


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2306-2311
Electrochemical behavior of graphite anode during anode effect in cryolite molten salts
CHEN Gong1, SHI Zhong-ning1, 2, GAO Bing-liang1, 2, HU Xian-wei1, 2, WANG Zhao-wen1, 2
1. School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China;
2. Engineering Research Center for Process Technology of Nonferrous Metallurgy of Ministry of Education,
Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China
Received 23 September 2011; accepted 13 January 2012
Abstract: Anodic electrochemical behavior was studied on graphite anode at 1000 ℃ in cryolite-alumina molten salt by means of cyclic voltammetry. The high current peak in a typical cyclic voltammogram was discussed. It is considered that a type of oxyfluoroaliminate complex anions reacts with carbon to form a high-resistance CF film on the anode surface at a high potential. The passivation potential is 3.28 V in 0.5% alumina-containing electrolyte, and the passivation potential increases with alumina content increasing which indicates that the alumina content determines the anodic process in the cryolite-alumina molten salt system.
Key words: anode behavior; aluminum electrolysis; perfluorocarbons; anode passivation
1 Introduction
In the primary aluminum production by the Hall-Héroult process, a departure from normal cell operation known as the anode effect (AE) results in the generation of the perfluorocarbons (PFCs) CF4 and C2F6 [1]. Especially, the anode effect not only produces high potential greenhouse effect gas, PFCs, but also consumes a number of energy for the higher cell voltage. Furthermore, the pressure of reducing emission of greenhouse gases, such as perfluorocarbons (PFCs) CF4 and C2F6 forces the smelters to search for the new solutions to reduce anode effect frequency in aluminium plants, and this project has consequently become an important research and development for the aluminium industry.
Though the studies on anode effect mechanism have been done for decades, the mechanism of PFCs generation is still uncertain yet. In summary, three opinions are advocated towards the mechanism of PFCs generation. One of those is described as F- discharges and forms F2, which directly reacts with carbon anode and produces two species of fluorine compound gas, CF4 and C2F6. Another view is that an intermediate compound COF2 generated on anode surface during the anode effect passivates the anode, and then the COF2 decomposes into CF4, C2F6 and CO2. ?YG?RD et al [2] believed that the reaction 2COF2+C=CO2+CF4 occurs during the anode effect according to a fact that molar ratio of CF4 to CO2 in anode effect gas is close to 1. Besides, AMPHLETT et al [3] proved that the reaction 2COF2+C=CO2+CF4 could happen at 1200 ℃ [3]. But, the third view of the mechanism is that F- discharges on anode surface and reacts with carbon to form a low surface energy species, graphite fluoride (CFx)n, which covers on anode surface and makes the anode passivate. On the point of this view, CF4 and C2F6 come from the decomposition of graphite fluoride at a high temperature.
Though the exact mechanism of the anode effect is not completely understood as yet due to the complexity of the electrochemistry of the system and the simultaneity of all the phenomena involved, F- discharging under low alumina concentration is a real fact. However, when a massive discharge takes place, a passivation layer is formed on the anode surface, or the anode is no longer able to evacuate the products and the reaction is no longer able to continue. Therefore, the nature of this layer has been a matter of discussion for a long time. And some possibilities could be summarized as: 1) poor wettability of the anode which causes the CO2 bubbles to adhere under the anode [4]; 2) an electrically insulating CFx film [5,6]; 3) an adsorbed layer of gas under the anode [7] or 4) a combination of these causes [8]. Nevertheless, ZHANG et al [9] advanced a different mechanism of anode effect. When the alumina content in electrolyte is less than 2%, the anode effect results from F- discharge; and when the alumina content is over 2%, the anode effect occurs because of the gas film adhering to and blocking anode surface. However, the dominant reason for anode effect in cell should be the alumina content under the low limit.
This study aims to investigate the electrochemical process of graphite anode in various alumina content cryolite molten salt by cyclic voltammetry, and to understand the real anodic electrochemical reactions. On the basis of these data, more reliable mechanism of anode effect will be ascertained.
2 Experimental
Analytical reagent cryolite (>99%) and aluminum fluoride (>99%) came from Xiya Reagent Company, Chengdu, while the aluminum oxide (>99%) came from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. Before experiment, aluminium oxide and cryolite were dried at 400 ℃ under argon atmosphere for about 3 h to remove the moisture. And the aluminum fluoride was purified by sublimation in a vacuum system at 1050 ℃. The cryolite-alumina melt was placed in a graphite crucible which was held inside a stainless steel crucible, as shown in Fig. 1.
