合金对于制造高要求的受力结构件有很重要的工程实际意义。
(AlSi9)合金,与其他压铸铝合金相比,AlMg5Si2Mn主要具有以下特点[5]:1) 具有较高的伸长率(13%~17%),无需热处理即可获得良好的力学性能,缩短零件制造周期;2) 由于含有5%(质量分数)的Mg元素,合金具有良好的耐腐蚀性能,可以应用于腐蚀性环境中;3) 加入0.8%的Mn元素,减缓了由于Fe含量降低导致的粘模现象。因此,深入研究该合金对于制造高要求的受力结构件有很重要的工程实际意义。
目前,关于AlMg5Si2Mn的研究主要集中在微观组织的形成机理、疲劳寿命和疲劳裂纹扩展速率等方面,例如OTARAWANNA等[6]和HIELSCHER[7]研究了压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的微观组织构成以及补缩机理,结果表明,压铸AlMg5Si2Mn的微观组织主要是由粗大α(Al)晶粒、细小α(Al)晶粒,体积分数为25%~35%的(Al+Mg2Si)共晶区以及沿晶界分布的Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2颗粒构成。WAN等[8]及胡祖麒等[9]对AlMg5Si2Mn的疲劳寿命和裂纹扩展速率进行了相关研究,结果表明,当应力比为0时,AlMg5Si2Mn压铸件的疲劳极限约为57 MPa,疲劳裂纹主要起源于表面孔洞、氧化夹杂物和塑性变形。此外,JOHANNESSON等[10]和GREVEN等[11]的研究表明,压力铸造AlMg5Si2Mn试样的力学性能优于砂型铸造和挤压铸造AlMg5Si2Mn试样的力学性能。
同时,5XXX铝合金具有良好的耐腐蚀性能,因此被广泛应用于航天和海洋工业中[12]。常见的5XXX铝合金相对于饱和甘汞电极(SCE,下同)的自腐蚀电位φcorr通常位于-700~-900 mV之间。研究表明,5XXX合金发生电化学腐蚀和腐蚀疲劳断裂的主要原因是均匀分布在晶界处的β-Al3Mg2(φcorr=-1100~-1200 mV)[13-14]。HOLTZ等[15]研究了中性腐蚀环境对5083-H131合金的腐蚀疲劳裂纹扩展速率的影响,结果表明,在真空环境或空气中,β-Al3Mg2相的分布对合金的疲劳裂纹扩展速率无显著影响,而在浓度为3.5%(质量分数)的NaCl腐蚀液中,合金的应力强度门槛值下降50%,裂纹扩展速率明显提高,抗疲劳性能下降。然而,对于AlMg5Si2Mn合金,由于加入了Si和Mn元素,因此,β-Al3Mg2相被Mg2Si枝晶和 Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2颗粒代替。显然,微观组织的变化将影响合金的耐腐蚀性能,因此,有必要对该合金的耐腐蚀性能进行深入研究。然而,目前国内外关于压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的腐蚀和腐蚀疲劳行为的研究鲜见报道,为此,本文作者以压铸AlMg5Si2Mn平板件为研究对象,通过疲劳寿命实验和电化学测试等手段对AlMg5Si2Mn合金的腐蚀行为进行研究,以推广该类合金在腐蚀环境下的应用。
1 实验
实验使用原材料为AlMg5Si2Mn铸锭,使用电阻丝加热炉将铸锭加热融化,当熔体温度上升至700 ℃时,用氩气精炼20 min,随后清理,静置10 min,准备浇注。初始试样是外形为200 mm×60 mm×4 mm的平板件(见图1),采用压铸机为280 t卧式冷室压铸机,压射压力为115 MPa,保压时间为15 s。光谱分析得出合金的化学成分如表1所列。
