Spatial distribution and environmental characterization of sediment-associated metals from middle-downstream of Xiangjiang River, southern China
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2010年第1期
论文作者:郭朝晖 宋杰 肖细元 明辉 苗旭锋 王凤永
文章页码:68 - 78
Key words:sediment; toxic elements; spatial distribution; environmental risk; Xiangjiang River
Abstract: The contamination and environmental risk assessment of the toxic elements in sediments from the middle-downstream (Zhuzhou—Changsha section) of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan Province of China were studied. The results show that As, Cd, Pb and Zn are major contaminants in sediments, and average concentrations of these elements significantly exceed both the Control Standards for Pollutants in Sludge of China (GB4284—84) for agricultural use in acidic soils and the effect range median (ERM) values. The average concentrations of As, Cd and Pb in the river water slightly exceed the limit of Surface Water Environment Quality Standard (GB3838—2002). The concentrations of As and Cr in depth profiles extensively change, but slight changes are observed in Pb and Zn. Cd and Zn in most sediment samples can easily enter the food-chain and bring possible ecotoxicological risk to organisms living in sediments according to the risk assessment code.
基金信息:the National Natural Science Foundation of China
the Foundation of Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Ecosystem Health
J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2010) 17: 68-78
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-010-0013-7 ![]()
GUO Zhao-hui(郭朝晖)1, 2, 3, SONG Jie(宋杰)3, XIAO Xi-yuan(肖细元)3,
MING Hui(明辉)4, MIAO Xu-feng(苗旭锋)3, WANG Feng-yong(王凤永)3
1. Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Ecological Health, Ministry of Education,
Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310029, China;
2. College of Natural Resources and Environmental Science, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310029, China;
3. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
4. Centre for Environmental Risk Assessment and Remediation, Mawson Lakes Campus,
University of South Australia, SA 5095, Australia
? Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2010
Abstract: The contamination and environmental risk assessment of the toxic elements in sediments from the middle-downstream (Zhuzhou—Changsha section) of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan Province of China were studied. The results show that As, Cd, Pb and Zn are major contaminants in sediments, and average concentrations of these elements significantly exceed both the Control Standards for Pollutants in Sludge of China (GB4284—84) for agricultural use in acidic soils and the effect range median (ERM) values. The average concentrations of As, Cd and Pb in the river water slightly exceed the limit of Surface Water Environment Quality Standard (GB3838—2002). The concentrations of As and Cr in depth profiles extensively change, but slight changes are observed in Pb and Zn. Cd and Zn in most sediment samples can easily enter the food-chain and bring possible ecotoxicological risk to organisms living in sediments according to the risk assessment code.
Key words: sediment; toxic elements; spatial distribution; environmental risk; Xiangjiang River
1 Introduction
Heavy metal contamination in the aquatic-terrestrial ecosystem has attracted great attention in recent years due to its toxicity, abundance and persistence in the environment, and subsequent accumulation in aquatic habitats [1-3]. Human activities in terrestrial environments are widely recognized to impact water quality, surrounding soil for use and vegetable growth from the industrialization zone. The sediment originates from the weathering of minerals and soils upstream and is transported the downstream by the river water. Heavy metals discharged into the river system by natural or anthropogenic sources during their transport are then distributed between the aqueous phase and bed sediments [3-4]. Contaminants discharged from the industrial areas eventually deposit as sediments in the lower reaches of the fluvial systems. Usually, sediments act as the sink [4-6] and the source for environmental contaminants in aquatic environment [3, 6]. The source, distribution, storage and the fate of potentially hazardous metals in sediment in river channels and on floodplains at the basin scale were studied [4, 7-10], particularly for a large river system. Some studies have documented elevated levels of sediment-associated metals on floodplains and riverbed due to input from anthropogenic wastes, especially linked to metal mining activities [4, 7]. Meanwhile, the contamination of metals in sediments is significantly related to the contamination history of different environments [5, 11-12] and seasonal change of river water [10]. Metal distribution depends on the characteristics of the studied sediments corresponding to the place of origin. The amount and type of organic and inorganic matters, redox properties, pH and oxygen are the most important chemical factors that affect the mobility of sediment-bound metals [6]. Therefore, a sound knowledge of toxic metals from sediments and river water can be beneficial for finding the solution of many environmental problems and can be of great importance for microorganisms, plants, animals, and human health [13].
