混合中度嗜热微生物浸出两种不同类型低品位铜尾矿的比较研究
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第9期
论文作者:郝晓东 刘学端 杨琴 刘宏伟 尹华群 邱冠周 梁伊丽
文章页码:1847 - 1853
关键词:生物浸出;尾矿;微生物群落动态;矿物学分析
Key words:bioleaching; tailings; microbial community dynamics; mineralogical analysis
摘 要:利用混合中度嗜热微生物浸出比较研究两种不同类型的低品位铜尾矿(酸浸尾矿和铜浮选尾矿)在浸出过程中矿物学和微生物学特征的变化。结果表明:两种尾矿的浸出行为具有很大的区别。与铜浮选尾矿相比,酸浸尾矿的浸出液中氧化还原电位较低,[Fe3+]/[Fe2+]的比例和微生物菌体密度较高,导致总铜、原生硫化铜和次生硫化铜的浸出率增加。XRD结果表明,在浸出浮选尾矿中,检测到石膏和金属有机复合物,这些物质会减缓硫化矿物的氧化过程。两种尾矿浸出过程的微生物群落变化明显:酸浸尾矿浸入过程中铁氧化菌的比例高于浮选尾矿浸出的,但硫氧化菌比例低于浮选尾矿浸出的,浸出酸浸尾矿时可以检测到F. thermophilum L1,但在浸出浮选尾矿中检测不到。
Abstract: The bioleaching of two different types of low-grade copper tailings, acid-leaching tailings (ALT) and copper flotation tailings (CFT) by mixed moderate thermophiles, and the variation of mineralogical and microbiological characteristics during their dissolution processes were comparatively investigated. Results showed that bioleaching behaviors of the two types of tailings were significantly different. In ALT bioleaching, lower redox potential, higher [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio and higher cell density in solution were obtained. These resulted in higher total copper, primary copper sulfide and secondary copper sulfide extractions, compared with CFT bioleaching. X-ray diffraction analysis suggested that gypsum and some metal organic complexes were detected in CFT bioleaching, which could cause the sluggish oxidation of sulphide minerals. The shifts of microbial community in the leachates and leaching residues varied greatly between ALT and CFT bioleaching. The percentage of iron-oxidizing bacteria in ALT bioleaching was higher than that of CFT, but the sulfur-oxidizing bacteria percentage was the opposite. The archaeon F. thermophilum L1 was detected in ALT but not in CFT.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 1847-1853
Xiao-dong HAO1,2, Xue-duan LIU1,2, Qin YANG1,2, Hong-wei LIU1,2, Hua-qun YIN1,2, Guan-zhou QIU1,2, Yi-li LIANG1,2
1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy of Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 18 May 2017; accepted 8 September 2017
Abstract: The bioleaching of two different types of low-grade copper tailings, acid-leaching tailings (ALT) and copper flotation tailings (CFT) by mixed moderate thermophiles, and the variation of mineralogical and microbiological characteristics during their dissolution processes were comparatively investigated. Results showed that bioleaching behaviors of the two types of tailings were significantly different. In ALT bioleaching, lower redox potential, higher [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio and higher cell density in solution were obtained. These resulted in higher total copper, primary copper sulfide and secondary copper sulfide extractions, compared with CFT bioleaching. X-ray diffraction analysis suggested that gypsum and some metal organic complexes were detected in CFT bioleaching, which could cause the sluggish oxidation of sulphide minerals. The shifts of microbial community in the leachates and leaching residues varied greatly between ALT and CFT bioleaching. The percentage of iron-oxidizing bacteria in ALT bioleaching was higher than that of CFT, but the sulfur-oxidizing bacteria percentage was the opposite. The archaeon F. thermophilum L1 was detected in ALT but not in CFT.
Key words: bioleaching; tailings; microbial community dynamics; mineralogical analysis
1 Introduction
The metallurgy industry accumulates approximately 100 million tons of tailings resulted from floatation, agitation, pyrometallurgy and tank leaching operations per year worldwide. Their disposal causes potential environmental contaminations and human health problems due to the toxic metals or compounds existing in tailings [1,2]. At the same time, the great contrast between the constant decrease of valuable mineral resources and the remaining valuable metals such as Cu, Co, Ni and Zn in tailings endows recovery of these metals from the tailings as secondary sources with an attractive issue in recent years [3]. Therefore, recycling of the tailings is a necessary subject not only with respect to treatment of hazardous wastes but also from the viewpoint of recovering valuable metals.