图1 压铸试样外形图
Fig. 1 Profile of die casting sample
表1 合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of alloy (mass fraction, %)

AlMg5Si2Mn合金的腐蚀疲劳实验在电液伺服疲劳试验机上完成(机器型号:Shimadzu EHF-UV 100k2-040-1A),疲劳试样的外形尺寸如图2所示。疲劳寿命实验采用的应力比R=-1,加载频率为10 Hz。腐蚀疲劳实验是将疲劳试样的标距段浸泡在浓度为3.5%的NaCl溶液中持续加载直至断裂,记录腐蚀疲劳寿命。疲劳寿命超过5×106次则定义为越出(Run out)。发生越出的试样在5×106次应力加载后,将应力水平提高至75 MPa反复拉伸至断裂,以观察断口形貌。
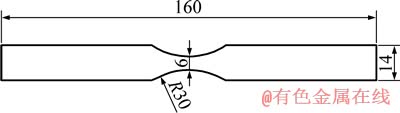
图2 疲劳试样示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of fatigue specimen (Unit: mm)
动电位极化曲线则是在1 mV/s的扫描速度下测量得出,试样的暴露面积为1 cm2,试样连接铜线后用环氧树脂镶嵌,随后用800、1500、2000和3000目的砂纸进行打磨。实验在标准三电极(铂电极、饱和甘汞电极和待测试样)测试系统中完成,腐蚀液是浓度为3.5%的NaCl溶液,在动态扫描得到稳定的开路电位以后迅速开始测量极化曲线并且自动记录合金的自腐蚀电位以及腐蚀电流密度。此外,根据ASTM G67和ASTM G110的要求,对该合金的晶间腐蚀倾向进行研究,通过线切割法从铸件上截取试样,试样外形尺寸约为50 mm×4 mm×4 mm,用400目砂纸将试样进行打磨,然后用酒精进行超声波清洗,烘干后称量试样初始质量m0,测量试样的准确面积A。将清洗干净的部分试样分别在35 ℃的65%~68%(质量分数)的HNO3溶液中浸泡24 h,随后进行烘干,称量腐蚀后试样的质量m。另一部分试样则在35 ℃的1%HCl+30 g/L NaCl溶液中浸泡24 h,用金相显微镜对经腐蚀后的试样进行观察并测量最大腐蚀深度。合金的金相组织经过粗磨、精磨和抛光后,用金相显微镜进行观察。腐蚀疲劳试样断口和电化学腐蚀试样均使用SEM进行观察,从而深入分析合金的断裂机理和腐蚀机理。
2 结果与讨论
图3(a)所示为压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的极化曲线;合金的腐蚀电流密度(Jcorr)、自腐蚀电位(φcorr)、点蚀电位(φp)以及Tafel斜率(ba和bc)等参数如表2所列。结果表明,压铸AlMg5Si2Mn的自腐蚀电位约为-1220 mV,该电位明显低于常见的5XXX铝合金的自腐蚀电位,尽管自腐蚀电位通常反映了合金的抗腐蚀性能,然而在AlMg5Si2Mn合金的阳极极化曲线部分(-1220~-690 mV)出现明显的平滑区域,合金在该区间内发生钝化,表面形成氧化膜,阻止合金发生进一步氧化,直到φ=φp=-690 mV 腐蚀电流密度开始明显提高,说明钝化层破裂,发生大范围的点蚀。尽管合金的自腐蚀电位比同类铝合金的低,但是合金的点蚀电位为-690 mV,宽度为530 mV的钝化区通常在钢铁材料和有涂层铝合金的极化曲线中才能观察到[13],该钝化区间体现了合金良好的耐腐蚀性能。