J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2007)04-0460-07
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-007-0090-4
Comparison of microbial communities in three different mine drainages and their bioleaching efficiencies to low grade of chalcopyrite
YIN Hua-qun(尹华群), QIU Guan-zhou(邱冠周), WANG Dian-zuo(王淀佐),
CAO Lin-hui(曹琳辉), DAI Zhi-min(戴志敏), WANG Jie-wei(王杰伟), LIU Xue-duan(刘学端)
(School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
________________________________________________________________________
Abstract: Microbial community diversities in the drainage from three mines (Dexing Copper Mine, Qibaoshan Copper Mine and Yaogangxian Tungsten Mine, China) were analyzed using 16S rDNA PCR-RFLP approach. The efficiencies of chalcopyrite bioleaching were compared using enrichment of the three cultures. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that the dominant microorganisms are clustered with the Proteobacteria, the remaining is affiliated with Nitrospira, Acidobacteria and Actinobacteria. At the genus level, Acidithiobacillus is the dominant group in both YTW and QBS samples, while Spingomonas is dominant in YGX sample. Moreover, the principal component analysis (PCA) reveals that QBS and YTW have similar geochemical character and microbial communities. The results also show that pH value and tungsten concentration play a key role in microbial community distribution and relative abundance. The bioleaching efficiency of the enrichment cultures from YTW and QBS is similar. After 15 d, the bioleaching rates of low grade chalcopyrite (0.99%) are both up to 99.5% when using 10 g/L pulp density due to the similar microbial composition of YTW and QBS. Moreover, the leaching efficiencies of enrichment cultures containing multiple bioleaching microorganisms are higher than that of pure culture Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans.
Key words: microbial community diversity; PCR-RFLP; principal component analysis; chalcopyrite; bioleaching
________________________________________________________________________
1 Introduction
The bacteria such as Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Leptospirillum ferooxidans associated with diverse acidic environments are acknowledged to play important roles in biometallurgical processing in mining activity, extraction of metals and the formation of acid mine drainage[1]. The interesting microbial communities in the acid environment have recently been researched as the discharge of acid mine drainage(AMD) that has caused considerable environmental damage via the release of metal-rich acidic effluents into groundwater[2-3]. The acidic, metal-rich fluids are formed by chemical weathering and microbial reaction of main metal sulfide-rich rocks such as chalcopyrite(CuFeS2), sphalerite (ZnS) and galena (PbS)[1]. Some researchers suggested that the microbial communities of the acid environment were closely related to physicochemical composition and geography of mine drainage. JOHNSON et al[4] systematically analyzed the physicochemical and microbiological characteristics of acid mine drainage from various sites worldwide, and found that the relative abundances of Fe-oxidizers, S-oxidizers and other Herotrophic acidophiles were different at different sites, as well as microorganism community composition. Even if the geography and geochemistry properties in different sites have showed some similarity, important differences were observed at microbiological level[5]. Although there are many reports on microbial community and ecology of the drainage of the sulfide-rich rocks, studies related to microbial community of the tungsten mine drainage are rare. Furthermore, the microbial communities of the drainage from the sulfide-rich minerals are poorly understood in China. In order to reveal the microbial community of different mine drainages, the compositions of microbial populations of the three samples from Dexing Copper Mine, Qibaoshan(QBS) Copper Mine and Yaogangxian(YGX) Tungsten Mine were analyzed, and the bioleaching efficiencies of chalcopyrite using three microbial communities enrichment were studied.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Collection of samples
Yangtaowu(YTW) sample was taken from acid mine drainage reservoirs in the Dexing Copper Mine, which is the biggest copper mine in China and has been in operation for more than 800 years[6]. QBS water sample was collected from Qibaoshan Copper Mine, Hunan Province, China. The chemical composition of the acid mine water at this site is abundant in Fe, S and As. YGX water sample was collected from the Yaogangxian Tungsten Mine, which is one of the largest sheelites in China and the ores contain 36 partner metals. These three water samples were transferred into a jar immediately after collection. The water sample used for chemical analysis was filtered in-situ through a 0.2 μm nylon filter with vacuum pump. The filters were kept at 20 ℃ for the molecular analysis.
