
Nanometer bismuth oxide produced by resistance heating vapor oxidation
HU Han-xiang(胡汉祥)1,2, QIU Ke-qiang(丘克强)1
1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Building Materials College, Hengyang 421008, China
Received 18 January 2006; accepted 25 April 2006
Abstract: Bismuth oxide has wide applications in superconductive material, photoelectric material, electronic ceramic, electrolyte, and catalysts. To produce ultrafine bismuth oxide powders, some costly heating sources, such as plasma, high frequency induction, electron beam or laser, have to be used in the conventional vapor oxidation methods. The vapor oxidation method was improved by adding a reducing agent in the reaction system, where heating source was resistance tubular oven, instead of special heat source requirement. Nanometer bismuth oxide was prepared at 1 000-1 140 ℃, and the particle characteristics were investigated by XRD, SEM, DTA, laser sedimentograph. With low oxygen concentration (less than 20%) in the carrier gas, the bismuth oxide particle was near-sphere β-Bi2O3 with uniform and fine particle size (d0.5=65 nm, GSD=1.42); while with higher oxygen content (more than 50%), the powders were mixture of Bi2O2CO3 and β-Bi2O3.
Key words: bismuth oxide; nanometer particles; resistance heating; carbon; reducing-evaporation
1 Introduction
Bismuth oxide has been widely used in high- temperature superconductors, photoelectric materials, electronic ceramic powders and catalysts and so on[1-3]. When bismuth oxide in nanometer replaces that in micron dimension for piezoelectric materials, the homogeneity and performance of devices can be improved and the additive dosage can be reduced[4]. Until now, vapor oxidation methods for nanometer bismuth oxide include plasma method, melting spraying oxidation method, and chemical vapor coacervation[5]. Among these, the first method has shortened process, but special apparatus requires high cost; the second method also has short process, but bismuth can not be completely oxidized, the nozzle life is limited, and the particles formed have large size and inhomogeneous distribution; for the last method, high quality equipment is necessary, which restricts its development in industry.
During the preparation of powders by vapor oxidation, metals are often evaporated by heating, and metal vapor is oxidized to powder oxide. However, when the metal vapor is oxidized, so is melting surface. Then oxide layer will overlay the melting surface to prevent metals from further evaporation and destroy the continuous formation of oxide powders. When the heating temperature is close or beyond the metal boiling point, huge vapor pressure will be generated on the metal melting surface, and the superficial oxide layer will be broken to form continuous evaporation[6]. For bismuth with high boiling point of 1 470 ℃, heating over its boiling temperature has to rely on special heating apparatus, such as plasma generator, high frequency induction heating equipment, and this inevitably results in high cost. In this study, carbon was chosen as reducing agent to destroy the oxide layer on melting surface, so that the ordinary heating, resistance heating can be applied for continuous preparation of bismuth oxide powders.
2 Experimental
The apparatus for bismuth oxide preparation was described in Ref.[7]. After preheating, the crushed refine bismuth and carbon were put together in a reactor and placed in the reaction tube. Then the vacuum pump was turned on to adjust carrier gas flow. After reaction completion, powders were collected for property testing.
Particle patterns were observed by FEI Sirion200 field emission scanning electron microscope (accele- ration voltage 5 kV). Bismuth oxide powders were adhered on conducting adhesive tape, and platinum of about 10 nm thickness was sprayed on the powder surface to make them conductive. Powder structure was measured by Rigaku D/Max 2500 X-ray diffractometer (Cu Kα (λ=1.540 64 nm), 40 kV, 300 mA). Particle distribution was tested by Mastersizer 2000 laser sedimentograph of Malvern Instrument Ltd. Before testing, samples were dispersed by water and the testing range was 0.02-2 000 μm. Thermal behavior of samples was measured by differential thermal analyse(DTA) in air. The heating rate was 10 ℃/min with α-Al2O3 as reference sample.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Theory on bismuth and oxygen reaction
Two reactions exist in the bismuth oxide preparation, namely 1) 4Bi(g)+3O2(g)=2Bi2O3(s); 2) 4Bi(l)+3O2(g)= 2Bi2O3(s). The saturation vapor pressure of bismuth is pBi/Pa=1.013×105exp(12.398-22 570/T)[8]. According to the equation  and corresponding thermodynamic data[9], the minimum oxygen partial pressure for reactions 1 and 2 at 1 100 ℃ can be calculated as 2.106×10-56 Pa and 6.124×10-269 Pa, respectively. It can be seen that the reaction conditions are easy to be satisfied, so both reactions 1 and 2 can occur easily. When using such reactions to prepare bismuth oxide powders, reaction 1 should be kept continuously, and then the bismuth oxide formed will enter the lower part of reaction system along with air flow. However, due to the existence of reaction 2, the bismuth oxide solid will float on the bismuth melting surface and the evaporation of bismuth will be obstructed.
