Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 323-328
Effect of surface diffusion alloying on erosion wear property of ZM5 magnesium alloy
You-ping MA, Xiu-lan LI, Lei YANG, Xi-peng HE
School of Metallurgical Engineering, Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology, Xi’an 710055, China
Received 6 September 2011; accepted 25 November 2012
Abstract: Specimens of ZM5 magnesium alloy were dipped into the mixed powder of Al and Zn at (390±5) °C for 8 h in argon gas protective environment and subjected to surface diffusion alloying processing (SDAP). The erosion wear behaviors of ZM5 magnesium alloy before and after SDAP were investigated in two different erosion wear environments: oil and quartz environment; tap water and quartz environment. The surfaces of erosion wear specimens exhibited cutting scratch grooves in the oil and quartz environment. Corrosive attack was weak and cutting wear mechanism was responsible for the mass loss. When the erosion wear medium was changed to tap water and quartz environment, corrosion pits and cracks were obviously observed after erosion wear test. The corrosion from tap water and the scour from quartz intensified mass losses. Compared with the untreated specimens, the application of SDAP improved the erosion wear resistance in the same environment.
Key words: magnesium alloy; ZM5 alloy; erosion; wear; surface diffusion alloying
1 Introduction
Due to their low density (1.74×10-3 kg/m3) and high specific strength, magnesium and its alloys have drawn much attention as a structural material, especially in the aircraft industry, vehicle production and portable electric devices [1]. Unfortunately, they are highly susceptible to corrosion, which greatly limits their further applications [2,3]. In practical applications, surface treatments are frequently applied to improving the corrosion and wear resistance of magnesium alloys. There are a number of possible coating technologies available for magnesium alloy, such as sol-gel technology [4,5], chemical conversion [6-8], polymer plating [9], anodizing [10], hydride coatings [11], laser treatment [12], nano- technology [13]. However, each has its own advantages and disadvantages [14,15]. For example, laser surface alloying is expensive. Chemical conversion, anodization and sol-gel technology involve a lot of environmental problems, and an organic coating normally needs a chemical conversion or anodized coating to prime the substrate firstly. Moreover, apart from the corrosion resistance, wear resistance and electrical conductivity are also important in some applications. From a practical point of view, an ideal surface treatment is expected to meet all these demands.
Surface diffusion alloying processing (SDAP) technique has many advantages [16]. The alloy layer prepared by diffusion had ideal thickness and good bond strength with the substrate, and the corrosion wear resistance performance was improved without sacrificing magnesium alloy own excellence. To date, there has been only relatively small amount of reported work concerning solid diffusion alloying of magnesium alloy. The micro-hardness near alloy surface has been well investigated, but the improvement of corrosion resistance was not mentioned [17].
In the present study, Mg-Al-Zn intermetallic compounds are formed on the surface of ZM5 magnesium alloy by surface diffusion alloying at (390±5) °C for 8 h in argon gas environment, which improves the corrosion wear resistance of magnesium alloys. The purpose of the present work is to explore the erosion wear characteristic of magnesium alloy before and after SDAP in different erosion slurry conditions.
2 Experimental
2.1 Surface diffusion treatment
ZM5 magnesium alloy was used as substrate in this study. The composition of the alloy is given in Table 1.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of ZM5 magnesium alloy (mass fraction, %)

Specimens of ZM5 magnesium alloy were dipped into the mixed powder of Al and Zn with the mass ratio of aluminum powder (purity 99.8%, size 45 μm) to zinc powder (purity 96.8%, size 45 μm) being 1:1. An 8 kW electric resistance furnace which could automatically control temperature was employed to heat the specimens at (390±5) °C for 8 h. During the process, the protective Ar gas was used to protect specimens from oxidation.
2.2 Testing method
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to study the cross-sectional characteristic of the alloy coatings and erosion-corrosion surface morphologies of the treated and untreated specimens after erosion wear test. The phase constituents of the alloy coatings were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) (D/max 2200PC). Micro-hardness of the coatings was measured by an MH-5 micro-hardness tester.
The simultaneous erosion wear tests were carried out on the untreated and treated specimens. In order to compare the corrosion and wear behaviors with and without corrosion medium, the media 1 (oil and quartz) and 2 (tap water and quartz) were selected for the slurry. The mass ratio of quartz (size 212-380 μm) and oil (5W30 machine oil) or tap water was 4:3. Figure 1 illustrates schematically the erosion wear testing device. In the erosion wear test, the specimens with the dimensions of 12 mm×12 mm×10 mm were embedded into a chucking, only the test surface was exposed to the slurry and the other surfaces were sealed with resin. The specimens were rotated for 15 h at 250 r/min in the medium 1 or 2.

Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of erosion-abrasion facility
Specimens were weighed before and after erosion wear test by TG328B electronic balance with a precision of 0.0001 g. The mass loss (△m) was the average of three repeated operations on each specimen. The erosion wear resistance effects of the treated and untreated specimens were evaluated by the wear resistance (β). β is described as follows: β=△m-1. It can be seen that the less the mass loss (△m) of the test material, the better the wear resistance (β).
3 Results
3.1 Microstructure of alloy coating
Figure 2 shows SEM image of cross-section of ZM5 magnesium alloy after SDAP. As can be seen from Fig. 2, the typical microstructure of the treated specimen was composed of ZM5 substrate (grey zone), transition zone and Mg-Al-Zn intermetallic compounds (white-bright zone). The transition zone referred to high solubility Al and Zn in the ZM5 substrate. The compositional results by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis (Fig. 3) indicated that the alloy coating (white-bright zone) mainly consisted of Mg-Al-Zn intermetallic compounds which are Al5Mg11Zn4 and Al6Mg10Zn.

Fig. 2 SEM image of cross section on treated specimen
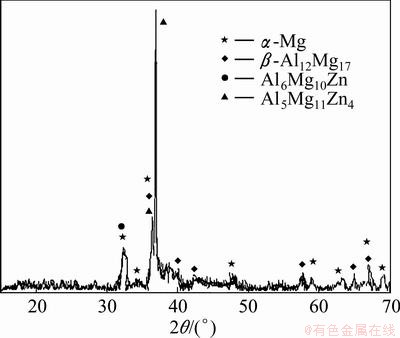
Fig. 3 XRD pattern of treated specimen
The formation of the alloy coating contained the following steps: aluminum and zinc deposition led to Al and Zn atoms diffusion into the ZM5 substrate. At the beginning, Al and Zn atoms were solid solution in ZM5 substrate in the form of substitutional solid solution because of the approximate atom radius (Al: 0.143 nm; Zn: 0.139 nm; Mg: 0.160 nm). Once aluminum and zinc concentration exceeded the maximum solid solubility in ZM5 substrate, aluminum and zinc would react with magnesium on the surface to form Mg-Al-Zn intermetallic compounds. The processes of diffusion, solid solution, and solid solution reaction to form Mg-Al-Zn intermetallics compounds were continuous during SDAP. The continuous Mg-Al-Zn intermetallics compounds were crucial for the erosion wear resistance. At the given experimental conditions, the thickness of diffusion alloying layer was uneven but continuous, the thickness range was 35-75 μm, and its average thickness was about 50 μm.
3.2 Micro-hardness
The average value of five measurements on each specimen was taken as micro-hardness values, as shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that the average micro-hardness (HV 172) of the alloy coating was far more than that of the substrate (HV 82). This was attributed to the presence of Al5Mg11Zn4 and Al6Mg10Zn intermetallic compounds (Figs. 2 and 3).
Table 2 Micro-hardness of different areas of diffusion layer

3.3 Results of simulated erosion test
The mass loss (△m) and the wear resistance (β) of the specimens after the erosion wear test are shown in Table 3. It can be seen that the wear resistance (β) of the treated specimen was 1.4 times that of untreated specimen in medium 1 (oil and quartz). When the medium was tap water and quartz, the erosion resistance of the treated specimen was greatly increased, and it was about 2.8 times more than that of the untreated specimen. In general, the treated specimen always exhibited the better wear resistance in the two different media, but the mass loss in medium 2 was always higher than that in medium 1. It was indicated that the tap water intensified the mass loss.
Table 3 Mass losses and wear resistance β of specimens
3.4 Surface characteristics of erosion wear
Figures 4 and 5 show the SEM micrographs of the treated and untreated specimens after erosion wear test in media 1 and 2, respectively. It can be observed that the surface of the treated specimen only showed short cutting scratch grooves and it was hard to find the corrosion trace when tested in medium 1. However, the surface of the untreated specimen (Fig. 4(b)) was characterized by deep and big cutting scratch grooves, and the impact pits were obviously found. In medium 2, there were only a few small pits and cracks on the treated surface, but the pitting areas were still small. As for the untreated specimen, long transverse cracks with strong directivity were observed on the surface. Moreover, small cracks finally enlarged and connected with big cracks (Fig. 5(b)).

