DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.10.08
氧对牙科用Ti-15Zr合金耐磨性能的影响
汤菡纯1,刘 咏1,赵大鹏2,成文娟1
(1. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 湖南大学 生物学院,长沙 410082)
摘 要:目前,在牙科临床应用的Ti-Zr合金依然存在耐磨性不足等力学性能问题,制约了其在牙科领域的进一步发展。本实验采用粉末冶金的方法,制备了氧含量较高的Ti-15Zr-0.72O(质量分数,%)和Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金,通过与传统铸锭冶金制备的Ti-15Zr合金对比,研究氧含量对材料力学性能的影响。Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金的显微维氏硬度达到449.9HV,比Ti-15Zr-0.72O的高8%,相对Ti-15Zr的高出76%。在模拟唾液中进行的摩擦磨损实验显示,Ti-15Zr-0.86O相对于Ti-15Zr-0.72O磨损质量减少,表面剥落现象更少,且两者磨损量远小于Ti-15Zr。实验结果表明通过添加氧元素,Ti-15Zr系列合金的硬度和耐磨性能得到大幅度提升。
关键词:Ti-Zr合金;粉末冶金;固溶氧;维氏硬度;摩擦磨损性能
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-10-2285-07 中图分类号:TG166.5;TH117.1 文献标志码:A
由于具有高比强度、优异的耐腐蚀性与生物相容性,钛及钛合金在齿科等领域得到了广泛的关注[1]。目前,最常用的是纯钛和Ti-6Al-4V合金[2-3]。然而,通过模拟体液中的耐蚀性研究,纯钛与Ti-6Al-4V具有一定的耐磨性能,但其耐磨性能不够高,不利于在齿科材料领域的应用[4-5]。此外,Ti-6Al-4V中的铝和钒也有潜在的细胞毒性和神经毒性,这制约了其在医用领域的安全使用[6]。因此在钛合金中,锆是一种无毒的合金元素[7-8],可使Ti-Zr合金的耐磨性等综合力学性能提高,更适合作为牙科医用材料[9]。氧化锆、氧化铝、羟基磷灰石等陶瓷基齿科材料是目前常采用的齿科医用材料。其中羟基磷灰石涂覆材料应用十分广泛,其耐磨性能较好,且生物相容性高,但是在模拟体液当中的稳定性还有待提高[10-11]。Ti-Zr合金的拉伸性能和抗疲劳性能明显优于氧化锆、氧化铝及羟基磷灰石涂层等陶瓷材料的拉伸性能和抗疲劳性能,在具有良好生物相容性的同时,其在模拟体液环境下的表现也相当稳定,但其硬度低、耐磨性能不足限制了其实际应用。
在钛基材料中,杂质元素的添加是增强合金力学性能的一个重要途径[12]。氧是重要的杂质元素,通过固溶强化和颗粒强化等机制能够对材料的硬度、强度和耐磨性等力学性能有所提高。LIM等[13]发现在Ti-8Al合金中掺入氧,可以在α″和α+α″相中起颗粒强化作用。OH等[14]研究了氧含量为1000×10-6~4000×10-6之间的Ti-6Al-4V合金的力学性能,发现随着氧含量的提高,合金的硬度和强度都有显著的提升。合金的硬度往往与耐磨性能密切相关,通过添加杂质元素也是提高Ti合金耐磨性的重要途径[15]。
本文采用粉末冶金方法,通过控制含氧量不同的原料粉末比例,制备氧含量不同的Ti-15Zr系列合金。通过与铸态低氧Ti-15Zr合金进行对比,研究了氧含量对合金显微组织、硬度和耐磨性能的影响,为新型齿科Ti-Zr合金的研究与应用提供了新途径。
1 实验
