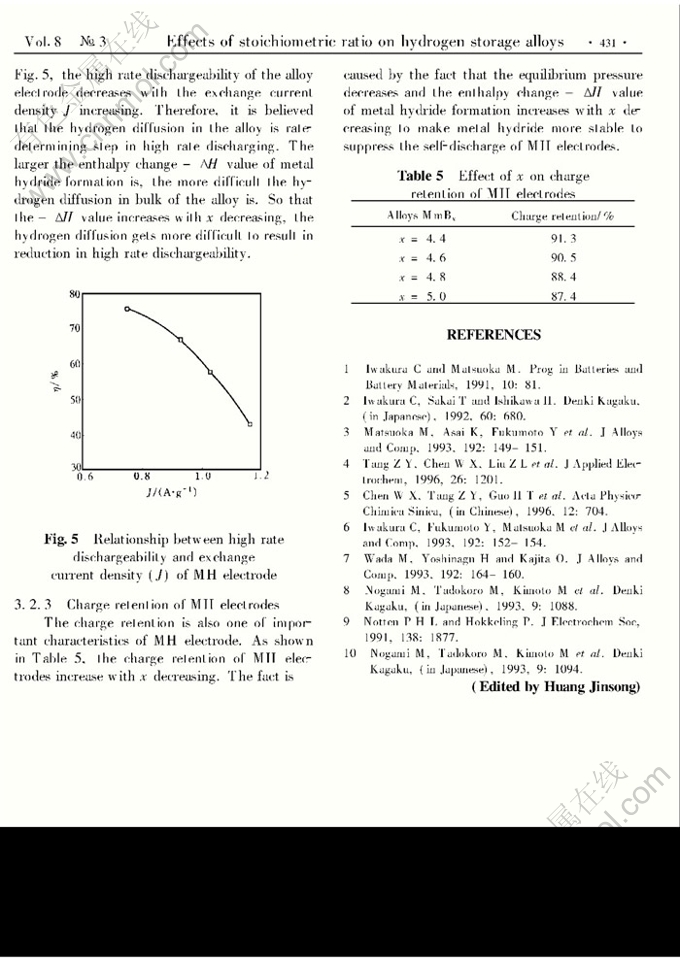
EFFECTS OF STOICHIOMETRIC RATIO ON STRUCTURE AND ELECTRODE PERFORMANCE OF HYDROGEN STORAGE ALLOYS
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)1998年第3期
论文作者:Chen Weixiang
文章页码:427 - 431
Key words:hydrogen storage alloy; stoichiometric ratio; structure; thermodynamic property
Abstract: The effects of stoichiometric ratioxon the structure, thermodynamic properties and electrode performances of the hydrogen storage alloys Mm(Ni0.72Co0.14Mn0.08Al0.06)x(Mm=Ce-rich mischmetal,x=4.4~5.0) were studied. The major phases of all alloys are of hexagonal CaCu5type structure. The unit cell volume increases with decreasing stoichiometric ratiox.A small quantity of the second phase Ce2Ni7is segregated in the alloy withx <5.0 and the amount of Ce2Ni7phase increases with decreasingx.The enthalpy change -ΔHvalue of hydride formation increases with decreasingxbecause of increasing unit cell volume and the Ce2Ni7phase forming more stable metal hydride. The discharge capacities of MH electrodes increase with increasingxbut for alloy with x=5.0, and have a maximum 306 mAh/g atx=4.8. The exchange current density of MH electrode reaction increases but the high rate dischargeability decreases with decreasingx.This fact indicated that the hydrogen diffusion in the alloy is a rate-determining step in high rate discharging.