Characterization and formation mechanisms of fractures and their significance to hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of Lower Ordovician mid-assemblage Formations in central Ordos Basin, China
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2018年第11期
论文作者:赵靖舟 赵子龙 任海姣 LI Jun(李军) 吴伟涛
文章页码:2766 - 2784
Key words:characterization of fracture; formation mechanism; quasi-continuous accumulation; Ordovician mid-assemblage formations; Ordos basin
Abstract: The lower Ordovician mid-assemblage Formations in the central Ordos Basin of China host prolific gas resources, and most hydrocarbon reserves are stored in naturally-fractured reservoirs. Thus, fracture pathway systems may have a significant impact on reservoir performance. This article focuses on the core- and laboratory-based characterization of fractures. Through the developmental degrees, extended scale, output state and filling characteristics of various types of fractures, the results show that there are three distinct fracture types: 1) nearly vertical fractures, 2) oblique fractures, and 3) horizontal fractures. Based on a systematic study of the characterization of reservoir space, the main geologic setting of natural gas accumulation and the regional tectonic background, type 1 is mainly driven by the tectonic formation mechanism, and type 3 and parts of low-angle fractures in type 2 are induced by the diagenetic formation mechanism. While recovered paleopressure for methane-rich aqueous inclusions trapped in fracture-filling cement indicates that the fracture opening and growth are consistent with gas maturation and charge and such high-angle fractures in type 2 are caused by the compound formation mechanism. The fractures to hydrocarbon accumulation may play a more significant role in improving the quality of reservoir porosity. Furthermore, connected fractures, dissolved pores and cavities together constitute the three-dimensional pore-cave-fracture network pathway systems, with faults serving as the dominant charge pathways of highly pressurized gas in the study area. Our results demonstrate that protracted growth of a pervasive fracture system is not only the consequence of various formation mechanisms but also intrinsic to quasi-continuous accumulation reservoirs.
Cite this article as: ZHAO Zi-long, ZHAO Jing-zhou, REN Hai-jiao, LI Jun, WU Wei-tao. Characterization and formation mechanisms of fractures and their significance to hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of the Lower Ordovician mid-assemblage Formations in the central Ordos Basin, China [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(11): 2766–2784. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3952-z.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2018) 25: 2766-2784
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3952-z
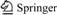
ZHAO Zi-long(赵子龙)1, 2, ZHAO Jing-zhou(赵靖舟)3, 4, REN Hai-jiao(任海姣)3, 4,LI Jun(李军)3, 4, WU Wei-tao(吴伟涛)3, 4
1. State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, Xi’an 710069, China;
2. Department of Geology, Northwest University, Xi’an 710069, China;
3. Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Petroleum Accumulation Geology, Xi’an Shiyou University,Xi’an 710065, China;
4. School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an 710065, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018
Abstract: The lower Ordovician mid-assemblage Formations in the central Ordos Basin of China host prolific gas resources, and most hydrocarbon reserves are stored in naturally-fractured reservoirs. Thus, fracture pathway systems may have a significant impact on reservoir performance. This article focuses on the core- and laboratory-based characterization of fractures. Through the developmental degrees, extended scale, output state and filling characteristics of various types of fractures, the results show that there are three distinct fracture types: 1) nearly vertical fractures, 2) oblique fractures, and 3) horizontal fractures. Based on a systematic study of the characterization of reservoir space, the main geologic setting of natural gas accumulation and the regional tectonic background, type 1 is mainly driven by the tectonic formation mechanism, and type 3 and parts of low-angle fractures in type 2 are induced by the diagenetic formation mechanism. While recovered paleopressure for methane-rich aqueous inclusions trapped in fracture-filling cement indicates that the fracture opening and growth are consistent with gas maturation and charge and such high-angle fractures in type 2 are caused by the compound formation mechanism. The fractures to hydrocarbon accumulation may play a more significant role in improving the quality of reservoir porosity. Furthermore, connected fractures, dissolved pores and cavities together constitute the three-dimensional pore-cave-fracture network pathway systems, with faults serving as the dominant charge pathways of highly pressurized gas in the study area. Our results demonstrate that protracted growth of a pervasive fracture system is not only the consequence of various formation mechanisms but also intrinsic to quasi-continuous accumulation reservoirs.
Key words: characterization of fracture; formation mechanism; quasi-continuous accumulation; Ordovician mid-assemblage formations; Ordos basin
Cite this article as: ZHAO Zi-long, ZHAO Jing-zhou, REN Hai-jiao, LI Jun, WU Wei-tao. Characterization and formation mechanisms of fractures and their significance to hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of the Lower Ordovician mid-assemblage Formations in the central Ordos Basin, China [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(11): 2766–2784. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3952-z.
1 Introduction
Natural fracture systems not only are major reservoir spaces but also the flow channel of fluid, and therefore early identification, accurate description, and exact prediction for natural fractures are the keys to effective development of carbonate reservoirs [1]. Abundant technologies and methodologies for identification purposes have been applied by geologists to study the characterization of natural fractures based on different research purposes [2, 3].
Accurate three-dimensional seismic data provide an effective way to acquire the fracture systems, but the technology and application of more advanced microseismic data are still limited [4, 5]. Integrated logging interpretation and cores’ observation, such as high-resolution borehole micro resistivity imaging logs, oriented cores, and mud losses, do reveal a detailed characterization of fractures and refer to those valid fractures [6]. Well log data and cores, however, only provide limited information of fracture width and spacing; besides this, well spacing is usually too large to express precise correlation and regularity of fracture patterns between wells [4, 7]. A geometrically- based method and outcropping analogs are used to predict stress-induced fracture aperture and flow in discrete fracture networks [8–10]. These technologies provide a wide range of possible geometries and spatial distributions for fracture systems, which can be applied to determining fracture patterns in some shallow reservoirs [11]. Fracture opening status, however, cannot be accurately acquired from outcropping rocks because weathering and eluviations have changed the in situ fractures. Diagenesis and carbon-oxygen isotope are used to study the types and characteristics of fractures [12, 13]. In these methods, however, the relative timing and formation mechanisms for natural fractures still remain unknown.
In this paper, several aspects were successfully selected to be considered to reflect the attributes and characteristics as well as formation mechanisms of fractures on the basis of core- and laboratory-based observation. These aspects include attitude of fractures, filling degrees, width, extent, and the included angle. In addition, fluid inclusions trapped in fracture-filling cement were analyzed using microthermometry and Raman microspectrometry to obtain a history of temperature, paleopressures, and fluid composition. Given this, we may synthetically draw some significant conclusions from these records.
