R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2玻璃的组成与其热膨胀系数的关系
肖卓豪, 卢安贤
(中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要: 采用传统熔体冷却方法制得R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2多元系统玻璃(R为碱金属元素,M为碱土金属元素),玻璃组成(质量分数)为:SiO2,55.0%~65.0%;MgO,0~15.2%;CaO,0~15.2%;SrO,0~15.2%;BaO,0~15.2%;Na2O,0~15.6%;K2O,0~15.6%。通过比较不同组成玻璃的热膨胀系数,讨论该体系玻璃组成与其热膨胀系数之间的关系。研究结果表明:当玻璃中碱金属氧化物的质量分数大于17.8%时,玻璃的热膨胀系数迅速增大;对于具有相同含量的不同碱土金属的玻璃,其热膨胀系数随着碱土金属原子半径的增大而增大;当2种以上不同碱土金属共存时,热膨胀系数呈现明显的混合碱效应;当Li,Na和K3种碱金属共存时,玻璃的热膨胀系数与组成的关系曲线出现2个极小点,且出现负的混合碱效应。
关键词: 玻璃; 热膨胀系数; 混合碱效应
中图分类号:TB321 文献标识码:A 文章编号: 1672-7207(2005)04-0566-05
Relationship between thermal expansion coefficient
and composition of R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2 system glass
XIAO Zhuo-hao, LU An-xian
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2 system glass was prepared by conventional melt quenching technology(R stands for alkali-earth element, M stands for alkali-metal element) and the composition range(in mass fraction) of the glass is as follows: SiO2, 55.0%~65.0%; MgO, 0~15.2%; CaO, 0~15.2%; SrO, 0~15.2%; BaO, 0~15.2%; Na2O, 0~15.6%; K2O, 0~15.6%. The relationship between the composition and the thermal expansion coefficient of the glass was investigated by comparing the thermal expansion coefficients of the glass with different chemical compositions. The results show that the thermal expansion coefficient of the glass increases sharply when the mass fraction of alkali-metal oxide is more than 17.8%; when introducing different kinds but the same quantity of alkali-earth metal oxide, the thermal expansion coefficient of the glass increases obviously with increasing the radius of alkali-earth metal ions; the mixed alkali effect appears when the glass contains a few kinds of alkali-earth metal oxides; when K+, Na+ and Li+ exist simultaneously in the glass, the two minimum peaks and complex mixed alkali effect can be observed from the composition-thermal expansion coefficient curve.
Key words: glass; thermal expansion coefficient; mixed alkali effect