The cyclic voltammetry technique was used in the studies, and the electroanalytical chemistry instrument was AUTOLAB PGSTAT30 (made in Netherland). All the experiments were conducted in a three-electrode system with a graphite bar (d2 mm, active surface area 0.45 cm2) wrapped with boron nitride tube as a work electrode (WE), Al/AlF3 as a reference electrode (RE) and graphite served as an counter electrode (CE). The electrolyte composition containing different molar ratios of NaF to AlF3 was used, and the alumina contents were 0.5%, 1.5%, 2.5% and 4.5%, respectively. The cyclic voltammetry scan rates were between 50 mV/s and 1000 mV/s. All the experiments were performed at 1000 ℃ in high purity argon atmosphere.
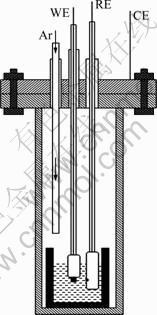
Fig. 1 Electrochemical experiment setup
3 Results and discussion
During the course of experiment of CV scans, the open circuit potential lay at 0.35 V-0.40 V at the initial state. After each scan, enough time was provided for the open circuit potential recovery.
A typical cyclic voltammogram is shown in Fig. 2. Two anodic peaks are distinguishable in the positive-going, arising at potentials of 3.28 V and 4.50 V, approximately. And all features of the voltammograms are reproducible on the reverse scan due to the high irreversibility of the graphite electrode system in cryolite-alumina molten salt. In Fig. 2, it is to be noted that the current curve seriously fluctuates when the applied potential is more than 2.17 V. And the fluctuation is more serious with the sweep potential going forward. The current falls sharply when the sweep potential reaches 3.28 V (point A). And it is supposed that the anode surface is passivated and covered with some kind of fluorocarbon film which insulates the electronics transfer rather than poor mass transport [5]. GROULT et al [10] suggested that the formation of a CF film will inhibit the electrode process and contribute to anode effect in an analogous system, molten KF-2HF. Besides, the weak current peak B at 4.50 V is considered F2 formed, but this peak was not discussed usually in some papers because there is no F2 detected in industry cell due to hydrogen existing in electrolyte [11]. ZHU and SADOWAY [12] also found the weak current peak at 4.30 V in the voltammograms on graphite electrode although they did not further discuss this weak peak.
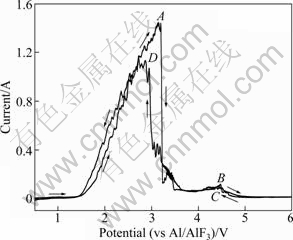
Fig. 2 Cyclic voltammogram for anodic oxidation processes at graphite electrode in 54.8%NaF-44.7%AlF3-0.5%Al2O3 molten salt (CR=2.45, sweep rate 75 mV/s)
Some studies [13-17] about the electrochemical behavior of carbon anode during the anode effect have been done, but their results are various and difficult to reproduce because of the complex anode electrochemical behaviors related to solid phase, liquid phase, and gaseous phase in cryolite-alumina molten salt. CALANDRA et al [16] studied the kinetics of carbon anode in cryolite-alumina molten salt at Al2O3 content of 0.05%-1.5% with various sweep rate of 0.04-600 V/s. They observed four current peaks at 1.10, 1.75, 2.38 and 3.60 V, and three of the four peaks were attributed to the formation of CO2, COF2, and CF4, respectively, while the fourth peak at 3.60 V was not discussed. However, only two peaks (points A and B in Fig. 2) were observed in this experiment on front scan process, and the peak at 3.28 V (point A) is complicated a little bit. The current peak at point A should not be considered a single reaction of the discharge by O2- or F-, but the result of O and F from two types of oxyfluoroaliminate complexes ions discharging together. It is supposed that this current peak is superimposed by discharge of O and F in oxyfluoroaliminate complexes ions respectively, as shown in Fig. 3. The phenomena of peaks superimposing by two ions discharging were also described by ZHANG and QIU [17]. The first current peak in cyclic voltammogram shown in Fig. 2 is very significant for anode effect because its value is treated as the critical value (commonly called critical current density, CCD) of anode effect. It is considered the consequence of increasing coverage of electrode by bubbles film and CF film.
