DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-37572
TiB2含量对TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料微观组织与力学性能的影响
李京京1, 2,李晨光1, 2,梁加淼1, 2,鞠 江1, 2,张 震1, 2,王朦朦1, 2,周 阳1, 2,王 俊1, 2
(1. 上海交通大学 材料科学与工程学院,凝固科学与技术研究所,上海 200240;
2. 上海市先进高温材料及其精密成型重点实验室,上海 200240)
摘 要:利用高能球磨结合放电等离子体烧结和热挤压工艺,制备出TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料。通过X射线衍射、扫描电镜和透射电镜表征以及拉伸力学性能测试,研究TiB2颗粒添加量对复合材料微观组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明:高能球磨诱导TiB2陶瓷颗粒形貌从多边形转变为近球形;随着TiB2含量从2%增加到10%(体积分数),铝基体晶粒逐渐细化,析出相含量减少,复合材料抗拉强度、屈服强度和弹性模量分别由381 MPa、231 MPa和78 GPa增加到679 MPa、645 MPa和96 GPa,伸长率从5.2%下降到1.0%;细晶强化和弥散颗粒强化为复合材料的主要强化机制。
关键词:铝基复合材料;TiB2增强相;粉末冶金;微观组织;力学性能
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-06-1221-09 中图分类号:TB331 文献标志码:A
近年来,随着航空、航天、国防及交通等现代化“高、精、尖”领域的飞速发展,对材料的综合性能提出了越来越高的要求[1-3],提高材料的比强度和比模量对于实现航空航天结构轻量化设计具有重要意义,而传统铝合金材料很难满足这一需求[4]。铝基复合材料的出现为解决这一挑战提供了新的思路。7系铝合金是目前已成功实现商业化应用的各种变形铝合金中强度最高的一类,具有密度低、耐腐蚀性能和抗损伤性能良好、易加工等优点,是较为理想的基体材料[5-7]。TiB2陶瓷颗粒具有强度高、弹性模量高、耐磨性好、热膨胀系数小等优异的综合性能,可作为理想的增强相材料[8-9]。目前,研究者主要通过原位自生TiB2颗粒来调控铝基复合材料显微组织和力学性能。CHEN等[10]通过混合盐法制备了TiB2/7055基复合材料。结果表明,与基体相比,10% TiB2/7055(质量分数)复合材料的弹性模量增加16%,屈服强度增加8%,抗拉强度增加6%。张建平等[11]同样采用混合盐法制备亚微米TiB2/7055铝基复合材料,并对其微观组织与力学性能进行研究发现,TiB2含量为12%的7055复合材料,抗拉强度达到718 MPa,屈服强度达到679 MPa,弹性模量达到86 GPa。但混合盐法目前的合成温度较高,副反应难以控制。粉末冶金工艺由于具有界面反应较易控制[12-14],避免成分偏析,增强体分布均匀等优点,引起人们广泛关注。徐世娇等[15]采用高能球磨法制备了不同体积分数的碳纳米管(CNT)与Al粉的混合粉末,用粉末冶金工艺制备了CNT/A1复合材料,拉伸实验表明,CNT体积分数为1.5%时,力学性能达到了最高值,屈服强度相对于纯A1基体提高了53.6%。SADEGHIAN等[16]以纯铝、纯钛和纯硼为原料,采用反应机械合金化的方法制备出Al-20% TiB2纳米复合材料,研究表明,复合材料屈服强度为480 MPa,抗拉强度为540 MPa,远远高于其他工艺制备的同类复合材料。
本研究选用高强度7系Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金为基体材料,以高弹性模量的亚微米级TiB2陶瓷颗粒为增强相,采用粉末冶金工艺制备出具有较高力学性能的铝基复合材料样品,研究TiB2颗粒含量对复合材料微观组织及力学性能影响。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
本研究所用铝合金基体原料为气雾化Al-Zn-Mg-Cu粉末,电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP)分析结果显示,其化学成分为Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu(质量分数,%),如表1所列。此外,粉末中还有少量Fe,Mn,Ti和Cr杂质元素存在。扫描电镜分析结果表明Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu粉末呈球形,粒径在3~8 μm之间,如图1(a)所示。图1(b)所示为Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg- 1.32Cu粉末的XRD谱,显示有面心立方结构的Al衍射峰出现。图1(c)所示为TiB2颗粒扫描电镜形貌像,可以看出,TiB2颗粒呈多边形,粒径在400~800 nm之间。XRD分析结果显示,TiB2为密排六方结构,并且粉末中没有其他杂质相出现,如图1(d)所示。
1.2 材料制备