Bioleaching is considered as a convincing technology for the extraction of metals from tailings due to low cost and simple infrastructure compared with conventional metallurgy methods [4]. Moreover, bioleaching is also widely used for the remediation of sludge contaminated by toxic heavy metals and recovery of precious base metals from urban and industrial wastes [5,6]. Bioleaching is characterized by dissolution of metals from solid matrices into aqueous solution under the mild conditions using acidophilic iron-/sulfur- oxidizing bacteria with contact and/or non-contact mechanisms [6]. Many efforts have been made to explore the bioleaching mechanisms and improve the dissolution kinetics during tailings bioleaching process. The low dissolution rates of tailings during the bioleaching process are mainly caused by the toxicity of tailings (e.g., heavy metal, alkaline substance, organic matter and gangue) and the formation of passivation layer such as jarosite, sulfur layer and gypsum [7-9]. However, the specific dissolution mechanism of tailing bioleaching is still under debate. The inconsistence of different studies may be attributed to various tailings with diverse physicochemical properties.
The understanding of the mineralogy, metal speciation transformation and microbial community succession in tailing dissolution process is essential to illuminate bioleaching mechanisms. Several reviews focused on the geochemical [10], mineralogical [11] and microbiological [12] aspects of sulfide mine tailings have been published. However, we still have a relatively limited understanding of the correlations among ore mineralogy, reaction chemistry, microbial ecology and leached residue mineralogy. Therefore, mineralogical and microbiological studies should be taken into consideration comprehensively to evaluate bioleaching of different types of low-grade copper tailings.
In this study, two typical low-grade copper tailings including acid-leaching tailings (ALT) and copper flotation tailings (CFT) were subjected to comparative bioleaching using mixed moderate thermophiles. It aimed to assess the difference of bioleaching behaviors and mineralogy changes in the dissolution process of two low-grade copper tailings and to investigate the effects of different tailings on microbial community succession.
2 Experimental
2.1 Mineral components
The acid-leaching tailings (ALT) and copper flotation tailings (CFT) were obtained from Chambishi Copper Mines in Zambia. Two tailings were crushed and sieved to less than 75 μm before using for leaching experiments. The element analysis was carried out by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES), which showed that ALT contained 0.47% Cu, 2.74% Fe, 0.22% S, 0.016% Co, 8.30% Al, 0.43% Ca and 1.77% Mg (mass fraction), and CFT contained 0.26% Cu, 2.22% Fe, 0.48% S, 0.012% Co, 4.88% Al, 2.58% Ca and 1.92% Mg (mass fraction). The copper phase analysis showed that ALT contained 0.04% free copper oxide (FCO), 0.18% combined copper oxide (CCO), 0.18% secondary copper sulfide (SCS) and 0.07% primary copper sulfide (PCS) (mass fraction), and CFT contained 0.02% FCO, 0.08% CCO, 0.13% SCS and 0.03% PCS (mass fraction).
2.2 Microorganisms and culture conditions
Four strains (Leptospirillum ferriphilum YSK, Ferroplasma thermophilum L1, Acidithiobacillus caldus S1 and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans A01) isolated from extreme acid mine drainage were used in this study. All strains were subcultured semimonthly and maintained in the basal salt medium at our laboratory. The basal salt medium contained 3.0 g/L (NH4)2SO4, 0.5 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, 0.5 g/L K2HPO4, 0.1 g/L KCl, 0.01 g/L Ca(NO3)2. The pH values of the medium were adjusted with 10 mol/L sulfuric acid. L. ferriphilum YSK was maintained in basal salt medium at initial pH of 1.6 and 40 °C and supplemented with 44.7 g/L FeSO4·7H2O; F. thermophilum L1 was cultivated at initial pH of 1.0 and 45 °C and supplemented with 44.7 g/L FeSO4·7H2O and 0.01% (w/v) yeast extract; A. caldus S1 was grown in basal salt medium at initial pH of 2.0 and 45 °C and supplemented with 10 g/L S0; A. thiooxidans A01 was maintained at initial pH of 2.0 and 30 °C and supplemented with 10 g/L S0.
