好氧条件下铬污染土壤中Cr(VI)的土著微生物还原
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第6期
论文作者:苏长青 李立清 杨志辉 柴立元 廖骐 石岩 黎佳未
文章页码:1304 - 1311
关键词:Cr(VI)污染土壤;土著微生物;微生物修复;动力学
Key words:Cr(VI)-contaminated soil; indigenous microorganisms; microremediation; kinetics
摘 要:生物修复是一种环境友好型的修复技术,在铬污染土壤修复中发挥着越来越重要的作用。为了研究土著微生物对土壤中Cr(VI)的还原过程,在生物反应器里进行一系列微生物好氧培养实验。结果显示:在土著微生物存在情况下,在铬污染土壤中添加培养基使Cr(VI)浓度在66 h内从1521.9降低至199.2 mg/kg,而灭菌土壤中Cr(VI)浓度稍微降低,表明Cr(VI)的还原归因于土著微生物的作用。在微生物修复过程中,Cr(VI)的生物还原发生在 、Mn4+和Fe3+的还原后,而先于 的还原。Cr(VI)还原过程可分为两个阶段,分别以生物还原作用的指数方程模型和主要离子综合效应的线性方程模型为特征。土著Cr(VI)还原菌在Cr(VI)污染土壤的原位修复中具有潜在的应用前景。
Abstract: Bioremediation plays an increasingly important role in the remediation of chromium-contaminated soil because it is an environmentally friendly technology. To investigate the Cr(VI) reduction process by indigenous microorganisms in soil, a batch of incubation experiments were carried out in a bioreactor under aerobic conditions. The results showed that in the presence of indigenous microorganisms, the Cr(VI) concentration in the chromium-contaminated soil decreased from 1521.9 to 199.2 mg/kg within 66 h with culture medium addition, while a slight decrease in the Cr(VI) concentration was found in the sterilized soil, implying that the indigenous microorganisms contributed to the Cr(VI) reduction. In the microbial remediation process, Cr(VI) microbial reduction occurred after the reduction of , Mn4+ and Fe3+ and, before reduction. The reduction process of Cr(VI) can be divided into two phases, characterized by the exponential equation model of microbial reduction and the linear equation model of the combined effect of the major ions. It can be concluded that indigenous Cr(VI)-reducing bacteria have a potential application for in-situ remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 1304-1311
Chang-qing SU1, Li-qing LI1,3, Zhi-hui YANG2,3, Li-yuan CHAI2,3, Qi LIAO2,3, Yan SHI2,3, Jia-wei LI2
1. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Control and Treatment of Heavy Metal Pollution, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 17 July 2018; accepted 14 January 2019
Abstract: Bioremediation plays an increasingly important role in the remediation of chromium-contaminated soil because it is an environmentally friendly technology. To investigate the Cr(VI) reduction process by indigenous microorganisms in soil, a batch of incubation experiments were carried out in a bioreactor under aerobic conditions. The results showed that in the presence of indigenous microorganisms, the Cr(VI) concentration in the chromium-contaminated soil decreased from 1521.9 to 199.2 mg/kg within 66 h with culture medium addition, while a slight decrease in the Cr(VI) concentration was found in the sterilized soil, implying that the indigenous microorganisms contributed to the Cr(VI) reduction. In the microbial remediation process, Cr(VI) microbial reduction occurred after the reduction of  , Mn4+ and Fe3+ and, before
, Mn4+ and Fe3+ and, before 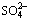 reduction. The reduction process of Cr(VI) can be divided into two phases, characterized by the exponential equation model of microbial reduction and the linear equation model of the combined effect of the major ions. It can be concluded that indigenous Cr(VI)-reducing bacteria have a potential application for in-situ remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil.
reduction. The reduction process of Cr(VI) can be divided into two phases, characterized by the exponential equation model of microbial reduction and the linear equation model of the combined effect of the major ions. It can be concluded that indigenous Cr(VI)-reducing bacteria have a potential application for in-situ remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil.
Key words: Cr(VI)-contaminated soil; indigenous microorganisms; microremediation; kinetics
1 Introduction
Chromium and its compounds are widely used in various industries and become pollutants in soil, industrial wastewater and groundwater [1]. Both valence states, trivalent and hexavalent, of chromium are ubiquitous in nature. Trivalent chromium (Cr(III)) has low toxicity and activity. However, hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) has high toxicity and mobility, causing serious pollution of surface water, groundwater and soil [2].