2 Geological setting
2.1 Regional tectonics and evolution
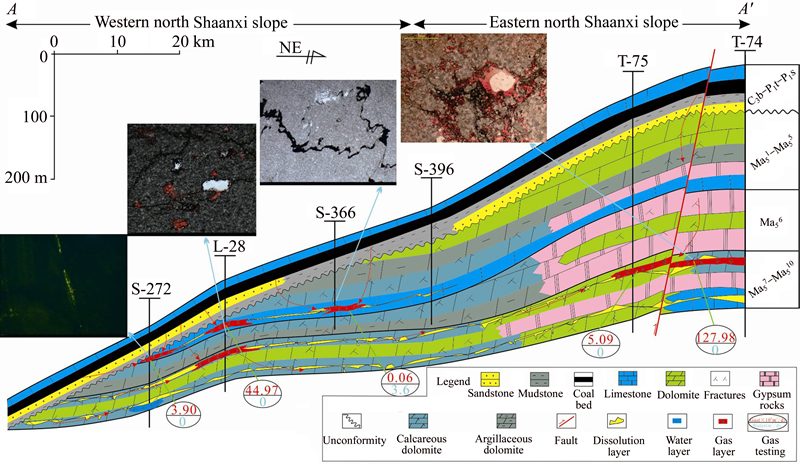
The Ordos Basin is an elongated, northeast- southwest-trending, polycyclic cratonic basin in midwestern China (Figure 1), developed during the Palaeozoic North China Craton, and had undergone multistage tectonic evolution [14, 15]. The approximately 650 m (~2133 ft)-thick Paleozoic Group is composed of the Lower Ordovician Majiagou Formations’ carbonate reservoirs and overlying coal, carbargilite, and carbonate in the Permo-Carboniferous Shanxi–Benxi Formations (Figure 2). The Caledonian-Indosinian orogeny was an important period of collision in the West Qinling orogenic belt, when the thrust-compression tectonic system in the E–W direction was formed, and such sinistral shear and the dextral shear stress field were developed on both sides of the western margin of the basin. During the Yanshan orogeny, owing to the strong sinistral shear between the Pacific plate and the Eurasian plate, the W–E and N–S regional fractures occurred in the interior of the basin. There are two main types of tectonic deformation in the Himalayan tectonic period, namely, the early thrust-compression deformation in the west of the basin and the gravity-slide tectonic deformation on the northern edge of bedrock mountains [16]. Meanwhile, the thrust-compression of the Liupanshan orogenic-belt is the major driving force in the formation of a series towards NW–NE- protruding arc thrust-tectonic systems [17]. In combination with the history of tectonic evolution, fault types and the depth of bedrock, and the characteristics of gravity-magnetic-magnetotelluric- seismic imaging, the Ordos basin can be subdivided into six first-order tectonic units. These units include Yimeng uplift, Western Shanxi fold belt, Weibei uplift, thrust belt on the Westernedge, Tianhuan depression, and North Shaanxi slope, respectively [18] (Figure 1).
The study area is located in the middle of the North Shaanxi slope of the Ordos Basin, where two hydrocarbon source rock systems of Mesozoic and Paleozoic are formed, and presented with their relatively independent petroleum system. Furthermore, both the Mesozoic petroleum system and the Paleozoic gas system are a quasi-continuous accumulation [19–21], and therefore more than one hundred billion tight sandstone gas fields have been confirmed in the Upper Paleozoic of the Ordos Basin, such as Sulige, Yulin, Wushenqi, Zizhou and Daniudi (Figure 1).
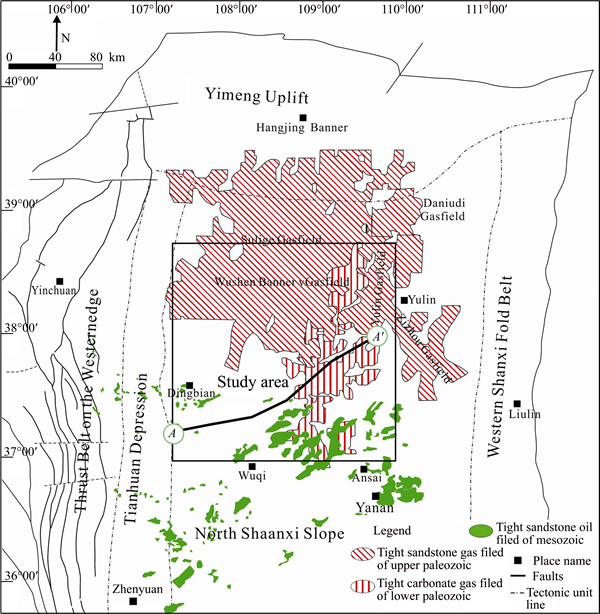
Figure 1 Location and distribution of structural units of Ordos Basin in midwestern China (location of basin boundaries from Ref. [22])
2.2 Stratigraphic and sedimentary characteristics
Based on the types and characteristics of gas reservoirs, the Lower Ordovician Majiagou Formations of the Ordos Basin (LOMOB) is subdivided into 1) the Upper–assemblage Formations, including Sub-member 1 to Sub- member 4 of Member 5 (Ma51–Ma54); 2) the Mid- assemblage Formations, including Sub-member 5 to Sub-member 10 of Member 5 (Ma55–Ma510); and 3) the Lower-assemblage Formations, namely, Member 4 (Ma4) and its lower Formations [23]. The studied stratigraphic unit is Ma55–Ma510, which is a large, low-relief, approximately 190×180 km (118× 112 squara miles) in area with a hydrocarbon column in excess of 200 m (~656 ft) in the study area (Figure 2). Since the late 20th century, an increasing number of investigations on the exploitation of hydrocarbon reserves in naturally- fractured reservoirs has been performed because of their importance in fluid flow predictions. It has been proven that 419×1010 m3 of natural gas geological reserves remain in the LOMOB [23].
The N–S countercurrent extruding, and concussive and intermittent regression in the LOMOB as a whole are interpreted by the underthrust of the southern Qinling and northern Xingmeng ocean crust that existed during the early sedimentary period of Member 5. With a large- amplitude regression background, however, there existed a secondary concussive transgression- regression [24, 25]. Subjected to this shock, the sedimentary environment and petrologic feature of Ma55–Ma510 indicate great diversity in different periods. Ma56, Ma58, and Ma510 were interpreted as the sedimentary microfacies of the tidal dolomitic flats, the intertidal gypsum-bearing dolomitite flats, the basin-marginal-gypsum dolomitite flats, and the gypsum depression from west to east during the rapid regression [26]. Ma55, Ma57, and Ma59, however, were deposited in the sedimentary microfacies of limestone/dolomitite flats, Jingxi table-flats subfacies, which would be subdivided into the sedimentary microfacies of the algal beach and the algal limestone plateau, Jingbian gentle- slope subfacies, including the microfacies of the subtidal mud mound, and the Eastern depression subfacies [27]. This interpretation is supported by the presence of the analytical geochemistry and information of well cores [28].
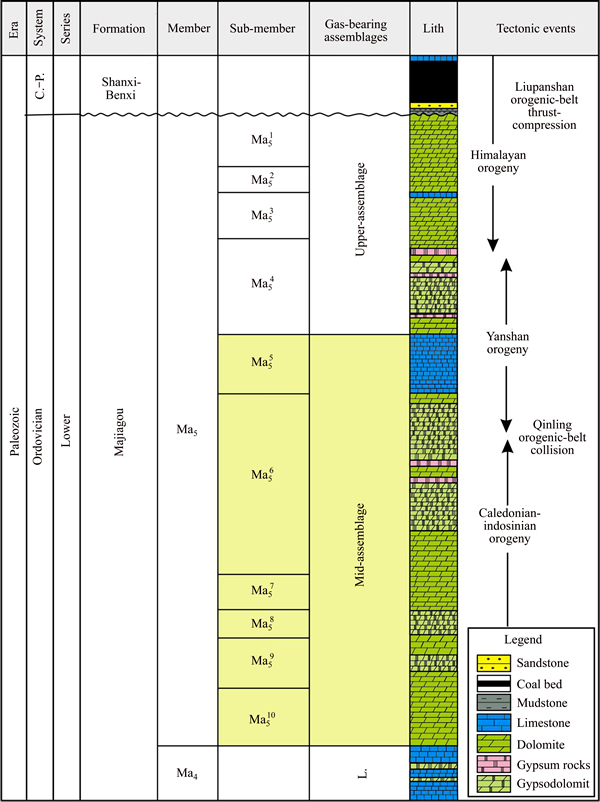
Figure 2 Stratigraphic column of study Formations (The study formation is highlighted in light yellow. Letters denoted in the Formation column are part of the subsurface nomenclature. C.=Carboniferous; Era=Erathem; L.=Lower; Lith=lithology; P.=Permian)
3 Sampling and analysis methods
3.1 Sample collection
Ma55 and the local portion of Ma57 and Ma59 are a well-developed dolomite reservoir, and the powder-coarse crystalline dolomite is the main type of its lithology. In order to fully discern the characterization and formation mechanisms of natural fractures and their significance to hydrocarbon accumulation, this paper not only estimates some fundamental aspects of present-day fractures, but also analyzes fluid inclusions in fracture-filling cement, the relative timing of natural fractures, the hydrocarbon accumulation and the configuration of pathway systems.
