J. Cent. South Univ. (2015) 22: 2043-2051
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-015-2727-z
Effects of temperature variation on LixFePO4/C (0<X<1) process
XIAO Zheng-wei(肖政伟)1, ZHANG Ying-jie(张英杰)1, HU Guo-rong(胡国荣)2
1. Faculty of Metallurgical and Energy Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology,Kunming 650093, China;
2. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2015
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2015
Abstract: LiFePO4/C was prepared via solid state reaction and characterized with X-ray powder diffraction and charge–discharge test. As-prepared LiFePO4/C has a triphylite structure and exhibits an excellent rate capability and capacity retention. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was applied to investigate LixFePO4/C (0+ ion accumulation and consumption in the electrode reaction. The surface layer impedance needs to be included in the equivalent circuit when LiFePO4/C is deeply delithiated at a relatively high temperature. EIS examination indicates that a temperature rise leads to a better reversibility, lower charge transfer resistance, higher exchange current density J0 and greater Li+ ion diffusion coefficient for the LixFePO4/C electrode process. The Li+ ion concentration in LixFePO4/C is potential to impact the Li+ ion diffusion coefficient, and a decrease in the former results in an increase in the latter.
Key words: lithium ion cell; LiFePO4/C; electrode process; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; equivalent circuit; Li+ ion diffusion coefficient
1 Introduction
The olivine-structured LiFePO4 owns the favorable attributes of abundant raw materials, non-toxicity, a high thermal stability, a medium voltage of 3.45 V (vs Li+/Li) and an attainable theoretical capacity of 170 mA·h/g. These desired properties have qualified LiFePO4 as a suitable cathode for the long life and safe lithium ion cells [1]. However, due to the poor electronic conductivity of pristine LiFePO4, nano-sizing [2], supervalent ion doping [3] and/or carbon coating/mixing [4-6] are/is requested for an enhanced electrochemical performance. Preparation of LiFePO4/C composite is by all means a simple but effective strategy for LiFePO4 achieving a practical capacity.
In order to make better use of the energy storage potential for LiFePO4/C, it is necessary to know the effects of related factors on its electrode process. The electronic and Li+ ion ionic conductivities are the key figures to determine the electrochemical behavior of an electrode material for lithium ion cells. As the electronic conductivity for LiFePO4/C is not so sensitive to temperature variation, the study of the Li+ ion diffusion in LiFePO4/C electrode reaction becomes a practical way. Temperature exerts influences on the LiFePO4/C electrode process, and its effect on the Li+ ion diffusion has been investigated [7]. It has also been reported that a higher temperature leads to higher charge–discharge capacities for LiFePO4 [8].
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is an efficient technique to study the kinetics involved in reversible and irreversible electrode processes [9-12]. EIS possesses the advantageous traits of a wide frequency range and a negligible disturbance on tested systems. It is usually adopted to study the kinetics, electronic conductivity and ion diffusion coefficient in an electrode reaction. In particular, EIS is adequate for the electrochemical system containing a Warburg resistance.
In this work, EIS is used to investigate LixFePO4/C (0xFePO4/C electrode process are introduced according to the electrode process and the criteria for EIS circuit design. Then, a fitting is carried out on the EIS data of LiFePO4/C electrode to determine the valid circuit. Finally, fittings are performed on the EIS data of LixFePO4/C electrode.
2 Experimental
Stoichiometric Fe2O3, NH4H2PO4 and Li2CO3 and a certain amount of C6H12O6·H2O were mixed in acetone and ball-milled using a speed of 300 r/min for 4 h to achieve homogenous mixing and thorough mechanical activation. After being dried at 80 °C overnight, the mixture was pulverized and sintered at 700 °C in a high-purity argon atmosphere to prepare LiFePO4/C.
As-prepared LiFePO4/C was characterized with X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) performed on a Philips X-pert powder diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation. The specific surface area of the as-prepared LiFePO4/C powder was obtained with the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis on an Autosorb-1-C.
