
Synthesis of ultrafine copper particles by complex-reduction-extraction method
YANG Jian-guang(杨建广), YANG Sheng-hai(杨声海), TANG Chao-bo(唐朝波),
HE Jing(何 静),TANG Mo-tang(唐谟堂)
School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 15 July 2007; accepted 10 September 2007
Abstract: A novel chemical process for producing well-defined copper particles with satisfied anti-oxidation property was described. The resultant particles were characterized by X-ray diffractometry and scanning electron microscopy. The results show that well-dispersed nano-copper particles with 70 nm in diameter are obtained from the water/organic solution containing 0.2 mol/L Cu2+ ion, with ammonia as ligand and ascorbic acid as reductant. In this process, the formation of copper-ligands in aqueous solution causes initial copper ions concentration very low, which is not only good to obtain homogeneous initial reaction solution, but also slower the initially drastic nucleation reaction rate. This makes the process more convenient for delaying the nuclei processes and for controlling the ultimate copper particles size. In addition, oleic acid acts as both a phase-transfer agent and a particle protector coordinating their carboxyl end groups on the new generated copper particles surface, the carbon tails of the oleic acids are pointed outwards from the surface of the synthesized particles. This organic film also seems to play an important role to prevent the new generated copper particles from oxidation.
Key words: copper nanoparticles; copper ligands; complex; extraction; reduction
1 Introduction
Currently copper particles preparation researches could be summarized into two main streams. One is developing new methods or designing new chemical reaction system to prepare well-defined particles, such as photolytic reduction, radiolytic reduction, sonochemical method, micro-emulsion techniques, polyol process, etc[1-5]. The other is developing new techniques to prepare well-dispersed colloidal system, i.e., separation nucleation and growth, inhibition of coagulation, choice of appropriate growth modes and reserve of monomers, etc.
In contrast with noble metals such as Ag and Au, pure metallic copper particles usually cannot be obtained via the reduction of simple copper salts such as copper chloride or copper sulfate in aqueous solutions, because the reduction tends to stop at the Cu2O stage due to the presence of a large number of oxygenous water molecules, unless other complex reagents carrying functional groups with copper ions are present or using soluble surfactants as capping agents to prepare copper particles in aqueous solutions. However, despite zero valent copper initially forming in the solvent ultimately, it has been found that the zero valent copper can be easily transformed into oxides in those solvents with high dipole moments under ambient conditions[1]. Therefore, the traditional fabrication methods are usually performed in non-aqueous media, at low precursor concentration, and in an inert atmosphere to avoid oxidation, which greatly hinders them in the application for mass- production[6-10].
In this paper, the synthesis and characterization of copper particles with specific size, shape, and narrow size distribution using a kind of new complex- reduction-extraction method were studied. In this method, cupric ions in the aqueous solution were firstly constructed into copper-ligands. Then, the copper-ligands were reduced into metallic copper by ascorbic acid/hypophosphite. In this process, chelating agents, such as EDTA, tartaric acid, ammonia, or citric acid were investigated as copper cation shield. These complex agents, especially ammonia, appeared to prevent both nucleation and coagulation during the particle growth by shielding the metallic ions.
Meanwhile, they could also liberate metal ions by degrees with the progress of precipitation, which was relatively easy to meet every requirement for preparing well-defined copper particles. On the other hand, oleic acid was introduced to act as both an extractant and a surfactant that could be adsorbed on the surface of the copper particles. Stable metallic copper particles could be obtained even in the presence of air oxygen. This method enables us to obtain highly stable nano-copper particles. Meanwhile, the presence of C═C bonds of oleic acid makes the final products easily react with polymer matrix, which is important for potential industrial process application.
2 Experimental 2.1 Materials
All chemicals used were reagent grade. Copper sulfate, EDTA, tartaric acid, ascorbic acid, oleic acid, ammonia, H3PO4 and NaH2PO2?H2O were purchased from Japan Nacalai Teceque Inc. They were used without further purification.
