应力-电场耦合时效对2524铝合金微观组织的影响
王琪1, 2, 3,傅上1, 2,王斌1, 2,易丹青1, 2,王宏伟1, 2,周明哲4
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 中南大学 教育部有色金属材料科学与工程重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083;
3. 航天材料及工艺研究所,北京,100076;
4. 湖南泰嘉新材料科技股份有限公司,湖南 长沙,410200)
摘要:采用光学显微镜(OM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、正电子淹没谱等分析手段,研究应力、应力-电场耦合时效后2524铝合金的微观组织。研究结果表明:在190 ℃时效10 h时,外加130 MPa应力抑制2524铝合金中S′相的均匀形核和长大。应力(130 MPa)+电场(16 V/cm)耦合时效后,合金中出现了高密度的位错环和蜷线位错,S′相在位错和含Mn相周围细小弥散析出,晶界处PFZ缩小并出现大量细小S′相。
关键词:2524铝合金;应力;电场;时效;微观组织
中图分类号:TG111.3 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)05-1428-09
Effect of stress coupled with electric field on microstructure of 2524 aluminum alloy
WANG Qi1, 2, 3, FU Shang1, 2, WANG Bin1, 2, YI Danqing1, 2, WANG Hongwei1, 2, ZHOU Mingzhe4
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Metal Materials Science and Engineering, Ministry of Education,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Aerospace Research Institute of Materials & Processing Technology, Beijing 100076, China;
4. Bichamp Cutting Technology (Hunan) Co. Ltd, Changsha 410200, China)
Abstract: The optical microscope (OM), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and positron annihilation spectroscopy were used to analyze the microstructures of 2524 aluminum alloy after stress-aging and stress-electric field-aging, respectively. The results show that the homogeneous nucleation and growth of the S′ phase in 2524 are restrained by the impressed 130 MPa stress