Currently, bioremediation has played an increasingly important role in the remediation of chromium-contaminated soil because it is an environmentally friendly technology. Various micro- organisms that reduce Cr(VI) to Cr(III), such as Achromobacter sp. [3], Acidiphilium sp. [4], Bacillus sp. [5], Burkholderia sp. [6], Cellulosimicrobium sp. [7], Exiguobacterium sp. [8], Leucobacter sp. [9], Pannoni- bacter sp. [10-15], and Pseudomonas aeruginosa sp. [16], have been isolated from different environ- mental media. In addition, Pseudochrobactrum asaccharolyticum LY6 has been isolated from chromium- contaminated soil [17]. Bacillus endophyticus (IS1), Microbacterium paraoxydans (IS2) and Bacillus simplex (IS3) have been isolated from a tannery waste disposal site [18]. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (CSB 9) has been isolated from chromite mine soil [19]. Leucobacter sp. CRB1 was able to tolerate 4000 mg/L of Cr(VI) with a reduction efficiency of 34.5% [9]. Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB completely reduced Cr(VI) at an initial concentration of 1917 mg/L under anaerobic conditions with a maximum reduction rate of 562.8 mg/(L·h) [10]. Bacillus sp. can reduce more than 90% of 100 mg/L Cr(VI) in 144 h at pH 7 and 35 °C [5]. The removal mechanism of Cr(VI) by Exiguobacterium sp. depends mainly on the action of enzymes secreted outside the cell [8]. Cellulosimicrobium funkei AR8 has a high capacity for Cr(VI) reduction, and its reduction mechanism is achieved through extra- and intra-cellular reduction [7]. SAYEL et al [20] reported that the reduction of Cr(VI) was mediated by cell membrane binding or cell soluble proteins of Enterococcus gallinarum.
Regarding the bioremediation of chromium-contaminated soil, some studies have shown that the presence of microorganisms in chromium-contaminated soil can reduce Cr(VI) [21]. JEYASINGH et al [22] revealed that Cr(VI)-contaminated soil/sludge was affected by moisture content, initial substrate and biomass concentrations during the process of bioremediation. Most of these studies focused on the independent effect of microorganisms on Cr(VI) reduction. In fact, soil is a complex ecosystem with multiple-interfaces. Reports about the bioremediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil by the comprehensive role of indigenous microorganisms and major ions in soil are rare.
In addition, the reduction kinetics of chromium has also been considered. JIANG et al [23] noted that chrome adsorption on humic acid coated magnetite was well fitted with the Langmuir isotherm model and that the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous media by HA- Fe3O4 particles followed pseudo-second-order kinetics. Indirect Cr(VI) bioreduction dominated the Cr(VI) reduction pathway in the presence of both Cr(VI) and sulfate [24]. WILLIAMS and SCHERER [25] reported the reduction kinetics of Cr(VI) by carbonate green rust at different pH values and reactant concentrations. The reduction rate of Cr(VI) was proportional to the surface area concentration of green rust and followed the psuedo-first-order reduction kinetics. CHEN et al [26] reported the effect of Al(III) on the reduction of Cr(VI) by α-hydroxy acids and the reduction of Cr(VI) was described as a pseudo-zero-order reaction when α-hydroxy acid was in excess. LI et al [27] also studied the reduction kinetics of Cr(VI) in soil by ferrous sulfate and sodium thiosulfate. Cr(VI) removal by indigenous bacteria of strain LY6 isolated from Cr(VI)- contaminated soil followed first-order kinetics [17]. Moreover, many factors such as the complex composition and properties of soil, can affect Cr(VI) reduction [28]. The reduction of Cr(VI) can occur during the process of sulfate metabolism to form S2- in soil [29].
Therefore, the objectives of this study were to investigate the characteristics of Cr(VI) reduction by indigenous microorganisms, discuss the effects of the redox potential (φh), pH values and Fe2+, Mn2+, 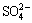 and
and 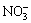 concentrations of soil on microbial reduction of Cr(VI), and further reveal the kinetics of microbial reduction of Cr(VI) to meet the needs of in-situ restoration.
concentrations of soil on microbial reduction of Cr(VI), and further reveal the kinetics of microbial reduction of Cr(VI) to meet the needs of in-situ restoration.
2 Experimental
2.1 Soil samples
The soil samples (0-50 cm) used in this study were collected from a chromite ore processing residue (COPR) disposal site in Hunan Province, China. All soil samples were air-dried and passed through a 250 mm polyethylene sieve prior to analysis. These samples were divided into two portions. One portion was thoroughly mixed for analyzing the soil characterization, and the other was stored in a sample bag prior to the bioremediation experiment. The main physical and chemical properties of the soil samples are presented in Table 1.
2.2 Cr(VI) remediation by indigenous micro-organisms
The soil samples used for Cr(VI) bioremediation were divided into two parts: sterilized (Autoclave, model YXQ-SG46-280S) and non-sterilized samples. For the Cr(VI) remediation by indigenous microorganisms under aerobic conditions, 1 kg soil was added to the sterilized culture medium (yeast extract 5 g/L and glucose 5 g/L) according to the soil-liquid ratio of 1:2. In addition, deionized water as a medium for soil suspension was compared with culture medium. All chemicals were of analytical grade and used without any further purification.
The soil suspension was put into a reactor that was placed in a constant temperature water bath (Model HZ-9212S) at 25 °C, as shown in Fig. 1. Then, the soil suspension was mixed with a mechanical stirrer (Model DJ1C) at 300 r/min. Samples were taken every 6 h to analyze the concentrations of Cr(VI), Fe2+, Mn2+, 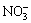 , and
, and 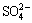 in the solution, and real-time determination of pH and redox potential (φh) values of soil suspension was carried out. Three replicates for each treatment were conducted.
in the solution, and real-time determination of pH and redox potential (φh) values of soil suspension was carried out. Three replicates for each treatment were conducted.