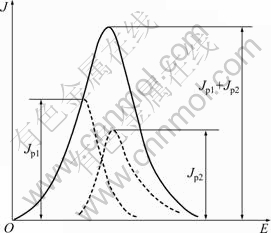
Fig. 3 Sketch of current superimposed [18]: Jp1—Discharge by O in oxyfluoroaliminate complexes ions; Jp2—Discharge by F in oxyfluoroaliminate complexes ions
Factually, the alumina content in aluminum cell is significant for cell operation, since the anode effect occurs easily with decreasing the content of alumina. In the laboratory cell, the cyclic voltammograms at graphite electrode with various alumina contents were measured, as shown in Fig. 4.
It is clearly observed that the alumina content has an obvious influence on critical current densities and passivation potential in Fig. 4. Not only the CCD increases with the increase of alumina content, but also the applied potential, where the anode effect occurs, increases accordingly. But in this completely irreversible system, there is nonlinear relation between current peak value and alumina content (see Fig. 5) in the range of 0.5%-4.5% alumina content.
In aluminum cell, usually, the overall cell reaction is as follows:
2Al2O3+3C=4Al+3CO2 (1)
And the anodic overvoltage (η) of the anodic reaction C+O2--2e=CO2 can be obtained by the Tafel equation:
η=a+blgJ (2)
where a and b are Tafel coefficients, and J is the current density.
The anodic overvoltage versus the logarithm of current density is shown in Fig. 6. It is observed that the overvoltage of graphite anode corresponds with Tafel equation in the current density range of 0.1-1 A/cm2, and the Tafel equation is shown as equation (3):
η=0.219+0.202lgJ (3)
So, the number of transfer electrons (n) is about 2 according to equation (4) based on the Tafel slop b. In equation (4), the apparent transfer coefficient α is 0.62 that is obtained from chronopotentiometry. Moreover, the exchange current density JΘ is 0.082 A/cm2 using extrapolation.
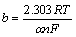 (4)
(4)
where b is Tafel slop; α is apparent transfer coefficient; n is exchange number of electron; F is Faraday constant; R is molar gas constant.
In the range of 0.1-1 A/cm2 of current density (the overvoltage is. 0.05-0.25 V), CO2 is formed. While CO is generated at a low current density (<0.1 A/cm2) [13]. In general, it is difficult to obtain good data at low current densities because the rate of gas generation is low. There is another linear relationship between η and lgJ when the current densities exceed 1.3 A/cm2 (point A in Fig. 6), as l2 shown in Fig. 6. It is supposed that F in oxyfluoroaliminate complexes ions involves in electrode reaction at higher current densities. And the high slop of l2 indicates that the number of transfer electrons of the reaction is small.
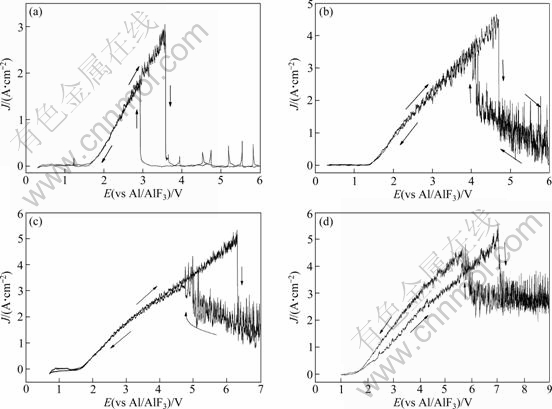
Fig. 4 Cyclic voltammograms for anodic oxidation processes at graphite electrode with various alumina contents (sweep rate 200 mV/s): (a) 52%NaF-47.5%AlF3-0.5%Al2O3; (b) 51.6%NaF-46.9%AlF3-1.5%Al2O3; (c) 51%NaF-46.5%AlF3-2.5%Al2O3; (d) 50%NaF-45.5%AlF3-4.5%Al2O3
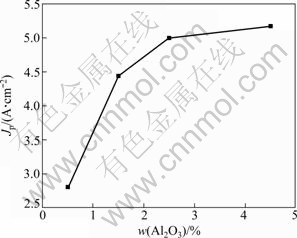
Fig. 5 Relationship between CCD and alumina content (temperature 1000 ℃; sweep rate 200 mV/s)
In cryolite-alumina molten salt, Raman data show that the ions AlF4-, AlF52-, AlF63-, and F- exist together with the oxyanions [Al2OF6]2- and [Al2O2F4]2- [19]. Furthermore, [Al2OF6]2- forms at a low alumina content, while [Al2O2F4]2- forms at a higher alumina content [20]. Consequently, according to the theory provided by ZHANG and QIU [17] and FENG [21], the anion [Al2O2F4]2- discharges on carbon electrode in the current densities no more than 1 A/cm2 at an enough high alumina content, in the following way:
O2-(complex)-2e→O(ad) (5)
O(ad)+xC→CxO(ad) (6)
