Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2890-2895
Microstructure and mechanical properties of cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 shape memory alloy
Yan-feng LI, Xiao-yu KANG, Xiang-qian YIN, Hao-feng XIE, Xu-jun MI
State Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Metals and Processes, General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals, Beijing 100088, China
Received 15 August 2013; accepted 29 November 2013
Abstract: Mechanical and shape memory properties of a Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h after a cold-rolled reduction of 25% were investigated by phase transformation analysis and microstructure characterization using tensile tests, Vickers hardness tests, electrical resistivity-temperature tests, SEM and TEM. From the results of the tensile, it can be inferred that the fracture stress and yield stress decreased and the fracture elongation increased as the annealing temperature increased for the rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy. They reached stead values when the temperature was above 650 °C. The change in Vickers hardness corresponded to the change in the fracture stress and yield stress. The electrical resistivity-temperature curves suggest that a two- stage martensitic transformation (B2-R-B19′) occurred during cooling and heating. The transformation temperatures decreased to lower temperatures when the annealing temperature was increased and maintained the same after the annealing temperature reached 650 °C. TEM revealed the distinct processes occurring at elevated temperatures: recovery, polygonization, and recrystallization.
Key words: TiNiFe alloy; shape memory alloy; cold rolling; microstructure; mechanical property
1 Introduction
TiNi-based shape memory alloys are attractive for structural and functional applications in engineering and medicine due to their unique and important mechanical and functional properties. Severe plastic deformation or thermomechanical treatment is necessary to improve shape memory effects and mechanical properties [1-3]. Much research has been focused on severe plastic deformation, which can significantly influence the microstructure and phase transformation of TiNi alloys [4-8]; in addition, the mechanical and shape memory properties are improved by forming nanostructures in the alloys. VALIEV et al [2] demonstrated that the nanocrystalline Ti49.4Ni50.6 alloy produced using severe plastic deformation through high pressure torsion exhibited an unusual increase in strength but low ductility at room temperature, and the strength and ductility were enhanced at higher temperatures. PUSHIN et al [8] pointed out that severe plastic deformation processing did not alter the phase transformation sequence of the alloys but changed the morphology of the martensite. In addition, the processing resulted in a greater recovery stress and a maximum reverse strain of the shape memory.
Among all the TiNi-based shape memory alloys, the TiNiFe alloy has the lowest martensitic transformation temperature and maintains good mechanical properties that are well used in the application of couplings in jet fighters [9,10]. Some research [11-13] has been carried out to study the effect of composition change or thermomechanical treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties of TiNiFe alloys. Recently, the focus of the research has been the effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiNiFe shape memory alloys after severe plastic deformation treatment (40%-70%). Medium-scale plastic deformation treatment (10%-30%) and its effects have hardly been studied. The purpose of the present work is to reveal the evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties as a function of the TiNiFe alloy after plastic deformation treatment.
2 Experimental
A Ti-47%Ni-3%Fe alloy, produced by vacuum induction melting using a CaO crucible, was used for this study. Samples of 10 mm×1 mm×1.2 mm were spark cut from this alloy and homogenized at 850 °C for 4 h under vacuum. They were then cold rolled at room temperature to a 25% reduction. Subsequent annealing was done at 450-750 °C for 1 h. With a heating/cooling rate of 3-5 K/min an electrical resistance apparatus was used to study the phase transformation. The microstructural characterization of the alloys was carried out by SEM (JSM-7001F, equipped with EDA) and TEM. The TEM specimens were electro-polished in an electrolyte with 90% (volume fraction) grain alcohol and 10% perchloric acid at -40 °C. Furthermore, these specimens were studied on an analytical transmission electron microscope (JEM-2000FX) at a nominal acceleration voltage of 200 kV. The mechanical properties were investigated by tensile tests carried out on a SHIMADZU AG-250KNIS type universal tensile test machine with a strain rate of 0.5 mm/min.