Coin cells comprising LiFePO4/C cathode electrodes were assembled in a glove box. For the coin cell fabrication, the electrolyte was 1 mol/L LiPF6 in a mixed solvent of ethylene carbonate (EC), dimethylene carbonate (DMC) and ethylmethyl carbonate (EMC) at a volume ratio of 1:1:1. The lithium disc was used as the anode electrode. The membrane was Celgard 2400 microporous polypropylene. LiFePO4/C, PVdF binder and acetylene black at a mass ratio of 8:1:1 were ground in N-methyl pyrrolidinone (NMP) solvent and evenly spread on an aluminum foil current collector. The wet cathode was dried at 120 °C under vacuum. Round cathode discs were punched for the coin cell assembly. The charge–discharge measurement was conducted galvanostatically on a LAND BTI-40 in the voltage window of 2.5-4.1 V at room temperature.
For both EIS and CV tests, the working electrode was LiFePO4/C or LixFePO4/C which had already been charged–discharged for ten cycles. The metallic lithium was used as the counter and reference electrode. The electrolyte was the same as that used above. The EIS measurement of LixFePO4/C electrode was carried out in the temperature range of 28-61 °C on a PAR Potentiostat/ Galvanostat, Model 273A, coupled to a PAR lock-in amplifier, Model 5210. The EIS test input was a sinusoidal alternate current with a frequency from 10 mHz to 100 kHz and a voltage amplitude of 5 mV. Each LiFePO4/C electrode was left to stand for 24 h prior to the EIS measurement. The CV measurement of LiFePO4/C electrode was performed with a PAR Potentiostat/Galvanostat, Model 273A, in the voltage window of 2.5-4.2 V at 34-60 °C with a scan rate of 0.5 mV/s.
3 Results and discussion
Figure 1 shows the XRD pattern for the as-prepared LiFePO4/C. The diffraction result is indexed to orthorhombic, space group Pnma. The characteristic peaks in the diffraction pattern are sharp and perfect, suggesting a high degree of crystallinity for the LiFePO4 in as-prepared LiFePO4/C. The pattern agrees well with that for triphylite (JCPDS NO. 40–1499), and no impurity phases consisting of lithium, iron and/or phosphorus have been detected, indicating a high purity for the as-prepared LiFePO4/C.
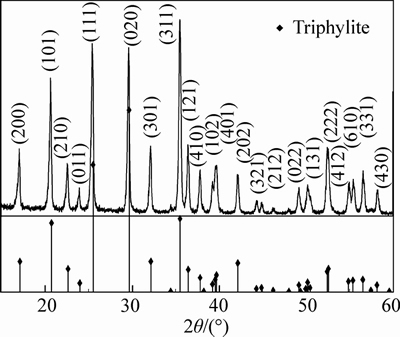
Fig. 1 XRD pattern for as-prepared LiFePO4/C
Figure 2(a) shows that at 0.1C the as-prepared LiFePO4/C exhibits an appreciable discharge capacity of 153.8 mA·h/g. Meanwhile, as indicated in Fig. 2(b),excellent rate capacity retentions without any fade are achieved by as-prepared LiFePO4/C at 0.1, 1 and 2C with average discharge capacities of 153.8, 128.3 and 121.0 mA·h/g, respectively, in the first 50 cycles.

