Soil heavy metal(loid)s and risk assessment in vicinity of a coal mining area from southwest Guizhou, China
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2016年第9期
论文作者:魏朝富 秦樊鑫 钟守琴 黄先飞 庞文品 姜鑫
文章页码:2205 - 2213
Key words:heavy metals; soil contamination; ecological risk; coal mining area; Xingren county
Abstract: Total concentrations of arsenic, lead, cadmium, mercury, nickel, chromium, and copper in the soils from near a coal mine area in southwest Guizhou, China, were measured to evaluate the level of contamination, and the potential ecological risks posed by the heavy metals were quantitatively estimated. Results reveal that all heavy metals/metalloid exceeded the background values for soil environmental quality of heavy metals in Guizhou area. Geo-accumulation index (Igeo) showed that arsenic had the highest contamination level (Igeo=4) among the seven heavy metals/metalloid, and the contamination levels of mercury and lead were also relatively high (Igeo=3). Pearson correlation and cluster analysis identified that mercury, copper and arsenic had a relationship, and their presence might be mainly related to mining activity, coal and oil combustion, and vehicle emissions. Improved Nemerow index indicated that the overall level of heavy metal contamination in the studied area ranged from moderately–heavily contaminated to heavily contaminated level. Potential ecological risk index (RI) analysis manifested that the whole ecological risk level ranged from high degree to very high degree (325.30≤RI≤801.02) in the studied soil samples, and the potential ecological risk factors of heavy metals/metalloid were as follows: Hg > As > Cd > Pb > Cu > Ni > Cr, and the of Hg and As reached very high risk grade.
J. Cent. South Univ. (2016) 23: 2205-2213
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3278-7
QIN Fan-xin(秦樊鑫)1, 2, WEI Chao-fu(魏朝富)1, ZHONG Shou-qin(钟守琴)1,
HUANG Xian-fei(黄先飞)2, PANG Wen-pin(庞文品)2, JIANG Xin(姜鑫)2
1. College of Resources and Environment, Southwest University, Chongqing 400716, China;
2. Key Laboratory for Information System of Mountainous Areas and Protection of Ecological Environment of
Guizhou Province, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550001, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016
Abstract: Total concentrations of arsenic, lead, cadmium, mercury, nickel, chromium, and copper in the soils from near a coal mine area in southwest Guizhou, China, were measured to evaluate the level of contamination, and the potential ecological risks posed by the heavy metals were quantitatively estimated. Results reveal that all heavy metals/metalloid exceeded the background values for soil environmental quality of heavy metals in Guizhou area. Geo-accumulation index (Igeo) showed that arsenic had the highest contamination level (Igeo=4) among the seven heavy metals/metalloid, and the contamination levels of mercury and lead were also relatively high (Igeo=3). Pearson correlation and cluster analysis identified that mercury, copper and arsenic had a relationship, and their presence might be mainly related to mining activity, coal and oil combustion, and vehicle emissions. Improved Nemerow index indicated that the overall level of heavy metal contamination in the studied area ranged from moderately–heavily contaminated to heavily contaminated level. Potential ecological risk index (RI) analysis manifested that the whole ecological risk level ranged from high degree to very high degree (325.30≤RI≤801.02) in the studied soil samples, and the potential ecological risk factors 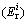 of heavy metals/metalloid were as follows: Hg > As > Cd > Pb > Cu > Ni > Cr, and the
of heavy metals/metalloid were as follows: Hg > As > Cd > Pb > Cu > Ni > Cr, and the  of Hg and As reached very high risk grade.
of Hg and As reached very high risk grade.
Key words: heavy metals; soil contamination; ecological risk; coal mining area; Xingren county
1 Introduction
Heavy metals/metalloid make a significant contribution to environmental pollution as a result of human activities such as mining, smelting, electroplating, energy and fuel production, power transformation, intensive agriculture, sludge dumping, and military operations [1]. The heavy metals in soil are major from the industrial and mining activities [2-3]. Statistics show that over 10 million hectares of land in China are threatened by heavy metal contamination. The heavy metals in soil pose a serious threat to the quality and safety of the agricultural and ecological environment in China [4-6]. According to the National Environmental Protection Twelfth Five–Year Plan for Technology Development, the prevention of soil heavy metal contamination is a key task for China, and typical mining areas are key areas of soil contamination studies. The Soil Environmental Protection and Comprehensive Management Arrangements recently issued by China’s State Council point out that partition assessment and the management of contaminated soil are imminent for typical areas, including mining areas in China.
