累积叠轧技术的研究现状与展望
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2007年第6期
论文作者:詹美燕 李元元 陈维平
文章页码:841 - 841
关键词:累积叠轧;超细晶;剧塑性变形;微观组织;力学性能;
Key words:accumulative roll-bonding; ultrafine grains; severe plastic deformation; microstructure; mechanical properties
摘 要:
Abstract: The process of accumulative roll-bonding was reviewed. The principle of ARB, the ARB processed microstructure and mechanical properties were described in detail. The shear strain, mechanism of grain refining and strengthening were analyzed. Large size materials with ultrafine grains can be achieved easily by ARB process, whose tensile strength is usually 2-4 times compared with those of coarse grain materials. The strengthening can be attributed to the ultrafine grains, dislocation and texture developed during ARB process, as well as the dispersed oxide films and inclusions on the surfaces by repetition. According to its advantages on the manufacture of high-strength bulk materials at a high level of productivity, ARB is a promising process in preparing materials with UFG microstructure.
基金信息:国家自然科学基金资助项目
广东省自然科学基金重点资助项目
中国博士后科学基金资助项目
文章编号:1004-0609(2007)06-0841-11
詹美燕,李元元,陈维平
(华南理工大学 机械工程学院,广州 510640)
摘 要:对采用累积叠轧工艺制备超细晶组织的技术进行详细的综述,介绍了累积叠轧技术的原理、ARB材料的组织与力学性能特征,并对ARB变形过程中的剪切变形、晶粒细化机制和强化机制进行分析。采用ARB技术可以制备大尺寸的超细晶组织材料,其室温抗拉强度通常比粗晶材料的高2~4倍。ARB材料的强化源于晶粒细化、位错强化、在大变形轧制时形成的稳定基面织构、表面的氧化膜以及内生原有夹杂物在强烈塑性变形情况下的破碎与弥散分布。分析了ARB技术的优越性,对其在制备超细晶材料领域的应用进行了展望。
关键词:累积叠轧;超细晶;剧塑性变形;微观组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG 142.1 文献标识码:A
ZHAN Mei-yan, LI Yuan-yuan, CHEN Wei-ping
(School of Mechanical Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China)
Abstract: The process of accumulative roll-bonding was reviewed. The principle of ARB, the ARB processed microstructure and mechanical properties were described in detail. The shear strain, mechanism of grain refining and strengthening were analyzed. Large size materials with ultrafine grains can be achieved easily by ARB process, whose tensile strength is usually 2?4 times compared with those of coarse grain materials. The strengthening can be attributed to the ultrafine grains, dislocation and texture developed during ARB process, as well as the dispersed oxide films and inclusions on the surfaces by repetition. According to its advantages on the manufacture of high-strength bulk materials at a high level of productivity, ARB is a promising process in preparing materials with UFG microstructure.
Key words: accumulative roll-bonding; ultrafine grains; severe plastic deformation; microstructure; mechanical properties
1 剧塑性变形工艺制备超细晶组织
近年来,关于纳米晶和超细晶/亚微米晶的加工工艺、组织和性能的研究受到广泛关注。通常认为纳米晶的晶粒尺寸范围为d<100 nm[1],超细晶(Ultrafine grains,UFG)的晶粒尺寸范围为100 nm
![]()