Fig. 2 Typical charge–discharge profiles at 0.1C (a) and rate capability (b) for LiFePO4/C electrode
Figure 3 illustrates the EIS and CV patterns for the LiFePO4/C electrode tested at different temperatures. It is evident that temperature has a great impact on the EIS and CV of LiFePO4/C electrode. The semicircle of EIS profile in the high frequency region represents the charge transfer resistance (Rct) in the LiFePO4/C electrode process. As indicated in Fig. 3(a), with the increase in temperature, Rct becomes smaller, which is beneficial to charge transfer. As shown in Fig. 3(b), with the elevation of temperature, the redox peaks for Fe3+/Fe2+ couple become sharper and closer, and the peak currents become bigger. The information indicates that an increase in temperature leads to a better reversibility and faster Li+ ion intrusion and extrusion for LiFePO4/C electrode process. The EIS and CV profiles in Fig. 3 show the same variation trend for the kinetics involved in the LiFePO4/C electrode process on temperature change. It can be safely concluded that a higher temperature results in a lower polarization, smoother redox reaction for Fe3+/ Fe2+ couple and smaller charge transfer resistance in LiFePO4/C electrode process.
In the LixFePO4/C electrode process, the main reaction is Fe3+/Fe2+ redox behavior, along with the Li+ ion intrusion and electron gain or Li+ ion extrusion and electron loss. As shown in Fig. 4, several basic steps are involved when Li+ ion is intercalated into the LixFePO4: 1) The Li+ ion dissolved from lithium anode migrates through bulk electrolyte to the electrolyte/cathode interface. 2) The Li+ ion is transferred across the electrolyte–cathode electrical double layer. 3) The Li+ ion enters the possibly existent surface layer and then the active material particle. 4) The Li+ ion diffuses in the LiFePO4 and FePO4 phases. 5) The Fe3+/Fe2+ redox couple undergoes reduction reaction. 6) The electron is gained from external circuit to maintain charge balance in the cathode. The Li+ ion extrusion process is reverse to the Li+ ion intrusion process.
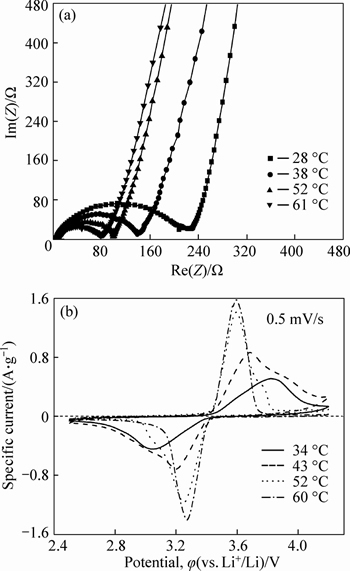
Fig. 3 EIS (a) and CV (b) patterns obtained at different temperatures for LiFePO4/C electrode
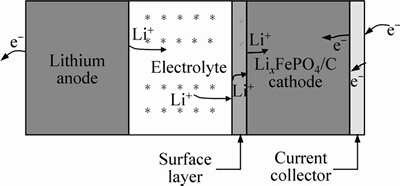
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of LixFePO4/C electrode process on Li+ ion intrusion
Step 4) is usually rate-determining in a solid electrode process. The electron transfer, however, may become a rate-determining step when the electrode material exhibits a very poor electronic conductivity. In this work, however, as the carbon coating/mixing has greatly improved the electronic conductivity of LiFePO4/C composite, this parameter may be excluded to be rate-determining to a certain extent. All the basic steps affect the overall kinetics of LixFePO4/C electrode process to different degrees. As a matter of fact, electrode kinetics is mainly determined by the nature of electrode material and the properties of electrolyte/ electrode interface. Exchange current density, the indicator of reversibility, depends on the charge transfer resistance which is dependent on the electrolyte– electrode properties.
In an electrode process, the impedance contributed by an electrolyte can be represented by a resistor (Re), a resistor of an electrical double layer (Rct) and a capacitor (Cct) in parallel for charge transfer, a Warburg resistance of a concentration polarization (or a resistor and a capacitor in series), and another electrochemical double layer of an surface or absorption layer. Different equivalent circuits have been put forward for investigating LiFePO4 electrode process [7-8, 13-14]. In order to reflect the LiFePO4/C electrode process properly, the electrode process shown in Fig. 4 and the criteria for equivalent circuit design [15-16] are followed rigorously.