In the interest of preventing soil heavy metal contamination caused by mining activities, local and international researchers have studied heavy metal contamination in different regions. By determining the total concentrations of toxic metals, ZHOU et al [2] studied soil contamination in the vicinity of the Dabaoshan mine, Guangdong Province, China, and found that the environmental pollution in this area over the past decades has been caused by the associated-contamination of Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb. After further analysis, the authors predicted that the potential environmental risk caused by those metals would increase with time. SUN et al [7] analyzed the spatial distribution of soil heavy metals and variation characteristics of Datong abandoned coal mine area in Huainan city. The results revealed concentration of heavy metal elements exceed the background values by 2.00-36.30 times and characteristics of spatial variation were related to the complex distribution object. JIANG et al [8] investigated distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in reclaimed land in Huainan coal mine. The results showed that the concentrations of heavy metals Zn, Cd, and As in soil from reclaimed coal mine were 4.38, 2.57, 2.20 times that of reference soil, and the highest risk was the Cd concentration in reclaimed soil. YUAN et al [9] examined characteristic of heavy metal concentrations in soil around coal mining area in Suzhou city and discovered that the concentrations of Cr, Cd, Hg and As exceeded the Class I Standard from the National Soil Environmental Quality Evaluation. TEIXEIRA et al [10] conducted a survey on distribution of heavy metals in fluvial sediments of coal mining region of Baixo Jacuí, RS, Brazil, and indicated that the average concentrations of Cu, Fe, Ni, Pb, and Zn in fluvial sediments in the study area were all above the natural soil background levels. SZCAEPANSKA and TWARDOWSKA [11] focused on heavy metal concentrations in the soils around Smolnica coal mining area, Poland. The results manifested the soils near the Smolnica coal mining were polluted by heavy metals. PANOV et al [12] estimated environmental impact of heavy metals in the Donets coal basin and made known the concentrations of Hg, As, Pb, Zn, Cd in numerous soil samples exceeding the National Soil Environmental Quality Standard in Russia. MOHAMMAD et al [13] evaluated heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. The results made clear the average concentrations of Ti, Mn, Zn, Pb, As, Fe, Rb, Sr, Nb and Zr exceeding the world normal averages, in some cases, Mn, Zn, As and Pb exceeding the toxic limit of the respective metals. In a word, numerous soils around coal mining were heavily contaminated with maximum heavy metals throughout the world.
The coal mine region from southwest Guizhou province, China is typical high-arsenic coal mine. Since 1970s, there were close to 3000 people who were poisoned with arsenic through coal burned in this area, and outnumber 100 people died of arsenic poisoning [14]. In the present study, previous studies focused only on arsenic contamination and behavior of arsenic in surface soils and sediments water [15]. However, other metal species in this area are not discussed by researchers and engineers. Therefore, in the present work we have investigated seven heavy metals/metalloid (As, Pb, Cd, Hg, Ni, Cr and Cu) in mining affected topsoil at a coal mine area, and further analyze their environmental behavior and the ecological risk. This work will contribute to future environmental monitoring, management, remediation, and planning for mining in the coal mine zone.
2 Study area
The study area, namely Xingren coal mine zone is located in the southwest Guizhou Province, China. It lies between elevations 1250 m and 1500 m, and latitudes 25°15′49″N and 25°46′58″N, and longitudes 104°54′33″E and 105°33′46″E, with an area of 1785 km2 (Fig. 1). It is a major production base of coals in Guizhou Province with over 40 years of mining history. The climate in the study area is characterized with mild and humid subtropical monsoon climate. The annual average temperature of the region is 15.2 °C and the average annual rainfall is 1300-1450 mm. The prevailing wind direction is from the southwest throughout the year. The mean annual wind speed is 1.96 m/s, and the maximum wind speed is 19 m/s. Xingren County is rich in coal mineral resources, is one of the 200 key coal producing counties,with proven 3.6 billion tons of coal resources reserves;long-term reserves of coal resources are more than 4.5 billion tons yields,and it is named “Xingren Coal Sea”. The geology of this region consists of the natural soil types, loess and dark brown soil are the main geological formations according to the classification and codes for Chinese soil [16]. The land contains cultivated land, planting corn and Coix lacryma–jobi L.

Fig. 1 Study area location and sampling sites
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Soil sample collection
A total of 14 samples (0-20 cm depth) in this area were collected from the vicinity of the high-arsenic coal mining in August, 2014, and one reference soil sample(S15) was collected at the approximate 40 km distance from mine zone. The sampling site locations are shown in Fig. 1. The samples were agricultural soils, and were chosen to be representative of the most common local land uses, including vegetable field, grain field, and land for planting Coix lacryma–jobi L. The soil samples were collected using a stainless steel grab sampler and a plastic scoop, and each sample was a composite of eight to ten sub-samples, making a total sample size of 1.0- 1.5 kg.