2.2 Procedure
Fig.1 shows the experiment procedure: in a typical experiment, two kinds of solutions were mixed firstly; one was aqueous solution of 0.2 mol/L CuSO4 with corresponding ligand, while the other was 0.5 mol/L oleic acid. Then, the mixed solution was shaken at normal condition for 30 min. The aqueous/organic solvent was reduced by ascorbic acid/hypophosphite. Reaction solution was kept under agitation at a moderate speed to maintain the uniformity of the system and to keep the precipitated particles dispersed until the reduction was completed. Also, the dropping rate was sufficiently low to avoid foaming of the reaction dispersion. After 2 h of ageing, the precipitation was separated from the liquid solution by centrifugation, and subsequently was washed with distilled water and alcohol for more than 3 times until a transparent solution
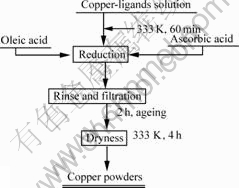
Fig.1 Sketch of process flow
was obtained. The ultimate powders were then dried in the vacuum stove at 333 K for 4 h.
Characterization of the metallic particles was achieved through different techniques. The X-ray diffraction patterns were obtained with an X-ray diffractometer (XRD; XRD-6000, Shimadzu Co., Japan) using Cu Kα radiation. The morphology of the final products was determined from microphotographs obtained with a scanning electron microscope (model S-800).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Particle size and structure
Fig.2 shows the XRD pattern and SEM image of a typical sample synthesized by reducing copper sulfate in extracted solution using ammonia as ligand.

Fig.2 XRD pattern(a) and SEM image(b) of typical sample (Cu2+ 0.2 mol/L, 333 K, 1 h, ammonia as ligand, and ascorbic acid as reductant)
It can be seen from Fig.2(a) that all the peaks can be readily indexed to pure copper (JCPDS file No. 04-0836). The average grain size of the powder is calculated to be around 70 nm according to half width of the strongest diffraction peak using Debye-Scherrer formula. Fig.2(b) reveals that the product consists of spherical particles, and all nanoparticles disperse very well. The average diameter estimated from SEM images analysis is 60- 70 nm.
3.2 Mechanism of process
Mechanism of this process can be demonstrated by Fig.3. Cupric ions in aqueous solution are firstly constructed into copper-ligands, then, upon fast addition of the reductant solution into the copper-ligand solution, the copper-ligand species are gradually reduced to Cu. As the reaction process, the concentration of Cu monomer in the solution increases, reaches the saturation concentration, then super-saturation and finally the nucleation concentration. Spontaneous nucleation takes place very rapidly and many nuclei are formed in a short time, lowering the Cu monomer concentration below the nucleation and super-saturation levels into the saturation concentration region. The cupric ions are reduced to nuclei until the system reaches the saturation concentration. New generated copper particles are extracted into oleic acid at the same time. On the other hand, in order to reconcile the two conflicting demands of a moderate super-saturation and an ample quantity of nuclei for high yield of copper particles, nuclei reservoirs are built in individual system. In this process, chelating agents, such as EDTA, tartaric acid, ammonia, or citric acid were investigated as copper cation shield. Thus, if one of these complexes was employed as a solute, the much higher super-saturation and the excessive ionic strength with copper cation can be moderated at the same time[11-13].
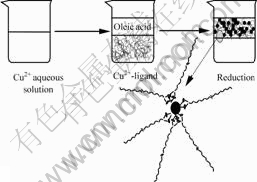
Fig.3 Scheme for mechanism of process
In addition, oleic acid was adopted in this process. It plays an important role throughout this process. It is not only used as a phase-transfer agent, but also acted as a surfactant to modify surface of the new generated particles coordinating their carboxyl end groups. The carbon tails of the oleic acids are pointed outwards from the surface of the synthesized particles. Oleic acid’s function in this process is generally proposed on the basis of the following reactions.
2C17H33COOH+Cu(A)m2+→Cu(C17H33COO)2+2H++mA (1)
(n-2)C17H33COOH+Cu(C17H33COO)2+C6H8O6→Cu(C17H33COOH)n+C6H6O6 (2)
2nC17H33COOH+2Cu(A)m2++PO23-+2H2O→PO43-+2Cu(C17H33COOH)n+4H++2mA (3)
where A represents copper ligand.