Based on the above discussion, equivalent circuits for the LiFePO4/C electrode process are introduced, as shown in Fig. 5, in which Re is the electrolyte resistance, Rsl is the surface layer resistance, Rct is the charge transfer resistance, Csl is the surface layer capacitance, Cct is the charge transfer capacitance, ZW and 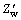 are the Warburg resistances for the faradic and non-faradic currents, respectively, Cint is the intercalation capacitance caused by Li+ ion accumulation and consumption in active material particles, Qsl is the surface layer CPE (constant phase element), and Qct is the charge transfer CPE.
are the Warburg resistances for the faradic and non-faradic currents, respectively, Cint is the intercalation capacitance caused by Li+ ion accumulation and consumption in active material particles, Qsl is the surface layer CPE (constant phase element), and Qct is the charge transfer CPE.
The EIS spectra in Fig. 3(a) are fitted with the possible equivalent circuits in Fig. 5 using Zsimpwin software and the results are given in Table 1. It can be seen that there is a negligible difference between the fitted values for Re by using the possible equivalent circuits to fit the same EIS spectrum. Due to the smallest Re among all the ohmic and non-ohmic resistances, the Circuit II can be excluded to be viable. From the value of errors, only the results by using the Circuit V have errors less than 10% each. Figure 3(a) shows that an increase in temperature reduces the charge transfer resistance in the LiFePO4/C electrode process, which is in agreement with the fitted results by using the Circuit V. For the Li+ ion intrusion–extrusion in LiFePO4/C electrode process, there exist the Li+ ion accumulation and consumption in the active material particles because of its sluggish diffusion kinetics. Thus, the inclusion of Cint in the Circuit V is reasonable and essential which is chosen to fit the EIS spectra of LixFePO4/C electrode.
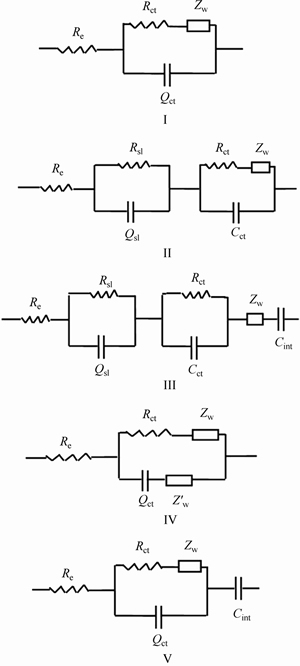
Fig. 5 Possible equivalent circuits for LiFePO4/C electrode process
As shown in Fig. 5, an important characteristic with regard to the Circuit V is the exclusion of surface layer resistance and capacitance. The products from solvent reactions are not detected at the carbon-treated LiFePO4 surface, contrary to the findings for other cathode materials, such as LiCoO2, LiMn2O4 and LiNiO2 [17]. The surface layer components for the LiFePO4/C electrode have been found to be mainly LiF, LiPF6, LixFy and LixPOyFz [17–20]. The Li+ ion diffusion in the fluorides is different from that in the solvent reaction products and Li2CO3. Moreover, no evidence of the formation of a resistive film is deduced from the evolution of EIS measurements for LiFePO4/C and LiFePO4 electrodes [20]. Hence, it is practicable not to include a surface layer resistance and capacitance in the Circuit V.
Figure 6 shows the EIS spectra for the LixFePO4/C electrode examined at different temperatures which are fitted by using the equivalent Circuit V. It must be noted that the EIS spectrum for the Li0.1FePO4/C at 67 °C contains two arcs in the high and middle frequency regions, which is singled out for clarity as the inset of the figure of the Li0.1FePO4/C EIS spectra. The equivalent circuit for fitting this exceptional spectrum should be a revision of equivalent Circuit V. Substantial fitting indicates that on the basis of the equivalent Circuit V, a good fitting effect can be achieved by the addition of a surface layer resistance Rsl and CPE Qsl and the replacement of Qct by Cct. This demonstrates that the surface layer impedance to Li+ ion migration must be considered when the LixFePO4/C is deeply delithiated at a relatively high temperature. A possible reason is that under the conditions, the thickness of surface layer may be greatly increased or surface layer composition may be significantly changed. The fitted result for the EIS spectra in Fig. 6 is given in Table 2. The errors for all fitted values are less than 10%.