在图3(b)中将多种压铸合金[15-18]的极化曲线进行对比,从图3(b)中可以看出,压铸镁合金(AZ91D)的自腐蚀电位最低,压铸A380(Al-Si-Cu)合金的自腐蚀电位约为-700 mV,明显高于5083和AlMg5Si2Mn合金的自腐蚀电位。另外,作为AlMg5Si2Mn合金主要组成相的α(Al)和Mg2Si,其自腐蚀电位分别为-900和-1150 mV。结果表明,AlMg5Si2Mn合金的自腐蚀电位和Mg2Si的自腐蚀电位比较接近,且该类合金在发生电化学反应时Mg2Si枝晶和α(Al)可以分别作为阳极和阴极,这主要是由于Mg2Si的自腐蚀电位明显低于α(Al)的自腐蚀电位,且合金的(Al+Mg2Si)共晶区的体积分数高达29.6%。此外,Al-Mg合金的耐腐蚀性能比Al-Si-Cu合金的更好,因此,A380合金的自腐蚀电位较高也反映出用电化学实验结果来评价铝合金腐蚀性能具有一定的不合理性[13, 16]。
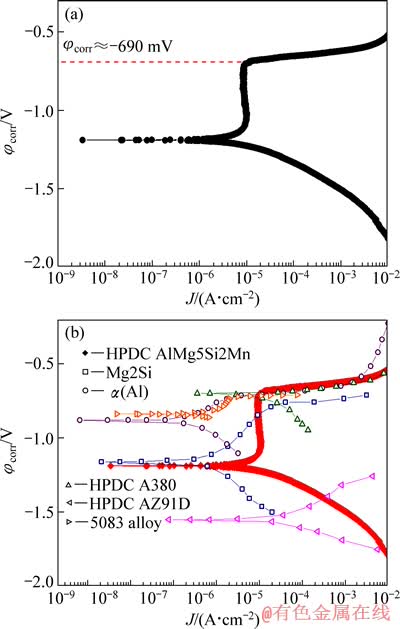
图3 压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金及几种常用压铸合金的极化曲线对比
Fig. 3 Comparison of potentiodynamic polarization curves of HPDC AlMg5Si2Mn (a) and some die cast alloys
表2 压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金试样在3.5%NaCl溶液中的动电位扫描结果
Table 2 Results of potentiodynamic tests of HPDC AlMg5Si2Mn in 3.5% NaCl solution
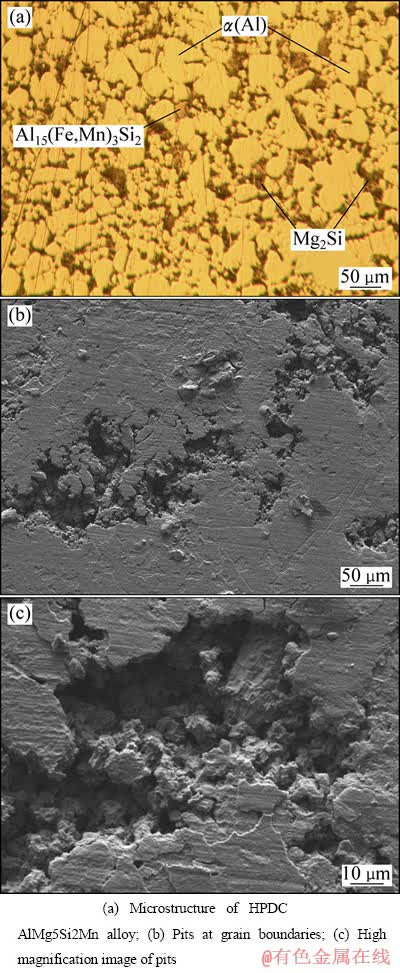
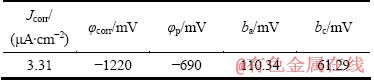

图4 压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的金相组织与腐蚀表面形貌
Fig. 4 Morphologies of microstructures and corroded surface HPDC AlMg5Si2Mn alloy
为了深入了解压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的电化学腐蚀机理,腐蚀试样表面用SEM观察,结果如图4所示。图4(a)所示为合金的金相组织。由图4(a)中可以观察到少量沿晶界分布的Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2颗粒。另外,为了得出(Al+Mg2Si)共晶区的体积分数,在本实验中采用图像处理软件对多张金相图片进行定量分析处理,结果表明,本合金中(Al+Mg2Si)共晶区的体积分数为29.6%。图4(b)和(c)所示为点蚀坑的形貌。从图4(b)中可以观察到大量连续腐蚀凹坑位于晶界处,枝晶间也出现了一些缝隙;图4(c)显示点蚀坑内的腐蚀产物。在晶界处形成点蚀坑主要是发生了以下两个电化学反应:
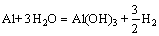 (1)
(1)
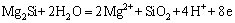 (2)
(2)