式中 d为晶粒的平均直径;σ0为其它强化方式作用项;k为常数。晶粒尺寸对材料流动应力的影响如图1所示[7]。
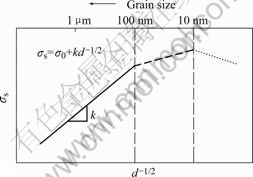
图1 晶粒尺寸对材料流动应力的影响
Fig.1 Effect of grain size on flow stress of materials
制备纳米晶和超细晶的方法主要有如下两种[1]:1) Top-down工艺,旨在细化常规组织材料的晶粒;2) Bottom-up工艺,旨在从原子和分子的基础上合成细小的晶粒组织。通常制备UFG组织的方法有[6]:快速凝固(Rapid solidification)、气相沉积(Vapor deposition)、机械合金化(Mechanical alloying)、低温金属成形(Cryogenic metal forming)和剧塑性变形(Severe plastic deformation, SPD)等,其中剧塑性变形被认为最适于工业化生产[8]。近20年来,开发了几种SPD技术来制备具有UFG组织的块材和板材[5, 9?13],如等通道挤压(Equal-channel angular extrusion/pressing,ECAE/P)、高压扭转(High-pressure torsion,HPT)和多轴压缩/锻造(Multi-axial compressions/forging,MAC/F)等技术用于制备块体材料的UFG组织;累积叠轧(Accumulative roll-bonding, ARB)和连续剪切变形(Conshearing process)等技术用于制备具有UFG组织的板带材。通常金属材料的晶粒细化主要是通过传统的塑性变形加工和随后的退火工艺(发生再结晶和晶粒长大)来获得的,这种常规工艺所制备的材料的晶粒尺寸最小约为10 μm。在传统的金属塑性变形工艺中,如轧制工艺,工业上传统冷轧加工所能达到的总应变量约为60%~80%,相当于von Mises 等效应变εvm=1.06~1.86,有效应变εvm>4的情况只有在轧制箔材时才能获得。相对传统的塑性变形工艺而言,SPD技术设计目的在变形过程中保持坯料的外形基本不变,从而可达到的应变不受材料外形的影响。大多数SPD过程实质上是一种循环的变形过程,但通常会有变形路径的变化。
2 累积叠轧技术原理
累积叠轧工艺最早是日本Saito等[6]于1999年左右提出来的,其工艺原理如图2所示。累积叠轧是将表面进行脱脂及加工硬化等处理后的尺寸相等的两块金属薄板材料在一定温度下叠轧并使其自动焊合,然后重复进行相同的工艺反复叠轧焊合,从而使材料的组织得到细化、夹杂物分布均匀,大幅度提高材料的力学性能。轧制是制备板材最具优势的塑性变形工艺,然而随着材料厚度的减小,材料的总应变量受到限制。在累积叠轧工艺中,材料可以反复轧制,累积应变可以达到较大值,在理论上能获得很大的压下量,突破了传统轧制压下量的限制,并可连续制备薄板类的超细晶金属材料,因此ARB工艺被认为是剧变形工艺中惟一有希望能工业化生产大块超细晶金属材料的方法。ARB工艺中材料的几何变化如表1所列[2]。
表1 ARB工艺过程中材料的几何变化
Table 1 Geometrical change of materials during ARB
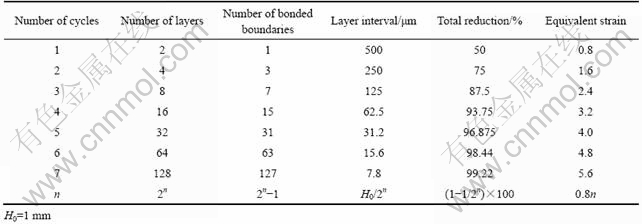
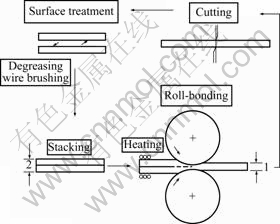
图2 累积叠轧工艺原理[6]
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process
ARB已被成功应用于纯铝、铝合金和无间隙钢 (Interstitial free, IF)及少量的变形镁合金[1,14-18] ,其中ARB铝合金包括纯铝(1100)、Al-Mn(3003)、Al-Mg(5083)、Al-Mg-Si(6061)、Al-Fe-Si(8011)、Al-Cu合金(Al-2Cu)和铝基复合材料。
3 累积叠轧材料的组织与性能
3.1 组织特征
研究发现[19]:通过SPD技术能制备的最小晶粒尺寸为亚微米的尺寸水平。SPD的等效应变大于4以后可以获得UFG组织,晶粒尺寸小于1 μm[20]。变形温度越低,晶粒尺寸越小。同时,低层错能材料以及材料中具有阻碍回复过程发生的元素,经过SPD变形的晶粒也会更小。对剧塑性变形温度与晶粒尺寸的研究表明[4],在变形温度小于0.4Tm时(Tm为变形材料的熔点,K),可以制备亚微米级的组织,而制备纳米晶的变形温度必须小于0.2Tm,但大多数合金在小于0.2Tm变形时会发生断裂。剧塑性变形温度与晶粒尺寸的关系如图3所示[4]。
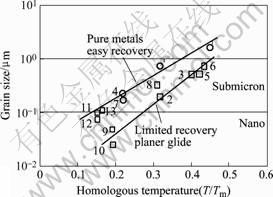
图3 SPD制备材料的晶粒尺寸与变形温度[4]
Fig.3 Grain sizes measured in severely deformed alloys processed by ECAE, ARB and SPTS plotted against homologous temperature: ECAE: (1) Al; (2) Al-3%Mg; (3) IF steel; (4) Cu; ARB: (5) I F steel; HPT: (6) Zn-22Al; (7) Cu; (8) Mg; (9) and (10) AlNi3; (11) Fe; (12) Ti; (13) Ni
铝合金和钢铁材料的ARB超细晶组织通常呈板条状组织,晶粒在轧制纵向呈明显的延伸状。典型的ARB组织如图4所示[21]。ARB变形能显著细化晶粒组织,如原始晶粒为23 μm的IF钢在ARB变形温度为500 ℃、等效应变εvm=4.0时,晶粒尺寸为210 nm×700 nm,长条状的UFG中存在位错和亚晶界,大多数UFG组织被大角度晶界所包围[22]。Al-Fe-Mn-Si (AA8006) 原始晶粒尺寸为16 μm,在ARB变形温度为200 ℃,等效应变εvm=2.4时,晶粒尺寸为0.4~0.8 μm,此后细化不明显[15]。TEM组织观察表明:亚晶或晶内的位错密度在整个ARB过程中几乎没有变化。1100Al的原始晶粒尺寸37 μm,在200 ℃下变形,ARB组织呈现薄片状,当ε=6.4时,薄片组织的尺寸约为240 nm×820 nm[8]。当εvm=1.6时,组织为大角度晶界(大于15?)和小角度晶界(小于15?)共同组成;当εvm更大时,主要是大角度晶界。6061Al在室温下进行ARB变形,原始晶粒尺寸25 μm[23],ARB3就出现了UFG组织,晶内位错密度很低,UFG的比例随ARB道次的增加而增加;经6道次后,UFG组织的尺寸为500 nm左右;经8道次后,UFG组织的尺寸为300 nm。界面TEM观察表明,界面组织由UFG及许多氧化物和析出相组成。氧化物来源于ARB处理之前表面形成的氧化物薄层[24]。
