电化学和水解-缩合方法制备具有防腐蚀和活化铜表面的多功能聚合纳米薄膜
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第11期
论文作者:王亚斌 黄玉东 亓玉台
文章页码:2947 - 2959
关键词:铜;均三嗪二硫醇硅烷;恒电流技术;多功能聚合纳米薄膜;功能化界面
Key words:copper; triazinedithiolsilane; galvanostatic technique; multifunctional polymeric nanofilm; functionalized interface
摘 要:通过恒电流技术和水解-缩合方法,在铜表面制备均三嗪二硫醇硅烷单钠盐多功能聚合纳米薄膜,该纳米薄膜能够防腐蚀和活化铜表面。采用电化学测试来评价该薄膜的防腐蚀性能;用傅里叶变换红外光谱学(FT-IR)和接触角技术监测纳米薄膜表面功能团的变化;用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)及扫描电子显微镜(SEM)分别研究聚合纳米薄膜的化学组成和形貌特征。结果表明:在整个制备过程,电化学聚合形成的二硫单元优先保护铜表面;紧接的水解(缩合)作用使得该薄膜形成新的、具有防腐蚀和活化铜的多功能聚合纳米薄膜。该界面(聚合纳米薄膜)使得其他含有羟基的化合物可能在铜表面键合,且能够应用在高要求的研究和工业中。
Abstract: A multifunctional polymeric nanofilm of triazinedithiolsilane monosodium salt, which can resist corrosion and activate copper surface concurrently, was prepared by galvanostatic technique and the following hydrolysis-condensation approach. Electrochemical tests were carried out to evaluate the resistant ability of nanofilm. The changes of functional groups atop the nanofilms were monitored with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and contact angles (CA) simultaneously. The chemical composition and the morphology of the polymeric nanofilm were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), respectively. The results reveal that the preferentially developed disulfide units protect the copper during the whole preparation process, and the subsequently hydrolyzed nanofilms without/with heating shape into new interface phases bearing the multifunctionality. This multifunctional interface (the polymeric nanofilm on copper surface) opens up the possibilities for other OH-containing reagents to be anchored onto copper surface in demanding researches or industrial applications.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 2947-2959
Ya-bin WANG1,2, Yu-dong HUANG1, Yu-tai QI1
1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;
2. Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xining 810008, China
Received 25 October 2015; accepted 10 May 2016
Abstract: A multifunctional polymeric nanofilm of triazinedithiolsilane monosodium salt, which can resist corrosion and activate copper surface concurrently, was prepared by galvanostatic technique and the following hydrolysis-condensation approach. Electrochemical tests were carried out to evaluate the resistant ability of nanofilm. The changes of functional groups atop the nanofilms were monitored with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and contact angles (CA) simultaneously. The chemical composition and the morphology of the polymeric nanofilm were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), respectively. The results reveal that the preferentially developed disulfide units protect the copper during the whole preparation process, and the subsequently hydrolyzed nanofilms without/with heating shape into new interface phases bearing the multifunctionality. This multifunctional interface (the polymeric nanofilm on copper surface) opens up the possibilities for other OH-containing reagents to be anchored onto copper surface in demanding researches or industrial applications.
Key words: copper; triazinedithiolsilane; galvanostatic technique; multifunctional polymeric nanofilm; functionalized interface
1 Introduction
According to the recently proposed design route of protecting metals against corrosion in our previous study [1], i.e., assembling two or more categories of protective groups to synthesize brand-new compounds and then fabricating the corresponding resistance structure from these novel compounds using various techniques, a type of triazinedithiolsilane compounds capable of resisting copper corrosion has been conceived and successfully synthesized by combining triazine- dithiol and silane groups. 6-(3-triethoxysilylpropyl) amino-1, 3, 5-triazine- 2, 4-dithiol monosodium salt (TESPA) is one representative of such triazinedithiol- silane compounds. TESPA polymeric nanofilm has been fabricated by self-assembled technique and the following heating based on the process shown in Fig. 1(a). The results showed that the polymeric nanofilm significantly inhibited copper corrosion; the formations of three- dimensional polymeric disulfide units (—SS—) and siloxane networks (Si—O—Si) accounted for the protective ability [2].
