南昌市污水处理厂污泥中重金属的污染危害
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第10期
论文作者:杨婷 黄华军 赖发英
文章页码:2249 - 2259
关键词:污泥;重金属;污染程度;环境风险
Key words:sewage sludge; heavy metal; contamination degree; environment risk
摘 要:对南昌市红谷滩、朝阳、青山湖和象湖4个主要污水处理厂污泥中重金属的污染危害进行探讨。依据污泥样品中重金属的总含量、化学形态和可浸出量,对污泥中Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Cr和Ni 6种重金属的污染特性和环境风险进行评估。研究结果表明,除了重金属Pb,青山湖污水厂污泥中重金属的总量高于其他3个污水厂污泥(红谷滩、朝阳和象湖)。大部分污水厂污泥中重金属Cd和Ni总含量超过了相应的标准。重金属Cu、Cr和Pb主要以潜在影响和稳定态的形式存在,而重金属Zn和Ni则具有较高的活性,重金属Cd的化学形态分布较为均衡。重金属的可浸出量几乎都超过相应的标准值,尤其是重金属Zn和Ni。污泥中重金属的潜在生态风险指数高达4263.34~7480.26,也即,重金属的生态风险处于“非常高”的水平。另外,污泥中重金属Cd的污染占主要地位。
Abstract: The pollution hazards of heavy metals were investigated in sewage sludge collected from four wastewater treatment plants in Nanchang City, China, including Honggutan (HGT), Chaoyang (CY), Qingshanhu (QSH) and Xianghu (XH). Contamination/risk characteristics of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cr and Ni) were evaluated based on their leachable content, total content and chemical speciation. The sewage sludge from QSH contained higher total contents of heavy metals (except Pb) than those from HGT, XH and CY. The total contents of Cd and Ni were mostly beyond standard. Cu, Cr and Pb were predominantly present in potential effect and stable fractions. Zn and Ni showed higher bioavailability. Cd presented roughly uniform distribution into four fractions. The leaching contents of heavy metals almost exceeded the threshold values, especially for Zn and Ni. The potential ecological risk indexes of heavy metals in sewage sludge were 4263.34-7480.26, indicating very high risks. Cd contamination is the major concern.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 2249-2259
Ting YANG, Hua-jun HUANG, Fa-ying LAI
School of Land Resources and Environment, Jiangxi Agricultural University, Nanchang 330045, China
Received 26 June 2016; accepted 24 March 2017
Abstract: The pollution hazards of heavy metals were investigated in sewage sludge collected from four wastewater treatment plants in Nanchang City, China, including Honggutan (HGT), Chaoyang (CY), Qingshanhu (QSH) and Xianghu (XH). Contamination/risk characteristics of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cr and Ni) were evaluated based on their leachable content, total content and chemical speciation. The sewage sludge from QSH contained higher total contents of heavy metals (except Pb) than those from HGT, XH and CY. The total contents of Cd and Ni were mostly beyond standard. Cu, Cr and Pb were predominantly present in potential effect and stable fractions. Zn and Ni showed higher bioavailability. Cd presented roughly uniform distribution into four fractions. The leaching contents of heavy metals almost exceeded the threshold values, especially for Zn and Ni. The potential ecological risk indexes of heavy metals in sewage sludge were 4263.34-7480.26, indicating very high risks. Cd contamination is the major concern.
Key words: sewage sludge; heavy metal; contamination degree; environment risk
1 Introduction
In recent years, with the fast development of economy and growing environmental protection consciousness of government and citizens, the sewage treatment capacity of China has been established quickly. According to the Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, by 2013, there were 5364 municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), and the sewage treatment capacity was about 1.7×108 m3/d. At present, many sewage treatment processes are used in WWTPs in China, including conventional activated sludge treatment, anaerobic- anoxic-oxic (A2/O), anaerobic-oxic (A/O), sequencing batch reactor (SBR), oxidation ditch, etc [1]. During these treatment processes, large amount of sewage sludge will be produced, which must be disposed in a non- hazardous manner. Total sewage sludge production in China had an average annual growth of 13% from 2007 to 2013, and 6.25 ×109 kg dry solids were produced in 2013 [2].
Nowadays, the main approaches to disposing sewage sludge can be classified into three categories: agricultural use, incineration, and landfill [3,4]. However, all of these approaches have potential risks of causing heavy-metal pollution, since sewage sludge usually contains certain quantities of heavy metals, such as Zn, Pb, Cu, Cr, Ni, Cd, Hg, and As (contents vary from less than 1 mg/kg to more than 1000 mg/kg) [5-7]. Hence, some pre-treatment procedures should be adopted to reduce/stabilize the heavy metals contained in sewage sludge before disposal. Thoroughly understanding the properties of heavy metals present in sewage sludge is basic but important for the control of heavy-metal pollution during the treatment of sewage sludge.