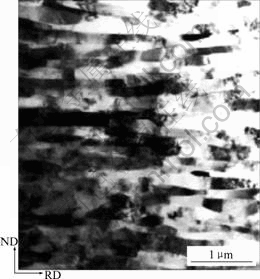
图4 1100Al经过4道次ARB变形后的微观组织
Fig.4 Microstructure of 1100Al sheet ARB process four cycles
关于镁合金ARB工艺及组织的研究较少,对AZ31和AZ91合金在400 ℃进行ARB处理,初始晶粒分别为38和23 μm。结果表明[1]:AZ31经过ARB1后,晶粒呈等轴晶状,晶粒尺寸为4 μm,此后稳定在3 μm左右;AZ91经过1道次后,晶粒尺寸小于1 μm,此后晶粒尺寸逐渐均匀化。经过4个道次ARB变形后的AZ31和AZ91组织如图5所示[1]。

图5 经过4个道次ARB变形后AZ31和AZ91的显微组织
Fig.5 Microstructures of AZ31 (a) and AZ91 (b) alloys processed by accumulative roll bonding after 4 cycles
以上研究表明:1) 铝合金和钢铁材料的ARB组织通常呈板条状组织,镁合金的ARB组织呈等轴晶状,可能是由于镁合金易发生再结晶;2) 晶粒细化主要发生在前面几道次,随后晶粒尺寸变化不大,但晶粒大小均匀性增加;3) ARB材料最终的晶粒大小取决于应变的累积程度,它受到动态回复的容易程度、加工温度和扩散程度的影响。如1100Al、5083 Al-Mg和IF钢在7道次ARB后,晶粒尺寸分别为670,280和420 nm[24]。通常在再结晶温度下进行大塑性变形并且没有中间退火,可以制备UFG组织;4) 增加第二相可以阻碍UFG组织晶粒长大。
3.2 取向差与织构
ARB变形过程中应变与组织取向差的关系如图6所示[8]。由图6可看出,随ε增加,取向差在εvm=3.2时达到饱和值36?。与常规冷轧组织比较,ARB组织与之具有相似性,如在大应变时形成薄片状组织,薄片状组织的层间距随ε的增加而下降。两者取向差随应变的变化如图7所示[8]。由图7可见,ARB工艺加速了组织的演变过程,可归因于ARB工艺中,在板厚方向产生了大的剪切变形。
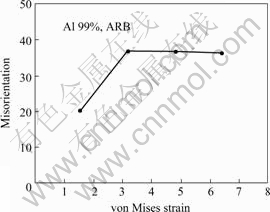
图6 层状组织的取向差与应变的关系
Fig.6 Relationship between mean misorientation angle across lamellar boundaries and strain
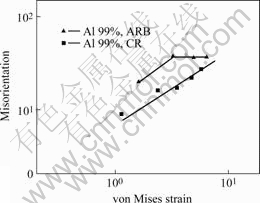
图7 ARB 和冷轧纯铝的层状组织的取向差与应变关系的比较
Fig.7 Comparison of misorientation across lamellar boundaries formed in ARB processed Al and in conventionally cold-rolled Al and strain
传统冷轧板在大应变时具有典型的轧制织构,表明板材发生了均匀的轧制变形。而ARB板材的极图测试表明[8],即使当ε为3.2和6.4时,织构仍然很弱,可能是由于大的剪切变形会改变滑移方式。对于纯铝ARB组织研究表明,轧制方向的织构明显弱化[8]。Saito等[25]对纯铝累积叠轧组织演变的研究表明,尽管经过剧烈的塑性变形,但ARB板材的织构较弱。此外,ARB材料在次表面的织构和厚度中心的织构完全不同,次表面为典型的剪切织构,而厚度中心部位与轧制织构相似,可归因于ARB过程中的剪切变形[22]。ARB过程中没有任何润滑,此时由于轧制金属和轧辊之间较大的摩擦力,在板材的厚向表面产生大的剪切变形。中心部位的织构与传统轧制的织构相似,而现在的中心部位是上一道次中的表面位置,说明表面剪切织构在传统的轧制中容易被破坏。
3.3 力学性能
3.3.1 抗拉强度
某些金属经过ARB变形后的组织和性能如表2所列[2, 6]。由表2可见,金属经过ARB变形后,组织细小,有的甚至为纳米级;较低的温度下的变形组织更细小;ARB材料的强度比常规材料高2~4倍。1100Al 和6060Al在ARB变形过程中力学性能随等效应变的变化(见图8)[23]。由图8可见,ARB材料的强度随应变的增加而增加。在200 ℃下经过6道次ARB变形,1100Al的抗拉强度由80 MPa增加到300 MPa,提高2.75倍[25]。通常商业结构金属材料的最小平均晶粒尺寸约为10 μm[20],小于1 μm的UFG组织的材料可能会呈现优异的性能,如高的强度、韧性和抗疲劳性能。实际上,SPD工艺制备的UFG材料通常比粗晶材料的强度高2~4倍。
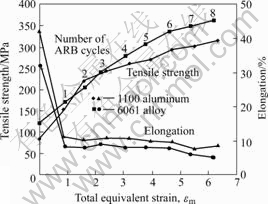
图8 1100Al和6061Al力学性能与ARB应变量的变化曲线
Fig.8 Change curves of mechanical properties of 1100Al and 6061Al alloys with total equivalent strain in ARB process
表2 各种材料经过ARB变形后的组织与拉伸性能
Table 2 Microstructure, grain size and tensile strength of various kinds of metals and alloys ARB processed
3.3.2 伸长率
