J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2007)02-0170-06
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-007-0034-z 
Bio-decomposition of rock phosphate containing pyrites
by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
CHI Ru-an(池汝安), XIAO Chun-qiao(肖春桥), HUANG Xiao-hui(黄晓慧),
WANG Cun-wen(王存文), WU Yuan-xin(吴元欣)
(Hubei Key Laboratory of Novel Chemical Reactor and Green Chemical Technology, Wuhan Institute of Technology,
Wuhan 430073, China)、
Abstract: Leaching soluble phosphorus from rock phosphate containing pyrites by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (A. f.) is feasible, and the reaction mechanism is as follows. Pyrites are oxidized by A. f. to produce H2SO4 and FeSO4; the rock phosphate is decomposed by H2SO4, forming soluble phosphorus compounds; and Fe2+ from FeSO4 is oxidized to Fe3+, providing energy for the growth of A. f.. In this process, as H2SO4 is produced in the reaction, an acidic condition in the culture medium is formed, which benefits the growth of A. f. and aids both continuous oxidation of pyrites and leaching of soluble phosphorus from rock phosphate. The fraction of phosphorous leached can reach the largest in the presence of 1.0 g/L Fe3+, 200 mg/L Mg2+ and 400 mg/L NH4+. The optimal technological parameters on the fraction of phosphorous leached are as follows: the volume fraction of inocula of A. f., the mass ratio of pyrites to rock phosphate and the pH value are in ranges of 5%-25%, 3?1- 5?1 and 1.8- 2.2, respectively.
Key words: bio-decomposition; rock phosphate; pyrites; Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
1 Introduction
Phosphorus(P), which is one of the essential elements for the growth of organism, largely exists in rock phosphate and other primary mineral resources formed in different geological ages. Their raw ores may be suitable to make chemical phosphoric fertilizer[1-3].
The bioleaching of ores has been widely developed recently, and is successfully applied to copper ores, uranium ores and so on[4]. The bioleaching of phosphate ores by microorganism has been reported little yet currently, although several reports have indicated that some microorganisms, such as bacteria[5], fungi[6], and cyanobacteria[7-8] are capable of solubilizing insoluble inorganic phosphate compounds, like calcium phosphate, dicalcium phosphate, hydroxyapatite, and rock phosphate[9-10]. Since these microorganisms are heterotrophic, it is generally accepted that the major mechanism of phosphate ore leaching is the action of organic acids synthesized by the solubilization of organic carbon sources of soil microorganisms[1, 11-12]. The pH in culture medium only ranges from 4.0 to 5.0 during the leaching process, thus phosphorus leaching is at a low rate[13]. In addition, the strict culture condition of these microorganisms and expensive culture medium also restrain seriously the application of this technology on leaching of phosphorus.
The bacterium, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (A. f.), which was found and nominated by TEMPLE et al[14] is commonly applied in bioleaching and bio-beneficiation of sulfide minerals. The growth energy of A. f. is obtained from chemical reactions, oxidizing minerals or inorganic solutes such as S0 and FeS2 rather than organic carbon compounds, and simultaneously producing inorganic acids such as H2SO4. It is well known for its ability to oxidize Fe2+ to Fe3+ in an acidic solution[15]. Being an autotrophy, it utilizes atmospheric CO2 as its sole carbon source[16]. The process of CO2 fixation is reported to be a function of Mg2+ concentration in the nutrient medium[17], and NH4+ is the most appropriate source of nitrogen. The reaction mechanism of leaching soluble phosphorus from phosphate ore by A. f. containing pyrites is discussed in the present study. The effects of the concentration of Fe3+, Mg2+ and NH4+ on the fraction of phosphorous leached are also assessed. In addition, some optimal technological parameters for culturing microorganisms that were applied to efficiently bioleach phosphorus from phosphate ore containing pyrites by A. f. are also suggested.
2 Experimental
2. 1 Materials and methods
2.1.1 Strain and rock phosphate
The strain of A. f. was kindly supplied by Central South University(Changsha, China). Rock phosphate (mostly calcium phosphate of particle size about 0.07-0.10 mm) was from Baokang phosphorite (Hubei, China), with CaO and P2O5 contents of 49.8% and 27.5%, respectively. The pyrites was from Daye iron ore (Hubei, China) and the content of S in the pyrites (particle size about 0.07-0.01 mm) was 48%.