CxO(ad)+ O2-(complex)-2e→CxO·O(surface) (7)
CxO·O(surface)→CO2(ad)+(x-1)C(surface) (8)
CO2(ad)→CO2↑ (9)
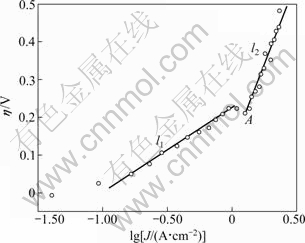
Fig. 6 Anodic overvoltage of graphite electrode at 1000 ℃ in 52%NaF-47.5%AlF3-0.5%Al2O3 molten salt
The overall reaction equation is
2O2-(complex)+C-4e→CO2↑ (10)
Usually, the single-step anode reaction by four transfer electrons is considerably impossible, because the first oxygen needs less energy releasing from [Al2O2F4]2- than the second one or from [Al2OF6]2- which was reported in Ref. [21]. In those step reactions, therefore, the four electrons are transferred averagely through two steps respectively, corresponding to the previous calculated value by equation (4).
Besides, the complex fluorine ions involve in discharge on graphite electrode surface under the condition of high current densities or potential. Although the CF film is not yet obtained, thus, it is still supposed that a high resistance passivation film, graphite fluoride ((CFx)n), is formed on the electrode surface. And then, the graphite fluoride decomposes into amorphous carbon and tetrafluoromethane (CF4) or hexafluoroethane (C2F6). The possible reaction process is as follows:
nxF-(complex)+nC-nxe→(CFx)n (11)
4(CFx)n→nxCF4↑+(4n-nx)C(amorphous) (12)
6(CFx)n→nxC2F6↑+(6n-2nx)C(amorphous) (13)
4 Conclusions
1) In the cryolite-alumina molten salt, the cyclic voltammograms at graphite electrode is high irreversibility and bad reproducibility. The high current peak in cyclic voltammogram is attributed to superimposition of O and F in oxyfluoroaliminate complexes ions discharging. What is more, the CCD is determined by alumina content and nonlinearly increases with alumina content increasing.
2) In the experiment, CO2 is generated at the current densities between 0.1 A/cm2 and 1 A/cm2 in 0.5% alumina-containing electrolyte. And the electron transfer is finished in two steps (two electrons transferred every time). While, under this experimental condition, when the current density is enough large (>1.3 A/cm2), the fluorine in oxyfluoroaliminate complex anions discharges on the graphite electrode surface and forms graphite fluoride ((CFx)n) resistance film which is bad wettability. And tetrafluoromethane (CF4) and hexafluoroethane (C2F6) in anode gas are considered decomposition of graphite fluoride.
References
[1] MARKS J. Global anode effect performance: 2010 PFC emissions reduction objective met [C]//BEARNE G. Light Metals 2009. Warrendale: Minerals, Metals & Materials Soc, 2009: 251-254.
[2] ?YG?RD A, HALVORSEN T A, THONSTAD J, ROE T, BUGGE M. A parameter study of the formation of C-F gases during anode effect in aluminum reduction cells [C]//JAMES W. Light Metals 1995. Warrendale: Minerals, Metals & Materials Soc, 1995: 279-287.
[3] AMPHLETT J C, DACEY J R, PRITCHARD G O. An investigation of the reaction 2COF2=CO2+CF4 and the heat of formation of carbonyl fluoride [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1971, 75: 3024-3026.
[4] VOGT H. Effect of alumina concentration on the incipience of the anode effect in aluminium electrolysis [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29: 779-788.
[5] ZHU Hong-min, SADOWAY D R. The electrode kinetics of perfluorocarbon generation [C]//ECKERT C E. Light Metals 1999. Warrendale: Minerals, Metals & Materials Soc, 1999: 241-246.
[6] CRASSOUS I, GROULT H, LANTELME F, DEVILLIERS D, TRESSAUD A, LABRUG?RE C, DUBOIS M, BELHOMME C, COLISSON A, MOREL B. Study of the fluorination of carbon anode in molten KF-2HF by XPS and NMR investigations [J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2009, 130: 1080-1085.
