文章编号:1004-0609(2014)11-2769-08
稀土元素Y和Ce对定向凝固镍基高温合金高温氧化行为的影响
肖 旋1,徐 乐1, 2,秦学智2,侯介山2,王常帅2,郭建亭2,周兰章2
(1. 沈阳理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110159;
2. 中国科学院 金属研究所,沈阳 110016)
摘 要:用热重法研究稀土元素Y和Ce对定向凝固镍基高温合金 DZ444 高温氧化行为的影响,用X 射线衍射仪和扫描电镜等观察和分析氧化膜组成和形貌。结果表明:合金在 700、850和 950 ℃下的恒温氧化动力学均符合抛物线规律,稀土元素的添加对其无影响;然而,添加稀土元素使其氧化激活能由 257.6 kJ/mol 降低至 246.8 kJ/mol;DZ444合金氧化膜分为3层:外层为疏松的 Cr2O3、TiO2和(Cr0.88Ti0.12)2O3的混合物;中间层为Cr2O3;内氧化物层为Al2O3。稀土元素未改变合金氧化膜的组成。稀土元素极易偏聚在合金表面,促进保护性Cr2O3膜的形成,从而阻止合金的进一步氧化,并能有效抑制合金的内氧化。
关键词:高温合金;稀土元素;高温氧化;定向凝固
中图分类号:TG141 文献标志码:A
Effect of elements Y and Ce on high temperature oxidation behavior of directionally-solidified Ni-based superalloy
XIAO Xuan1, XU Le1, 2, QIN Xue-zhi2, HOU Jie-shan2, WANG Chang-shuai2, GUO Jian-ting2, ZHOU Lan-zhang2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenyang Ligong University, Shenyang 110159, China;
2. Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract: The effect of rare earth elements Y and Ce on the oxidation behavior of Ni-based superalloy DZ444 at elevated temperatures was studied by TGA method. The composition and morphology of the oxide films of DZ444 alloy were measured by XRD and SEM. The results indicate that rare earth elements has no effect on the oxidation kinetics, which obey parabolic law at 700, 850 and 950 ℃. However, the values of activation energy decrease from 257.6 kJ/mol to 246.8 kJ/mol when Y and Ce elements are added to the alloy. The oxide films of DZ444 alloy consist of three layers, loose upper layer consists of TiO2, Cr2O3 and (Cr0.88Ti0.12)2O3, compact intermediate layer is mainly Cr2O3, and discrete internal oxides are Al2O3. The composition of oxide films is not changed by rare earth elements, which can easily segregate on the surface of the alloy and accelerate the formation of protective oxidation film to prevent further oxidation. Therefore, it can be concluded that the addition of rare earth elements Y and Ce can effectively inhibit the development of internal oxidation.