For geochemical analysis at these sites, the elements contained in the water samples were measured using an inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscope (ICP-AES; Baird Plasma Spectrovac PS-6(N+1)). The composition of chalcopyrite was analyzed by atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS).
2.2 Bioleaching of chalcopyrite
To investigate the bioleaching efficiency of chalcopyrite, the mixed microbial communities applied to chalcopyrite bioleaching were enriched using 9K medium at 30 ℃. The pure culture of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans was used as control. After culturing 7 d, 100 mL culture containing Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and the enrichment of three cultures was applied to leach 10 g chalcopyrite. The concentration of Cu2+ in the solution was measured every 3 d.
2.3 Extraction and purification of DNA
For all three sites, the microbial DNA was extracted from 5 g filters using a protocol described by Zhou et al[7]. The crude DNA was purified by the minicolumn purification method and quantified by agarose gel electrophoresis[8].
2.4 Polymerase chain reaction(PCR) and fraction- ation of 16S rDNA genes
The 16S rDNA genes were amplified by PCR. The PCR protocol is described by O’SULLIVAN et al[9]. Bovine serum albumin(400 ng/μL final concentration) was added to the reaction system to promote high G+C templates amplification. PCR products of the expected size (approximately 1.3 kb) were excised through 1.0% low-melting-point agarose gel and purified with the Promega purification columns according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5 Cloning and restriction fragment length polymor- phism(RFLP) analysis
The purified PCR products were cloned into plasmid vector PCR2.1 TOPO and then were used to transform Escherichia coli TOP10F’ competent cells according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.). After blue-white screening, 130 white colonies from each of the three libraries were randomly selected and the cloned inserts were re-amplified by PCR. Aliquots of re-amplified products were digested with restriction endonuclease HinPI and MspI (New England Biolabs, Beverly, Mass.) at 37 ℃. Jaccard coefficients were calculated for all pairwise comparisons of RFLP banding patterns and dendrograms were constructed for the unweighted pair group using average value method in Molecular Analyst (version 1.1; Bio-Rad, Hercules, Calif.). Cohesive groupings of highly similar RFLP banding patterns were identified, and a representative clone was selected for sequencing.
2.6 Sequencing and phylogenetic analysis
36 16S rDNA clones were sequenced and these sequences identification was initially estimated using the BLASTN facility of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/BLAST/). Based on all available sequences, the initial phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining method with Felsenstein correction in ARB[10]. Based on the initial phylogenetic results, appropriate subsets of 16S rDNA sequences were selected and submitted to final phylogenetic analysis with CLUSTAL W.
2.7 Statistical methods
Principal components analysis (PCA) was performed using the SYSTAT statistical computing package (version 13.0; SPSS, Inc., Chicago,Ill.) for each sampling site. Based on the biogeochemical parameters for each site (cuprum, tungsten, zinc, manganese, sulfur, chromium, iron, aluminum, calcium), PCA was used to group or separate sites similar or different and to ascertain which biogeochemical parameters contribute to the differences among sites. Similarly, correlation analysis of these sites was applied to the biological parameters; the relative abundances of operational taxonomic units (OTUs, mean unique RFLP patterns in this study) at each site were used as variables.
Rarefaction analysis was performed with SigmaPlot software. An exponential model y= a(1-e-bx) where a, b are filling coefficient was used with SigmaPlot 8.0 nonlinear regression software to fit the clone distribution data. A software SAS was used primarily for PCA of the clone data[11]. The diversity index, Shannon-Weaver index(H) is computed for each site and the frequency distribution of each OTU as follows[12]:
H=-∑Pi lbPi
where Pi is the proportion of the each OTU.