2.3 Bioleaching experiments
Bioleaching experiments were performed in Erlenmeyer flasks with a total volume of 250 mL. The experiment conditions were as follows: work volume, 100 mL (basal salt medium); pulp density, 5% (w/v); rotation rate, 175 r/min; temperature, 40 °C and pH, 1.8.
Four acidophilic microorganisms were harvested individually by centrifugation at 1×104 r/min for 10 min and equal cell concentration of each of the four microorganisms was pooled. Then, the collected cells were inoculated into Erlenmeyer flasks with an approximately initial population of 4×107 cell/mL. Besides, acid leaching control experiments were also carried out in parallel without adding microorganisms. The pH values in the solution of acid leaching and bioleaching tests were kept constant at 1.8±0.2 with 10 mol/L sulfuric acid or sodium hydroxide throughout the experiments. All experiments were run in triplicate.
2.4 Physicochemical and XRD analysis
The copper concentrations in solution and elemental analysis of two tailings were determined by ICP-AES (America Baird Co., Ltd., PS-6). The Fe2+ and total iron concentrations were measured with phenanthroline spectrophotometry method, while Fe3+ concentration was the difference between the concentrations of total iron and Fe2+. The pH values were measured with a pH meter (INESA Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., pHS-25). The redox potentials in solution were measured using a Pt electrode with reference to an Ag/AgCl electrode (BPP-922). Solid samples after bioleaching were collected for mineralogical analysis by X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Model DX-2700). The microbial concentration in solution was counted with a blood cell counting chamber under an optical microscope (Olympus Instrument, BX41).
2.5 Microbial community dynamics analysis
Leachate (50 mL) containing tailing residues and microorganisms was collected regularly and centrifuged at 3000 r/min for 5 min, then the liquid phase was transferred into a new centrifuge tube to collect free cells with a further centrifugation at 1×104 r/min for 10 min. Attached microorganisms were detached from tailing residues according to the previous study [13]. Total DNA extraction of free and attached cells and real-time quantitative PCR were as described previously [14].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Bioleaching of two low-grade copper tailings
The chemical elements analysis showed that two tailings had similar characteristics although ALT had higher Cu content than CFT. However, the S content in ALT (0.22%) was lower than that of CFT (0.48%). Concerning the copper phase analysis, two tailings contained a little bit more sulfide copper but less oxide copper (shown in Section 2.1).
The leaching experiments of ALT and CFT at pulp density of 5% by mixed moderate thermophiles were carried out over a period of 16 d. As shown in Fig. 1(a), in the first 4 d, the copper extractions by acid leaching were 52.4% for ALT and 48.4% for CFT, respectively. After 8 and 4 d, no more copper from AFT and CFT was dissolved by acid leaching, respectively. The final copper extractions of acid leaching were 57.5% (ALT) and 49.8% (CFT) in 16 d, respectively. However, 70.7% Cu and 58.7% Cu were dissolved in ALT and CFT by bioleaching in 16 d, which were 13.2% and 8.9% higher than the dissolved copper by acid leaching, respectively. These results indicated that copper recovery from both tailings was more efficient by means of bioleaching instead of acid leaching. Furthermore, the copper recovery of ALT bioleaching had superiority to that of CFT.
Figure 1(b) presents the changes of redox potentials in leaching processes of two tailings. The redox potentials of ALT and CFT from acid leaching reached approximately 440 and 400 mV, respectively, and then the copper extractions were stationary after the 4th day. For ALT and CFT bioleaching, the redox potentials increased sharply in 6 d, and the copper extractions still increased when the redox potentials maintained within a high range at 560 and 600 mV for a long period of time, respectively. Figure 1(c) shows that the ratio of [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] increased rapidly in the first 8 d, and then kept stable in bioleaching process, which was in accordance with the copper extractions of ALT and CFT. The [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio was near zero in acid leaching. The variation trend of [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio indicated the increase of ferric iron could improve the copper recovery rate.
