高放核废料存储环境下温度对纯铜腐蚀的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第6期
论文作者:孔德成 董超芳 肖葵 李晓刚
文章页码:1431 - 1438
关键词:铜腐蚀;硫化物;核废料处置;温度;电化学性能
Key words:copper corrosion; sulfide; nuclear waste disposal; temperature; electrochemical performance
摘 要:系统研究在高放核废料存储环境下温度对纯铜腐蚀的影响。采用交流阻抗谱、Mott-Schottky技术、动电位以及恒电位极化曲线分析纯铜在不同温度下的腐蚀行为;并采用体视显微镜以及扫描电镜观察样品表面形貌,同时结合X射线光电子能谱分析钝化膜成分。结果表明,钝化膜阻抗并不随着温度的升高而一直降低,在60 °C由于致密的外层结构阻抗反常增大;点蚀在此环境下可能发生且钝化膜的点蚀电位随着温度的升高而降低;钝化膜主要成分为Cu2S,而CuS的含量随着温度的升高而增加;钝化膜主要呈p型半导体特性,阳离子空位密度在1023 cm-3数量级且随着温度的升高其密度增大。
Abstract: The effect of temperature on the corrosion behavior of copper in simulated high-level nuclear waste environment was systematically studied. Electrochemical methods, including electrochemical impendence spectra, Mott–Schottky technology, cyclic polarization, and potentiostatic polarization, were employed to characterize the corrosion behavior of copper at different temperatures. Stereoscopic microscopy and scanning electron microscopy were used to examine the surface morphology, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis was used to identify the composition of the passive film. The experimental results show that corrosion resistance of the passive film does not blindly decrease with the increase of temperature but increases at 60 °C owing to a compact outer layer; there is a potential for pitting corrosion, which decreases as the temperature increases. The main product of copper in an anaerobic aqueous sulfide solution is Cu2S but the content of CuS increases at higher temperatures. The whole passivation range shows p-type semiconductor characteristics and the magnitude of the acceptor density is 1023 cm-3, which increases with increasing temperature.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 1431-1438
De-cheng KONG, Chao-fang DONG, Kui XIAO, Xiao-gang LI
Corrosion and Protection Center, Key Laboratory for Corrosion and Protection, Ministry of Education, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
Received 8 March 2016; accepted 16 June 2016
Abstract: The effect of temperature on the corrosion behavior of copper in simulated high-level nuclear waste environment was systematically studied. Electrochemical methods, including electrochemical impendence spectra, Mott–Schottky technology, cyclic polarization, and potentiostatic polarization, were employed to characterize the corrosion behavior of copper at different temperatures. Stereoscopic microscopy and scanning electron microscopy were used to examine the surface morphology, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis was used to identify the composition of the passive film. The experimental results show that corrosion resistance of the passive film does not blindly decrease with the increase of temperature but increases at 60 °C owing to a compact outer layer; there is a potential for pitting corrosion, which decreases as the temperature increases. The main product of copper in an anaerobic aqueous sulfide solution is Cu2S but the content of CuS increases at higher temperatures. The whole passivation range shows p-type semiconductor characteristics and the magnitude of the acceptor density is 1023 cm-3, which increases with increasing temperature.
Key words: copper corrosion; sulfide; nuclear waste disposal; temperature; electrochemical performance
1 Introduction
A proposed method for the disposal of Swedish, Finnish, or Canadian high-level nuclear waste is to place it in corrosion resistant containers and bury it 500-1000 m deep in a granitic repository [1-4]. These containers would be fabricated with an inner layer of cast iron and an outer shell of oxygen-free copper (30-50 mm in thickness). Although Cu was chosen for its thermodynamic resistance to corrosion in anoxic environments, the long-term corrosion behavior of copper in contact with sulfide-containing, saline, anoxic environments is far from being well-understood. So, a fundamental understanding of the passive state on this metal in relevant environments is urgently required. The most likely corrosive agent in the groundwater to which the containers will be exposed is sulfide, derived from either mineral dissolution (i.e., pyrite, FeS2) or microbial production from sulfates (i.e., via reaction of sulfate- reducing bacteria) [5,6]. In ground water anticipated in a geologic repository, the sulfide and chloride concentrations will be in the range of 10-7-10-4 mol/L and 0.1-1.4 mol/L, respectively [7].