2.1.2 Culture medium
A. f. was grown in a modified 9K medium: 3 g/L (NH4)2SO4, 0.5 g/L MgSO4?7H2O, 0.5 g/L K2HPO4, 0.1 g/L KCl, 0.01 g/L Ca (NO3)2 and 44.2 g/L FeSO4?7H2O. pH value was adjusted to 2.5 with about 50% H2SO4.
2.2 Activation of A. f.
A 10% A. f. cell was inoculated into 90 mL of 9 K medium in a rotary shaker at 160 r/min at 30 ℃. The culture was transferred several times by gradually reducing the volume of inocula in the same way. The active cells were harvested from the culture medium at the beginning of the stationary phase of their growth. The solution containing the cells was filtered through biological filter paper and washed twice with dilute sulfuric acid (pH=2.5).
2.3 Bio-leaching of rock phosphate
A proper volume of inocula of active A. f. cells was inoculated into 30 mL of 9K medium in a 100 mL flask containing some rock phosphates and pyrites in a rotary shaker at 160 r/min.
2.4 Analytical methods
The medium was centrifuged at 9 000 r/min for 15 min. The supernatant was collected and the content of P2O5 was determined by using phosphomolybate method on a UV-VIS 8500 spectrophotometer at 420 nm. The pH was examined by pH machine (DELTA 320). The concentration of Fe2+ was determined by colorimetric method[18]. The concentration of Fe3+ was determined using phenanthroline method with a UV-VIS 8500 spectrophotometer at 510 nm[19].
3 Results
3.1 Suggestion of reaction mechanism
Based on the method described above, equal volume culture medium in five flasks was inoculated with 10% inocula containing A. f., respectively. The quantity of A. f., the fraction of phosphorous leached, pH value and the concentration of Fe2+ and Fe3+ at different culture time were examined, respectively. The experiment was repeated three times and the observations were recorded.
The effects of culture time on the concentration of Fe2+ and Fe3+ are shown in Fig.1. It could be seen that the concentration of Fe2+ decreases, and that of Fe3+ increases, with the culture time increasing. In the initial 12 h inoculation, the concentration of Fe2+ hardly changes. The reason is that there is an adaptive process when the A. f. is transferred to a novel condition, and the growth of it is in inducement phase. Then the A. f. gradually adapts to the novel condition, and begins to enter the growth phase slowly. Fe2+ is gradually oxidized, and the concentration of it begins to decrease. When being cultured more than 84 h, Fe2+ is fully oxidized, and the growth of the A. f. keeps stable. The concentration of Fe3+ increases with the culture time increasing, but when being cultured more than 84 h, it hardly increases.
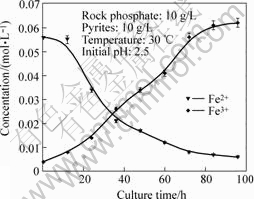
Fig.1 Effect of culture time on concentration of Fe2+ and Fe3+
The counts of A. f. on microscope in the culture medium show that, when the A. f. transforms from inducement phase to steady growth phase, the quantity of A. f. rises from 106/mL to 109 /mL (Fig.2). The result is similar to that observed in 9K medium by SILVERMAN et al[20].

Fig.2 Effect of culture time on quantity of A. f.
As can be seen from Fig.3, the fraction of phosphorous leached is different at different culture time. With increasing culture time, the fraction of phosphorous leached increases rapidly. But when being cultured over 84 h, the fraction of phosphorous leached hardly increases. Fig.3 also shows that, the pH gradually decreases during the culture process, and it decreases to 1.8 when the growth of A. f. is stable, as A. f. is a kind of bacterium that can produce acid in the culture medium. Along with the process of bio-leaching and A. f. growing, the concentration of H+ and Fe3+ increases continuously, thus causing the decreasing of pH.