材料的制备过程包括:高能球磨、放电等离子烧结(SPS)和热挤压。首先分别配制TiB2颗粒含量为2%、5%、10%(体积分数)的混合粉末,然后将混合好的粉末在行星式球磨机中球磨,球磨机转速为500 r/min,球磨时间为12 h;将球磨好的复合粉末以500 ℃/50 MPa的参数进行SPS烧结,最后将SPS烧结样品进行热挤压,挤压温度为500 ℃,挤压比为9:1[17]。材料制备流程如图2所示。
表1 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu铝合金化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy (mass fraction, %)

1.3 样品表征
本研究采用D8 DaVinci型多功能X射线衍射仪对粉末材料进行物相分析,扫描速度为5 (°)/min,10°~90°耦合连续扫描,测量步长为0.02°;采用NOVA Nano-SEM 230型低真空扫描电子显微镜和JSM-7600F型场发射扫描电子显微镜进行形貌观察和EDS能谱分析;借助JEM-2100F型场发射透射电子显微镜进行微观结构观察;利用Z100 万能材料试验机进行拉伸性能测试,拉伸试验样品通过线切割切成片状“哑铃型”试样,每组样品测量3个试样,然后取平均值,拉伸试样详细尺寸如图3所示。

图1 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金和TiB2粉末形貌及XRD谱
Fig. 1 Morphologies and corresponding XRD patterns of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy((a), (b)) and TiB2 powder((c), (d))

图2 材料制备流程示意图
Fig. 2 Flow chart of experiment
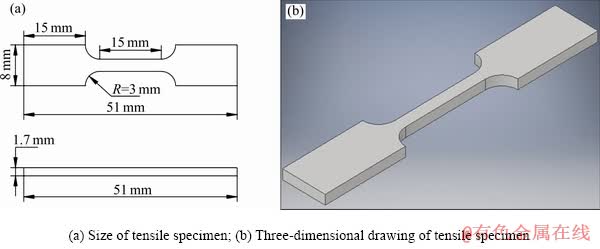
图3 拉伸试样示意图
Fig. 3 Schematic diagrams of tensile samples
2 结果和讨论
图4所示为TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料的XRD谱。对照PDF卡片分析发现,在2θ为38.5°、44.8°、65.3°、78.5°和82.7°的位置有面心立方Al的衍射峰出现,在2θ为27.7°、34.2°、57.2°、61.33°、68.5°和88.7°的位置有密排六方TiB2的衍射峰出现。进一步观察发现,随着TiB2含量增加,TiB2衍射峰相对强度增加,并且Al衍射峰出现宽化,表明铝合金基体晶粒发生细化。此外,并未发现MgZn2析出相衍射峰出现。
图5所示为TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料挤压棒横截面SEM形貌及其对应的TiB2颗粒尺寸分布。如图5(a)~(c)所示,当添加的TiB2体积分数为2%时,颗粒出现了一定程度的偏聚。随着TiB2含量的增加,颗粒分布的均匀性增加。基于Nano Measurer软件对三种样品中TiB2颗粒尺寸统计结果,绘制TiB2颗粒尺寸分布图,如图5(a′)~(c′)所示。可以看出TiB2颗粒尺寸主要分布在0.2~1.4 μm之间,其平均尺寸分别为537 nm、569 nm和599 nm。这与原始TiB2颗粒尺寸相一致(如图1(c)所示),表明TiB2颗粒在放电等离子体烧结和热挤压过程中并未发生明显长大。
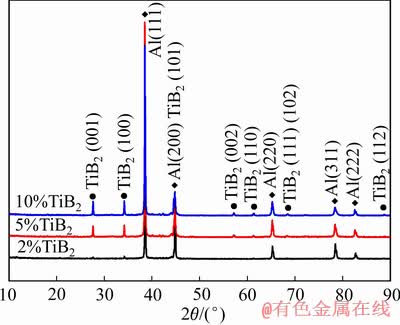
图4 TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料挤压棒XRD谱
Fig. 4 X-ray diffraction pattern of extruded TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu composite rods

图5 TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料挤压棒截面SEM像及其对应的TiB2颗粒尺寸分布
Fig. 5 Cross-section SEM images((a), (b), (c)) of extruded TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu composite rods and corresponding size distribution((a′), (b′), (c) ′) of TiB2 particles
图6所示为TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料横截面高倍SEM像及其对应的Al和Ti元素EDS面扫图像。如图6(a)~(c)所示,可以看出,多边形TiB2颗粒尖角消失,颗粒表面相对平滑,呈近球形。这可能是由于高能球磨过程中较高的能量导致TiB2颗粒尖角溶解所致。图6(a″)~(c″)为Ti元素EDS面扫图像,显示TiB2颗粒附近铝基体中有钛元素分布,再次证实了高能球磨过程中部分TiB2颗粒发生溶解,进入到铝基体中。