The main control factors on fractured distribution in deep hydrocarbon reservoirs may be distinguished using criteria such as fracture intensity, spacing, fillings, and others [1, 29, 30]. According to the mid-assemblage stratigraphic distribution characteristic, ranges of wells, and the gas-bearing location in the reservoir, we have analyzed 18 exploratory wells to estimate the characterization of natural fractures. In addition, the relative timing and formation mechanisms of fractures may be solved as a method to weigh their significance to hydrocarbon accumulation because paleopressure represented by fluid inclusion assemblages (FIAs) in fracture-filling cement may reflect the forming stages and machanisms of fractures, which were calculated with the consideration of the thermodynamic model [31] and the Laser-Raman microspectrometry.
3.2 Experimentation and analysis methods
3.2.1 Microthermometry and fluid inclusion studies
Fluid inclusions have been widely and successfully used in hydrocarbon accumulation geology [32, 33]. Types and characteristics of FIAs were observed by a dual-channel, fluorescence- transmission microscope (Leica DM4500P), and the microthermometric analyses of inclusions were conducted using a Linkam, Inc.-adapted, U.K. THMS 600G-type, gas-flow heating-freezing stage mounted on a Zeiss Axio Scope. A1. The microscope was equipped with a 100× objective (numerical aperture [NA]=0.85) and 10× oculars. The stage was calibrated using the test method for fluid inclusion in sedimentary basins through microthermometry of the petroleum industry standards of China (SY/T 6010-2011). The liquid– vapor homogenization temperature (Th) was accurately calibrated to ±0.5 °C of error ranges through thermal cycling using the initial heating rate of 5 °C/min, and adjusted to 2 °C/min near uniform state.
FIAs trapped in fracture-filling cement contain coexisting two-phase, liquid-rich gaseous hydrocarbon inclusions, single-phase aqueous inclusions, and slight bituminous gaseous hydrocarbon inclusions in Ma55–Ma510 at room temperature (Figures 3 and 4). The two-phase gaseous hydrocarbon inclusions contain 5% to 10% (vol.) vapor and range from an approximate oval to irregular in shape. The single-phase aqueous inclusions are less than 1 to 10 μm in size (Figure 3). FIAs reflecting the relative timing of natural fractures may have two petrographic characteristics as follows: 1) the cements in the fracture such as calcite cement, quartz-cement bridges, and euhedral quartz cement are defined as isolated cement occurrences that connect across fracture walls and typically grow with the c crystallographic axis, oriented probably perpendicular to the fracture walls [34]; and 2) the core of cementation is composed of subparallel trails of FIAs oriented parallel to the fracture walls [32, 35].
3.2.2 Laser-Raman spectrometry
Laser-Raman spectroscopy provides an unambiguous identification of composition in fluid inclusions [33, 36], and the spectral features of the methane (CH4) Raman spectrum may be used to determine the pressure in the fluid inclusion [37]. The paleo-fluid composition and paleopressure were calculated using the Raman spectroscopic analyses of CH4 within aqueous fluid inclusions.
Figure 3 Photomicrographs of representative fluid inclusions under transmitted light and ultraviolet light observed in study area taken at room temperature:
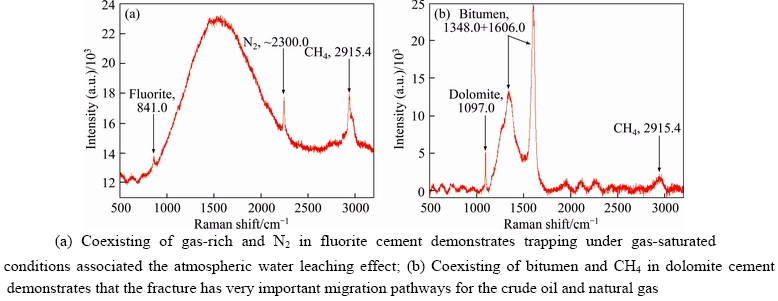
Figure 4 Raman spectrum showing Raman stretching (ν1) band for CH4 (2915.40 cm–1), bitumen (1348.0 and 1606.0 cm–1), dolomite (1097.0 cm–1), fluorite (841.0 cm–1) and N2 emission lines (±2300.0 cm–1) collected simultaneously:
We cannot identify the pressure of all inclusions using the determined Th. This is because the movement of the vapor bubbles in some of the inclusions reduces the analysis accuracy.
Micro-Raman spectra analyses were conducted in the Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Petroleum Accumulation Geology in China using a Renishaw inVia Reflex (532-nm) spectrometer, with 1200 grooves/mm gratings, 10 s/6 times superimposed scanning speed, and a spectrometer slit width of 20 μm at a controlled temperature of 22 °C and a controlled relative humidity of 50%. Excitation was provided using a 514.5 nm Laser 785-linefocus Ar+ laser. At the source, the laser power was 20 mW. The detector was an electronic Renishaw CCD. The characteristic peaks of laser Raman spectrograms show that gaseous composition in inclusions is basically dominated by CH4 in different Formations; meanwhile, the measured peak position for the nitrogen (N2) ±2300 cm–1 lines (shown in Figure 4(a)) indicates that part of the N2 resource was from the eluviation and dissolution of ancient meteoric water.
3.2.3 Numerical simulation
Based on the Th, salinity of the aqueous fluid, and the equation of state of DUAN et al [31] on the thermodynamic model for calculating the gas-phase composition of methane-bearing aqueous fluids, the method and technique for restoring paleopressure are effective [31, 32]. The H2O–NaCl– CH4 system and the vapor phase through pure CH4 may be assumed in fluid inclusions while this formula will be put into use [33]. Burial- and temperature- history models for the bottom of Ma55–Ma510 were recalculated using the one-dimensional basin- modeling program PetroMod 12 (USA Schlumberger, Inc.), available vitrinite-reflectance, wellbore-temperature data [38, 39], and the highest Th were used as an evaluation criterion for the maximum burial temperature (Figure 5(a)).
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Characterization of reservoir space
Reservoir space consists of caverns, fractures and pores by means of observation and analysis of cores and casting thin (Figure 6), where the cavern includes dissolved pores and dissolved cavities (Figures 6(a), (b)), fractures of multiple types are shown in the shape of pore-cave-fracture(Figures 6(c), (d)) (detailed later in this paper), and the pores mainly contain intergranular pores, intercrystal pores and intragranular pores (Figures 6(d), (e)). The matrix is mainly composed of coarse- and fine-crystalline dolomite, and euhedral and semi-euhedral crystalline calcitic dolomites occurring in the LOMOB (Figure 6(f)). Its pore types are mainly intercrystal pores, second dissolved pores and fractures by quantitative statistics (Figure 7). But the scale of pores is evidently different in different horizons, where intergranular pores and dissolved pores take 69.51% and 23.93% in Ma55–Ma56, and occupy 55.54% and 35.96% in Ma57–Ma510, respectively.