CHEN et al [8-10] studied the kinetics of corrosion film growth and long-term corrosion of copper in chloride solution containing sulfide at room temperature. Kinetic studies revealed that two types of growth processes are dependent on [SH-]. At relatively high concentrations ([SH-]=5.0×10-4 mol/L), film growth follows a parabolic law and is governed by the transport of Cu+ ions through the Cu2S matrix or along grain boundaries in the Cu2S film. However, when [SH-] is lower ([SH-]=5.0×10-5 mol/L), film growth is controlled by SH- diffusion and the kinetics follow a linear growth law, leading to a porous non-protective film. MARTINO and PARTOVI [11] focused on a wide range of sulfide and chloride concentrations using rotating disk electrodes at room temperature. These studies show that three distinct types of films are formed depending on the sulfide concentration, flux of sulfide to the electrode surface, and chloride concentration of the solution.
Further, the film properties and the growth mechanism were determined by the competition between sulfide diffusion in solution and the rate of interfacial reactions on the copper surface.
It is obvious that most of the above studies focused on comparison of the materials performance at room temperature and relatively few studies on the effect of temperature on the corrosion behavior of copper in ground water environments. However, the canister material might experience a wide range of temperatures in a high-level nuclear waste repository depending on the location; time and temperature definitely have a great influence on the corrosion of copper canisters, which changes the service life of the copper canister. The canisters will experience different environmental scenarios (initially oxic, but then anoxic) and an increase in temperature up to 90 °C in around 10 years, and then a decrease to 30 °C after closure for 2000 years [7]. Therefore, it is the main objective of this study to systematically study the effect of temperature on the corrosion behavior of copper in the repository environment.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and electrode preparation
All experiments were performed with phosphorous- doped, oxygen-free copper (Cu-OF) with a purity of 99.999%. Working electrodes were prepared using copper billets of 1 cm × 1 cm and threading them into thin copper rods. Electrodes were then encased in poly- tetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) holders using epoxy resin to prevent any contact of the aqueous environment with the copper rod. All samples were ground with SiC paper up to 2000 grit and to a mirror finish using 1 μm Al2SiO5 suspensions, and then washed with deionized millipore water (18.2 MΩ·m), ultrasonically cleaned in ethanol and deionized water for 20 min, and dried with cool air prior to the experiments.
2.2 Solutions
All solutions were prepared using deionized millipore water (18.2 MΩ·m). Solutions contained 2×10-4 mol/L reagent-grade sodium sulfide (Na2S·9H2O, 98.0%) and 0.1 mol/L sodium chloride (analytical grade NaCl, 99.0%) to simulate the disposal repository underground environment. A solution with a pH of 9.0 was established with 0.2 mol/L borate buffer solution. To avoid contamination from atmospheric O2, all experiments were performed in an anoxic chamber in N2-purged solutions, and electrodes were cathodically cleaned at -1.3 V (vs SCE) for 60 s prior to the experiments.
2.3 Electrochemical cell and equipment
The electrochemical measurements were performed in a conventional three-electrode cell. A saturated calomel electrode (SCE) and Pt plate were employed as reference electrode (RE) and counter electrode (CE), respectively. The reference electrode was connected to the cell through an electrolyte bridge/Luggin capillary. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) with a frequency range from 100 kHz to 10 mHz and potentiodynamic polarization curves with a scanning rate of 0.1667 mV/s were obtained using a PARSTAT 2273 workstation. While investigating the influence of temperature, we used a water bath to stabilize the temperature of the electrochemical cell.