after aging at 190 ℃ for 10 h. After stress (130 MPa) coupled with electric field (16 V/cm) aging, high density of dislocation loops and helical dislocations form in the alloy, fine S′ phase dispersedly precipitates around the dislocations and Mn-rich phase, and the PFZ along the grain boundaries is narrowed and extensive S′ phase precipitates.
Key words: 2524 aluminum alloy; stress; electric field; aging; microstructure
2524系列合金是一种时效硬化型耐疲劳铝合金,时效过程中析出相数量、形貌等决定了合金强化效果[1-3]。在时效过程中,小于屈服极限的应力-应力时效会使析出过程产生显著的变化[4-5]。Zhu等[5]以Al-Cu合金为模型,研究了成分、应力、温度和时效时间等对微观组织的影响,发现在压应力下,时效形成的θ″相垂直于应力轴;拉应力下,形成的θ″相平行于应力轴。Hargarter等[6]研究发现:Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金应力时效后,合金的屈服强度降低,且各向异性增大。Hosford等[7-8]则提出了不同扩散的模型来解释应力位向效应的形成机制。近年来,有学者发现电场对铝合金时效过程有一定的影响。Liu等[9-13]研究结果表明,2091铝合金经电场固溶、电场均匀化热处理后,依赖位错环、蜷线位错和亚晶界的T1(Al2CuLi)相和S′(Al2CuMg)相体积分数增大,且尺寸减小。ZHOU Mingzhe等[14]研究了电场时效对2E12铝合金微观组织和力学性能的影响,发现电场促进了S′相的析出。在此,本文作者将这2种有益的外场进行耦合,在时效过程中同时施加力场-电场,改变析出相的数量、形貌及大小,以2524铝合金为对象,考察2524铝合金在应力-电场耦合场时效处理后的微观组织演变,分析外场对合金时效过程的影响机理。
1 实验材料和方法
实验合金为1.7 mm厚2524铝合金冷轧薄板。样品规格如图1(a)所示,合金化学成分为:Cu 4.0%~4.23%;Mg 1.1%~1.42%;Mn 0.56%~0.6%;Fe≤ 0.08%,Si≤0.08%(质量分数);铝余量。固溶热处理采用混合硝盐加热,其温度为500 ℃,保温1 h,然后迅速放入水中淬火。本实验采用自制的“温度-应力-电场”耦合时效处理设备,如图1(b)所示。该装置使用3块平行横板和弹簧组合的施加拉力。样品两侧施加强静电场。时效温度为190 ℃,应力水平为0,25和130 MPa,电场强度为16 kV/cm。采用Lecia DMILM金相显微镜检测微观组织,采用TecnaiG220型电子显微镜观察析出相变化。采用武汉大学正电子湮没分析仪测量合金中空位缺陷。
2 应力-电场耦合时效对2524铝合金微观组织的影响
2.1 应力-电场耦合时效对合金晶粒组织的影响