Although the total metal concentrations may indicate the overall level of heavy metals in sewage sludge, the mobility of heavy metals, their bioavailability and eco-toxicity to plants, depend strongly on their specific chemical forms or ways of binding [8,9]. The chemical speciation of heavy metals can be determined with selective sequential extraction analysis, which consists of several extraction steps that use different chemical reagents and conditions. Sequential extraction provides information about the differentiation of the relative bonding strength of metals on various solid phases and about their potential reactivity under different physicochemical environmental conditions [10]. The two most widely used sequential extraction methods are Tessier [11] and BCR (the European Community Bureau of Reference, now the Standards, Measurements and Testing Program) [12]. The BCR sequential extraction method provides a compromise between analysis time and the amount of information obtained. Up to now, many studies have been carried out on heavy metal pollution using the BCR sequential extraction method in samples such as soils [13], sediments [14], street dust [10,15] and sewage sludge [16,17].
Multivariate statistical analysis is a useful technique for identifying common patterns in data distribution, leading to a reduction of the initial dimension of data sets and facilitating its interpretation [18]. Principal component analysis (PCA) is a multivariate technique widely used to reduce data and to extract a smaller number of independent factors for analyzing the relationships among observed variables. Cluster analysis (CA) classifies a set of observations into two or more mutually exclusive unknown groups based on a combination of internal variables [19]. Multivariate statistical techniques (PCA and CA) have been widely applied to environmental samples such as sediments [20-23], dust [10,24,25], fly ash [26], sludge [18,27], and soil [28].
Nanchang is a very important provincial capital city in Central China. However, there have been limited researches regarding the pollution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sewage sludges produced from the sewage treatment industry. In this work, sewage sludge samples were collected from the four main wastewater treatment plants in Nanchang City. Some significant physicochemical properties, such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC), organic matter and ash contents, were determined. The total contents of six heavy metals (Cr, Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn) were investigated using acid digestion method. The BCR separation procedure was used to determine the chemical fraction of heavy metals and their leachable contents were analyzed by the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP). The contamination degree and risk of heavy metals were evaluated with the aid of geo-accumulation index (Igeo), potential ecological risk index (RI) and risk assessment code (RAC). Cluster analysis and principal component analysis were also used to identify correlations among sewage sludges from different plants. This work aims to identify the pollution hazards of heavy metals in sewage sludges produced in Nanchang (China), which will provide significant references for sewage sludge treatment/disposal.
2 Experimental
2.1 Sample collection and pre-treatment
The study area, the city of Nanchang, is located in the northern part of Jiangxi province, Southeast China. This city consists of nine counties with a population of 5.24×106, and covers 7402.36 km2. The main industrial sectors include manufacture, cottonocracy, chemical, medicine and electronic information. The high variability of industrial and agricultural activities generates wastes of various characteristics and quantities. Sewage sludge samples were obtained from four wastewater treatment plants located in different sites of the main urban area of Nanchang City, namely, Honggutan (HGT), Qingshanhu (QSH), Xianghu (XH) and Chaoyang (CY). The details about these plants are given in Table 1. Sewage sludge samples were collected immediately after being dewatered by the belt or rotary press filter. The samples were firstly air dried and then ground into <150 μm. Then, the powder samples were dried in an oven at 105 °C for 24 h and finally stored in jars at room temperature.
Table 1 Detailed information on four wastewater treatment plants

2.2 Chemical analysis
2.2.1 Physicochemical analysis
Determination method for municipal sludge in wastewater treatment plant [29] was applied to determine the pH value and organic matter content of each sludge sample. The content of organic matter (OM) in sludge was analyzed by burning at 550 °C in a muffle for 1 h. The pH of sludge was obtained through measuring the sludge extracts (1:10 solid/deionized water (w/V)) using a digital pH meter (PHS-3C, China). Electrical conductivity (EC) was obtained through measuring the sludge extracts (1:5 solid/deionized water (w/V)) using a conductivity meter (DDS-11A, China). Ultimate analysis was conducted by an elemental analyzer (Flash EA1112, Thermo, America). Total phosphorus (TP) and total kalium (TK) were determined by a visible spectrophotometer (722S, China) and a flame photometer (FP640, China), respectively. The higher heating value (HHV, MJ/kg) was calculated according to the Dulong formula [30,31]:
 (1)
(1)
where ωc, ωh and ωo are the mass fractions of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, respectively.
2.2.2 Analysis of total metal concentration
0.2 g of each sample and a solution of 5 mL HNO3, 5 mL HClO4 and 3 mL H2O2 (30%) were placed into a polytetrafluoroethylene beaker (25 mL). Next, the mixture was heated on a electric hot plate (EH35B, China). The contents were evaporated till being nearly dry. After cooling down, the residue obtained was dissolved with 5% HNO3, transferred into a volumetric flask (50 mL) through a 0.45 μm membrane filter and then diluted to the mark.
2.2.3 Sequential extraction
The BCR three-step sequential extraction procedure described by URE et al [32] was adopted in this work. For an internal check on the procedure, an additional step (Step 4) was applied. After the sequential extraction steps, the residual metal content was determined.
Step 1: Acid soluble/exchangeable fraction (F1, exchangeable metal and carbonate-associated fractions). Sludge samples (0.5 g) were introduced into a 50 mL polypropylene centrifuge tube containing 20 mL of acetic acid (0.1 mol/L) and then shaken for 16 h at room temperature. The solution and solid phases were separated by centrifugation at 4000 r/min for 20 min. Subsequently, the suspension was filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter and the solid residues were preserved for subsequent extractions.