Table 1 Fitted results based on possible equivalent circuits for EIS spectra of LiFePO4/C electrode
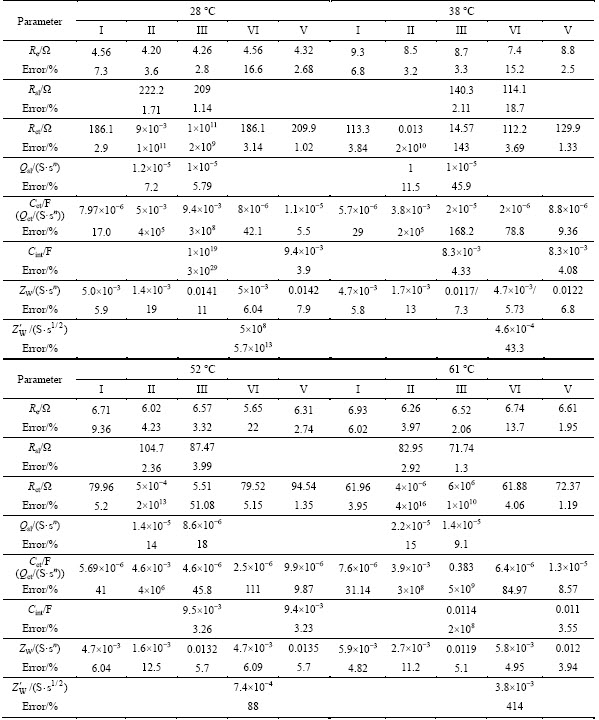
From Table 2, it can be seen that Re exhibits different values for the LixFePO4/C electrode with different Li+ ion concentrations. This can be ascribed to the different cells used for each set of EIS tests on the cathode with same Li+ ion concentration in the temperature range of 37-69 °C. In fact, it is not scientific to just regard the fitted values as the physical resistance or capacitance for the physical parts in an electrode process, such as electrolyte, electrical double layer, surface layer and FePO4–LiFePO4 phase. However, it is valid to investigate the effect of temperature on the electrode process through analyzing the change trend for the value of each element in the equivalent circuit.Table 2 shows that for any x value in LixFePO4/C with the increase in temperature the charge transfer resistance Rct decreases, indicative of a temperature elevation favoring Li+ ion migration across the electrical double layer. Exchange current density J0 is inversely proportional to Rct:
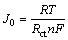 (1)
(1)
where R is the gas constant; T is the absolute temperature; n is the number of electron transferred; F is the Faraday constant. According to Eq. (1), with the rise in temperature, J0 increases even more rapidly as Rct simultaneously decreases. A higher exchange current density means a better reversibility. Here, it can be safely concluded that temperature is a potential factor to affect the reversibility of a LiFePO4/C electrode. As proved by the EIS spectra fitting, a temperature increase can greatly improve the reversibility of LiFePO4/C electrode, which agrees with the conclusion drawn from CV data analysis.