2.4 Morphology observation and composition analysis
The surface of the samples was observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Quanta 250) and the chemical composition of the surface films formed was investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) (ESCALAB 250xi, Thermo Fisher) on an instrument equipped with an Al Kα X-ray source (hv= 1486.6 eV) operated at 150 W. Because of the possible oxidation of the electrodes in air, they were sputter- coated with a 5 nm passive film using a 3 kV, 1 μA Ar+ ion beam. The charge shift of the spectra was corrected by assuming that the C 1s peak was at 284.8 eV; curve fitting was performed with commercial software XPS peak version 4.1 using Shirley background subtraction and a Gaussian–Lorentzian tail function.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
EIS is an efficient method to study surface conditions of metals, and is also a powerful tool for evaluating the protectiveness of a corrosion product layer formed on metals [12,13]. Figure 1 shows Nyquist and Bode plots recorded on oxygen-free copper in anoxic 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O and 0.1 mol/L NaCl solution after 2 h immersion at various temperatures. The spectra recorded in the two different frequency sweep directions (high-to-low and low-to-high) curves in the Nyquist and Bode plots are almost the same, which implies that steady state conditions were largely achieved. We can clearly see that the corrosion resistance did not decrease blindly with increasing temperature. There was a rise while the temperature reached 60 °C and the impedance of the sample at 60 °C was larger than that at either 50 °C or 70 °C, which simply indicates that the protectiveness of the corrosion products at this temperature was much better. There is an evidence that the sulfide film forms as two distinct layers: an inner layer (IL) that is thin and coherent and an outer layer (OL) that is composed of deposited products [8,11].

Fig. 1 Nyquist (a) and Bode (b) plots recorded for oxygen-free copper in anoxic 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O and 0.1 mol/L NaCl solution after 2 h immersion at various temperatures
The equivalent circuit used to fit the EIS experimental data is shown in Fig. 2, where Rs is the solution resistance, Col and Rol are the capacitance and resistance of the outer layer, respectively, Cdl is the double layer capacitance, Rct is the charge-transfer resistance for the formation of (CuSH)ads species at the interface between the matrix and the barrier layer, and ZW is an infinite Warburg impedance in the barrier layer which was defined by MACDONALD [14]:
ZW=δW(1-j)ω-0.5 (j2=-1) (1)
where ω is the angular frequency, and δw is the Warburg coefficient given for an ideal solution by the following equation:
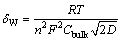 (2)
(2)
where n is the number of electrons involved, Cbulk and D are the bulk concentration and diffusion coefficient of the diffusing species, respectively, and R, T, and F have their usual meanings. The fitting results of the equivalent circuit are given in Table 1.
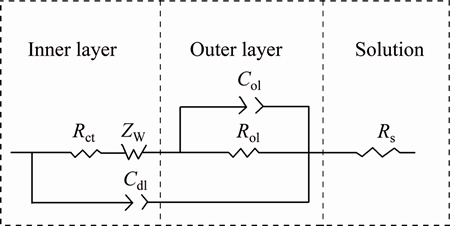
Fig. 2 Equivalent circuit used to fit EIS experimental data
The resistance of the solution (Rs) decreases at higher temperatures because the ionization of H2S (weak electrolyte) increases with increasing temperature, and the temperature can also accelerate the charge transfer, which is reflected in the reduction of the charge transfer resistance; however, this influence is gradually weakened, which is in agreement with the slope of the curve in Fig. 3 flattening off at higher temperatures. An interesting result is that the resistance of the outer layer (Rol), shown in Fig. 3, firstly decreases, before increasing and then finally decreases again; the Rol at 60 °C is especially large, which can be cautiously attributed to a change in the outer layer structure. Additionally, the ZW increases on the whole with increasing temperature, which means that to some extent, diffusion plays a less significant role at higher temperatures.