图6 TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料横截面高倍SEM像及其对应的Al和Ti元素EDS面扫图像
Fig.6 High magnification SEM images((a), (b), (c)) of cross-section of TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu composites and corresponding EDS mapping of Al((a′), (b′), (c′)) and Ti((a″), (b″), (c″)) elements
图7所示为不同TiB2颗粒含量的复合材料TEM明场像。可以看出TiB2颗粒主要分布在铝合金基体晶界附近。随着TiB2添加量的增加,基体晶粒尺寸逐渐减小,如图7(a)~(c)所示。同时,对比图7(a′)~(c′)可以看出,随着TiB2颗粒含量增加,晶内析出相数量明显减少,表明TiB2颗粒的添加对MgZn2析出相的形成具有一定的抑制作用。这可能是由于随着TiB2颗粒含量增加,复合材料晶界以及Al/TiB2界面密度增加,系统自由能升高,导致热机械固结过程中Mg、Zn溶质原子易向晶界和界面偏聚,晶内溶质原子浓度下降,降低了析出相形核和生长的化学驱动力,从而导致析出密度下降。同时还可以发现,在铝合金基体晶粒内部有位错出现,这可能是由于热挤压导致晶粒发生塑性变形的结果,位错的出现可以为析出相提供形核质点,促进析出相异质形核和生长。
图8所示为TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料挤压棒样品拉伸工程应力-应变曲线,详细拉伸性能数据如表2所列。可以看出,随着TiB2颗粒含量(体积分数)由2%增加到5%,复合材料屈服强度从231 MPa增加到516 MPa,抗拉强度从381 MPa增加到585 MPa,伸长率从5.4%下降到1.4%。进一步增加TiB2颗粒含量到10%,材料屈服强度和抗拉强度分别增加到645 MPa和679 MPa,伸长率进一步下降到1.0%。同时,随着TiB2颗粒体积分数增加,复合材料弹性模量有较大提升,从78 GPa逐渐增大到96 GPa。以上结果表明,添加TiB2颗粒对材料强度和弹性模量均有明显的提升作用。
本研究中复合材料强度增加主要是由于铝合金基体晶粒细化导致的晶界强化,以及TiB2颗粒添加导致的第二相颗粒强化。晶界强化可以由霍尔佩奇公式[18-19]表示:
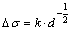 (1)
(1)
式中: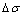 代表材料的屈服极限;k是常数;d是晶粒平均直径。由霍尔佩奇公式可知,材料强度与晶粒尺寸成反比关系。
代表材料的屈服极限;k是常数;d是晶粒平均直径。由霍尔佩奇公式可知,材料强度与晶粒尺寸成反比关系。
第二相颗粒强化由奥罗万公式[20-22]表示:
 (2)
(2)
式中: 是奥罗万强化引起的屈服强度;m是泰勒因子;G是剪切模量;b是伯氏矢量;
是奥罗万强化引起的屈服强度;m是泰勒因子;G是剪切模量;b是伯氏矢量; 是颗粒平均尺寸;
是颗粒平均尺寸; 是颗粒间距,表达式为
是颗粒间距,表达式为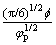 ;
;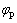 是颗粒体积分数。由奥罗万公式可知,材料强度与第二相颗粒含量成正比。本研究中随着TiB2颗粒添加量增加,铝合金基体晶粒逐渐细化,两种强化机制对材料强度贡献增加,这与拉伸试验结果一致。
是颗粒体积分数。由奥罗万公式可知,材料强度与第二相颗粒含量成正比。本研究中随着TiB2颗粒添加量增加,铝合金基体晶粒逐渐细化,两种强化机制对材料强度贡献增加,这与拉伸试验结果一致。

图7 TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料样品TEM明场像
Fig. 7 TEM bright field images of TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu composites
根据混合法制可知,复合材料理论弹性模量可通
过以下公式计算[23-24]:
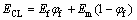 (3)
(3)
式中:ECL是复合材料的模量;Ef和Em是基体和增强相弹性模量; 是基体体积分数。计算结果如表2所列,通过公式计算的模量和测量值基本吻合,表明复合材料固结质量较高,TiB2颗粒与铝合金基体之间界面结合较好,弹性变形过程中铝合金基体可以将载荷有效传递给TiB2颗粒,从而使TiB2颗粒弹性模量得到充分发挥。同时发现,随着TiB2颗粒体积分数的增加,模量的测量值和计算值之间的偏差越来越大。这可能是由于随着TiB2颗粒添加量增加,颗粒在基体中的分散性变差,存在一定的团聚现象,减弱了增强相和铝基体之间的模量传递。