Hunan Province is well known for its abundant reserves of non-ferrous metals in China. Most of the ores for mining, mineral processing and smelting of non-ferrous and rare metals are located in the middle-downstream of the Xiangjiang River valley [14], which is heavily populated and well developed area in Hunan Province. The major pollution sources of water are also loaded from these industrial towns and agricultural areas of this zone [15], and the contamination of heavy metals in the Xiangjiang River has been increased dramatically [16-17]. Due to the Chinese economic boom in recent years, a great quantity of industrial wastewater containing toxic wastes including As, Cd and Pb, which account for 91.1%, 79.6% and 90.1% of the total element quantity, have been discharged into the Xiangjiang River [16]. The uncontrolled historical and current non-ferrous metal industrial activities accompanied with environmental vitalization pose a major challenge for the sustainable development of the Xiangjiang River basin region. However, very little work has been done in risk assessment on heavy metal contamination of sediment in the Xiangjiang River basin.
The contamination of heavy metals in river water and sediments from the middle-downstream of the Xiangjiang River (Zhuzhou—Changsha section) was investigated in this work. The objectives were: (1) to determine the concentration, longitudinal and spatial distribution of toxic elements in the river water and sediments; (2) to ascertain the long-term fate and environmental significance of sediment-associated metals in sediments; and (3) to evaluate potential environmental risk of sediment-associated metals, specifically river water quality and regional ecology.
2 Experimental
2.1 Study area
The Xiangjiang River, lying between 110.5?- 114.0?E and 24.52?-28.75?N, is an important river branching from the Yangtze River in southern China and flows from the south to north. The total length of the river is 856 km and the mainstream of the river is mainly fed from rain and mountain springs. The studied areas, including Zhuzhou, Xiangtan and Changsha, are located on both sides of the middle-downstream of the Xiangjiang River. These constitute the centre of politics, economics and culture in Hunan Province (Fig.1). Qingshuitang district of Zhuzhou and Yuetang district of Xiangtan where old industrial areas of mineral refinery and chemical industries were located, are of particular significance. In recent years, due to the rapid development in this region, many industrial wastes have been discharged into the middle-downstream of the Xiangjiang River so that the water in this region is heavily polluted by toxic elements, such as As, Cd and Pb [14, 16].

Fig.1 Sampling sites for sediments from middle-downstream of Xiangjiang River
2.2 Sample collection and pretreatment
The samples were collected with plastic scoop during the rainless water season at the beginning of March in 2008. A total of 21 sites at Zhuzhou—Changsha section of the Xiangjiang River were selected for sampling. At each site, samples were collected from surface sediments on riverbank and riverbed as well as water. Among the 21 sites, five of them were in Zhuzhou section (from Z1 to Z5), another five sites in Xiangtan section (from X1 to X5) and 11 sites in the Changsha section (from C1 to C11) of the Xiangjiang River (Fig.1). The distance between the neighboring sites is approximately 2 km. Six of these sites including Z1 and Z5 in Zhuzhou Reach, X2 and X5 in Xiangtan Reach, and C5 and C10 in Changsha Reach (Fig.1), were further selected to collect sediment profile samples of riverbank exposure at depth intervals of 0-10, 10-20, 20-30, 30-40 and 40-50 cm according to estuary and pollution sources. All samples were stored in polyethylene bags and transported to the laboratory. The samples were stored for further analysis after air drying and sieving. The pH values of water samples were determined in the field using a portable pH meter (pH1120, Mettler Toledo, USA) and then the water samples were acidified, and brought back to the laboratory and stored in the refrigerator.
2.3 Pollution evaluation and risk assessment
The concepts of effects-range-low (ERL) and effects-range-median (ERM) were adopted to assess the risk of metals in sediments [18]. The ERL value (E1) represents chemical concentrations below which adverse biological effects are rarely observed, while the ERM value (E2) represents concentrations above which toxic effects are probable. The possible toxicity of sediments were assessed through the mean ERM quotient (E3), which is calculated by dividing each contaminant by its respective ERM value, then summarizing the results for all contaminants detected and dividing by the number of contaminants [19]:
![]() (1)
(1)
where Ci is the concentration of compound i in sediment; E2i is the ERM for compound i; and n is the number of compounds. A mean ERM quotient of less than 0.1 has a 9% probability of toxicity; a mean ERM quotient of 0.11-0.50 has a 21% probability of toxicity; a mean ERM quotient of 0.51-1.50 has a 49% of toxicity; and a mean ERM quotient of larger than 1.50 has a 76% of toxicity [19]. The risk assessment code (RAC) classification based on the percentage of metal in the carbonate and exchangeable fractions was also used to assess the bioavailability of metals in sediments according to the extracted-metals from the step 1 of BCR (Community Bureau of Reference, now the Standards Measurement and Testing Program) sequential extraction procedure [20]. According to the RAC guidelines, for any metal, sediments with 11%-30% carbonate and exchangeable fractions belong to a medium risk to the environment. Furthermore, if more than 50% of metals in sedimentary are associated with these fractions, these metals are considered to be a very high risk and can easily enter the food chain [1].