Table 1 Fitting results of equivalent circuit
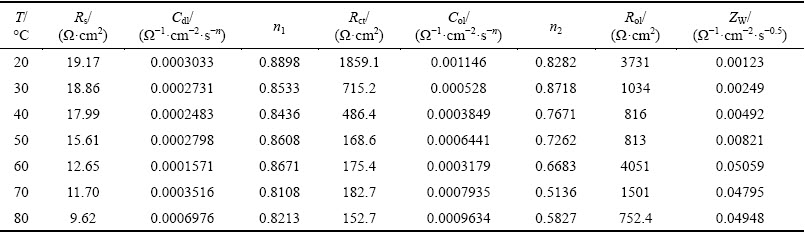
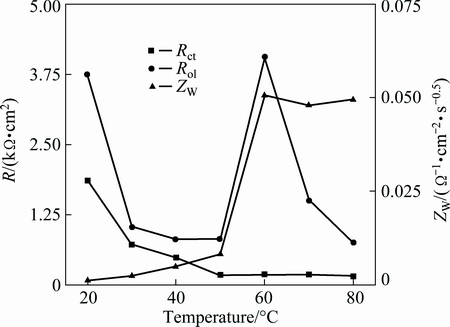
Fig. 3 Evolution of Rct, Rol, and ZW with increasing temperature
3.2 Morphology and composition analysis of passive film
We conducted the SEM analysis after the EIS measurements under open circuit potential. Figure 4 shows the surface morphologies of specimens at 20 , 40, 60, and 80 °C. The first step in the copper corrosion reaction in high-level nuclear waste environment is anion adsorption, which produces an adsorbed Cu(I) species:
Cu+SH-→Cu(SH)ads+e (3)
This is then followed by a slow subsequent reaction step and reaction (5) will be accelerated at higher temperatures owing to the fast diffusion of SH-.
Cu+Cu(SH)ads+SH-→Cu2S+H2S+e (4)
Cu2S+SH-+OH-→2CuS+H2O (5)
It can clearly be seen that the film initially becomes more porous with increasing temperature. However, at 60 °C, the deposits form a more compact structure, which could effectively protect the matrix from further corrosion. When the temperature rises up to 80 °C, and the corrosion products become loose and completely cover the substrate. This structure coincides with a variation in the behavior of Rol calculated from the EIS data.
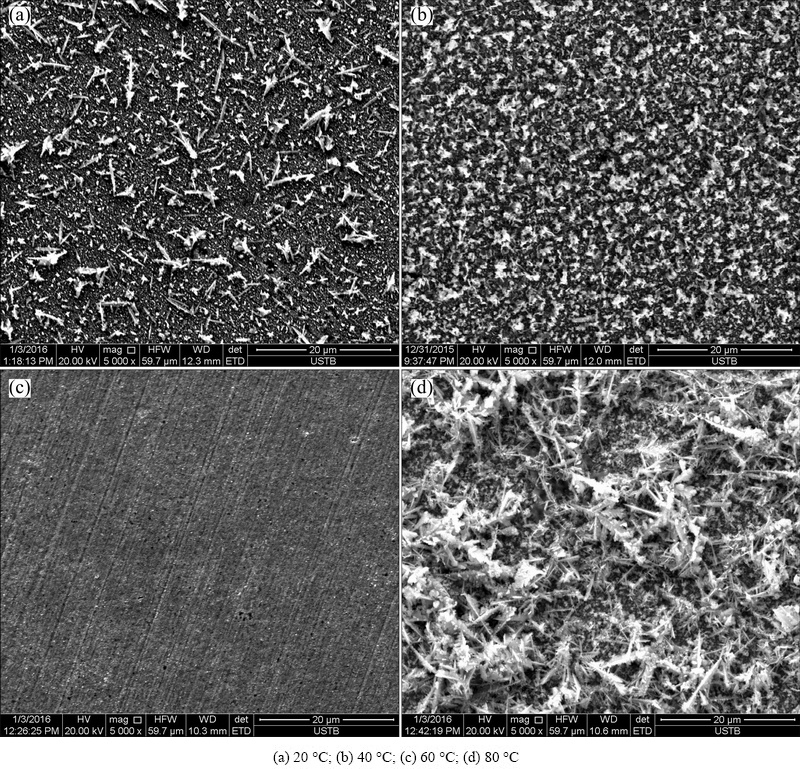
Fig. 4 Surface SEM morphologies after EIS measurements at different temperatures
With increasing temperature, the porosity of the copper surface firstly increased and then subsided again, which can be attributed to the nucleation and growth of fine particulates that were observed on the electrode surface after a relatively short period of corrosion. Further, the whole resistance was mainly governed by a combination of the outer layer porosity and the charge transfer speed; at low temperatures, the charge transfer resistance was as high as the outer layer resistance. Nevertheless, the resistance of the outer layer varied like a cosine curve with increasing temperature and the charge transfer resistance at higher temperatures only changed a little with respect to the change of outer layer resistance in Fig. 3. Therefore, the whole resistance of the corrosion products also varied like a cosine curve for changing temperatures.