Fig. 4 SEM micrographs of treated (a) and untreated (b) specimens after erosion wear test in medium 1
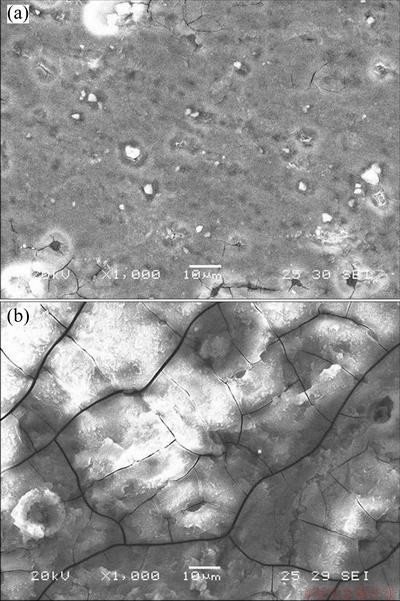
Fig. 5 SEM micrographs of treated (a) and untreated (b) specimens after erosion wear test in medium 2
4 Discussion
4.1 Corrosion processing
The thickness of alloy coating and the adhesion of coating to the substrate were two important factors affecting the erosion resistance. The thickness of the coating was not uniform (Fig. 2). It was thick in some areas but very thin in other areas (Fig. 2). Due to the imperfect combination of Al-Zn powder and the ZM5 substrate in some local areas, there were possibly some pinholes. Pitting corrosion preferentially initiated at these defects (pinholes and very thin areas) in the coating. If some pinholes were initially formed in some local areas, the alloy coatings adjacent to these defects acted as cathode and the exposed ZM5 substrate was severely corroded due to the galvanic effect between them [18].
It was suggested that the corrosion resistance of alloy layer and transition layer (Figs. 2) was close to that of the untreated ZM5 magnesium alloy at the initial stage [19]. However, once the Mg-Al-Zn intermetallic compounds were entirely exposed to the medium, the Mg-Al-Zn intermetallics compounds acted as a corrosion barrier for protecting the substrates from contacting the corrosive media, which significantly reduced the corrosion rate. Some authors [20,21] reported that the corrosion resistance of Mg-Al-Zn intermetallic compounds was better than that of α-Mg or Mg-Al intermetallic compounds, so the treated specimens exhibited better corrosion resistance.
In addition, the existence of Al5Mg11Zn4 and Al6Mg10Zn intermetallic compounds increased the micro-hardness (Table 2), which was helpful to the improvement of wear resistance. So the wear resistance of the treated specimens was all higher than that of the untreated specimens both in media 1 and 2.
4.2 Erosion wear difference in two media
By carefully examining these photos (Figs. 4 and 5), the surface morphology of the specimen in medium 1 (oil and quartz) was better than that in medium 2 (tap water and quartz) after erosion wear test. The wear mass loss in medium 1 was less than that in medium 2 (Table 3). Under the experiment conditions, the treated and untreated specimens were all under the same erosion wear conditions except for the medium solutions. So the variation of surface morphology and change of wear mass losses were attributed to the effects of different medium solutions. In medium 1 (oil and quartz), it was hard to find the corrosion trace. This indicated that the mass loss was mainly caused by the cutting of quartz sand rather than by corrosion. According to Ref. [22], magnesium and magnesium alloy steadily existed in methylether, aether, ethanol, petroleum, gasoline and so on. Therefore, the oil in medium 1 has no contribution to corrosion, but pure cutting scratch mechanism was responsible for the mass loss of erosion wear. It was well known that when the cutting wear mechanism predominated the wear process, the increase of micro-hardness of alloy coating was beneficial for the improvement of erosion wear resistance. The micro- hardness of the alloy coating in treated specimen reached up to HV 172, which was higher than that of the untreated specimen (HV 82). So, the wear resistance was remarkably enhanced with increasing micro-hardness after DAP. In medium 2, tap water greatly aggravated the corrosion, so the mass loss and corrosion degree of the treated and untreated specimens were higher than those in medium 1.