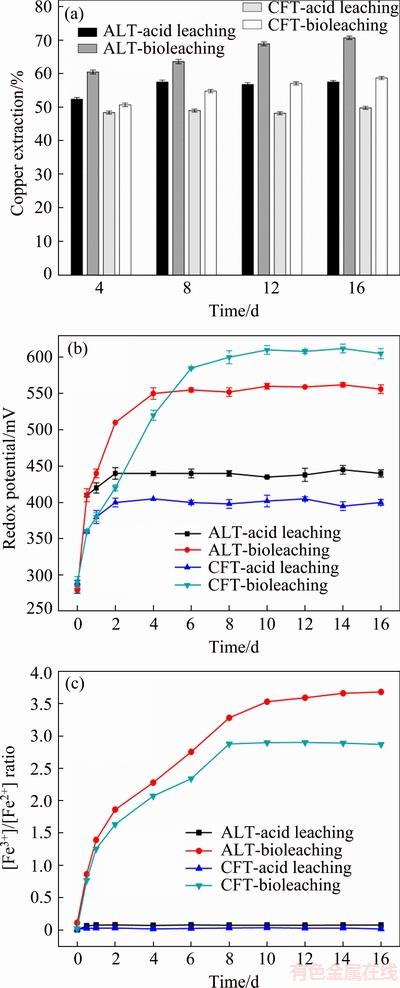
Fig. 1 Variation of copper extraction (a), redox potential (b) and [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio (c) in solution during acid leaching and bioleaching processes of acid-leaching tailings (ALT) and copper flotation tailings (CFT)
In two low-grade copper tailings leaching process, different bioleaching behaviors were observed. The variations of physicochemical parameters (redox potential and [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio) in solution were consistent with copper extractions. Improved copper bioleaching efficiency was presented in bioleaching groups, which could be mainly attributed to the increase of redox potentials. The redox potential was considered as a determining factor in the leaching of sulphide ores. Numerous researchers had confirmed that high redox potentials in bioleaching facilitated the effective dissolution of sulphide ores compared with acid leaching [15]. Furthermore, it was well known that the [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio was partially correlated to redox potential, and had a close connection with copper extraction. It was generally accepted that Fe3+ as oxidant was effective for dissolving sulfide minerals [16]. Higher Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio resulted from Fe2+ released from tailings and oxidized to Fe3+ rapidly was observed in ALT bioleaching (Fig. 1(c)). As a consequence, higher copper extraction of ALT was obtained, although low redox potential values were observed in ALT bioleaching group.
3.2 Mineralogical analysis of two low-grade copper tailings and bioleached residues
The copper phase of low-grade copper tailings and bioleached residues was analyzed (Fig. 2). The mineralogical forms of copper remained in residues were quite noteworthy between acid leaching and bioleaching processes. It showed that primary copper sulfide (PCS) and secondary copper sulfide (SCS) extractions in bioleaching were improved by 6.35% and 15.08% from ALT, and 8.44% and 8.14% from CFT in the early 4th day compared with acid leaching. In the 16th day, PCS and SCS extractions reached 66.43% and 65.60% in ALT, and 34.85% and 57.17% in CFT, respectively. While there is no more copper dissolved from free copper oxide (FCO) and combined copper oxide (CCO) of two tailings since the 4th day. This indicated that bioleaching had more evident advantage in copper recovery from copper sulfide than copper oxide.

Fig. 2 Copper extractions of tailings in residues during acid leaching and bioleaching processes of acid-leaching tailings (ALT) (a) and copper flotation tailings (CFT) (b)
It was worth noting that PCS (31.58%) and SCS (8.43%) extractions were greatly improved from ALT compared with those from CFT, which were connected with the low redox potentials in bioleaching solution of ALT. Previous studies reported that low redox potentials were in favor of the bioleaching of copper sulfide minerals especially for chalcopyrite in the presence of bioleaching bacteria. Additionally, at low redox potential, less passivation layer which was mainly composed of disulfide 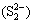 , polysulfide
, polysulfide 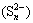 , elemental sulfur (S0) and jarosite could be formed, which slightly slowed down bioleaching performance [7,17]. Previous study also indicated that high redox potentials caused the rapid deterioration of ion diffusion performance of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) [18]. Hence, many efforts had been made to control the redox potential in an appropriate range to improve copper sulphide bioleaching efficiency [19,20].
