


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 1655-1660
Effects of boric acid on microstructure and corrosion resistance of boric/sulfuric acid anodic film on 7050 aluminum alloy
DU Nan, WANG Shuai-xing, ZHAO Qing, SHAO Zhi-song
National Defense Key Discipline Laboratory of Light Alloy Processing Science and Technology,
Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
Received 13 July 2011; accepted 14 October 2011
Abstract: The microstructure and corrosion resistance of different boric/sulfuric acid anodic (BSAA) films on 7050 aluminum alloy were studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and scanning Kelvin probe (SKP). The results show that boric acid does not change the structure of barrier layer of anodic film, but will significantly affect the structure of porous layer, consequently affect the corrosion resistance of anodic film. As the content of boric acid in electrolyte increases from 0 to 8 g/L, the resistance of porous layer (Rp) of BSAA film increases, the capacitance of porous layer (CPEp) decreases, the surface potential moves positively, the pore size lessens, and the corrosion resistance improves. However, the Rp, CPEp and surface potential will change towards opposite direction when the content of boric acid is over 8 g/L.
Key words: aluminum alloy; anodic film; corrosion resistance; boric acid
1 Introduction
As an environment-friendly anodizing technique, boric/sulfuric acid anodic (BSAA) film provides a excellent corrosion resistance and does not decrease fatigue life of aluminum alloy [1], so it has broad application prospects in aviation industry. Since WONG and MOJI [2] proposed BSAA technique, many scholars [3-6] have carried out extensive investigations. However, the role of boric acid in this anodizing system is still disputed in recent years. THOMPSON et al [3] found that boric acid has a negligible influence in boric/sulfuric acid anodic (BSAA) system. Whereas, some scholars thought that boric acid can balance acid-base and improve the film appearance.
In the present study, the influence of boric acid on microstructure and corrosion resistance of BSAA film on 7050 aluminum alloy was studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), atomic force microscopy (AFM). In addition, scanning Kelvin probe (SKP) technique is extremely sensitive to the small changes of material surface state, so, many scholars studied the corrosion state and behavior of materials by SKP [7-10]. But it has not been reported to study the surface morphology of anodic aluminum by SKP. Because the distinction of thickness, structure and others among different anodic films, the work function for electronic effusion is different. So, the surface morphology of anodic film can be characterized through measuring the surface potential by SKP. On the basis of these researches, the role of boric acid in BSAA system was analyzed comprehensively.
2 Experimental
The material used in this experiment was 7050 Al alloy. The main composition (mass fraction) was 6.65%Zn, 2.29%Cu, 2.12%Mg, 0.27%Cr, 0.12%Si, balanced with Al. The samples for electrochemical test were 10 mm×10 mm×1.5 mm; the others were 50 mm×25 mm×1.5 mm.
Prior to anodizing, the following pretreatments were conducted: degreasing in acetone; alkaline etching in a solution containing 60 g/L NaOH and 5 g/L Na2S at 60 ℃ for 2-3 min; desmutting in 30%-50% (volume fraction) HNO3 at room temperature for 1 min, and finally rinsing thoroughly in deionized water. The anodizing was processed in different boric/sulfuric acid electrolyte systems (B0: 50 g/L H2SO4; B5: B0+5 g/L H3BO3; B8: B0+8 g/L H3BO3; B15: B0+15 g/L H3BO3; B20: B0+20 g/L H3BO3) at 24-26 ℃. The anodizing voltage was 15 V, and the anodizing time was 25 min.
The EIS of unsealed anodic specimens was measured using CHI660C potentiostat in a neutral 3.5% NaCl solution at room temperature. A saturated calomel electrode (SCE) was used as the reference electrode, and the counter electrode was a platinum sheet. The anodic specimens were coated with epoxy resin, leaving an area of 1 cm2 exposed for electrochemical testing. Prior to testing, the specimens were immersed in NaCl solution for about 1 h in order to stabilize the open circuit potential. The testing was applied to an AC potential of 10 mV varied about the open circuit potential, over the frequency range from 100 kHz to 0.01 Hz. The equivalent circuits were fitted using the Zsimpwin software after testing to obtain the resistance and capacitance of the anodic film.