图2所示为2524铝合金在190 ℃×10 h、不同外场时效后的金相显微组织。从图2(a)可知:无应力时,晶粒基本呈等轴状,晶粒取向呈无序状态分布。施加25和130 MPa应力(图2(b)和2(c))后,晶粒的取向分布仍比较分散。当应力与电场耦合作用时(图2(d)),晶粒形貌也没有发生变化。这说明,外加的弹性应力和强静电场对合金的晶粒形貌无影响。
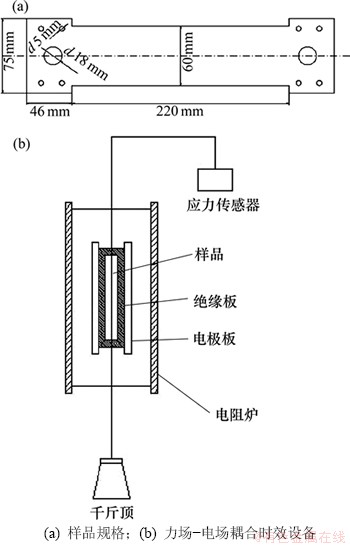
图1 固溶/时效处理样品规格和试验设备示意图
Fig. 1 Sketch map of sample and test equipment for solid solution and aging treatment
2.2 电场对合金中空位的影响
为研究电场对合金时效过程的影响机理,采用正电子湮没技术对2524铝合金190 ℃时效过程的正电子湮没寿命及维氏硬度进行测定,结果如图3所示。合金的时效硬化曲线呈现3个不同阶段(图3(b)):(Ⅰ) 时效初期,硬度迅速增加,而正电子寿命迅速下降;(Ⅱ) 随时效时间的延长,合金的硬度增加至最大值,而正电子寿命相对平稳;(Ⅲ) 继续延长时效时间,合金硬度开始下降,而正电子寿命上升。正电子湮没寿命与测试的材料中空位数量有直接关系,正电子湮没寿命越长对应越多的空位数量[15]。这说明在190 ℃人工时效时,合金中空位型缺陷数量先急剧降低,随后经较长时间的平稳阶段后增加。
参考经典物理理论,若将空位V与溶质原子A形成的空位-原子对看成是V-A复合体,空位被周围原子的外层电子包围,可视为负电中心;与该负电中心最近邻的溶质原子的外层电子向负电中心方向偏移,此时V-A复合体可视为有极性。由于V-A复合体在基体中是随机分布的,故基体表现出电中性。而在电场的作用下,合金基体中V-A复合体将由原来的无序化向相对有序化转变,如图4所示。此时,除了合金外表面在电场(场强E)作用下形成的电荷重新分布外,合金内部由于V-A复合体的定向排列也将产生一个与外加电场方向相反的内势场(场强E′)。
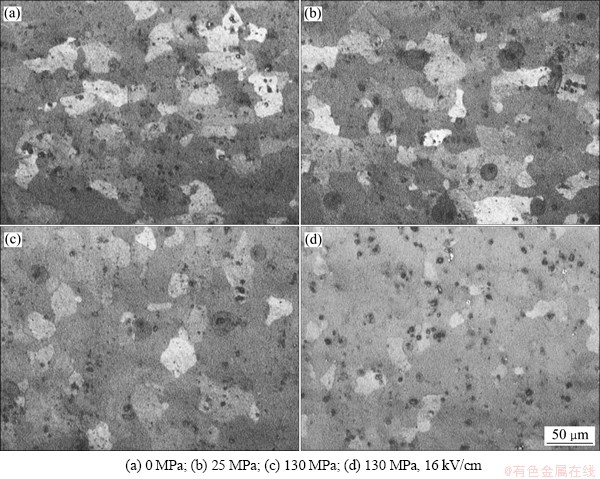
图2 190 ℃×10 h不同外场条件下的金相显微组织
Fig. 2 Metallographic microstructure of alloy aging under different field condition at 190 ℃ for 10 h
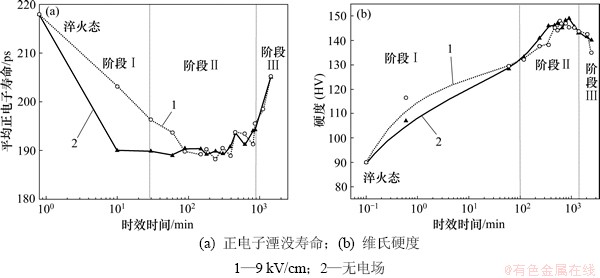
图3 合金190 ℃强电场和无电场时效正电子湮没寿命及硬度随时效时间变化曲线
Fig. 3 Evolution of Vickers hardness and positron lifetime of alloy during aging with and without electric field at 190 ℃
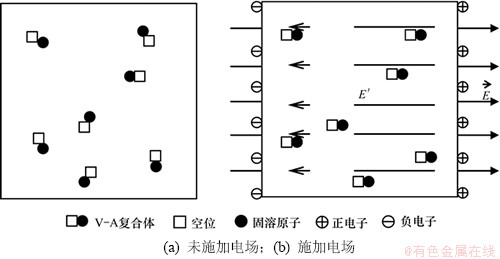
图4 电场影响合金时效过程模型
Fig. 4 Model of mechanism for effect of electric field of alloy
若先不考虑电场的作用,根据Zurbo等[16]的理论,V-A复合体的迁移主要依靠空位的跳动,其跳动的概率为:
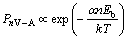 (1)
(1)