, elemental sulfur (S0) and jarosite could be formed, which slightly slowed down bioleaching performance [7,17]. Previous study also indicated that high redox potentials caused the rapid deterioration of ion diffusion performance of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) [18]. Hence, many efforts had been made to control the redox potential in an appropriate range to improve copper sulphide bioleaching efficiency [19,20].
Raw minerals and bioleached residues collected after bioleaching were analyzed by XRD (data not shown). The results showed that quartz and silicon sulfide were the main components in the two tailings. ALT was composed of microcline, mackinanite, aluminum iron silicide, iron silicide, potassium disulfate, wollastonite and diopside. Wollastonite and diopside were undetectable after 16 d while other components were difficult to be dissolved. In addition, CFT contained microcline, silicon sulfide, lead iodate and murdochite, which were undetectable after bioleaching, while quartz was unchanged. Gypsum and some metal organic complexes (C2H12F6HfN6 and C6H8MgO4·4H2O) were detected after bioleaching, which were prone to combine with copper-containing minerals, making them immobile and refractory. Sulphur layer or jarosite, which could hamper further oxidation of sulphide minerals, was not discovered in bioleached residues.
The most important parameters affecting the tailings dissolution processes were the amount of gangue, the ore size as well as the nature of the oxide rock, temperature and pH [21]. It was reported that hydrion in leach liquor attacked gangue minerals, e.g., carbonate and silicate, leading to the loss of rock integrity [22]. Then, the copper oxide minerals were quickly dissolved by the hydrion entering the rock pores, producing a leached rim or shell surrounding an unaffected core of the rock. It accelerated acidophilic bacteria to attach to the ores and produce hydrion, which benefited the liberation of copper oxides and copper sulfides inside.
It was interesting that gypsum and some metal organic complexes were present in CFT after bioleaching. It has been proposed that Ca2+ and 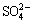 within the gypsum from the sulfide-rich environments were derived from pH-buffering reactions between pore water and Ca-bearing carbonates and the oxidation of sulfide minerals, respectively. Indeed, gypsum has been considered as a common initial cementing phase within the cemented layers in sulfide-bearing environments where mineral oxidation occurs naturally [23]. It should be noted that secondary minerals (such as gypsum, jarosite, and goethite) were prone to combine with copper-containing minerals, making them immobile and refractory. Therefore, no jarosite or sulphur was detected by XRD in bioleached residues, and gypsum was a principal control on the transport of sulfide-mineral oxidation products [24,25].
within the gypsum from the sulfide-rich environments were derived from pH-buffering reactions between pore water and Ca-bearing carbonates and the oxidation of sulfide minerals, respectively. Indeed, gypsum has been considered as a common initial cementing phase within the cemented layers in sulfide-bearing environments where mineral oxidation occurs naturally [23]. It should be noted that secondary minerals (such as gypsum, jarosite, and goethite) were prone to combine with copper-containing minerals, making them immobile and refractory. Therefore, no jarosite or sulphur was detected by XRD in bioleached residues, and gypsum was a principal control on the transport of sulfide-mineral oxidation products [24,25].
3.3 Microbial community dynamics analysis during ALT and CFT bioleaching processes
In this study, four strains were mixed, such as sulfur- and iron-oxidizing bacteria, autotrophs and heterotrophs. L. ferriphilum YSK was strictly chemoautotrophy and gained energy from ferrous iron-oxidation but unable to oxidize sulfur, while A. caldus S1 and A. thiooxidans A01 had the opposite abilities. F. thermophilum L1 was capable of chemomixotrophic growth on ferrous iron and organic matters such as yeast extract, glucose and sucrose. Therefore, it could relieve the toxicity of organic matters to autotrophic bacteria [26].