4.2 Types and development characteristics of fractures
4.2.1 Nearly vertical fractures
Nearly vertical-forming, nearly vertical fractures exhibit characteristic vertical growth increments and are parallel to the core axis. Of the three natural fracture types, nearly vertical fractures appear to have the greatest apertures. The fracture surface is relatively flat and vertically extended over a large distance. The width range of fractures is 1–15 mm, and they are also observed throughout some cores of exploratory wells (Figures 8(a)–(d)). The filling characteristics possess very significant difference, and therefore calcite is interpreted as a primary filling (Figures 8(a), 9(a), 9(b)), followed by black asphalt (Figures 8(b), 9(a)), and a few are unfilled (Figures 8(c), (d)).
4.2.2 Oblique fractures
The angle between the fracture and the core axis is defined as alpha (α), and thus oblique fractures may be further subdivided into the low- angle fractures (30°<α<45°) and the high-angle fractures (45°<α<60°). Restricted by the cores diameter, the length of the fracture is usually no more than 13 cm on a core scale. Based on the width and types of fillings of the oblique fracture, they may be subdivided into three types: calcite- filling oblique fractures (Figures 9(a), (b), (c)), asphalt-filling oblique fractures (Figures 9(b), (d)) and gypsum-filling oblique fractures (Figures 9(d), (e)). The characterization of fracture-filling cement is of calcite-semi-filling and/or full-filling, and asphalt-semi-filling in oblique fractures(Figures 8(c), (d); Figures 9(a), (b)). The width ranges filled by calcite and asphalt extend from 2 to 18 mm. Asphalt is mainly distributed along the low- angle fracture zone (Figures 9(b), (d)), whereas gypsum is seen in a small amount of high-angle fractures, and found in Ma56and Ma58, where it is dominated by gypsum-salt rocks (Figures 9(d), (e)).
4.2.3 Horizontal fractures
Horizontal fractures are more developed, including those roughly perpendicular to the core axis of horizontal fractures (Figure 3(e)) and highly-developed bedding-parallel pressolutional stylolites (Figure 8(f)), and they range from 1 to 7 mm in width. Fillings in fracture are mainly argillaceous and asphaltene, and its filling patterns are semi-filling and unfilling. Calcsparite are also occasionally observed in fracture cement(Figures 8(e), 9(f)). Pressolutional stylolites in these observations of core wells have varying degrees of development, especially in Ma55 and Ma57, and its linear density approximately attains 8 m–1, but the fracture width is no more than 0.1–2.0 mm (Figure 10(b)).
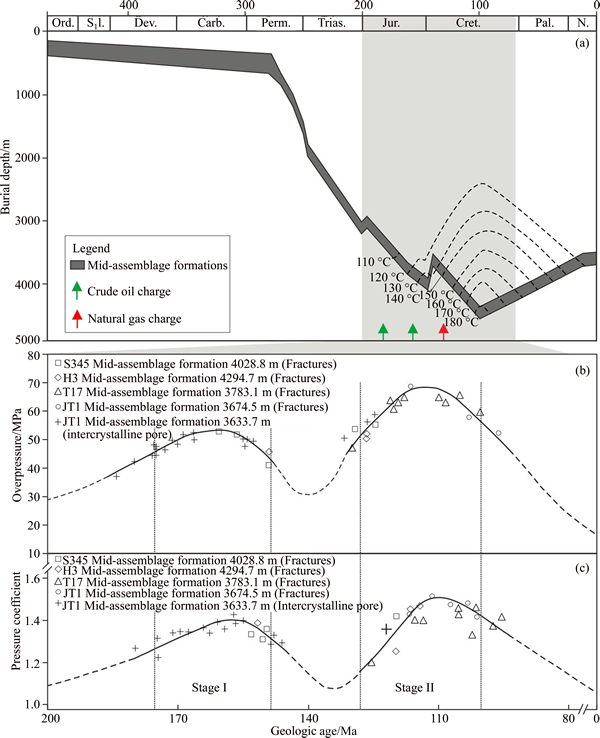
Figure 5 One-dimensional burial history model of Ma55–Ma510 in well S-272 (a), overpressure and pressure coefficient (b) and evolution models of Ma55–Ma510, showing an apparent overpressure development from 175 Ma to the present, illustrating varying pressure conditions during fracture opening and growth (c) (The dashed line represents the tendency of the overpressure and pressure coefficient without measured data. Carb.=Carboniferous; Cret.=Cretaceous; Dev.=Devonian; Jur.=Jurassic; N.=Neogene; Ord.=Ordovician; Pal.=Paleogene; Perm.=Permian; Trias.=Triassic)
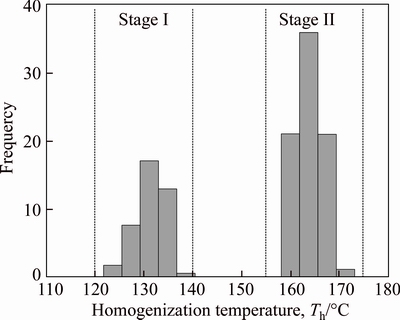
The fracture is additionally subdivided into two aspects so that the formation mechanism may be conveniently interpreted. Meanwhile, the development characteristic for natural fracture may be shown by a relatively accurate description and quantitative statistics. These two aspects include the following: 1) nearly vertical fractures and high-angle fractures, and 2) low-angle fractures and horizontal fractures. Therefore, the fracture density refers to the linear density of the fractures, which is defined herein as the number of the fractures in the unit length within a single layer, and the average core recovery reaches 97% in vertical wells. The density of low-angle fractures and horizontal fractures in Ma55, Ma56, Ma57 and Ma59-10 is 0–60 m–1, 0–70 m–1, 6–85 m–1, 6–85 m–1, respectively, and the peak value is 36–40 m–1, 6–20 m–1, 6–30 m–1, 6–40 m–1, respectively (Figure 10(a)). Considering the development degree of low-angle fractures and horizontal fractures, high-angle fractures and nearly vertical fractures are lower in the study area. The density of nearly vertical fractures and high-angle fractures in Ma55, Ma56, Ma57 and Ma59–10 is 0–35 m–1, 0–40 m–1, 0–30 m–1, 0–30 m–1, respectively, and the peak value is 6–10 m–1, 3–15 m–1, 5–10 m–1, 11–15 m–1, respectively (Figure 10(b)). The fracture density may not only help to improve the reservoir quality and high permeability quality, but also indicate that the closer the Upper Paleozoic coal-measure source rocks are, the greater the fracture density from Ma55–Ma510 is (Figure 10).