The surface morphology, the pore distribution and structure of anodic film were observed by AJ-Ⅲa AFM. The scanning area was 20 μm×20 μm. The surface potential of anodic film was measured by SKP system of UK at room temperature in air. The scanning step was 250 μm, the scanning area was 2 mm×2 mm, and the probe vibration amplitude was 50 μm.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Impedance spectra of anodic films
The impedance spectra for different anodic films are shown in Fig. 1. The impedance spectra for sulfuric acid anodic (SAA) film only showed one time constant when it was immersed in NaCl solution. For the SAA film, the pore was large, the corrosive Cl- easily passed through the porous layer, and therefore only the information of barrier layer was detected in the impedance spectra. However, the impedance spectra for all BSAA films were similar, and two time constants clearly appeared. For the BSAA films, the pores were smaller, the Cl- needed to overcome greater obstruction to penetrate the porous layer, so the information of barrier layer and porous layer could be measured in impedance spectra. Some authors [11,12] also thought that the unsealed anodic film produced easily the self-sealing effect when immersed in NaCl solution, if the pore size was smaller.
Compared with the impedance spectroscopy of different BSAA films, it was found that the medium-high-frequency impedance of anodic film changed significantly, but the low-frequency impedance was almost unchangeable with the increase of the boric acid. According to Ref.[13], the medium-high- frequency part of the impedance—frequency diagram mainly reflected the performance of the porous layer, the low frequency part mainly showed the information of barrier layer; and for the porous anodic film, the ability against water and corrosive media was strong, the corrosion resistance was good if the resistance of porous layer was great. Therefore, it could be speculated that boric acid could not change the barrier layer structure of BSAA film, but would significantly affect the structure of porous layer, and then affected the corrosion resistance of anodic film. Besides, the B8 film has the greatest medium-high-frequency impedance resistance, the smallest pore size and the best corrosion resistance.

Fig. 1 Phase angle (a) and impedance impedance (b) of different anodic films
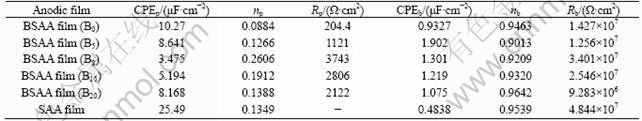
According to the structure of the anodic film, various equivalent circuits can be used to simulate the corrosion behavior of anodic film [14-16]. Figure 2(a) shows the equivalent circuit model of completely uniform anodic film, which can well fit the impedance spectra of unsealed BSAA films. In this model, Cpw is the capacitance of the pore wall; Rp and CPEp reflect the average resistance and capacitance of the porous layer; Rb and CPEb represent the average resistance and capacitance of the barrier layer. CPE is defined as: CPE=1/(2πJfC)n, where n is the frequency dispersion factor and varies from 1 to 0, only when n=1 can be considered as real capacitances. But the impedance spectra for unsealed SAA film could not detect the information of the porous layer, so the Rp could be removed in the model, and the equivalent circuit was simplified as Fig. 2(b). In addition, the solution resistance (Rsol) was decreased under appropriate experimental conditions, so the Rsol was ignored in the model. The simulated results are shown in Table 1.
From Table 1, it can be seen that the Rb and CPEb values of BSAA films only have slight fluctuation with the increase of boric acid in the electrolytes. The Rb maintained at 107 Ω·cm2, but the Rp and CPEp values changed significantly. With the addition of boric acid, the Rp gradually increased, the CPEp evidently decreased, the np also constantly raised. This indicated that the film became more uniform, the pore size of porous layer constantly reduced, and the corrosion resistance gradually improved. However, the Rp, CPEp and np would change towards opposite direction when the content of boric acid in electrolyte was very high. A reasonable explanation was that the solubility of electrolyte was strong, the pore was big, the obstruction of Cl- penetrating porous layer was small, and the corrosion resistance was poor when not adding boric acid. It was helpful to reduce the solubility of electrolyte, improve the film appearance and the structure of porous layer when adding an appropriate amount of boric acid into electrolyte. The film would become more uniform and compact, the pore size would decrease, the Cl- penetrating porous layer would become more difficult, the Rp would increase, and the corrosion resistance would improve. Besides, the shrinkage of pore also made the content of free water in pores reduce, which resulted in the decrease of CPEp [13]. However, the higher content of boric acid will have an opposite effect. The Rp decreased, and the CPEp increased when the content of boric acid was over 8 g/L.