The variation of bacterial concentration in solution during two tailings bioleaching processes is shown in Fig. 3. The growth of bacteria in ALT and CFT bioleaching showed lag time of 2 and 4 d, respectively. A higher cell density was measured in ALT bioleaching compared with CFT, indicating that flotation reagents existing in CFT might have an inhibitory effect on microbes [27]. In addition, the formation of gypsum and metal organic complexes could disturb the flourish and colonization of bacteria onto tailing surface in CFT bioleaching, which restrained the growth of bioleaching microorganisms.
Microbial community dynamics analysis showed that L. ferriphilum YSK, A. caldus S1 and A. thiooxidans A01 flourished in two tailings bioleaching processes although different microbial populations were identified, and F. thermophilum L1 in ALT bioleaching process was also quantifiable (Fig. 4).
In ALT bioleaching system, L. ferriphilum YSK was the dominant species throughout the bioleaching process (43.48%, 61.86% and 68.61% on days 5, 10 and 16, respectively). In the initial stage, A. caldus S1 was accounted for 28.36%, and subsequently decreased to 24.99% and 11.80% on day 10 and 16, respectively. A. thiooxidans A01 and F. thermophilum L1 held relatively fixed proportions although continuously descend. During CFT bioleaching, A. caldus S1 was over 50% as the predominant species on day 5, then L. ferriphilum YSK displaced A. caldus S1 and became the dominant species in the middle (40.59%) and final bioleaching stages (47.88%), and A. thiooxidans A01 held a gradually increasing trend.

Fig. 3 Variation of bacterial concentration in solution during bioleaching processes of acid-leaching tailings (ALT) and copper flotation tailings (CFT)

Fig. 4 Microbial community dynamics analysis of mixed moderate thermophiles on days 5, 10 and 16 during bioleaching processes of acid-leaching tailings (ALT) and copper flotation tailings (CFT)
Bioleaching of sulphide ores was affected by the structure and dynamics of microbial community [26]. Ferrous iron and reduced inorganic sulfur compounds (RISCs) were released from tailings dissolution, and were the main intermediates of tailings bioleaching. The oxidation of RISCs by sulphur oxidizers yielded considerably more energy than the oxidation of ferrous iron [28]. Thus, A. caldus S1 and A. thiooxidans A01, which could utilize RISCs as energy source, grew better and had higher proportions in the initial stage. However, S0 oxidizers were unable to oxidize sulfide minerals directly. Therefore, the copper extractions did not increase significantly in initial bioleaching stage compared with acid leaching. As bioleaching of tailings progressed, the [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio increased rapidly, and iron oxidizers gained a competitive advantage and became the predominant species in the middle and final stages. The increased proportion of L. ferriphilum YSK resulted in an enhanced capacity for ferrous iron oxidation, further promoted the copper extractions. The microbial diversity during ALT bioleaching was relatively high, and F. thermophilum L1 from the original mixed inoculums was detected but not existed in CFT bioleaching. The absence of F. thermophilum L1 seemed to have more important effect on bioleaching performance, as indicated by the differences in copper extractions of 70.7% from ALT and 58.7% from CFT (Fig. 1(a)).
Our results also showed that the proportions of four species in mixed moderate thermophiles varied greatly in two tailings bioleaching. In ALT bioleaching, the percentage of iron-oxidizing bacteria (L. ferriphilum YSK and F. thermophilum L1) was higher than that of CFT bioleaching, but contrary to sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. The reason might be that ALT contained a little bit more iron but less sulfur. In addition, flotation reagents existing in CFT also changed the microbial community succession. OKIBE and JOHNSON [27] investigated the toxicity of 15 flotation reagents to five species of mineral-oxidizing, moderately thermophilic and acidophilic microorganisms. The results showed that different microorganisms presented multiple sensitivities to the flotation reagents, and the Leptospirillum and Ferroplasma were the most sensitive to the acidophilic microorganisms.
4 Conclusions
1) Low redox potential, high [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] ratio and high copper extraction of more than 70% were obtained in bioleaching of acid-leaching tailings (ALT). However, low copper extraction (58.7%) was achieved in bioleaching of copper flotation tailings (CFT).