Oleic acid preventing the copper particles from aggregation and oxidation were the two main roles in this process, which occurred both during the growth step and the washing processes. For the former case, the steric effect arising from the long alkyl chain of oleic acid on the surface of copper particles may contribute to the anti-oxidation. For the latter case, chemical bonding between the oleic acid and copper powders may play a positive role in prohibiting oxidation of copper particles, because washing with water and alcohol several times have not completely removed the oleic acid from the surface of the copper particles. By which, this fabrication method realizes to prepare nano-copper particles and anti-oxidation in one process.
3.3 Effect of ligand species on particle size and structure
Synthesis was preformed in fixed other experiment parameters and only varied different ligands. Figs.4-7 show the XRD patterns and SEM images of the resultant samples synthesized by reducing copper sulfate in this process. From Fig.4, one can also easily see that all XRD peaks are identified to cuprous oxide (JCPDS file No. 34-1354). The SEM images reveal that the product consists of irregular morphology, and all particles are not dispersed very well. It can be seen from Fig.5(a) that all the peaks can be readily corresponded to oxidized copper (JCPDS file No. 04-0836) and (JCPDS file No. 34-1354). The average grain size of the powder is estimated to be around 1 μm according to SEM image and half width of the strongest diffraction peak. The SEM image also reveals that the product consists of spherical particles, and all particles are dispersed very well.
From Figs.6 and 7, it can be seen that all XRD patterns’ peaks are indexed to oxidized copper (JCPDS file No. 04-0836) and (JCPDS file No. 34-1354), the products consist of nearly regular shape particles, but the particles’ average size is different. The reason may be account of different ligands causing different ionic strength.
It can be seen from these results that well-defined copper nanoparticles could be obtained only when ammonia is used as ligand and ascorbic acid is used as the reductant. The reaction may be explained by Eqns.(a) and (2): the added ammonia accelerates the reaction rate, all Cu(NH3)42+ ions are firstly turned into Cu(C17H33COO)2, and then be reduced into metallic copper, the new generated copper particles are extracted

Fig.4 XRD pattern(a) and SEM image(b) of typical sample without any ligand (Cu2+ 0.2 mol/L, 333 K, 1 h, no ligand, and hypophosphite as reductant)
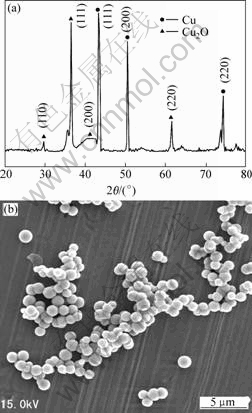
Fig.5 XRD pattern(a) and SEM image(b) of typical sample(Cu2+ 0.2 mol/L, 333 K, 1 h, EDTA as ligand, and hypophosphite as reductant)
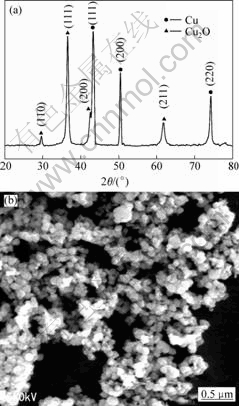
Fig.6 XRD pattern(a) and SEM image(b) of typical sample (Cu2+ 0.2 mol/L, 333 K, 1 h, citric acid as ligand, and hypophosphite as reductant)
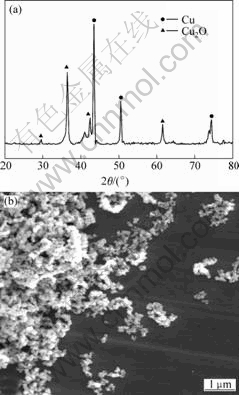
Fig.7 XRD pattern(a) and SEM image(b) of typical sample (Cu2+ 0.2 mol/L, 333 K, 1 h, tartaric acid as ligand, and hypophosphite as reductant)
into oleic acid. In this course, the new generated particles hardly have any chance to contact with the oxygen, therefore, the resultant particles are all metallic copper. While in the case of Figs.4-7, the reaction is followed as Eqn.(3), copper ligands are firstly reduced into copper in aqueous solution and then be extracted into oleic acid. During this course, some new generated copper particles are oxidized due to the presence of a large number of oxygenous water molecules in ambience solution[14-15].