The surfaces of copper sulfide passive films formed in a deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution at 20 °C and 80 °C, respectively, were examined using XPS. Figure 5 shows spectra of the sulfide films on copper. As can be seen, Cu, S, O, and C were detected on the surface of the passive films. The presence of carbon and oxygen is generally attributed to contamination, and air causes the formation of an oxide layer during the handling of the samples.

Fig. 5 XPS spectra of passive sulfide films on copper formed in deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O at 20 °C and 80 °C, respectively
A high-intensity peak at 932.3 eV for Cu 2p3/2 is close to the reported peak position of CuS (932.2 eV) [15] and Cu2S (952.3 eV) [16], which means that both compounds were likely present in the passive films in Fig. 6, but it was hard to obtain a clearer distinction. It was proposed that a clearer distinction between these two compounds could be obtained by analyzing a high resolution XPS spectrum of S 2p [17].
A high resolution XPS spectrum of S 2p is shown in Fig. 7. This spectrum showed more promising results in terms of the surface analysis of the passive film. The observed peak position in the spectrum is in good agreement with CuS and Cu2S positions (161.3 eV and 162.4 eV, respectively) [10,17,18]. Figure 8 shows the CuS and Cu2S contents of the corrosion products measured after being immersed for 2 h in a deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution at 20 °C and 80 °C, respectively; the CuS content increases at higher temperatures, which may be attributed to a faster diffusion of SH- while the temperature increases, which provides enough sulfide for the generation of CuS.

Fig. 6 High resolution XPS spectra of Cu 2p for passive sulfide film on copper formed in deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution at 20 °C and 80 °C, respectively
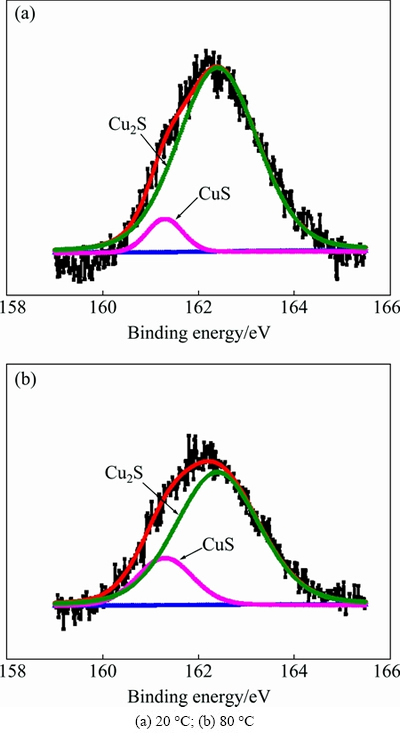
Fig. 7 High resolution XPS spectra of S 2p of passive sulfide film on copper formed in deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution
3.3 Cyclic polarization tests
To study the surface condition of the samples (susceptibility to pitting corrosion) and to obtain information about the temperature effect on the corrosion rate and corrosion potential, it was necessary to perform cyclic polarization tests. The results are shown in Fig. 9. The passive current of the backward scan was lower than that of the forward scan, which indicates that the structure of the passive film became more impact after anodic polarization. Additionally, there were several reduction current peaks from the backward scan; φ1 was attributed to the reduction reaction Cu2O→Cu; the formation of Cu2O can be attributed to the passive film breakdown and to the oxidation of the bare copper substrate by water at a relatively high potential. φ2 and φ3 are attributed to the reduction reactions CuS→Cu2S and Cu2S→Cu, respectively.