2.4 Laboratory analysis
The pH value of sediments was determined by a pH meter in a ratio of sediment to deionized water of 1?2.5 (mass to volume). Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in sediments was obtained by shaking a mixture of sediment and water (the ratio of sediment mass to water volume is 1?10) for 1 h, followed by centrifuging the mixture at 3 000 r/min for 15 min. The solution phase was filtered with 0.45 μm membrane before being analyzed using a total organic carbon analyzer (TOC-V CPH, Shimadzu, Japan). The total organic carbon (TOC) of river water was also filtered and measured using the same instrument. The total metal content in sediments was extracted using an acid mixture HF-HClO4-HNO3 (GB/T 17138, 17141-1997) and water samples were digested using an acid mixture of HClO4-HNO3 (1?5, volume ratio) in an open system [21]. The three-stage BCR sequential extraction procedure was employed to determine the available metal fractions, including acid-extractable (step 1, exchangeable and bound to carbonate), reducible (step 2, bound to Fe/Mn oxide) and oxidizable (step 3, bound to organic matter and sulfide) forms [22]. Elements analysis of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, Fe and Mn in solution was carried out using inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Intrepid II XSP, USA). The accuracy and precision of the analytical method were estimated by analyzing a sediment standard reference material (GBW 07304 (GSD-4)) and the results were found to be ±5% of certified values.
2.5 Data analysis
Mean-separations were carried out using a multiple range of tests with Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD). A probability level of 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Correlations were evaluated using the bivariation method, with two-tailed significance and Pearson correlation coefficients. A sampling map was generated using ArcGIS 9.2. All calculations were computed using Microsofts Excel 2003 and SPSS 11.0.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Metal elements concentration in surface sediments and river water
The general characterization of sediment and water samples collected along the Xiangjiang River (Zhuzhou—Changsha section) is summarized in Table 1. The results show that the pH value of riverbed sediments is between 6.93 and 7.83, and that of riverbank sediments is between 6.27 and 7.56, which implies that variation of pH value in sediments is slight along the river. The mean values of DOC in riverbank sediments and riverbed sediments are 12.95 and 16.59 mg/kg, respectively. In contrast, the pH value of the Xiangjiang River’s water is quite stable regardless of the sampling location with a mean value pH of 7.51. The concentration of TOC in river water is very low with an average of 2.08 mg/L. High concentrations of Fe and Mn are noted in the riverbank and riverbed sediments.
Table 1 pH, concentrations of TOC (ρ(TOC), mg/L) in water, of DOC (w(DOC), mg/kg) in sediments, of metals in water (mg/L) and of metals in sediments (mg/kg) from middle-downstream of Xiangjiang River
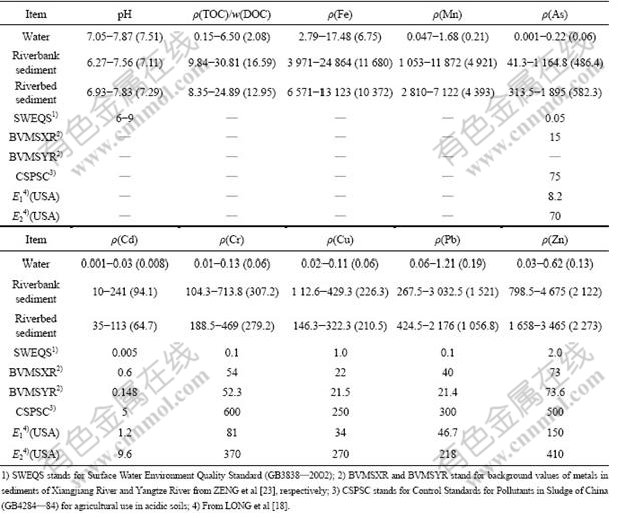
According to the results from Table 1, the concentrations of heavy metals in river water vary in the range of 0.001-0.22 mg/L for As, 0.001-0.03 mg/L for Cd, 0.01-0.13 mg/L for Cr, 0.02-0.11 mg/L for Cu, 0.06-1.21 mg/L for Pb and 0.03-0.62 mg/L for Zn (Table 1), respectively. Average concentrations of As, Cd and Pb in the river slightly exceed the limit of Surface Water Environment Quality Standard of China (GB3838—2002), posing potential health risks to local residents. In the cases of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn, the average concentrations determined in sediments substantially exceed the corresponding background levels of metals in sediments of the Xiangjiang River and the Yangtze River and the levels of ERL [23]. Especially, average concentrations of As, Cd, Pb and Zn in sediments are significantly higher than both the Control Standards for Pollutants in Sludge of China (GB4284—84) for agricultural use in acidic soils and E2. The concentrations are so high that adverse biological effects are easily observed [18]. However, the percentage of the concentration of As, Cr and Cu in sediment samples exceeding the Control