2.3 Analytical methods
The φh value of the soil suspension system was directly determined by the platinum electrode method. The platinum electrode was inserted into the soil suspension system as a special electron conductor. The soluble oxidant or reducing agent in the soil suspension either accepted electrons or donated electrons from the platinum electrode. A balanced electrode was established through a salt bridge and the standard hydrogen electrode, which formed the φh of the system. The water-soluble Cr(VI) concentration of soil samples was measured according to the standard method described by HAN et al [30]. The soil was digested with an acid mixture (HCl, HNO3, HClO4 and HF) on an electric heating plate. The concentration of total chromium in the digested solution was measured by atomic absorption spectrometry (TAS-990, Beijing Purkinje General Instrument Co., Ltd., China). The Fe2+ concentration was measured by titration with 1,10-phenanthroline (phen.) according to the description of RAASHID et al [31]. The Mn2+ concentration was measured by atomic absorption spectrometry (TAS-990, Beijing Purkinje General Instrument Co., Ltd., China). The concentrations of 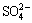 and
and 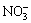 were measured by ion chromato- graphy (Metrohm Model 861AC). Furthermore, the species identification of the bacterium was performed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. DNA of the bacterial strains was extracted using the methods described by CHAI et al [32] and MIN et al [33].
were measured by ion chromato- graphy (Metrohm Model 861AC). Furthermore, the species identification of the bacterium was performed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. DNA of the bacterial strains was extracted using the methods described by CHAI et al [32] and MIN et al [33].
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of soil samples

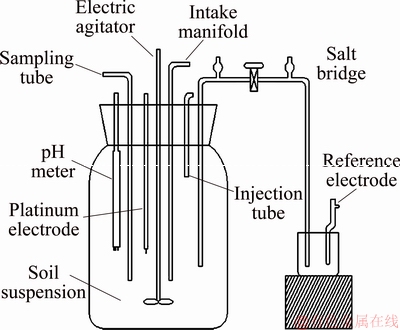
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of bioreactor
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using SPSS statistical software. The data shown in the corresponding figures are the mean values of the experiment and are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Soil characterization
As shown in Table 1, the soil used in this study was alkaline, and the pH value of the soil was approximately 10.75. The chromite ore processing residue (COPR) is known to contain a large amount of calcia, which resulted in the strong alkalinity of the leachate and led to the strong alkalinity of the soil around the COPR disposal site [34]. Cr(VI) in such a pH condition might be leached and enter into the soil. As shown in Table 1, the concentration of Cr(VI) was about 1608 mg/kg in the soil sample, and the total chromium concentration reached up to about 2538 mg/kg, which indicated that the soil was severally contaminated by Cr(VI). In addition, the Cr(III) concentration was approximately 930 mg/kg in the soil, since soil organic matter and microorganisms in soil can reduce Cr(VI) to Cr(III).
The particle size of the sample can influence the leaching of Cr(VI) from the soil, and mass transfer limitation might play a significant role in impeding the dissolution of COPR minerals under acid addition and hence hinder the remediation of COPR. Therefore, greater percentages of Cr(VI) were reduced for acid pretreatment and for COPR samples with smaller particle size. Soil particle size analysis showed that particle sizes larger than 100 mm accounted for 50.1%. Particle sizes smaller than 10 mm comprised approximately 11.8% of the total soil sample, and the sizes between 10 and 100 μm accounted for approximately 38.1%. These results indicated that greater Cr(VI) quantities can be released as the particle size of the soil samples is reduced, and the bioremediation efficiency can also be influenced.
3.2 Cr(VI) microbial remediation in soil
The results of Cr(VI) reduction by indigenous microorganisms are shown in Fig. 2. The concentration of Cr(VI) changed little in Treatments II and IV, in which deionized water replaced culture medium. However, medium supplementation of soil in the presence of microorganisms (non-sterilized sample, Treatment III) significantly promoted Cr(VI) reduction. In particular, a rapid reduction of Cr(VI) occurred after 18 h, and the Cr(VI) concentration decreased from 1521.9 mg/kg at beginning to 199.2 mg/kg at 66 h. The results indicated that the Cr(VI) reduction by microorganisms needed to be stimulated by culture medium. In Treatment Ⅰ with sterilized sample + sterilized medium, the Cr(VI) concentration decreased from 1370.3 to 1008.9 mg/kg within 66 h, which revealed that Cr(VI) was reduced by the culture medium rather than microorganisms.