2.8 Nucleotide sequence accession numbers
The Genbank accession numbers of the OTUs’ nucleotide sequence in this paper are listed as follows: DQ840459-DQ840474, DQ458042, DQ457999, DQ458003, DQ458012, DQ458048, DQ458000, DQ458045, DQ458041, DQ458017, DQ458044, DQ458007, DQ458006, DQ458046, DQ458013, DQ458027, DQ458040, DQ458009, DQ458020.
3 Results
3.1 Biogeochemical properties of three sites
Descriptions of sampling sites and the properties of samples are shown in Table 1. All sites combined could take up 84% of the total geochemical variances. PCA of biogeochemical properities is shown in Fig.1. Fig.1 shows that the sites YTW and QBS are clustered together but the site YGX is clearly separated from YTW and QBS sites.
Table 1 Biogeochemical properties and diversity index for three samples


Fig.1 PCA of biogeochemical properties
The contents of almost all the heavy metal elements at the QBS site are the highest compared to that at other two sites, except for the element tungsten. The PCA of the physical and chemical parameters reduces the data to two principal components that explain all (99.9%) of the variation in the geochemical parameters(Fig.2). Tungsten is separated from other biogeochemical parameters with regard to PC1, which takes up 73.6% of the variables. PC1 also separates the pH value from the other variables. PC2 separates the copper from the other variables. These elements clustered together may explain the diversity of microbial community in different sites(Fig.3). Also, the Tungsten and pH value are two key differences among sites.

Fig.2 PCA based on pH, and biogeochemical data from three different sites
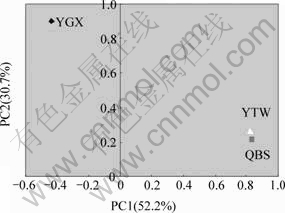
Fig.3 PCA of OTUs from three stations
3.2 RFLP analysis of 16S rDNA clone libraries
130 clones containing entire 16S rDNA inserts were obtained from each of the mine waters. 25-40 unique 16S rDNA fragments from each sample are detected while all of the unique 16S rDNA clones among these samples were digested with the restriction enzymes. The least unique 16S rDNA is found in the samples from the site QBS (25 OTUs), whereas the most unique clones is found in samples from the site YGX (40 OTUs).
RFLP analysis reveals extensive genetic diversity of 16S rDNA for the three samples. Only one RFLP pattern (YTW3) is common to the three sampling sites. However, seven OTUs are common between sample YTW and QBS. 2-4 dominant 16S rDNA clones are detected in each sample. In sample YGX, 40 OTUs are detected and three different OTUs (YGX6, YGX35 and YGX123) are more frequently recovered, and they take up 40% of the whole clone library. Moreover, other 37 different OTUs are recovered much less frequently and make up less than 5% of the clone library except for YTW 59(7.6% of the clone library). QBS13, YTW29 and YTW 52 from sample YTW are the dominant clones and represent 22.3%, 7.7% and 10% of the total clone populations recovered respectively, and they are not present in YGX samples. Otherwise, the most abundant clone QBS13 from site QBS (17% of the total clone) has the same RFLP pattern as the most dominant clones from site YTW.
Composition similarity in 16S rDNA community structure of the three samples shows that 3.3% of the 16S rDNA clones detected from the YGX sample are also present in the QBS sample and 2.9% of the 16S rDNA clones detected from the YGX sample are found in the YTW sample. However, 43.3% of the 16S rDNA clones are detected in both QBS and YTW samples. The diversity index shows that YGX sample is more diversified than the other samples.
After rarefaction analysis testing 100 clones of sample YGX, 60 clones of sample QBS and 120 clones of sample YTW respectively, no-more unique clone was found. It indicates that the analysis is sufficient to detect the community diversity and to infer microorganism distribution within these communities.
3.3 Phylogenetic analysis
Sequences of 36 RFLP band patterns are fully sequenced, which occur more than once in these three clone libraries. Based on 16S rDNA sequence similarity, all these sequences are classified into 5 major clusters (Fig.4). Among the 5 clusters, α-Proteobacteria and γ-proteobacteria are dominant groups. Fig.4 shows that 4 different subgroups and 10 sequences are assigned to α-Proteobacteria. The dominant subgroup is affiliated with Sphingomonas sp.(56%) and occurs only in sample YGX. A sequence related to Acidiphillium sp is found in both QBS and YTW samples but not in sample YGX.