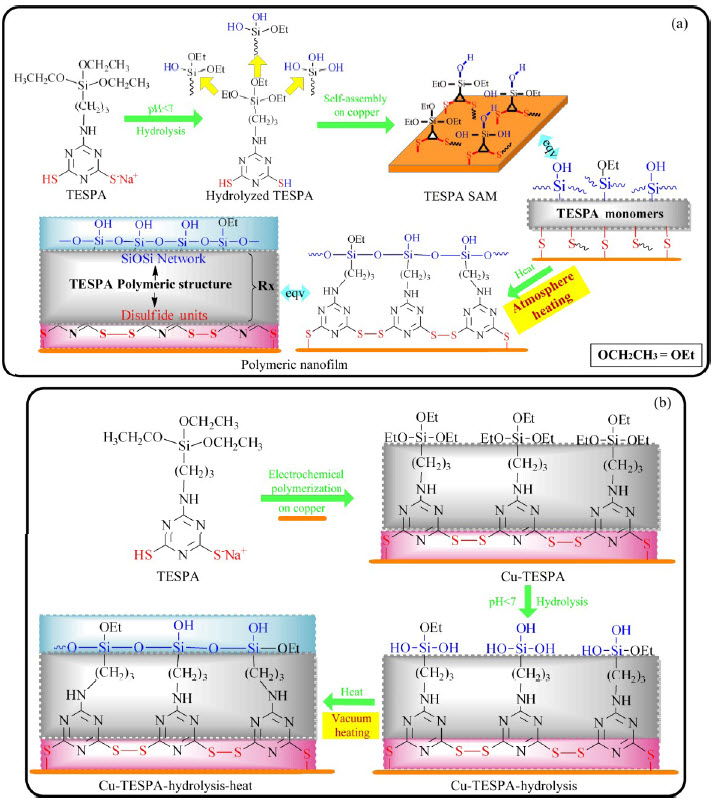
Fig. 1 Fabricating TESPA polymeric nanofilm via self-assembled technique and following heating method (a) and via electrochemical and following hydrolysis-condensation approaches (b)
In fact, the disulfide units obtained from the polymerization of triazinedithiols can be generated either by heating the nanofilm after triazinedithiols/their monosodium salt derivatives self-assemble onto copper in acidic alcohol/water solution [3], or by electrochemical polymerization of their monosodium salts in a Na2CO3-water electrolyte environment [4]. That is the fundamental reason that the designed and synthesized TESPA molecule is a style of an inorganic monosodium salt (one —SH and a —SNa groups) rather than an organic monomer with two —SH groups. When the protective triazinedithiol moiety in TESPA is conceived throughout the design route, various techniques to fabricate the according resistant disulfide structure are considered accordingly.
This study concentrates on the latter part of the design route, i.e., fabricating the corresponding resistance structure from triazinedithiolsilane compounds using various techniques. A TESPA polymeric nanofilm will be prepared by electrochemical approach, followed with hydrolysis-condensation technique, instead of self- assembly method. The experimental procedure is represented in Fig. 1(b). A polymeric nanofilm with disulfide structure could be preferentially developed by electrochemical methods. The obtained surface with hydrophobic SiOCH2CH3 groups could be hydrolyzed to yield hydrophobic Si—OH groups; condensation reactions would occur among Si—OH groups at high temperature, giving rise to Si—O—Si networks on the basis of silane chemistry [5]. For simplification, a bare copper reference is defined as Cu-bare, and an electrochemically prepared sample as Cu-TESPA. The hydrolyzed Cu-TESPA without and with curing are recorded as Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis and Cu-TESPA- hydrolysis-heat, respectively.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and reagents
6-(3-triethoxysilylpropyl)amino-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-dithiol monosodium salt was synthesized by reacting 6-(3-triethoxysilylpropylamino)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4- dichloride with NaSH according to our earlier study [6]. Distilled water was used as solvent and Na2CO3 as supporting electrolyte. The concentrations of TESPA and supporting electrolyte were kept constant at 5 mmol/L and 0.15 mol/L, respectively. All of the chemicals were employed as analytical reagent (AR) without further purification. Test specimens (50 mm × 30 mm × 0.1 mm) of pure copper were abraded with emery paper of 800 grit and 1000 grit, and followed by fine polishing with alumina paste of 0.35 mm, 0.2 mm, 0.1 mm particle size to achieve a mirror finish [7]. The samples were then degreased with acetone and alcohol in an ultrasonic bath for 15 min, rinsed with copious distilled water, and finally dried by cold air from a hair dryer.