ARB材料的伸长率在第一道次后急剧下降,此后基本保持不变。如1100Al在ARB1后,伸长率由50%下降到8%[25]。经过大塑性变形后,材料的组织和结构会发生明显的变化,晶粒内部出现各种形变亚结构,位错密度会大幅度增加,因而会出现加工硬化现象,这是材料强度增加塑性降低的主要原因。此外,试样表面的氧化物在轧制过程中进入了试样内部,这也对材料的强度起到了增强作用,但同时它也是材料伸长率下降的原因,氧化物的聚居区就成了断裂的裂纹源,因而伸长率下降。但随着实验的进行,氧化物分布逐渐均匀,因而伸长率略有升高。此外,Tsuji等[26]认为,当ARB变形后的晶粒小于1 μm时,屈服后没有出现明显的硬化现象,即抗拉强度和屈服强度相近,而硬化是发生均匀变形的必要条件,因此使拉伸变形时断裂伸长率下降。换言之,晶粒小于1 μm后的材料出现了塑性不稳定性。
经过ARB变形的材料在性能上的局限性,即延性比变形前下降,会在高道次ARB过程中容易出现边裂和中心断裂[6]。可以通过以下措施改善ARB材料的伸长率:1) 通过加强材料本身的加工硬化能力,如在基体中引入细小的弥散分布的第二相,来改善具有UFG组织材料的拉伸延性;2) 通过退火来获得最佳的综合力学性能[27]。低应变材料在退火中,可以发生不连续再结晶,期间离散形核的晶粒会发生长大。SPD材料具有70%以上的HAGB,在退火过程中发生连续的再结晶,HAGB的含量不变。退火过程中晶界局部发生重排,以平衡表面张力,新晶粒不会发生长大[4]。但是在1100纯Al的ARB试样退火时,尽管延性有大的增加,由于退火时很容易发生再结晶与晶粒长大,因此材料的强度也下降较多[23]。如果材料中含有细小的析出相或增强相颗粒,可以预料退火过程不仅可以使延性增加,且由于第二相的钉轧作用,强度下降不会很大,从而获得优良的综合性能。
3.4 强化机制
ARB工艺制备的UFG材料通常比粗晶材料的强度高2~4倍。其强化机制可归纳为以下几种:1) ARB材料在较低的应变时强度迅速上升,可归因于亚晶界的形成,而不是晶粒细化,因为在较低温度下,组织的演变主要是位错密度的增加和多方向滑移带的形 成[28],材料中形成了传统的亚晶结构,取向差较小;2) 最终ARB材料的强化源于晶粒细化[25]、位错强 化[20]以及在大变形轧制时形成的稳定的基面织构[29]。文献[30]认为ARB材料强度增加是晶粒细化和织构的共同影响。当基面织构平行于拉伸轴时,激活基面滑移的临界剪切应力(Critical resolved shear stress,CRSS)会动态地增加,使拉伸强度大大增加。详细的强化机制尚在讨论中;3) 经过多道次ARB,金属表面的氧化膜以及内生原有夹杂物在强烈塑性变形的情况下破碎,在基体内均匀分布。这些微小粒子的存在起到了钉扎晶界阻碍晶粒移动长大的作用,从而使材料强化;4)表面层在金属刷打磨时形成的硬化层,以及由于大应变使金属间化合物相固溶而引起的硬化作用,也是ARB材料强化的机制之一[30?31]。
4 ARB过程中的剪切变形和晶粒细化机理
4.1 剪切变形
轧制板材的变形受轧辊和金属间摩擦条件的影响很大。众所周知,在较大的摩擦条件下,如热轧时,或在轧辊辊面没有润滑的情况下,轧制过程中在板材的次表面会发生较大的剪切变形[2]。由于表面区域大的剪切变形,金属在厚度方向上的变形是很不均匀的[32?33]。
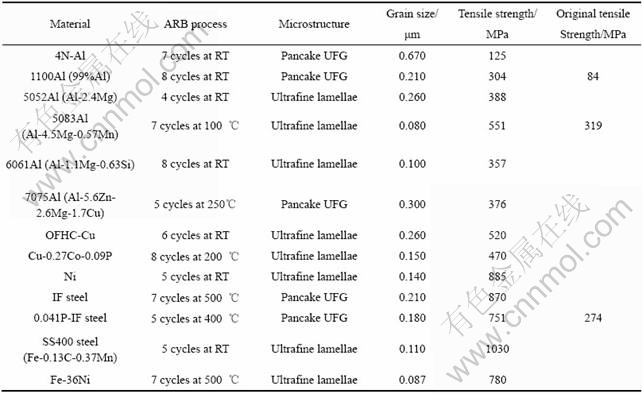
ARB工艺通常轧辊不进行润滑,由于大的轧机和轧辊表面之间的摩擦,在材料的次表面可能产生大的剪切应变。Tsuji等[2]在板材的厚度方向钉入一枚钉子,ARB变形后钉子的变形如图9所示[2]。由图9可见,经过1 道次的ARB变形,钉子发生大的剪切变形。
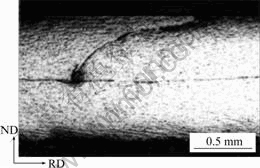
图9 埋入1100Al板材厚度方向的钉子经1道次ARB变后的弯曲形貌
Fig.9 Optical microstructure of flection of embedded pin in 1100Al sheet ARB processed by one cycle at ambient temperature without lubrication
根据图9计算出的板材沿厚度方向不同道次剪切应变的分布如图10所示[18]。由图10可见,多道次后,剪应变分布很复杂,因为每次叠轧后,板材的表面又进入中心,因此与传统轧制比较,发生剪切变形不仅在板材的表面区域。ARB过程实际上是平面应变和剪切应变的共同作用,而剪切变形并不改变板材的厚度,因此在剪切变形和平面变形叠加的区域,等效应变中必须加上剪切应变,从而使等效应变大大增加,远大于0.8 n(道次变形量为50%时)。文献[34]比较了经过相同变形量的冷轧和ARB变形的1100Al的组织和力学性能。研究结果表明,当变形量ε=4.8时,1100Al冷轧层状组织的尺寸为0.33 μm×1 μm,ARB后层状组织的尺寸为0.2 μm×0.57 μm,表明ARB的实际总应变量更高。据计算,道次等效应变为0.8时,每ARB道次引入的剪切应变是1.2左右[23]。文献[8]认为,在同样的应变下,99%Al通过ARB变形形成UFG组织的速度比常规轧制变形要快得多,可能的原因之一是由于在ARB工艺中会发生大的剪切变形。Utsunomiya等[23]的研究表明,在有润滑的条件下,Al板即使经过7道次的ARB,仍然很难形成UFG组织。
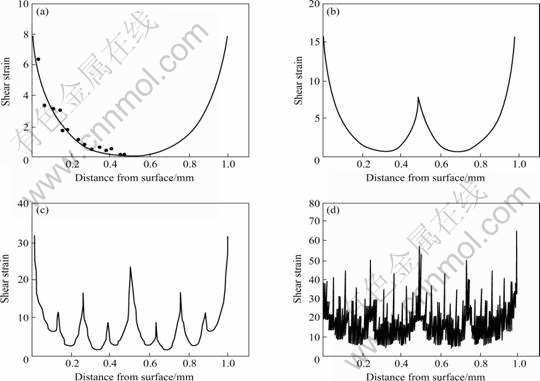
图10 ARB变形过程中沿板材厚度方向的剪切应变分布
Fig.10 Distribution of shear strain through thickness of 1100Al ARB processed by different cycles at RT: (a) 1 cycle; (b) 2 cycle; (c) 4 cycle; (d) 8 cycle
大的剪切变形会使板厚方向的组织和织构分布不均匀。沿板厚方向晶粒大小与剪切应变分布的关系如见图11所示[23]。在剪切应变的峰值位置对应出现更细小的UFG组织,表明在ARB过程中,剪切应变在UFG形成过程中扮演了重要的作用。在ARB过程中,厚度方向不仅存在剪切应变,且不同位置剪切应变存在较大的应变梯度。在剪切应变的峰值位置对应出现更细小的UFG组织,可以认为是由于在该位置出现了较大的应变梯度。研究[35]发现,几种金属在εvm=4.8的组织在厚度方向是均匀的,表明ARB工艺制备的组织,在εvm较大时是可以达到均匀的。因为当εvm较小时,剪切应变沿厚度方向分布很不均匀;当εvm很大时,其分布逐渐均匀。
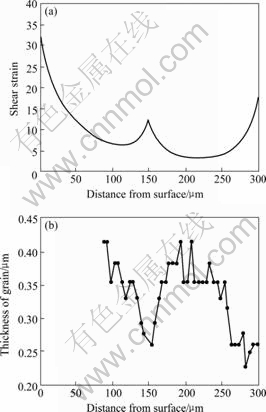