3 Results and discussion
In order to understand the mechanical properties of cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloys annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h, tensile tests were carried out at room temperature and the typical stress versus strain curves obtained are shown in Fig. 1. Elastic deformation with 2% strain can be seen beside the stress reduced R phase transformation with a strain of 0.3%-0.6%. Plastic deformation occurred following the elastic deformation. For all the cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy samples, the fracture stress Rm and yield stress Rp0.2 decreased following the increase of the annealing temperature and kept stable after the annealing temperature reached 650 °C.
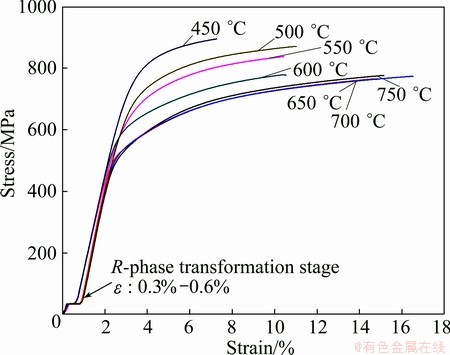
Fig. 1 Stress-strain curves for Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450 °C, 500 °C, 550 °C, 600 °C, 650 °C, 700 °C, and 750 °C for 1 h after cold rolling of 25% reduction
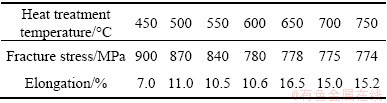
The fracture stress Rm values and fracture elongations for Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloys annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h are listed in Table 1. This phenomenon is believed to be due to the elimination of the residual stress field and vacancies caused by cold rolling as well as a decrease in dislocation density with the increasing annealing temperatures.
Table 1 Fracture stress and elongation for Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h after cold rolling of 25% reduction
It is an interesting discovery that in the tensile tests a stress-induced R-phase transformation stage appeared in all the cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloys. The induced stress is about 40 MPa with a strain of 0.3%-0.6%. It is inferred that the austenite B2 phase transforms to the R-phase although the temperature is far higher than Rs. This is stress-induced R-phase transformation. The dislocations cause the stress concentration, which promotes the nucleation for the R-phase under external stress and makes it easy to transform to the R-phase from the austenite B2 phase even at a temperature higher than Rs.
The experimental results of the Vickers hardness test for the cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy samples annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h are shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen that as the annealing temperature increases, the hardness decreases and the changes in the fracture stress and yield stress correspond to this.
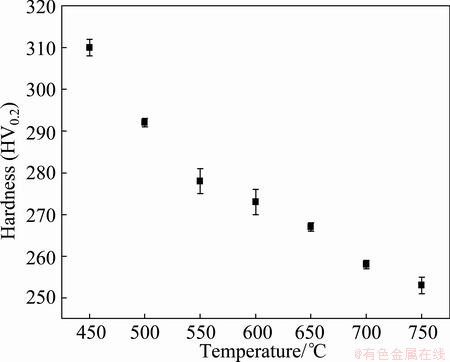
Fig. 2 Vickers hardness for Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h after cold rolling of 25% reduction
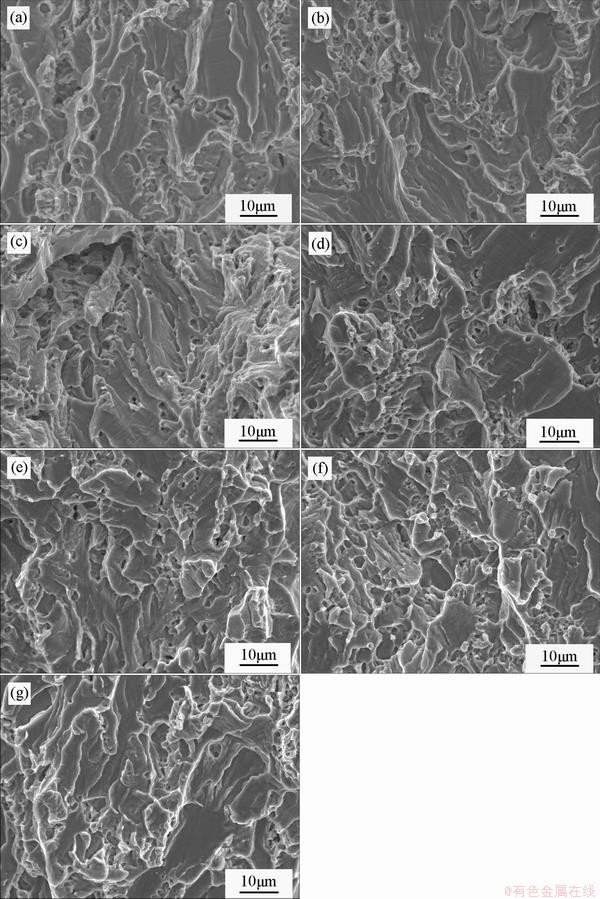
Fig. 3 SEM fractographs of Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450 °C (a), 500 °C (b), 550 °C (c), 600 °C (d), 650 °C (e), 700 °C (f) and 750 °C (g) for 1 h after cold rolling of 25% reduction