2.2 Electrochemical fabrication of TESPA polymeric nanofilm
The electrochemical polymerization of TESPA was performed by using a PARSTAT 2273 workstation (Princeton Applied Research, USA) in a standard three-electrode system at room temperature. The electrolytic cell was equipped with working electrode (copper), Pt counter electrode (2 cm2), and reference electrode (saturated calomel electrode, SCE). All potential values were referred to φ(vs SCE). The cell was filled with electrolytic solution containing TESPA or not. Cyclic voltammetry that can elucidate the electrochemical polymeric mechanism and fabricate the polymeric nanofilm, was carried out at a sweep rate of 30 mV/s with potentials ranging from -0.2 to 1.1 V by six scanning cycles on trial; then, an accurate potential scope of preparing TESPA polymeric nanofilm was determined according to the obtained plots. The as-deposited Cu-TESPA was hydrolyzed in a 0.1 mol/L acetic acid (CH3COOH) solution at 25 °C for 30 min to yield Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis surface. The obtained hydrolyzed surface was heated at 90 °C for 15 min under vacuum to produce Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis-heat substrate. The aim of using vacuum curing is to eliminate the effect of copper oxide probably obtained from atmosphere heating.
2.3 Electrochemical measurements
Electrochemical measurements were conducted in a solution of 3.5% NaCl. The electrolyte was not deoxygenated and opened to the air during each process. The above four kinds of surfaces were successively applied as the working electrode with an exposed area of 0.785 cm2 to the NaCl solution. The SCE with a salt bridge in a Luggin capillary serves as the reference electrode and a platinum panel (2 cm2) as the counter electrode. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was carried out in the frequency range from 100 kHz to 10 mHz with 12 points per decade at a 10 mV amplitude of the excitation signal under the open circuit potential (φocp). All EIS data were collected after immersing the working electrodes in the electrolyte for 50 min to reach a stable situation. The potentiodynamic polarization curves (Tafel) were recorded from φocp-350 mV to φocp +350 mV at a scan rate of 1 mV/s. Before the data were recorded, the tested coupons were also immersed in the electrolyte for 50 min in an attempt to achieve a steady state.
By comparing experimental data with the simulated ones, the configurations of equivalent circuits (EC) concerning the TESPA containing surfaces were tested using ZSimpWin software [8]. The quality of EC was first judged by chi-square (χ2) value, and second by error distribution.
2.4 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), contact angle (CA) and scanning electron microscope (SEM)
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used to determine the chemical functional groups using Nicolet iS5 (Thermo Fishe, USA) by high-performance reflection absorption spectroscopy (RAS). A reflection attachment was applied at an incident angle of 80° together with a wire grid polarizer. The scanning range is between 4000 and 500 cm-1 with scan times of 128. Contact angle measurements were performed on a contact angle analyzer, XG-CAMB manufactured by Xuanyichuangxi Industrial Equipment Co., Ltd. (China, Shanghai). The data were collected at five different points on each sample surface to obtain an average value.
SEM study was performed at JSM-5610LV/INCA (JEOL Ltd., Japan), using a high-resolution environmental scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDAX, Japan). Energy dispersive spectroscopy of each surface was carried out in random areas five times to identify the existed elements and their contents, which can further confirm the uniform coverage of the nanofilms.
2.5 X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
XPS experiments were carried out on an ESCALAB 250Xi (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) with Al Kα radiation (hυ=1486.6 eV; analysed area= 600 μm2). Unless specified otherwise, the X-ray anode was run at 250 W and the high voltage was kept at 15.0 kV with a detection angle of 45°. The software of XPS Peak 4.1 was adopted to de-convolve the S2p peaks using the Shirley-type background. We kept a combination of 80% Gaussian and 20% Lorentzian line shape [9], and maintained the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the various components in a given spectrum as close as possible [10].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Fabricating TESPA polymeric nanofilm by cyclic voltammetry
Cyclic voltammetry was carried out in TESPA-free and TESPA-containing solutions to elucidate the electrochemical polymeric mechanism and to fabricate the TESPA polymeric nanofilm. A referred copper was first examined between -0.2 V and 1.1 V in Na2CO3 solution without TESPA. Figure 2 exhibits the cyclic processes of the first to the sixth cycle. From the magnified inset of the first circle, there exists a sharp rise in current at the beginning and a corresponding remarkable peak A1 appears, owing to the oxidation of copper with the Cu(Ⅰ) and Cu(II) products [11]. A broad peak, then observed as peak A2, can be assigned to the sustained slow oxidation of the copper to a certain extent [12]. The third vigorous peak A3 shown after 0.8 V is a result of the water electrolysis under such high potential, because numerous bubbles on the surfaces of copper plate and the two counter electrodes can be seen. The disappearance of peaks A1 and A2 from the second to the sixth circle, as well as the decline of the peaks A3 from the first to the sixth circle displayed in the purple ellipse, indicates that the oxidative products of copper slightly preserve the oxidation process and depress the water electrolysis.