图11 ARB变形过程中剪切应变和晶粒尺寸分布的关系
Fig.11 Relationship between shear strain distribution and grain size distribution in 1100Al sheet ARB processed by four cycles
4.2 晶粒细化机理
在大应变诱发晶粒细化的变形中,形成新的大角度晶界(High angle grain boundary, HAGB)的机制有两种[4]:1) 原有晶界随着应变的增加成比例扩展[36];2) 通过晶粒细分而形成新的HAGB[37]。第二种机制在传统应变(εvm<3)中进行了广泛的研究[36?38]。晶粒被大角度晶界细分是一个主要的机制。在亚微米尺寸领域,变形诱发大角度晶界形成,使晶粒被细分。此后通过回复形成具有平衡晶界的UFG。因此在厚度方向,剪切变形越大,则晶粒会越细,由于大的等效应变会导致大的位错积累,即晶粒被分得更细。
ARB可以制备UFG组织(Sub-micron),并使材料大大强化。通常认为,ARB工艺中的晶粒组织演变过程可以归纳为[28]:当ε较小时(ε<1.6),可以观察到位错胞的形成,然后,由于多方向滑移的启动,位错胞不断得到细化,位错胞内的位错密度相对较低;随着ε增加(ε>1.6),位错胞转变为超细的亚晶;在更大的ε时,组织的演变主要是亚晶界转变为大角度晶界,而不是晶粒细化。电子选区衍射SAD花样随ε增加逐渐呈环状,表明大角度晶界的比例不断增加。文献[15]认为ARB晶粒细化的机理是小角度晶界转变为大角度晶界。
与其他大应变工艺相比,ARB晶粒细化机制可以归纳为以下几种[6, 39?40]:1) 在板表面及次表面存在剧烈的剪切变形。ARB过程中通常为了获得良好的界面结合而不使用润滑,因此每次ARB过程中均会在表面区域产生大的剪切变形。这个剪切应变大大增加了ARB过程的等效应变,且在下一道次中有一半的表面又进入厚度中心,从而使高道次ARB之后具有较大剪切变形的表面区域沿厚度分布很复杂,经过多道次后,在整个厚度区域均发生大的应变。这可能是ARB中UFG组织的形成机制之一;2) 另一种机制是引入新的表面,多道次后,ARB材料中引入大量新的表面。这些表面呈现良好的纤维组织。表面的氧化膜和夹杂物通过反复的ARB过程,均匀弥散分布。这些物质可强化材料,成为晶粒长大的障碍物;3) 应变路径对组织细化也有影响[39]。在ECAP制备Al-Mg合金UFG组织的研究中,Iwahashi等[40]报道了应变路径对UFG组织形成的巨大影响,即在ECAP道次间旋转90?,可以更快获得UFG组织,即使最终总的剪切变形量相等。在ARB中,具有大的剪切变形的表面区域在下一道次中进入中心部位,发生传统的平面轧制变形,这种应变模式也可以看作应变路径的改变,可能在UFG组织的形成中起了重要作用;4) 在ARB变形过程中还有其它一些过程也比较重要,如在剪切带发生集中的滑移会形成HAGB[41];在某些合金中有时孪生变形也会形成新的大角度晶界[42]。而织构的影响可能是理解ARB过程中UFG组织形成机制的关键因素之一。
ARB变形后的UFG不是亚晶,而是晶粒,相互之间具有较大的取向差,从边界取向差的意义上来说,它们具有再结晶晶粒的特征。从另一个方面,UFG组织具有被拉长的形貌,且内部具有位错亚结构,这是变形组织的特征。这些特征可以为在剧塑性变形过程中UFG组织的形成机制提供更多的信息,尽管这些机制还没有完全清楚。
5 ARB技术在镁合金中的研究
大多数关于ARB技术的研究集中在钢铁和铝合金方面,采用ARB技术制备镁合金材料的报道很少。镁及其合金作为21世纪最具潜力的绿色环保结构材料,具有许多优越性,但也有局限性,除了易氧化腐蚀外,镁合金的强度和延性与其他结构材料相比较低(如铝和钢铁),从而限制了镁合金的成形性能[43?45]。
本文作者采用累积叠轧工艺对AZ31镁合金板材进行了实验研究,结果表明:ARB变形对AZ31镁合金板材力学性能的影响与其铝合金和钢铁材料的影响不同,AZ31镁合金板材经过400 ℃ARB变形后的力学性能如图12所示。镁合金轧制板材纵向伸长率小于横向,是由于HCP晶体结构的不对称性和轧制过程中形成的板织构引起的,文献[46]也得相同的研究结果。由图12可看出,经过3道次的累积叠轧,AZ31镁合金板材的强度略有下降,但延性得到很大的改善,且轧制纵向和横向的各向异性减小。这应该与镁合金在ARB变形过程中的织构演变和动态再结晶有关,详细的变形机理正在深入研究中。
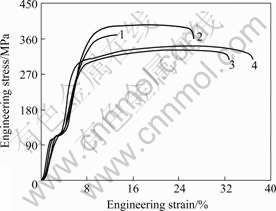
图12 ARB变形对AZ31板材室温力学性能的影响
Fig.12 Effect of ARB process on mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy: 1—As-rolled, longitudinal; 2—As-rolled, transversal; 3—ARBed, longitudinal; 4—ARBed, transversal
此外,ARB变形过程中AZ31的晶粒没有象铝合金一样随着应变的增加发生持续的细化(最终细化到0.5~1.0 μm左右)。这可归因于ARB变形温度的影响:铝合金延性好,ARB温度低于200 ℃(小于其再结晶温度),甚至可以在室温下进行ARB变形。而AZ31镁合由于HCP的晶体结构的脆性,200 ℃下进行ARB发生了表面裂纹,通常ARB变形的温度为400 ℃[1],道次间的加热使细化的晶粒发生明显长大。研究结果表明:300 ℃下AZ31板材经过3道次的ARB变形,平均晶粒尺寸约为1.6~2.0 μm左右(见图13)。此后晶粒没有进一步细化,但组织均匀性有所增加。
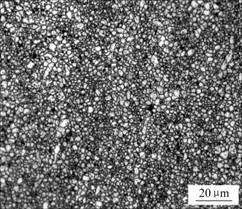
图13 经过ARB变形的AZ31镁合金板材的显微组织
Fig.13 Microstructure of ARBed AZ31 magnesium alloy sheet
6 ARB技术的应用前景与展望