是基体体积分数。计算结果如表2所列,通过公式计算的模量和测量值基本吻合,表明复合材料固结质量较高,TiB2颗粒与铝合金基体之间界面结合较好,弹性变形过程中铝合金基体可以将载荷有效传递给TiB2颗粒,从而使TiB2颗粒弹性模量得到充分发挥。同时发现,随着TiB2颗粒体积分数的增加,模量的测量值和计算值之间的偏差越来越大。这可能是由于随着TiB2颗粒添加量增加,颗粒在基体中的分散性变差,存在一定的团聚现象,减弱了增强相和铝基体之间的模量传递。
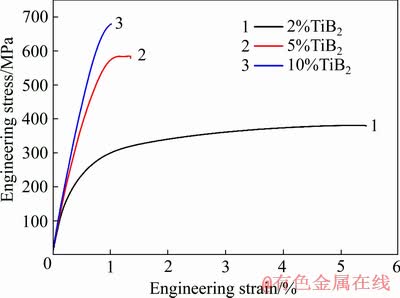
图8 TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料样品拉伸工程应力-应变曲线
Fig. 8 Tensile engineering stress-strain curve of TiB2/ Al-3.8 Zn-1.85 Mg-1.32 Cu composite samples
图9所示为TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料拉伸样品断裂表面的SEM像。可以看出,在TiB2颗粒添加量为2%时,断口有较多韧窝存在,韧窝尺寸在1~3 μm之间,显示复合材料为韧性断裂。随着TiB2颗粒含量增加到5%和10%时,韧窝尺寸没有明显变化,但数量急剧减少,复合材料表现出脆性断裂特征。TiB2颗粒为陶瓷相,具有较高的强度和硬度,大量TiB2颗粒在晶界上的偏聚以及颗粒聚集区域的形成导致复合材料缺陷敏感性增加。因此,当基体中出现较多的陶瓷颗粒时,材料在缺陷处容易发生裂纹形核和扩展,从而导致断裂,使得材料塑性降低。
表2 TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料样品拉伸力学性能
Table 2 Tensile mechanical properties of TiB2/Al-3.8 Zn-1.85 Mg-1.32 Cu composite samples
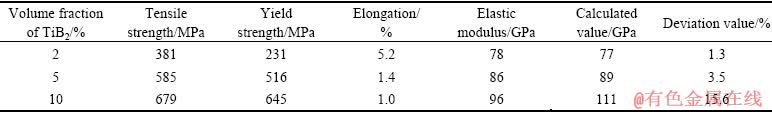
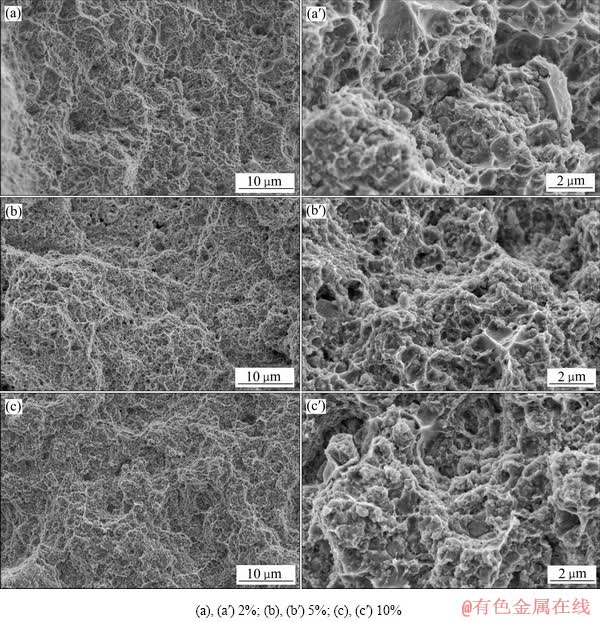
图9 TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu复合材料样品拉伸断口形貌
Fig. 9 Tensile fracture surface morphologies of TiB2/Al-3.8 Zn-1.85 Mg-1.32 Cu composite samples
3 结论
1) 高能球磨诱导TiB2颗粒尖角溶解,致使TiB2颗粒形貌从多边形转变为近球形。
2) 随着TiB2含量从2%增加到10%(体积分数),复合材料抗拉强度、屈服强度和弹性模量分别从381 MPa、231 MPa和78 GPa增加到679 MPa、645 MPa和96 GPa,伸长率从5.2%下降到1.0%,断裂方式由塑性断裂转变为脆性断裂。
3) 增加TiB2颗粒含量导致晶界和Al/TiB2颗粒界面密度升高,析出密度下降,析出相的形成可能与位错诱导的非均匀形核有关。
4) 复合材料较高的弹性模量,表明材料固结质量较高,TiB2颗粒与铝合金基体之间界面结合较好,变形过程中铝合金基体可以将载荷有效传递给TiB2颗粒,促使TiB2颗粒弹性模量得到充分发挥。
REFERENCES
[1] WANG Zhi-guo, LI Chuan-peng, WANG Hui-yuan, ZHU Xian, WU Min, LI Jie-hua, JIANG Qi-chuan. Aging behavior of nano-SiC/2014Al composite fabricated by powder metallurgy and hot extrusion techniques[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2016, 32(10): 1008-1012.
[2] 张 荻, 张国定, 李志强. 金属基复合材料的现状与发展趋势[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010, 29(4): 1-7.
ZHANG Di, ZHANG Guo-ding, LI Zhi-qiang. The current state and trend of metal matrix composites[J]. Materials China, 2010, 29(4): 1-7.
[3] SURAPPA M K. Aluminium matrix composites: Challenges and opportunities[J]. Sadhana, 2003, 28(1/2): 319-334.
[4] 樊建中, 石力开. 颗粒增强铝基复合材料研究与应用发 展[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2012, 42(1): 1-7.
FAN Jian-zhong, SHI Li-kai. Development and application of particulate reinforced aluminum matrix composites[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology, 2012, 42(1): 1-7.