Standards for Pollutants in Sludge of China (GB4284—84) for agricultural use in acidic soils was only 86% for riverbank sediment samples for As, 5% for Cr and 24% for Cu, while 10% riverbed sediments for Cu, respectively. The concentration variation of heavy metals (in particular As, Cd and Pb) in water and sediments is considerable. This may be due to the varied amount of industrial waste and sewage discharged into the river at different sampling sites [16]. The storage and distribution of heavy metals in sediments are slightly affected by the quality of river water. However, it is shown that the concentrations of heavy metals in sediments are significantly affected by the anthropogenic activities. Especially, the industrial activities of Pb/Zn mining, mineral processing and smelting with the sulfur-containing ores of Pb/Zn, are mainly associated with toxic elements such as As and Cd, and pose potentially serious risk to water quality and aquatic organisms.
The longitudinal distribution of sediment-associated metals in the riverbank and in the riverbed sediments is displayed in Fig.2. The significantly positive correlation (P<0.05) between sediment-associated heavy metals (especially Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) and Fe, Mn in sediment provides a strong support for the process of heavy metal sequestration by Fe/Mn oxides, hydroxides and oxyhydroxides [2]. The concentrations of total As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn in the riverbank sediments significantly increase with the river flow movement from Zhuzhou Reach to Changsha Reach (Fig.2). The peak concentration of As is found in sampling sites of Zhuzhou Reach and Changsha Reach, while the peak concentration of Cr is found at the sampling sites of Xiangtan Reach and Changsha Reach, suggesting that there may be possibly different contamination sources involved. The total Pb load in the riverbank sediment remains stable along the water flow. In riverbed sediments, longitudinal variation of metal concentrations is obviously different from that of these metals in riverbank sediments. The distribution trends of Cd, Cu, Cr, Pb and Zn in the riverbed sediments are stable with the flow from Zhuzhou Reach to Changsha Reach, while concentrations of As, Fe and Mn slightly decrease along the water flow. The peak concentration of As is also observed at site C2 in Changsha Reach. The results from the above findings suggest that the concentrations of the most metal species in the sediments remain either stable or increasing with the increase of the distance from Zhuzhou Reach to Changsha Reach along the water. Heavy metals in the sediments can transport downstream and lead to the potential risk of contamination increasing with the flow. The accumulation of metals in the river sediments may be significantly affected by the anthropogenic activities along the river.
A significant variation in longitudinal distribution of metal concentrations is visible in the surface riverbank sediments from Zhuzhou to Changsha section of the Xiangjiang River (Fig.2). The concentrations of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn exceed E1 at all sampling sites, in particular, the concentrations of As, Cd, Pb and Zn in riverbank sediments far exceed E2 (Table 1). Based on the above two sets of sediment quality guidelines, a high concentration of sediment-associated toxic elements suggests a greater potential environmental risk to the resident along the Xiangjiang River. In comparison with E1 among sediment-associated metals, the harmful effect among the toxic elements in sediments from the riverbank exposure is in the order of Cd>As>Pb>Zn>Cu>Cr, and that in sediments from the riverbed is in the order of As>Cd>Zn>Pb>Cu>Cr, respectively. E3 ranges from 1.46 at site Z1 to 9.15 at site C9 for the riverbank sediments and from 2.71 at site Z5 to 8.63 at site C2 for the riverbed sediments, respectively. Almost all of sampling sites in the either riverbank or riverbed have an E3 greater than 1.50, which classifies them as high priority sites [19] for the biological adverse effects. The probabilities of toxicity for toxic elements in the riverbank and the riverbed environments suggest that the hazardous levels of metals in the riverbank sediments are relatively high at most sampling sites.