利用很高的应变,使晶粒细化到亚微米水平,从而改善材料的性能,这种指导思想是很具有吸引力的,因为通过这种工艺可以使一些简单的不可热处理强化的合金获得很高的强度,甚至可以和高合金化材料相媲美,且由于材料的合金化程度低,材料可回收性增强,更加符合绿色环保的要求。但大多数SPD工艺有两个主要的局限性[47?50]:1) 对成型设备要求高,要求设备具有较大的载荷能力,模具价格昂贵;2) 生产率低,制备的材料体积小。因此这些工艺不适于工业化生产,尤其不适于制备大尺寸结构材料,如板材。而恰恰是大尺寸的结构材料对强度和韧性的要求较高。
与其他SPD工艺相比,ARB技术具有自身突出的优越性,主要表现在:1) 成本较低,工艺简单。仅通过ARB变形,而不需要添加合金元素,获得UFG和高的强度,具有和高合金化合金相媲美的强度,这种工艺对于降低生产成本和材料密度以及提高金属材料的回收利用性能具有很大的优越性。此外,该工艺不需要特殊的设备,由于在金属包覆生产中,轧制焊合已被广泛应用;2) 生产率高,可以生产大尺寸的材料,容易实现工业化生产。尽管在实验中仅采用宽度为20 mm的薄板,但工业上应用于宽度大的薄板应该不会存在困难;3) 尽管轧制是连续制备大尺寸板材的最优选的工艺,但是厚度方向的总应变受到限制,由于随轧制压下量增加,材料的厚度减小。在ARB工艺中,轧制的材料被切断、层叠,使其厚度与轧制前相同然后进行轧制,这样的过程反复进行,由于反复叠轧在原理上可以进行无数次。因此,材料在厚度方向可以获得的应变是不受限制的。
ARB技术具有诱人的应用前景,但大多数研究集中在变形后材料的组织,对于在变形中出现的晶粒细化机理以及工艺参数和材料参数对最终材料组织的影响,以上方面的研究仍然非常不系统,值得进一步深入研究。
近年来,在镁合金晶粒细化方面进行了一些研究,主要是ECAE和快速凝固粉末的挤压,可以制备晶粒尺寸小于1 μm的材料,然而两者均有局限性,ECAE只能制备小尺寸材料,而粉末冶金?挤压工艺的成本很高[51]。很多努力致力于制备更高强度和延性的镁合金材料,而开发成本经济、适合于工业推广应用的工艺尤其重要。ARB技术的特点及作者的研究初步表明,ARB工艺是一种很有潜力的制备具有细晶组织的大尺寸镁合金板材、改善镁合金强度和延性的工艺技术,镁合金铸锭组织和ARB变形工艺优化、变形机制及经过ARB变形的细晶镁合金的热稳定性尚待进一步研究。
[1] Pérez-Prado M T, del Valle J A, Ruano O A. Grain refinement of Mg-Al-Zn alloys via accumulative roll bonding[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 51(11): 1093?1097.
[2] Tsuji N, Saito Y, Lee S H, Minamino Y. ARB (Accumulative roll-bonding) and other new techniques to produce bulk ultrafine grained materials[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2003, 5(5): 338?344.
[3] del Valle J A, P?erez-Prado M T, Ruano O A. Accumulative roll bonding of a Mg-based AZ61 alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, A410/411: 353?357.
[4] Prangnell P B, Bowen J R, Apps P J. Ultra-fine grain structures in aluminium alloys by severe deformation processing[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, A375/377: 178?185.
[5] Cherukuri B, Nedkova T S, Srinivasan R. A comparison of the properties of SPD-processed AA-6061 by equal-channel angular pressing, multi-axial compressions/forgings and accumulative roll bonding[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, A410/411: 394?397.
[6] Saito Y, Utsunomiya H, Tsuji N, Sakai T. Novel ultra-high straining process for bulk materials development of the accumulative roll-bonding(ARB) process[J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(2): 579?583.
[7] Kumar K S, Van Swygenhoven H, Suresh S. Mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals and alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(19): 5743?5774.
[8] Huang X, Tsuji N, Hansen N. Microstructural evolution during accumulative roll-bonding of commercial purity aluminum[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, A340: 265?271.
[9] Iwahashi Y, Wang J, Horita Z, Nemoto M. Principle of equal-channel angular pressing for the processing of ultra-fine grained materials[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1996, 35(2): 143?146.
