MnS深度除去镍电解液中的铜
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第11期
论文作者:李江涛 陈爱良
文章页码:3802 - 3807
关键词:硫化锰;除铜剂;除铜;除锰;镍电解阳极液
Key words:MnS; decoppering reagent; copper removal; manganese removal; nickel anodic electrolyte
摘 要:由于镍电解液中铜浓度低(0.53 g/L)、镍浓度高(75 g/L),因此,很难从镍电解液中分离除去铜。采用硫化锰(MnS)除去镍电解液中的铜。结果表明:在MnS用量为理论量Dt,MnS(Dt,MnS=0.74 g)的1.4倍、pH值为4~5、温度高于60 °C时反应至少60 min后,电解液中铜浓度ρ(Cu)从530 mg/L降低至3 mg/L,渣中铜、镍质量比RCu/Ni达到15以上。采用氧化法可将新产生的除铜后液中锰浓度ρ(Mn)降低至3 mg/L。除铜后液中铜、锰浓度,渣中铜、镍质量比均能满足生产要求。因此,硫化锰是一种高效除铜剂。
Abstract: Copper is difficult to separate from nickel electrolyte due to low concentration of copper (0.53 g/L) with high concentration of nickel (75 g/L). Manganese sulfide (MnS) was used to deeply remove copper from the electrolyte. Experimental results show that the concentration of copper (ρ(Cu)) decreases from 530 to 3 mg/L and the mass ratio of copper to nickel (RCu/Ni) in the residue reaches above 15 when the MnS dosage is 1.4 times the theoretical valueDt,MnS (Dt,MnS=0.74 g) and the pH value of electrolyte is 4-5 with reaction time more than 60 min at temperatures above 60 °C. The concentration of newly generated Mn2+(ρ(Mn)) in the solution is also reduced to 3 mg/L by the oxidation reaction. The values ofρ(Cu), ρ(Mn)and RCu/Ni meet the requirements of copper removal from the electrolyte. It is shown that MnS can be considered a highly effectivedecoppering reagent.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 3802-3807
Jiang-tao LI, Ai-liang CHEN
School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 22 September 2014; accepted 8 September 2015
Abstract: Copper is difficult to separate from nickel electrolyte due to low concentration of copper (0.53 g/L) with high concentration of nickel (75 g/L). Manganese sulfide (MnS) was used to deeply remove copper from the electrolyte. Experimental results show that the concentration of copper (ρ(Cu)) decreases from 530 to 3 mg/L and the mass ratio of copper to nickel (RCu/Ni) in the residue reaches above 15 when the MnS dosage is 1.4 times the theoretical value Dt,MnS (Dt,MnS=0.74 g) and the pH value of electrolyte is 4-5 with reaction time more than 60 min at temperatures above 60 °C. The concentration of newly generated Mn2+(ρ(Mn)) in the solution is also reduced to 3 mg/L by the oxidation reaction. The values of ρ(Cu), ρ(Mn) and RCu/Ni meet the requirements of copper removal from the electrolyte. It is shown that MnS can be considered a highly effective decoppering reagent.
Key words: MnS; decoppering reagent; copper removal; manganese removal; nickel anodic electrolyte
1 Introduction
Nickel, a strategic metal, has been widely used in the electroplating industry and steel production [1]. In the process of producing nickel, even a small amount of other heavy metals can significantly affect nickel application. This demands that the contents of heavy metals (e.g., Cu) with electric potential lower than that of nickel in the nickel electrolytic solution have to be strictly controlled [2]. Moreover, copper is difficult to separate from the nickel solution due to similar chemical properties of copper and nickel [3,4]. To obtain high purity nickel, the residual copper concentration in the nickel electrolyte (containing 0.4-1.2 g/L Cu) should be less than 3 mg/L [5]. In addition, complete copper separation from nickel solution requires that the mass ratio of copper to nickel in the residue (RCu/Ni) should be larger than 15. In this case, the residue can be sent for copper smelting, and copper can be returned to the copper metallurgy system [5]. However, most available technologies produce residues with RCu/Ni between 1:2 and 2:1, making copper and nickel difficult to be recovered.