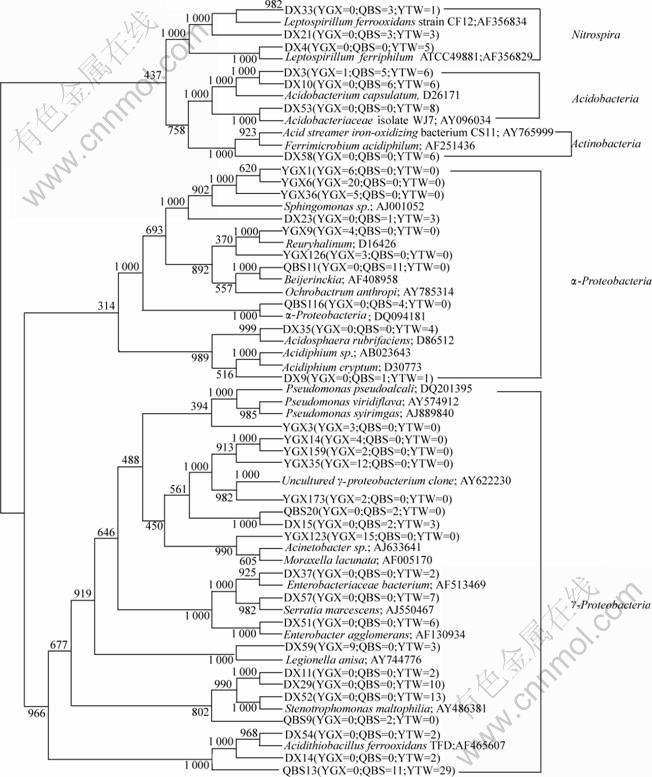
Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree based on 16s rDNA sequences
Of all 5 groups, sequences affiliated with the γ-proteobacteria are the most diversified and abundant. 19 sequences belong to 6 subgroups of this family. Among them, three sequences (YTW54, YTW14 and QBS13) are related to Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans that is the most abundant one (31% of the γ- proteobacteria), however, they are only found in QBS and YTW samples. Four sequences (YTW11, YTW29, YTW52 and QBS9) are related to Stenotrophomonas, and they are only discovered in the YTW sample except for QBS9, which only occur in sample QBS.
Three other phylogenetically distinct clusters (Nitrospira, Acidobacteria and Actinobacteria) are also detected, and they take up 17%. However, none of the clones affiliated with the Nitrospira and the Actinobacteria is detected in the YGX sample.
The phylogenetic distributions of the sequences in QBS sample and YTW sample are similar for some divisions. For example, the clones associated with genus Acidithiobacillus are prevalent in both QBS (17%) and YTW samples (25%) but not in YGX sample. Likewise, some clones affiliated with the Nitrospira are observed in both QBS sample and YTW sample but not in the YGX sample. The clones affiliated with the Acidobacteria are prevalent in both QBS (17%) and YTW samples (15%) but low in YGX sample.
At the same time, the similarities and differences among three samples are prominent at the genus level. Clones similar to Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans occur and dominant in both QBS and YTW samples but not in YGX sample. Similarly, clones affiliated with Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidiphillium cryptum also occur in both QBS and YTW samples but not present at YGX sample. Clones similar to Sphingomonas genus are dominant in YGX sample but not found in QBS and YTW samples.
3.4 Atomic absorption spectrometry(AAS) analysis of chalcopyrite and comparison of bioleaching efficiency of different cultures
The results from AAS analysis of chalcopyrite show that the content of Cu is only 0.99% (Table 2).
