J. Cent. South Univ. (2012) 19: 1639-1644
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-012-1187-y
Impact of light-weight external thermal insulation materials on building surrounding thermal environment in summer
LI Nan(李楠)1, 2, LUO Guo-zhi(罗国志)1, 2, LI Bai-zhan(李百战)1, 2, HUANG Yan-qi(黄彦祺)1, 2
1. Faculty of Urban Construction and Environmental Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400045, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Three Gorges Reservoir Region’s Eco-Environment (Chongqing University),
Ministry of Education, Chongqing 400045, China
? Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012
Abstract: The method for calculating wall surface heat storage coefficient was introduced, and the coefficients of several common walls with light-weight external thermal insulation materials and the traditional solid clay brick wall were calculated. In order to study the impact of light-weight external thermal insulation materials, a contrasting experiment was carried out between an external insulated room and an uninsulated room in August, 2010, in Chongqing, China. The result shows that outside surface heat storage coefficient of the insulated wall is much less than that of the traditional wall. However, during sunny time, the surface temperature of external walls of the insulated room is obviously higher than that of the uninsulated room. In different orientations, due to different amounts of solar radiation and being irradiated in different time, the contrasting temperature difference (CTD) appears different regularity. In a word, using light-weight external thermal insulation materials has a negative impact on building surrounding thermal environment and people’s health. Finally, some suggestions on how to eliminate the impact, such as improving the surface condition of the building envelop, and plating vertical greening, are put forward.
Key words: surface heat storage coefficient; external thermal insulation; building; thermal environment; building envelop
1 Introduction
The external wall thermal insulating technology, an effective energy-saving measure, has been used on a large scale. While meeting the original purpose of reducing building energy consumption, it shows some advantages in creating comfortable indoor thermal environment [1-2]. Currently, external wall insulation has three forms: external insulation, sandwich insulation and internal insulation, and the most popular form is the external insulation with light-weight insulation materials, for the following several reasons: 1) wide application range; 2) almost eliminating the effect of ‘hot bridge’; 3) protecting the building subject structure well; 4) being convenient for energy efficiency retrofit of existing residential buildings [3-6].
However, the use of light-weight insulation materials has caused a new problem. In summer, because the light-weight external thermal insulating materials have lower heat storage coefficient, it makes a noticeable decline in heat storage capability of the outside surface of external wall. Combined with the good thermal insulation capability of the wall itself, large amount of heat will accumulate on the outside surface, thus causing the outside surface temperature to rise significantly. For the presence of convective heat transfer effect, the temperature of air near buildings will increase. The use of light-weight external thermal insulation materials will be likely to deteriorate the building surrounding thermal environment. However, the problem has not caught people’s attention. For one aspect, currently, the research of external thermal insulation is mainly focused on how to reduce energy consumption of buildings, how to improve insulation materials and the effect on indoor thermal environment when using insulation materials [7-9]; on the other hand, the researches on the building surrounding thermal environment mainly focus on the surface condition of envelope (absorption rate, reflection rate and rough degree) and vertical greening [10-11]. In the work, the problem will be discussed.
2 Methods
2.1 Calculation of surface heat storage coefficient
When the outside surface of external wall receives a certain amount of heat, the temperature change directly depends on the surface heat storage capacity. At present, the common used light-weight external insulation materials are extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), expanded polystyrene foam (EPS), adhesive polystyrene granule thermal insulation polystyrene and granule thermal insulation mortar etc. The common external insulation walls were selected and a calculation of their outside surface heat storage coefficient was made, in order to study the heat storage capacity of outside surface when using the light-weight external thermal insulation materials.
Surface heat storage coefficient means the amount of heat being absorbed or released in 1 m2, when the surface temperature varies by 1 K in 1 h, under the influence of periodic thermal impact [12]. The calculation method is as follows [13]:
1) The outside surface heat storage coefficient of each layer of multilayer wall is calculated from inside to outside:
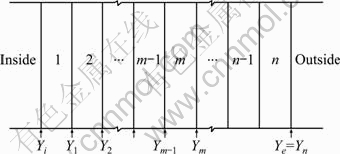
Fig. 1 Structure of multilayer wall
If the thermal inertia index of any layer D≥1, then Y =S. The heat storage coefficient of this material is got.
If the thermal inertia index of the first layer D<1, then:
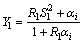 (1)
(1)
If the thermal inertia index of the second layer D<1, then:
 (2)
(2)
For the last layer (layer n),
 (3)
(3)
where D is thermal inertia index; S1, S2, …, Sn are heat storage coefficients of each layer, W·m-2·K-1; R1, R2, …, Rn are heat resistances of each layer, m2·K·W-1; Y1, Y2, …, Yn are heat storage coefficients of the outside surface of each layer, W·m-2·K-1; αi is heat exchange coefficient of inner surface, W·m-2·K-1.