To meet the above-mentioned requirements, much work has been done by taking advantages of the chemical differences of copper and nickel in the solution. There are many methods for copper removal, such as hydrogen peroxide precipitation, ion exchange and solvent extraction, replacement and electrochemical deposition [6-9]. Nevertheless, these methods are not suitable for copper removal from the nickel electrolysis anode solution due to high cost [10-12]. Sulfidation seems to be a sound method because of stronger affinity of sulfur with copper compared with nickel. Copper will preferentially precipitate in the form of CuS or Cu2S by the addition of sulfide additives to the solution, resulting in the rapid separation of copper from nickel electrolysis anode solution. Several decoppering sulfide reagents, such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S), sodium sulfide (Na2S), active sulfur powder (S), active nickel sulfide (NiS) and nickel thiosulfate (NiS2O3), have been used for removing copper [13-18]. Although these reagents are effective for copper removal, they are not appropriate for industrial production due to some obvious disadvantages. For instance, H2S reacts with nickel easily due to high concentration of nickel (≥70 g/L Ni) in the solution, forming a residue containing large amounts of nickel (the mass ratio of nickel to copper arrives up to 5:1). Na2S will bring some Na+ ions into the solution. Na+ ions at high levels increase the solution viscosity and resistance, thus hindering the diffusion of nickel ions to the septum bag [5]. NiS2O3 is another decoppering reagent adopted to remove copper from the nickel electrolysis anode solution [13]. NiS2O3 is effective for decoppering, but is not stable due to its rapid decomposition in aqueous solution. In addition, the preparation process of NiS2O3 is complex. Like NiS2O3, active sulfur powder has not been used in industrial production due to the complex preparation process. For active nickel sulfide, it is usually prepared by the reaction of NiSO4 and Na2S. The prepared active nickel sulfide is easily oxidized to NiOHS and loses reactivity in a short period of time (6 h). Moreover, the slurry containing active nickel sulfide and Na+ ions formed during the preparation process is difficult to be filtered and has to be added into nickel electrolysis anode solution for copper removal, which leads to the accumulation of Na+ ions in the solution [4,17,18]. It is evident that these decoppering sulfide reagents have not strong decoppering capability to separate copper from nickel electrolysis anode solution. It is necessary to develop a new effective decoppering reagent without affecting the production of nickel from the solution. Considering the requirements in nickel production, MnS may be a good choice for copper removal from nickel electrolysis anode solution since the solubility product of pink MnS (Ksp=2.5×10-10) is higher than that of α-NiS (Ksp=3.2×10-19). This indicates that MnS has a higher reactivity with Cu2+ ions than NiS. Previous studies also indicated that Mn2+ ions (≤20 g/L) do not affect the quality of the electrolytic nickel [14].
Based on the above analysis, a novel reagent, manganese sulfide (MnS), was used in this work to remove copper from nickel electrolysis anode solution by considering selective reactions between Cu2+ or Ni2+ and S2- ions. The effects of MnS dosage, pH value, reaction temperature and reaction time on the concentration of copper (ρ(Cu)) and RCu/Ni were investigated. Also, due to the decomposition of MnS, the newly generated Mn2+ ions should be removed. This was achieved by adding oxidizing agent, like KMnO4, into the solution.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
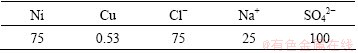
Nickel electrolysis anode solution was provided by Jinchuan Group Ltd., China. Its chemical composition is listed in Table 1. The solution has a high concentration of nickel and a low concentration of copper (75 g/L Ni and 0.53 g/L Cu at pH = 4.0).
Analytical grade reagents, including MnSO4, Na2S, HCl and NaOH, were used for experiments.
Table 1 Chemical composition of nickel electrolysis anode solution (g/L)
2.2 Equipment and procedure
Figure 1 presents the experimental apparatus for copper removal. Figure 2 illustrates the experimental process which includes three steps: preparation of MnS, copper removal and removing manganese brought by manganese sulfide.