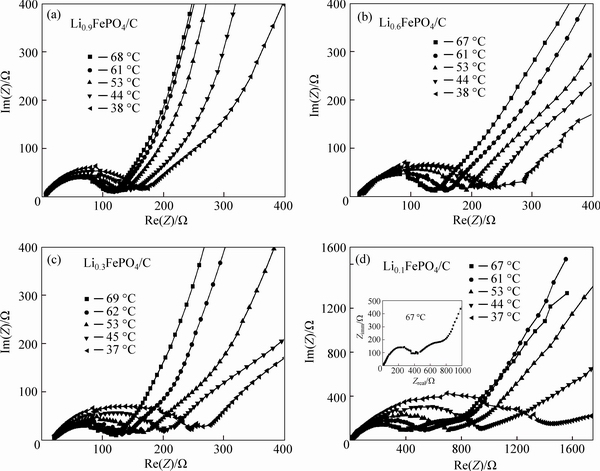
Fig. 6 EIS spectra for LixFePO4/C (0<X<1) electrode at different temperatures
Table 2 Fitted results for EIS spectra of LixFePO4/C electrode by using equivalent Circuit V
Plot the real part of Warburg impedance Re(Z) as the function of (2πf)–1/2 to obtain Fig. 7. As can be seen, except for very few cases, most curves in Fig. 7 exhibit a linear pattern. OriginLab8 software is used to find the slope (σ) for each curve and the following equation is applied to calculating the Li+ ion diffusion coefficient DLi+:
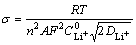 (2)
(2)
where R is the gas constant; T is the absolute temperature; n is the number of electrons transferred; A is the effective area for LixFePO4/C electrode; F is the Faraday constant; 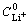 is the concentration of Li+ ion in LixFePO4/C.
is the concentration of Li+ ion in LixFePO4/C.
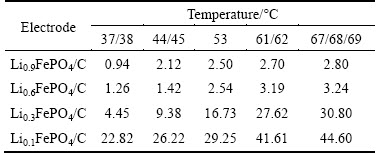
While an electrode reaction only takes place at the points where a LiFePO4 particle, conductive carbon and electrolyte meet, Li+ ion charge transfer proceeds at the sites where at least a LiFePO4 particle and electrolyte meet. In as-prepared LiFePO4/C, the lighter carbon accounts for 8.03% by mass and its contribution to the surface area must be considerable. Thus, it is impossible to know the real effective surface area for LiFePO4 in LiFePO4/C electrode. The BET test shows that the specific surface area for the as-prepared LiFePO4/C is 1.5×105 cm2/g. In this work, the specific effective area for LiFePO4/C is determined to be 5×104 cm2/g due to the [010] direction-oriented Li+ ion diffusion in FePO4- LiFePO4 system and intentional ommision of carbon’s contribution. Using Eq. (2), the Li+ ion diffusion coefficient is calculated for the LixFePO4/C electrode tested at different temperatures and given in Table 3.
The Li+ ion diffusion coefficient obtained from the EIS spectra is 10-19-10-17 cm2/s, which is close to the reported value [21]. Under the test conditions in this work, at the same temperature, the Li+ ion diffusion coefficient increases with the decrease in Li+ ion concentration in LixFePO4/C electrode. With the increase in temperature, Li+ ion diffusion coefficient increases for LixFePO4/C electrode with the same Li+ ion concentration. In addition, at any temperature, the decrease in x from 0.9 to 0.1 gives rise to a (10–20)-fold increase in Li+ ion diffusion coefficient. Thus, Li+ ion concentration in LixFePO4/C electrode is another important factor to affect the Li+ ion diffusion in the electrode process. To any x in LixFePO4/C electrode, however, the increase in the temperature from 37 to 69 °C leads to only a 2-fold increase in Li+ ion diffusion coefficient.