Fig.3 Effect of culture time on fraction of phosphorous leached and pH
A. f. can oxidize pyrites to form H2SO4 and FeSO4 when water and the atmosphere are present, and Fe2+ is further oxidized to Fe3+. Under the action of A. f., Fe3+ can oxidize pyrites to sulfur, and then the sulfur can also be oxidized to H2SO4. Finally, the pyrites are oxidized to H2SO4 and FeSO4 that act as a solvent and energy source for the bio-leaching process. The reactions are as follows:
2FeS2+7O2+2H2O→2H2SO4+2FeSO4 (1)
2H2SO4+4FeSO4+O2→2Fe2(SO4)3+2H2O (2)
FeS2+Fe2(SO4)3→3FeSO4+2S (3)
2S+3O2+2H2O→2H2SO4 (4)
3H2SO4+Ca3(PO4)2→3CaSO4+2H3PO4 (5)
The reactions above include direct and indirect actions of A. f. on bio-oxidation of pyrites. The indirect action of A. f. indicates that H2SO4 and Fe2(SO4)3 produced in direct action take part in the bio-oxidation of pyrites. Therefore, the reaction mechanism of the leaching phosphorus from the rock phosphate in the culture medium containing pyrites by the bio-oxidation of A. f. is as follows: pyrites are oxidized by A. f. to produce H2SO4 and FeSO4; the rock phosphate is dissolved by H2SO4, forming soluble phosphorus compounds; and Fe2+ from the FeSO4 is oxidized to Fe3+, producing energy for the growth of A. f.. In this process, as H2SO4 is produced in the reaction, an acidic condition is formed in the culture medium, which benefits the growth of A. f., aiding the continuous oxidation of pyrites and the leaching of the phosphorus from the rock phosphate.
3.2 Effect of Fe3+ on fraction of phosphorous leached
A set of four different flasks were arranged with each containing equal volume of culture medium and fixed volume of inocula containing A. f.. Each flask was supplemented with a different dosages of ferric sulphate so as to obtain Fe3+ with a concentration range from 0.1 to 1.5 g/L. A flask containing the same amount of medium and inocula but lack of Fe3+ was kept at experimental control. Samples were drawn from the flasks at fixed intervals and analyzed for the fraction of phosphorous leached.
The effect of Fe3+ on the fraction of phosphorous leached is presented in Fig.4. It could be seen that the higher the concentration of Fe3+, the lower the fraction of phosphorous leached, indicating that the excessive Fe3+ can inhibit the leaching process of phosphorus. When the concentration of Fe3+ varies from 0 to 1.0 g/L, there is no substantial difference in the time required for bio-oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+ and subsequent increase in the fraction of phosphorous leached. But when the concentration of Fe3+ is up to 1.5 g/L, the fraction of phosphorous leached is obviously lower than that of Fe3+varing from 0 to 1.0 g/L. The ferrous oxidation kinetics by A. f. in the presence of Fe3+ was proposed in Ref.[21]. A trend of competitive inhibition by Fe3+ at ferrous sulphate concentration of 1 109 mg/L was also reported, which was similar to this work. It also can be seen from Fig.4 that, with increasing culture time, the fraction of phosphorous leached increases rapidly. However, when the culture time is over 5 d, the fraction of phosphorous leached begins to decrease slightly.
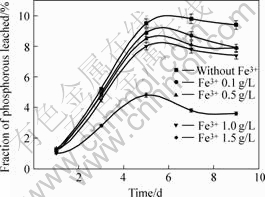
Fig.4 Effect of Fe3+ on fraction of phosphorous leached
3.3 Effect of the presence of Mg2+ on fraction of phosphorous leached
A set of five flasks, each containing the same volume of the culture medium, was inoculated with a fixed volume of inocula containing A. f.. These flasks were supplemented with varying concentration of magnesium sulphate to give Mg2+ concentration ranging from 5 to 200 mg/L. Samples were drawn from the flasks and analyzed for the fraction of phosphorous leached at fixed intervals.
Mg2+ is essential for the bio-oxidation of Fe2+ using A. f., and the dosage of magnesium sulphate required for an efficient oxidation process to take place is essential to the fraction of phosphorous leached. The effect of Mg2+ concentration on the fraction of phosphorous leached is shown in Fig.5. It appears that the higher the concentration of Mg2+, the higher the fraction of phosphorous leached. It can also be seen from Fig.5 that, with increasing culture time, the fraction of phosphorous leached increases gradually. But when being cultured over 5 d, the fraction of phosphorous leached hardly increases.