Fig. 2 Cyclic voltammograms of copper in TESPA-free Na2CO3 solution from -0.2 V to 1.1 V with six circles
As copper was examined in the TESPA-containing Na2CO3 solution, peak A1 seems to disappear with a residual tiny A′1 peak, and two apparent anodic peaks of A′2 and A′3 are observed (Fig. 3). The enlarged view of the first cyclic process was also given as the inset. Peak A′1 similar to the feature in the case of TESPA-free solution almost vanishes with a much lower current density of 0.3 mA/cm2, whereas it is approximately 1.5 mA/cm2 in the blank solution. Although the copper oxidation exists under this situation, peak A′1 is unconspicuous in the presence of TESPA, which can be ascribed to the protection of an ad-layer obtained from chemical absorption/interaction between copper atoms and dithiol groups [1]. Peak A′2 measured at 0.34 V as a new sharp one is suggested to the electrochemical polymerization of triazinedithiol monosodium salt groups (TESPA) [13]. The resultant polymeric nanofilm in the form of three dimensional disulfide units suppresses the oxidation of copper leading to a lower current density (below 0.9 mA/cm2) than that in the absence of TESPA solution (above 1.0 mA/cm2). Peak A′3 was expected to the electrolysis of water likewise. However, a difference can be seen that peak A′3 from the second to the last circle is higher than that of the first one. This anomaly indicates that the polymeric nanofilm fabricated by CV cannot perfectly protect copper above 0.8 V, and partial polymeric structure of disulfide units may be decomposed or consumed. As a result, an appropriate potential range should be utilized to develop the polymeric nanofilm without damage of the disulfide structure. It also should be mentioned that although the copper oxidation exists during the whole process, peak A′3 is still lower in the presence of TESPA than that from TESPA-free solution. This implies that the polymeric nanofilm partly inhibits the oxidation process under these potentials. No reduction peak could be observed in negative directions.
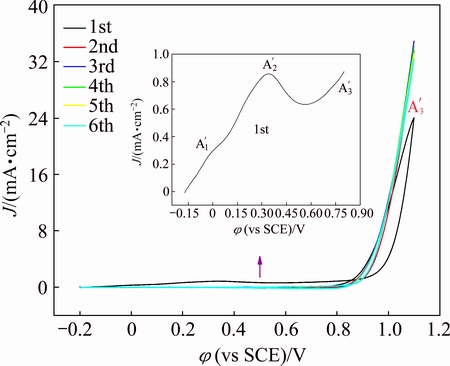
Fig. 3 Cyclic voltammograms of copper in TESPA-containing Na2CO3 solution from -0.2 V to 1.1 V with six circles (The inset is the enlarged view of the first circle)
On the basis of the above results, a proper scope from -0.2 V to 0.8 V was chosen to develop a complete polymeric nanofilm by CV, including the absorption potential (A′1), polymerization potential (A′2) of triazinedithiol monosodium salt, but free of water electrolysis potential (A′3). The peak shape and peak position between -0.2 V and 0.8 V in Fig. 4 are practically identical with those in Fig. 3. However, a decrease tendency from the first circle to the sixth one can be attained, indicating that the polymeric nanofilm resists the copper oxidation and does not decompose/ consume. The result demonstrates that the moiety of triazinedithiol monosodium salt in triazinedithiolsilane compounds could be electrochemically polymerized on copper surface as other triazinedithiol monosodium salts do [4,14], whereas the triethoxysilyl groups do not affect their electrochemical polymerization behaviors due to the chemical inertness (unhydrolyzed SiOCH2CH3 groups are inert and comparatively hydrophobic).