2) The heat storage coefficient of outside surface of multilayer wall should be the heat storage coefficient of last layer, that is, Ye=Yn.
3) The calculation method of heat storage coefficient of inner surface of multilayer wall works from the last layer (layer n) to layer 1.
2.2 Field measurements
In order to further study the effect on outside surface temperature change when the surface heat storage coefficient is reduced, a contrasting experiment between an insulated room and a based room was carried out (Fig. 2). The external wall of the insulated room is 1# wall (Table 1), while others are built with the traditional solid clay brick. They are located on the roof of a three-floor building in Chongqing and built in the same geometric dimensions and nearby each other (without mutual occlusion). The structure of floor and roof is the same. Because the two rooms are both with white cement plaster wall surface, there is no difference on surface reflectance, absorption rates and roughness. The experiment was taken between 8:00 and 22:00 on August 30, 2010. A small weather station near the experiment platform was used to record the data of outdoor air dry-bulb temperature, relative humidity and solar radiation intensity. The outside surface temperature of exterior wall was measured by self-made copper-constantan thermocouples. During the experiment, the two split-type air conditioners which were installed at the same place in each room both run in continual state, and the set temperature was 26 ℃, while the air change rate was controlled to be 1/h.

Fig. 2 Contrasting experiment platform
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Outside surface heat storage coefficient
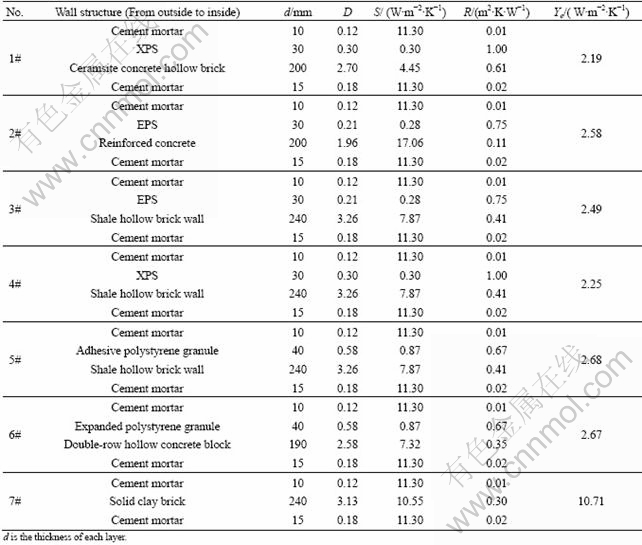
According to Ref. [13], αi =8.7 W/(m2·K). Using the method referred in Section 2.1 and making a calculation of outside surface heat storage coefficient of several walls composed of light-weight external thermal insulation materials and traditional solid clay bricks wall, the results are given in Table 1. There are four kinds of common external thermal insulation materials: XPS, EPS, latex polystyrene granule thermal insulation mortar and expanded polystyrene granule thermal insulation mortar, and their D values are all less than 1.5, being consistent with the definition of light building materials in Ref. [10]. The Ye values of 1#-6# walls are between 2.19 and 2.68, far less than that of traditional solid clay brick wall (10.71). When all of them are in the same condition, the outside surface will absorb same amount of heat, and the temperature of 1#-6# walls will rise significantly, due to the lower Ye value.
Table 1 Thermal parameters of common external insulation walls and solid clay brick wall
3.2 Weather data
Figures 3 and 4 describe the changes of outdoor air dry-bulb temperature, relative humidity and solar radiation intensity at intervals of 0.5 h during the experiment. As shown in Figs. 3 and 4, outdoor air dry-bulb temperature, relative humidity and intensity of solar radiation are all at a high level during the experimental period. This reflects the summer climate features of Chongqing.
3.3 Outside surface temperature trends
Figure 5 shows the changes of outside surface temperature of external wall of based room, while Fig. 6 shows the changes of outside surface temperature of external wall of insoulation room. From Figs. 5 and 6, the eastern wall has been irradiated by the sun before 11:00 in the morning, and the surface temperature is higher than that of others. As solar azimuth angle changes, the amount of solar radiation accepted by the eastern wall is less and surface temperature begins to fall. Around 10:00, the sun irradiates to southern wall. Due to the increasing solar radiation intensity, the outside surface temperature of the southern wall rises sharply and finally reaches to the maximum at about 14:00. In the afternoon, the western wall begins to receive sunlight and outside surface temperature rises rapidly. The temperature reaches to the maximum at nearly 17:30, because the amount of solar radiation is at the highest level. The maximum west outside surface temperature values of the two rooms are both higher than 47 ℃. Because northern wall accepts little sun all the daytime, heat convection effect between wall and air becomes dominant, so the trends of the outside surface temperature is similar with outdoor air dry-bulb temperature.