[5] CHEN C, CUI C, ZHAO L, LIU S, LIU S, CHEN C. The formation mechanism and interface structure characterization of in situ AlN/Al composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2016, 50(4): 495-506.
[6] 滕海涛, 熊柏青, 张永安, 刘红伟, 贺 昕. 高Zn含量Al-Zn-Mg-Cu系铝合金的凝固态显微组织[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(4): 852-865.
TENG Hai-tao, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHANG Yong-an, LIU Hong-wei, HE Xin. Solidification microstructure of high zinc-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(4): 852-865.
[7] PRAMANIK A. Effects of reinforcement on wear resistance of aluminum matrix composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(2): 348-358.
[8] 甘贵生, 杨 滨, 杜长华, 甘树德. TiB2颗粒对7075铝合金流变成形显微组织的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(12): 4168-4174.
GAN Gui-sheng, YANG Bin, DU Chuang-hua, GAN Shu-de. EffectofTiB2particleon microstructureof7075Al alloy in rheological forming[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science andTechnology), 2014, 45(12): 4168-4174.
[9] 甘贵生, 杨 滨. TiB2/7075铝基复合材料流变挤压成形工艺[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(5): 1133-1140.
GAN Gui-sheng, YANG Bin. Rheo-casting forming process of TiB2/7075 aluminium matrix composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(5): 1133-1140.
[10] CHEN Dong, LE Yong-kang, BAI Liang, MA Nai-heng, LI Xian-feng, WANG Hao-wei. Mechanical properties and microstructure of in situ TiB2-7055 composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautic, 2006, 19(S1): 66-70.
[11] 张建平, 乐永康, 毛建伟. 原位自生TiB2/7055复合材料的组织与力学性能[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2009, 29(3): 249-251.
ZHANG Jian-ping, LE Yong-kang, MAO Jian-wei. Microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ sub-micron TiB2/7055 matrix composites[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2009, 29(3): 249-251.
[12] THAM L M, GUPTA M, CHENG L. Predicting the failure strains of Al/SiC composites with reacted matrix– reinforcement interfaces[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2003, 354(1): 369-376.
[13] WU Z, KANG P C, WU G H, GUO Q, CHEN G Q, JIANG L T. The effect of interface modification on fracture behavior of tungsten fiber reinforced copper matrix composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 536: 45-48.