3.2 Analytical methods and quality assurance
The soil samples were air-dried and crushed to pass through a 1-mm plastic sieve after removing stones and plant material, and stored in plastic containers for routine laboratory studies. The pH of each sample was measured with a METTLER TOLEDO pH Meter (Model FE20) [17]. The total organic carbon content (TOC) in soil samples was determined by titration method, using FeSO4 after digestion of samples with K2Cr2O7–H2SO4 solution [17]. Basic properties for these samples are given in Table 1. On the basis of the properties, the soils in the study area were typical for loess and dark brown soil, characterized by very high acidity (pH<4.5), and moderate total organic carbon content.
Each soil sample (100-200 mg) was digested in 4 mL of 69% (w/w) HNO3 and 1 mL of 70% (w/w) HClO4 in a stainless steel high-pressure digestion bomb at 140 °C for 6 h. After completely cooling the system, the open vial was transferred to a hot plate (about 190 °C) to evaporate the solution until the volume had decreased to several hundred microliters, then 1.0 mL of 36% (w/w) HF was added and the sample was evaporated again. The HF treatment was repeated several times until the silicate minerals had been completely dissolved. Finally, the residual solution was diluted to 10.0 mL with 0.5% (w/w) HNO3 and filtered through a syringe filter (0.45 μm). As and Hg concentrations were determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS–933, Beijing Jitian). The rest of metal elements were measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (Optima 5300V, PerkinElmer) or by Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (ZEEnit700P , Analytikjena) when elemental concentration was lower than ICP detection limit, in the Center of Analysis and Testing, Guizhou Normal University, China.
, Analytikjena) when elemental concentration was lower than ICP detection limit, in the Center of Analysis and Testing, Guizhou Normal University, China.
Table 1 Basic property and heavy metals concentrations of soil samples in study area

Quality assurance and quality control procedures were performed to ensure reliability of the results. Blanks were used for background correction and other sources of error. All chemicals used in this work were of analytical grade or better. Ultrapure water was used. For each set of 10 samples, a matrix sample spiked with standards was used to determine the accuracy. Each soil sample was analyzed in triplicate (n=3). The relative standard deviations (RSD) were all between 0.02% and 4.76%. The method detection limits of metals were in the range of 0.001-0.10 mg/kg. The spiked recoveries for metals ranged from 91% to 113%. Additionally, standard reference materials purchased from the Center of National Standard Reference Materials (GSS–4/5) of China were analyzed. The analyses were found at 90%-110% of the certified values in the reference materials, and the RSD was <5%.
3.3 Quantification of soil pollution
3.3.1 Cluster analysis
Cluster analysis (CA) of the seven heavy metals was performed to identify the relationship among the heavy metals and to group them according to their possible sources. Using SPSS 20.0 software (IBM, Beijing, China), this study selected relatively homogenous groups of variables through hierarchical cluster analysis. Before the start of the cluster analysis, heavy metal concentrations in each sampling point were standardized by means of Z–scores. The Euclidean distances for similarities were calculated using the following formulae [18]:
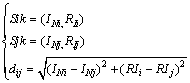 (1)
(1)
A dendrogram was constructed using SPSS 20.0 software environment to assess the cohesion of readily seen clusters. The seven kinds of heavy metals were then divided into groups of different sources.
3.3.2 Geo-accumulation index (Igeo)
To make a comprehensive assessment of soil contamination, the Nemerow index should be applied in this study. However, the traditional Nemerow index, which uses a single factor index method as the basis of the degree of contamination, couldn’t accurately reflect the heavy metal contamination with the impact of human behaviors. Therefore, in this work, the geo-accumulation index, which could reduce the interference of human factors on assessment of soil contamination, is introduced to replace the traditional single factor index. Igeo was introduced by  [19] to assess metal pollution in sediments, and it has been applied in recent pollution studies to enable the qualitative assessment of soil heavy metal contamination [20–21]. Igeo is computed by Eq. (2):
[19] to assess metal pollution in sediments, and it has been applied in recent pollution studies to enable the qualitative assessment of soil heavy metal contamination [20–21]. Igeo is computed by Eq. (2):
 (2)
(2)
where Cn is the heavy metal concentration in the soil samples, and Bn is the geochemical background value in the average shale of the heavy metal element. To reduce the effect of parent rocks on heavy metal concentration and prominent heavy metal contamination in artificial soil, this study selected the geochemical background value (Table 2) as the average background value of elements in Guizhou province soils by referring to previous studies [22-23] and by considering the soil type of the study area. The constant 1.5 compensates for the natural fluctuations of a given metal and for minor anthropogenic impacts. The seven classes of Igeo as proposed by  [19] are as follows: Igeo≤0, uncontaminated (Class 0); 0geo≤1, uncontaminated to moderately contaminated (Class 1); 1geo≤2, moderately contaminated (Class 2); 2geo≤3, moderately to heavily contaminated (Class 3); 3geo≤4, heavily contaminated (Class 4); 4geo≤5, heavily to extremely contaminated (Class 5); and Igeo>5, extremely contaminated (Class 6).