R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2(M代表碱土金属,R代表碱金属)系统玻璃属硅酸盐玻璃,它是玻璃工业中用途最广泛、作用最重要的玻璃体系之一,广泛应用于瓶罐玻璃、器皿玻璃、平板玻璃、电真空玻璃以及光学玻璃等领域[1-3]。在生产实践中,不同用途的玻璃有不同的性能要求,热膨胀系数是其重要性能之一。比如在电真空领域,往往需要将不同的玻璃、玻璃与金属、玻璃与陶瓷结合,如果其热膨胀系数Δα超过5×10-7 K-1,当温度低于玻璃化温度Tg时,封接点处在应力作用下将发生开裂,导致封接件被破坏[4]。所以,在电真空领域,玻璃的热膨胀系数是决定其使用性能的关键。此外,热膨胀系数对玻璃的成形、退火、钢化以及玻璃的热稳定性都具有极其重要的影响。玻璃的热膨胀系数主要由其化学组成决定,因此,可通过测定热膨胀系数对玻璃生产进行控制[5]。尽管R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2玻璃是使用最早的玻璃之一,但是,由于该玻璃组元多、成分复杂,且不同碱金属与不同碱土金属之间存在混合碱效应[6](复离子效应),所以,人们对该系统玻璃热膨胀系数的研究往往局限于几种简单的组成,而对多组元复杂系统玻璃的研究极少。为此,作者对该系统玻璃组成对热膨胀系数的影响进行研究。
1 实 验
1.1 基础玻璃成分设计
以R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2系统为基础组分,设计了21个玻璃配方(见表1)。根据S.English[7]等的研究结果,用Al2O3逐渐取代SiO2时,玻璃的膨胀系数无明显的变化;此外,G.Gavriliu[8]由实验得出结论:玻璃中Al2O3对热膨胀系数的影响比Ca和Zn等二价金属氧化物对热膨胀系统的影响都要小。为了简化实验,本实验中保持Al2O3含量不变。
1.2 玻璃制备
原料经孔径为0.149 mm筛子过筛,按表1所示数据准确称量各物质,混合均匀后转入刚玉坩锅中,将坩锅置于硅钼棒电炉中于1420 ℃熔制并保温3 h,待玻璃熔化均匀后将其倒入预热的铁模中成型,随后放入马弗炉中于560 ℃退火,保温1 h后断电,样品随炉冷却。
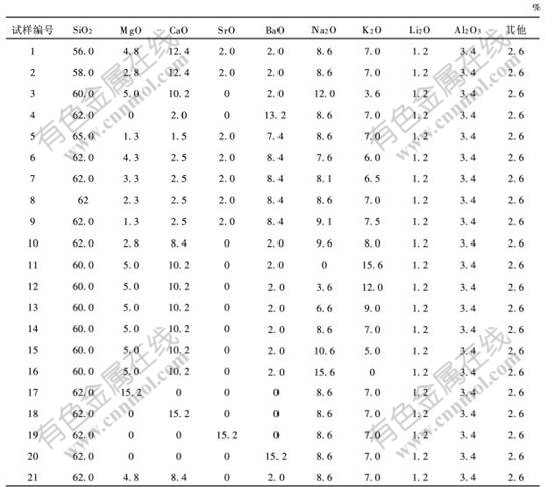
表 1 R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2系统玻璃的化学物组成
Table 1 Chemical compositions of glasses of R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2 system
1.3 性能测试
将无气泡和明显条纹的玻璃切割成尺寸为5 mm×5 mm×20 mm(宽×厚×长)的块状试样,并将其边长为5 mm的2个端面磨成平行面,然后对该2个面进行抛光处理。在TAS100型膨胀仪上测定其热膨胀系数。测试条件为:升温速率为10 ℃/min;热膨胀系数测试的温度范围为25~700 ℃。
2 结果与讨论
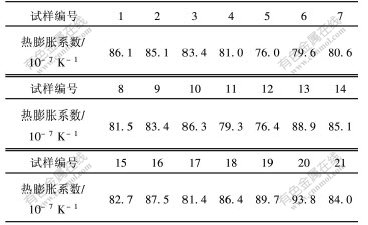
表2所示为表1中21个玻璃试样在温度为25~300 ℃的热膨胀系数。
表 2 试样的热膨胀系数
Table 2 Thermal expansion coefficients of glasses samples
2.1 热膨胀系数与SiO2含量的关系
在玻璃中除了网络形成体以外,碱金属含量对热膨胀系数的影响最大。因此,为了比较热膨胀系数与SiO2含量的关系,分别取试样1~5共5个试样进行分析。由表1可知,这5个试样中SiO2质量分数由56.0%逐渐增加到65.0%,而总碱金属的质量分数均为16.8%。
图1所示为玻璃的热膨胀系数与SiO2含量的关系曲线。可见,随着玻璃中SiO2含量的增加,其热膨胀系数降低,这主要是因为随着SiO2含量的增加,玻璃结构中桥氧数目增多,硅氧键的键强增大,[SiO4]之间的连接程度增强,导致玻璃网络结构更紧凑;同时,玻璃在热振动中的振幅及热振动的位移减小,使热膨胀系数下降。
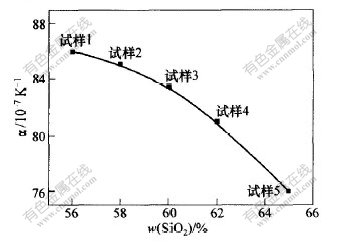
图 1 玻璃的热膨胀系数与SiO2含量的关系
Fig. 1 Relationship between thermal expansion coefficient and content of SiO2 in glass
2.2 热膨胀系数与碱金属含量关系
图2所示为试样6~10共5个玻璃试样的热膨胀系数与碱金属含量的变化情况。此5个试样中SiO2的质量分数均为62%,其碱金属的质量分数由14.8%增加到18.8%(见表1),各试样的碱金属氧化物增量为1%,并且在增加过程中保持氧化钠与氧化钾含量的比例不变,以防止因混合碱效应而引起数值突变。
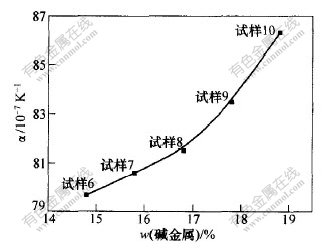
图 2 玻璃的热膨胀系数与碱金属含量关系
Fig. 2 Relationship between thermal expansion coefficient and content of alkali metal in glass
由图2可以看出,在网络形成体含量不变的情况下,玻璃的热膨胀系数随着碱金属含量的增加而增加;当碱金属含量增加到17.8%后,热膨胀系数急剧增大。这是因为随着碱金属氧化物引入量的增加,碱土金属氧化物引入量减少,前者断键作用较强,使玻璃结构中非桥氧数目增多,而导致硅氧键断裂,破坏了玻璃网络结构的完整性;另一方面,由于碱金属氧化物的键能较低,抵抗热振动的能力较差,随温度升高,热膨胀系数增加较快[3,9]。
2.3 多种碱金属氧化物对热膨胀系数的影响
分别对试样3和试样11~16共7个试样进行分析。从表1可知,此7个试样碱金属总的质量分数均为16.8%,且其中Li2O含量均为1.2%。以氧化钠含量与总碱金属氧化物含量的比值为横坐标,热膨胀系数为纵坐标,得到热膨胀系数随组成变化的关系图如图3所示。