[10] Saito Y, Utsunomiya H, Suzuki H, Sakai T. Improvement in the r-value of aluminium strip by a continuous shear deformation process [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 42(12): 1139?1144.
[11] Lee J C, Seok H K, Han J H, Chung Y H. Controlling the textures of the metal strips via the continuous confined strip shearing(C2S2) process [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2001, 36(5/6): 997?1004.
[12] Valiev R Z, Langdon T G. Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2006, 51(7): 881?981.
[13] Furukawa M, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon T G. The use of severe plastic deformation for microstructural control[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, A324: 82?89.
[14] H?ppel H W, May J, G?ken M. Enhanced strength and ductility in ultrafine-grained aluminium produced by accumulative roll bonding[J]. Adv Eng Mater, 2004, 6(4): 219?222.
[15] Karlík M, Homolaa P, Slámová M. Accumulative roll-bonding: first experience with a twin-roll cast AA8006 alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 378(1/2): 322?325.
[16] Xing Z P, Kang S B, Kim H W. Softening behavior of 8011 alloy produced by accumulative roll bonding process[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001,45(5): 597?604.
[17] Tsuji N, Toyoda T, Minamino Y. Microstructural change of ultrafine-grained aluminum during highspeed plastic deformation[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, A350: 108?116.
[18] Kim H W, Kang S B, Tsuji N. Elongation increase in ultra-fine grained Al-Fe-Si alloy sheets[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(6): 1737?1749.
[19] Bowen J R, Prangnell P B, Humphreys F J. Microstructural evolution during formation of ultrafine grain structures by severe deformation[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2000, 16(11/12): 1246?1250.
[20] Tsujia N, Iwata T, Sato M. Aging behavior of ultrafine grained Al-2%Cu alloy severely deformed by accumulative roll bonding[J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2004, 5(1/2): 173?180.
[21] Lee S H, Saito Y, Tsuji N, Utsunomiya H, Sakai T. Role of shear strain in ultragrain refinement by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 46(4): 281?285.
[22] Tsuji N, Ueji R, Minamino Y. Nanoscale crystallographic analysis of ultrafine grained IF steel fabricated by ARB process[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 47(2): 69?76.
[23] Lee S H, Saito Y, Sakai T, Utsunomiya H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of 6061 aluminum alloy processed by accumulative roll-bonding[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, A325: 228?235.