反应(1)一般发生在两个位置即α(Al)(阴极)和Mg2Si(阳极)以及α(Al)(阴极)和Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2(阳极)的界面处,在反应(1)的发生过程中α(Al)同时作为阳极和阴极在不同界面处发生电化学反应,由于Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2粒子的数量较少,因此,发生在该处的反应并不明显,Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2粒子附近的基体组织仍然比较稳定。反应(2)则是Mg2Si相自身的溶解反应,使该反应发生的主要原因是Mg元素的反应活性较高以及Mg2Si的自腐蚀电位较低。有研究表明,Mg2Si在发生了自身溶解后,Mg2Si枝晶中的Mg元素大量消耗,从而形成了富Si区,且在富Si区表面沉积了大量腐蚀产物,该覆盖层对于合金的进一步腐蚀起到了一定的阻碍作用,从而避免了合金的进一步腐蚀[19]。
晶间腐蚀实验的结果表明,合金在65%~68%HNO3溶液中浸泡24 h后,试样单位面积质量损失(m-m0)/A为62.1 mg/cm2,在25~75 mg/cm2之间,质量损失较大。在HCl+ NaCl溶液中浸泡24 h后,试样的最大腐蚀深度为130 μm,在0.1~0.3 mm之间。根据GB7998—2005,该腐蚀深度对应4级晶间腐蚀,因此,该合金晶间腐蚀倾向明显。另外,从图5中可以直接观察到腐蚀试样表面形貌,可以看出,在晶粒和枝晶间存在大量孔隙,这是由合金发生晶间腐蚀和(Al+Mg2Si)共晶区的溶解反应所致。
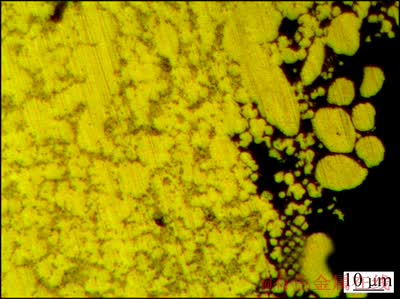
图5 在65%~68%HNO3溶液中浸泡24 h后合金腐蚀界面金相组织
Fig. 5 Microstructure of corroded surface of sample immersed in 65%-68% HNO3 solution for 24 h
图6所示为合金的疲劳寿命实验结果。从图6中可以看出,当应力水平为125 MPa时,试样的腐蚀疲劳寿命略低于常规疲劳寿命;当应力水平降到100 MPa时,试样的常规疲劳寿命已经超过了5×106 cycle(越出),而在3.5% NaCl腐蚀液中试样的疲劳寿命仅为201133 cycle,明显低于常规疲劳寿命;当应力载荷继续下降至50 MPa时,腐蚀疲劳寿命超过5×106 cycle(越出,run out)。因此,3.5%NaCl腐蚀液对压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的疲劳寿命有明显的不利影响,且随着疲劳载荷的降低腐蚀疲劳寿命与常规疲劳寿命的差距逐渐增大。
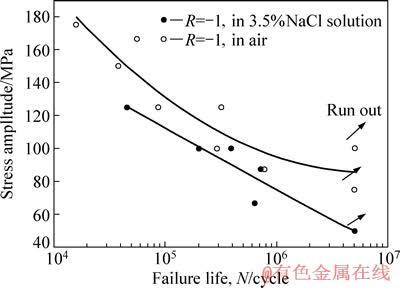
图6 压铸AlMg5Si2Mn在空气和3.5% NaCl溶液中的疲劳寿命
Fig. 6 Fatigue life of HPDC AlMg5Si2Mn in air and 3.5% NaCl solution