由图3可知,Li2O的含量较低时,加入相同含量的K2O比加入相同含量的Na2O对玻璃热膨胀系数的影响小;在含少量Li2O的三元碱金属氧化物共存时,改变Na2O与K2O的比例,热膨胀系数出现复杂的混合碱效应,其曲线出现2个极小值;当氧化钠含量与总碱金属氧化物的比值约为0.4时,曲线出现极大值,此时的热膨胀系数比单碱时的热膨胀系数大(孙玉珍等[10]称该现象为负的混合碱效应)。
人们提出了多种不同的观点以解释混合碱效应,但至今尚无统一的看法,其中影响较大的有不同大小碱金属离子的相互阻挡论,该观点认为异类碱金属离子的排斥力小于同类碱金属离子而增大了扩散活化能。此外,还有近年来提出的电动力学交互作用论等。然而,每种观点都是基于异种碱金属离子共存影响离子迁移能力的思想[11,12]。作者认为,组成与热膨胀系数关系中的混合碱效应可能是由于多种碱金属氧化物共存时,削弱了碱金属氧化物提供游离氧的能力,使玻璃网络结构破坏程度减少。
有关二元碱金属的混合碱效应已有较多研究。对于其热膨胀系数出现极小值的现象,已有较深入的理论分析[13-15]。然而,对于三元碱金属混合效应所引起的极大值现象,尽管也有少量报道,但很少对其机理进行分析[10,15]。
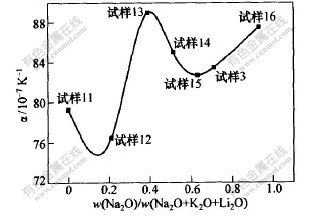
图 3 混合碱对玻璃热膨胀系数的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of content of mixed alkalis on thermal expansion coefficient of glass
2.4 热膨胀系数与碱土金属氧化物含量的关系
取含量相同而种类不同的碱土金属4个玻璃试样(试样17~20)和在同一个试样中含有多种碱土金属的3个玻璃试样(试样21,4和8)进行对比分析。试样4、试样8、试样17~21共7个玻璃试样。由表1可知,前4个试样均只含1种碱土金属氧化物,后3个试样含有2~3种碱土金属氧化物,且每个试样碱土金属氧化物的含量均为15.2%。
图4所示是上述7个试样的热膨胀系数与碱土金属氧化物种类的关系。可见,试样17~20的热膨胀系数依次增加,试样21的热膨胀系数比试样18的热膨胀系数明显减小,试样4和8的热膨胀系数比试样20的热膨胀系数小得多。可以认为,不同碱土金属对玻璃热膨胀系数的影响随其离子半径的增大而增大,即MgO的影响最小,BaO的影响最大。这主要是因为离子半径愈大,断键作用愈强,使网络结构变得更疏松,从而使其热膨胀系数增大。
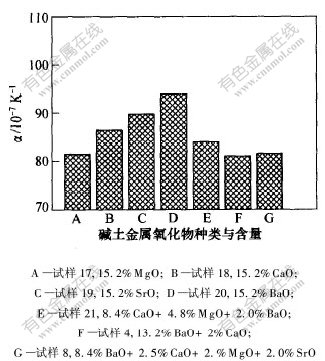
图 4 热膨胀系数与碱土金属氧化物种类及含量的关系
Fig. 4 Relationship between thermal expansion coefficient of glass and contents of different alkali-earth metal oxides
对于试样4,8及21,当用另一种或2种碱土金属氧化物部分代替原有的碱土金属氧化物时,玻璃的热膨胀系数明显降低。尽管在相同情况下,引入BaO时对玻璃热膨胀系数影响最大,然而,将2%的BaO替换为同量CaO时,热膨胀系数从93.8×10-7 K-1降低到81.0×10-7 K-1。这是由于多种碱土金属氧化物共存时削弱了碱土金属氧化物提供游离氧的能力,使玻璃网络结构破坏程度减少。因此,碱土金属对玻璃热膨胀系数的影响为:金属离子半径越大,玻璃热膨胀系数越大;当用另一种或几种碱土金属氧化物部分代替原有的碱土金属氧化物时,热膨胀系数均有不同程度的降低,即出现明显的混合碱效应;对于多种碱土金属共存所产生的混合碱效应,二元碱的混合碱效应最显著,当再增加其他种类的碱土金属氧化物时,混合碱效应有所减弱。
3 结 论
a. R2O-MO-Al2O3-SiO2多元系统玻璃中的质量分数碱金属氧化物含量增加到17.8%以上时,玻璃的热膨胀系数迅速增加;当存在3种碱金属氧化物时,在含少量Li2O的情况下,热膨胀系数曲线图上出现2个极小值,同时出现负的混合碱效应。
b. 碱土金属氧化物对玻璃热膨胀系数的影响随其离子半径增大而增大。
c. 多种碱土金属氧化物在玻璃中共存时,玻璃的热膨胀系数随组成的变化也出现类似于碱金属氧化物的混合碱效应;且当存在2种碱土金属离子时,这种效应最显著,增加碱土金属离子的种数后,由混合碱效应导致的膨胀系数降低的趋势减弱。
参考文献:
[1]西北轻工业学院.玻璃工艺学[M].北京:中国轻工业出版社,1997.
Northwestern Light Industry College. The technique for glass[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 1997.
[2]卢安贤.无机非金属材料导论[M].长沙:中南大学出版社,2004.
LU An-xian. Introduction to inorganic non-metal materials[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2004.