Step 2: Reducible fraction (F2, fraction associated with Fe and Mn oxides). The residues from Step 1 were shaken with 20 mL of 0.1 mol/L hydroxylammonium chloride (adjusted to pH 2 with nitric acid) for 16 h. The extraction procedure followed that described in Step 1.
Step 3: Oxidizable fraction (F3, fraction bound to organic matter). The residues from Step 2 were dispersed in 5 mL of hydrogen peroxide (30%) and digested at room temperature for 1 h with occasional shaking. A second 5 mL aliquot of hydrogen peroxide was introduced and digested at 85 °C (water bath) for 1 h. The contents were evaporated to a small volume (1-2 mL). About 25 mL of ammonium acetate (1.0 mol/L, adjusted to pH 2 with nitric acid) was added to the cool and moist residue, after which the mixture was shaken and centrifuged. The extract was separated according to the procedure described in Step 1.
Step 4: Residual fraction (F4). The residues from Step 3 were digested using the method mentioned in Section 2.2.2.
2.2.4 Analysis of leachable metal concentration
The TCLP test is designed to determine the mobility of both organic and inorganic analytes present in liquid, solid and multiphasic wastes [33,34]. Here, TCLP was applied to assessing the leaching characteristics of heavy metals in sewage sludge. And the TCLP leaching of sewage sludge was carried out by extraction (liquid-to- solid ratio of 20:1) using glacial acetic acid solution (pH=2.8) as medium. The sewage sludge samples along with leaching fluid were placed in a rotary shaker and shaken at 120 r/min for 20 h. After the extraction, the samples were centrifugated at 4000 r/min for 20 min and the water phase was filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter.
The contents of Zn, Cu, Pb, Cd, Cr and Ni were determined by an atomic absorption spectrometer (Hitachi Z-2000, Japan). Each experiment was conducted in triplicate and the results reported in this work are the average values with standard deviation.
2.3 Contamination degree and risk analysis
2.3.1 Geo-accumulation index (Igeo)
The geo-accumulation index method (Igeo), which was first described by  [35], is widely used to estimate the pollution level of heavy metals in various environment media [36-38]. Geo-accumulation index method (Igeo) is calculated as
[35], is widely used to estimate the pollution level of heavy metals in various environment media [36-38]. Geo-accumulation index method (Igeo) is calculated as
 (2)
(2)
where Ci is the measured content of metal i in sewage sludge (total content); Bi is the geochemical background value of a particular heavy metal. The constant factor of 1.5 was introduced to analyze natural fluctuations in the contents of a given substance in the environment and very small anthropogenic influence. The geometric mean values of heavy metals in the surface soil of Jiangxi Province, China, were used as background reference values. The background contents of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr and Ni are 17.7, 63.7, 29.7, 0.0696, 39.4 and 15.8 mg/kg, respectively [39].
2.3.2 Potential ecological risk index (RI)
The potential ecological risk index (RI, R) was proposed by HAKANSON [40] and can be used to evaluate the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sewage sludge [17,41,42]. RI method covers a variety of research domains, i.e., biological toxicology, environmental chemistry as well as ecology, and can be used to evaluate ecological risks caused by heavy metals comprehensively. The calculation of RI is given below:
 (3)
(3)
where  is the potential ecological risk coefficient of a particular heavy metal;
is the potential ecological risk coefficient of a particular heavy metal;  is the toxicity coefficient of specific pollutant that reflects the toxicity, pollution levels and sensitivity of the environment to heavy metals;
is the toxicity coefficient of specific pollutant that reflects the toxicity, pollution levels and sensitivity of the environment to heavy metals;  is the pollution factor; Ci is the tested value of heavy metal i (total content);
is the pollution factor; Ci is the tested value of heavy metal i (total content);  is the reference value of heavy metal i, defined as Bi. The toxicity coefficients of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr and Ni are 5, 1, 5, 30, 2 and 5, respectively.
is the reference value of heavy metal i, defined as Bi. The toxicity coefficients of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr and Ni are 5, 1, 5, 30, 2 and 5, respectively.
2.3.3 Risk assessment code (RAC)
The risk assessment code (RAC) was developed to estimate the environment risk of heavy metals by applying a scale to the percentage of metals presented in the acid soluble/exchangeable fraction (F1) [16]. RAC grades the risk into five risk classes. There is no risk when the proportion of metals in F1 is lower than 1% (NR), low risk for a range of 1%-10% (LR), medium risk for a range of 11%-30% (MR), high risk from 31% to 50% (HR) and very high risk for higher F1 percentages (VHR) [9,26,43].
2.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by SPSS v18.0. The most common PCA type, producing more interpretable components, is varimax rotation, which has been applied in the current work. Hierarchical CA (HCA), as the most commonly applied CA method for environmental analysis, looks for groups of samples according to their similarities. In clustering, the objects are grouped so that ‘similar’ objects fall into the same class. HCA was performed by the Ward’s method and the Euclidean distances for similarities in the variables/ samples were calculated [10,18].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Physicochemical analysis
Table 2 lists the physicochemical characteristics of sewage sludges. All sewage sludge samples show acidity with pH values of 5.70-6.64. The content of organic matters ranged from 20.75% to 53.09%. The electrical conductivity of sludge varied from 1400 to 3200 μs/cm. The contents of TP and TK in the sludge were distributed in the range of 3.606-4.806 and 1.146-4.449 g/kg, respectively. There was obvious difference in the caloric values of different sludges, varying from 3.97 to 11.68 MJ/kg. Major elements contributing to the caloric value are carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. It is clearly shown in Table 2 that those sludges, containing higher contents of carbon and hydrogen, usually had higher caloric values. The caloric values of sludges also presented an obviously positive correlation with organic matter content. LIANG et al [18] reported that the caloric values had a negative correlation with volatile components when volatile components were below 30%, while it had a positive correlation with volatile components when volatile components were above 37%.