The fractographs of the cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h are shown in Fig. 3. These can help to identify the fracture mechanism. Dimples in the cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450 °C are rare and fine. They appear to be caused by the quasi-cleavage fracture mechanism [14]. As the annealing temperatures increase, the dimples become slightly bigger and easier to find. The fracture mechanism turns into a dimple rupture fracture mechanism. Correspondingly, as the temperature raises, the fracture elongation increases and then after the temperature reaches 650 °C, it remains stable.
Figure 4 shows the electrical resistivity versus temperature curves of the cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h. For the Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloys with following annealing at different temperatures, a martensitic transformation occurs at the two-stage transformation pass B2-R-B19′. The temperature range of both B2-R and R-B19′ phase transformation (including Ms, which is the martensite start temperature upon cooling, and Rs, which is the R phase start temperature upon cooling) decreased to lower temperatures when the annealing temperature increased. These temperature ranges maintained the same after the annealing temperature reached 650 °C. OTSUKA and REN [15] reported that the Ms of Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy can be as low as -120 °C. The present work shows that Ms of the cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy is lower than -120 °C. The result is believed to be due to a significant difference in the influence of the cold rolling processing. The cold rolling induces dislocations in the substructure and the high dislocation density acts as a great impediment on the interface movement, which results in the martensitic transformation being suppressed by introduction of elastic strain, lattice defects, and crystal refinement. The corresponding curves exhibit elongated curves forward of the martensitic transformation and the R-phase transformation without typical temperature hysteresis. This result is similar to that reported by LIN and WU [16] that the plastic deformation essentially stabilized the B2 phase by chemical disordering and/or a high density of lattice defects, such as dislocations and vacancies. Furthermore, the internal stress field interacts with the newly formed martensite or R-phase plates. In the case of cold-rolled alloy, as the B2-R phase transformation has a smaller transformation strain than the R-B19′ transformation, the former is affected less by the stress field. This leads to a larger martensitic transformation interval.
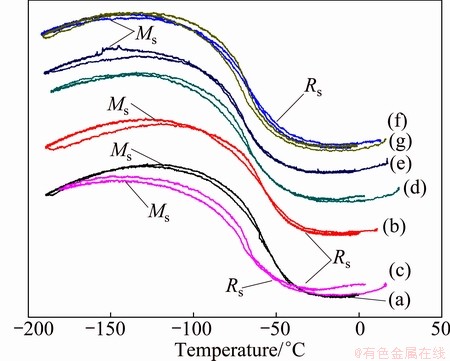
Fig. 4 Electrical resistivity vs temperature curves of Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450 °C (a), 500 °C (b), 550 °C (c), 600 °C (d), 650 °C (e), 700 °C (f), and 750 °C (g) for 1 h after cold rolling of 25% reduction
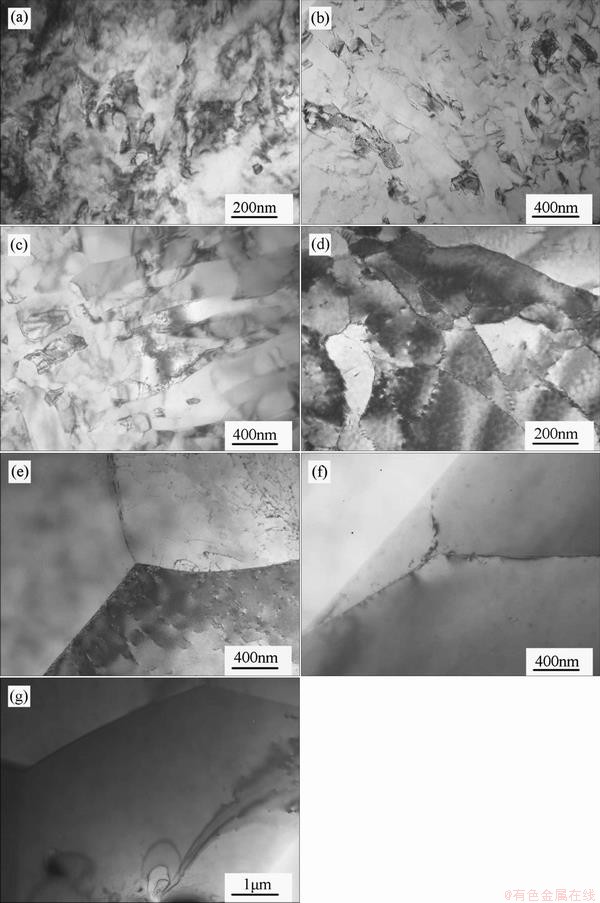
Fig. 5 Bright field TEM images of Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450 °C (a), 500 °C (b), 550 °C (c), 600 °C (d), 650 °C (e), 700 °C (f), and 750 °C (g) for 1 h after cold rolling of 25% reduction