2) Primary copper sulfide and secondary copper sulfide extractions were greatly improved from ALT than those from CFT resulted from lower redox potential in ALT bioleaching.
3) ALT and CFT affected microbial community dynamics greatly. The percentage of iron-oxidizing bacteria in ALT bioleaching was higher than that in CFT bioleaching, but the sulfur-oxidizing bacteria percentage was lower. In addition, the archaeon F. thermophilum L1 was not detected in CFT bioleaching.
References
[1] NAGAJYOTI P C, LEE K D, SREEKANTH T V M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review [J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2010, 8: 199-216.
[2] MIN X B, XIE X D, CHAI L Y, LIANG Y J, LI M, KE Y. Environmental availability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in zinc leaching residue [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 208-218.
[3] WANG Y G, SU L J, ZENG W M, QIU G Z, WAN L L, CHEN X H, ZHOU H B. Optimization of copper extraction for bioleaching of complex Cu-polymetallic concentrate by moderate thermophiles [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 1161-1170.
[4] CONIC V T, VUJASINOVIC M M R, TRUJIC V K, CVETKOVSKI V B. Copper, zinc, and iron bioleaching from polymetallic sulphide concentrate [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 3688-3695.
[5] BEOLCHINI F, FONTI V, DELL ANNO A, ROCCHETTI L, VEGLIO F. Assessment of biotechnological strategies for the valorization of metal bearing wastes [J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32: 949-956.
[6] JOHNSON D B. Biomining-biotechnologies for extracting and recovering metals from ores and waste materials [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2014, 30: 24-31.
[7] MAJUSTE D, CIMINELLI V S T, ENG P J, OSSEO-ASARE K. Applications of in situ synchrotron XRD in hydrometallurgy: Literature review and investigation of chalcopyrite dissolution [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 131: 54-66.
[8] LI Y B, KAWASHIMA N, LI J, CHANDRA A P, GERSON A R. A review of the structure, and fundamental mechanisms and kinetics of the leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 197: 1-32.
[9] HAO X D, LIANG Y L, YIN H Q, LIU H W, ZENG W M, LIU X D. Thin-layer heap bioleaching of copper flotation tailings containing high levels of fine grains and microbial community succession analysis [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2017, 24: 360-368.
[10] SCHIPPERS A, KOCK D, SCHWARTZ M,  M E, VOGEL H, HAGGER M. Geomicrobiological and geochemical investigation of a pyrrhotite-containing mine waste tailings dam near Selebi-Phikwe in Botswana [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 92: 151-158.
M E, VOGEL H, HAGGER M. Geomicrobiological and geochemical investigation of a pyrrhotite-containing mine waste tailings dam near Selebi-Phikwe in Botswana [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 92: 151-158.
[11] LIU J Y, SUN S Y. Total concentrations and different fractions of heavy metals in sewage sludge from Guangzhou, China [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 2397-2407.
[12] LIU J, HUA Z S, CHEN L X, KUANG J L, LI S J, SHU W S, HUANG L N. Correlating microbial diversity patterns with geochemistry in an extreme and heterogeneous environment of mine tailings [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80: 3677-3686.
[13] ZENG W M, QIU G Z, ZHOU H B, PENG J H, CHEN M, TAN S N, CHAO W L, LIU X D, ZHANG Y S. Community structure and dynamics of the free and attached microorganisms during moderately thermophilic bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101: 7068-7075.
[14] LIU Y, YIN H Q, ZENG W M, LIANG Y L, LIU Y, BABA N, QIU G Z, SHEN L, FU X, LIU X D. The effect of the introduction of exogenous strain Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans A01 on functional gene expression, structure and function of indigenous consortium during pyrite bioleaching [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102: 8092-8098.
[15] HAO X D, LIANG Y L, YIN H Q, MA L Y, XIAO Y H, LIU Y Z, QIU G Z, LIU X D. The effect of potential heap construction methods on column bioleaching of copper flotation tailings containing high levels of fines by mixed cultures [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 98: 279-285.
[16] MA L Y, WANG X J, FENG X, LIANG Y L, XIAO Y H, HAO X D, YIN H Q, LIU H W, LIU X D. Co-culture microorganisms with different initial proportions reveal the mechanism of chalcopyrite bioleaching coupling with microbial community succession [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 223: 121-130.