3.2 Total concentrations of heavy metals
The total contents of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cr and Ni in the four sludge samples and the corresponding discharge standards are presented in Table 3. The results showed a wide range of heavy metal contents in the sewage sludge. The sewage sludge obtained from QSH contained the highest content of heavy metals except Pb, followed by XH, CY and HGT, which can be ascribed to the different treatment processes of sewage sludge. In QSH, anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge was carried out before the dehydration process. FUENTES et al [27] also reported that the anaerobic sludge and digested sludge usually had higher contents of heavy metals. The total contents of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cr in the four sewage sludge samples fell within the threshold values. However, the contents of Cd in the four sewage sludge samples all exceeded the threshold values for acidic soil, but still in the neutral/basic soil control range [44]. In addition, except HGT, the sewage sludges produced in the other three wastewater treatment plants all contained undesirably high contents of Ni, especially for QSH. The content of Ni in the sludge obtained from QSH reached up to (2180.13±169.38) mg/kg, nearly ten times higher than the threshold value of Ni in sewage sludge (200 mg/kg, for neutral/basic soil). Therefore, the sewage sludge produced in these four wastewater treatment plants cannot be directly applied in agriculture. In consideration of the accumulation effects of heavy metals, necessary pretreatment measures should be adopted to immobilize the bioavailability of heavy metals, especially for Cd and Ni.
Table 2 Physicochemical characteristics of sewage sludges

Table 3 Total contents of heavy metals in sewage sludge samples

3.3 Chemical speciation of heavy metals
It is widely accepted that the bioavailability and eco-toxicity of heavy metals in the environment mainly depend on their chemical speciation. The detailed relations among the chemical speciation, eco-toxicity and bioavailability of heavy metals have been established in recent years [3,8,45]. The acid soluble/exchangeable fraction (F1) and reducible fraction (F2) belong to the direct effect fractions, having direct eco-toxicity and high bioavailability to the environment. The organic fraction (F3) is identified as the potential effect fraction. The potential toxicity of F3 should not be ignored. The residual fraction is recognized as a stable fraction and has no eco-toxicity to the environment.
The chemical speciation of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr and Ni represented as the percentage of total content is shown in Fig. 1. The statistical results of each fraction of heavy metals in the four sewage sludge samples are listed in Table 4. The distribution of the metal fractions varied widely by sludge source, with a few similarities.
Cu was predominantly present in F3 and F4, accounting for 75.42%-88.53%. The percentage of Cu bound to F3 was up to 76.76%, 64.54% and 69.96% for the QSH, XH and CY, respectively. Thus, Cu from the above three plants had a higher potential eco-toxicity and bioavailability to the environment. The copper complexes with organic matters have high stability and hence, Cu is preferentially bound to the organic fraction (F3) [10,46]. In addition, it is also noted that 11.48%-24.58% of Cu was associated with the direct effect fractions (F1 and F2).
Pb is usually preferentially bound to the residue fraction (F4) [47]. Similar results were also observed in this work. Pb was primarily present in F4, accounting for 61.49%-69.50%. However, the content of Pb in the direct fractions (F1 and F2) was up to 17.08%-22.51%. Hence, the eco-toxicity of Pb to environment should not be taken lightly.
Zn showed the greatest bioavailability in all heavy metals, which had the highest direct toxicity to the environment. It is primarily present in F1 and F2, accounting for 59.57%-79.12%.
Cd presented nearly uniform distribution into four fractions in each sewage sludge sample. The percentages of Cd present in F1 and F2 were 48.90%-60.52%, indicating that Cd had a high direct eco-toxicity and bioavailability despite its low content in the sewage sludge (Tables 3 and 4).
Cr was just distributed in F3 and F4 fractions. For HGT and CY, Cr uniquely existed in residual fraction (F4) and thus had no toxicity to the environment. But for QSH and XH, the percentages of Cr present in the oxidizable fraction (F3) were 64.86% and 44.44%, respectively, revealing that Cr had a high potential bioavailability to the environment.
Ni is a potentially mobile and water-soluble element and is usually distributed in F1 and F2 [18]. Except for HGT, Ni in the other three wastewater treatment plants was found abundant in all four fractions. The direct effect fractions (F1+F2) of Ni accounted for 70.34%, 45.85% and 34.67% in QSH, XH and CY, respectively, showing high bioavailability to environment. However, Ni was only present in F3 and F4 for the HGT sample and the percentage of F4 peaked at 86.95%.
A check on the results of BCR sequential extraction procedure was performed by comparing the sum of the four fractions (Table 4) with the total contents of heavy metals from HNO3, HClO4 and H2O2 digestion procedure (Table 3). The detailed calculations are expressed as
 (4)
(4)
where R1 is the recovery rate of heavy metals (%); CT is the total content of heavy metals (mg/kg); F1, F2, F3, F4 are contents of heavy metals extracted in each fraction.