[19] are as follows: Igeo≤0, uncontaminated (Class 0); 0geo≤1, uncontaminated to moderately contaminated (Class 1); 1geo≤2, moderately contaminated (Class 2); 2geo≤3, moderately to heavily contaminated (Class 3); 3geo≤4, heavily contaminated (Class 4); 4geo≤5, heavily to extremely contaminated (Class 5); and Igeo>5, extremely contaminated (Class 6).
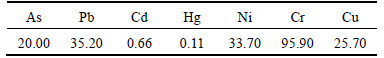
Table 2 Geochemical background values (mg/kg)
3.3.3 Improved Nemerow index (IN)
As Igeo could reduce the effects of parent rocks and prominent artificial effects on soil heavy metal contamination, it is suitable for the evaluation of soil heavy metal contamination in mining area. However, the evaluation of Igeo is only for a single heavy metal contaminant, thus this index cannot provide a comprehensive description of the contamination status of the study area. Thus, an evaluation based on the comprehensive index method is necessary. In this study, the traditional Nemerow index was improved by replacing the single factor index with Igeo. The following Eq. (3) was developed:
 (3)
(3)
where IN is the comprehensive contamination index of a sample; Igeomax is the maximum Igeo value of such sample; and Igeoave is the arithmetic mean value of Igeo. To be consistent with Igeo, the classification of IN was adjusted based on the results proposed by  et al [24]. This classification is as follows: 0N≤0.5, uncontaminated (Class 0); 0.5N≤1, uncontaminated to moderately contaminated (Class 1); 1N≤2, moderately contaminated (Class 2); 2N≤3, moderately–heavily contaminated (Class 3); 3N ≤4, heavily contaminated (Class 4); 4N≤5, heavily to extremely contaminated (Class 5); and IN>5, extremely contaminated (Class 6).
et al [24]. This classification is as follows: 0N≤0.5, uncontaminated (Class 0); 0.5N≤1, uncontaminated to moderately contaminated (Class 1); 1N≤2, moderately contaminated (Class 2); 2N≤3, moderately–heavily contaminated (Class 3); 3N ≤4, heavily contaminated (Class 4); 4N≤5, heavily to extremely contaminated (Class 5); and IN>5, extremely contaminated (Class 6).
3.3.4 Potential ecological risk index (RI)
As soil contaminated with heavy metals can enter the human body through various exposure approaches [25], highly toxic heavy metals in soil can cause serious ecological and health risks [26]. The excessive accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soil can affect food quality and safety and further increase the morbidity of severe diseases, such as cancer, leukemia, and kidney or liver damage [27]. In mining area, which has a high degree of heavy metal exposure, especially arsenic, the assessment of potential ecological risks is necessary. To quantify the potential hazard from soil heavy metal contamination, the RI was calculated in the present study as the sum of all the seven heavy metals. The RI shows the sensitivity of the study area to soil heavy metal contamination and presents potential ecological risks.
The potential ecological risks posed by the heavy metals were quantitatively evaluated using  ’s method [28-29]. These risk indices are calculated as follows:
’s method [28-29]. These risk indices are calculated as follows:
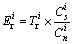 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
where 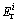 is the potential ecological risk index of an individual metal i;
is the potential ecological risk index of an individual metal i; 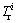 is the toxic–response index for heavy metals i.
is the toxic–response index for heavy metals i.  [28] suggested that appropriate
[28] suggested that appropriate  values for Pb, Cr, Cd, Hg, As, Cu and Ni were 5, 2, 30, 40, 10, 5 and 5, respectively.
values for Pb, Cr, Cd, Hg, As, Cu and Ni were 5, 2, 30, 40, 10, 5 and 5, respectively.  is the measured concentration of metal i at sampling sites s;
is the measured concentration of metal i at sampling sites s;  is the background value (BGV) of heavy metal i in the research area. RI is the potential ecological risk index that results from the combination of multiple metals. The higher the E and RI are, the higher the risk is. Table 3 summarizes the potential ecological risk indices and corresponding risk grades.