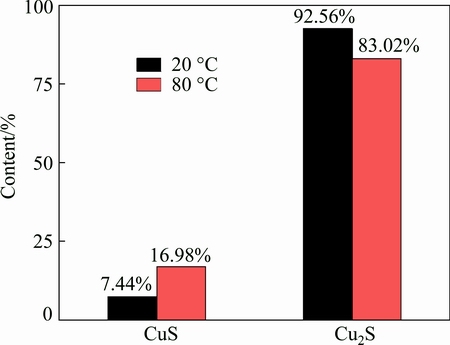
Fig. 8 CuS and Cu2S contents of corrosion products measured after being immersed for 2 h in deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution at 20 °C and 80 °C, respectively
The shape of the cyclic polarization curve indicates the pitting potential and the re-passivation or protection potential whether the sample is in a passive or active state. In a passive system, the potential at which the current sharply increases is defined as the passivation breakdown potential (φb) and where the loop is close on the reverse scan is the protection or re-passivation potential (φp) [19,20]. We can clearly see in Fig. 9 that φp is more negative than φb, which simply indicates that pitting could happen. Figure 10 shows that the φb decreases with increasing temperature with an almost linear relationship. However, the difference between φb and φp only varies a little around 30 mV (vs SCE) for all the tested temperatures. Further, we also discovered a typical pitting morphology after the cyclic polarization test at 60 °C, shown in Fig. 11. The diameter of the pits was about 80 μm; the appearance of pitting may threaten the safety of a copper canister to a very large degree in a high-level nuclear waste repository.

Fig. 9 Cyclic polarization test results of copper in deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution at different temperatures
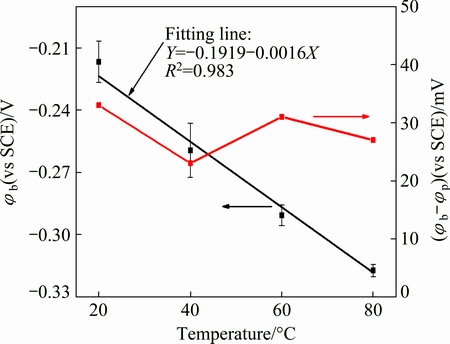
Fig. 10 Results of φb and (φb-φp) after cyclic polarization tests at different temperatures

Fig. 11 Typical pitting morphology of copper after cyclic polarization in deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution at 60 °C
3.4 Potentiostatic transients
As we can see from the polarization curves, the passivation potential range was from -0.85 to -0.35 V (vs SCE) for all temperatures; therefore, we applied -0.6 V (vs SCE) to form a steady passive film structure. Mott–Schottky analyses were performed to ascertain the electronic character of the passive film that formed on copper in a deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution as a function of temperature. The interfacial capacitance was measured at 1 kHz while sweeping the passivation potential at a sufficiently high sweep rate (25 mV/s), so that the crystallographic defect concentrations are “frozen-in” and only the electronic defects respond to changes in the applied potential. As we know, different types of defects can exist within the barrier layer, including cation vacancies, cation interstitials, and anion vacancies based on the type of semiconductor (according to the PDM) [21]. In agreement with Mott-Schottky theory, the space charge capacitance (CSC) of a semiconductor is expressed as
 , n-type (6)
, n-type (6)
 , p-type (7)
, p-type (7)
where ε is the dielectric constant of the passive film (assumed to be equal to 16, here), ε0 is the vacuum permittivity (8.854×10-14 F/cm), e is the electron charge (1.602×10-19 C), k is the Boltzmann constant (1.38×10-23 J/K), V is the applied potential, VFB is the flat band potential, T is temperature (K), NA is the acceptor density (cm-3), and ND is the donor density (cm-3). Therefore, the 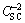 vs V plot should be linear with a negative slope for p-type semiconductors, while that for n-type semiconductors should be positive.
vs V plot should be linear with a negative slope for p-type semiconductors, while that for n-type semiconductors should be positive.