The corresponding results are shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen clearly that the sum of the four fractions was in good agreement with the total content of heavy metals with satisfactory recoveries (72.00%-123.88%), similar to those recorded by other researchers using the same procedure [18,46]. It was indicated that this modified BCR sequential extraction method used for detecting the chemical speciation of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr and Ni in sewage sludge was exact and reliable.

Fig. 1 Chemical speciation of heavy metals in HGT (a), QSH (b), XH (c) and CY (d)
Table 4 Statistical results of each fraction of heavy metals in sewage sludge samples


Fig. 2 Recovery rate of heavy metals in four sewage sludge samples
3.4 Leachable contents of heavy metals
The leachable contents of heavy metals in sewage sludges are given in Table 5. In general, the sewage sludges (QSH and XH) contained higher leachable contents of heavy metals than those in HGT and CY. Cr was not detected in the leaching solution of four kinds of sewage sludges. The leachable contents of Zn, Pb and Cd all exceeded the corresponding threshold values, especially for Zn. The standard-exceeding multiples of Zn were about 13, 43, 34 and 26 for HGT, QSH, XH and CY, respectively. The leachable contents of Ni in HGT were under the threshold value, while those in QSH, XH and CY were all higher than the threshold value, especially for QSH, exceeding the standard value by approximate 173 fold. The amount of leached Cu in the four sewage sludge samples ranged from 3.9 mg/kg to 42.1 mg/kg.
The leaching rate (R2) of heavy metals was proposed as one indicator for investigating the proportions of heavy metals bound to the leachable fraction. R2 is defined as the ratio of the leachable content of individual heavy metal to the total content of each heavy metal:
 (5)
(5)
where i is one kind of heavy metal; CL,i is the leachable content of heavy metals (mg/kg) (Table 5); CT,i is the total content of heavy metals (mg/kg) (Table 3).
Figure 3 depicts the leaching rate of heavy metals in the four kinds of sewage sludge samples. On the whole, the leaching rate of Zn, Ni and Cd is higher than that of Cu and Pb. The leaching rate of Zn was approximately 25% and for Cd, about 15%. The leaching rate of Ni in QSH was up to 39.95%, while it was only 3.62% for HGT. As regards to Cu and Pb, the leaching rates were all below 10%.
3.5 Contamination degree and risk of heavy metals
Geo-accumulation method (Igeo) was used to evaluate the contamination degree of heavy metals in sewage sludge. The Igeo values are presented in Table 6. All Igeo values for heavy metals in any sewage sludge sample were in the increasing order of (Cr, Pb) < (Cu, Zn) < (Ni, Cd). The Igeo values for Cr and Pb in the four kinds of sewage sludge samples were below 2.0. This indicates that the pollution levels of Cr and Pb in sewage sludge were below moderately contaminated grade. The pollution degrees of Cu and Zn in different sewage sludge samples ranked in the following order: HGT (MC) < CY (MHC) < XH (HC-HEC) < QSH (HC-HEC). Ni moderately-to-heavily contaminated HGT and CY sewage sludges, and the XH and QSH sewage sludges were heavily and extremely polluted by Ni, respectively. Every sewage sludge sample was extremely contaminated by Cd.
Table 5 Leachable contents of heavy metals based on TCLP test


Fig. 3 Leaching rate of heavy metals in four kinds of sewage sludge samples
The assessment results of heavy metals’ ecological risk in sewage sludges are also listed in Table 6. It was found that the risk indices ( ) of heavy metals ranked in the following order: Cr < Zn < Pb < (Cu, Ni) < Cd.
) of heavy metals ranked in the following order: Cr < Zn < Pb < (Cu, Ni) < Cd.  values for Cr, Zn and Pb in all sewage sludges were below 40, suggesting low risk. The monomial ecological risk values of Cd in sewage sludges reached up to 4150.86-6521.55. That was to say, Cd posed a very high risk to the local ecosystem, which should be given rise to wide-spread concerns. The ecological risk of Cu and Ni in different sewage sludge samples varied in the order of QSH (HR-VHR) > XH (CR) > CY (LR-MR) > HGT (LR). The RI values of heavy metals in sewage sludges were as high as 4263.34-7480.26, corresponding to very high risk. In other words, the security of the ecological environment will be seriously threatened if theses sewage sludges are directly discharged to the environments without any pretreatments. In addition, the high ecological risk of sewage sludge was primarily dominated by Cd.
values for Cr, Zn and Pb in all sewage sludges were below 40, suggesting low risk. The monomial ecological risk values of Cd in sewage sludges reached up to 4150.86-6521.55. That was to say, Cd posed a very high risk to the local ecosystem, which should be given rise to wide-spread concerns. The ecological risk of Cu and Ni in different sewage sludge samples varied in the order of QSH (HR-VHR) > XH (CR) > CY (LR-MR) > HGT (LR). The RI values of heavy metals in sewage sludges were as high as 4263.34-7480.26, corresponding to very high risk. In other words, the security of the ecological environment will be seriously threatened if theses sewage sludges are directly discharged to the environments without any pretreatments. In addition, the high ecological risk of sewage sludge was primarily dominated by Cd.