实验以高纯氢化脱氢(HDH) 钛粉(纯度>99.9%,粒径<45 μm,w(O)=0.15%),经过机械进氧的高含氧量HDH 钛粉(纯度>99.9%,粒径<45 μm,w(O)= 0.43%),和高纯HDH 锆粉(纯度>99.9%,粒径<75 μm)为原料粉末。将高纯氢化脱氢(HDH) 钛粉、高含氧量HDH钛粉和高纯HDH锆粉分别按照34:51:15和51:34:15的成分配比在氩气环境中分别充分混合6 h。混合后的两种粉末被分别紧密装填在圆柱形的模压模具(~d 26 mm)中,在188 MPa的压力下保压10 s,进行模压成型。随后将压坯置于真空烧结炉中进行烧结,真空度为1×10-3 Pa,在1300 ℃下保温4 h。烧结后的样品在750 ℃下进行热轧,轧制变形率为70%。最终得到氧含量不同的两种Ti-15Zr-xO(质量分数,%)合金。用DHL-400高真空电弧熔炼炉制备铸态Ti-15Zr合金作为对比。
使用Leco TCH600氧氮分析仪测定Ti-15Zr系列合金的氧含量,结果如表1所示。
表1 Ti-15Zr系列合金的氧含量
Table 1 Oxygen contents of Ti -15Zr alloys

三种合金的物相由Rigaku D/max 2550 X射线分析仪进行分析。将抛光过后的Ti-15Zr-0.72O合金经过10 min刻蚀制成电镜样品,采用ESCALAB250Xi型X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)检测氧化物的形成。采用FEI Quanta FEG 250扫描电镜表征形貌。采用BUEHLER5104型微压痕硬度试验机测试材料显微维氏硬度。
摩擦磨损实验采用HT-1000型高温摩擦磨损试验机。将试样置于人工唾液中进行37 ℃下的摩擦磨损试验。采用ISO/TRl0271标准配置人工唾液。人工唾液的成分如表2所示。采用半径为2 mm的Si3N4球形压头绕试样转动,转速为0.1 m/s。材料的摩擦性能并不是固有不变的特性,而是与各种环境因素相关的性能,如载荷、温度、摩擦速度和液体环境等的影响。HEINTZE等[16]研究指出口腔中牙齿正常咀嚼时所受的咬合力在3~36 N之间。为了模拟口腔的力学环境,试验采用20 N为下压载荷,摩擦时间为60 min。称量试样在摩擦磨损前后的质量损失,并用FEI Quanta FEG 250扫描电镜观察摩擦后试样的表面形貌。将摩擦磨损后有磨痕的试样置于人骨肉瘤细胞(MG-63)中培养24 h,并在FEI Quanta FEG 250扫描电镜观察细胞的生长形态和依附情况。
表2 人工唾液的成分表
Table 2 Ingredient concentrations of artificial saliva (g·L-1)
2 结果与讨论
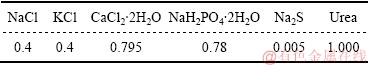
图1所示为Ti-15Zr系列合金的XRD谱。由图1可以看出, Ti–15Zr-0.72O、Ti–15Zr-0.86O和Ti-15Zr三种合金的物相组成只有单一的α相。通过对比三种不同氧含量的Ti-15Zr合金,可发现氧含量的增大会导致衍射峰红移,这主要是由于氧原子在八面体间隙当中引起一定程度的晶格畸变,使衍射峰红移。
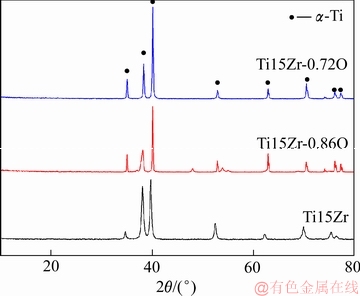
图1 Ti-15Zr系列合金的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Ti-15Zr alloys
图2所示为Ti-15Zr系列合金的XPS衍射谱的Zr3d区域。将图中谱线上的衍射峰通过分离得到了Zr峰和ZrO2峰。Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86O的峰型相似,并且ZrO2峰强度远高于Ti-15Zr的。说明Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金中有氧化物的存在。而Ti-15Zr合金在氧元素分析测试时的氧含量很低,XPS谱仍然出现较低的氧化物峰是表面接触空气后产生,虽然经过了刻蚀处理仍有少量残留。但由于氧化物的含量低于XRD可检测值,所以XRD中只检测得到单一的α衍射峰。
如表3所示,氧元素的添加明显提高了Ti-15Zr合金的硬度。通过粉末冶金方法进氧的Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86Os合金试样的显微维氏硬度远大于铸态Ti-15Zr合金试样的显微维氏硬度,接近Ti-15Zr硬度值的两倍。且Ti-15Zr-0.86O的氧含量仅比Ti-15Zr-0.72O的高出1400 ×10-6,却使硬度值有明显的提升。