Figure 6 Photographs of characteristics and types of reservoir space in cores and casting thin:

Figure 7 Histogram of pore types in reservoir space in Ma55–Ma510 (Inter P.=Intergranular pores; Intra P.= Intragranular pores; ICP.=Intercrystal pores; DP.= Dissolved pores; F.=Fracture; n=point number)

Figure 8 Photographs of selected filling characteristics and types of fractures in cores:
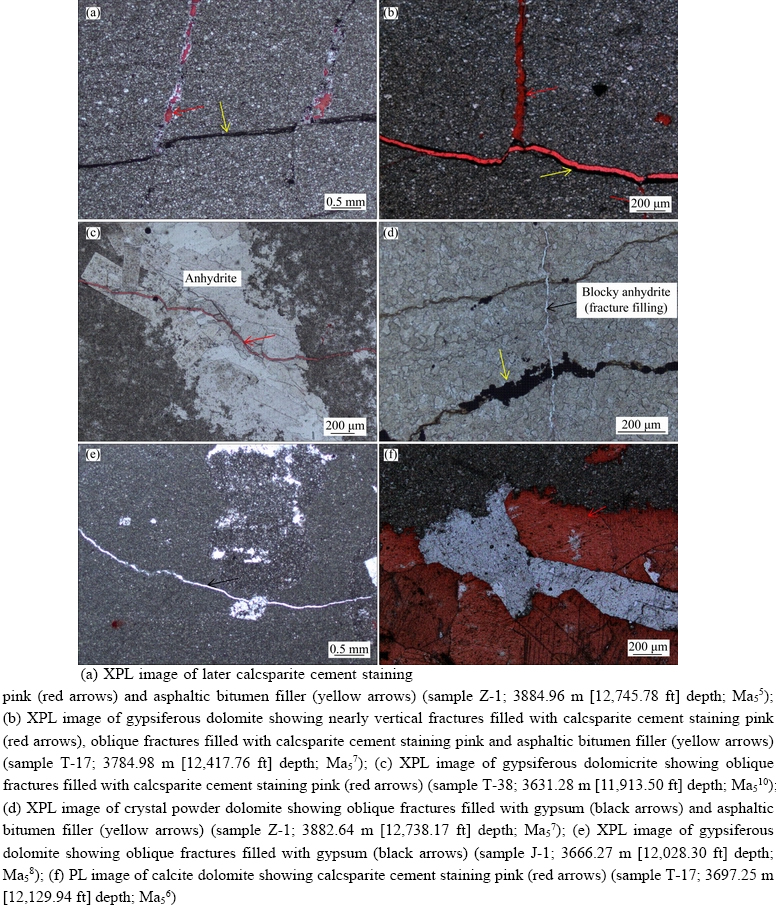
Figure 9 Photomicrographs and casting thin images of selected filling characteristics in partial fractures of Ma55–Ma510 under plane-polarized light (PL), and cross-polarized light (XPL):

Figure 10 Histogram of linear density in cores samples in Ma55–Ma510:
4.3 Relative timing of natural fractures
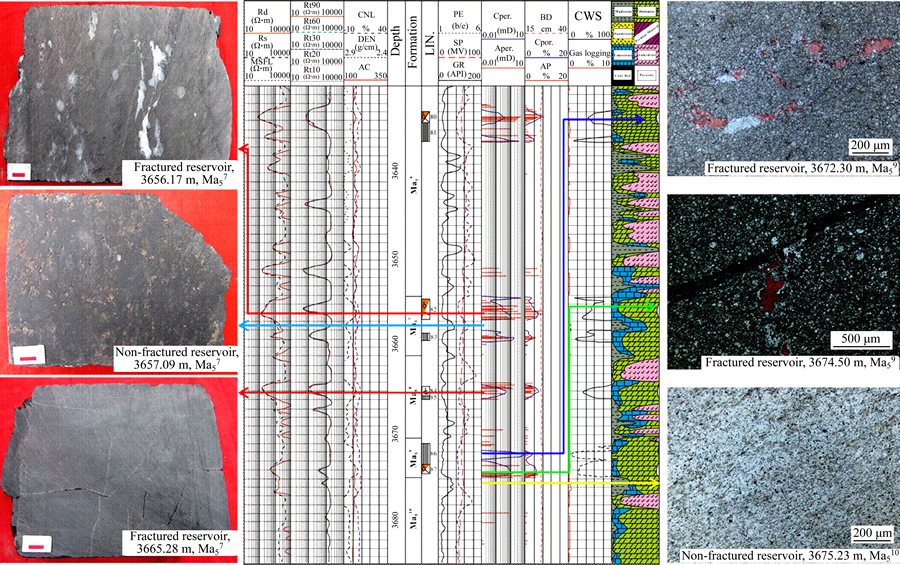
Figure 8 shows that the early oblique fracture (O1) is cut by the paulopost development for nearly vertical fractures (V1 and V2); and the later oblique fracture (O2) would stop growing until near the nearly vertical fracture (V2), which may cut the nearly vertical fracture (V1) afterwards. We believe that the nearly vertical fracture (V2) may have the latest development compared with the others (Figure 11). Based on the cutting relationship between fractures, the sequence of fracture development may be determined, namely, O1 Figure 11 Sketch map of interaction cutting relations and their stage division shown in Figure 3(d) core image (Some of uncertainties regarding the uncolored mesh fractures through the observation of core scale. O1=Early oblique fractures; O2=Later oblique fractures; V1=Early nearly vertical fractures; V2=Later nearly vertical fractures) The longitudinal axis of FIAs is nearly parallel to the fracture surface that may be selected in this paper. Measured Th from brine inclusions associated with gaseous hydrocarbon inclusions ranges from approximately 110 to 180 °C throughout the sampled wells, and its peak values are between 125–140 °C and 155–175 °C (Figure 12). Several samples show clear trends in Th from the oldest to the youngest in fracture-filling cement, as determined by variations in fluid temperature. To determine the relative timing of natural fracture opening and the gas charge of the reservoir, we correlated these temperature trends with burial- temperature models obtained using available thermal maturity and pore-fluid pressure data from J-1 and S-396 wells. Based on this fluid inclusion data, the detailed model of paleotemperature and time-temperature burial history, the relative timing of natural fractures would have been formed during the Mid-Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. Thus, considerable fractures developed during the Early Cretaceous period may reveal favorable pathways and excellent reservoir space for gas accumulation (Figure 5). Figure 12 Histogram of homogenization temperature (Th) in brine inclusion samples in coexistence with hydrocarbon inclusions in mid-assemblage formations reservoir of fractures and intercrystal pores 4.4 Formation mechanisms for natural fractures 4.4.1 Tectonic formation mechanism Nearly vertical fractures are characterized by relatively flat edge, long-extension, one-to-one correspondence orientation and systems (Figures 8(a), 8(b); 9(b)), which may be developed under the condition of tectonic compression and mechanical stress. During the Late Cretaceous-Paleogene, the Ordos Basin might have suffered from a NNE-SSW trending horizontal tectonic compression [40]; therefore, the nearly vertical fractures are mainly controlled by the comprehensive effect of tectonic and stress factors. 4.4.2 Diagenetic formation mechanism Our data show that some of the distribution of fractures may be limited by stratigraphic sequence; meanwhile, most of the fractures are nearly parallel to the fracture surface and to a bifurcate phenomenon by chance (Figrues 8(e), 8(d); 9(d)). The horizontal fractures and parts of low-angle fractures in oblique fractures may have suffered from compaction, dehydration shrinkage, corrosion and recrystallization in the sediment deposition, burial, and later diagenetic process. We attribute these fracture developments to the diagenetic formation mechanism. 4.4.3 Compound formation mechanism A substantial research effort has been undertaken on gas sources of the LOMOB, which may belong to a mixture of the coal-type gas and the oil–associated gas, and furthermore, the coal-type gas generation and expulsion from the Permo-Carboniferous Shanxi-Benxi Formations of Upper Paleozoic reached its peak during the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous [19, 23] (Figure 2). Present-day pressure of the Permo-Carboniferous Shanxi-Benxi Formations increases gradually from 9 to 20 MPa (1305–2900 psi) [41]. Trapping- pressure estimates of the fluid inclusion of 35–68 MPa (5076–9862 psi) (Figure 5(b)) indicate that paleopressures are approximately triple as high as present-day values close to the maximum burial and at the time of initial fracture growth. Our results show that paleopressures had reached peaks at the time that fracture growth began and that these high pressures were associated with the presence of a free, methane-rich hydrocarbon phase (Figure 4(b)). Two major stages could be divided and would be consistent with fracture formation and gas charge based on the recovery paleo-fluid pressures. Stage I indicates that high pressure in fractures is mainly due to a relatively closed pathway system in the Early Jurassic when the Permo-Carboniferous source rocks tended to migrate and accumulate after entering the critical threshold of hydrocarbon generation, which is consistent with the yellow- green fluorescence of asphalt (Figures 9(d), 13). In the early Yanshan orogeny, progressive extension for natural fractures may form the predominant hydrocarbon migration pathway and be further extended as faults under the differential stress. Therefore, the high pressures gradually decrease to near-normal pressures with an increase in the porosity and permeability of the fracture. Stage II is that large-scale, compound genetic fractures were developed by overpressure-strong overpressure. The link between strong overpressure and kerogen pyrolysis gas generation and charge that can be inferred is also supported by our results, that is, there is little bitumen in fractures and massive gaseous hydrocarbon inclusions in calcsparite cement (Figure 8(b)). Trapping instantaneous fluid pressure suggests that fracture formation is concurrent with gas generation and charge close to the maximum burial depth, and the migration of natural gas would persistently move forward under the pressure- difference gradient of resource-reservoir. More micro-fracture systems, wider aperture and farther extent occur predominantly through the early faults and fractures induced from overpressure during gas charge. The diameter of the natural gas molecule is far less than the oil molecular diameter, and therefore the standard pathway system and reservoir space greatly lower. Furthermore, the efficient fractured- porous and fractured-porous-hole reservoir are well developed in the study area (Figures 9(e), 9(f)). Therefore, the compound formation mechanism is not only induced by tectonization and diagenesis, but also overpressure during gas generation and charge could favor fracture opening and growth. 