图7所示为压铸AlMg5Si2Mn疲劳试样的断口形貌。图7(a)所示为应力幅值为50 MPa的腐蚀疲劳试 样的裂纹源区。在裂纹源处观察到一些相对平整、没有明显特点的平面区域。研究表明,在含Cl元素的溶液中,当应力载荷较小,腐蚀液和循环载荷对裂纹面的共同作用时间长,容易导致阳极溶解反应的发生;并且由于在疲劳失效过程中试样表面发生塑性变形,在局部容易形成应力集中区,该区域容易成为阳极,周围应力集中较小的区域作为阴极发生电化学反应,从而加剧裂纹萌生倾向[20]。金属的疲劳寿命一般由裂纹萌生寿命和裂纹扩展寿命两部分组成,研究表明,前者所占比例高达90%[20],阳极溶解缩短了裂纹萌生所需时间,从而显著降低了合金的疲劳寿命。图7(b)和(c)所示分别为常规疲劳试样和腐蚀疲劳试样的裂纹扩展区域。在7(b)中可以观察到大量撕裂棱以及局部区域的疲劳条带,该形貌反映出合金在循环载荷作用下的良好塑性。但是,与应力比为0时的疲劳断口形貌不同,局部疲劳条纹的形成是由于拉压应力的反复作用导致裂纹面之间发生摩擦和接触,因此,条纹变得不清晰甚至完全消失[20-21]。从图7(c)中可以看出腐蚀疲劳裂纹扩展时也有一定的塑性变形,同时可以观察到断口表面存在一些白色的腐蚀残留物。图7(d)所示为应力幅值为87.5 MPa时腐蚀疲劳试样的裂纹扩展区,该区域中可观察到大量开裂结构。
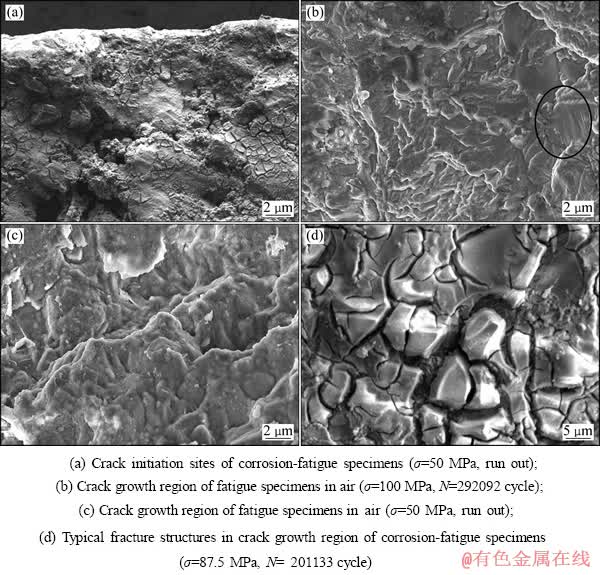
图7 疲劳试样的断口形貌
Fig. 7 Morphologies of fatigue fracture surface
形成上述结构的原因应该是合金基体发生脆化以后,局部区域的抗拉强度低于外界应力,从而产生大量二次裂纹,二次裂纹的进一步扩展则形成了上述开裂结构。MEYN[22]在7075合金的应力腐蚀表面也观 察到了类似的开裂结构,并且提出形成该结构的主要原因是氢元素的富集导致金属基体发生脆裂。在腐蚀疲劳实验中,循环载荷的反复作用加剧了氢元素的不利影响,电化学反应(1)和(2)都会产生大量的氢原子,这些氢原子富集在裂纹尖端部位的空洞处,并且重新组合成氢分子,导致裂纹尖端产生较高的氢分子压力,加剧了该区域的局部塑形变形,直接提高裂纹扩展速率[15, 23]。在开裂结构上覆盖的亮白色物质则是腐蚀产物,该腐蚀产物为Al(OH)3,在干燥脱水后变成Al2O3。另外,常规疲劳试样的裂纹扩展机理为穿晶断裂,而上述开裂结构则证明腐蚀环境使得裂纹扩展机理已经部分转变为沿晶断裂,该现象与之前的电化学实验结果相符。在腐蚀环境中共晶区的Mg2Si相发生电化学和自溶解反应,从而直接弱化了晶界强度,使其成为微观组织中的薄弱环节。因为裂纹扩展时选择阻力最小的路径扩展,故裂纹扩展机理由穿晶断裂转变为沿晶断裂。因此,应力腐蚀开裂和疲劳载荷的共同作用导致裂纹扩展机理发生变化并且产生大量的开裂结构。
3 结论
1) 压铸AlMg5Si2Mn合金的自腐蚀电位和点蚀电位分别为-1220和-690 mV,钝化区间约为530 mV,说明合金的耐腐蚀性良好。
2) 合金在HNO3中浸泡24 h后的质量损失为62.1 mg/cm2,在HCl+NaCl溶液浸泡24 h后的最大腐蚀深度为130 μm,晶间腐蚀倾向明显。在(Al+Mg2Si)共晶区观察到大量点蚀坑和腐蚀产物。
3) 合金在空气中的疲劳寿命明显高于在3.5% NaCl溶液中的疲劳寿命,且随着应力水平的降低,疲劳寿命差距增大,这主要是由于阳极溶解反应加速了裂纹萌生。
4) 腐蚀环境导致裂纹扩展方式由穿晶断裂转变为沿晶断裂模式,腐蚀反应产生的大量氢原子则可能导致试样出现应力腐蚀开裂结构和裂纹扩展机理发生转变。
REFERENCES
[1] LUO A A, SACHDEV A K, POWELL B R. Advanced casting technologies for lightweight automotive applications[J]. China Foundry, 2010, 7(4): 463-469.