and corresponding thermodynamic data[9], the minimum oxygen partial pressure for reactions 1 and 2 at 1 100 ℃ can be calculated as 2.106×10-56 Pa and 6.124×10-269 Pa, respectively. It can be seen that the reaction conditions are easy to be satisfied, so both reactions 1 and 2 can occur easily. When using such reactions to prepare bismuth oxide powders, reaction 1 should be kept continuously, and then the bismuth oxide formed will enter the lower part of reaction system along with air flow. However, due to the existence of reaction 2, the bismuth oxide solid will float on the bismuth melting surface and the evaporation of bismuth will be obstructed.
3.2 Influence of reducing agent on vaporizing rate of bismuth
The vaporized mass as a function of vaporizing time is described in Fig.1. The sample weighs 5 g, vaporizing at 1 140 ℃ with air inflow of 120 L/h.
It can be seen that without carbon, the vaporized mass is less than zero, and the negative value is slightly increased with increasing time. At the inlet of air, oxygen will immediately react with bismuth on the melting surface, and bismuth oxide will be generated. The density of bismuth oxide is lower than that of bismuth. Therefore, bismuth oxide will float on the bismuth melting to form a dense layer of bismuth oxide film. The film is difficult to be vaporized, and its existence on surface will hinder the further evaporation of bismuth and oxidation of bismuth in deep melting. The direct oxidation of bismuth will result in the increment of residue in the reactor, so that with time increasing, the apparent vaporized mass decreases a little. When the carbon is added, it will react with bismuth oxide on the surface and then bismuth is generated. With the new formation of bismuth on the surface, enough bismuth can be supplied for its continuous evaporation and the vaporized mass will increase with increasing time.
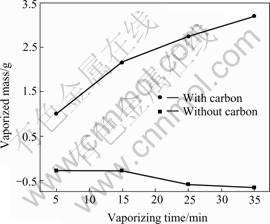
Fig.1 Influence of carbon on vaporizing rate of bismuth
3.3 Influence of carbon on sample property
3.3.1 Composition
The vapor oxidation method for bismuth oxide preparation includes the processes of bismuth evaporation, chemical reaction to form bismuth oxide, and its nucleation, condensation, collision and growth. To determine the influence of carbon on the sample composition, powders prepared under different reaction conditions were analyzed by XRD.
From Table 1, it can be seen that when air is used as carrier gas, the variation of reaction temperature (No.1, 2, 3 in Table 1) or carrier gas flow (No.4, 5, 6, 7 in Table 1) will result in the same XRD pattern (Fig.2). Compared with standard PDF card No.27-0050, it is determined that the diffraction peaks all belong to the tetragonal structure β-Bi2O3. However, when the oxygen concentration in carrier gas is increased, other phases will be formed (No.8, 9, 10 in Table 1). Fig.3 shows the coexistence of β-Bi2O3 and Bi2O2CO3, which suggests that carbon will be involved in the reaction process if the oxygen content is high in the system.
3.3.2 Morphology
The morphology of samples listed in Table 1 were observed by SEM. It can be seen that with air as carrier gas (oxygen about 20%), no matter the changes of temperature and flow, all sample particles are near sphere shape but of different particle sizes. Fig.4 shows the SEM image of sample No.3. When the oxygen concentration is increased, the particle tends to be mixture of near spherical and dendritic shapes within
Table 1 Chemical composition of sample under different conditions
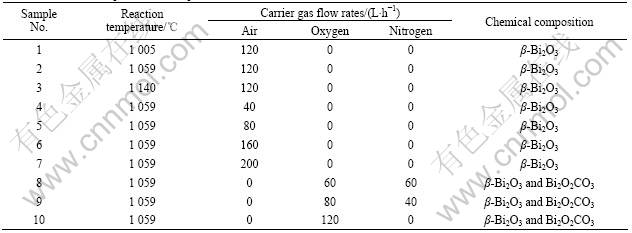
Fig.2 XRD pattern of sample No.3 in Table 1
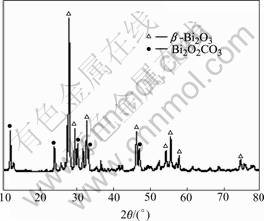
Fig.3 XRD pattern of sample No.9 in Table 1
nanometer size. The SEM image of sample No.9 is shown in Fig.5, where the dendritic particle should be Bi2O2CO3 as determined by its XRD pattern in Fig.3.