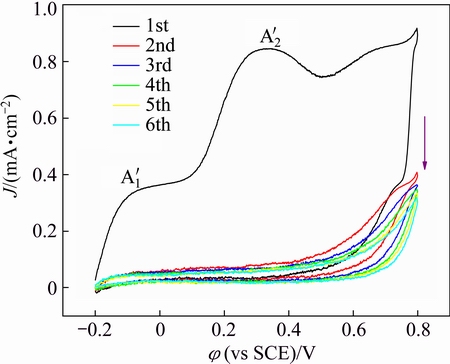
Fig. 4 Cyclic voltammograms of copper in TESPA-containing Na2CO3 solution from -0.2 V to 0.8 V with six circles
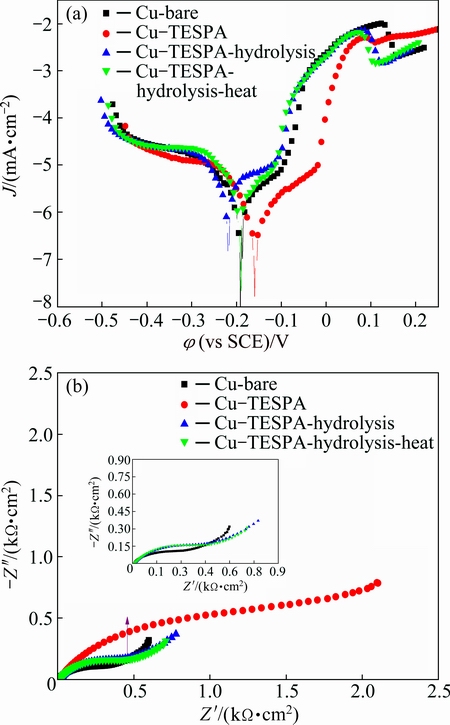
Fig. 5 Polarization plots (a) and Nyquist impedance plots (b) of bare copper, TESPA-deposited copper prepared by cyclic voltammetry (CV), hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by CV, and hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by CV along with heating in 3.5% NaCl solution
3.2 Tafel and EIS curves of nanofilms fabricated by CV
Polarization and EIS were carried out to evaluate the protective abilities of the TESPA polymeric nanofilm fabricated by CV method with/without hydrolysis- condensation. The changes in Tafel plots of the four samples were compared in Fig. 5(a). For bare copper, the anodic polarization curve can be split into three main regions, an apparent Tafel region close to the corrosion potential (the formation of CuCl adlayer), a limiting-current region with an anodic current peak centered around 0.095 V (the dissolution of CuCl film), and a mixed-kinetics region above the limiting-current potential (the formation of divalent copper species) [15]. It is apparent that the plot of Cu-TESPA dramatically decreases among the four studied surfaces, and the corrosion potential shifts to a more positive direction. These results indicate that the polymeric nanofilm from Cu-TESPA most efficiently inhibits the copper corrosion or dissolution. The curve of Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis increases and turns to be the highest accompanied with the biggest negative shift in corrosion potential, implying the worst corrosion resistance. The breakdown of protection ability clearly shows a marked effect of surface wettability on the copper protection against corrosion. The polymeric nanofilm prepared by CV method without any further modification includes exclusively hydrophobic SiOCH2CH3 groups; however, the following hydrolysis generates hydrophilic Si—OH groups. The polar Si—OH groups have high affinities with chlorine anions inside the NaCl solution, which promotes the adsorption process of Cl– onto polymeric nanofilm and the permeation into copper surface, accelerating the corrosion and depressing the protection ability [16]. This result deviates from the purpose of using TESPA polymeric nanofilm as corrosion resistance. In theory, the hydrolyzed surface still contains the protective disulfide structure and it should be protective to some extent. The TESPA polymeric nanofilm fabricated by self-assembled method can confirm the above assumption [1], because it resists corrosion with the disulfide structure accompanied with Si—OH groups in part one. However, none of this can be seen except damage here. The three-dimensional disulfide units in polymeric nanofilm are insufficient to resist corrosion well, and they should be developed in a great number. The following heated surface owns the similar behavior compared with the hydrolyzed one, but the plot and the potential fall between the bare and the Cu-TESPA- hydrolysis. The result indicates that the resistant ability of the heated surface improves, but is still of inferior quality. Overall, the polymeric nanofilm obtained by CV without hydrolysis greatly protects copper from corroding, whereas the hydrolyzed Cu-TESPA surface without/with heating becomes harmful to copper. The decline of the protective abilities reveals that the coverage of polymeric nanofilm fabricated by CV approach is not extensive.
The Nyquist impedance diagrams of the three surfaces fabricated by CV method are exhibited in Fig. 5(b) to reveal the structural changes of the nanofilms. Bare copper consists of a depressed semicircle at the high frequency and a straight line at low frequency. The former, caused by the charge transfer process, is related to the time constant of the charge-transfer resistance (Rct) and the double-layer capacitance (Cdl) at the interface of copper-NaCl solution [17]. The latter typically known as Warburg impedance (W) can be ascribed to the anodic diffusion process of copper chloride compounds from the electrode surface to the bulk solution [18], the presence of which indicates that diffusion rather than charge transfer process dominates under this circumstance. A larger capacitive loop emerges with a tiny Warburg impedance at low frequencies in Cu-TESPA. For the hydrolyzed surface, an evident Warburg impedance emerges at low frequencies, which demonstrates that the process is controlled by diffusion other than charge transfer. The diameter of the capacitive loop decreases for the hydrolyzed surface compared with that from Cu-TESPA, revealing that the hydropathy is crucial for resistance ability of the polymeric nanofilm. A reduced Warburg impedance, observed as the hydrolyzed surface condenses in Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis-heat, confirms the formation of the Si—O—Si network. The capacitive loops of the latter two surfaces are practically same, revealing that the Si—O—Si network is too rare to act as the protective structure. EIS result is in a good agreement with that from the Tafel.