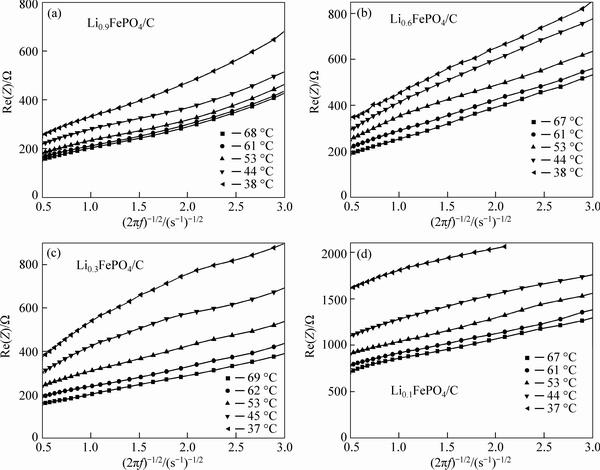
Fig. 7 Relation between real part of Warburg impedance and reciprocal of square root of angular frequency for LixFePO4/C electrode
Table 3 Li+ ion diffusion coefficients (DLi+/(10-18 cm2·s-1)) for LixFePO4/C electrode at different temperatures
The above discussion shows that at any state of charge, an elevation of temperature results in a better reversibility, smaller charge transfer resistance, larger exchange current density and higher Li+ ion diffusion coefficient for the LixFePO4/C electrode process. Faster Li+ diffusion is beneficial to prompting the deep charge– discharge ability of a LiFePO4/C electrode at higher rates. Here, the study also gives the direct evidence for higher Li+ ion diffusion coefficient at an elevated temperature accounting for a capacity enhancement of LiFePO4 electrode.
This work demonstrates that temperature elevation is effective to tackle the sluggish kinetics in LiFePO4/C electrode process. However, the interface of LiFePO4/ electrolyte based on LiPF6 is sensitive to temperature variation and the side reactions resulting in Fe2+ dissolution become severe in temperature increasing period [22]. Therefore, the strategy of temperature elevation for improving the slow kinetics of LiFePO4/C electrode can be adopted on the condition that a suitable electrolyte is used. It is anticipated that a solid electrolyte compatible with LiFePO4/C will be a viable choice.
4 Conclusions
1) LiFePO4/C cathode material for lithium ion cells is synthesized through solid state reaction. Superior rate capability of 153.8, 128.3 and 121.0 mA·h/g at 0.1C, 1C and 2C, respectively, and very good capacity retentions are achieved by the as-prepared LiFePO4/C.
2) The equivalent circuit containing the intercalation capacitance for Li+ ion accumulation and consumption is valid for fitting the EIS spectra of LiFePO4/C electrode. The surface layer should be included in the equivalent circuit when LixFePO4/C is deeply delithiated at a relatively high temperature.
3) A temperature elevation results in an increased exchange current density, decreased charge transfer resistance and higher Li+ ion diffusion coefficient for LixFePO4/C electrode. Li+ ion concentration in LixFePO4/C electrode is potential to impact the Li+ ion diffusion coefficient, and a decrease in the former brings about an increase in the latter.
4) The adoption of temperature elevation to circumvent the slow kinetics in LiFePO4/C electrode reaction needs the realization of a suitable electrolyte capable of reducing its reaction with LiFePO4 to an acceptable low level at an elevated temperature.
References
[1] GOODENOUGH J B, PARK K S. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: A perspective [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(4): 1167-1176.
[2] BAI P, COGSWELL D A, BAZANT M Z. Suppression of phase separation in LiFePO4 nanoparticles during battery discharge [J]. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(11): 4890-4896.
[3] BILECKA I, HINTENNACH A, ROSSELL M D, XIE D, NOVAKB P, NIEDERBERGER M. Microwave-assisted solution synthesis of doped LiFePO4 with high specific charge and outstanding cycling performance [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(16): 5881-5890.
[4] SUN B, WANG Y, WANG B, KIM H S, KIM W S, WANG G. Porous LiFePO4/C microspheres as high-power cathode materials for lithium ion batteries [J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2013, 13(5): 3655-3659.
[5] YU S, CHUNG Y, SONG M S, NAM J H, CHO W I. Investigation of design parameter effects on high current performance of lithium-ion cells with LiFePO4/graphite electrodes [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2012, 42(6): 443-453.