The microstructures of the Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloys annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h after a cold rolling reduction of 25% are illustrated in Fig. 5. The post-deformation annealing results reveal distinct processes occurring at elevated temperatures: recovery, polygonization, and recrystallization. When annealed at 600 °C, new grains begin to form as very small nuclei with size varying from 50 to100 nm. The grains then grow rapidly following the temperature elevated to 650 °C when the recovery is completed and the parent material is completely replaced; the final sizes of the grains are 20-30 μm. After annealing at 650 °C, no noticeable differences can be observed in the structure; the recrystallization results in the austenite grains a similar size. Nanocrystalline and even amorphous structures were not found, which is not in accordance with the results from other studies [16-19] that the last two structures appear in the TiNi alloy after cold rolling of 40-70% reduction. The energy provided by a cold rolling reduction of 25% cannot drive the formation of the nanocrystalline and even amorphous structures.
4 Conclusions
1) The microstructures of a Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy annealed at 450-750 °C for 1 h after a cold-rolled reduction of 25% exhibited distinct processes occurring at elevated temperatures: recovery, polygonization, and recrystallization. The fracture stress and yield stress decrease following an increase in the annealing temperatures and the fracture mechanism transforms from quasi-cleavage fracture to dimple rupture fracture.
2) The cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy followed by annealing at different temperatures exhibits a two-stage martensitic transformation (B2-R-B19′) during cooling and heating. The transformation temperatures decreased as the annealing temperature increased and maintained the same after the annealing temperature reached 650 °C. All the cold-rolled Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloys have R-phase transformation stages.
References
[1] OTSUKA K, REN X. Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2005, 50: 511-678.
[2] VALIEV R Z, GUNDEROV D V, LUKYANOV A V, PUSHIN V G. Mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline TiNi alloy produced by severe plastic deformation [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47(22): 7848-7853.
[3] CHU C L, CHUNG J C, CHU P K. Effects of heat treatment on characteristics of porous Ni-rich NiTi SMA prepared by SHS technique [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(1): 49-53.
[4] KHELFAOUI F, GUENIN G. Influence of the recovery and recrystallization processes on the martensitic transformation of cold worked equiatomic Ti-Ni alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 355: 292-298.
[5] JIANG S Y, ZHAO Y N, ZHANG Y Q, TANG M, LI C F. Equal channel angular extrusion of NiTishape memory alloytube [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(7): 2021-2028.