Table 2 Components of chalcopyrite(mass fraction, %)

The chalcopyrite bioleaching results show that the leaching efficiency of the mixed enrichment cultures in YGX and QBS is similar (Fig.5). After 15 d, the bioleaching efficiency of chalcopyrite with 0.99% copper is up to 99.5%. Meanwhile, the leaching efficiency of chalcopyrite of the enrichment culture (YTW and QBS) is higher than that of the pure culture (F10 in Fig.5). However, there is almost no leaching effect at the mixed culture YGX.
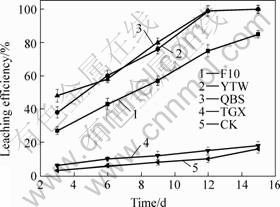
Fig.5 Leaching efficiency of different cultures
4 Discussion
Typically, 16S rDNA gene is used for diversity studies of microbial community because this gene is present in all microorganisms and has well-defined regions for taxonomic classification. Meanwhile there are massive 16S rDNA sequences available for researchers in database[13]. In this study, the recovery of sequence cluster provides some evidence about attribution of microbial community from three difference mine drainages.
The phylogenetic analytical result shows that Acidithiobacillus-like and Leptospirillum-like micro- organisms are more abundant both in QBS and YTW samples than in YGX sample. The difference may be caused by different geochemical properties such as pH value and iron or sulfur concentrations of these three sample sites. Acidithiobacillus-like and Lepto- spirillum-like microorganisms are acidophilic chemolithotrophic bacteria that can grow in lower pH environment and utilize ferrous iron or sulfur compounds for energetic metabolism[14]. The higher pH value and lower concentration of ferrous iron or sulfur compound in YGX may inhibit the growth of these bacteria. Our results also show that most of the populations from the YGX sample have unique 16S rDNA gene sequences (Fig.4). Among these samples, two key geochemical differences (W concentration and pH value) suggest that different geochemical properties inhabit different microbial communities[15]. PCA analysis based on biogeochemical properties (Fig.1) suggests that W concentration together with pH may have a significant impact on microbial community composition.
Interesting, Sphingomonas sp. is the most abundant genus in YGX samples. The bacterial strains of the genus Sphingomonas are relatively ubiquitous in soil, water, and sediment[16]. More importantly, the genus has various catabolic capabilities to produce at least 8 highly useful gellan extracellular acid heteropolysaccharides and has unique abilities to degrade refractory contaminant[17]. These characteristics of genus Spingomonas may make the microbial better situate to the geochemical condition of site YGX. However, whether genus Spingomonas has the ability to degrade tungsten needs to be further confirmed. Our results also suggested that genus Spingomonas may lack the capability to survive under the condition of lower pH. The explanation is in accordance with the results in Ref.[18], which claims that Sphingomonas chlorophenolica cannot grow at pH=4.0.
An important characteristic of the acidophilic chemolithotrophs is their general tolerance of high concentrations of metallic and other ions[11]. However, different acidophilic chemolithotrophs have different tolerance capabilities, which lead to the difference of microbial community in niches with different metal concentrations. In this study, samples QBS and YTW have great differences in the concentration of As, Zn and Fe. Therefore they have the different microbial communities.
Moreover, the bioleaching efficiencies of enrichment cultures at three sites were compared. The results show that the bioleaching efficiencies of enrichment cultures at QBS and YTW are similar. This may be because of the similar microbial communities between these two sites. In addition, mixed culture of YGX shows almost no bioleaching effect probably due to lack of bioleaching microorganisms.
5 Conclusions
The geochemical properties and the microbial communities of copper mine QBS and YTW samples show more similarity than that of tungsten mine YGX sample. In both QBS and YTW samples, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is the dominant group, but genus Spingomonas is the dominant group in YGX sample. pH value and tungsten concentration play a key role in microbial communities composition. Samples with similar tungsten concentration and pH have similar microbial community. The bioleaching efficiency of chalcopyrite shows that the bioleaching effect of YTW and QBS enrichments is similar. This may be explained by similar microbial composition at these two sites. Moreover, the leaching efficiency of enrichment cultures containing combined bioleaching microorganisms is higher than that of pure culture Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans.
References
[1] BAKER B J, BANFIELD J F. Microbial communities in acid mine drainage[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2003, 44(2): 139-152.