3.2 Metal elements speciation in surface sediments and risk assessment
Most of the metals in sediments are often associated with carbonates, Fe/Mn oxides, hydroxides and oxyhydroxides bearing sediments and the sorption or co-precipitation of the dissolved metals [20]. Most of As exists as reducible and oxidizable forms, Cr is predominantly associated with acid-extractable fraction, and Cu mainly occurs in oxidizable fraction (Table 2). Pb in the riverbank and riverbed sediments mostly exists in reducible fraction. The percentage of extractable Pb observed in the sampling sites near Changsha Reach is higher than that of the other sampling sites near Zhuzhou Reach and Xiangtan Reach (P<0.05). In particular, the percentage of Pb in the Fe/Mn oxide phase from step 2 reaches 79% in the riverbank exposure and 34% at site C3 in the channel environment, which is in agreement with results that Fe/Mn hydrous oxides are important sinks of Pb in sediments [24]. For riverbank exposure, the percentage of acid-extractable Cd is up to 68% at site C2, and that of acid-extractable Zn is up to 29% at site X4 and 37% at site C2, respectively. The percentages of acid-extractable Cd and Zn in the riverbed sediments at both Zhuzhou Reach and Xiangtan Reach are significantly higher than those at Changsha Reach (P<0.05), suggesting that industrial activities may result in a high metal content in the sediment. In both the riverbank exposure and riverbed environment, Fe and Mn are also mainly associated with reducible fraction, which are up to 75% at site C5 and 62% at site C2 in the riverbank sediments, and 75% at site C11 and 71% at site X5 in the riverbed sediments, respectively. The results suggest that the proportions of Cd, Pb and Zn in the riverbank and the riverbed sediments are mainly presented in available fractions that might be susceptible to re-mobilize if the river conditions change (e.g. pH and redox potential) [25]. Based on the above results, the re-mobilization of heavy metals in the sediment may be of significance and should be considered in future remediation strategies.
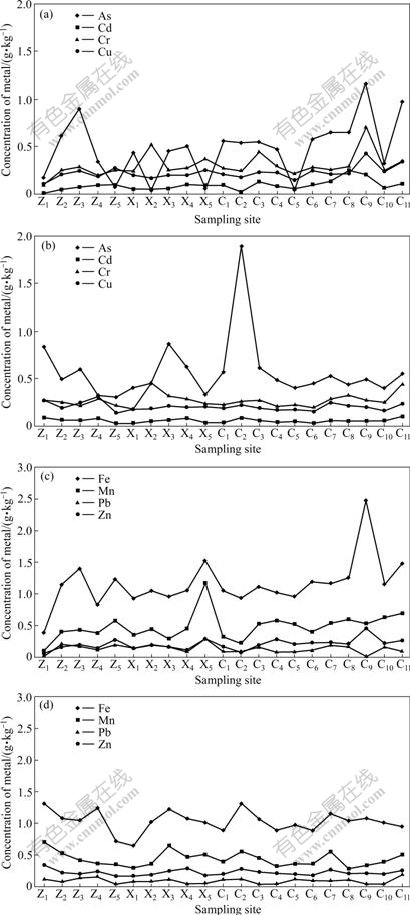
Fig.2 Longitudinal variation of metal concentrations in sediments from riverbank ((a) and (c)) and riverbed ((b) and (d))
Table 2 Range and arithmetic mean of mass fraction for metal fractions in sediments through BCR sequential extraction procedure
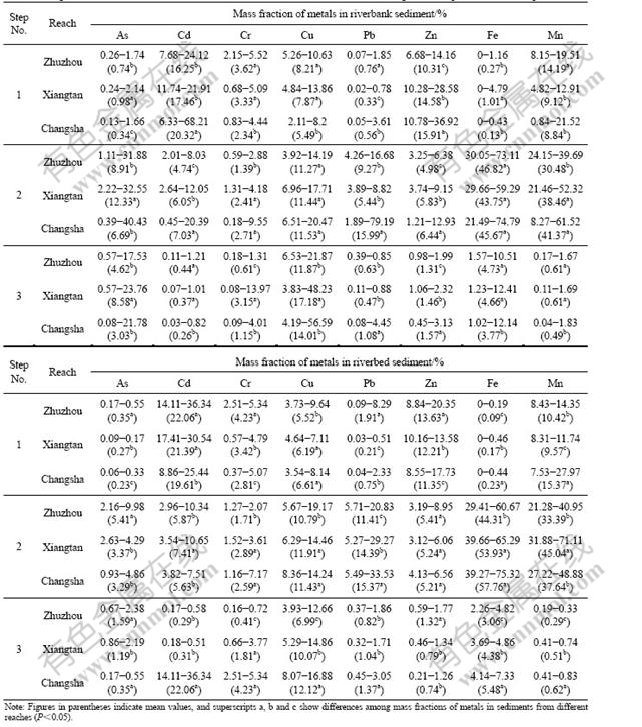
The percentages for the metal fractions in the sediments of Cd, Pb and Zn in acid-extractable (exchangeable fraction and associated to carbonated phase) and reducible (fraction associated with Fe and Mn oxides) forms are very high. The peak values of the metal fractions are 89% for Cd at site C2, 83% for Pb at site C9 and 50% for Zn at site C2 in the riverbank sediment from Changsha Reach, and 47% for Cd at site Z5, 27% for Zn at site Z2 in the riverbed sediment from Zhuzhou Reach, and 35% for Pb at site C3 from Changsha Reach. The high percentages of acid-extractable and reducible forms of Cd, Pb and Zn indicate that both precipitation and sorption processes are important for the distribution of these metals in the sediments [17].