式中:Eb为溶质原子与空位之间的结合能;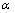 和k为常数;n为空位周围的原子数量;T为热力学温度。当结合能Eb为正值时,溶质原子与空位相遇将形成V-A复合体。当溶质原子团簇区数量达到一定值时,空位周围原子数量n增大,空位可动性降低,最终湮灭在原子团簇区位置。施加外静电场的情况下,由于合金内部产生的感应电场E′,溶质原子与空位之间的结合能由原来的Eb变为了Eb-E′,即结合能减小。根据式(1),空位与溶质原子结合能的降低意味着空位跳动概率的增加。根据Esmaeili等[17]的研究结果,空位跃迁概率越大,可形成的团簇区的数量也必定增大。这说明:电场的施加可提高空位的跳动概率,即可有效促进原子团簇的形成。
和k为常数;n为空位周围的原子数量;T为热力学温度。当结合能Eb为正值时,溶质原子与空位相遇将形成V-A复合体。当溶质原子团簇区数量达到一定值时,空位周围原子数量n增大,空位可动性降低,最终湮灭在原子团簇区位置。施加外静电场的情况下,由于合金内部产生的感应电场E′,溶质原子与空位之间的结合能由原来的Eb变为了Eb-E′,即结合能减小。根据式(1),空位与溶质原子结合能的降低意味着空位跳动概率的增加。根据Esmaeili等[17]的研究结果,空位跃迁概率越大,可形成的团簇区的数量也必定增大。这说明:电场的施加可提高空位的跳动概率,即可有效促进原子团簇的形成。
2.3 应力-电场耦合时效对位错形貌的影响
图5所示为合金不同应力水平及应力电场耦合时效190 ℃×10 h下的微观组织。无外力时,合金内部分布有少量的平直位错线和位错环,位错线上分布有细小的S′相(图5(a))和粗大的Al20Cu2Mn3相。当施加应力为25 MPa时,位错环沿某个方向被拉长,部分呈菱形状(图5(b))。当外力增加到130 MPa,部分位错环椭球化(图5(c))。当应力与电场同时作用时,位错形貌发生了较大变化:位错环直径相对变小,并且大量的位错环重叠在一起(或为蜷线位错);部分位错环同时沿2个方向拉长,呈花瓣状(图5(d))。
刃型位错的攀移实质是一个由空位扩散控制的过程。根据原子迁移动力学理论[18-19]可知:无外应力时,铝合金各方向扩散系数之比为1;当有外应力时,扩散系数呈现明显的各向异性,即施加外应力后,空位开始定向扩散,借助于空位迁移的位错环也在某个方向的扩张较快,呈现被拉长的形态(图5(b))。当同时施加应力和电场后,电场作用下的空位定向扩散亦起作用。晶界处的空位向晶内扩散,从而导致晶内空位浓度增大,位错环密度大大增加,且直径也较前3种的小。同时,在电场的作用下,空位也会发生定向的迁移,若电场和力场引起的定向扩散互相垂直,位错环仍保持为圆形状;若2种机制同时处于水平方向,则位错呈现出一定的花瓣状(图5(d))。
无序化向相对有序化转变,除了合金外表面在电场(场强E)作用下形成的电荷重新分布外,合金内部由于V-A复合体的定向排列也将产生一个与外加电场方向相反的内势场(场强E′)。
2.4 应力-电场耦合时效对晶内析出相的影响
图6所示为190 ℃×10 h无应力时效合金的微观组织。在Al-Cu-Mg系合金中,半共格的S′相可在位错线处形核,并和基体成一定的惯析取向(图6(a))。位错环也是S′相的择优形核场所(图6(b)),析出S′相成一定方向排列。S′相也可以在基体中无位错的局部区域均匀形核(图6(c))。190 ℃×10 h时效条件下,外加应力为25 MPa,130 MPa及130 MPa+16 V/cm电场耦合时所对应的TEM显微组织如图7所示。