4.5 Significance of natural fractures to hydrocarbon accumulation As a significant vertical migration channel during gas charge, a fault around T-74 well cut through the Upper Paleozoic coal-measure source rocks in Shanxi-Benxi Formations upward and Ma55–Ma510 downward, effectively connects source rocks with reservoirs up and down (Figure 13). Ma57, Ma59, and Ma510 near the denudation plane were exposed to the earth’s surface, which had undergone a long period of the eluviation and dissolution of ancient meteoric water. Insoluble rocks such as argiloid and gypsiferous rocks in Ma56 and Ma58 formed effective isolated intervals. Due to palaeogeomorphology being high in the west and low in the east, Ma57 and Ma59 may be more prone to bedding dissolution and develop longer-distance fractures and larger-dissolved pores and cavities, providing important paths for the large-scale migration of natural gas (Figure 6). Furthermore, the transporting properties of dissolved pores-fractures have been revealed by the yellow–green fluorescence in fractures and have also revealed permeable, connected sand bodies connecting hydrocarbon generation in the center and accumulation area (Figures 3(c), 3(d); Figure 13). Scales of a near-source vertical pathway system and distal horizontal pathway system progressively became larger with the continuous migration and charging of natural gas during the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous. Connected fractures of the multistage tectonic movement and dissolution and gas charge, and dissolved pores and cavities together, constitute the three-dimensional pore-cave-fracture network pathway systems, with faults serving as the dominant charge paths of highly pressurized gas (Figure 13). The frequently-appearing gas shows in Ma57 and Ma58 of J-1 well by the comprehensive logging interpretation and logging display have been proven effective with the fractured layers in the continuous observation of core (Figure 14). Meanwhile, a larger density of fractures have developed in the layer of gas showing, which is based on the casting and conventional thin section inspection data (Figure 14). At the fractured reservoir, the porosity and permeability of the calculation and analysis have an obvious increasing trend (Figure 14), which is regarded as the dominant target area for distinguishing good reservoirs. The porosity of the reservoir in Ma55–Ma510 shows no obvious exponential relationship with the permeability in Figure 15. And in comparing fractured reservoir and fractured-porous reservoir with the porous reservoir, the former porosity values are 5.7%–7.8% (Figure 15(a)) if the permeability value ranges from 100 to 101 mD, while the latter porosity values are 4.5%–5.2% (Figure 15(b)). The results of gas testing show that there are 44.97×104 m3 of gas production per day (44.97×104 m3/d) in Ma56 of L-28 well and 127.98×104 m3 of gas production per day (127.98×104 m3/d) in Ma57 of T-74 well, which proves that the interconnected systems of dissolved pores-fractures effectively increase the reservoir space (Figure 13). Therefore, fractured, fractured- porous and pore-cave reservoir are vitally better than porous reservoir under the same permeability. Such a result has revealed that the fracture in carbonate reservoirs plays a decisive role in improving carbonate reservoir quality. The connectivity of the fracture network is in favour of the mutual contact and reaction of oil, gas and water so that dissolved pores and cavities could thus contribute significantly to an increase in permeability and porosity during both gas charge and production. Meanwhile, the thermochemical sulfate reduction (TSR) and its products for hydrogen sulphide plays an important role in the dissolution of carbonate reservoirs after being dissolved in formation water [42]. Although TSR may be seen in local layers of the study area [38], dissolution is more intense under the acidic water–rock interaction (Figures 9(e), (f); Figure 13). These dissolution pores and fractures of the fracture-pore type reservoir in Ma55–Ma510 will not only help in strategizing the future drilling activities, but will also be useful in future exploration studies of modelling the hydrocarbon column height, top seal integrity, and migration and accumulation of hydrocarbon. Figure 13 West-to-east cross section of Ordos Basin (migration direction is indicated by red arrows. C3b=Upper Carboniferous Benxi Formation; P1t=Lower Permian Taiyuan Formation; P1s=Lower Permian Shanxi Formation) Figure 14 Coupling relationship between comprehensive logging interpretation and development degree of fractures of J-1 well (AC=Acoustic; AP=Analysis porosity; BD=Borehole diameter; CNL=Compensated neutron log; Cper.=Computation permeability; Cpor.=Computation porosity; CWS=Computation water saturation; DEN=Density; GR=Natural gamma ray; LIN.=Logging interpretation conclusions; MSFL=Microspherically focused log; PE=Photoelectric absorption coefficient; Rd=Deep investigate double lateral resistivity log; Rs=Shallow investigate double lateral resistivity log; Rt=True formation resistivity; SP=Spontaneous potential) Figure 15 Cross plots of measured permeability vs porosity for carbonate rocks from Ma55–Ma510: 5 Summary and conclusions Cores and casting thin section images demonstrate the specific textures, revealing types of fractures and cement precipitation concurrent with fracture opening and growth. Based on the characterization of natural fractures, temperatures, composition and paleopressure of FIAs trapped in fracture, the relative timing and formation mechanisms of natural fractures, and their significance to hydrocarbon accumulation have been drawn from this study. Natural fractures may be divided into three main types in Ma55–Ma510. These types of fractures include nearly vertical fractures, oblique fractures and horizontal fractures. Thus, the nearly vertical fractures are mainly driven by the comprehensive effect of tectonic and stress factors. The horizontal fractures and parts of low-angle fractures in oblique fractures are induced by the diagenetic formation mechanism due to compaction, dehydration shrinkage, corrosion, recrystallization, etcetera. While the calculated paleopressure for methane-rich aqueous inclusions of 35–68 MPa (5076–9862 psi) indicates that the fracture growth is consistent with gas maturation and charge and the high-angle fractures in oblique fractures are caused by the compound formation mechanism, which are induced by tectonization and diagenesis. Additionally, overpressure during gas generation and charge could favor fracture opening and growth. The fractures to hydrocarbon accumulation may have a significantly positive effect on improving the reservoir permeability and porosity quality. Therefore, the protracted growth of a pervasive fracture system is not only the consequence of various formation mechanisms but also intrinsic to quasi-continuous accumulation reservoirs. Acknowledgments We are grateful to reviewers for the improvement of the submitted article. In particular, we acknowledge Changqing Oilfield Company of PetroChina for the help provided during the research work. References [1] AWDAL A, HEALY D, ALSOP G I. Fracture patterns and petrophysical properties of carbonates undergoing regional folding: A case study from Kurdistan, N Iraq [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 71: 149–167. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.12.017. [2] LAUBACH S E. Practical approaches to identifying sealed and open fractures [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2003, 87(4): 561–579. DOI: 10.1306/11060201106. [3] ABEDI B, KHARRAT R. Study the effect of fracture inclination, spacing and intensity on polymer flooding efficiency [J]. J Nat Gas Sci Eng, 2016, 34: 645–649. DOI: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.07.007. [4] M [5] LIU Shi-qi, SANG Shu-xun, ZHU Qi-peng, LIU Hui-hu, GAO He-feng. Structure and production fluid flow pattern of post-fracturing high-rank coal reservoir in Southern Qinshui Basin [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(10): 3970–3982. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-014-2385-6. [6] FERN [7] BISDOM K, GAUTHIER B D M, BERTOTTI G, HARDEBOL N J. Calibrating discrete fracture network models with a carbonate three-dimensional outcrop fracture network: Implications for naturally fractured reservoir modeling [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2014, 98(7): 1351–1376. DOI: 10.1306/02031413060. [8] ZAHM C K, HENNINGS P H. Complex fracture development related to stratigraphic architecture: Challenges for structural deformation prediction, Tensleep Sandstone at the Alcova anticline, Wyoming [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(11): 1427–1446. DOI: 10.1306/08040909110. [9] ZEEB C, GOMEZ-RIVAS E, BONS P D, BLUM P. Evaluation of sampling methods for fracture network characterization using outcrops [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(9): 1545–1566. DOI: 10.1306/02131312042. [10] BISDOM K, BERTOTTI G, HAMIDREZA M N. A geometrically based method for predicting stress-induced fracture aperture and flow in discrete fracture networks [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(7): 1075–1097. DOI: 10.1306/ 02111615127. [11] FAN Jian-ming, QU Xue-feng, WANG Chong, LEI Qi-hong, CHENG Liang-bing, YANG Zi-qing. Natural fracture distribution and a new method predicting effective fractures in tight oil reservoirs of Ordos Basin, NW China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(5): 806–814. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1876- 3804(16)30096-9. [12] ZENG Lian-bo, LI Zhong-xing, SHI Cheng-en, WANG Zheng-guo, ZHAO Ji-yong, WANG Yong-kang. Characteristics and origin of fractures in the extra low-permeability sandstone reservoirs of the upper triassic Yanchang formation in the Ordos basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(2): 174–180. http://www.geojournals.cn/ dzxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20070222&flag=1&journal_id=dzxb&year_id=2007. [13] GUO Ling, JIA Chao-chao, DU Wei. Geochemistry of lower Silurian shale of Longmaxi Formation, Southeastern Sichuan Basin, China: Implications for provenance and source weathing [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23: 669–676. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3112-2. [14] BAI Yu-bin, ZHAO Jing-zhou, ZHAO Zi-long, YIN Yue-yue, TONG Jiang-nan. Accumulation conditions and characteristics of the Chang 7 tight oil reservoir of the the Yanchang Formation in Zhidan area, Ordos Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 34(5): 631–639. DOI: 10.11743/ ogg20130508. [15] FU Jin-hua, DENG Xiu-qin, WANG Qi, LI Ji-hong, QIU Jun-li, HAO Le-wei, ZHAO Yan-de. Compaction and hydrocarbon accumulation of Triassic Yanchang Formation Chang 8 Member, Ordos Basin, NW China: Evidence from geochemistry and fluid inclusions [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 48–57. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30007-1. [16] TAN Yong-jie, QIU Rui-zhao, XIAO Qing-hui, ZHOU Su. Indosinian movement characteristics and its significance in China and neighboring areas [J]. Coal Geology of China, 2014, 26(8): 8–14. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2014. 08.03. [17] PANG Chong-you, ZHANG Ya-dong, WANG Jing, WU Tie-ling. Structural features of the middle section and its petroleum exploration prospects in the west margin of Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(2): 274–285. http://en. cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XDDZ201602003.htm. [18] YANG Jun-jie. Tectonic evolution and petroleum distribution of Ordos Basin [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002: 228. (in Chinese) [19] ZHAO Jing-zhou, CAO Qing, BAI Yu-bin, ER Chuang, LI Jun, WU Wei-tao, SHEN Wu-xian. Petroleum accumulation: From the continuous to discontinuous [J]. Petroleum Research, 2017, 2(2): 131–145. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.ptlrs.2017.02.001. [20] ZHAO Jing-zhou, LI Jun, CAO Qing, BAI Yu-bin, ER Chuang, WANG Xiao-mei, XIAO Hui, WU Wei-tao. Hydrocarbon accumulation patterns of large tight oil and gas fields [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 34(5): 573–583. DOI: 10.11743 /ogg20130501. [21] ZHAO Jing-zhou, CAO Qing, BAI Yu-bin, ER Chuang, LI Jun, WU Wei-tao, SHEN Wu-xian. Petroleum accumulation from continuous to discontinuous: Concept, classification and distribution [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 145–159. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201602001. [22] ZHAO Jing-zhou, ZHANG Wen-zheng, LI Jun, CAO Qing, FAN Yuan-fang. Genesis of tight sand gas in the Ordos Basin, China [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 74: 76–84. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.03.006. [23] LI Jun, ZHAO Jing-zhou, WANG Da-xing, SUN Liu-yi, REN Jun-feng, WU Chun-ying, WU Wei-tao, ZHAO Zi-long, QU Fu-tao. Genesis and source of the Ordovician mid-assemblage natural gas in the east side of the central paleo-uplift, Ordos Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(7): 821–831. DOI: 10.7623/syxb201607001. [24] YANG Hua, LIU Xin-she, ZHANG Dao-feng. Main controlling factors of gas pooling in Ordovician marine carbonate reservoirs in the Ordos Basin and advances in gas exploration [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2013, 33(5): 1–12. DOI: 10.3787/j.issn. 1000-0976.2013.05.001. [25] HUANG Zheng-liang, CHEN Tiao-sheng, REN Jun-feng, BAO Hong-ping. The characteristics of dolomite reservoir and trap accumulation in the middle assemblages of Ordovician in Ordos Basin, China [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(S2): 118–124. http://www.syxb-cps.com.cn/CN/10. 