The results of the environment risk assessment according to RAC are also given in Table 6. The environment risk values of Cr in sewage sludges were all less than 1, reflecting no risk to the environments. Zn, with higher percentages in acid soluble/exchangeable fraction (F1, 41.18%-46.63%), came under high risk category. And Cd posed medium risk to the environments. The environment risk of Ni in different sewage sludge samples followed the order of QSH (VHR) > XH (HR) > CY (MR) > HGT (NR). Cu and Pb in QSH and CY had low risk, while medium risk was suggested for Cu and Pb in HGT and XH.
It is noteworthy that the determination of the contamination degree/risk of one heavy metal should be based on the comprehensive results of three assessment methods mentioned above. In this way, more accurate evaluation results can be gotten. Igeo method mainly focuses on the accumulation levels of individual metal. Potential ecological risk index not only involves the total content of one heavy metal but also its toxic response factor. RAC only considers the percentage of a given metal bound to F1 but overlooks the effect of metal type (different toxicity) and its total content [16,41].
Table 6 Assessment results of heavy metal pollution degree and risk in sewage sludge

3.6 Multivariate analysis
3.6.1 Cluster analysis
Figure 4 depicts the dendrogram of the cluster analysis based on the total content of six heavy metals and several physicochemical parameters (pH, EC, TP, TK, OM and TN). The distance axis represented the degree of association between groups of variables, i.e. the lower the value on the axis is, the more significant the association is. Elements belonging to the same cluster had strong correlations among themselves and may originate from a common source.
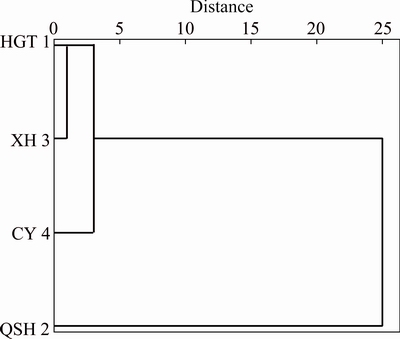
Fig. 4 Dendrogram of cluster analysis for four kinds of sewage sludge samples
The dendrogram was divided into two main clusters. Cluster I contained HGT, XH and CY. QSH was more specialized than the other sewage sludge samples. So, it belonged to Cluster II. The sewage sludge produced from QSH contained higher contents of heavy metals. The significance of these results revealed that the sewage sludge from HGT, XH and CY can be processed together under some circumstance. However, for the sewage sludge from QSH, extra processing should be considered, or handled individually.
3.6.2 Principal component analysis
The results of PCA for six heavy metals are reported in Tables 7 and 8. Three principal components were obtained, accounting for 89.27% of the total variance: components 1, 2, and 3 accounted for 39.19%, 33.02%, and 17.06%, respectively. The principal component (PC1) was highly loaded by Zn, Cd and Ni. An association between Zn, Cd and Ni was found due to the high mobility of these elements in the first two fractions (F1 and F2, except for Ni in HGT). The negative loading of Cu, Pb and Cr in PC1 suggested an antagonistic effect with respect to Zn, Cd and Ni. The second principal component (PC2) was loaded by Cu and Cr. It could be proven that there existed an association between Cu and Cr, which were mainly associated with the oxidizable fraction (F3) and residual fraction (F4) of the sludge. Principal component (PC3) was dominated by Pb, which is mainly distributed as stable forms in residual fraction (F4) and had low eco-toxicity and bioavailability. On the whole, it is considered that a PCA using three principal components is suitable for examining the data set of the sludge samples. PC1 included Zn, Cd and Ni, PC2 included Cu and Cr, and PC3 corresponded completely with Pb (Fig. 5). The results were in agreement with the finding of the chemical speciation distribution of heavy metals in Section 3.3.
Table 7 Total variance for sewage sludges
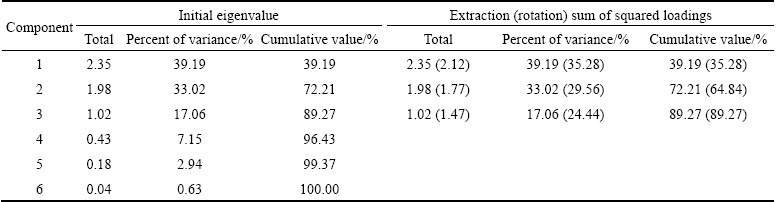
Table 8 Component matrixes (three principal components selected) for sewage sludges


Fig. 5 3D plot of principal component analysis corresponding to metal fractions
4 Conclusions
1) The sewage sludges obtained from QSH and CY contained higher amounts of organic matters, resulting in higher caloric values. Total contents of heavy metals (except Pb) in sewage sludge produced from QSH were higher than those in the other three sewage sludges (HGT, XH and CY). The total contents of Cd and Ni exceeded the corresponding limited values.
2) Zn, Cd and Ni showed higher bioavailability. The leaching contents of heavy metals almost exceeded the corresponding threshold values. The overall potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sewage sludge lay in a high level. Comparatively speaking, Cd was likely to result in more harmful effects.
3) On the whole, the four sewage sludges cannot be directly used in agriculture. Necessary measures must be performed to control the heavy metal pollution during the resource utilization of sewage sludge.
References
[1] JIN L Y, ZHANG G M, TIAN H F. Current state of sewage treatment in China [J]. Water Research, 2014, 66: 85-98.