[2] 左宏志, 刘昌明, 邹茂华, 谷忠明, 范 增, 李德全, 吴 均. ZL112Y压铸铝合金摩托车零件的半固态高压铸造成形[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(4): 949-955.
ZUO Hong-zhi, LIU Chang-ming, ZOU Mao-hua, GU Zhong-ming, FAN Zeng, LI De-quan, WU Jun. Semi-solid die casting process of motorcycle parts of ZL112Y die cast alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(4): 949-955.
[3] XIAO-GUANG Y, HONG-JUN H, RONG-DE L I, YANG C, SHI-FANG S U. Die casting technology develops steadily—A commentary on the 5th China international die casting congress[J]. China Foundry, 2006, 3(4): 322-324.
[4] COLE G S, SHERMAN A M. Light weight materials for automotive applications[J]. Materials Characterization, 1995, 35(1): 3-9.
[5] KAUFMANN H, UGGOWITZER P J. Metallurgy and processing of high-integrity light metal pressure castings[M]. Berlin: Schiele &  , 2007.
, 2007.
[6] OTARAWANNA S, GOURLAY C M, LAUKLI H I, DAHLE A K. Microstructure formation in AlSi4MgMn and AlMg5Si2Mn high-pressure die castings[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009, 40(7): 1645-1659.
[7] HIELSCHER U. New diecasting alloy with good mechanical properties without heat treatment[J]. Fonderia (Italy), 1999, 48(11/12): 33-36.
[8] WAN L, HU Z, WU S, LIU X. Mechanical properties and fatigue behavior of vacuum-assist die cast AlMgSiMn alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 576: 252-258.
[9] 胡祖麒, 万 里, 吴 晗, 刘学强, 邹 广, 吴树森. 高强韧压铸Al-Mg-Si-Mn合金的微观组织及力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(3): 616-622.