Magnesium was very reactive in water environments, exhibiting a very high anodic standard electrode potential of around -2.36 V [23]. Magnesium dissolution in aqueous environments proceeded an electrochemical reaction with water to produce magnesium hydroxide. In neutral H2O solution, two oxidation/reduction reactions can be expected, which can been given by the following equations:
2Mg+O2+2H2O→2Mg(OH)2 (1)
Oxidation: Mg→Mg2++2e (2)
Reduction: O2+2H2O+4e→4OH- (3)
Mg+2H2O→Mg(OH)2+H2↑ (4)
Oxidation: Mg→Mg2++2e (5)
Reduction: 2H2O+2e→H2+2OH- (6)
According to Ref. [24], the Mg(OH)2 film was supposed to form spontaneously. Eqs. (1)-(3) and (4)-(6) would likely occur equally when magnesium was placed in water exposed to the atmosphere. The presence of oxygen influenced the reaction, keeping the solution at a neutral pH. As one can see from Eqs. (1) and (4), hydrogen gas and magnesium hydroxide formed on the specimens surface. Magnesium hydroxide can protect the matrix from corrosion. However, in the given dynamic continuously stirring environment, a uniform film of Mg(OH)2 was prone to fall off, regenerated by the presence of oxygen, further fall off, and so on. Moreover, dynamic continuously stirring promoted the H2 escaping from H2O, thus, the corrosion rate was greatly accelerated. The corrosion mechanism was the main mechanism of degradation for such alloy.
The volume change between Mg(OH)2 film and matrix brought about stress [25]. The combined effects of corrosion stress and quartz scour wear encouraged the presence of surface cracks. Compared with the untreated specimen (Fig. 5(b)), the cracks of the treated specimen were less and smaller due to the presence of Al5Mg11Zn4 and Al6Mg10Zn intermetallic compounds coatings. continuous intermetallic compounds effectively protected alloy from corrosion. It was believed that Al5Mg11Zn4 and Al6Mg10Zn intermetallic compounds had a critical role in determining corrosion resistance.
5 Conclusions
By SDAP, the micro-hardness value of the diffusion alloying layer was much higher than that of the ZM5 substrate, which was favorable to the improvement of wear resistance. The specimens after SDAP always exhibited the better erosion wear resistance in two different medium environments. This was attributed to the presence of Mg-Al-Zn intermetallic compounds in the alloying layers, which acted as corrosion barrier for protecting the substrate. In medium 1 (oil and quartz), oil had little contribution to corrosion, but the degradation of such alloy was predominated by the cutting wear mechanism. In medium 2 (water and quartz), cracks and pits were formed on the specimens surface, and the combined effects of corrosion from water and wear from quartz aggravated mass losses. The corrosion mechanism was dominant for the erosion wear process.
References
[1] AVEDESIAN M M, BAKER H. ASM specialty handbook: Magnesium and magnesium alloys [M]. New York: ASM International, 1999: 78.
[2] ZHANG Rong-chang, ZHANG Jin, HUANG Wei-jiu. Review of studies on corrosion of magnesium alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(2): 763-771.
[3] WANG Lei, SHINOHARA T, ZHANG Bo-ping. Characterization of surface products on AZ31 magnesium alloy in dilute NaCl solution [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 485(2): 747-752.
[4] JOHANSEN C G, HUANG H C, LU T M. Diffusion and formation energies of adatoms and vacancies on magnesium surfaces [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2009, 47(1): 121-127.
[5] ZHANG Shi-yan, LI Qing, CHEN Bo, YANG Xiao-kui. Preparation and corrosion resistance studies of nanometric sol-gel-based CeO2 film with a chromium-free pretreatment on AZ91D magnesium alloy [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 155(3): 870-877.
[6] MD. BHUIYAN S, OSTUKA Y, MUTOH Y, MURAI T, IWAKAMI S. Corrosion fatigue behavior of conversion coated AZ61 magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(18): 4978-4984.
[7] JIN Hua-lan, YANG Xiang-jie, WANG Ming. Chemical conversion coating on AZ31B magnesium alloy and its corrosion tendency [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 22(1): 65-70.
[8] XU S Q, LI Q, LU Y H, CHEN B, FAN J M. Preparation and characterisation of composite double phosphate conversion coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloy [J]. Surface Engineering, 2010, 26(5): 328-333.
[9] KANG Zhi-xin, SANG Jing, SHAO Ming, LI Yuan-yuan. Polymer plating on AZ31 magnesium alloy surface and film evaluation of corrosion property [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(9): 4590-4594.
[10] ARDELEAN H, FRATEUR I, ZANNA S, ATRENS A, ARCUS P. Corrosion protection of AZ91 magnesium alloy by anodizing in niobium and zirconium-containing electrolytes [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(12): 3030-3038.