Though the protection ability decreases as the Cu-TESPA surface is hydrolyzed and even condensed, the most significant aspect of the results lies in whether we can develop a functional polymeric nanofilm of triazinedithiolsilane that concurrently activates the copper surface and protects the copper to a certain degree by electrochemical techniques. The significance of using CV largely embodies the ability to provide information about the chemistry of redox couples [19], which is the most attractive feature of this technique [20, 21]. Hence, galvanostatic technique (GT), which offers a continuous current and a stronger effect to prepare the polymeric nanofilm, was conceived and adopted to achieve such a conceived multifunctional surface.
3.3 Fabricating TESPA polymeric nanofilm by galvanostatic technique
In order to fabricate a more compact and uniform polymeric nanofilm, galvanostatic technique was carried out with a current density of 0.05 mA/cm2 in TESPA-free and TESPA-contating Na2CO3 solutions (5 mmol/L and 0.15 mol/L) at ambient temperature for 30 min. Figure 6 shows the increasing potentials in the initial time period and plateaus at longer time for the two samples. The φ-t curve of copper in TESPA-free solution is presented as the black line. An acute increase in potential was observed before 6 min during which two oxidation peaks successively emerge. Peak A initiated around 1 min indicates the oxidation of copper with the production of Cu+, and this oxidation effect remains till 4 min. After that, Cu and Cu+ further oxidize to produce Cu2+, which is identified by peak B [22]. No obvious potential change can be seen after 15 min, revealing that the surface keeps stable. The red line was recorded for copper tested in TESPA-containing solution. A quasi electrochemical behavior is noticeable accompanied with peaks A' and B'; however, the potentials in TESPA situation are higher than those in blank solution during the first 7 min. These observations demonstrate that the adsorption (A') and electrochemical polymerization (B') of triazinedithiol groups have happened [23]. The potentials become steady in the presence of TESPA solution after 15 min as well. It is supposed that the polymeric nanofilm has been generated on copper surface by chemical reaction of copper and TESPA.
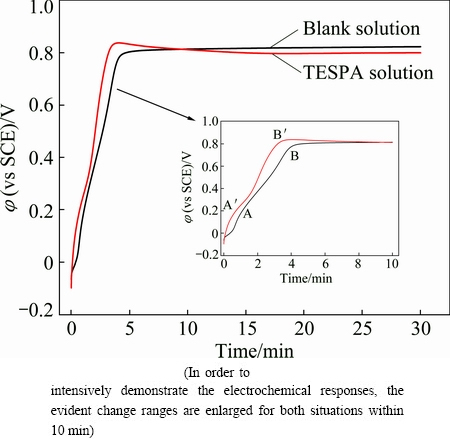
Fig. 6 Relationship between potential and time by galvanostatic polymerization in Na2CO3 solution without TESPA (black line) and with TESPA (red line) on copper for 30 min
3.4 Tafel and EIS curves of nanofilms fabricated by galvanostatic technique
The polarization behavior of galvanostatically polymerized nanofilm was compared in Fig. 7(a). The plot of Cu-TESPA remarkably decreases among the studied nanofilms, and the copper corrosion is the most efficiently inhibited by the TESPA polymeric nanofilm. The curve of Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis also declines accompanied with a positive shift in corrosion potential; however, it is higher than that of Cu-TESPA, implying an inferior corrosion resistance. As the hydrolyzed surface is heated under vacuum condition, the diagram shows a further decrease, which means that the protection ability of the condensed polymeric nanofilm remains inferior despite the assistance of the SiOSi protective architecture. The decrease tendency of hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper surface and the heated one can be interpreted with the same reasons as deciphered in CV situation. Nonetheless, the hydrolyzed and condensed polymeric nanofilms developed by galvanostatic method protect the copper instead of destroying.