3.3.3 Thermal behavior
Thermal behaviors of samples No.3 and No.9 were examined by DTA. As described in Fig.6, two samples exhibit similar peaks at 300-450 ℃ and 750 ℃. The first peak is caused by the transformation of granular β-Bi2O3
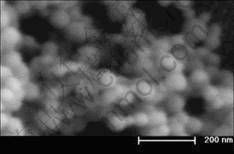
Fig.4 SEM image of sample No.3 in Table 1
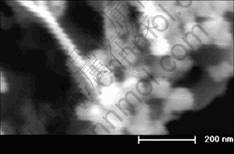
Fig.5 SEM image of sample No.9 in Table 1
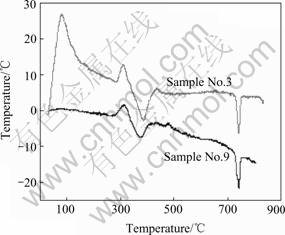
Fig.6 DTA curves of products
to α-Bi2O3, and the second one is due to α-Bi2O3 trans- forming to δ-Bi2O3[10]. There is also a different peak between two samples at about 100 ℃, which results from the exothermic decomposition of Bi2O2CO3 as determined by XRD and SEM analysis.
3.3.4 Particle distribution
The particle distribution of sample No.3 is described in Fig.7. It can be seen that the average particle size d0.5 is 63 nm with standard deviation (GSD) of 1.42. Such result means that the obtained particles of bismuth oxide have homogenous size distribution within nanometer.
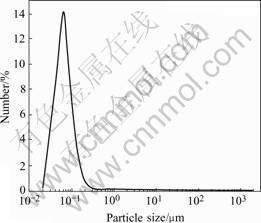
Fig.7 Particle distribution of sample No.3 in Table 1
4 Conclusions
1) During the bismuth evaporation and vapor oxidation, the bismuth oxide formed on the bismuth melting surface obstructs both the further evaporation of bismuth and vapor oxidation. With the addition of carbon, the oxide film on the bismuth melting surface will be destroyed, which can accelerate the evaporation of bismuth. Thus the ordinary heating method, resistance heating can be applied to vaporize bismuth and bismuth oxide powders can be continuously prepared.
2) Resistance heating for bismuth vapor oxidation requires less for apparatus, which results in lower cost, shorter process, no environmental pollution and clean production surface.
3) When the carrier gas contains lower oxygen (air), the bismuth oxide prepared is pure spherical β-Bi2O3 and the particle distribution is homogeneous with d0.5=65 nm and GSD=1.42; when the oxygen concentration is high (beyond 50%), the obtained powder is a mixture of Bi2O2CO3 and β-Bi2O3. The DTA result shows that Bi2O2CO3 will be decomposed above 100 ℃.
References
[1] TAKEYAMA T, TAKAHASHI N, NAKAMURA T, ITOH S. Bi2O3 rods deposited under atmospheric pressure by means of halide CVD on c-sapphire [J]. Solid State Communications, 2005, 133: 771-774.
[2] JIANG N X, WACHSMAN E D, JUNG S H. A higher conductivity Bi2O3-based electrolyte [J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 150: 347- 353.
[3] ZENG Y, LIN Y S. Catalytic properties of yttria doped bismuth oxide ceramics for oxidative coupling of methane [J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 1997, 159: 101-117.
[4] YANG Bang-chao, JING Lu-wei. Study on preparation of nanometer Bi2O3 and its effect on the properties of ZnO varistor [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2003, 31(12): 1184-1187.(in Chinese)
[5] LI Wei. Preparation technology of nanometer bismuth oxide [P]. Chinese Patent: 200310110558.7, 2003-11-25.(in Chinese)
[6] CHEN Yi-feng, PENG Chang-hong, YANG Sheng-hai, TANG Mo-tang. Kinetics of oxidizing zinc vapor at elevated temperature [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(1): 133-140.(in Chinese)
[7] HU Han-xiang, QIU Ke-qiang, XU Guo-fu. Preparation of nanometer δ- andβ-bismuth trioxide by vacuum vapor-phase oxidation [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2006, 16: 173-177.
[8] WEGNER K, WALKER B, TSANTILIS S, PRATSINIS S E. Design of metal nanoparticle synthesis by vapor flow condensation [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2002, 57: 1753-1762.
[9] LIANG Ying-jiao, CHE Yin-chang, LIU Xiao-xia. Handbook of Inorganic Thermodynamic Data [M]. Shenyang: Northeastern University Press, 1993.(in Chinese)
[10] SAMMES N M, TOMPSETT G A, N?FE H, ALDINGER F. Bismuth based oxide electrolytes-structure and ionic conductivity [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1999, 19: 1801-1826.
(Edited by PENG Chao-qun)
Corresponding author: HU Han-xiang; Tel: +86-734-8432456; E-mail: hanxianghu_63@hotmail.com