[2] YANG G, ZHANG G M, WANG H C. Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China [J]. Water Research, 2015, 78: 60-73.
[3] HUANG H J, YUAN X Z. The migration and transformation behaviors of heavy metals during the hydrothermal treatment of sewage sludge [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 200: 991-998.
[4] QIAN L L, WANG S Z, XU D H, GUO Y, TANG X Y, WANG L S. Treatment of municipal sewage sludge in supercritical water: A review [J]. Water Research, 2016, 9: 118-131.
[5] HUANG H J, YUAN, X Z. Recent progress in the direct liquefaction of typical biomass [J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2015, 49: 59-80.
[6] MANARA P, ZABANIOTOU A. Towards sewage sludge based biofuels via thermochemical conversion—A review [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2012, 16: 2566-2582.
[7] TYAGI V K, LO S L. Microwave irradiation: A sustainable way for sludge treatment and resource recovery [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 18: 288-305.
[8] CHEN M, LI, X M, YANG Q, ZENG G M, ZHANG Y, LIAO D X, LIU J J, HU J M, GUO L. Total concentrations and speciation of heavy metals in municipal sludge from Changsha, Zhuzhou and Xiangtan in middle-south region of China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 160: 324-329.
[9] ZHAO S, FENG C H, YANG Y R, NIU J F, SHEN Z Y. Risk assessment of sedimentary metals in the Yangtze Estuary: New evidence of the relationships between two typical index methods [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 241-242: 164-172.
[10]  Heavy metal speciation in various grain sizes of industrially contaminated street dust using multivariate statistical analysis [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 124: 369-376.
Heavy metal speciation in various grain sizes of industrially contaminated street dust using multivariate statistical analysis [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 124: 369-376.
[11] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extaction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace matals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51: 844-851.
[12] RAURET G, LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J F, SAHUQUILLO A, RUBIO R, DAVIDSON C, URE A, QUEVAUVILLER P. Improment of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1999, 1: 57-61.
[13] YANG S L, ZHOU D Q, YU H Y, WEI R, PAN B. Distribution and speciation of metals (Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb) in agricultural and non-agricultural soils near a stream upriver from the Pearl River, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 177: 64-70.
[14] YANG J, CHEN L, LIU L Z, SHI W L, MENG X Z. Comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in lake sediment from public parks in Shanghai [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 102: 129-135.
[15] LI H M, QIAN X, HU W, WANG Y L, GAO H L. Chemical speciation and human health risk of trace metals in urban street dusts from a metropolitan city, Nanjing, SE China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 456-457: 212-221.
[16] GUSIATIN Z M, KULIKOWSKA D. The usability of the IR, RAC and MRI indices of heavy metal distribution to assess the environmental quality of sewage sludge composts [J]. Waste Management, 2014, 34: 1227-1236.
[17] LI J, LUO G B, GAO J F, YUAN S, DU J, WANG Z H. Quantitative evaluation of potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sewage sludge from three wastewater treatment plants in the main urban area of Wuxi, China [J]. Chemistry and Ecology, 2015, 31: 235-251.
[18] LIANG X, NING X A, CHEN G X, LIN M Q, LIU J Y, WANG Y J. Concentrations and speciation of heavy metals in sludge from nine textile dyeing plants [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 98: 128-134.
[19] LU X W, WANG L J, LI L Y, LEI K., HUANG L, KANG D. Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 173: 744-749.
[20] FU, J, ZHAO C P, LUO Y P, LIU C S, KYZAS, G Z, LUO Y, ZHAO D Y, AN S Q, ZHU H L. Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: Their relations to environmental factors [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 270: 102-109.
[21] GUPTA S K, CHABUKDHARA M, KUMAR P, SINGH J, BUX F. Evaluation of ecological risk of metal contamination in river Gomti, India: A biomonitoring approach [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 110: 49-55.
[22] ZHANG Z Y, LI J Y, MAMAT Z, YE Q F. Sources identification and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Bortala River, Northwest China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 126: 94-101.
[23] LONG Y Z, DAI T G, CHI G X, YANG L. Assessment of heavy metals in sediment cores from Xiangjiang River, ChangZhuTan region, Hunan Province, China [J]. Jounal Central South University, 2012, 19: 2634-2642.
[24] CHEN H, LU X W, LI L Y, GAO T N, CHANG Y Y. Metal contamination in campus dust of Xi’an, China: A study based on multivariate statistics and spatial distribution [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 484: 27-35.
[25] LI Z G, FENG X B, LI G H, BI X Y, ZHU J M, QIN H B, DAI Z H, LIU J L, LI Q H, SUN G Y. Distributions, sources and pollution status of 17 trace metal/metalloids in the street dust of a heavily industrialized city of central China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 182: 408-416.
[26] PAN Y, WU Z M, ZHOU J Z, ZHAO J, RUAN X X, LIU J Y, QIAN G R. Chemical characteristics and risk assessment of typical municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash in China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 261: 269-276.
[27] FUENTES A,  MESEGUER V F. Comparative study of six different sludges by sequential speciation of heavy metals [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99: 517-525.
MESEGUER V F. Comparative study of six different sludges by sequential speciation of heavy metals [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99: 517-525.