[17] LIU H, GU G H, XU Y B. Surface properties of pyrite in the course of bioleaching by pure culture of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and a mixed culture of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108: 143-148.
[18] HE Z G, YANG Y P, SHAN Z, HU Y H, HUI Z. Effect of pyrite, elemental sulfur and ferrous ions on EPS production by metal sulfide bioleaching microbes [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 1171-1178.
[19] AHMADI A, SCHAFFIE M, MANAFI Z, RANJBAR M. Electrochemical bioleaching of high grade chalcopyrite flotation concentrates in a stirred bioreactor [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104: 99-105.
[20] THIRD K A, CORD-RUWISCH R, WATLING H R. Control of the redox potential by oxygen limitation improves bacterial leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2002, 78: 433-441.
[21] HELLE S, JEREZ O, KELM U, PINCHEIRA M, VARELA B. The influence of rock characteristics on acid leach extraction and re-extraction of Cu-oxide and sulfide minerals [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2010, 23: 45-50.
[22] OLSON G J, BRIERLEY J A, BRIERLEY C L. Bioleaching review part B: Progress in bioleaching: Applications of microbial processes by the minerals industries [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2003, 63: 249-257.
[23] QUISPE D,  R, ACERO P, AYORA C, NIETO J M, TUCOULOU R. Formation of a hardpan in the co-disposal of fly ash and sulfide mine tailings and its influence on the generation of acid mine drainage [J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 355: 45-55.
R, ACERO P, AYORA C, NIETO J M, TUCOULOU R. Formation of a hardpan in the co-disposal of fly ash and sulfide mine tailings and its influence on the generation of acid mine drainage [J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 355: 45-55.
[24] MCGREGOR R G, BLOWES D W. The physical, chemical and mineralogical properties of three cemented layers within sulfide-bearing mine tailings [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2002, 76: 195-207.
[25] BLOWES D W, REARDON E J, JAMBOR J L, CHERRY J A. The formation and potential importance of cemented layers in inactive sulfide mine tailings [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55: 965-978.
[26] YU R L, SHI L J, GU G H, ZHOU D, YOU L, CHEN M, QIU G, ZENG W. The shift of microbial community under the adjustment of initial and processing pH during bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by moderate thermophiles [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 162: 300-307.
[27] OKIBE N, JOHNSON D B. Toxicity of flotation reagents to moderately thermophilic bioleaching microorganisms [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2002, 24: 2011-2016.
[28] OKIBE N, GERICKE M, HALLBERG K B, JOHNSON D B. Enumeration and characterization of acidophilic microorganisms isolated from a pilot plant stirred-tank bioleaching operation [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69: 1936-1943.
郝晓东1,2,刘学端1,2,杨 琴1,2,刘宏伟1,2,尹华群1,2,邱冠周1,2,梁伊丽1,2
1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 生物冶金教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:利用混合中度嗜热微生物浸出比较研究两种不同类型的低品位铜尾矿(酸浸尾矿和铜浮选尾矿)在浸出过程中矿物学和微生物学特征的变化。结果表明:两种尾矿的浸出行为具有很大的区别。与铜浮选尾矿相比,酸浸尾矿的浸出液中氧化还原电位较低,[Fe3+]/[Fe2+]的比例和微生物菌体密度较高,导致总铜、原生硫化铜和次生硫化铜的浸出率增加。XRD结果表明,在浸出浮选尾矿中,检测到石膏和金属有机复合物,这些物质会减缓硫化矿物的氧化过程。两种尾矿浸出过程的微生物群落变化明显:酸浸尾矿浸入过程中铁氧化菌的比例高于浮选尾矿浸出的,但硫氧化菌比例低于浮选尾矿浸出的,浸出酸浸尾矿时可以检测到F. thermophilum L1,但在浸出浮选尾矿中检测不到。
关键词:生物浸出;尾矿;微生物群落动态;矿物学分析
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Projects (31570113, 41573072) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Yi-li LIANG; Tel: +86-731-88836943; E-mail: liangyili@hotmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64829-0