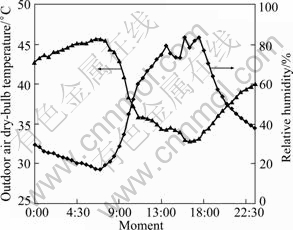
Fig. 3 Changes of outdoor air dry-bulb temperature and relative humidity
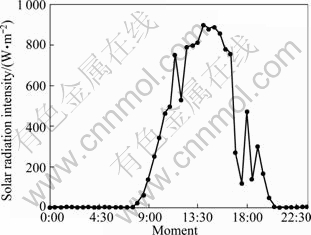
Fig. 4 Change of solar radiation intensity
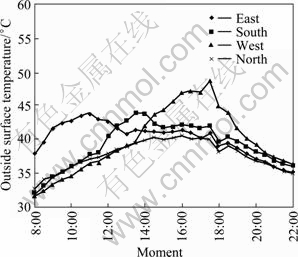
Fig. 5 Changes of outside surface temperature of external wall of based room
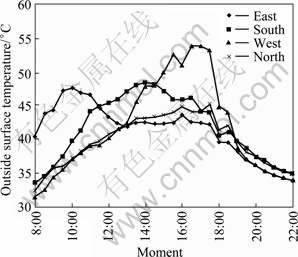
Fig. 6 Changes of outside surface temperature of external wall of insulation room
3.4 Comparison of outside surface temperature
As shown in Figs. 7-10, the outside surface temperature of external walls in different orientations presents different variations with time, and the outside surface temperature of wall of thermal insulation room in the same orientation is higher than that of the based one during sunny time. Meanwhile, the contrasting temperature difference (CTD) of each orientation also shows different trends.
DCT =Tins-Tbas (4)
where DCT is the contrasting temperature difference; Tins is the outside surface temperature of external wall of the insulation room; Tbas is the outside surface temperature of external wall of based room.
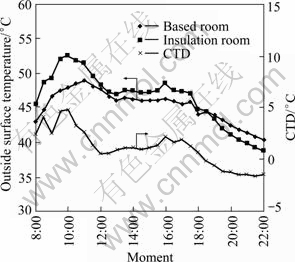
Fig. 7 Comparison of outside surface temperature of eastern external wall
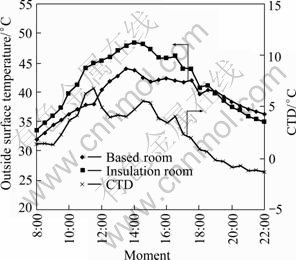
Fig. 8 Comparison of outside surface temperature of southern external wall
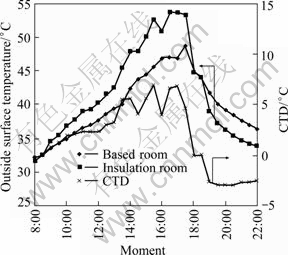
Fig. 9 Comparison of outside surface temperature of western external wall

Fig. 10 Comparison of outside surface temperature of northern external wall
Taking Fig. 7 for example, from 8:00 to 10:00, the eastern wall is under the sun, and CTD changes with the increase of solar radiation. At 10:00, CTD reaches the maximum (4.8 ℃). Later, with the drop of the amount of accepted solar radiation, eastern wall surface gets to cool and CTD gradually drops. After 18:30, the eastern wall surface temperature of insulated room is lower than that of others. As shown in Figs. 8-10, CTD of southern external wall reaches the maximum (6.8 ℃) at 11:30; western CTD reaches the maximum (7 ℃) at 15:30; northern CTD reaches the maximum (4 ℃) at 17:30. Besides, during day time, the range of CTD towards four orientations is different from each other: West (10 ℃)> South (7.0 ℃)>East (3.9 ℃)> North (2.8 ℃). There are two reasons for the discrepancy: 1) Because external walls in different orientations are irradiated by sun in different time, the maximum values appear in different period. Because northern external wall couldn’t accept sunlight all the day time, the CTD could not appear an obvious fluctuation; 2) The wall facing different directions accepts different amounts of sun radiation, which makes the maximum value and fluctuations of CTD range different. For western external wall, at nearly 15:00, solar radiation is at the highest level of the day and the sun directly irradiates the western wall, so the maximum CTD of the western wall is significantly greater than that of others, and the fluctuations is also the greatest.