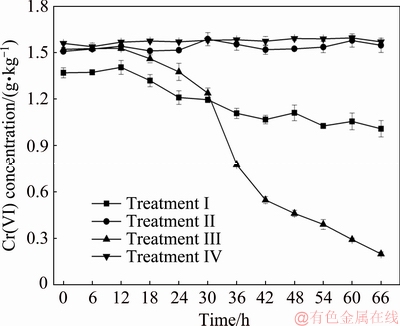
Fig. 2 Change of Cr(VI) concentration under different experimental programs of sterilized sample + sterilized medium (Treatment I), sterilized sample + sterilized deionized water (Treatment II), non-sterilized sample + sterilized medium (Treatment III) and non-sterilized sample + sterilized deionized water (Treatment IV)
The microorganisms from the original soil sample were roughly divided into 10 genera, as shown in Fig. 3. Among them, Exiguobacterium sp. accounted for the largest proportion of the microbial community, reaching up to 42%, while Delftia sp. accounted for 19.33%. In addition, there were also a large proportion of uncertain microorganisms, which accounted for 16.67%. The bacteria Pannonibacter sp. reached a proportion of 2.67% in the original soil samples. The addition of exogenous nutriments could activate the growth and reproduction of these microorganisms, thus vastly enhancing synergy with the soil composition for the bioremediation of Cr(VI).
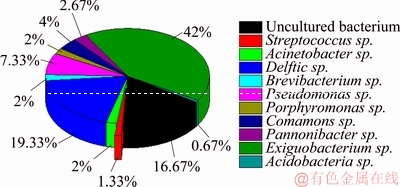
Fig. 3 Species of microorganisms in original soil
3.3 Kinetics of Cr(VI) microbial reduction
The kinetic profile of Cr(VI) reduction by indigenous microorganisms with additional medium under aerobic conditions is shown in Fig. 4.

Fig. 4 Reduction kinetic characteristics of Cr(VI) reduction in soil
There were three different mathematical models for Cr(VI) reduction under acidic to neutral pH conditions: zero-order [35], first-order [36-39], and second-order [40,41]. The reduction process of Cr(VI) was divided into two distinct phases (Fig. 4). In Phase A, the main reduction process of Cr(VI) was due to microorganism action. The culture medium in the soil system enhanced the reduction ability of indigenous microorganisms. Based on the kinetic data (Phase A), it can be concluded that the Cr(VI) reduction process can be described by the exponential kinetic model as follows:
 , R2=0.995 (1)
, R2=0.995 (1)
where C is the concentration of soluble Cr(VI) (mg/kg), and t is time (h).
However, the result of kinetic model fitting was inconsistent with previous studies of pseudo-first-order kinetics of Cr(VI) reduction with amorphous FeS2 [38], sulphur (IV) in acidic conditions [36], and zero-valent iron in groundwater [39]. For microbial reduction, it was not in accord with the bacterial metabolic kinetics of sulfate-reducing bacteria [42]. The trend of Cr(VI) reduction kinetics in this study might be attributed to differences in the factors that affect Cr(VI) removal by the corresponding matters (e.g., S, Fe) and reduction conditions (e.g., pH). The reduction kinetics model of Cr(VI) in chromium-contaminated soil has not been reported, and the reduction of Cr(VI) involved the interaction of microorganisms with the characteristics of the soil system.
In Phase B, Cr(VI) reduction was fitted to the linear equation kinetics model as follows:
C=1157.65-14.43t, R2=0.999 (2)
The results were in agreement with previous studies, which reported Cr(VI) reduction kinetics with metallic iron [35] and with bivalent manganese [37]. Interestingly, Phase B of Fig. 4 was consistent with the results of the degradation of phenol by Sphingomonas sp. GY2B embedded beads at pH 7.0 and 30 °C [43,44]. Equation (2) indicated that the reduction of Cr(VI) was maintained at a constant rate of 14.43 mg/(kg·h) in the reduction process of Cr(VI) in Phase B, which was caused by the synergy of multiple substances in the soil system.
3.4 Change of pH and φh during Cr(VI) microbial reduction
The valence of chromium is related to the pH and φh values in the aqueous soil solution. Cr(III) derivatives have better stability than Cr(VI) in the environment, and they mainly form stable complexes with organic and inorganic ligands. In a neutral pH aqueous solution, Cr(III) tends to associate with OH- and form precipitates [45]. The change of pH in the reduction process of Cr(VI) is shown in Fig. 5. In Treatments II and IV, the change in soil pH was not obvious. The soil pH slightly decreased within 12 h for Treatments I and III. Thereafter, the pH values decreased sharply and then remained stable at 8.0.

Fig. 5 Change of pH values in reduction process of Cr(VI) under different treatments
Many factors influence the pH value of soil, such as the contents of carbon dioxide and salt, organic acids generated in the degradation process of organic matter and inorganic acids generated in the oxidization process of mineral substances in the soil [46]. As seen in Fig. 5, the change in pH values for Treatments II and IV supported the above statements. These findings suggested that pH was an important factor influencing bioremediation of the soil. The optimal pH value for indigenous microorganisms was alkaline condition in the range of 9.0 to 10.0 [9]. The activity of the indigenous microorganisms could also be influenced by other factors (e.g., soil organic matter; culture medium). Furthermore, the change in pH values in Treatment III was positively related to the reduction of Cr(VI), which maintained a balance in the indigenous microorganisms metabolic environment.