[11] da CONCEICAO T F, SCHARNAGL N, BLAWER C. Surface modification of magnesium alloy AZ31 by hydrofluoric acid treatment and its effect on the corrosion behaviour [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518(18): 5209-5218.
[12] Wang H M, Chen Z H, Li L L. Corrosion resistance and microstructure characteristics of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings formed on AZ31 magnesium alloy [J]. Surface Engineering, 2010, 26(5): 385-391.
[13] FEIL F,  M. Nanoparticle based inorganic coatings for corrosion protection of magnesium alloys [J]. Surface Engineering, 2008, 24(3): 198-203.
M. Nanoparticle based inorganic coatings for corrosion protection of magnesium alloys [J]. Surface Engineering, 2008, 24(3): 198-203.
[14] RUDD A L, BRESLIN C B. The corrosion protection afforded by rare earth conversion coatings applied to magnesium [J]. Corrosion Science, 2000, 42(2): 275-288.
[15] TRUONG V T, LAI P K, MOORE B T. Corrosion protection of magnesium by electroactive polypyrrole/paint coatings [J]. Synthetic Metals, 2000, 110(1): 7-15.
[16] SUN H Q, Shi Y N, Zhang M X. Surface alloying of an Mg alloy subjected to surface mechanical attrition treatment [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2008, 202(16): 3947-3953.
[17] SHIGEMATSU I, NAKAMURA M, SIATOU N. Surface treatment of AZ91D magnesium alloy by aluminum diffusion coating [J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2000, 19(6): 473-475.
[18] ZHU Li-qun, SONG Guang-ling. Improved corrosion resistance of AZ91D magnesium alloy by an aluminium-alloyed coating [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2006, 200(8): 2834-2840.
[19] MA You-ping, XU Ke-wei, WEN Wei-xin. The effect of solid diffusion surface alloying on properties of ZM5 magnesium alloy [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2005, 190(3): 165-170.
[20] MAZURKIEWICZ B. The electrochemical behaviour of the Al8Mg5 intermetallic compound [J]. Corrosion Science, 1983, 23(7): 687-692.
[21] BOURGOIS L, MUDDLE B C, NIE J F. The crystal structure of the equilibrium Φ phase in Mg–Zn–Al casting alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(14): 2701-2711.
[22] WU Zhen-ning, LI Pei-jie. Present state of research on corrosion of magnesium alloys [J]. Foundry, 2001, 50(10): 583-586. (in Chinese)
[23] FONTANA M G. Corrosion principles [M]//FONTANA M G. Corrosion engineering. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 1986.
[24] YANG Li-jing, WEI Ying-hui, HOU Li-feng. Corrosion behaviour of die-cast AZ91D magnesium alloy in aqueous sulphate solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(2): 345-351.
[25] GUO Jia, YANG Shan-wu, SHANG Cheng-jia. Influence of carbon content and microstructure on corrosion behaviour of low alloy steels in a Cl-containing environment [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(2): 242-251.
表面扩散合金化对ZM5镁合金冲蚀磨损性能的影响
马幼平,李秀兰,杨 蕾,贺西鹏
西安建筑科技大学 冶金工程学院,西安 710055
摘 要:将ZM5镁合金置入铝、锌混合粉末中,在氩气保护下,于温度(390±5) °C保温8 h进行表面固态扩渗合金化处理。研究表面固态扩渗合金化处理前和处理后ZM5镁合金在两种不同冲蚀磨损环境中(油和石英砂,水和石英砂)的冲蚀磨损行为。结果表明:当冲蚀磨损介质为油和石英砂时,冲蚀磨损表面形貌为切削沟痕。油对试样的腐蚀很弱,切削磨损是主要的磨损机制。当冲蚀介质为水和石英砂时,冲蚀磨损试样表面为腐蚀坑和裂纹。水的腐蚀和石英砂的冲刷作用加剧试样的磨损质量损失。在相同的冲蚀介质中,经过表面固态扩渗合金化处理的试样的耐冲蚀磨损性能均比未经过表面固态扩渗合金化处理的试样好。
关键词:镁合金;ZM5合金;冲蚀;磨损;表面扩渗合金化
(Edited by Sai-qian YUAN)
Foundation item: Project (2011JY009) supported by Education Department of Shaanxi Province, China
Corresponding author: You-ping MA; Tel: +86-29-82202923; E-mail: youpingma615@yahoo.com.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62464-4