由于外加应力产生了大量的界面位错,使得S′相有足够的形核地点,因而在位错线附近析出的S′相数量较多,且呈点状或者短棒状;与无应力时效态相比(图6(b)),其尺寸明显减小。从图7(a)可以看出:S′相产生的衍射斑点呈2个互相垂直的方向分布,说明几种方向的变体同时存在,并没有观察到发生文献[4-5]中的应力位向效应。从图7(b)中没有发现位错,也没有发现S′相,在相应的衍射斑点中也未发现由S′相的特征斑点。这说明施加较大的应力后,S′相的均匀形核可能被抑制或延缓。而在有位错线的区域,则发现了一些细小的棒状S′相(图7(c));这些S′相都呈一定取向在位错环线上排列,呈棒状分布,其长度仅有40 nm左右(图7(d))。从图7(e)中也未观察到明显呈棒状或针状的S′相。施加电场的一个明显的效应是产生了大量的位错环和蜷线位错(图7(f))。由于S′相极易在位错线异质形核,在蜷线位错线上发现了较小的S′相。细小的S′相和高密度的位错都为合金的强化做出了极大的贡献。
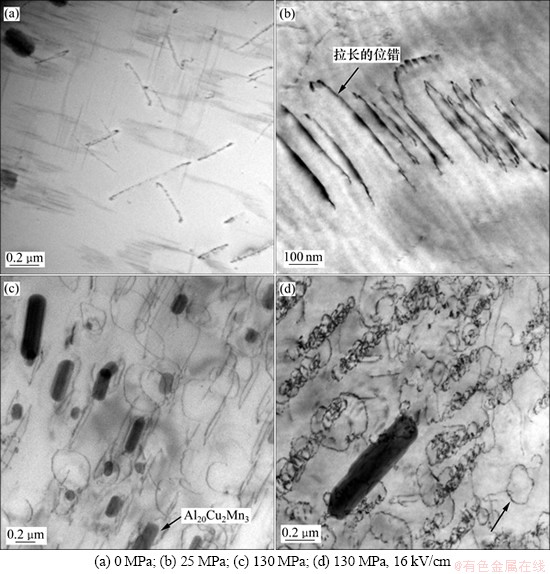
图5 合金190 ℃×10 h、不同应力水平及应力电场耦合时效的位错分布状态
Fig. 5 Distribution of dislocation aging under different stress field and stress coupled with electric field at 190 ℃ for 10 h
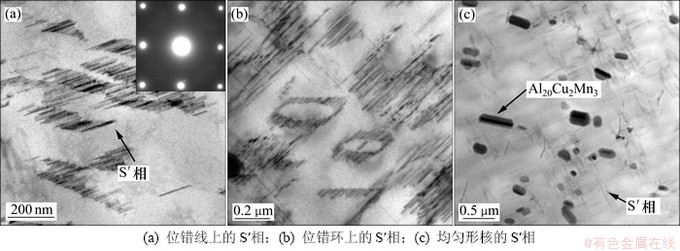
图6 无应力时效190 ℃×10 h的微观组织
Fig. 6 Microstructure of alloy aging without stress field at 190 ℃ for 10 h
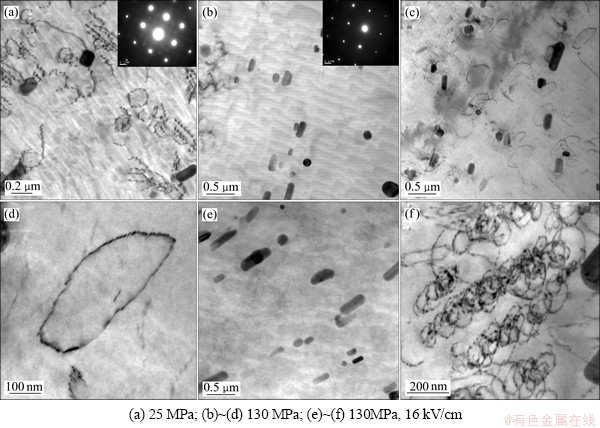
图7 190 ℃×10 h时效条件下,外加应力σ=25 MPa、130 MPa及应力电场耦合130 MPa+16 V/cm时的TEM显微组织
Fig. 7 TEM images of stress aging under σ=25 MPa, 130 MPa and stress coupled with electric field under 130 MPa+16 V/cm at 190 ℃ for 10 h
为了进一步揭示低温时效时应力对S′相的影响规律,将应力时效时间延长到20 h,并观察其显微组织。从图8(a)中仍难以找到较大的S′相,从其衍射斑点,可以发现一些微弱的S′相产生的斑点,这说明合金内部的S′相数量仍比较少,难以产生较强的衍射效应。从图8(b)可见一些较大的S′相,这些相都在粗大的含Mn弥散相周围的位错线[20]上形成。这进一步表明在施加应力后,晶内的绝大多数S′相都要依靠位错线进行异质形核长大,而均匀形核的S′相在很大程度上被抑制。
2.5 应力-电场耦合时效对晶界析出相的影响
190 ℃×10 h应力时效和应力电场耦合时效后晶界处的微观形态如图9所示。无应力时效时,晶界两侧呈现一条明显的亮带,即无沉淀析出带PFZ(图9(a))。当施加应力后,无沉淀析出带尺寸大幅缩小(图9(b)和(c))。当应力电场耦合时效时,发现晶界上析出了大量细小弥散相(图9(d)),其长度为30~80 nm。这些相形貌不规则,呈现短棒状,相之间还分布着一些细小的位错线。对晶界处析出相的EDS分析结果显示(图9(e)和(f)),Cu和Mg的物质的量比接近1:1,名义成分为Al2CuMg,与S系列析出相一致。