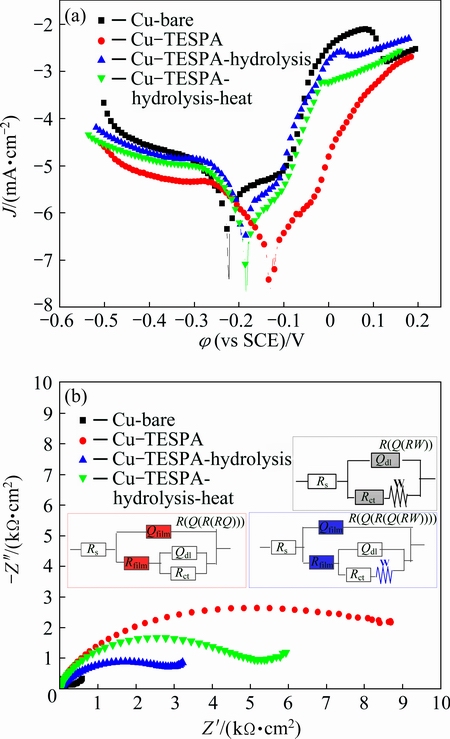
Fig. 7 Polarization plots (a) and Nyquist impedance plots (b) of bare copper, TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT, hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT, and hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT along with heating in 3.5% NaCl solution
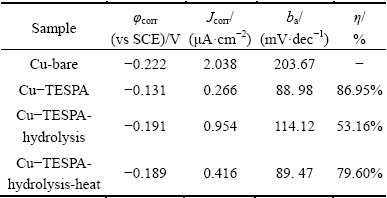
From polarization curves, the corrosion potentials (φcorr vs SCE) and corrosion current densities (Jcorr) are given by extrapolating the anodic Tafel (ba) lines to the corrosion potentials [24,25], and recorded in Table 1. The protection efficiency (η) of each surface can be calculated by the following equation [24,25]:
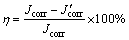 (1)
(1)
where Jcorr and J'corr represent the corrosion current densities of the bare and other three samples, respectively. The values of η are also listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Electrochemical polarization parameters of bare copper, TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT, hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT, and hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT along with heating in 3.5% NaCl solution
EIS was performed to further understand the resistance structure and the protective abilities of the samples prepared by means of galvanostatic technique (Fig. 7(b)). Obvious changes of the electrochemical behavior can be observed in comparison with the surfaces obtained from CV technique. The Warburg impedances disappear at low frequencies with only a large capacitive loop in terms of Cu-TESPA surface, revealing that the polymeric nanofilm sufficiently hinders the diffusion and the process is controlled by charge transfer. For both the hydrolyzed and condensed surfaces, the Warburg impedances emerge again at low frequencies, which demonstrates that the two processes are controlled by diffusion other than charge transfer. These transformations can be accordingly attributed to the structural changes of the nanofilms, i.e., SiOCH2CH3 groups in Cu-TESPA, Si—OH groups in hydrolyzed nanofilm, and Si—O—Si networks plus Si—OH groups in condensed film. The polar groups in the latter two substrates have influence on Cl– adsorption and diffusion that accelerate corrosion, thus we obtain a conclusion confirmed by Tafel result. The diameters of the capacitive loops in galvanostatically prepared samples outweigh the ones obtained by CV, revealing a denser and more compacted coverage of the polymeric nanofilm. These observations manifest that galvanostatic technique can successfully deposit a multifunctional polymeric nanofilm on copper surface; the film not only activates copper with the Si—OH groups, but also protects the copper bulk from corroding partly.
In order to fully understand the properties of the galvanostatically fabricated polymeric nanofilms, the configurations of equivalent circuits (EC) were carried out and shown as insets in Fig. 7(b). The Nyquist plot of bare copper in this investigation is very similar to other research works where a equivalent circuit of R(Q(RW)) was proposed [26,27]. Thus, R(Q(RW)) is applied to analyzing the EIS result of bare copper as well. For both Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis and Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis-heat, a equivalent circuit of R(Q(R(Q (RW)))) is fitted according to the Nyquist impedance diagrams, as well as the plots of impedance and phase angle. The quality of EC was first judged by chi-square (χ2) value, and second by error distribution. The fitted figures are simple and abbreviated here. The calculated values of each element in the equivalent circuits are listed in Table 2, where Rs, Rfilm and Rct are the solution resistance, resistance of coating and charge transfer resistance, respectively; Qfilm and Qdl stand for capacitance of coating and capacitance of copper-solution interface, respectively; W acts as Warburg impedance.