Figure 12 displays the Mott-Schottky plots for the passive sulfide film formed on copper potentiostatically in a deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution at -0.6 V (vs SCE) and different temperatures. It is obvious that there is a negative linear relationship between 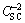 and V, which means that cation vacancies are the dominant defects in the passive film for all the experimental temperatures, and consequently that the passive film behaves like a p-type semiconductor. This is consistent with the results reported for copper sulfide thin films [22].
and V, which means that cation vacancies are the dominant defects in the passive film for all the experimental temperatures, and consequently that the passive film behaves like a p-type semiconductor. This is consistent with the results reported for copper sulfide thin films [22].
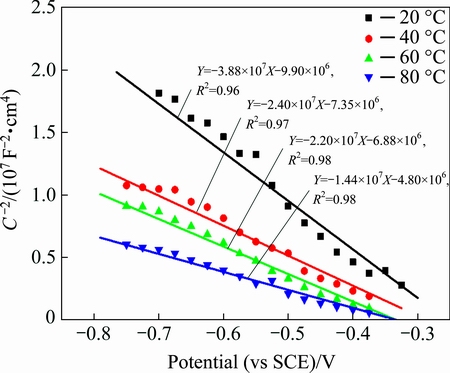
Fig. 12 Mott-Schottky plots for passive sulfide films formed on copper potentiostatically in deaerated 0.1 mol/L NaCl and 2×10-4 mol/L Na2S·9H2O solution at -0.6 V (vs SCE) for 2 h at different solution temperatures
The acceptor density can be calculated from the fitting Eq. (7). The results, as a function of temperature, are shown in Table 2. The order of magnitude of the acceptor density was around 1023 cm-3 for all experimental temperatures and increased at higher temperatures, which coincides with the variation of the passive breakdown potential in Fig. 10. Moreover, there is a high possibility of pitting occurring at higher temperatures, which threatens the security of a copper canister in high-level nuclear waste environments.
Table 2 Acceptor density (NA) of passive films formed at -0.6 V (vs SCE) and different temperatures

4 Conclusions
1) Temperature has a complicated effect on the response of the impedance of copper in a NaCl solution containing sulfide. As the immersion temperature increased, the total impedance originally decreased and then increased, and finally decreased again, which can be attributed to the nucleation and growth of deposits on the copper surface.
2) The XPS results showed that the passive films consisted of both Cu2S and CuS; and the content of CuS increased with increasing immersion temperature.
3) The cyclic polarization results indicated that the structure of the passive film became more impact after anodic polarization and the passivation breakdown potential decreased roughly linearly with increasing temperature. However, the difference between φb and φp showed little variation and was around 30 mV (vs SCE) for all the test temperatures.
4) The p-type semiconductor characteristics were obtained for the whole passivation range and the magnitude of the acceptor density was around 1023 cm-3 and increased with increasing temperature.
References
[1] KONG F. Predicting the lifetimes of nuclear waste containers [J]. The Journal of the Minerals Metals & Materials Society, 2014, 66(3): 526-537.
[2] HEDIN A. Semi-analytic stereological analysis of waste package/ fracture intersections in a granitic rock nuclear waste repository [J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2008, 40(6): 619-637.
[3] BIRCH K, BELADHELM B, FREIRE-CANOSA J, GARISTO F, GIERSZEWSKI P. Technical research and development program for long-term management of Canada’s used nuclear fuel—Annual report 2007 [R]. Canosa: Ontario Power Generation, 2007.
[4] IREN S A, ASKLING P, WANSTEDT S. Geologic site characterization for deep nuclear waste disposal in fractured rock based on 3D data visualization [J]. Engineering Geology, 1999, 52(S3-S4): s319-s346.
[5] HEDIN A, KAUTSKY U, MOREN L, SELROOS J, STROM P, PAPP T. SR 97: Post-closure safety for a KBS 3 deep repository for spent nuclear fuel—Overview [J]. Materials Research Society, 1999, 663(1): 739-746.
[6] PEDERSEN K. Microbial processes in radioactive waste disposal [J]. Cheminform, 2001, 32(7): 31-38.