According to the BCR sequential extraction, about 8%-24% of Cd and 7%-14% of Zn in the riverbank sediment from Zhuzhou Reach, 12%-22% of Cd and 10%-29% of Zn in the riverbank sediment from Xiangtan Reach and 6%-68% of Cd and 11%-37% of Zn in the riverbank sediment from Changsha Reach exist in acid-extractable fractions (including exchangeable and bound to carbonate fractions). Therefore, the metals in the riverbank sediments are considered to be within the medium or high risk category and can easily enter the food chain according to the criteria for RAC. Meanwhile, the percentage of extracted Cd concentration in the riverbed sediments ranges from 14% to 36% in Zhuzhou Reach, from 17% to 31% in Xiangtan Reach and from 9% to 25% in Changsha Reach, suggesting a medium level of risk for these metals in riverbed sediments according to the criteria for RAC. The findings of 11%-21% Zn with carbonate and exchangeable forms in most sampling sites can also be categorized as a medium level of risk. Observed high percentages of Cd and Zn associated with the carbonate and exchangeable forms in the sediments (11%-30% at most sampling sites and more than 50% at site C2 from Changsha Reach) are consistent with the data published by JAIN [1] and SINGH et al [20]. However, the percentages of As, Cr, Cu and Pb in exchangeable and carbonate-bound forms in the riverbank and riverbed sediment samples are lower than 10%, and these elements would pose a low risk to the environment according to the criteria for RAC.
3.3 Metal elements concentrations in sediment profiles from riverbank exposure
Fig.3 shows that the metal concentration distribution in sediment profiles of the riverbank can demonstrate the risk of contamination of sediments from the past and current anthropogenic activities, especially the mining and smelting activities in the studied areas. In comparison with metal concentration in sediment profiles between the upstream and downstream of Zhuzhou Reach, concentrations of As, Cr, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in the riverbank sediment profiles from the downstream are higher than those from the upstream. The concentration depth profiles of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe and Mn exhibit similar trends to those in the surface layer and significantly increase along the river flow from Zhuzhou Reach to Changsha Reach. The concentrations of Cd, Zn, Fe and Mn in sediment profiles at the upper of Zhuzhou Reach show homogeneous distribution that is considerable fluctuation distribution in the lower zone. The distribution of As and Cr in the sediment profiles extensively changes and the concentrations of As and Cr are significantly elevated in the upper zones of the sediment profiles from Xiangtan Reach. The distribution characteristics of metals in sediments can represent an industrial history along the river catchment. There are significant differences in concentration profiles among many metals in the riverbank sediments between the top layers and the bottom layers. An overall increasing trend for the majority of elements (in particular Cu) in the depth profile is noticed at site Z1 and is more significant at site Z5 in Zhuzhou Reach. Similarly, the concentrations of toxic metals generally decrease at the same sediment profile depths from Xiangtan Reach and Changsha Reach. The concentrations of As, Cr, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn at the surface depths are less than those of the bottom depths.