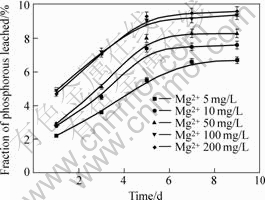
Fig.5 Effect of Mg2+ on fraction of phosphorous leached
3.4 Effect of the presence of NH4+ on fraction of phosphorous leached
A set of five flasks, each containing the same volume of culture medium, was inoculated with a fixed volume of inocula containing A. f.. These flasks were supplemented with varying concentrations of (NH4)2SO4 to give an NH4+ concentration ranging from 200 to 600 mg/L. Samples were drawn from the flasks and analyzed for the fraction of phosphorous leached at fixed intervals.
NH4+ is the most appropriate source of nitrogen. (NH4)2SO4 is thus added to 9K culture medium in the initial period of oxidizing pyrite with A. f., promoting the growth and multiplication of A. f., lessening the staying time and thereby accelerating the oxidization of pyrite. The effect of NH4+ concentration on the fraction of phosphorous leached is shown in Fig.6. It indicates that the fraction increases with increasing the concentration of NH4+ in a certain range of 200-600 mg/L. However, excessive NH4+ would restrict the bio-leaching of phosphorous by producing some sediment. In order to restrain the precipitating of complex and improve leaching efficiency without influencing the activity of A. f., the concentration of NH4+ needs to be maintained at approximately 400 mg/L, correspondingly 1.0 g/L (NH4)2SO4. It can also be seen from Fig.6 that, with increasing culture time, the fraction of phosphorous leached increases gradually. But when the culture time is over 5 d, the fraction of phosphorous leached begins to decrease.
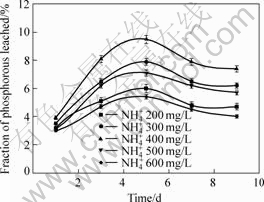
Fig.6 Effect of NH4+ on fraction of phosphorous leached
3.5 Assessment of some optimal technological parameters on fraction of phosphorous leached
Based on the method described above, equal volume culture media in five flasks were inoculated with A. f. cells. The effects of inocula volume of A. f., the mass ratio of pyrites to rock phosphate and the culture pH on the fraction of phosphorous leached were examined, respectively. The fraction of phosphorous leached in each flask was checked 4 d later. Samples were drawn from these flasks at fixed intervals and the fraction of phosphorous leached was analyzed. The results are shown in Figs.7, 8 and 9.
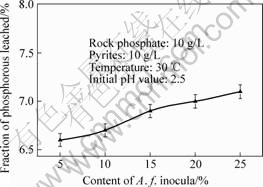
Fig.7 Effect of content of A. f. on fraction of phosphorous leached
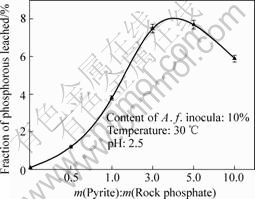
Fig.8 Effect of mass ratio of pyrite to rock phosphate dosage on fraction of phosphorous leached

Fig.9 Effect of pH on fraction of phosphorous leached
As can be seen from Fig.7, the fraction of phosphorus leached increases from 6.6% to 7.1% gradually with the content of inocula of A. f. increasing from 5% to 25%, but the change is not obvious.
Fig.8 shows that, the fraction of phosphorous leached increases gradually with raising the mass ratio of pyrites to rock phosphate, indicating that abundant pyrites can supply enough energy for A. f. and produce H2SO4 to transform rock phosphate to soluble phosphorus. However, when the mass ratio of pyrites to rock phosphate exceeds 5?1, the fraction of phosphorous leached begins to decrease; when the mass ratio of pyrites to rock phosphate is 10?1, it is as low as 5.9%, implying that excessive pyrites may inhibit the contact of the rock phosphate and the solvent, thus the leaching process would be restricted. Furthermore, it can be seen that the optimal mass ratio of pyrites to rock phosphate is from 3?1 to 5?1. Accordingly the fraction of phosphorous leached is from 7.5% to 7.7%.