Key words: superalloy; rare element; high temperature oxidation; directional solidification
工程应用中,高温下使用的金属材料最基本的要求是合金要具有优异的高温力学性能及足够好的抗高温腐蚀性能[1]。国内外许多学者的研究表明,高温合金的抗氧化性能依赖于其表面形成的一层生长缓慢又能保持完整的氧化膜[2]。通常情况下,高温合金中 Al2O3、Cr2O3 和 SiO2 是3种致密的氧化膜,生长相当缓慢,具有较好的高温热力学稳定性。DZ444 是一种新型定向凝固抗热腐蚀高温合金,主要用于制作工业燃气轮机热端部件涡轮叶片和导向叶片[3]。与航空发动机相比,工业用燃气轮机工作环境更为苛刻,工作时间也更长,要求合金叶片不仅具有良好的高温力学性能,还应具有优异的抗高温氧化和热腐蚀性能[4]。郭建亭[3]研究认为,稀土元素可作为活性元素改善合金的抗氧化性能,提高表面稳定性。而且稀土元素的加入可促使 Cr2O3 形成,使合金氧化动力学的抛物线速率常数下降 1~2 个数量级、降低 Cr2O3 或 Al2O3 膜的临界 Cr 或 Al 含量,并起到改善 Cr2O3 或 Al2O3 膜的抗剥落性能等作用[3, 5-9]。本文作者利用恒温氧化实验、扫描电子显微镜、能谱仪、X射线衍射仪等分析方法和手段研究了添加适量稀土元素 Y 和 Ce 对 DZ444 合金 700、850和950 ℃恒温氧化动力学规律以及氧化膜的组成、形貌及形成机理的影响,从而为稀土元素 Y 和 Ce 在高温合金中的添加原则提供实验依据和理论基础。
1 实验
待试验样品尺寸为 10 mm×10 mm×3 mm,表面光洁。DZ444 原合金的化学成分为(质量分数,%):0.11 C,14.96 Cr,10.50 Co,5.29 W,1.99 Mo,2.85 Al,4.55 Ti,0.37 Ta,0.43 Hf,0.008 B,余量Ni,可表示为DZ444B。为探索稀土元素对氧化性能的影响,向合金中添加 0.01% Y和0.02% Ce,得到新合金DZ444C。
恒温氧化实验依据 HB5258-83 标准进行。试样置于预烧至质量恒定的 Al2O3 坩埚中,与坩埚壁保持点(线)接触。氧化试验在箱式电炉内进行,其控温精度为±2 ℃,试验温度分别是700、850和950 ℃;时间设定为1,3,5,10,25,50,75和100 h。实验结束,当坩埚和试样刚出炉时,立即给坩埚加盖,避免氧化物崩落到坩埚外。在 DT-100 光电分析天平进行称量,其感量为 0.1 mg,实验值为 3 个试样的平均值。采用静态增重法测定合金的氧化动力学曲线,用 XRD和SEM 等观察和分析氧化膜的组成和形貌。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 氧化动力学
DZ444合金在700、850及950 ℃下静态空气中的氧化动力学曲线见图1。从氧化曲线可以看出,DZ444B和DZ444C 合金具有相似的氧化过程。随着氧化温度的升高,两种合金的氧化速率明显增大。3个温度下,氧化初期的氧化速率较大,而氧化10 h后,氧化速率有所降低。两合金在所有试验温度下均属于完全抗氧化级别。从氧化增量的平方与氧化时间的关系曲线(见图2)可以看出,两种合金的氧化符合抛物线规律。研究表明[10],对于镍基高温合金,氧化机制会从初期的表面反应控制转化为扩散控制。DZ444合金在950 ℃下的(ΔM)2-t关系曲线在 5 h处发生轻度转折,说明此时可能发生了氧化机制的转变。然而,由于700 ℃及850 ℃下的合金氧化增量很小,无法观测出(ΔM)2-t曲线是否存在转折。