[6] MAHESH K K, FERNANDES B, GURAU G. Stability of thermal-induced phase transformations in the severely deformed equiatomic Ni-Ti alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47(22): 6005-6014.
[7] NAKAYMA H, TSUCHIYA K, UMEMOTO M. Crystal refinement and amorphisation by cold rolling in TiNi shape memory alloys [J]. Scripta Materials, 2001, 44: 1781-1785.
[8] PUSHIN V G, STOLYAROV V V, VALIEV R Z, LOWE T C, ZHU Y T. Nanostructured TiNi-based shape memory alloys processed by severe plastic deformation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 410-411: 386-389.
[9] HARA T, OHBA T, OKUNISHIE. Structural study of R-phase in Ti-50.23 at.%Ni and Ti-47.75 at.%Ni-1.50 at.%Fe alloys [J]. Materials Transactions, JIM, 1997, 38(1): 11-17.
[10] YOSHIDA I, MONMA D, ONO T. Damping characteristics of Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 448: 349-354.
[11] FRENZEL J, PFETZING J, NEUKING K, EGGELER G. On the influence of thermomechanical treatments on the microstructure and phase transformation behavior of Ni-Ti-Fe shape memory alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 440-482: 635-638.
[12] DUARTE L I, KLOTZ U E, LEINENBACH C, PALM M, STEIN F, LOFFLER J F. Experimental study of the Fe-Ni-Ti system [J]. Intermetallics, 2010, 18(3): 374-384.
[13] XU H B, JIANG C B, GONG S K, FENG G. Martensitic transformation of the Ti50Ni48Fe2 alloy deformed at different temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 281: 234-238.
[14] CHARLI R, ASHOK C. Failure analysis of engineering materials [M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc, 2002: 105-115.
[15] OTSUKA K, REN X. Recent developments in the research of shape memory alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7(5): 511-528.
[16] LIN H C, WU S K. Determination of heat of transformation in a cold-rolled martensitic TiNi alloy [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1993, 24(3): 293-299.
[17] BRAILOVSKI V, PROKOSHKIN S D, KHMELEVSKAYA I Y, INAEKYAN K E, DEMERS V, BASTARACHE E, DOBATKIN S V, TATYANIN E V. Interrelations between the properties and structure of thermomechanically-treated equiatomic Ti-Ni alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 438-440: 597-601.
[18] TSUCHIYA K, INUZUKA M, TOMUS D, HOSOKAWA A, NAKAYAMA H, MORII K, TODAKA Y, UMEMOTO M. Martensitic transformation in nanostructured TiNi shape memory alloy formed via severe plastic deformation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 438-440: 643-648.
[19] LIN H C, WU S K. The tensile behavior of a cold-rolled and reverse-transformed equiatomic TiNi alloy [J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1994, 42(5): 1623-1630.
Ti50Ni47Fe3形状记忆合金冷轧变形后的组织与性能
李艳锋,康小宇,尹向前,解浩峰,米绪军
北京有色金属研究总院 有色金属材料制备加工国家重点实验室,北京 100088
摘 要:采用拉伸测试、维氏硬度测试、电阻率-温度曲线测试及扫描电镜和透射电镜观察显微组织的方法研究冷轧变形量为25%的Ti50Ni47Fe3合金经450~750 °C下1 h退火后的显微组织和性能。结果表明,冷轧变形增强了合金的抗拉强度和屈服强度,冷轧变形后形成的应力场有助于R相变的发生。随着退火温度的升高,合金的抗拉强度和屈服强度下降,伸长率增大;当退火温度高于650 °C时,强度和伸长率趋于稳定。电阻-温度曲线表明,在升、降温过程中发生两阶段相变B2-R-B19′。随着退火温度的升高,合金的相变温度降低;当退火温度高于650 °C时,相变温度趋于稳定。随着退火温度的升高,合金依次发生回复、再结晶和晶粒长大。
关键词:钛镍铁合金;形状记忆合金;冷轧;显微组织;力学性能
(Edited by Hua YANG)
Foundation item: Project (51201014) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Yan-feng LI; Tel: +86-10-82241176; E-mail: lyf@grinm.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63423-3