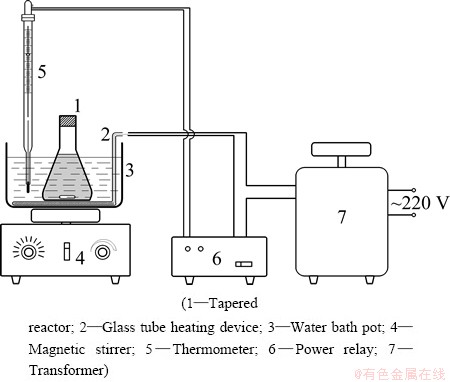
Fig. 1 Experimental apparatus for copper removal
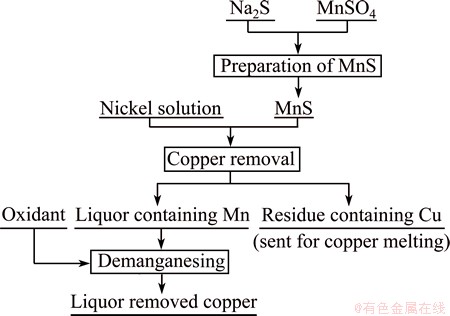
Fig. 2 Flow sheet for removing copper from nickel electrolysis anode solution using MnS
Preparation of manganese sulfide: 1 mol/L Na2S solution was added into a glass beaker with 1 mol/L MnSO4 solution. The mixture was stirred at 150 r/min and room temperature for 10 min and then filtrated for separating solid phase from liquid phase. The obtained solid was identified as MnS, which was used as the decoppering reagent.
Copper removal: 200 mL nickel electrolysis solution was transferred to a 500 mL flask which was kept in a water-bath heating device. MnS was added into the nickel electrolysis solution at temperatures between 40 and 80 °C and then the slurry formed. After stirring (250 r/min) for a certain period of time, the slurry was cooled and filtered. The solution was then sent to remove Mn.
Demanganesing: Potassium permanganate was added to the decoppered solution for demanganesing (0.42 g/L Mn) at room temperature with magnetic stirring at 250 r/min for 30 min.
The residual concentrations of copper (ρ(Cu)) and manganese (ρ(Mn)) in the filtered solution were measured by atomic absorption spectroscopy (3510 model, Shanghai Morning Field Equipment Co., Ltd., China). The residues were generally washed 3-4 times using water for further analysis. Mass concentrations of copper, manganese and nickel were analyzed using complexometric titration. The mass ratio of copper to nickel (RCu/Ni) or that of nickel to manganese (RNi/Mn) in the residues was determined by the following formula:
RM1/M2=w(M1)/w(M2) (1)
where RM1/M2 denotes the mass ratio of M1 to M2; M1 and M2 represent Cu, Ni and Mn, respectively; w(M1) and w(M2) are the mass fractions of Cu, Ni and Mn, respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Copper removal
3.1.1 Effect of MnS dosage on copper removal
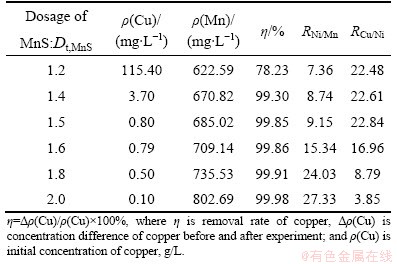
Table 2 illustrates the effect of MnS dosage on copper removal under given conditions (temperature 60 °C; reaction time 90 min; pH 4.5). It is shown that the residual copper concentration in the electrolytic solution decreases from 115.40 to 0.10 mg/L as the dosage of MnS increases from 1.2 to 2.0 times the theoretical value Dt,MnS (Dt,MnS = 0.74 g). The copper removal rate also increases from 78.23% to 99.98%. This can be explained by the fact that the solubility product of CuS (Ksp=6.3×10-36) is much less than that of MnS (pink) (Ksp=2.5×10-10). Cu2+ ions selectively react with S2- ions from MnS, producing CuS precipitate, as indicated by Reaction (2).