图3所示为Ti-15Zr、Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金试样的SEM像。三种不同氧含量试样的组织形貌均为片层状α相,这与XRD结果相符。通过粉末冶金这种固态烧结方法制备的Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金,由于存在一定程度上的扩散不充分,与Ti-15Zr 合金相比,前两者的片层间距更大。
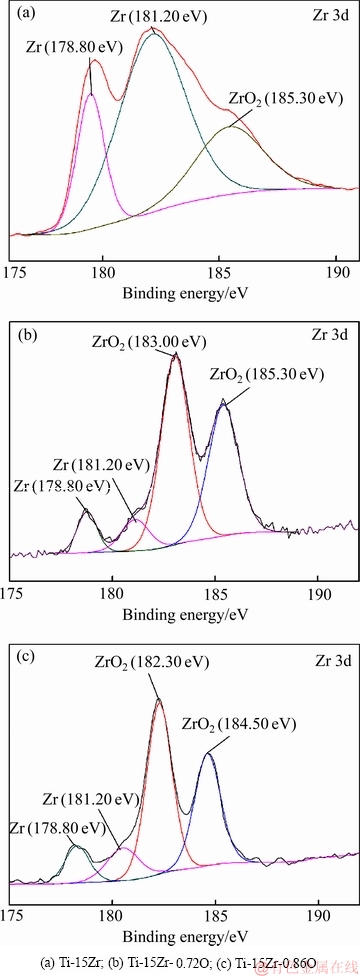
图2 Ti-15Zr系列合金的XPS衍射谱
Fig. 2 XPS patterns of Ti-15Zr alloys
本实验用粉末冶金方法,利用粉末表面吸附氧,并用含氧量高的钛粉进行了调控,相对于添加ZrO2粉末能更加均匀地掺入氧元素,而不会形成较大的难以扩散的氧化物大颗粒。在钛基材料中,氧是重要的杂质元素,通常以间隙原子的形式存在于八面体间隙中[17]。氧元素通常以固溶氧原子形式存在,引起了一定程度的晶格畸变。固溶氧原子阻碍了位错的运动,导致材料硬化,从而提高了钛基材料的硬度[16-17]。并且在α-Ti合金中,高的固溶氧含量会使位错交滑移的发生变得困难,从而使位错的滑移模式从波状滑移向平面滑移转变,阻碍位错运动从而有利于提高力学性能[18]。含氧Ti-15Zr系列合金为典型的α-Ti合金,氧原子主要作为间隙固溶原子存在于α-Ti合金中,溶质原子阻碍位错运动并产生位错钉扎效应,引起固溶强化。并且,还可以通过形成氧化物小颗粒的方式存在于钛基材料中,可以起到颗粒强化作用,对硬度也会有所提高[19]。XPS结果还验证了氧原子与锆形成了微小的ZrO2颗粒,较小的氧化物颗粒能阻碍位错运动,提供颗粒强化作用,从而提高了材料的耐磨性。
表3 Ti-Zr系列合金的维氏硬度
Table 3 Microhardness of Ti-Zr alloys


图3 Ti-Zr系列合金的SEM像
Fig. 3 SEM images of Ti-15Zr alloys
表4所示为Ti-15Zr系列合金的磨损质量损失和摩擦因数。由表4可见,Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金在摩擦磨损实验中的质量损失量明显低于Ti-15Zr-0.72O合金的,Ti-15Zr合金的质量损失量是前两者的3倍。这说明氧含量的提高可以明显提升材料的耐磨性能。结合三种合金硬度数据与摩擦磨损试验结果来看,在本实验条件范围内,Ti-15Zr合金的硬度与磨损质量损失呈负相关;氧含量越高,Ti-15Zr系列合金的硬度越高,耐磨性越好。此外,Ti-15Zr合金的摩擦因数高出很多,和通常认为的摩擦因数高的试样更容易磨损一致。值得注意的是,Ti-15Zr-0.72O合金的摩擦因数比Ti-15Zr- 0.86O合金的略高,原因是在摩擦磨损试验中,对偶与合金表面之间的摩擦引发绝热升温,使得Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金表面形成摩擦因数较高的氧化物膜。该氧化膜的耐磨性优于基体的,而且不容易剥落,使得试样的剥落速率更缓慢。
表4 Ti-15Zr合金磨损量和摩擦因数
Table 4 Weight loss and coefficient of wear of Ti-15Zr alloys