图1 DZ444B和DZ444C合金在700、850及950℃时的氧化曲线
Fig. 1 Oxidation kinetics curves of superalloy DZ444 at 700, 850 and 950 ℃
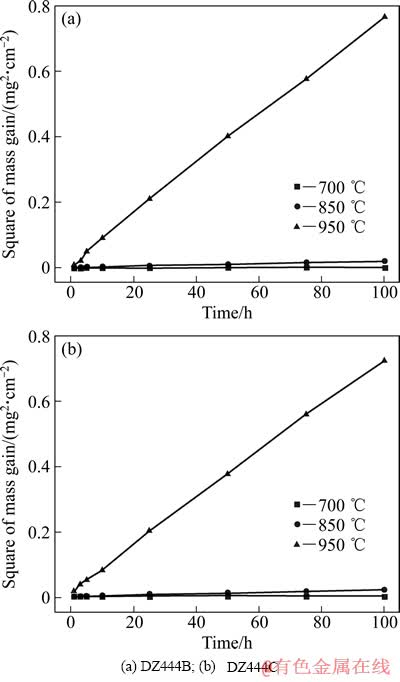
图2 DZ444合金在试验温度范围内(ΔM)2-t关系曲线
Fig. 2 Dependence of square of mass gain (ΔM)2 on oxidation time for superalloy DZ444 at test temperature
表1 不同温度下合金的抛物线速率常数值kp和氧化激活能值Qp
Table 1 Parabolic reaction rate constants kp at different temperatures and oxidation active energy Qp of superalloy DZ444

用回归分析求出不同温度的抛物线速率常数 kp(见表1)。根据Arrhenius方程式[2]
kp=Aexp[-Q/(RT)] (1)
式中:kp为氧化速率常数,mg2/(cm4·h);A为常数;Q为氧化激活能,kJ/mol;R为摩尔气体常数;T为氧化温度,K。对ln kp和1/T作图,其结果见图3。
由图3可知,氧化激活能QpB和QpC分别为257.6和246.8 kJ/mol。其值与 Cr3+在Cr2O3中扩散激活能259 kJ/mol相近,因而可以推断,在实验温度范围内,合金的氧化控制步骤为Cr3+在以Cr2O3为主的氧化膜中的扩散[11]。稀土元素的加入降低了合金的氧化激活能,使DZ444C合金表面连续保护性氧化膜的形成更加迅速。因此,950 ℃氧化初期,DZ444C合金的氧化增量略高于DZ444B合金的。然而,当合金表面形成连续的选择性氧化膜后,合金的进一步氧化受到抑制,因此,氧化5 h之后,DZ444C的氧化增量小于DZ444B的。
2.2 氧化膜的组成
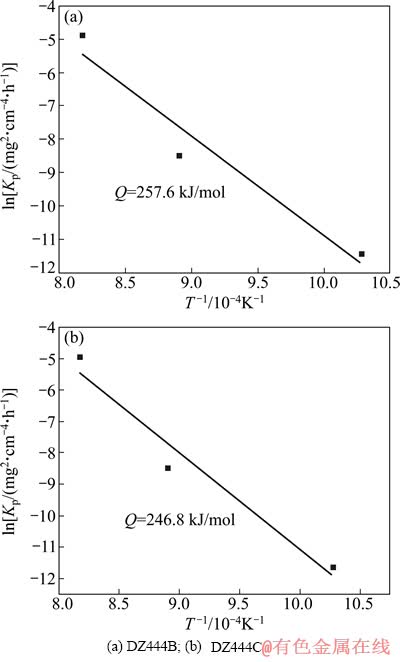
图3 DZ444合金ln kp-1/T曲线
Fig. 3 ln kp-1/T curves of superalloy DZ444
表2 DZ444合金700和850 ℃下氧化100 h后表面的氧化相
Table 2 Phase constitution of on surface of oxidized DZ444 superalloy at 700 and 850 ℃ for 100 h

利用 D/MAX-2500PC型X射线衍射仪对氧化试样的氧化膜进行X射线衍射分析。两合金在 700和850 ℃下氧化100 h后表面氧化产物的XRD分析结果列于表2。在950 ℃下经不同时间氧化后表面氧化产物XRD分析结果列于表3。从表2和3可以看出,经过100 h的氧化后,除了950 ℃下DZ444B合金氧化层中含有极微量的NiCr2O4外,其他温度下两合金外层氧化物组成相同,均为Cr2O3、TiO2和(Cr0.88Ti0.12)2O3。陈武[12]指出,高温下NiO、Cr2O3和TiO2可以反应得到氧化物(Cr0.88Ti0.12)2O3。此外,在 GH4720Li 的高温氧化性能研究中也发现了此种氧化物[13]。950 ℃下,氧化初期在氧化膜中检测到少量 Al2O3 存在,而随着氧化的不断进行,Al2O3 的衍射峰消失。这是由于随着外氧化膜厚度的不断增加,X 射线已无法触及内氧化层中的 Al2O3。另外,NiO存在“吸氧效应”[14],可与合金中的 Cr 发生反应:
NiO+Cr(合金中)→Ni(合金)+Cr2O3 (2)
所以,NiO 在合金的氧化过程中只是一种中间产物,一般试验中检测不到 NiO 的存在。
2.3 氧化膜表面形貌
图4所示为950 ℃下经不同时间氧化后 DZ444B 及 DZ444C 合金氧化膜的表面形貌。由图4可以看出,两合金的氧化过程基本相似,均包含氧化膜的形成、连接、增厚,氧化物颗粒的团聚并在氧化膜表面析出块状氧化物等过程。
表3 DZ444合金在950 ℃氧化不同时间后表面的氧化相