电场时效后合金晶界PFZ缩小的现象[21]如图10所示。由于晶界处为原子排列较为紊乱的区域,在时效过程中,基体中由于淬火时留下的过饱和空位在随机跳动的过程中更倾向于在晶界处运动,从而释放其引起的畸变能。在其运动过程中又将带动溶质原子向晶界处迁移,从而导致晶界处的析出。施加电场时效的合金试样,由于空位的迁移受到电场的影响而加速,其迁移至晶界处几率增加,即溶质原子在晶界处脱溶几率增加,进而导致了晶界处第二相数量增加,进而促使PFZ区域缩小。
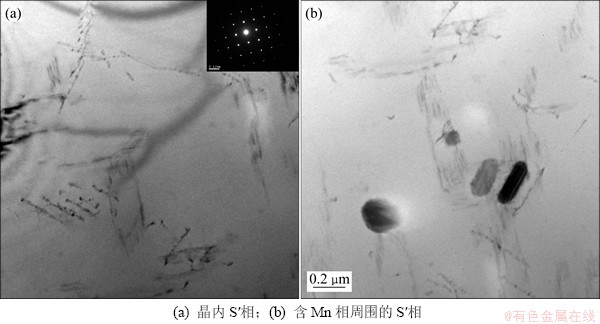
图8 190 ℃×20 h/130 MPa时效对应的TEM组织
Fig. 8 TEM images of alloy aging under stress field of 130 MPa at 190 ℃ for 20 h
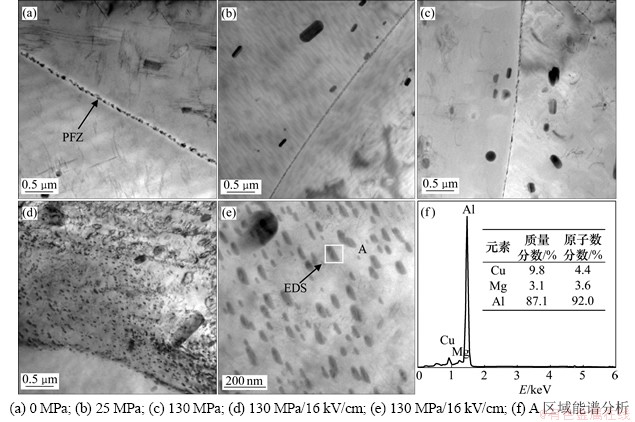
图9 应力及应力电场耦合下合金晶界处析出示意图
Fig. 9 Characteristics of grain boundary and phase under stress and stress coupled with electric field
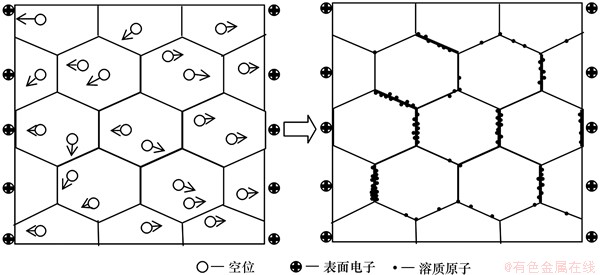
图10 电场影响合金晶界处析出示意图
Fig. 10 Sketch map of influence of electric field on precipitates at grain boundaries
3 结论
(1) 190 ℃时效时,2524铝合金中空位数量变化趋势与硬度的变化趋势相反,即先急剧降低,后进入平稳阶段,最后在过时效阶段有所增加。
(2) 外加25~130 MPa应力时效抑制了合金中S′相的均匀形核;而促使其在位错线附近出现。而在外力(130 MPa)+电场(16 kV/cm)耦合时效时,出现高密度的位错环和蜷线位错,促进了S′相的异质形核。
(3) 外力(130 MPa)+电场(16 kV/cm)耦合时效时, PFZ变窄,S′相沿晶界大量析出。
参考文献:
[1] 周明哲, 易丹青, 王斌, 等. 固溶处理对2E12铝合金组织及疲劳断裂行为的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(1): 66-73.
ZHOU Mingzhe, YI Danqing, WANG Bin, et al. Effect of solution treatment on fatigue behavior of 2E12 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(1): 66-73.
[2] 王昌臻, 潘清林, 何运斌, 等. 2124 铝合金热轧厚板的热处理制度[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 38(3): 386-393.
WANG Changzhen, PAN Qinglin, HE Yunbin, et al. Heat treatment of thick hot-rolled plate of 2124-alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2007, 38(3): 386-393.
[3] 刘志义, 周杰, 刘延斌, 等. 高温短时人工时效对2524合金疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(1): 112-116.