Therefore, it can be deduced that although those complex agents can do good to obtain homogeneous initial reaction solution, and relatively easy to obtain well-defined copper particles, only when ammonia is used as ligand, can metallic copper particles be obtained.
4 Conclusions
1) Well-dispersed and anti-oxidation nano-copper particles with 70 nm in diameter were obtained through the complex-reduction-extraction process. By this process nano-Cu particles, anti-oxidation at the same time are successfully achieved.
2) By using complex agent, ammonia, as copper cation shield, this process realizes to prevent both nucleation and coagulation during the particle growth by shielding the metallic ions. Meanwhile, the copper-ligands liberate metal ions by degrees with the progress of precipitation, which are also relatively easy to meet the requirement for preparing well-defined copper particles.
3) This process adopts oleic acid as surface modification agent, which can not only prevent the copper particles from aggregation, but also can prevent the copper particles form oxidation.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (50404011) and COE program of Department of Material Science and Engineering, Nagoya University, Japan. The authors sincerely thank their foundation support.
References
[1] SHUN Xin-yu, SONG Si-xiu, ZHANG Wei-min, YANG Zhi-lei. A method for the synthesis of spherical copper nanoparticles in the organic phase[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2004, 273(2): 463-469.
[2] SINHA A, SHARMA B P. Preparation of copper powder by glycerol process[J]. 




 Materials Research Bulletin, 2002, (37): 407-416.
Materials Research Bulletin, 2002, (37): 407-416.
[3] ZAO Bin, LIU Zhi-jie, ZHANG Zong-tao. Improvement of oxidation resistance of ultra-fine copper powders by phosphating treatment[J]. 


 Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1997(130):157-160.
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1997(130):157-160.
[4] JIANG Ding. Ultrafine Cu particles prepared by mechanochemical process[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1996(234): L1-L3.
[5] QU Xuan-hui, HUANG Bo-yun, L.Chang-ming. Preparation of atomized Cu powder with low apparent density[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 1995, 26(6): 781-784. (in Chinese)
[6] KAZUSHI S, OKADA Y, MIYOSHI H. Copper powders for electrically conductive paste: U.S. Patent, 6881240[P].
[7] ZAO Xie-bin, DONG Xue-chen. Study on preparation of nanometer copper powder by ultrasonic electrolytic process[J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 25(3): 97-99. (in Chinese)
[8] YANG Jian-guang, OKAMOTO T, ICHINO R, BESSHO T, et al. A simple way for preparing antioxidation nanocopper powders[J]. Chemistry Letters, 2006, 35(6): 648-649.
[9] YANG Jian-guang, OKAMOTO T, ICHINO R, BESSH T. Synthesis of copper monolayer and particles at aqueous-organic interface[J]. Surface Science Letters, 2006, 600(24): L318-L320.
[10] OKAMOTO T, YANG Jian-guang, ICHINO R, BESSHO T. Preparation of size and aggregation controlled nickel oxalate dehydrate particles from nickel hydroxide[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2007, 15/17: 581-586.
[11] FUJIMORI Y, GOTOH Y, TAMAKI N, OHKOSHI Y, NAGURA M. Introduction of copper iodide fine particles into a poly(acrylic acid) matrix via a complex of polymer–polyiodide ions[J]. J Mater Chem, 2005, 15 (45): 4816-4822.
[12] SAWANT P, KOVALEV E, KLUG J T, EFRIMA S. Alkyl xanthates: New capping agents for metal colloids. capping of platinum nanoparticles[J]. Langmuir, 2001, 17(10): 2913-2917.
[13] SUDHIR K, PALIT D K, TULSI M. Preparation, characterization and surface modification of Cu metal nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2002(5): 383-387.
[14] SUI Z M, CHEN X , WANG L Y, XU L M, ZHUANG W C, CHAI Y C, YANG C J. Capping effect of CTAB on positively charged Ag nanoparticles[J]. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures , 2006(8): 308-314.
[15] CHEN Si-hai, KEISAKU K. Synthesis and characterization of carboxylate-modified gold nanoparticle powders dispersible in water[J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15(4): 1075-1082.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Projects(50404011) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: YANG Jian-guang; E-mail: jianguang_y@163.com