Table 3 Phase constitution on surface of oxidized DZ444 superalloy at 950 ℃ for different times
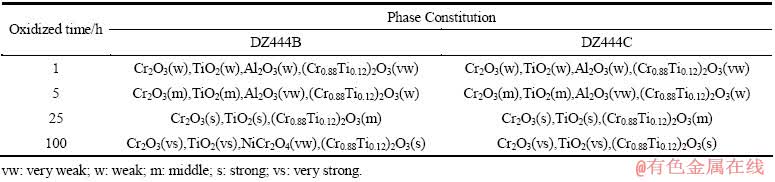

图4 高温合金DZ444在950 ℃下经不同时间氧化后的表面形貌
Fig. 4 Surface morphologies of superalloy DZ444 oxidized at 950 ℃ for different times
氧化进行1 h后,两合金表面氧化膜已基本形成。与 DZ444C 合金相比,DZ444B 合金表面氧化膜较薄,且存在较大的孔隙。DZ444C 合金表面的TiO2颗粒尺寸 (约400 nm) 明显大于 DZ444B 合金表面的TiO2颗粒尺寸 (约200 nm),且 DZ444C 合金氧化物颗粒团聚明显。这说明稀土元素的加入加快了合金氧化膜的形成。氧化5 h后,DZ444B 合金表面均匀分布着大量 TiO2 颗粒(见图4(c)),而 DZ444C 合金表面氧化团聚物明显长大,团聚物之间存在较宽的缝隙(见图4(d))。两种合金 TiO2 颗粒尺寸相同,为 1~2 μm。 DZ444B 氧化膜中部分 TiO2 颗粒发生团聚,与 DZ444C 合金相同,团聚物除了颗粒状的氧化物以外,还含有起粘合剂作用的连接物。这些连接物存在于 TiO2 颗粒之间,促使 TiO2 颗粒的团聚。能谱分析显示颗粒状氧化物中含有较高的 Ti,而连接物中 Cr 含量较高,综合 XRD 分析结果可以确定颗粒状氧化物为 TiO2,而连接物为 Cr2O3 和 (Cr0.88Ti0.12)2O3 (见表4)。氧化25 h后,DZ444B 合金表面氧化物团聚明显(见图4(e)),其形貌与 DZ444C 合金氧化5 h 时的形貌(见图4(c))类似。然而,DZ444C 合金氧化团聚物已开始分解为独立分布的块状 TiO2 氧化物(见图4(f))。氧化进行100 h后,两合金表面都已析出大量离散分布的块状TiO2颗粒(见图4(g)和(h)),并形成覆盖层。DZ444B合金的表面 TiO2 颗粒尺寸 (约4 μm) 明显大于DZ444C合金的表面TiO2颗粒尺寸(约3 μm)。
DZ444C 合金氧化膜形成较快与稀土元素在合金表面的偏聚有关[12]。表5所列为一种 Ni-Cr-Al 合金表面存在和不存在氧吸附时合金表面的偏聚能。可见,无论合金表面是否有氧吸附,稀土元素 Y 都比 Cr、Al 更容易向表面偏聚。氧原子在 NiM(111) 表面的吸附能列于表6。吸附能越高,氧在表面的吸附越稳定。虽然 Y 的吸附能略低于 Cr的,但是 Y 优先偏聚于合金表面与氧反应生成 Y2O3。Y2O3 可作为 Cr2O3 和 Al2O3 形成的核心,从而促进氧化膜的形成[15]。这也是 DZ444C 合金氧化激活能较DZ444B低的原因。
表4 DZ444合金经950 ℃氧化5 h后氧化物的能谱分析结果
Table 4 EDXS results of oxidation on superalloy DZ444 at 900 ℃ for 5 h

表5 Ni-Cr-Al合金表面存在和不存在氧吸附时合金表面的偏聚能
Table 5 Energy of element segregation on surface of Ni-Cr-Al alloy with and without oxygen

2.4 氧化膜截面形貌
图5所示为不同温度下两合金经100 h氧化后的氧化膜截面形貌及能谱面分析结果。
表6 氧原子在NiM(111)表面的吸附能
Table 6 Energy of oxygen adsorption on surface of Ni(111) and NiM(111)


图5 不同温度下DZ444合金经100 h氧化后的氧化膜截面形貌及EDS面分析
Fig. 5 Section morphologies of oxidation film and EDS element mapping results of superalloys DZ444 oxidized at different temperatures for 100 h