As shown in Fig. 6, the φh value only slightly increased for Treatments I, II and IV, and the concentration of Cr(VI) was also at high levels. The soil system was always in a high oxidation-reduction state during these experiments, relying solely on soil components (Treatments II and IV) and exogenous medium (Treatment I). In Treatment III, the φh value initially increased within 12 h and then decreased continuously. The increase in the oxidation-reduction potential of the soil system was related to the dissolution of the major ions in the soil. The results indicated that the relation between the change of φh and Cr(VI) reduction was clear. The reduction of Cr(VI) with the change in φh values played a stabilizing role in the soil bioremediation system. The φh value in the soil system stabilized until 42 h, which suggested that the reduction of Cr(VI) might be related to the other factors after 42 h.

Fig. 6 Change of φh in reduction process of Cr(VI) under different treatments
3.5 Change in concentrations Fe2+, Mn2+, 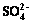 and
and 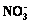
The effect of major ions in the soil on Cr(VI) reduction was complex. To elucidate the reduction sequence of Cr(VI) in the soil system, the samples extracted by Treatment Ⅲ were used to detect the concentrations of Fe2+, Mn2+, 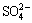 and
and 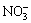 in the reduction process of Cr(VI).
in the reduction process of Cr(VI).
The concentration changes of Fe2+ and Mn2+ are shown in Fig. 7(a). The concentration of Fe2+ decreased slightly in the initial 30 h and thereafter increased rapidly and was maintained at a concentration of 4.4 mg/kg. At the same time, Mn2+ was not notable in the initial 30 h but then increased sharply and maintained at a stable concentration of approximately 0.278 mg/kg. The changes in the concentration curves of Fe2+ and Mn2+ were nearly identical. In addition, some reaction intermediates and major ion complexes in the soil (e.g., Mn2+, Fe2+) during the reduction stage enhanced the reduction rate of Cr(VI). The concentration of Cr(VI) decreased sharply with decreasing φh and pH values for Treatment Ⅲ at 30 h, which indicates that Fe2+ and Mn2+ had an additional effect on the reduction of Cr(VI). Moreover, the reduction of Fe3+ and Mn4+ occurred after the reduction process of Cr(VI) according to the standard electrode potential, and the reduction of Cr(VI) contributed to the dissolution of Fe2+ and Mn2+ in the bioremediation system.
As displayed in Fig. 7(b), the concentration of 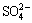 decreased slightly during the process of Cr(VI) reduction, which implied that
decreased slightly during the process of Cr(VI) reduction, which implied that 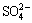 had little effect on the reduction of Cr(VI). The change of
had little effect on the reduction of Cr(VI). The change of 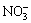 concentration was not obvious in the initial 12 h. After 12 h, it decreased sharply to an undetectable level at 18 h. As shown in Fig. 2, the change of Cr(VI) concentration in the soil was not notable in the initial 18 h. The concentration of Cr(VI) began to decrease substantially when the concentration of
concentration was not obvious in the initial 12 h. After 12 h, it decreased sharply to an undetectable level at 18 h. As shown in Fig. 2, the change of Cr(VI) concentration in the soil was not notable in the initial 18 h. The concentration of Cr(VI) began to decrease substantially when the concentration of 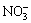 decreased to the minimum value. Therefore,
decreased to the minimum value. Therefore, 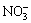 was reduced prior to the reduction of Cr(VI).
was reduced prior to the reduction of Cr(VI).

Fig. 7 Concentration change of Fe2+, Mn2+ (a), and 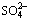 ,
,  (b) in bioremediation process of Cr(VI)
(b) in bioremediation process of Cr(VI)
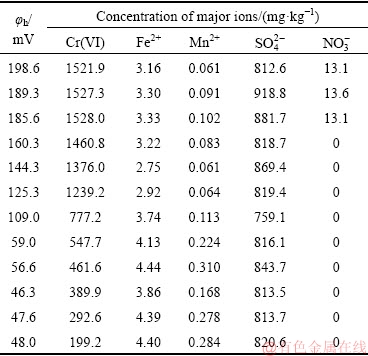
The concentration change of major ions in the soil during the process of Cr(VI) reduction with the decrease of φh values is shown in Table 2. 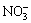 was reduced rapidly, when φh value was lower than 185.6 mV, and was reduced completely at the φh value of 160.3 mV. The change in the concentrations of Mn2+ and Fe2+ was not obvious when φh value was higher than 125.3 mV. However, the concentrations of Mn2+ and Fe2+ increased quickly as φh value decreased. The change in the concentration of
was reduced rapidly, when φh value was lower than 185.6 mV, and was reduced completely at the φh value of 160.3 mV. The change in the concentrations of Mn2+ and Fe2+ was not obvious when φh value was higher than 125.3 mV. However, the concentrations of Mn2+ and Fe2+ increased quickly as φh value decreased. The change in the concentration of 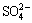 in the reduction process was not obvious. It was presumed that high-valent irons were reduced to Fe(II) during the reduction process of Cr(VI), then electrons were transferred to Cr(VI), and Cr(VI) was reduced to Cr(III). The reduction potentials of these major ions in soil were inconsistent with their standard reduction potential and were influenced by the complex effects of soil composition (such as pH value and organic matter) and the comprehensive effect of the Cr(VI) bioremediation system. Hence, the apparent reduction sequence of the major ions in the chromium- contaminated soil system was:
in the reduction process was not obvious. It was presumed that high-valent irons were reduced to Fe(II) during the reduction process of Cr(VI), then electrons were transferred to Cr(VI), and Cr(VI) was reduced to Cr(III). The reduction potentials of these major ions in soil were inconsistent with their standard reduction potential and were influenced by the complex effects of soil composition (such as pH value and organic matter) and the comprehensive effect of the Cr(VI) bioremediation system. Hence, the apparent reduction sequence of the major ions in the chromium- contaminated soil system was: 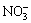 >Mn4+>Fe3+> Cr(VI)>
>Mn4+>Fe3+> Cr(VI)>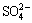 . Consequently, the reduction sequence of bioremediation by indigenous microorganisms was significant in the chromium-contaminated soil.