HU Zu-qi, WAN Li, WU Han, LIU Xue-qiang, ZOU Guang, WU Shu-sen. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high strength and toughness die casting Al-Mg-Si-Mn alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(3): 616-622.
[10] JOHANNESSON B,  C H. Effect of Si additions and heat treatment on the mechanical behaviour of an Al-5Mg cast alloy[J]. International Journal of Cast Metals Research, 2004, 17(2): 94-98.
C H. Effect of Si additions and heat treatment on the mechanical behaviour of an Al-5Mg cast alloy[J]. International Journal of Cast Metals Research, 2004, 17(2): 94-98.
[11] GREVEN K, DRAGULIN D. Ductile high pressure die casting—Heat treated or temper F?[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Light Metals Technology. LKR: Verlag, 2005.
[12] SEONG J K, SEOK K J, MIN S H, JAE C P, JAE Y J, SANG O C. Mechanical and electrochemical characteristics in sea water of 5052-O aluminum alloy for ship[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(3): 636-641.
[13] VARGEL C. Corrosion of aluminum[M]. New York: Elsevier Science, 2004: 96-108.
[14] ZENG F, WEI Z, LI J, LI C, TAN X, ZHANG Z, ZHENG Z. Corrosion mechanism associated with Mg2Si and Si particles in Al-Mg-Si alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(12): 2559-2567.
[15] HOLTZ R, PAO P, BAYLES R, LONGAZEL T, GOSWAMI R. Corrosion-fatigue behavior of aluminum alloy 5083-H131 sensitized at 448 K (175 ℃)[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012, 43(8): 2839-2849.
[16] ABALLE A, BETHENCOURT M, BOTANA F J, CANO M J, MARCOS M. Influence of the cathodic intermetallics distribution on the reproducibility of the electrochemical measurements on AA5083 alloy in NaCl solutions[J]. Corrosion Science, 2003, 45(1): 161-180.
[17] AMBAT R, AUNG N N, ZHOU W. Evaluation of microstructural effects on corrosion behaviour of AZ91D magnesium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2000, 42(8): 1433-1455.
[18] 张 莉, 王渠东, 胡茂良, 丁文江. Al-Si-Cu压铸铝合金的耐腐蚀性能[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2011(11): 1021-1024.
ZHANG Li, WANG Qu-dong, HU Mao-liang, DING Wen-jiang. Corrosion resistance of Al-Si-Cu die casting aluminum alloy[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2011(11): 1021-1024.
[19] YASAKAU K A, ZHELUDKEVICH M L, LAMAKA S V, FERREIRA M G S. Role of intermetallic phases in localized corrosion of AA5083[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(27): 7651-7659.
[20] SURESH S. Fatigue of structures and materials[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1991: 362-369.
[21] 胡祖麒, 万 里, 吴 晗, 刘学强, 邹 广, 吴树森. 时效处理对高强韧压铸Al-Mg-Si-Mn合金力学性能的影响[J]. 铸造, 2013(1): 13-16.
HU Zu-qi, WAN Li, WU Han, LIU Xue-qiang, ZOU Guang, WU Shu-sen. Effect of aging treatment on the mechanical properties of die cast Al-Mg-Si-Mn alloys with high strength and toughness[J]. Foundry, 2013(1): 13-16.
[22] MEYN D A. Fractographic diagnosis of stress corrosion cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys[J]. Corrosion, 1970, 26(10): 427-429.
[23] MENZEMER C, SRIVATSAN T S. The effect of environment on fatigue crack growth behavior of aluminum alloy 5456[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 271(1/2): 188-195.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:广东省省部产学研结合重大专项资助项目(2012A090300016)
收稿日期:2013-06-24;修订日期:2013-09-30
通信作者:万 里,副教授,博士;电话:027-87556262;E-mail:liwan@mail.hust.edu.cn