Cu2++MnS=CuS↓+Mn2+ (2)
Copper has a stronger selectivity to S2- than nickel and a large amount of copper may precipitate in the residue. The mass ratio of copper to nickel (RCu/Ni) in the residue remains approximately 22 when the dosage of decoppering reagent MnS increases from 1.2Dt,MnS to 1.5Dt,MnS. It then tends to decrease with increasing dosage of MnS. For example, the value of RCu/Ni decreases to 16.96 and 3.85 when the dosage of decoppering agent MnS increases to 1.6Dt,MnS and 2.0Dt,MnS. The corresponding content of Cu in the residue decreases from 62.47% to 52.09% and that of Ni increases from 3.68% to 13.53%, while that of Mn is below 0.5%. The mass ratio of nickel to manganese (RNi/Mn) in the residue and the concentration of manganese in the solution keeps increasing as the MnS dosage increases. For instance, the value of RNi/Mn increases from 7.36 to 27.33 and the concentration of manganese increases from 622.59 to 802.69 mg/L when MnS dosage changes from 1.2Dt,MnS to 2.0Dt,MnS. This is because the solubility product of α-NiS (Ksp=3.2×10-19) is smaller than that of MnS. When there is insufficient copper in the solution, the superfluous sulfur will react with nickel in the solution, leading to NiS precipitate. The reaction can be expressed by Reaction (3).
Ni2++MnS=NiS↓+Mn2+ (3)
As indicated by Reaction (3), nickel will present in the residue and the concentration of manganese in the solution will increase after the reaction. It is evident that MnS dosage should be optimized. The experimental results show that the optimal MnS dosage is (1.4-1.6)Dt,MnS.
Table 2 Effect of MnS dosage on copper removal
3.1.2 Effect of pH value
Based on the above results, the effect of pH on copper removal is presented in Fig. 3. There is a high residual copper concentration in the electrolyte at low pH values after removing copper. This is because S2- ions can react with H+ and produce HS- and H2S at high acidity, as shown by Reactions (4) and (5).
S2-+H+=HS- (4)
HS-+H+=H2S (5)
H2S is released from the solution, which leads to a higher residual copper concentration and a lower ratio of copper to nickel in the residue. Additionally, HS- can combine easily with Cu2+ ions to form coordination complexes Cu(HS)+ ions under low pH values, preventing CuS precipitation [15,16]. At pH 4, the mass ratio of copper to nickel in the residue reaches the maximum. This suggests that the reaction between free S2- and Cu2+ ions in the solution is completed and there are insufficient free S2- ions which can react with Ni2+ ions. With the increase of pH value (pH≥4), a gradual decrease in residual copper concentration in the electrolyte is observed. The copper concentration is lower than 3 mg/L that meets production requirements. The concentration of Mn in the solution decreases with increasing pH value. This indicates that the more manganese precipitation forms at a higher pH value, the less manganese goes to the solution.
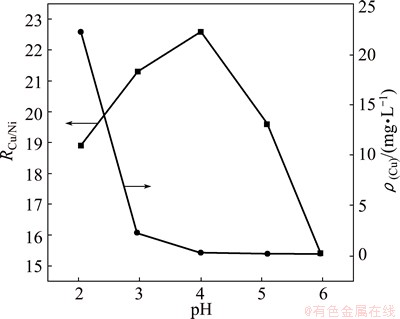
Fig. 3 Effect of pH on copper removal at MnS dosage of 1.4 Dt,MnS, reaction time of 60 min and 60 °C
3.1.3 Effect of reaction temperature
Figure 4 shows the effect of reaction temperature on residual copper concentration (ρ(Cu)) and on the mass ratio of copper to nickel (RCu/Ni) in the residue. ρ(Cu) decreases with increasing reaction temperature while the variation of RCu/Ni shows an opposite tendency. This indicates that Cu2+ ions easily react with S2- at high temperatures. For example, ρ(Cu) in the electrolyte decreases from 61.83 mg/L at 40 °C to 2.43 mg/L at 60 °C. It subsequently keeps ~1 mg/L when temperature is higher than 60 °C. In contrast, RCu/Ni increases from 10.68 at 40 °C to 22.61 at 60 °C and to 31.02 at 80 °C. Inspection of the data suggests that ρ(Cu) and RCu/Ni at 60 °C meet production requirements. Thus, one may expect that the optimum temperature for copper removal is 60 °C.