[28] WU Y G, XU Y N, ZHANG J H, HU S H. Evaluation of ecological risk and primary empirical research on heavy metals in polluted soil over Xiaoqinling gold mining region, Shaanxi, China [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 688-694.
[29] CJ/T 221-2005. China’s Ministry of Construction. Determination method for municipal sludge in wastewater treatment plant [S]. (in Chinese)
[30] HUANG H J, YUAN X Z, LI B T, XIAO Y D, ZENG G M. Thermochemical liquefaction characteristics of sewage sludge in different organic solvents [J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2014, 109: 176-184.
[31] VARDON D R, SHARMA B K, SCOTT J, YU G, WANG Z, SCHIDEMAN L, ZHANG Y, STRATHMANN T J. Chemical properties of biocrude oil from the hydrothermal liquefaction of Spirulina algae, swine manure, and digested anaerobic sludge [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102: 8295-8303.
[32] URE A M, QUEVAUVILLER P, MUNTAU H, GRIEPINK B. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments: An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities [J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1993, 51: 135-151.
[33] YADAV S, YADAV S. Investigations of metal leaching from mobile phone parts using TCLP and WET methods [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2014, 144: 101-107.
[34] YUAN X Z, LENG L J, HUANG H J, CHEN X H, WANG H, XIAO Z H, ZHAI Y B, CHEN H M, ZENG G M. Speciation and environmental risk assessment of heavy metal in bio-oil from liquefaction/pyrolysis of sewage sludge [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 120: 645-652.
[35]  G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. Geojournal, 1969, 2: 108-118.
G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. Geojournal, 1969, 2: 108-118.
[36] CHEN H Y, CHEN R H, TENG, Y G, WU J. Contamination characteristics, ecological risk and source identification of trace metals in sediments of the Le’an River (China) [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 125: 85-92.
[37] LEE P K, YOUM S J, JO H Y. Heavy metal concentrations and contamination levels from Asian dust and identification of sources: A case-study [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91: 1018-1025.
[38] WEI X, GAO B, WANG P, ZHOU H D, LU J. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dusts from different functional areas in Beijing, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 112: 186-192.
[39] China’s Ministry of Environmental Protection. China’s soil element background values [M]. 1st ed. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 1990. (in Chinese)
[40] HAKANSON L. Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14: 975-1001.
[41] HUANG H J, YUAN X Z, ZENG G M, ZHU H N, LI H, LIU Z F, JIANG H W, LENG L J, BI W K. Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals’ pollution hazards in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102: 10346-10351.
[42] ZHAI Y B, CHEN H M, XU B B, XIANG B B, CHEN Z, LI C T, ZENG G M. Influence of sewage sludge-based activated carbon and temperature on the liquefaction of sewage sludge: Yield and composition of bio-oil, immobilization and risk assessment of heavy metals [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 159: 72-79.
[43] ZHU H N, YUAN X Z, ZENG G M, JIANG M, LIANG J, ZHANG C, YIN J, HUANG H J, LIU Z F, JIANG H W. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 1470-1477.
[44] GB 18918-2002. China’s Ministry of Environmental Protection. Discharge standard of pollutants for municipal wastewater treatment plant [S]. (in Chinese)
[45] LI L, XU Z R, ZHANG C L, BAO J P, DAI X X. Quantitative evaluation of heavy metals in solid residues from sub- and super-critical water gasification of sewage sludge [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 121: 169-175.
[46] YUAN X Z, HUANG H J, ZENG G M, LI H, WANG J Y, ZHOU C F, ZHU H N, PEI X K, LIU Z F, LIU Z T. Total concentrations and chemical speciation of heavy metals in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102: 4104-4110.
[47] ZHANG X Q, TIAN Y, WANG Q, CHEN L, WANG X. Heavy metal distribution and speciation during sludge reduction using aquatic worms [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 126: 41-47.
杨 婷,黄华军,赖发英
江西农业大学 国土资源与环境学院,南昌 330045
摘 要:对南昌市红谷滩、朝阳、青山湖和象湖4个主要污水处理厂污泥中重金属的污染危害进行探讨。依据污泥样品中重金属的总含量、化学形态和可浸出量,对污泥中Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Cr和Ni 6种重金属的污染特性和环境风险进行评估。研究结果表明,除了重金属Pb,青山湖污水厂污泥中重金属的总量高于其他3个污水厂污泥(红谷滩、朝阳和象湖)。大部分污水厂污泥中重金属Cd和Ni总含量超过了相应的标准。重金属Cu、Cr和Pb主要以潜在影响和稳定态的形式存在,而重金属Zn和Ni则具有较高的活性,重金属Cd的化学形态分布较为均衡。重金属的可浸出量几乎都超过相应的标准值,尤其是重金属Zn和Ni。污泥中重金属的潜在生态风险指数高达4263.34~7480.26,也即,重金属的生态风险处于“非常高”的水平。另外,污泥中重金属Cd的污染占主要地位。
关键词:污泥;重金属;污染程度;环境风险
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (20151BAB213024) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China; Project (GJJ14302) supported by the Scientific Research Fund of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department, China; Project (YC2015-S186) supported by the Jiangxi Province Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate, China
Corresponding author: Hua-jun HUANG; Tel: +86-791-83828028; E-mail: huanghuajun2004@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60251-6