由图5可见,随着氧化温度的增加,氧化膜厚度随之增大,内氧化加剧。能谱分析表明:外层主要是 TiO2 及Cr2O3的混合层,较为疏松;中间层是比较致密的 Cr2O3 层,对合金起到保护作用;内层由“树根”状的内氧化物Al2O3及少量的 TiN 组成。“树根”状内氧化物的存在增加了氧化膜与基体的结合力。内氧化物及氮化物形成可能的解释为,由于外层的 Ti-Cr 混合层较为疏松,而中间的 Cr2O3 层又有一些孔洞存在,给氧及氮的内扩散造成通道,氧、氮渗入基体首先与标准生成自由能更负的金属反应[9]。950 ℃下,DZ444B合金的内氧化层明显厚于 DZ444C 合金的,且含有更多的TiN颗粒,这说明DZ444C合金的氧化膜较为致密能,更好地阻止氧和氮向合金内部扩散。在700、850和950 ℃下氧化100 h后,DZ444B合金的氧化膜平均厚度分别为小于1、8.89和27.14 μm,而DZ444C合金的分别为3.13、8.77和21.23 μm。
上述结果表明,稀土元素 Y 和 Ce 的加入可以减小氧化膜厚,并有效阻止内氧化的发生,从而改善了合金的抗氧化性能。
2.5 氧化膜附近组织变化
图6所示为950 ℃下氧化100 h后DZ444合金氧化膜的截面及附近组织形貌。
很显然,在氧化膜下方的基体组织中出现了两个特殊区域,即γ′分解区和过渡分解区。在分解区中已无γ′相存在,而在过渡分解区中存在大量发生形态变化的γ′相。DZ444B 合金的γ′分解区宽度约为 20 μm,明显大于 DZ444C 合金的(约12 μm)。另外,在γ′分解区存在很多白亮的颗粒,能谱分析结果表明其为 TiN 颗粒。同样地,DZ444B 合金的过渡分解区宽度(7 μm) 大于 DZ444C 合金的过渡分解区宽度 (4 μm)。过渡区形貌显示(见图6(c)和(d)),合金内部靠近过渡区一侧的γ′形态已由热处理态下的立方体变为球形并存在多个γ′相互连接的现象。过渡分解区γ′成长条状,其靠近氧化膜一侧(外侧)的边缘已开始回熔而靠近合金内部一侧(内侧)保存完好。这说明分解区及过渡区的形成均是为氧化膜的形成提供合金元素,即部分氧化膜形成元素如 Ti、Al 源于γ′相的分解。
可见,稀土元素 Y 和 Ce 的加入可以缩小γ′相分解区及过渡分解区的宽度。

图6 950 ℃氧化100 h后DZ444合金氧化膜截面及附近组织形貌
Fig. 6 Microstructures of oxided films section and near oxidation film of DZ444 superalloy at 950 ℃ for 100 h
3 结论
1) DZ444B及DZ444C合金在700~950 ℃下均属于完全抗氧化级别。
2) DZ444B及DZ444C合金在700~950 ℃的氧化动力学规律符合抛物线规律,其高温氧化过程主要受Cr3+离子在以Cr2O3为主的氧化膜中的扩散控制。稀土元素极易偏聚于合金表面,促进保护性Cr2O3膜的形成从而阻止合金的进一步氧化并能有效抑制合金的内氧化。
3) DZ444B及DZ444C合金的氧化膜由3个区域组成:外层主要为疏松的TiO2、Cr2O3和(Cr0.88Ti0.12)2O3的混合层;中间层是比较致密的Cr2O3层;内层由“树根”状的内氧化物Al2O3及少量的TiN组成。稀土元素的加入可减小950 ℃下氧化膜的厚度,提高合金的氧化性能。
4) 氧化膜下方存在γ′分解区,稀土元素的加入可以降低分解区的宽度。γ′的分解及基体中元素不断向合金表扩散维持着合金的持续氧化。
REFERENCES
[1] BERTHOD P. Kinetics of high temperature oxidation and chromia volatilization for a binary Ni-Cr alloy[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 2005, 64(3/4): 235-252.
[2] 李美栓. 金属的高温腐蚀[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2001: 5-150.