The effect of pH on the fraction of phosphorous leached is presented in Fig.9. The results indicate that the fraction of phosphorous leached remains constant from 7.2% to 7.5% in the pH range from 1.8 to 2.2. However, the fraction of phosphorous leached varies once the pH value exceeds the range above. A. f. has been reported to grow in pH range from 1.4 to 3.0 utilizing the energy from oxidation of Fe2+[22]. There is transference movement of H+ and electron in the bio-oxidation of Fe2+, the change of pH value has great influence on the bio-oxidation of Fe2+. If pH value is unsuitable, the metabolism balance in cells of A. f. would be destroyed,
and the activity of A. f. would be inhibited. Considering that it will produce acid in the growth of A. f., the acid degree in the culture medium should be adequate, and then the change of pH will not retard the growth of A. f..
4 Discussion
In the process of culture, the bio-oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+ is presented with the growth of A. f. in 9K culture medium, and the color of the culture medium also changes obviously, namely from clear to buff and brown finally. A. f. promotes the formation of the over layer through the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+, which is released to solution and precipitated with PO43- from the medium. It is also observed that there is a yellow precipitation in the wall as well as at the bottom of the flask.
A. f. can oxidize pyrites to form H2SO4 and FeSO4 water and atmosphere are present, and Fe2+ is further oxidized to Fe3+. Under the action of A. f., the pyrites can be oxidized to sulfur and the sulfur then can also be oxidized to H2SO4. Finally, the pyrites are oxidized to H2SO4 and FeSO4, acting as a solvent and energy source for the bioleaching process.
The chemo-biochemical process for the desul- phurization of pyrites requires ferric sulphate as an oxidant for oxidation of pyrites. The second stage of the process is a biochemical process where A. f. is used as a bio-catalyst for bio-oxidation of ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate for recycle and reuse in the process. Thus, the ferrous sulphate solution contains Fe3+ when the complete ferric sulphate is not utilized for the oxidation of pyrites. Therefore, the effect of Fe3+ on bio-oxidation of ferrous sulphate has to be assessed prior to designing the system. Mg2+ is also one of the requirements for A. f. during bio-oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+.
5 Conclusions
1) The reaction mechanism of leaching phosphorus from the rock phosphate containing pyrites by the bio-oxidation of A. f. is suggested as follows: pyrites are oxidized by A. f. to produce H2SO4 and FeSO4; the rock phosphate is dissolved by H2SO4, forming soluble phosphorus compounds; and Fe2+ from the FeSO4 is oxidized to Fe3+, producing energy for the growth of A. f.. In this process, as H2SO4 is produced in the reaction, an acidic condition is formed in the culture medium. It benefits the growth of A. f., aiding the continuous oxidation of pyrites and the leaching of the phosphorus from the rock phosphate.
2) The bio-oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+ and bioleaching of phosphorus from rock phosphate by A. f. could be achieved effectively in the presence of Fe3+ with concentration in the range from 0 to 1.0 g/L, with Mg2+ concentration no less than 5 mg/L and NH4+ concentration approximately 400 mg/L. When the concentrations of Fe3+ and NH4+ exceed 1.0 g/L and 400 mg/L respectively, the fraction of phosphorous leached obviously declines. The higher the concentration of Mg2+, the higher the fraction of phosphorous leached.
3) Some optimal technological parameters on the fraction of phosphorous leached are as follows: the volume of inocula of A. f., the mass ratio of pyrites to rock phosphate and pH value are in the range of 5%- 25%, 3?1- 5?1 and 1.8- 2.2, respectively.
4) When pyrites act as substrates, A. f. is used to leach the soluble phosphorus that can be absorbed by plants. So this is feasible and significant work. However, further study is still needed in order to successfully apply it.
References
[1] HALDER A K, MISHRA A K, BHATTACHARYYA P,et al. Solubilization of rock phosphate by Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium[J]. Gen Appl Microbiol, 1990, 36: 81-92.
[2] JANA B B, SAHU S N. Effect of frequency of rock phosphate application in carp culture[J]. Aquaculture, 1994, 122: 313–321.
[3] JANA B B, SAHU S N. Relative performance of three bottom grazing fishes (Cyprinus carpio, Cirrhinus mrigala, Heteropneustes fossilis) in increasing the fertilizer value of phosphate rock[J]. Aquaculture, 1993, 115: 19–29.