[14] MAJUMDAR B S, MATIKAS T E, MIRACLE D B. Experiments and analysis of fiber fragmentation in single and multiple-fiber SiC/Ti-6Al-4V metal matrix composites[J]. Composites B (Engineering), 1998, 29(2): 131-145.
[15] 许世娇, 肖伯律, 刘振宇, 王文广, 马宗义. 高能球磨法制备的碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料的微观组织和力学性能[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(7): 882-888.
XU Shi-jiao, XIAO Bo-lü, LIU Zhen-yu, WANG Wen-guang, MA Zong-yi. Microstructures and mechanical properties of CNT/Al composites fabricated by high energy ball-milling method[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(7): 882-888.
[16] SADEGHIAN Z, LOTFI B, ENAYATI M H, BEISS P. Microstructural and mechanical evaluation of Al-TiB2 nanostructured composite fabricated by mechanical alloying[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(29): 7758-7763.
[17] ALIZADEH A, ABDOLLAHI A, RADFAR M J. Processing, characterization, room temperature mechanical properties and fracture behavior of hot extruded multi-scale B4C reinforced 5083 aluminum alloy based composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(6): 1233-1247.
[18] SPRIANO S, DOGLIONE R, BARICCO M. Texture, hardening and mechanical anisotropy in AA 8090-T851 plate[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 257: 134-138.
[19] TUZEMEN C, YAVAS B, AKIN I,YUCEL O, SAHIN F, GOLLER G. Production and characterization of TZM based TiC or ZrC reinforced composites prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS)[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 781: 433-439.
[20] GUTIERREZ-URRUTIA I, MUNOZ-MORRIS M A, PUERTAS I, LUIS C, MORRIS D G. Influence of processing temperature and die angle on the grain microstructure produced by severe deformation of an Al-7% Si alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 475(1/2): 268-278.
[21] WANG Fu-lin, BHATTACHARYYA J J, AGNEW S R. Effect of precipitate shape and orientation on Orowan strengthening of non-basal slip modes in hexagonal crystals, application to magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 666: 114-122.
[22] BARNETT M R, WANG Huan, GUO Ting-ting. An Orowan precipitate strengthening equation for mechanical twinning in Mg[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2019, 112: 108-122.
[23] SENDECKYJ G P. Mechanics of composite materials: Composite materials[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1974.
[24] FLYNN J, AMIRI A, ULVEN C. Hybridized carbon and flax fiber composites for tailored performance[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 102: 21-29.
Influences of TiB2 particles content on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu composites
LI Jing-jing1, 2, LI Chen-guang1, 2, LIANG Jia-miao1, 2, JU Jiang1, 2, ZHANG Zhen1, 2, WANG Meng-meng1, 2, ZHOU Yang1, 2, WANG Jun1, 2
(1. Institute of Solidification Science and Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China;
2. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Advanced High-temperature Materials and Precision Forming, Shanghai 200240, China)
Abstract: TiB2/Al-3.8Zn-1.85Mg-1.32Cu composites were prepared by high energy ball milling in combination with spark plasma sintering and hot extrusion. The materials were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope and tensile testing machine to investigate the effects of TiB2content on microstructure and mechanical properties. The results show that the morphology of TiB2 particles changes from polygon to nearly spherical as a result of high energy ball milling. With increasing TiB2 content from 2% to 10% (volume fraction), the grain size of aluminum matrix gradually is refined and the precipitates density decreases; the tensile strength, yield strength and elastic modulus of the composites increase from 381 MPa, 231 MPa and 78 GPa to 679 MPa, 645 MPa and 96 GPa, respectively, and the elongation to fracture decreases from 5.2% to 1.0%. Fine grain strengthening and dispersion strengthening are the main strengthening mechanisms.
Key words: Al-based composites; TiB2 particles; powder metallurgy; microstructure; mechanical property
Foundation item: Project(51971143) supported by the General Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017-VI-0013-0085) supported by the National Science and Technology Special Grant, China
Received date: 2019-07-09; Accepted date: 2019-10-08
Corresponding author: LIANG Jia-miao; Tel: +86-18117100519; E-mail: jmliang@sjtu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目(51971143);国家科技重大专项(2017-VI-0013-0085)
收稿日期:2019-07-09;修订日期:2019-10-08
通信作者:梁加淼,工程师,博士;电话:18117100519;E-mail:jmliang@sjtu.edu.cn