is the background value (BGV) of heavy metal i in the research area. RI is the potential ecological risk index that results from the combination of multiple metals. The higher the E and RI are, the higher the risk is. Table 3 summarizes the potential ecological risk indices and corresponding risk grades.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Total contents of heavy metals
Total concentrations of heavy metals (As, Pb, Cd,Hg, Ni, Cr, Cu) in the soil samples varied widely (Table 1); total organic carbon contents ranged from 42.3 to 49.2 g/kg with a mean value of 46.2 g/kg; pH varied from 3.03 to 4.37 (mean value of 3.89), which were all higher than reference soil values. The soil was contaminated by continuous weathering of tailings from a high-arsenic coal mine for more than 40 years, and thus was heavily polluted by As (215.00-609.30, averaging 477.58 mg/kg) followed by Pb (190.79-286.90, averaging 240.61 mg/kg) and Hg (0.32-0.95, averaging 0.71mg/kg), and Cu (85.60-169.57 with 134.09 mg/kg on average) were much higher than local geochemical background values (Table 2), and Cd (0.77-1.58 with 1.09 mg/kg on average), Cr (66.78- 224.05 with 173.63 mg/kg on average) and Ni (54.70- 98.57 with 64.89 mg/kg on average) were higher than local geochemical background values (Table 2).
Inter-element relationships in soil matrix provide information on heavy metal sources and pathways in the geo-environment [30]. In general, correlations between metals agreed with the results obtained by CA. According to the values of Pearson correlation coefficients (Table 4), the extremely significant positive correlation (p<0.01) exists between As vs. Hg (r=0.911, p<0.01), Cu (r=0.946, p<0.01), and between Cu vs. Hg (r=0.890, p<0.01). The significant positive correlation exists between As vs. Pb (r=0.607, p<0.05), Cr (r=0.725, p<0.01), and between Pb vs. Cd(r=0.550, p<0.05), Hg(r=0.598, p<0.05), Cu(r=0.691, p<0.01), and between Hg vs. Cr((r=0.609, p<0.05), and between Cr vs. Cu(r= 0.644, p<0.01). The strong correlation of Hg, Cu and As indicates that the elements were derived from similar sources and also moving together, especially from coal bearing minerals in mining activities. ZHANG et al [31] also reported similar results for source identification of soil inorganic pollutants in China. Negative correlation between soil pH and heavy metal content was observed for the analyzed soils. TOC shows strong positive correlations with As (r=0.946, p<0.01), and Pb (r=0.691, p<0.01), and Hg (r=0.890, p<0.01), especially a linear relationship (r=1.000, p<0.01) between TOC content and Cu was found in current study. The correlations between heavy metal concentrations and soil organic matter content obtained in this study agreed with those of LEE et al [32] and MOHAMMAD et al [13] who indicated that soil organic matter content played a fundamental role in the control of Pb adsorbed soils.
Table 3 Indices and grades of potential ecological risk

Table 4 Pearson correlation coefficients among total content of heavy metals, pH value, TOC content in topsoil samples

4.2 Cluster analysis
Cluster analysis was performed to further divide the clusters of heavy metal contaminants and to analyze possible sources. The results are illustrated in a dendrogram in Fig. 2. The distance cluster represents the degree of association among heavy metals; a low distance cluster value indicates a significant relationship [33]. As shown in Fig. 2, the first group includes Hg, Cu and As, the distance clusters of which are very close, indicating that Hg, Cu and As have a relationship, and their presence might be mainly related to mining activity, vehicle emission, coal and oil combustion. Plastics, batteries, and electronics are also important sources of these elements [34]. As shown in Table 1, the contaminated levels of both As and Hg are relatively high. The second group includes Pb and Cr. According to previous studies [20, 35], this group of heavy metals might be associated with atmospheric deposition because Cr enters soils mainly through deposition and Pb is heavy metal that draw attention to anthropogenic sources, such as metal smelting, oil combustion and mining activity. Given the high contamination level of Pb(Table 1), emissions as well as industrial wastewater and waste gases are the main contamination sources of this group. The third group includes Cd and Ni, the distance clusters of which is a long distant. This manifests that there is no significant relationship for sources of these metals. Cd is mainly from mining, smelting, processing and solid waste [36]. Ni is generally detected in industrial wastewater [37]. As the contamination levels of Cd, Ni and Cr are low in this study, they are unlikely to be directly emitted by coal mining activity. The results of cluster analysis show the same trends as the Pearson correlation results.