[4] TANG Y, GUI B W, LIU Q. Experimental study on bacterial transformation[J]. Non-Ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2000, 16(6): 23-28. (in Chinese)
[5] LOUW H A, WEBLY D M. A study of soil bacteria dissolving bacteria, certain mineral phosphate fertilizers and related compounds[J]. Appl Bacteriol, 1959, 22: 227-233.
[6] AGNIHOTRI V P. Solubilization of insoluble phosphates by some soil fungi isolated from nursery seed beds[J]. Can Microbiol, 1970, 16: 877–880.
[7] ROYCHOUDHURY P, KAUSHIK B D. Solubilization of Mussoorie rock phosphate by cyanobacteria[J]. Curr Sci, 1989, 58: 569–570.
[8] CHI Ru-an, XIAO Chun-qiao, GAO Hong, et al. Biodecomposition of low-grade rock phosphate with some bacteria and fungi[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2005, 5(6): 636-639. (in Chinese)
[9] BOSECKER K. Biotransformation: metal solubilization by microorganisms[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 1997, 20: 591–604.
[10] GOLDSTEIN A H. Bacterial solubilization of mineral phosphates: historical perspective and future prospects[J]. Am Altern Agri, 1986, 1: 51–57.
[11] LEYVAL C, BERTHELIN J. Interaction between Laccaria laccata, Agrobacterium radiobacter and beech roots: influence on P, K, Mg and Fe movilization from minerals and plant growth[J]. Plant Soil, 1989, 117: 103–110.
[12] SALIH H M, YAHYA A Y, ABDUL-RAHEM A M, MUNAM B H. Availability of phosphorus in a calcareus soil treated with rock phosphate or superphosphate as affected by phosphate dissolving fungi[J]. Plant Soil, 1989, 120: 181–185.
[13] ZHANG Y K, WANG A, CHEN M C. Fundamental research on the dissolution of phosphate rock by microorganisms[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resource, 2000, 12(6): 32-34. (in Chinese)
[14] LIU J S, XIE X H, LI B M, et al. Adsorption characteristics of thiobacillus ferrooxidans on surface of sulfide minerals[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2005, 12(6): 671-676.
[15] CHI R A, XIAO C Q, GAO H. Bioleaching of phosphorus from rock phosphate containing pyrites by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 6: 23-24.
[16] SILVER M. Oxidation of elemental sulphur and sulphur compounds and CO2 fixation by Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans (Thiobacillus ferrooxidans)[J]. Can J Microbiol, 1970, 16: 845–849.
[17] MALHOTRA S, TANKHIWALE A S, RAJVAIDYA A S, et al. Optimal conditions for bio-oxidation of ferrous ions to ferric ions using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2002, 85: 225–234.
[18] LAZAROFF N, SIGAL W, WASSERMAN A. Iron oxidation and precipitation of ferric hydroxysulfates by resting thiobacillus ferrooxidans cells[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1982, 43: 924-938.
[19] LI H, ZHANG X. Examination of the content of ferrum in stibium by phenanthroline method[J]. Liaoning Chemistry, 2004, 32(2): 6-9. (in Chinese)
[20] SILVERMAN M P, LUNDGREN D G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium thiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. J Bacteriol, 1959, 77: 642-647.
[21] BRIERLY J A, NORRIS P R, KELLY D P, et al. Characteristics of a moderately thermophillic and acidophillic iron oxidising thiobacillus[J]. Eur Appl Microbiol Biotechno, 1978, 5: 291–299.
[22] KELLY D P, JONES C A. Bio-oxidation of ferrous ions to ferric ions using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans[C]// SACHEM F D. Metallurgical Application of Bacterial Transformation and Related Microbiological Phenomena. Princeton: Academic Press, 1978, 8: 19-44.
Foundation item: Project(2004CB619200) supported by the State Basic Research Development Program of China; Project(Z200515002) supported by the Key Project Foundation of the Education Department of Hubei Province, China
Received date: 2006-05-21; Accepted date: 2006-07-27
Corresponding author: CHI Ru-an, Professor; Tel: +86-27-87194500; E-mail: rac@mail.wit.edu.cn
(Edited by YANG Bing)