7623/syxb2012S2011. [26] BAO Hong-ping, YANG Chen-yun. Study on microfacies of Majiagou Formation, Lower Ordovician, eastern Ordos, north China [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2000, 2(1): 31–42. DOI: 10.7605/gdlxb.2000.01.004. [27] BAO Hong-ping, ZHANG Yun-feng, WANG Qian-ping, DONG Zhao-xiong, WU Chun-ying, YANG Xi-yan. Distribution and evolution of sedimentary microfacies of submember 5 Majiagou Formation in the Ordos basin [J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2016, 44(5): 16–21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.05.003. [28] ZHANG Zhuang, YANG Xi-yan, DONG Zhao-xiong. Characteristics and genesis of Ordovician Majiagou Submember-55 dolostone in middle assemblage, Ordos Basin [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2016, 21(2): 65–71. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2016.02.008. [29] L [30] ZHAO Wen-zhi, ZHU Guang-you, ZHANG Shui-chang, ZHAO Xue-feng, SUN Yu-shan, WANG Hong-jun, YANG Hai-jun, HAN Jian-fa. Relationship between the later strong gas-charging and the improvement of the reservoir capacity in deep Ordovician carbonate reservoir in Tazhong area, Tarim Basin [J]. Chinese Sci Bull, 2009, 54(20): 3218–3230. DOI: 10.1007/s11434-009-0457-z. [31] DUAN Zhen-hao, MAO Shi-de. A thermodynamic model for calculating methane solubility, density and gas phase composition of methane-bearing aqueous fluids from 273 to 523 K and from 1 to 2000 bar [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(13): 3369–3386. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2006.03.018. [32] FALL A, EICHHUBL P, CUMELLA S P, BODNAR R J, LAUBACH S E, BECKER S P. Testing the basin-centered gas accumulation model using fluid inclusion observations: Southern Piceance Basin, Colorado [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(12): 2297–2318. DOI: 10.1306/05171211149. [33] GUO Xiao-wen, LIU Ke-yu, JIA Cheng-zao, SONG Yan, ZHAO Meng-jun, LU Xue-song. Effects of early petroleum charge and overpressure on reservoir porosity preservation in the giant Kela-2 gas field, Kuqa depression, Tarim Basin, northwest China [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(2): 191–212. DOI: 10.1306/11181514223. [34] BECKER S P, EICHHUBL P, LAUBACH S E, REED R M, LANDER R H, BODNAR R J. A 48-m.y. history of fracture opening, temperature, and fluid pressure: Cretaceous Travis Peak Formation, East Texas Basin [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2010, 122(7, 8): 1081–1093. DOI: 10.1130/B30067.1. [35] GOLDSTEIN R H, REYNOLDS T J. Systematics of fluid inclusions in diagenetic minerals [J]. SEPM (Society for Sedimentary Geology) Short Course, 1994, 31: 199. DOI: 10.2110/scn.94.31. [36] CHEN Yong, BURKE E A J. Laser Raman microspectroscopy of fluid inclusions; theory, method, problems and future trends [J]. Geological Review, 2009, 55(6): 851–861. DOI: 10.16509/j .georeview.2009.06.010. [37] LIN F, BODNAR R J, BECKER S P. Experimental determination of the Raman CH4 symmetric stretching (υ1) band position from 1–650 bar and 0.3–22 °C; application to fluid inclusion studies [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(15): 3746–3756. DOI: https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.gca.2007.05.016. [38] ZHAO Jing-zhou. Development characteristics of gas reservoir of the Ordovician mid-assemblage natural gas in the east side of the central paleo-uplift, Ordos Basin [D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Shiyou University, 2015. (in Chinese) [39] YAO Jing-li, WANG Cheng-cheng, CHEN Juan-ping, GAO Gang, WANG Fei-yan, LI Xiao-feng, LI Jia-ye, LIU Yan. Distribution characteristics of sub-salt carbonate source rocks in Majiagou Formation, Ordos Basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(12): 2115–2126. DOI: 10.11764/ j.issn.1672-1926.2016.12.2115. [40] ZENG Lian-bo, QI Jia-fu, WANG Cheng-gang, LI Yan-lu. The influence of tectonic stress on fracture formation and fluid flow [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(3): 292–298. http://www.earthsciencefrontiers.net.cn/CN/article/searchArticle.do. [41] WANG Zhen-liang, WEI Li, WANG Xiang-zeng, WANG Nian-xi, FAN Chang-yu, LI Yan-jing, ZHAO Xue-jiao, ZHAO Xiao-dong, REN Lai-yi, CAO Hong-xia. Accumulation process and mechanism of Lower Paleozoic gas reservoir in Yan’an area, Ordos Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(S1): 99–110. DOI: 10.7623/ syxb2016S1010. [42] HAO Fang, ZOU Hua-yao. Cause of shale gas geochemical anomalies and mechanisms for gas enrichment and depletion in high-maturity shales [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 44: 1–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo. 2013.03.005. (Edited by YANG Hua) 中文导读 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系中组合裂缝特征及其成藏意义 摘要:近年来中国海相碳酸盐岩油气勘探发现了一批大型油气田,其中鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系马家沟组中组合蕴藏着丰富的天然气资源,储集空间类型主要有裂缝、裂缝-孔隙、孔隙和裂缝-孔洞型储层,输导体系由断层、裂缝、溶蚀孔洞和晶间溶孔构成。然而有关奥陶系中组合裂缝特征、裂缝的形成机制、古压力演化及其成藏意义的报道很少。基于钻井岩心观察、镜下微观分析、流体包裹体系统表征、生烃增压数值模拟等研究结果,结合天然气成藏地质背景,厘定了鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系中组合裂缝特征、形成机制及其成藏意义。研究发现,鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系中组合碳酸盐岩裂缝主要可分为近垂直缝、斜交缝和水平缝3种类型。基于裂缝类型特征和发育的主控因素,裂缝的成因机制归类为构造-成岩机制和复合成因机制。这些裂缝的形成期次主要有2期:第一期为中-晚侏罗世,第二期为早白垩世,且在早白垩世时期大量发育的裂缝成为研究区奥陶系中组合天然气运聚成藏的优势通道和良好储集空间。重点探讨了超压成藏演化所反映裂缝的形成和天然气运聚成藏过程,明确了多期次构造运动叠合和天然气超压-强超压运移充注构筑的裂缝网络体系与奥陶系中组合优势输导能力和良好储集性能的关系,建立了相应的机制与模式,为下一步有利勘探靶区评价及开发部署提供理论指导和地质依据。 关键词:裂缝特征;形成机制;准连续型成藏;奥陶系中组合;鄂尔多斯盆地 Foundation item: Project(2011ZX05007-004) supported by the National Sciences and Technologies, China; Project(41502132) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Received date: 2017-05-26; Accepted date: 2018-06-04 Corresponding author: ZHAO Jing-zhou, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-29-88382785; E-mail: jzzhao@xsyu.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0001- 5963-7733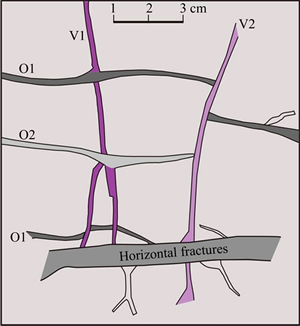

 KEL G H. The modelling of fractured reservoirs: Constraints and potential for fracture network geometry and hydraulics analysis [C]// JOLLEY S J, BARR D, WALSH J J, KNIPE R J. Structurally Complex Reservoirs. London: Geological Society, 2007. DOI: 10.1144/SP292.21.
KEL G H. The modelling of fractured reservoirs: Constraints and potential for fracture network geometry and hydraulics analysis [C]// JOLLEY S J, BARR D, WALSH J J, KNIPE R J. Structurally Complex Reservoirs. London: Geological Society, 2007. DOI: 10.1144/SP292.21. NDEZ-IB
NDEZ-IB
 EZ F, DEGRAFF J M, IBRAYEV F. Integrating borehole image logs with core: A method to enhance subsurface fracture characterization [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2018, 102(6): 1067–1090. DOI: 10.1306/ 0726171609317002.
EZ F, DEGRAFF J M, IBRAYEV F. Integrating borehole image logs with core: A method to enhance subsurface fracture characterization [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2018, 102(6): 1067–1090. DOI: 10.1306/ 0726171609317002. N
N Y A. Making sense of carbonate pore systems [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(9): 1381–1405. DOI: 10.1306/03130605104.
Y A. Making sense of carbonate pore systems [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(9): 1381–1405. DOI: 10.1306/03130605104.