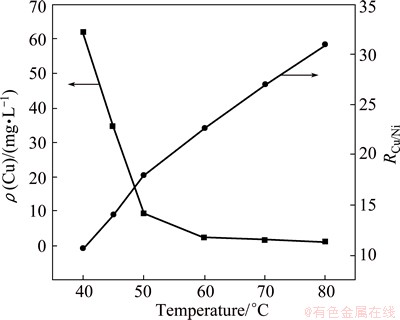
Fig. 4 Effect of temperature on copper removal at MnS dosage of 1.4Dt,MnS and pH 4.5
3.1.4 Effect of reaction time on copper removal
Figure 5 shows the effect of reaction time on the residual copper concentration. ρ(Cu) decreases substantially in the reaction time period up to 20 min. It then decreases slowly with increasing reaction time. This is due to the reaction between S2- and Cu2+. The formation of CuS precipitate leads to a sharp decrease in copper concentration. With the extension of reaction time, the copper concentration decreases. The copper reaction rate and copper concentration decrease slowly if the reaction time is further extended. It thus becomes far more difficult for S2- ions to react with Cu2+ ions. ρ(Cu) is as low as 1.6 mg/L at 60 min, so optimum reaction time appears to be approximately 60 min.
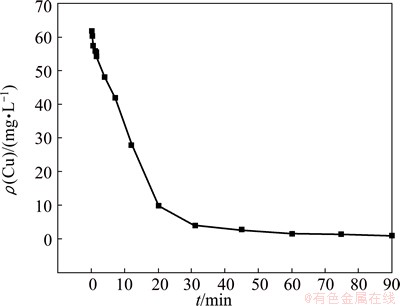
Fig. 5 Effect of reaction time on residual copper concentration at MnS dosage of 1.4Dt,MnS, pH 4.5 and 60 °C
3.2 Manganese removal
During the process of copper removal by using MnS, 0.30-0.48 g/L Mn2+ ions enter into the electrolyte solution. Although previous studies indicated that Mn2+ ions (≤20.0 g/L) do not affect the quality of the electrolytic nickel [14], it is necessary to remove manganese to avoid the enrichment of Mn in the nickel solution. It has shown that Mn2+ ions can be oxidized to MnO2 by many oxidants, such as potassium permanganate, perchloric acid, chlorine, ozone and oxygen [19,20]. Due to its low cost, potassium permanganate (KMnO4) was used in this study for demanganesing. The effect of KMnO4 dosage concentration on manganese removal was discussed as follows. Under optimal conditions, the cost of MnSO4 (57%), KMnO4 (93%), Na2S (57%) and electricity are $49.66, $121.54, $55.45 and $3.38 per ton nickel, respectively. The total cost (per ton nickel) of the copper removal is $230.2/t, which saves at least $148.98/t compared with the existing method of nickel concentrate and active sulfur [16].
3.2.1 Effect of KMnO4 dosage on manganese removal
Figure 6 shows the effect of KMnO4 dosage on demanganesing under the conditions of 0.42 g/L Mn2+, 0.1 mol/L KMnO4 and pH 5.0. It is found that the demanganesing rate increases and the residual manganese concentration decreases by adding KMnO4 to the solution after copper removal. The mass ratio of manganese to nickel in the residue also decreases, suggesting that nickel was oxidized and precipitated. For example, the residual manganese concentration and the mass ratio of manganese to nickel are respectively 52.24 mg/L and 23.1 at KMnO4 dosage of 0.9 times the theoretical value Dt,KMnO4 (Dt,KMnO4=0.81 g KMnO4). The contents of Mn and Ni in the residue are 60.65% and 2.60%, respectively. The residual manganese concentration and the mass ratio of manganese to nickel, respectively decrease to 1.24 mg/L and 2.47 when the dosage increases to 1.3Dt,KMnO4. This is due to the reaction between MnO4- and Mn2+ ions, as indicated by Reaction (6).
2MnO4-+3Mn2++2H2O=5MnO2↓+4H+ (6)
The reaction happens spontaneously as the standard Gibbs free energy of Reaction (6) is -273.47 kJ/mol at 25 °C. Mn2+ ions are oxidized by MnO4-, which leads to MnO2 precipitate. Hence, Mn2+ ions can be easily removed from the solution. The change of the solution oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) increases with increasing the KMnO4 dosage. However, the ORP decreases rapidly from 1126 to 1086 mV and then increases. The changing point is called point mutation, which indicates that Mn2+ ions are completely consumed. Similarly, potassium permanganate is capable of oxidizing nickel in the solution, as shown by the following equation [16,19,20]:
2MnO4-+6Ni2++5H2O=2MnO2↓+3Ni2O3↓+10H+ (7)
According to Reaction (7), Ni may lose in the demanganesing process. However, the experimental result shows that only 0.1-0.5 g/L Ni (0.13%-0.67% Ni) precipitates during the process, which indicates a negligible loss of Ni. Moreover, the pH value of the solution after Mn removal is about 4.5, which is suitable for subsequent purification processes, such as Co removal.