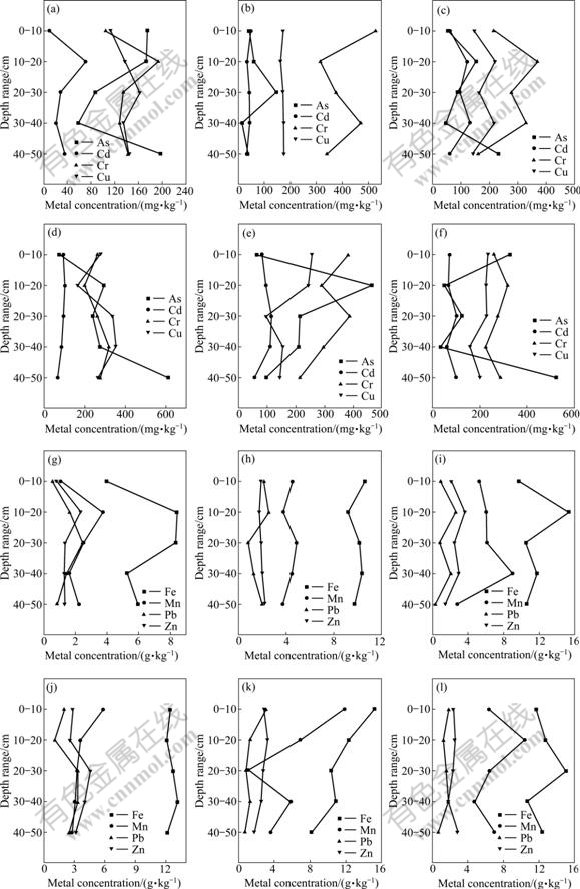
Fig.3 Concentrations of metals in typical sediment profiles from riverbank of middle-downstream of Xiangjiang River: (a), (g) Site Z1; (b), (h) Site X2; (c), (i) Site C5; (d), (j) Site Z5; (e), (k) Site X5; (f), (l) Site C10
However, the concentration depth profiles of Pb and Zn show a slight change, supporting the idea that the contamination of Pb and Zn in sediment profiles is a result of the long period of Pb/Zn mining and smelting activities in the middle-downstream of the Xiangjiang River. Although the contamination of heavy metals from non-ferrous smelting activities in Zhuzhou Reach has reduced in recent years, it has covered by the effect of urbanization, chemical industries and other human activities in Xiangtan Reach and Changsha Reach. The contamination of heavy metals, especially that of Pb and Zn in sediments is still serious. The results indicate that the contamination of metals in sediments not only results from non-ferrous metal industrial activities, but also is affected by the rapid urbanization along the Xiangjiang River.
Controlling the amount of industrial waste discharged into the river system to some extent in recent years has led to the reduction of toxic metal accumulation in river sediments. However, high metal concentrations in the sediment in the surface layer of the riverbank are still visible (such as As, Cd, Pb and Zn). The contents of many metals exceed the sediment quality guidelines (E2) (Fig.3) and pose potential risk to the local residents. The historical, modern industrial activities and urbanization along the Xiangjiang River catchment have resulted in high concentrations of As, Cd, Pb and Zn in depth profile of riverbank sediments. Immediate action is needed to prevent toxic metals in the sediment from releasing.
4 Conclusions
(1) The toxic metals contamination occurs in the river water and sediments from the middle-downstream (Zhuzhou—Changsha section) of the Xiangjiang River, causing significant potential environmental problems within the fluvial ecosystem and possible ecotoxicological risk to organisms living in the sediments. The average concentrations of As, Cd, Pb and Zn in the sediment exceed both the Control Standards for Pollutants in Sludge of China (GB 4284—84) for agricultural use in acidic soils and E2. The potential health risk for the river sediments from the middle- downstream of the Xiangjiang River is mainly due to Cd in sediments.
(2) The spatial metal concentrations distribution in the sediment profiles of the riverbank shows that the concentrations of As, Cr, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn at sediment profiles from the downstream are higher than those from the upstream. The concentration depth profiles of As and Cr change extensively, but only slight changes are observed in Pb and Zn. The results indicate that the contamination of metals in the sediments results from both non-ferrous metal industrial activities and urbanization along the Xiangjiang River.
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Dr. YANG Jun, in Centre for Environmental Remediation, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for drawing the sampling map.
References
[1] JAIN K. Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India [J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(3): 569-578.
[2] CHATTERJEE M, SILVA FILHO E V, SARKAR S K, SELLA S M, BHATTACHARYA A, SATPATHY K K, PRASAD M V R, CHAKRABORTY S, BHATTACHERYA B D. Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance [J]. Environment International, 2007, 33(3): 346-356.
[3] SIN S N, CHUA H, LO W, NG L M. Assessment of heavy metal cations in sediments of Shing Mun River, Hong Kong [J]. Environment International, 2001, 26(5/6): 297-301.
[4] SANTOS BERMEJO J C, BELTR?N R, G?MEZ ARIZA J L. Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel River (Southwest Spain) [J]. Environment International, 2003, 29(1): 69-77.
[5] LI X D, WAI W H, LI Y S, COLES B J, RAMSEY M H, THORNTON I. Heavy metal distribution in sediment profiles of the Pearl River estuary, South China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2000, 15(5): 567-581.