通常齿科材料容易发生的磨损机制有:磨粒磨损、粘着磨损、疲劳磨损、腐蚀磨损[20-21]。CORREA等[22]认为Ti-15Zr系列合金在摩擦磨损实验中,主要是发生了磨粒磨损和粘着磨损。在磨损过程中磨粒的浓度会逐渐累积,由于单位体积内磨粒颗粒数上升,合金表面的切削点增加,合金表面易于产生应力集中现象,导致摩擦表面不断产生塑性变形,最后合金质量明显流失。而在模拟唾液环境下,以磨粒磨损为主并伴随有一定程度的腐蚀磨损。试样表面受到腐蚀性离子侵蚀,导致沟槽边沿堆积起来的材料变得疏松而易被磨掉,在磨损与腐蚀反复相互作用下,从而加剧材料流失[23]。图4(a)所示为铸态Ti-15Zr合金摩擦磨损表面的显微形貌,表面有大量的犁沟和凹坑,发生了剧烈的塑性变形,有大量的磨粒和氧化层剥落现象,主要是粘着磨损和磨粒磨损。图4(b)所示为Ti-15Zr-0.72O合金的显微形貌,表面有明显的犁沟和塑性变形。塑性变形是粘着磨损的典型特征,是由于摩擦副表面的凸出部分受到了压力而发生,黏着点受到了剪切应力,从表面受到撕扯而形成大片剥落。从图4(b)中可以看到由于塑性变形产生的犁沟和剥落形成的凹坑,Ti-15Zr-0.72O合金以粘着磨损和磨粒磨损为主。

图4 摩擦磨样品表面形貌
Fig. 4 SEM micrograph of Ti-15Zrwear track
图4(c)所示为Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金的显微形貌,样品表面主要可以看到一些较深的沟槽状划痕和少量的剥落磨粒,剥落的程度不明显,较为光滑,说明塑性变形程度较低。Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金的磨损方式以磨粒磨损为主。Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金在磨粒磨损过程产生了磨粒,会在表面受到压力时发生加工硬化,形成硬质层。而氧含量高的合金表面硬度更高,磨屑难以从表面剥落,磨屑剥落之后产生的犁沟也会比较浅,并且减少了塑性变形的发生,所以会有效避免粘着磨损的发生,降低了摩擦磨损的质量损失。
图5所示为对摩擦磨损后的试样进行生物相容性实验的结果。在三种试样的磨痕表面采用人骨肉瘤细胞(MG-63)进行培养,培养时间为24 h。由图5可见,三种试样的磨痕表面都生长有大量的人骨肉瘤细胞,细胞依附状况良好,且具有很好的活性,部分细胞长出丝状伪足。 相对于表面大部分都是椭圆形细胞的Ti-15Zr合金来说,Ti-15Zr-0.72O和 Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金表面的细胞多为梭型,且长出丝状伪足的细胞数量较多。梭型的细胞相比于圆形和椭圆形细胞而言,其生存活力更强,尤其是长出的伪足有利于细胞运动,说明细胞存活状况良好。合金试样及残留磨屑均不具有细胞毒性,且表面具有优异的生物相容性,适用于作为牙科医用材料。
图5 摩擦磨损表面MG-63细胞生长形貌的SEM像
Fig. 5 SEM micrograph of MG-63 cells on wear tracks
3 结论
1) 通过控制原料粉末的比例,用粉末冶金的方法得到Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金;并用真空电弧熔炼制备不添加氧的Ti-15Zr合金作为对比。
2) 相对于铸态不添加氧的Ti-15Zr合金,添加氧的Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金的维氏硬度有大幅度提高。少量的氧元素作为间隙固溶原子能产生很强的固溶强化作用,形成的氧化物小颗粒会有颗粒强化作用,提高了Ti-Zr合金的硬度。
3) 提高氧含量能够减少Ti-15Zr合金的摩擦磨损质量损失,Ti-15Zr-0.86O和Ti-15Zr-0.72O合金的质量损失远远低于Ti-15Zr合金的。这说明氧含量提高了Ti-15Zr合金的表面硬度,使得材料耐磨性能明显提升。
4) 通过细胞实验,验证了Ti-15Zr、Ti-15Zr-0.72O和Ti-15Zr-0.86O合金及残留磨屑均不具有细胞毒性,适用于牙科医用材料。
REFERENCES
[1] GEETHA M, SINGH A K, ASOKAMANI R, GOGIA A K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2009, 54(3): 397-425.