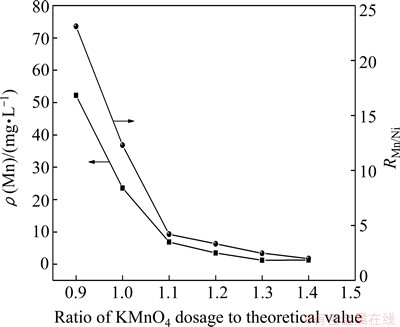
Fig. 6 Effect of KMnO4 dosage on manganese removal
3.2.2 Effect of KMnO4 concentration on manganese removal
Figure 7 presents the effect of KMnO4 concentration on the residual manganese concentration and the mass ratio of manganese to nickel under the conditions of 0.42 g/L Mn2+ and 1.4Dt,KMnO4. It is seen that the residual manganese concentration increases and the mass ratio of manganese to nickel decreases as the KMnO4 concentration increases. This is because the higher the concentration of potassium permanganate is used, the more the nickel is oxidized in the nickel solution. In fact, black nickel precipitate (Ni2O3) is easily generated [19,20]. The content of newly generated MnO2 may be reduced. Therefore, the residual concentration of manganese should be properly controlled at a low level (about 1 mg/L) by using KMnO4 with concentration less than 0.11 mol/L.
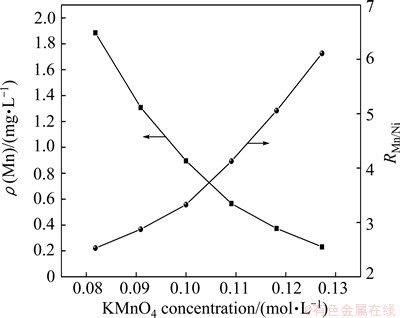
Fig. 7 Effect of KMnO4 concentration on manganese removal
4 Conclusions
1) A new decoppering agent, MnS, was used for removing copper from nickel electrolyte. It is indicated that residual concentration of copper ρ(Cu) decreases with increasing MnS dosage, pH value, temperature and reaction time. The ρ(Cu) decreases from 530 to 3 mg/L and the mass ratio of copper to nickel (RCu/Ni) in the residue reaches above 15 when MnS dosage is 1.4 times the theoretical value (Dt,MnS=0.74 g MnS) and pH value of electrolyte is 4-5 with reaction time more than 60 min at temperatures above 60 °C.
2) The concentration of newly generated Mn2+ ions (ρ(Mn)) in the solution is also reduced to 3 mg/L by adding KMnO4 as an oxidizing reagent. It is found that only small nickel (0.1-0.5 g/L or 0.13%-0.67% Ni) loss occurs during the process of manganese removal. Moreover, the residual concentration of manganese should be properly controlled at a low level (approximately 1 mg/L) by using an oxidant like potassium permanganate. The total cost per ton nickel of the copper removal is $230.2/t. The experimental results demonstrate that MnS is considered a highly effective decoppering reagent for copper removal.
References
[1] HUANG Qi-xing, WANG Li-chuang, ZHU Ding-yuan. Nickel metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Science and Technology Press, 1990: 8-10. (in Chinese)
[2] HU Hui-ping, LIU Chun-xuan, HAN Xue-tao, LIANG Qi-wen, CHEN Qi-yuan. Solvent extraction of copper and ammonia from ammoniacal solutions using sterically hindered β-diketone [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(10): 2026-2031.
[3] DEAN J A. Lange’s handbook of chemistry [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1991: 1467-1532.
[4] ZHAO Zhong-wei, CHEN Ai-liang, SUN Pei-mei, CHEN Xing-yu, HUO Guang-sheng, LI Hong-gui. Removing copper from nickel electrolyte solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(4): 749-753.
[5] PENG Rong-qiu. Nickel metallurgy [M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[6] XIE Keng, WEN Jian-kang, HUA Yi-xin, RUAN Ren-man. Selective separation of Cu(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II) by solvent extraction [J]. Rare Metals, 2008, 27(3): 228-232.