Fig. 2 Dendrograms produced by hierarchical clustering
4.3 Overview of Igeo
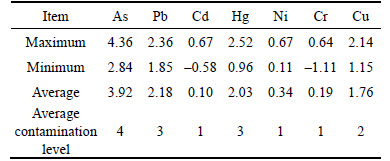
The main calculation results of Igeo in the topsoil samples in the study area are presented in Table 5. The average Igeo values of As, Pb, Cd, Hg, Ni, Cr and Cu are all more than 0. The contamination level of As is categorized as Class 4, heavily contaminated. The contamination levels of Pb and Hg are categorized as Class 3, moderately to heavily contaminated. The contamination level of Cu is categorized as Class 2, moderately contaminated. And the contamination levels of other three metals are categorized as Class 1, uncontaminated to moderately contaminated. This result indicates that the topsoil in the study area has been mostly contaminated with As, Pb, Hg and Cu. The suitability of soils for agricultural uses could be further assessed by using pollution index, such as Nemerow index, which assesses the environmental risk caused by the contaminated soils.
Table 5 Contamination index (Igeo) and level of different heavy metals
4.4 Improved Nemerow index
To quantify the soil heavy metal contamination in the study area, the improved Nemerow index (IN), which describes the integrated contamination levels, was calculated as the sum of the seven heavy metals (Fig. 3).
The IN results at all sampling points indicate the following. 1) In general, the IN value of the study area is between 2 and 4, given the maximum and minimum values of 3.34 and 2.16, respectively. This finding reveals that the overall level of heavy metal contamination in the study area is between moderately– heavily contaminated and heavily contaminated, which indicates serious heavy metal contamination. 2) The IN values of eight sampling points exceed 3, which indicates that the contamination level is heavily contaminated. The distribution of the sampling points with high IN values is similar to that of the sampling points of Hg and As with high Igeo values. Given the high toxicity of Hg and As, the distribution of Hg and As contamination levels have significant effect on the integrated contamination level.3) The uneven distribution of the contamination degree is another important feature of heavy metal contamination in the study area. As shown in Fig. 3, the most polluted areas (IN>2.16) are not distributed in any concentrated area.

Fig. 3 IN of heavy metals in each sampling point
4.5 Potential ecological risk analysis
As a complement to the study on integrated contamination levels, the potential ecological risk of soil heavy metal contamination in the study area was quantified by calculating the potential ecological risk factor ( ) and the potential ecological risk index (RI), which describe the ecological risk level in the area (Table 6). The
) and the potential ecological risk index (RI), which describe the ecological risk level in the area (Table 6). The  results for all sample points show that
results for all sample points show that  values of heavy metals are as follows: Hg>As>Cd> Pb>Cu>Ni>Cr. The average
values of heavy metals are as follows: Hg>As>Cd> Pb>Cu>Ni>Cr. The average  values of Hg and As exceed 160, which reach very high risk grade. The RI results for all sampling points reveal the following. 1) The RI of the study area for all sampling points is from 300 to 800, which shows an overall ecological risk level ranging from very high to extremely high. A total of 14 sampling points have RI values higher 300, which indicates that the ecological risk level in a large portion of the study area is very high. 2) The maximum RI reaches 801.02, with eight sampling points exceeding 600. Table 6 shows that very high ecological risk (RI>600) can be observed mainly in the vicinity of high-arsenic coal mine region. The figure also indicates a certain degree of even distribution, especially these sampling sites (S5, S6, S7, S8, S14) which distance coal mine location, have RI values all lower than 600, and more than 300. (3) RI distribution shows the same trends as the IN results.
values of Hg and As exceed 160, which reach very high risk grade. The RI results for all sampling points reveal the following. 1) The RI of the study area for all sampling points is from 300 to 800, which shows an overall ecological risk level ranging from very high to extremely high. A total of 14 sampling points have RI values higher 300, which indicates that the ecological risk level in a large portion of the study area is very high. 2) The maximum RI reaches 801.02, with eight sampling points exceeding 600. Table 6 shows that very high ecological risk (RI>600) can be observed mainly in the vicinity of high-arsenic coal mine region. The figure also indicates a certain degree of even distribution, especially these sampling sites (S5, S6, S7, S8, S14) which distance coal mine location, have RI values all lower than 600, and more than 300. (3) RI distribution shows the same trends as the IN results.
Table 6 Ecological risk factor and potential ecological risk index of heavy metals in coal mining area

5 Conclusions
This work presents the contamination levels of As, Pb, Cd, Hg, Ni, Cr and Cu in soil of a typical high-arsenic coal mining area in southwest Guizhou (China). The relationship among Hg, Cu, and As revealed that they may be mainly from mining activity, coal and oil combustion, and vehicle emissions. Therein, As poses an extremely serious pollution threat because it shows the highest contamination level (class 4). The contamination levels of Hg and Pb are relatively high (class 3). The contamination levels of the other assessed heavy metals (Cd, Ni, Cr and Cu) are lower moderately contaminated (class 2). The results of the improved Nemerow index indicate that the overall level of heavy metal contamination in the study area ranges from moderately–heavily contaminated to heavily contaminated, and that the contamination level shows an uneven distribution. Analysis of potential ecological risk shows an uneven distribution of ecological risk in the study area. The overall ecological risk level ranges from high to very high.