LI Mei-shuan. High temperature corrosion of metals[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2001: 5-150.
[3] 郭建亭. 高温合金材料学(下册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 317-319.
GUO Jian-ting. Materials science and engineering for superalloys (III)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 317-319.
[4] SIMS C T, HAGEL W C. In superalloys II[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1987: 187-189.
[5] SHENG Li-yuan, YANG Fang, XI Ting-fei, LAI Chen, YE Heng-qiang. Influence of heat treatment on interface of Cu/Al bimetal composite fabricated by cold rolling[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2011, 42(6): 1468-1473.
[6] SHENG Li-yuan, WANG Li-jun, XI Ting-fei, ZHENG Yu-feng, YE Heng-qiang. Microstructure, precipitates and compressive properties of various holmium doped NiAl/Cr (Mo, Hf) eutectic alloys[J]. Materials & Design, 2011, 32(10): 4810-4817.
[7] 郭建亭, 袁 超, 侯介山. 稀土元素在NiAl合金中的作用[J]. 金属学报, 2008, 44(5): 513-520.
GUO Jian-ting, YUAN Chao, HOU Jie-shan. Effects of rare earth elements on NiAl-based alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2008, 44(5): 513-520.
[8] BERANGER G, ARMANET F, LAMBERTIN M. Active elements in oxidation and their properties[C]//LANG E. The Role of Active Elements in the Oxidation Behaviour of High Temperature Metals and Alloys. Berlin: Elsevier Applied Science, 1989: 33-51.
[9] 梁 艳, 龙媛媛, 付广艳. 稀土元素对合金抗高温氧化和耐腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 四川化工, 2004, 3: 37-41.
LIANG Yan, LONG Yuan-yuan, FU Guang-yan. Influence of rare earth elements on high temperature oxidation and corrosion resistance of alloys[J]. Sichuan Chemical Industry, 2004, 3: 37-41.
[10] 李 云, 袁 超, 郭建亭, 杨洪才. 铸造镍基高温合金K35的氧化动力学[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 24(1): 75-77.
LI Yun, YUAN Chao, GUO Jian-ting, YANG Hong-cai. The oxidation kinetics of cast Ni-base superalloy K35[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2003, 24(1): 75-77.
[11] 李 云, 尚海波, 郭建亭, 袁 超, 杨洪才. 铸造镍基高温合金K35的高温氧化行为[J]. 金属学报, 2003, 39(7): 749-754.
LI Yun, SHANG Hai-bo, GUO Jian-ting, YUAN Chao, YANG Hong-cai. Isothermal oxidation behavior of a cast Ni-base superalloy K35[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2003, 39(7): 749-754.
[12] 陈 武. 高温高发射率红外辐射涂层的制备与研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2008: 39-40.
CHEN Wu. Preparation and study of infrared radiation coating with high emissivity at high temperature[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2008: 39-40.
[13] 王民庆, 曲敬龙, 殷铁志, 盛俊英, 邓 群, 吕旭东. GH4720Li合金高温氧化行为研究[J]. 钢铁研究学报. 2010, 22(9): 33-37.
WANG Min-qing, QU Jing-long, YIN Tie-zhi, SHENG Jun-ying, DENG Qun,  Xu-dong. Study on oxidation behavior of alloy GH4720Li at high temperatures[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2010, 22(9): 33-37.
Xu-dong. Study on oxidation behavior of alloy GH4720Li at high temperatures[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2010, 22(9): 33-37.
[14] HUSSAIN N, SHAHID K A, KHAN I H., RAHAMAN S. Oxidation of high-temperature alloys (superalloys) at elevated temperatures in air: II[J]. Oxid Met, 1995, 43(3/4): 363-378.
[15] 梁 婷. Ni-Cr-Al合金高温氧化及影响机理研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳师范大学, 2011: 21-22.
LIANG Ting. Studies on high-temperature oxidation and its influence mechanism of Ni-Cr-Al alloy[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Normal University, 2011: 21-22.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51172101,51001101)
收稿日期:2014-01-06;修订日期:2014-07-20
通信作者:肖 旋,副教授,博士;电话:024-24681920,13998179063;E-mail:xiaoxuan1029@163.com