[7] SHEN Xiao-yi, SHAO Hong-mei, WANG Jia-dong, ZHAI Yu-chun. Preparation of ammonium jarosite from clinker digestion solution of nickel oxide ore roasted using (NH4)2SO4 [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(11): 3434-3439.
[8] WEN Jun-jie, ZHANG Qi-xiu, ZHANG Gui-qing, CAO Zuo-ying. Deep removal of copper from cobalt sulfate electrolyte by ion-exchange [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(8): 1534-1540.
[9] TSAKIRIDIS P E, AGATZINI S L. Simultaneous solvent extraction of cobalt and nickel in the presence of manganese and magnesium from sulfate solutions by Cyanex 301 [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 72(3-4): 269-278.
[10] WANG J K. Preferential transport behaviors of ternary system ferric-cupric-nickel ions through cation ion exchange membrane with a complex agent by dialysis [J]. Desalination, 2004, 161(3): 277-285.
[11] KIRJAVAINEN V, SCHREITHOFER N, HEISKANEN K. Effect of some process variables on flotability of sulfide nickelores [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2002, 65(2): 59-72.
[12] ZHAI Yu-chun, MU Wen-ning, LIU Yan, XU Qian. A green process for recovering nickel from nickeliferous laterite ores [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(S1): s65-s70.
[13] ZENG De-wen, LI Zuo-gang, XU Sheng-ming, TAN Peng-fu, ZHANG Chuang-fu. Experimental research of removing copper from nickel electrolysis anolyte with nickel thiosulfate [J]. Hunan Metallurgy, 1996, 12(4): 49-52. (in Chinese)
[14] FU Cong-yue. Applied basic research of non-ferrous metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993: 36-42. (in Chinese)
[15] ZHAO Zhong-wei, SHI Yu-chen, CHEN Ai-liang, HUO Guang-sheng, LI Hong-gui. Study of removing copper from nickel anode electrolyte by sulfide method [J]. The Chinese Journal Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 10(2): 9-12. (in Chinese)
[16] CHEN Ai-liang. Study on novel technology and basic theory of removing copper from nickel sulfide anodic electrolyte [D]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[17] CHEN Ai-liang, ZHAO Zhong-wei, CHEN Xing-yu, LIU Xu-heng, CAO Cai-fang. Decoppering capability of nickel thiocarbonate in nickel electrolyte [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 144-145: 23-26.
[18] CHEN Xing-yu, CHEN Ai-liang, ZHAO Zhong-wei, LIU Xu-heng, SHI Yu-chen, WANG De-zhi. Removal of Cu from the nickel electrolysis anolyte using nickel thiocarbonate [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 133: 106-110.
[19] DAS P K, ANAND S, DAS R P. Minimization of Ni (II) precipitation in the Ni(II)-NH3-SO2-(NH3)2SO4-MnO2 system [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1997, 50: 77-86.
[20] ZHANG P, YOKOYAMA T, ITABASHI O, WAKUI Y, SUZUKI T M, INOUE K. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of metal values from spent nickel–metal hydride secondary batteries [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1998, 50: 61-75.
李江涛,陈爱良
中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:由于镍电解液中铜浓度低(0.53 g/L)、镍浓度高(75 g/L),因此,很难从镍电解液中分离除去铜。采用硫化锰(MnS)除去镍电解液中的铜。结果表明:在MnS用量为理论量Dt,MnS(Dt,MnS=0.74 g)的1.4倍、pH值为4~5、温度高于60 °C时反应至少60 min后,电解液中铜浓度ρ(Cu)从530 mg/L降低至3 mg/L,渣中铜、镍质量比RCu/Ni达到15以上。采用氧化法可将新产生的除铜后液中锰浓度ρ(Mn)降低至3 mg/L。除铜后液中铜、锰浓度,渣中铜、镍质量比均能满足生产要求。因此,硫化锰是一种高效除铜剂。
关键词:硫化锰;除铜剂;除铜;除锰;镍电解阳极液
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51104183) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project supported by the China Scholarship Council
Corresponding author: Ai-liang CHEN; Tel: +86-731-88830476; E-mail: chenailiang@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64024-9