This work presents important information about soil heavy metal contamination in coal mining area and provides systematic methods for the assessment of heavy metal contamination and the identification of contamination sources in these areas. In future study, the partition of study area based on human health risk and food safety should be considered as a research focus.
References
[1] LI Jing, XIE Zheng-miao, ZHU Yong-guan, NAIDU R. Risk assessment of heavy metal contaminated soil in the vicinity of a lead/zinc mine [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2005, 17(6): 881-885.
[2] ZHOU Jian-min, DANG Zhi, CAI Mei-fang, LIU Cong-qiang. Soil heavy metal pollution around the Dabaoshan mine, Guangdong Province, China [J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(5): 588-594.
[3] LIU Xiang-hong, SUN Lin-hua, CHEN Song. Heavy metal pollution of soil around the gangue hill: A case study from Zhuxiangzhuang Coal Mine, Northern Anhui Province, China [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 356-360: 114-118.
[4] ZHOU Mi, LIAO Bin, SHU Wen-sheng, YANG Bing, LAN Chong-yu. Pollution assessment and potential sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils around four pb/zn mines of shaoguan city, China [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 2015, 24(1): 76-89.
[5] ABDELHAFEZ A A, LI J H. Environmental monitoring of heavy metal status and human health risk assessment in the agricultural soils of the Jinxi river area, China [J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 2015, 21(4): 952-971.
[6] CHENXiu-ling,ZHANGWen-kai,LIMing-hui,LIZhi-zhong. Brief summarization of study on heavy–metal pollution of soil in China [J]. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 2009, 21(6): 8-13. (in Chinese)
[7] SUNXian-bin,LIYu-cheng. The spatial distribution of soil heavy metals and variation characteristics of datong abandoned coal mine area in Huainan City [J]. ScientiaGeographicaSinica, 2013, 13(10): 1238-1244. (in Chinese)
[8] JIANG Pei-long, FANG Feng-man, ZHANG Jie-qiong, LIN Yue- sheng, DENG Zheng-wei, YU Jian. Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in reclaimed land in Huainan coal mine [J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 33(6): 161-165. (in Chinese)
[9] YUAN Xin-tian, ZHANG Chun-li, SUN Qian, WU Yi-chun. Characteristics of heavy metal concentrations in the soils around coal mining area in Suzhou city [J]. EnvironmentalChemistry, 2011, 30(8): 1451-1455. (in Chinese)
[10] TEIXEIRA E, ORTIZ L, ALVES M, SANCHEZ J. Distribution of selected heavy metals in fluvial sediments of coal mining region of Baixo Jacuí, RS, Brazil [J]. Environmental Geology, 2001, 41(1/2): 145-154.
[11] SZCAEPANSKA J, TWARDOWSKA I. Coal mine spoil tips as a large area source of water contamination [J]. Advances in Mining Science & Techudogy, 1987, 2: 267-280.
[12] PANOV B S, DUDIK A M, SHEVCHENKO O A, MATLAK E S. On pollution of the biosphere in industrial areas: the example of the Donets coal basin [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1999, 40(2): 199-210.
[13] BHUIYAN M A H, PARVEZ A, ISLAM A, DAMPARE S B, SUZUKI S. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 173(1/2/3): 384-392.
[14] DING Z H, FINKENLMAN R B. Distribution of high arsenic coals from southwest Guizhou province [J]. Geochimica, 2000, 29(5): 493-494. (in Chinese)
[15] LIU Hong, WU Pan, ZHANG Chi-peng, CAO Zhen-xing, XIE Huan-huan. Characteristics of arsenic distributing in soils irrigated by high–arsenic coal drainage [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2010, 33(8): 57-61. (in Chinese)
[16] LIUHong, WUPan. Vertical distribution characteristics of arsenic in the soils irrigated by high-arsenic coal drainage [J]. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 2014, 28(2): 55-60. (in Chinese)
[17] APOLONIA O,  P. Assessment of TOC–SOM and SOM–TOC conversion in forest soil [J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2012, 12(6): 1767-1775.
P. Assessment of TOC–SOM and SOM–TOC conversion in forest soil [J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2012, 12(6): 1767-1775.
[18] GUAN Yang, SHAO Chao-feng, JU Mei-ting. Heavy metal contamination assessment and partition for industrial and mining gathering areas [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2014, 11(7): 7286-7303.
[19]  G. Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. Geology, 1969, 2: 108-118.
G. Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. Geology, 1969, 2: 108-118.