. Consequently, the reduction sequence of bioremediation by indigenous microorganisms was significant in the chromium-contaminated soil.
Table 2 Concentration change of major ions in chromium- contaminated soil system
4 Conclusions
(1) Indigenous microorganisms played an important role in Cr(VI) reduction in contaminated soil. Culture medium supplementation in soil significantly promoted Cr(VI) reduction.
(2) The concentration of Cr(VI) decreased from 1521.9 to 199.2 mg/kg within 66 h, and approximately 87% of Cr(VI) was reduced. The reduction process of Cr(VI) was divided into two phases significantly (Phase A and Phase B). In Phase A, Cr(VI) reduction was well described by the exponential equation kinetic model, which contributed to bioremediation. In Phase B, Cr(VI) reduction was fitted to the linear equation kinetic model, probably due to the synergy of multiple substances.
(3) The reaction model can accurately predict the reduction of Cr(VI) and guide the in-situ bioremediation of chromium-contaminated soil. The results imply that indigenous microorganisms have a potential application for in-situ bioremediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil.
References
[1] MADHAVI V, REDDY A V B, REDDY K G, MADHAVI G, PRASAD T N V K V. An overview on research trends in remediation of chromium [J]. Research Journal of Recent Sciences, 2013, 2(1): 71-83.
[2] DAI Yu, YANG Zhong-fa, ZHENG Yuan-ming. A reviewon the environmental behaviors and toxicity assessment of chromiumin soil-plant systems [J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(11): 3432-3440.
[3] WANG Yun-yan, CHAI Li-yuan, WANG Qing-wei, YANG Zhi-hui, DENG Rong. Electrochemical response to biomass of bacterial cells of Achromobacter sp. CH-1 growth [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(4): 932-938.
[4] CUMMINGS D E, FENDORF S, SINGH N, SANI R K, PEYTON B M, MAGNUSON T S. Reduction of Cr(VI) under acidic conditions by the facultative Fe(Ⅲ)-reducing bacterium Acidiphilium cryptum [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(1): 146-152.
[5] DHAL B, THATOI H, DAS N, PANDEY B D. Reduction of hexavalent chromium by Bacillus sp. isolated from chromite mine soils and characterization of reduced product [J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2010, 85: 1471-1479.
[6] ALVAREZ G S, FOGLIA M L, CAMPOROTONDI D E, TUTTOLOMONDO M V, DESIMONE M F, DIAZ L E. A functional material that combines the Cr(VI) reduction activity of Burkholderia sp. with the adsorbent capacity of sol–gel materials [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(17): 6359-6364.
[7] KARTHIK C, BARATHI S, PUGAZHENDHI A, RAMKUMAR V S, THI N B D, ARULSELVI P I. Evaluation of Cr(VI) reduction mechanism and removal by Cellulosimicrobium funkei strain AR8, a novel haloalkaliphilic bacterium [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 333: 42-53.
[8] ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Ying-ying, TANG Jie, MA Jiong. Characterization of reduction of hexavalent chromium by Exiguobacterium sp. MH3 [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2014, 20(5): 791-797.
[9] ZHU Wen-jie, YANG Zhi-hui, MA Ze-min, CHAI Li-yuan. Reduction of high concentrations of chromate by Leucobacter sp. CRB1 isolated from Changsha, China [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 24(7): 991-996.
[10] SHI Yan, CHAI Li-yuan, YANG Zhi-hui, JING Qing-xiu, CHEN Run-hua, CHEN Yue-hun. Identification and hexavalent chromium reduction characteristics of Pannonibacter phragmitetus [J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2012, 35(5): 843-850.
[11] WANG Yang-yang, YANG Zhi-hui, PENG Bing, CHAI Li-yuan, WU Bao-lin, WU Rui-ping. Biotreatment of chromite ore processing residue by Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013, 20(8): 5593-5602.
[12] WANG Yang-yang, PENG Bing, YANG Zhi-hui, TANG Chong-jian, CHEN Yue-hui, LIAO Qi, LIAO Ying-ping. Treatment of Cr(VI) contaminated water with Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 71(10): 4333-4339.
[13] WANG Yang-yang, PENG Bing, YANG Zhi-hui, CHAI Li-yuan, LIAO Qi, ZHANG Zhi, LI Chuang. Bacterial community dynamics during bioremediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil [J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2015, 85: 50-55.