[24] Tsuji N, Saito Y, Utsunomiya H. Ultra-fine grained bulk steel produced by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 40(7): 795?800.
[25] Saito Y, Tsuji N, Utsunomiya H, Sakai T, Hong R G. Ultra-fine drained bulk aluminium produced by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1998, 39(9): 1221?1227.
[26] Tsuji N, Ito Y, Saito Y, Minamino Y. Strength and ductility of ultra-fine grained aluminum and iron produced by ARB and annealing[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 47(12): 893?899.
[27] Hayes J S, Kyte R, Prangnell P B. Effect of grain size on the tensile behaviour of. a submicron grained Al-3%Mg alloy produced by severe deformation[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2000, 16(11/12): 1259?1263.
[28] Park K T, Kwon H J, Kim W J. Microstructural characteristics and thermal stability of ultrafine grained 6061 Al alloy fabricated by accumulative roll bonding process[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, A316: 145?152.
[29] Pérez-Prado M T, del Valle J A, Ruano O A. Achieving high strength in commercial Mg cast alloys through large strain rolling[J]. Materials Letters, 2005, 59(29): 3299?3303.
[30] Kim H W, Kang S B, Xing Z P, Tsuji N, Minamino Y. Texture properties of AA8011 aluminum alloy sheet manufactured by accumulative roll bonding process (ARB) [J]. Mater Sci Forum, 2002, 408/412: 727?732.
[31] Sato M, Tsuji N, Minamino Y, Koizuni Y. Fabrication of surface nanocrystalline aluminum alloys[J]. Mater Sci Forum, 2003, 426/432: 2753?2758.
[32] Truszkowski W, Krol J, Major B. Inhomogeneity of rolling texture in fcc metals[J]. Metall Trans A, 1980, 11(5): 749?758.
[33] Sakai T, Saito Y, Matsuo M, Kawasaki K. Inhomogeneous texture formation in high speed hot rolling of ferritic stainless steel[J]. ISIJ International, 1991, 31(1): 86?94.
[34] Hansen N, Huang X, Ueji R, Tsuji N. Structure and strength after large strain deformation[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, A387/389: 191?194.
[35] Li B L, Tsuji N, Kamikawa N. Microstructure homogeneity in various metallic materials heavily deformed by accumulative roll-bonding[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, A423: 331?342.
[36] Sevillano J G, van Houtte P, Aernoudt E. Large strain work hardening and textures[J]. Prog Mater Sci, 1980, 25(2/4): 69?134.
[37] Hughes D A, Hansen N. High angle boundaries formed by grain subdivision mechanisms[J]. Acta Materialia, 1997, 45(9): 3871?3886.
[38] Bay B, Hansen N, Hughes D A, Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf D. Evolution of f.c.c. deformation structures in polyslip[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1992, 40(2): 205?219.
[39] Iwahashi Y, Furukawa M, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon T G. Microstructural characteristics of ultrafine grained aluminum processed using equal channel angular pressing[J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 1998, 29: 2245?2252.
[40] Iwahashi Y, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon T G. The process of grain refinement in equal-channel angular pressing[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46: 3317?3331.
[41] Malin A S, Hatherly M. Microstruture of cold-rolled copper [J]. Metal Sci, 1979, 13: 463?472.
[42] Valiev R Z, Ivanisenko Y V, Rauch E F, Baudelet B. Structure and deformation behaviour of Armco iron subjected to severe plastic deformation[J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44(12): 4705?4712.
[43] Mukai T, Yamanoi M, Watanabe H, Higashi K. Ductility enhancement in AZ31 magnesium alloy by controlling its grain structure [J]. Scripta Materials, 2001, 45(1): 89?94.
[44] Drozd Z, Trojanová Z, Kúdela S. Deformation behaviour of Mg-Li-Al alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 378(1/2): 192?195.
[45] Agnew S R, Horton J A, Lillo T M, Brown D W. Enhanced ductility in strongly textured magnesium produced by equal channel angular processing [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(3): 377?381.
[46] 汪凌云,范永革,黄光杰,黄光胜,潘复生,刘正宏. AZ31B镁合金板材的织构[J]. 材料研究学,2004, 18(5): 466?470.
WANG Ling-yun, FAN Yong-ge, HUANG Guang-jie, HUANG Guang-sheng, PAN Fu-sheng, LIU Zheng-hong. Texture of AZ31B magnesium alloy sheets [J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2004,18(5): 466?470.
[47] Valiev R Z, Islamgaliev R K, Alexandrov I V. Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2000, 45(2): 103?189.
[48] 周晓龙,陈敬超,孙加林,张昆华,杜 焰. AgSnO2触头材料的反应合成制备与大塑性变形加工[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(5): 829?834.
ZHOU Xiao-long, CHEN Jing-chao, SUN Jia-lin, ZHANG Kun-hua, DU Yan. Reactive synthesis and severe plastic deformation of AgSnO2 contact materials [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(5): 829?834.
[49] Segal V M. Materials processing by simple shear [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1995, A197: 157?164.
[50] Kim H S. Finite element analysis of high pressure torsion processing [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 113(1/3): 617?621.
[51] Pérez-Prado M T, Del Valle J A, Contreras J M, Ruano O A. Microstructural evolution during large strain hot rolling of an AM60 Mg alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(5): 661?665.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50575076);广东省自然科学基金重点资助项目(36547);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(20060400748)
收稿日期:2006-09-13;修订日期:2007-02-26
通讯作者:李元元,教授;电话:020-87112948;E-mail:mehjli@scut.edu.cn