[20] SHI P, XIAO J, WANG Y, CHEN L. Assessment of ecological and human health risks of heavy metal contamination in agriculture soils disturbed by pipeline construction [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and PublicHealth, 2014, 11(3): 2504-2520.
[21] SRINIVASA G S, RAMAKRISHNA R M, GOVIL P K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils at Jajmau (Kanpur) and Unnao industrial areas of the Ganga plain, Uttar Pradesh, India [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174(1/2/3): 113-121.
[22] NING Xiao-bo, XIANG Wen-hua, FANGXi, YANWen-de, DENGXiang-wen. Heavy metal concentrations and pollution assessment of limestone forests in Huaxi district, Guiyang City [J]. Acta Ecologic Sinica, 2009, 29(4): 2169-2177. (in Chinese)
[23] ZHANG Qing-hai, LIN Shao-xia, LIN Chang-hu. The content characteristics of soil heavy mentals and regional differences study on agricultural non-point source pollution in Guizhou province [J]. EnvironmentalMonitoringinChina, 2011, 27(1): 88-91. (in Chinese)
[24]  U, AHLF W, CALMANO W. Sediment quality objectives and criteria development in Germany [J]. Water Science and Technology, 1990, 28(8/9): 307-316.
U, AHLF W, CALMANO W. Sediment quality objectives and criteria development in Germany [J]. Water Science and Technology, 1990, 28(8/9): 307-316.
[25] BADE R, OH S, SHIN W S, HWANG I. Human health risk assessment of soils contaminated with metal(loid)s by using DGT uptake: A case study of a former Korean metal refinery site [J]. Humanand EcologicalRiskAssessment, 2013, 19(3): 767-777.
[26] DONG Xiao-qing, LI Chao-lin, LI Ji, WANG Jia-xin, LIU Su-ting, YE Bin. A novel approach for soil contamination assessment from heavy metal pollution: A linkage between discharge and adsorption [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 175(1/2/3): 1022-1030.
[27] KHAN M N, WASIM A A, SARWAR A, RASHEED M F. Assessment of heavy metal toxicants in the roadside soil along the N–5, National Highway, Pakistan [J]. Environ Monit Assess, 2011, 182: 587-595.
[28]  L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001.
L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001.
[29] DOUAY F,  A, PLANQUE J, FOURRIER H, RICHARD A, ROUSSEL H, GIRONDELOT B. Assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants living near a former lead smelter, Part 1: Metal concentrations in soils, agricultural crops, and homegrown vegetables [J]. Environ Monit Assess, 2013, 185(5): 3665-3680.
A, PLANQUE J, FOURRIER H, RICHARD A, ROUSSEL H, GIRONDELOT B. Assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants living near a former lead smelter, Part 1: Metal concentrations in soils, agricultural crops, and homegrown vegetables [J]. Environ Monit Assess, 2013, 185(5): 3665-3680.
[30]  B. Heavy metals in soils: Distribution, relationship with soil characteristics and radionuclides and multivariate assessment of contamination sources [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 72(3): 491-549.
B. Heavy metals in soils: Distribution, relationship with soil characteristics and radionuclides and multivariate assessment of contamination sources [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 72(3): 491-549.
[31] ZHANG C, WU L, LUO Y, ZHANG H, CHRISTIE P. Identifying sources of soil inorganic pollutants on a regional scale using a multivariate statistical approach: Role of pollutant migration and soil physicochemical properties [J]. EnvironmentalPollution, 2008, 151(3): 470-476.
[32] LEE S Z, CHANG L, YANG H H, CHEN C M, LIU M C. Adsorption characteristics of lead onto soils [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1998, 63(1): 37-49.
[33] CHEN X, XIA X H, ZHAO Y, ZHANG P. Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1/2/3): 640-646.
[34] ZHONGGe-mei,TANGZhen-zhu. Environmental cadmium, lead and arsenic pollution and health impact–research progress in China [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2006, 23(6): 562-565. (in Chinese)
[35] ZENG Hai-ao, WU Jing-lu. Heavy metal pollution of lakes along the mid–lower reaches of the Yangtze river in China: Intensity, sources and spatial patterns [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2013, 10(3): 793-807.
[36] PENGShao-bang,CAILe,LISi-qing. Remediation methods of cadmium contaminated soil and research progress on bioremediation [J]. Inner Mongolia Environmental Protection, 2014, 26(3): 86-91. (in Chinese)
[37] WANG Rui, YU Zong-ling, GUAN Yang. Overview on phytoremediation of nickel contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Science andManagement, 2013, 38(8): 111-115. (in Chinese)
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project(21467005) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2015-05-26; Accepted date: 2015-08-06
Corresponding author: WEI Chao-fu, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-23-68251249; E-mail: weicf@swu.edu.cn