[7] GROULT H. Interfacial properties and gas bubble formation during the electrolytic preparation of fluorine [J]. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 2004, 151: D121-D126.
[8] PHILIPPE M, BARRY W, MARIA S K. An electrochemical study of the anode effect in the aluminium smelting process [C]//ANJIER J L. Light Metals 2001. Warrendale: Minerals, Metals & Materials Soc, 2001: 337-341.
[9] ZHANG Ming-jie, QIU Zhu-xian, WANG Hong-kuan. Electrode processes in aluminium electrolysis:Ⅰanodic process [J]. Journal of Northeast Institute of Technology (Science), 2001(2): 123-126. (in Chinese)
[10] GROULT H, DURAND-VIDAL S, DEVILLIERS D, LANTELME F. Kinetics of fluorine evolution reaction on carbon anodes: Influence of the surface C-F films [J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2001, 107: 247-254.
[11] DJOKIC S S, CONWAY B E, BELLIVEAU T F. Specificity of anodic processes in cyclic voltammetry to the type of carbon used in electrolysis of cryolite-alumina melts [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1994, 24: 827-834.
[12] ZHU Hong-min, SADOWAY D R. An electroanalytical study of electrode reaction on carbon anodes during electrolytic production of aluminum [C]//PETERSON R D. Light Metals 2000. Warrendale: Minerals, Metals & Materials Soc, 2000: 257-263.
[13] ZHANG Ming-jie. Study on anodic process of aluminum electrolysis [D]. Shenyang: Northeast University, 1985: 55-56. (in Chinese)
[14] NISSEN S S, SADOWAY D R. Perfluorocarbon (PFC) generation in laboratory-scale aluminum reduction cells [C]//TABEREAUX A T. Light Metals 1997. Warrendale: Minerals, Metals & Materials Soc, 1997: 159-164.
[15] ZHU Hong-min, THONSTAD J. Anode reaction in aluminium electrolysis prior to and during anode effect [C]//CREPEAU P N. Light Metals 2003. Warrendale: Minerals, Metals & Materials Soc, 2003: 343-349.
[16] CALANDRA A J, CASTELLANO C E, FERRO C M. The electrochemical behaviour of different graphite/cryolite alumina melt interfaces under potentiodynamic perturbations [J]. Electrochim Acta, 1979, 24: 425-437.
[17] ZHANG Ming-jie, QIU Zhu-xian. Anodic process in the electrolysis of cryolite-alumina melts [J]. Journal of Northeast Institute of Technology (Science), 1984(1): 49-59. (in Chinese)
[18] JIA Zheng, DAI Chang-song, CHEN Ling. Electrochemical measurement methods [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006: 140-141. (in Chinese)
[19] ROBERT E, OLSEN J E, DANEK V, TIXHON E, ?STVOLD T, GILBERT B. Structure and thermodynamics of alkali fluoride-aluminum fluoride-alumina melts: Vapor pressure, solubility, and Raman spectroscopic studies [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1997, 101: 9447-9457.
[20] HU Xian-wei, QU Jun-yue, GAO Bing-liang, SHI Zhong-ning, LIU Feng-guo, WANG Zhao-wen. Raman spectroscopy and ionic structure of Na3AlF6-Al2O3 melts [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 402-406.
[21] FENG Nai-xiang. Aluminium electrolysis [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006: 56. (in Chinese)
冰晶石熔盐中阳极效应时石墨阳极的电化学行为
陈 功1,石忠宁1, 2,高炳亮1, 2,胡宪伟1, 2,王兆文1, 2
1. 东北大学 材料与冶金学院,沈阳 110004;
2. 东北大学 有色金属冶金过程技术教育部工程研究中心,沈阳 110004
摘 要:在1000 ℃下采用循环伏安法研究石墨阳极在冰晶石氧化铝熔盐中的阳极电化学行为。讨论了循环伏安曲线中较高的电流峰。结果表明,在高电位条件下,一种含氧氟络合阴离子中的氟与碳阳极反应,且在阳极表面生成一层高电阻的CF膜。在含0.5%氧化铝的电解质中,石墨电极钝化电位为3.28 V,并随着氧化铝含量的增加而增大。这一现象表明,在冰晶石-氧化铝熔盐体系中氧化铝含量对阳极过程起着主导作用。
关键词:阳极行为;铝电解;全氟碳化物;阳极钝化
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Projects (50804010, 51074046) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: SHI Zhong-ning; Tel: +86-24-83686464; E-mail: znshi@mail.neu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61464-7