Fig. 2 Equivalent circuits of anodic films: (a) Boric/sulfuric acid anodic (BSAA) film; (b) Sulfuric acid anodic (SAA) film
Table 1 Fitting parameter of EIS of different anodic films
3.2 Surface morphology of anodic films
Figure 3 shows the surface morphology and microstructure of different BSAA films. Vague trace of pore structure appears on the surface of all BSAA films, but different anodic films have different pore structures and distributions. The pore on anodic film is large and the porosity is low when boric acid is not added. The film surface will become more uniform, the roughness decreases significantly, the pore size lessens when adding boric acid into electrolyte. But if the boric acid content in electrolytes is too high, the film pore will largen. The pore size of B20 film is bigger than that of B8 film, which is consistent with the test results of EIS.

Fig. 3 AFM images of different BSAA films: (a) B0 film; (b)B8 film; (c) B20 film
3.3 Kelvin potential distribution of anodic films
Figure 4 shows the surface potential (V) distribution of different anodic films on 7050 Al alloy, which can reflect the transformation of surface morphology. The surface potential of untreated Al 7050 (Fig. 4(h)) is very negative and changes greatly. The potential range is from -767 to -658 mV, and the potential difference between the cathode and anode reaches 109 mV. This indicates that untreated 7050 Al alloy easily forms local corrosion micro-cell as the heterogeneity of the composition, the surface is in the active state, the work function for electronic effusion is small, and thus the corrosion resistance is poor.

Fig. 4 Distribution of surface potential of different anodized films: (a) BSAA film(B0); (b) BSAA film(B5); (c) BSAA film(B8); (d) BSAA film(B15); (e) BSAA film(B20); (f) SAA film; (g) CAA film; (h) 7050 Al alloy
However, the surface potential moves positively, the potential difference between the cathode and anode decreases when 7050 Al alloy is treated by anodizing. The surface potential of SAA film (Fig. 4(f)) with thickness of 4 μm varies from -154 to -87 mV, the surface potential of CAA film (Fig. 4(g)) also moves from -103 to -80 mV, and the surface potential of BSAA film with the same thickness is obviously positive. This result might be due to the formation of Al2O3 film, which can make the surface composition of aluminum alloy become uniform and significantly hinder the electronic effusion. As for different anodic films with the same thickness, the main factor that affects the surface potential is the surface structure of film. The work function for electronic effusion is small when the pore size is large or the porosity is high. It is more difficult for electronic effusion when the pore size lessens or the porosity decreases. Therefore, the surface morphology of film can be determined, according to the movement of the surface potential. This reveals that the pore size of SAA film is maximal, the pore size of CAA film comes second, the surface of BSAA film is the most compact and the pore size is minimal.
Compared with the surface potential distribution of different BSAA films (Figs. 4(a)-(e)), it can be seen that the surface potential of B0 film is slight negative and varies from -36 to 27 mV, as shown in Fig. 4(a). The surface potential increases significantly when boric acid is added. The surface potential of B8 film is the most positive and the potential difference is also the smallest, which is 96-135 mV. The surface potential will reduce slightly if continuously adding boric acid into electrolytes, the surface potential of B15 film is 45-89 mV, the surface potential of B20 film is down to 19-61 mV. This reveals that the pore of film is big, the work function for electronic effusion is less, due to the chemical dissolution of electrolyte on the anodic film when the boric acid is not added. The pore on film decreases, the work function for electronic effusion increases when adding an appropriate amount of boric acid into electrolyte. However, the effects of boric acid on anodizing are relative. The high content of boric acid will make the pore of film broaden, the work function reduce and the corrosion resistance decrease. These results are consistent with the analyses of EIS and AFM.
4 Conclusions
1) In the boric/sulfuric acid anodizing system, boric acid mainly affects the structure of porous layer of anodic film, consequently changes the corrosion resistance of anodic film. It is helpful to improve the film appearance, lessen the pore on film, and improve the corrosion resistance when adding an appropriate amount of boric acid into electrolyte.
2) As the content of boric acid in electrolyte increases from 0 to 8 g/L, the Rp increases, the CPEp decreases, the surface potential moves positively, the pore size lessens, and the corrosion resistance improves. However, the higher content of boric acid will make the pore of film broaden, the resistance reduce, the work function fall, and the corrosion resistance decrease.
References
[1] CAI Jian-ping, LI Bin, LIU Ming-hui, XIONG Jia-jin, ZHENG Liang. Effect of anodizing on fatigue performance of aeronautic aluminum alloys [J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2007, 27(2): 25-28. (in Chinese)
[2] WONG C M, MOJI Y. Method for anodizing aluminum: US, 4894127 [P]. 1989-05-24.