LIU Zhiyi, ZHOU Jie, LIU Yanbin, et al. Effect of artificial ageing on fatigue behaviour of 2524 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2009, 40(1): 112-116.
[4] Eto T, Nachi M, Mori T. Study of GP zones in Al-Cu alloys by stress aging[J]. Trans JIM, 1979, 20: 459-467.
[5] Zhu A W, Starke A. Stress aging of Al-xCu alloys: Experiments[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(12): 2285-2295.
[6] Hargarter H, Lyttle M T, Starke E A. Effects of preferentially aligned precipitates on plastic anisotropy in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag and Al-Cu alloys[J]. Materials Science Engineering A, 1998, 257(1): 87-99.
[7] Hosford W F, Agrawal S P. Effect of stress during aging precipitation of θ′ in Al-4%Cu[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1975, 6(3): 487-491.
[8] Sankaran R. Discussion of “effect of stress during aging on the precipitation of θ′ in Al-4%Cu”[J]. Metallurgical Transaction A, 1976, 7(5): 770-771.
[9] Liu W, Liang K M, Zheng Y K, et al. Study of the diffusion of Al-Li alloys subjected to an electric field[J]. Journal of Material Science, 1998, 33(4): 1043-1047.
[10] Liu W, Liang K M, Zheng Y K, et al. Effect of an electric field during solution treatment of 2091 Al-Li alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1996, 15(15): 1327-1329.
[11] Liu W, Cui J Z. A study on the ageing treatment of 2091Al-Li alloy with an electric field[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1997, 16(16): 1410-1411.
[12] Liu W, Ding H, Cui J Z. Effect of solution treatment in an electric field on mechanical properties and microstructure of 2091 Al-Li alloy[J]. Acta Materials Sinica, 1994, 7(3): 208-214.
[13] Conrad H, Guo Z, Sprecher A F. Effect of an electric field on the recovery and recrystallization of Al and Cu[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1989, 23(6): 821-824.
[14] ZHOU Mingzhe, YI Danqing, LIU Huiqun, et al. Enhanced fatigue crack propagation resistance of an Al-Cu-Mg alloy by artificial aging under influence of electric field[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(16/17): 4070-4075.
[15] Wu Y C, Teng M K, Hsia Y, et al. An estimation of the dislocation density and vacancy concentration in iron under different strain rates[J]. Materials Science Forum, 1995, 175/176/177/178: 573-576.
[16] Zurbo H S, Seyedrezai H. A model for the growth of solute clusters based on vacancy trapping[J]. Scripta Materilia, 2009, 61(2): 141-144.
[17] Esmaeili S, Vaumousse D, Zandbergen M W, et al. A study on the early-stage decomposition in the Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy AA6111 by electrical resistivity and three-dimensional atom probe[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2007, 87(25): 3797-3816.
[18] Ardell A J, Prikhodko S V. Coarsening of γ′ in Ni-Al alloys aged under uniaxial compression Ⅱ: Diffusion under stress and retardation of coarsening kinetics[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(17): 5013-5019.
[19] Flynn C P. Atomic migration in monatomic crystals[J]. Physical Review, 1968, 171(3): 682-698.
[20] 王宏伟, 易丹青, 蔡金伶. 应力时效对2E12铝合金的力学性能和微观组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(12): 3019-3025.
WANG Hongwei, YI Danqing, CAI Jinling. Effect of stress aging on mechanical properties and microstructures of 2E12 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(12): 3019-3025.
[21] 李智燕, 易丹青, 周明哲. 电场时效对2E12铝合金力学性能和微观组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(8): 1392-1397.
LI Zhiyan, YI Danqing, ZHOU Mingzhe. Effect of electric field aging on mechanical properties and microstructures of 2E12 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(8): 1392-1397.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2013-05-06;修回日期:2013-08-28
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51071177);国家重大基础研究发展计划(“973”计划)项目(2012CB619506)
通信作者:王斌(1971-),男,陕西宝鸡人,博士,副教授,从事铝合金研究;电话:0731-88830263;E-mail: wangbin325@263.net