[2] PARR G R, GARDER L K, TOTH R W. Titanium: The mystery metal of implant dentistry. Dental materials aspects[J]. Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 1985, 54(3): 410-414.
[3] 刘 畅, 王辰宇, 刘 贺, 王中汉, 林高用. 3D打印Ti6Al4V钛合金支架的力学性能及生物相容性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(4): 120-127.
LIU Chang, WANG Chen-yu, LIU He, WANG Zhong-han, LIN Gao-yong. Mechanical properties and biocompatibility of 3D printed Ti6Al4V titanium alloy stent[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(4): 120-127.
[4] BASSEVILLE S, CAILLETAUD G. An evaluation of the competition between wear and crack initiation in fretting conditions for Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Wear, 2015, 328/329: 443-455.
[5] 刘 冰, 周 清, 瞿瑞锋, 常王桃. CP-Ti和Ti-0.2Pd合金的显微组织对其耐蚀性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(4): 959-966.
LIU Bing, ZHOU Qing, QU Rui-feng, CHANG Wang-tao. Effect of microstructure on corrosion resistance of CP-Ti and Ti-0.2Pd alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(4): 959-966.
[6] SCHIFF L J, GRAHAM J A. Cytotoxic effect of vanadium and oil-fired fly ash on hamster tracheal epithelium[J]. Environmental Research 1984, 34(2): 390-402.
[7] ALTUNA P, LUCAS-TAULE E, GARGALLO-ALBIOL J, FIGUERAS-ALVAREZ O, HERNANDEZ-ALFARO F, NART J. Clinical evidence on titanium-zirconium dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 2016, 45(7): 842-850.
[8] ITO A, OKAZAKI Y, TATEISHI T, ITO Y. In vitro biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Pd and Ti-Sn-Nb-Ta-Pd alloys[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1995, 29(7): 893-899.
[9] IKARASHI Y, TOYODA K, KOBAYASHI E, DOI H, YONEYAMA T, HAMANAKA H, TSUCHIYA T. Improved biocompatibility of titanium-zirconium (Ti-Zr) alloy: Tissue reaction and sensitization to Ti-Zr alloy compared with pure Ti and Zr in rat implantation study[J]. Materials Transactions, 2005, 46(10): 2260-2267.
[10] GU Y W, KHOR K A, CHEANG P. In vitro studies of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite/Ti-6Al-4V composite coatings in simulated body fluid (SBF)[J]. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(9): 1603-1611.
[11] FU Y, BATCHELOR A W, YING W, KHOR K A. Fretting wear behaviors of thermal sprayed hydroxyapatite (HA) coating under unlubricated conditions[J]. Wear, 1998, 217(1): 132-139.
[12] 武晓峰, 杨会齐, 王春雨. Mn对生物医用Ti-Mo合金组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(9): 1902-1908.
WU Xiao-feng, YANG Hui-qi, WANG Chun-yu. Effect of manganese addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-Mo biomedical alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(9): 1902-1908.
[13] LIM J Y, MCMAHON C J, POPE D P, WILLIAMS J C. The effect of oxygen on the structure and mechanical behavior of aged Ti-8 wt pct Al[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1976, 7(1): 139-144.
[14] OH J M, LEE B G, CHO S W, LEE S W, CHOI G S, LIM J W. Oxygen effects on the mechanical properties and lattice strain of Ti and Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2011, 17(5): 733-736.
[15] 韩立影, 王存山, 羌建兵. 激光快速成形Ti64.52Fe29.32Zr5.86Y0.30医用合金组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(3): 474-482.