[7] HODGKINSON D, BENABDERRAHMANE H, ELERT M, HAUTOJARVI A, SELROOS J O. An overview of Task 6 of the Aspo task force: Modelling groundwater and solute transport: Improved understanding of radionuclide transport in fractured rock [J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2009, 17(5):1035-1049.
[8] CHEN J, QIN Z, SHOESMITH D W. Kinetics of corrosion film growth on copper in neutral chloride solutions containing small concentrations of sulfide [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(10): C338-C345.
[9] CHEN J, QIN Z, SHOESMITH D W. Rate controlling reactions for copper corrosion in anaerobic aqueous sulphide solutions [J]. Corrosion Engineering Science & Technology, 2011, 46(2): 138-141.
[10] CHEN J, QIN Z, SHOESMITH D W. Long-term corrosion of copper in a dilute anaerobic sulfide solution [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(23):7854-7861.
[11] MARTINO T, PARTOVI R. Mechanisms of film growth on copper in aqueous solutions containing sulphide and chloride under voltammetric conditions [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 127(5): 439-447.
[12] WANG J, WANG Z Y, KE W. A study of the evolution of rust on weathering steel submitted to the Qinghai salt lake atmospheric corrosion [J]. Materials Chemistry & Physics, 2013, 139(1): 225-232.
[13] KATAYAMA H, KURODA S. Long-term atmospheric corrosion properties of thermally sprayed Zn, Al and Zn-Al coatings exposed in a coastal area [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 76(2): 35-41.
[14] MACDONALD J R. Impedance spectroscopy: Models, data fitting, and analysis [J]. Solid State Ionics, 2005, 176(25):1961-1969.
[15] ROMAND M, ROUBIN M, DELOUME J P. ESCA studies of some copper and silver selenides [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy & Related Phenomena, 1978, 13(3): 229-242.
[16] WAGNER C D. Chemical shifts of Auger lines, and the Auger parameter [J]. Faraday Discussions of the Chemical Society, 1975, 60(60): 291-300.
[17] KRYLOVA V, ANDRULEVIC M. Optical, XPS and XRD studies of semiconducting copper sulfide layers on a polyamide film [J]. International Journal of Photoenergy, 2009, 279(1): 53-58.
[18] PERRY D L, TAYLOR J A. X-ray photoelectron and Auger spectroscopic studies of Cu2S and CuS [J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1986, 5(4): 384-386.
[19] PEREZ N. Electrochemistry and corrosion science [M]. Dordrechers: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2005.
[20] REVIE R W, UHLIG H H. Corrosion and corrosion control: An introduction to corrosion science and engineering [M]. New Jersey: Wiley, 2008.
[21] MACDONALD D D. Passivity–the key to our metals-based civilization [J]. Pure & Applied Chemistry, 1999, 71(6): 951-978.
[22] GROZDANOV I, NAJDOSKI M. Optical and electrical properties of copper sulfide films of variable composition [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1995, 114(2): 469-475.
孔德成,董超芳,肖 葵,李晓刚
北京科技大学 腐蚀防护中心教育部重点实验室,北京 100083
摘 要:系统研究在高放核废料存储环境下温度对纯铜腐蚀的影响。采用交流阻抗谱、Mott-Schottky技术、动电位以及恒电位极化曲线分析纯铜在不同温度下的腐蚀行为;并采用体视显微镜以及扫描电镜观察样品表面形貌,同时结合X射线光电子能谱分析钝化膜成分。结果表明,钝化膜阻抗并不随着温度的升高而一直降低,在60 °C由于致密的外层结构阻抗反常增大;点蚀在此环境下可能发生且钝化膜的点蚀电位随着温度的升高而降低;钝化膜主要成分为Cu2S,而CuS的含量随着温度的升高而增加;钝化膜主要呈p型半导体特性,阳离子空位密度在1023 cm-3数量级且随着温度的升高其密度增大。
关键词:铜腐蚀;硫化物;核废料处置;温度;电化学性能
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (FRF-TP-14-011C1) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China; Project (2014CB643300) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Chao-fang DONG; Tel: +86-10-62333931-518; Fax: +86-10-62334005; E-mail: cfdong@ustb.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60165-1