[2] OKIBE N, GERICKE M, HALLBERG K.B, et al. Enumeration and characterization of acidophilic microorganisms isolated from a pilot plant stirred-tank bioleaching operation[J]. Applied and nvironmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(4): 1936-1943.
[3] DOPSON M, BAKER-AUSTIN C, HIND A, et al. Characterization of Ferroplasma Isolates and Ferroplasma acidarmanus sp. nov., extreme Acidophiles from acid mine drainage and industrial bioleaching environments[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(4): 2079-2088.
[4] JOHNSON D B, HALLBERG K B. The microbiology of acidic mine waters[J]. Research in Microbiology, 2003, 154(7): 466-473.
[5] Lo? PEZ-ARCHILLA A I, AMILS R. A comparative ecological study of two acidic rivers in southwestern spain[J]. Microb Ecol, 1999, 38(2): 146-156.
[6] WEN Xiang-hua, HERBERT E A. Mobilization of heavy metals from Le An River sediment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 227(2/3): 101-108.
[7] ZHOU J M. BRUNS A, TIEDJE J M. DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1996, 62(2): 316-322.
[8] HURT R A, QUI X, WU L, et al. Simultaneous recovery of RNA and DNA from soils and sediments[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2001, 67(10): 4495-4503.
[9] O’SULLIVAN L A, WEIGHTMAN A J, FRY J C. New degenerate cytophaga-flexibacter-bacteroides-specific 16S ribosomal DNA- targeted oligonucleotide probes reveal high bacterial diversity in river taff epilithon[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2002, 68(1): 201-210.
[10] SMITH S W, OVERBEEK R, WOESE C R, et al. The genetic data environment: An expandable GUI for multiple sequence analysis[J]. Comput Applic Biosci, 1994, 10(6): 671-675.
[11] DOPSON M, BAKER-AUSTIN C, RAM K P, et al. Growth in sulfidic mineral environments: Metal resistance mechanisms in acidophilic micro-organisms[J]. Microbiology, 2003, 149(8): 1959- 1970.
[12] MARGALEF R. Information theory in ecology[J]. Genetics and Systematics, 1958(3): 36-71.
[13] JENNIFER L K, LEE A, PETER M, et al. Methods of studying soil microbial diversity[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2004, 58(2): 169-188.
[14] BRASSEUR G, BRUSCELLA P, BONNEFOY V, et al. The bc1 complex of the iron-grown acidophilic chemolithotrophic bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans functions in the reverse but not in the forward direction—Is there a second bc(1) complex?[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2002, 1555(1): 37-43.
[15] LIU Xue-duan, SONIA M T, Gina Holguin, et al. Molecular diversity of denitrifying genes in continental margin sediments within the oxygen-deficient zone off the pacific coast of mexico[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2003, 69(6): 3546-3560.
[16] YABUUCHI E, YANO I, OYAIZU H, et al. Proposals of Sphingomonas gen. nov., Sphingomonas parapaucimobilis sp. nov., Sphingomonas yanoikuyae sp. nov. Sphingomonas adhaesiva sp. nov., Sphingomonas capsulata comb. nov., and two genospecies of the genus[J]. Microbiol Immunol, 1990, 34(2): 99-119.
[17] DUTTA T K, SELIFONOV S A, GUNSALUS I C. Oxidation of methyl-substituted naphthalenes: Pathways in a versatile Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1998, 64(5): 1884-1889.
[18] ZHOU Ji-zhong, XIA Bei-cheng, HUANG He-shu, et al. Microbial diversity and heterogeneity in sandy subsurface[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2004, 70(3): 1723-1734.
__________________________
Foundation item: Project(50621063) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2004CB619204) supported by the National Basic Research and Development Program of China
Received date: 2006-10-20; Accepted date: 2006-12-23
Corresponding author: LIU Xue-duan, Professor; Tel: +86-731-8830546; E-mail: xueduanliu@yahoo.com
(Edited by ZHAO Jun)