[3] THOMPSON G E, ZHANG L, SMITH C J E, SKELDON P. Boric/sulfuric acid anodizing of aluminum alloys 2024 and 7075: Film growth and corrosion resistance [J]. Corros Sci Sec, 1999, 55(11): 1052-1061.
[4] DOMINGUES L, FERNANDES J C S, DA CUNHA BELO M, FERREIRA M G S, GUERRA-ROSA L. Anodising of Al 2024 T3 in a modified sulphuric acid/boric acid bath for aeronautical applications [J]. Corros Sci, 2003, 45: 149-160.
[5] ZHANG Jin-sheng, ZHAO Xu-hui, ZUO Yu, XIONG Jin-ping. The bonding strength and corrosion resistance of aluminum alloy by anodizing treatment in a phosphoric acid modified boric acid/sulfuric acid bath [J]. Surf Coat Technol, 2008, 202: 3149-3156.
[6] CRITCHLOW G W, YENDALL K A, BAHRANIB D, QUINNB A, ANDREWS F. Strategies for the replacement of chromic acid anodising for the structural bonding of aluminium alloys [J]. Int J Adhes Adhes, 2006, 26: 419-453.
[7] AHARA A, KODAMA T. Potential distribution measurement in galvanic corrosion of Zn/Fe couple by means of Kelvin probe [J]. Corros Sci, 2000, 42(4): 655-673.
[8] de WIT J H W. Local potential measurements with the SKPFM on aluminum alloy [J]. Electrochim Acta, 2004, 49: 2841-2850.
[9] JUZELIUNAS E, SUDAVICIUS A, JUTTNER K, FURBETH W. Study of initial stages of AI-Mg alloy corrosion in water,chloride and Cu(Ⅱ) environment by a scanning Kelvin probe and XPS [J]. Electrochem Commun, 2003, 5: 154-158.
[10] SCHMIDT W, STRATMANN M. Scanning Kelvin probe investigations of filiform corrosion on aluminum alloy 2024-T3 [J]. Corros Sci, 1998, 40(8): 1441-1443.
[11] SUAY J J, GIMENEZ E, RODRIGUEZ T, HABBIB K, SAURA J J. Characterization of anodized and sealed aluminium by EIS [J]. Corros Sci, 2003, 45: 611-624.
[12] ZHAO Xu-hui, ZUO Yu, ZHAO Jing-mao, XIONG Jin-ping, TANG Yu-ming. A study on the self-sealing process of anodic films on aluminum by EIS [J]. Surf Coat Technol, 2006, 200: 6846-6853.
[13] HITZIG J, JUTTNER K, LORENZ W J. AC impedance measurements on porous aluminum oxide films [J]. Corros Sci, 1984, 24(11-12): 945-952.
[14] van der LINDEN B, TERRYN H, VEREECKEN J. Investigation of anodic aluminium oxide layers by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1990, 20 (5): 798-803.
[15] GONZALEZ J A, LOPEZ V, BAUTISTA A. Characterization of porous aluminium oxide films from a.c. impedance measurements [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1999, 29(2): 229-238.
[16] GIRGINOV A, POPOVA A, KANAZIRSKI I, ZAHARIEW A. Characterization of complex anodic alumina films by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 515(4): 1548-1551.
硼酸对7050铝合金硼酸-硫酸阳极氧化膜结构及耐蚀性的影响
杜 楠,王帅星,赵 晴,邵志松
南昌航空大学 轻合金加工科学与技术国防重点学科实验室,南昌 330063
摘 要:通过AFM、交流阻抗谱及扫描Kelvin探针技术,研究硼酸对7050铝合金硼酸-硫酸阳极氧化膜结构及耐蚀性的影响。结果表明,在硼酸-硫酸阳极氧化体系中,硼酸不会改变氧化膜阻挡层的结构,但会显著影响氧化膜多孔层的结构形式,进而影响氧化膜的耐蚀性。在0~8 g/L的范围内,随着电解液中硼酸含量的增加,氧化膜的多孔层电阻增大,电容减小,表面势正移,孔径缩小,耐蚀性变好。在高于8 g/L时,随着硼酸含量的增加,氧化膜的孔隙变大,阻抗变小,电子逸出功降低,耐蚀性变差。
关键词:铝合金;阳极氧化膜;耐蚀性;硼酸
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Corresponding author: DU Nan; Tel: +86-791-83863187; E-mail:d_unan@sina.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61369-1