[6] SEGURA R, ARANCIBIA V, Z??IGA M C, PAST?N P. Distribution of copper, zinc, lead and cadmium concentrations in stream sediments from the Mapocho River in Santiago, Chile [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 91(1/3): 71-80.
[7] OWENS P N, WALLING D E. Temporal changes in the metal and phosphorus content of suspended sediment transported by Yorkshire rivers, UK, over the last 100 years, as recorded by overbank floodplain deposits [J]. Hydrobiologia, 2003, 494(1/3): 185-191.
[8] WALLING D E, OWENS P N, CARTER J, LEEKS G J L, LEWIS S, MEHARG A A, WRIGHT J. Storage of sediment-associated nutrients and contaminants in river channel and floodplain systems [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2003, 18(2): 195-220.
[9] CHAPAGAIN S K, SHRESTHA S, DU L G, VERLOO M, KAZAMA, F. Spatial distribution of arsenic in the intertidal sediments of River Scheldt, Belgium [J]. Environment International, 2009, 35(3): 461-465.
[10] TAYLOR M P, HUDSON-EDWARDS K A. The dispersal and storage of sediment-associated metals in an arid river system: The Leichhardt River, Mount Isa, Queensland, Australia [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 152(1): 193-204.
[11] RIBA I, DELVALLS T A, FORJA J M, G?MEZ-PARRA A. Influence of the Aznalcollar mining spill on the vertical distribution of heavy metals in sediments from the Guadalquivir estuary (SW Spain) [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2002, 44(1): 39-47.
[12] von der HEYDEN C J, NEW M G. Sediment chemistry: A history of mine contaminant remediation and an assessment of processes and pollution potential [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 82(1/3): 35-57.
[13] GRANEY J R, ERIKSEN T M. Metals in pond sediments as archives of anthropogenic activities: A study in response to health concerns [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2004, 19(7): 1177-1188.
[14] WANG Qiu-heng, WANG Shu-yun, LIU Mei-ying. Safety evaluation on pollution of Xiangjiang River valley in Hunan Province [J]. China Water and Wastewater, 2004, 20(8): 104-106. (in Chinese)
[15] GUO Zhao-hui, LIAO Bo-han, HUANG Chang-yong. Leaching potential and changes in components of metals in two acidic ferrisols [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 13(6): 631-636.
[16] CHEN Yong-shu, WU Fu-cheng, LU Huan-zhe, YAO Cheng-sheng. Analysis on the water quality changes in the Xiangjiang River from 1981 to 2000 [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2004, 13(5): 508-512. (in Chinese)
[17] YAO Qing-zheng, ZHANG Jing, WU Ying, XIONG Hui. Hydrochemical processes controlling arsenic and selenium in the Changjiang River (Yangtze River) system [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 377(1): 93-104.
[18] LONG E R, MACDONALD D D, SMITH S L, CALDER F D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments [J]. Environmental Management, 1995, 19(1): 81-97.
[19] CASADO-MARTINEZ M C, BUCETA J L, BELZUNCE M J, DELVALLS T A. Using sediment quality guidelines for dredged material management in commercial ports from Spain [J]. Environment International, 2006, 32(3): 388-396.
[20] SINGH K P, MOHAN D, SINGH V K, MALIK A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments: A tributary of the Ganges, India [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 312(1/4): 14-27.
[21] LU Ru-kun. Analytical methods of soil agricultural chemistry [M]. Beijing: Agriculture Science and Technology Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[22] DAVIDSON C M, DUNCAN A L, LITTLEJOHN D, URE ALLAN M, GARDEN LOUIES M. A critical evaluation of the three-stage BCR sequential extraction procedure to assess the potential mobility and toxicity of heavy metals in industrially-contaminated land [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1998, 363(1): 45-55.
[23] ZENG Bei-wei, PANG You-min, HUANG Zhang. Preliminary evaluation on the contamination of Xiangjiang River sediment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1982, 1(5): 352-358. (in Chinese)
[24] MORILLO J, USERO J, GRACIA I. Heavy metal distribution in marine sediments from the southwest coast of Spain [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 55(3): 431-442.
[25] DANG T C, JEFFREY P O. Metal speciation in coastal marine sediments from Singapore using a modified BCR-sequential extraction procedure [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2006, 21(8): 1335-1346.
Foundation item: Project (20507022) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (EREH050303) supported by the Foundation of Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Environmental Remediation and Ecosystem Health
Received date: 2009-03-29; Accepted date: 2009-07-05
Corresponding author: GUO Zhao-hui, PhD, Associate professor; Tel: +86-731-88836442; E-mail: zhguo@mail.csu.edu.cn
(Edited by CHEN Wei-ping)