[14] LIAO Ying-ping, MIN Xiao-bo, YANG Zhi-hui, CHAI Li-yuan, LIAO Qi, WU Bao-lin. Assessment of the stability of chromium in remedied soils by Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB and its risk to groundwater [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2014, 14(6): 1098-1106.
[15] WANG Yang-yang, CHAI Li-yuan, LIAO Qi, TANG Chong-jian, LIAO Ying-ping, PENG Bing, YANG Zhi-hui. Structural and genetic diversity of hexavalent chromium-resistant bacteria in contaminated soil [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2015, 33(3-4): 222-229.
[16] KANG Chun-xi, WU Ping-xiao, LI Li-ping, YU Lang-feng, RUAN Bo, GONG Bei-ni, ZHU Neng-wu. Cr(VI) reduction and Cr(III) immobilization by resting cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa CCTCC AB93066: Spectroscopic, microscopic, and mass balance analysis [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24(6): 5949-5963.
[17] LONG Dong-yan, TANG Xian-jin, CAI Kuan, CHEN Guang-cun, SHEN Chao-feng, SHI Ji-yan, CHEN Ling-gui, CHEN Ying-xu. Cr(VI) resistance and removal by indigenous bacteria isolated from chromium-contaminated soil [J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 23(8): 1123-1132.
[18] PANNEERSELVAM P, CHOPPALA G, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, BOLAN N. Potential of novel bacterial consortium for the remediation of chromium contamination [J]. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 2013, 224(12): 1-11.
[19] DAS S, MISHRA J, DAS S K, PANDEY S, RAO D S, CHAKRABORTY A, SUDARSHAN M, DAS N, THATOI H. Investigation on mechanism of Cr(VI) reduction and removal by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, a novel chromate tolerant bacterium isolated from chromite mine soil [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 96: 112-121.
[20] SAYEL H, BAHAFID W, JOUTEY N T, DERRAZ K, BENBRAHIM K F, KORAICHI S I, GHACHTOULI N E. Cr(VI) reduction by Enterococcus gallinarum isolated from tannery waste-contaminated soil [J]. Annals of Microbiology, 2011, 62(3): 1269-1277.
[21] LIAO Ying-ping, MIN Xiao-bo, YANG Zhi-hui, CHAI Li-yuan, ZHANG Shui-juan, WANG Yang-yang. Physicochemical and biological quality of soil in hexavalent chromium-contaminated soils as affected by chemical and microbial remediation [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(1): 379-388.
[22] JEYASINGH J, SOMASUNDARAM V, PHILIP L, BHALLAMUDI S M. Bioremediation of Cr(VI) contaminated soil/sludge: Experimental studies and development of a management model [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 160(2): 556-564.
[23] JIANG Wen-jun, CAI Quan, XU Wei, YANG Ming-wei, CAI Yong, DIONYSIOU D D, O'SHEA K E. Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction by humic acid coated on magnetite [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(14): 8078-8085.
[24] QIAN Jin, ZHOU Jun-mei, WANG Lian-lian, WEI Li, LI Qin, WANG Dong-bo, WANG Qi-lin. Direct Cr(VI) bio-reduction with organics as electron donor by anaerobic sludge [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 309: 330-338.
[25] WILLIAMS A G B, SCHERER M M. Kinetics of Cr(VI) reduction by carbonate green rust [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(17): 3488-3494.
[26] CHEN Na, LAN Ye-qing, WANG Bo, MAO Jing-dong. Reduction of Cr(VI) by organic acids in the presence of Al(III) [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 260: 150-156.
[27] LI Dong, JI Guo-zhu, HU Jing, HU Si-yang, YUAN Xing-dong. Remediation strategy and electrochemistry flushing & reduction technology for real Cr(VI)-contaminated soils [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 1281-1288.
[28] ALOWITZ M J, SCHERER M M. Kinetics of nitrate, nitrite, and Cr(VI) reduction by iron metal [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(3): 299-306.
[29] LI De-fu, LI Xin, XIE Yi-fei. Removal of heavy metals and arsenic by microorganisms: Mechanism and techniques of compound sulfate reducing bacteria [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2011. (in Chinese)
[30] HAN X, WONG Y S, WONG M H, TAM N F Y. Biosorption and bioreduction of Cr(VI) by a microalgal isolate, Chlorella miniata [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 146: 65-72.
[31] RAASHID S, RIZVI M A, KHAN B. Coordination inspired redox behaviour of Fe(II) and Co(II) explored for simultaneous iron oxidation state analysis [J]. Journal of Pharmacy Research, 2012, 5(5): 2715-2720.
[32] CHAI Li-yuan, DING Chun-lian, TANG Chong-jian, YANG Wei-chun, YANG Zhi-hui, WANG Yang-yang, LIAO Qi, LI Jia-wei. Discerning three novel chromate reduce and transport genes of highly efficient Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB: From genome to gene and protein [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 162: 139-146.
[33] MIN Xiao-bo, WANG Yang-yang, CHAI Li-yuan, YANG Zhi-hui, LIAO Qi. High-resolution analyses reveal structural diversity patterns of microbial communities in chromite ore processing residue (COPR) contaminated soils [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 183: 266-276.