[6] XIAO Zheng-wei, HU Guo-rong. A novel synthesis of LiFePO4/C from Fe2O3 without extra carbon or carbon-containing reductant [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(6): 2143-2149.
[7] GAO F, TANG Z. Kinetic behavior of LiFePO4/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(15): 5071-5075.
[8] TAKAHASHI M, TOBISHIMA S, TAKEI K, SAKURAI Y. Reaction behavior of LiFePO4 as a cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries [J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 148(3/4): 283-289.
[9] ZHU Y, WANG C. Galvanostatic intermittent titration technique for phase-transformation electrodes [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(6): 2830-2841.
[10] PARK M, ZHANG X, CHUNG M, LESS G B, SASTRY A M . A review of conduction phenomena in Li-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(24): 7904-7929.
[11] QU Tao, TIAN Yan-wen, ZHAI Yu-chun. Measurement of diffusion coefficient of lithium in LiFePO4 cathode material for Li-ion battery by PITT and EIS [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(8): 1255-1259. (in Chinese)
[12] PARK C K, PARK S B, SHIN H C, CHO W, JANG H. Li ion diffusivity and rate performance of the LiFePO4 modified by Cr doping [J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2011, 32(1): 191-195.
[13] ZHUNG D, ZHAO X, XIE J. One-step solid-state synthesis and electrochemical performance of Nb-doped LiFePO4/C [J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2006, 22(7): 840-844. (in Chinese)
[14] ILLIG J, ENDER M, CHROBAK T, SCHMIDT J P, KLOTZ D, IVERS-TIFFEE E. Separation of charge transfer and contact resistance in LiFePO4-cathodes by impedance modeling [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(7): A952-A960.
[15] THOMAS M G S R, BRUCE P G, GOODENOUGH J B. AC impedance analysis of polycrystalline insertion electrodes: Application to Li1-xCoO2 [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1985, 132(7): 1521-1528.
[16] ZHANG Ya-li, SUN Dian-ting, GUO Guo-lin, GUI Lin-lin. Transfer rule of equivalent circuits of similar plots on the impedance complex plane and on the capacitance complex plane for an AC impedance measurement (II) [J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2000, 21(7): 1086-1092. (in Chinese)
[17] HERSTEDT M, STJERNDAHL M, NYTEN A, GUSTAFSSON T, RENSMO H, SIEGBAHN H, RAVET N, ARAMAND M, THOMAS J O, EDSTROM K. Surface chemistry of carbon-treated LiFePO4 particles for Li-ion battery cathodes studied by PES [J]. Electrochemical Solid-State Letters, 2003, 6(9): A202-A205.
[18] EDSTROM K, GUSTAFSSON T, THOMAS J O. The cathode- electrolyte interface in the Li-ion battery [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 50(2/3): 397-403.
[19] LI W, LUCHT B L. Inhibition of solid electrolyte interface formation on cathode particles for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 168(1): 258-264.
[20] DUPRE N, MARTIN J F, DEGRYSE J, FEMANDEZ V, SOUDAN P, GUYOMARD D. Aging of the LiFePO4 positive electrode interface in electrolyte [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(21): 7415-7425.
[21] ZHU Y, WANG C. Novel CV for phase transformation electrodes [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(3): 823-832.
[22] AMINE K, LIU J, BELHAROUAK I. High-temperature storage and cycling of C-LiFePO4/graphite Li-ion cells [J]. Electrochemistry Communication, 2005, 7(7): 669-673.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Foundation item: Project(2010ZC051) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province, China; Project(20140439) supported by Analysis and Testing Foundation from Kunming University of Science and Technology, China; Project(14118245) supported by Starting Research Fund from Kunming University of Science and Technology, China
Received date: 2014-08-12; Accepted date: 2014-12-10
Corresponding author: ZHANG Ying-jie, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-18808804528; E-mail: zhangyingjie09@126.com; HU Guo-rong, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-731-88830474; E-mail: hgrhsj@263.net