Above all, it is clear that the use of light-weight insulation materials exactly has an effect on building surrounding thermal environment. The external wall orientated differently will be irradiated in different time and can receive different amounts of solar radiation, so the outside surface temperature of each wall presents different variation. And solar radiation has a great effect on CTD.
3.5 Improving measures
The primary target of using thermal insulation material is to reduce the building energy consumption effectively. The problem discussed is not contradictious, but to evaluate the light-weight thermal insulation materials in a more comprehensive view. According to following measures, we can get win-win between reduction of building energy consumption and decrease of impact on building surrounding thermal environment:
1) It is effective to reduce surface temperature of external wall by changing the color, roughness of outside surfaces [10, 14].
2) Reduction of surface temperature of external wall can be achieved by planting climbing plants on building envelop, which can improve the surrounding thermal environment, and play a part in greening and heat insulation [15].
3) Protect people from direct influence of high radiation temperature of building envelope by planting some plants nearby exposed buildings.
4) As refer to solar radiation and air temperature at high level, people should reduce outdoor activities as less as possible, and don’t active near western external wall, in summer afternoon.
4 Conclusions
1) Theoretic calculation indicates that the use of light-weight external thermal insulation materials will reduce the outside surface heat storage capacity obviously.
2) Results of the compared experiment illustrate that the surrounding thermal environment of building enveloped by external insulation wall is much worse than that of buildings enveloped by heavy-weight wall.
3) Some corrective measures, such as improving outside surface condition of wall, and plating vertical virescence, can reduce the negative influence from using light-weight external thermal insulation materials.
References
[1] JIAN Yi-wen, JIANG Yi. Impacts of architectural design on thermal performances of residential buildings [J]. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 2002, 32(5): 26-29. (in Chinese).
[2] JIAN Yi-wen, JIANG Yi. Evaluation of thermal performance of exiting residential buildings in Beijing [J]. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 2002, 32(3): 7-10. (in Chinese).
[3] DYLEWSKE R, ADAMCZYK J. Economic and environmental benefits of thermal insulation of building external walls [J]. Building and Environment, 2011, 46(12): 2615-2623.
[4] HOGLUND T, BURSTRAND H. Slotted steel studs to reduce thermal bridges in insulated walls [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 1998, 32(1/3): 81-109.
[5] MAHLIA T M I, TAUFIQ B N, ISMAIL, MASJUKI H H. Correlation between thermal conductivity and the thickness of selected insulation materials for building wall [J]. Energy and Buildings, 2007, 39(2): 182-187.
[6] UCAR A, BALO F. Determination of the energy savings and the optimum insulation thickness in the four different insulated exterior walls [J]. Renewable Energy, 2010, 35(1): 88-94.
[7] LI Bai-zhan, ZHUANG Chun-long, DENG An-zhong, LI Sheng-bo. Improvement of indoor thermal environment in light weight building combining phase change material wall and night ventilation [J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering, 2009, 31(3): 109-113. (in Chinese)
[8] YU Jing-hua, YANG Chang-zhi, TIAN Li-wei, LIAO Dan. A study on optimum insulation thicknesses of external walls in hot summer and cold winter zone of China [J]. Applied Energy, 2009, 86(11): 2520-2529.
[9] ASAN H. Investigation of wall’s optimum insulation position from maximum time lag and minimum decrement factor point of view[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2000, 32(2): 197-203.
[10] OU Yan-qiong. Study on the residential districts air temperature variation: Under the influence of heat emission from building facades [D]. Guangzhou: School of Architecture, South China University of Technology, 2010. (in Chinese)
[11] LIN Bo-rong. Studies of greening's effects on outdoor thermal environment [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2004. (in Chinese)
[12] Civil Construction Engineering Dictionary Writing Group. Terms [J]. Construction Technology, 1981(10): 63. (in Chinese)
[13] China Academy of Building Research. GB50176—1933. Hot-civil construction design standards [S]. Beijing: China Architecture Industry Press, 1996. (in Chinese)
[14] BANSAL N K. Effect of exterior surface color on the thermal performance of buildings [J]. Building and Environment, 1992, 27(1): 31-37.
[15] PERINI K, OTTELE M, FRAAIJ A L A, HAAS E M, RAITERI R. Vertical greening systems and the effect on air flow and temperature on the building envelope [J]. Building and Environment, 2011, 46(11): 2287-2294.
(Edited by HE Yun-bin)
Foundation item: Project(2011BAJ03B13) supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China
Received date: 2011-07-26; Accepted date: 2011-11-14
Corresponding author: LI Nan, Associate, Professor; Tel: +86-13658378086; E-mail: nanlicqu@yahoo.com.cn