[34] SU Chun-ming, LUDWIG R D. Treatment of hexavalent chromium in chromite ore processing solid waste using a mixed reductant solution of ferrous sulfate and sodium dithionite [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(16): 6208-6216.
[35] GHEJU M, BALCU I, VANCEA C. An investigation of Cr(VI) removal with metallic iron in the co-presence of sand and/or MnO2 [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 170: 145-151.
[36] PETTINE M, TONNINA D, MILLERO F J. Chromium (VI) reduction by sulphur (IV) in aqueous solutions [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2006, 99(1-4): 31-41.
[37] LI Chen, LAN Ye-qing, DENG Bao-lin. Catalysis of manganese (II) on chromium (VI) reduction by citrate [J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(3): 318-323.
[38] LI Yun-yi, LIANG Jia-liang, HE Xiao, ZHANG Li, LIU Yang-sheng. Kinetics and mechanisms of amorphous FeS2 induced Cr(VI) reduction [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 320: 216-225.
[39] LV Jin-fang, TONG Xiong, ZHENG Yong-xing, XIE Xian, HUANG Ling-yun. Reduction of Cr(VI) with a relative high concentration using different kinds of zero-valent iron powders: Focusing on effect of carbon content and structure on reducibility [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25: 2119-2130.
[40] WU Ping-xiao, LI Shu-zhen, JU Li-ting, ZHU Neng-wu, WU Jin-hua, LI Ping, DANG Zhi. Mechanism of the reduction of hexavalent chromium by organo-montmorillonite supported iron nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 219-220: 283-288.
[41] HAN Chong, JIAO Ya-nan, WU Qian-qian, YANG Wang-jin, YANG He, XUE Xiang-xin. Kinetics and mechanism of hexavalent chromium removal by basic oxygen furnace slag [J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 2016, 46: 63-71. (in Chinese)
[42] HUANG W H, DONG C D, CHEN C W, SURAMPALLI R Y, KAO C M. Application of sulfate reduction mechanisms for the simultaneous bioremediation of toluene and copper contaminated groundwater [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 124: 215-222.
[43] GONG Bei-ni, WU Ping-xiao, HUANG Zhu-jian, LI Yue-wu, DANG Zhi, RUAN Bo, KANG Chun-xi, ZHU Neng-wu. Enhanced degradation of phenol by Sphingomonas sp. GY2B with resistance towards suboptimal environment through adsorption on kaolinite [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 148: 388-394.
[44] RUAN Bo, WU Ping-xiao, CHEN Mei-qing, LAI Xiao-lin, CHEN Li-ya, YU Lang-feng, GONG Bei-ni, KANG Chun-xi, DANG Zhi, SHI Zhen-qing, LIU Ze-hua. Immobilization of Sphingomonas sp. GY2B in polyvinyl alcohol-alginate-kaolin beads for efficient degradation of phenol against unfavorable environmental factors [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 162: 103-111.
[45] BARRERA-DIAZ C E, LUGO-LUGO V, BILYEU B. A review of chemical, electrochemical and biological methods for aqueous Cr(VI) reduction [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 223-224: 1-12.
[46] THOMAS G W. Methods of soil analysis [M]. Madison: Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy, 1996: 475-490.
苏长青1,李立清1,3,杨志辉2,3,柴立元2,3,廖 骐2,3,石 岩2,3,黎佳未2
1. 中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083;
3.中南大学 国家重金属污染防治工程技术研究中心,长沙 410083
摘 要:生物修复是一种环境友好型的修复技术,在铬污染土壤修复中发挥着越来越重要的作用。为了研究土著微生物对土壤中Cr(VI)的还原过程,在生物反应器里进行一系列微生物好氧培养实验。结果显示:在土著微生物存在情况下,在铬污染土壤中添加培养基使Cr(VI)浓度在66 h内从1521.9降低至199.2 mg/kg,而灭菌土壤中Cr(VI)浓度稍微降低,表明Cr(VI)的还原归因于土著微生物的作用。在微生物修复过程中,Cr(VI)的生物还原发生在  、Mn4+和Fe3+的还原后,而先于
、Mn4+和Fe3+的还原后,而先于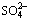 的还原。Cr(VI)还原过程可分为两个阶段,分别以生物还原作用的指数方程模型和主要离子综合效应的线性方程模型为特征。土著Cr(VI)还原菌在Cr(VI)污染土壤的原位修复中具有潜在的应用前景。
的还原。Cr(VI)还原过程可分为两个阶段,分别以生物还原作用的指数方程模型和主要离子综合效应的线性方程模型为特征。土著Cr(VI)还原菌在Cr(VI)污染土壤的原位修复中具有潜在的应用前景。
关键词:Cr(VI)污染土壤;土著微生物;微生物修复;动力学
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (2018SK2044) supported by the Innovation Program of Science & Technology of Hunan Province, China; Project (51304250) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Zhi-hui YANG; Tel: +86-731-88830875; E-mail: yangzh@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65037-5