HAN Li-ying, WANG Cun-shan, QIANG Jian-bing. Microstructure and properties of Ti64.52Fe29.32Zr5.86Y0.30 biomedical alloy produced by laser rapid prototyping[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(3): 474-482.
[16] HEINTZE S D, ROUSSON V. Survival of zirconia- and metal-supported fixed dental prostheses: A systematic review[J]. International Journal of Prosthodontics 2010, 23(6): 493-502.
[17] OBERSON P G, WYATT Z W, ANKEM S. Modeling interstitial diffusion controlled twinning in alpha titanium during low-temperature creep[J]. Scripta Materialia 2011, 65(7): 638-641.
[18] WILLIAMS J C, SOMMER A W, TUNG P P. The influence of oxygen concentration on the internal stress and dislocation arrangements in α-titanium[J]. Metallurgical Transactions 1972, 3(11): 2979-2984.
[19] YU Q, QI L, TSURU T, TRAYLOR R, RUGG D, MORRIS J W JR, ASTA M, CHRZAN D C, MINOR A M. Origin of dramatic oxygen solute strengthening effect in titanium[J]. Science, 2015, 347(622): 635-639.
[20] KüBARSEPP J, KLAASEN H, PIRSO J. Behaviour of TiC-base cermets in different wear conditions[J]. Wear, 2001, 249(3): 229-234.
[21] ZHOU Y, ZHANG Q Y, LIU J Q, CUI X H, MO J G, WANG S Q. Wear characteristics of a thermally oxidized and vacuum diffusion heat treated coating on Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Wear 2015, 344: 9-21.
[22] CORREA D R N, KURODA P A B, GRANDINI C R, ROCHA L A, OLIVEIRA F G M, ALVES A C, TOPTAN F. Tribocorrosion behaviorof β-type Ti-15Zr-based alloys[J]. Materials Letters, 2016, 179: 118-121.
[23] 郑自芹, 王振国, 黄伟九. Hank’s模拟体液中Ti-25Nb-3Mo-3Zr-2Sn与Ti-2.5Al-3Mo-2.5Zr合金的微磨损行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(6): 1222-1227.
ZHENG Zi-qin, WANG Zhen-guo, HUANG Wei-jiu. Micro-scale wear behavior of biomedical material Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-25Nb and Ti-2.5Al-3Mo-2.5Zr alloy in Hank’s solution[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(6): 1222-1227.
Influence of oxygen on grindability of Ti-15Zr-based alloy as dental material
TANG Han-chun1, LIU Yong1, ZHAO Da-peng2, CHENG Wen-juan1
(1. State Key Laboratory for Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
2. College of Biology, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: Clinical Ti-Zr alloys still have the problem of insufficient wear resistance, which limits its further development in the dental field. Therefore, the wear resistance can be improved by introducing oxygen into the Ti-Zr alloy. In this work, Ti-15Zr-0.72O (mass fraction, %) and Ti-15Zr-0.86O alloys were prepared with the method of powder metallurgy. Ti-15Zr was prepared by arc-melting. The effect of oxygen content on the mechanical properties of Ti-15Zr alloys was studied. The Vickers hardness of Ti-15Zr-0.8O reaches 449.9 MPa, which is 8% higher than Ti-15Zr-0.7O, and 76%higher than Ti-15Zr. The tribological behavior of sintered composites was studied in artificial saliva solution. Ti-15Zr-0.86O hardness weight loss and surface peeling than Ti-15Zr-0.72O. Both of their weight losses are less than that of Ti-15Zr. The results show that the hardness and wear resistance of Ti-15Zr alloys are significantly improved by adding oxygen.
Key words: Ti-Zr alloy; powder metallurgy; oxygen solute; Vickers hardness; wear resistance
Foundation item: Projects(5162500387, 51604104) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2018-08-26; Accepted date: 2019-05-08
Corresponding author: LIU Yong; Tel: +86-731-88876630; E-mail: yonliu@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(5162500387,51604104)
收稿日期:2018-08-26;修订日期:2019-05-08
通信作者:刘 咏,教授,博士;电话:0731-88876630;E-mail:yonliu@csu.edu.cn