[3]Eldin F M E, Alaily N A. Electrical conductivity of some alkali silicate glasses[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 1998, 52(2): 175-179.
[4]马英仁.封接玻璃: 对玻璃的要求及适于封接的玻璃[J].玻璃与搪瓷, 1992, 20(4): 59-65.
MA Ying-ren. Sealing glass: the requests for glass and the feasible sealing glass[J]. Journal of Glass and Porcelain Enamel, 1992, 20(4): 59-65.
[5]Peterson M I, Tien Y T. Thermal expansion and glass transition temperatures of Y-Mg-S-A-O-N glasses[J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 1995, 78(1): 1977-1979.
[6]杨如玺, 唐多强, 张涛华, 等. 三元玻璃的复离子效应[J]. 天津大学学报,1996,29(3):402-406.
YANG Yu-xi, TANG Duo-qiang, ZHANG Tao-hua. The compound ionic effect of ternary glass[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 1996, 29(3): 402-406.
[7]English S, Hodkin W F, Turner S E W. Further investigation of the influence of alumina on the properties of glass[J]. J Soc Glass Technol, 1974(8):173-182.
[8]Gavriliu G. Thermal expansion and characteristic points of Na2O-SiO2 glass with added oxides[J]. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2002,22(8): 1375-1379.
[9]Greaves G N. Structural studies of the mixed alkali effect in disilicate glasses[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1998, 105(1-4): 243-248.
[10]孙玉珍, 苏友安, 王北辰. 碱土氧化物对玻璃中混合碱效应的影响[J]. 特种玻璃, 1989, 6(1): 27-31.
SUN Ru-zhen, SU You-an, WANG Bei-chen. Influence of alkali-earth oxide on mixed alkali effect of glass[J]. Special Type Glass, 1989, 6(1): 27-31.
[11]Philipp M. Towards a theory for the mixed alkali effect in glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1999, 255(1): 35-46.
[12]J.扎齐斯基.材料科学与技术丛书(第9卷):玻璃与非晶态材料[M]. 干福熹,译. 北京:科学出版社,2001.
Zarzycki J. Material science and technology (Vol(9)): glass and amorphous materials[M]. GAN Fu-xi translates. Beijing: Science Press, 2001.
[13]Minoru T. The mixed alkali effect and thermodynamic state of glasses[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1998, 105(1-4): 249-255.
[14]Kim K D, Lee S H. Viscosity behavior and mixed alkali effect of alkali aluminosilicate glass melts[J]. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 1997, 105(1226): 827-832.
[15]Swenson J, Adams S. Mixed alkali effect in glasses[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 90(15): 1-4.
收稿日期:2004-11-15
作者简介:肖卓豪(1978-),男,湖南隆回人,博士研究生,从事无机非金属材料研究
论文联系人: 肖卓豪,男,博士研究生; 电话: 0731-8830351; E-mail: xiaozhuohao@126.com