Generally, the value of Rs as the uncompensated solution resistance (Ω) is only several tens of Ω (small) and has no effects on the coated films. The values of Rs obtained from Fig. 7(b) in Table 2 coincide with the rule. The values of Rfilm and Rct in TESPA-treated systems are greater than those of the bare Cu; they gradually decrease with the order of Cu-TESPA, Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis- heat and Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis. These can be explained as the Tafel results do. For a given coating, the changes in Qfilm are often taken as a measure of water uptake in the coating [28]. Qfilm decreases from Cu-TESPA to Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis and Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis-heat, which demonstrates that the adsorption of water onto the latter two nanofilms becomes harder. However, the latter two surfaces theoretically possess hydrophilic Si—OH groups that adsorb water easily; accordingly, the Qfilm values should increase. This irregularity will be deciphered accompanied with SEM images. Meantime, when copper surface is treated with TESPA, and when TESPA-treated surface is hydrolyzed and condensed, Qdl values decrease, which can be ascribed to a decrease of dielectric constant [29] due to the chemical interaction between TESPA and copper (the formation of —SCu and —SS—), as well as the structural change (the formation of Si—O—Si) of the polymeric nanofilm.
3.5 High-resolution XPS spectra of S 2p from TESPA powder and investigated surfaces
The polymerization of —SH groups cannot be directly verified by EIS, hence XPS spectra of S 2p were investigated in Fig. 8 for TESPA powder and the TESPA-deposited copper surfaces by galvanostatic technique. All the S 2p peaks were fitted using one doublet with a splitting of 1.2 eV and 2:1 area ratio [30]. Six distinguishable peaks with three chemical states, located at 162.36 eV (161.16 eV), 162.93 eV (161.73 eV), and 168.32 eV (167.12 eV), are resolved for S 2p1/2 (S 2p3/2) in TESPA powder (Fig. 8(a)). The lowest- energy state arises from S- [31], because sulfur in this chemical environment has the most electron density. Peaks at 162.93 eV (161.73 eV) are assigned to dithiol groups in TESPA [32]. The highest chemical state can be assigned to SO32– [33,34] which has been oxidized because of X-ray during the process. As TESPA monomers in Na2CO3 electrolyte have been electro- chemically deposited on copper surface, three chemical states of S 2p yield. Sub-bands of 161.79 eV (162.99 eV) (Fig. 8(b)) are ascribed to bound thiolate species of —SCu in Cu-TESPA [12,35], because of the chemical/ electrochemical reaction between SH groups and copper. The second type of peaks at 164.76 eV (163.56 eV) stands for polymerization of SH groups to disulfide units [3,30,36]. Another type of peaks at 168.94 eV (167.74 eV) is assigned to the sulfate radical (SO42–) [34] caused by the oxidation of SH groups under electrochemical action. Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis holds the same peaks like Cu-TESPA. However, the peak and their positions are more close to theoretical value due to the removal of by-products in acetic acid solution, such as Cu(II) complex which covers the surface and hampers the direct detection in Cu-TESPA situation. After heating Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis, no obvious difference can be seen, except peaks of contaminative SO42- disappear (Fig. 8(d)).
Table 2 Values of elements in equivalent circuit to fit EIS for bare copper, TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT, hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT, and hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT along with heating in 3.5% NaCl solution
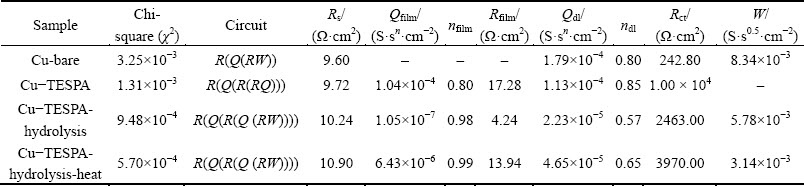
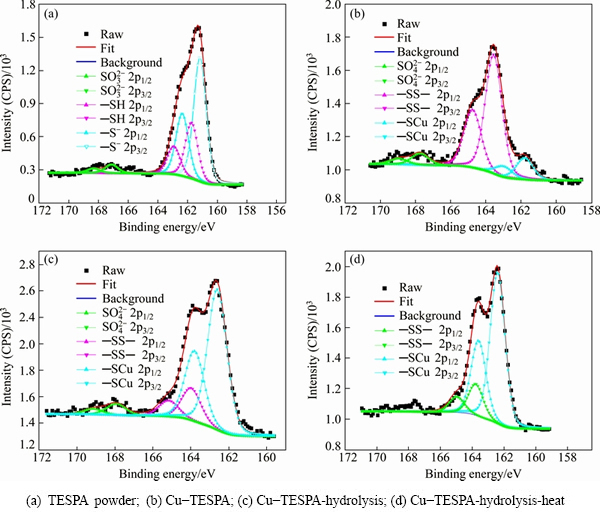
Fig. 8 High-resolution XPS spectra of S 2p from TESPA powder, as well as surfaces of TESPA-deposited copper, hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper, and hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper plus following heating under vacuum
3.6 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), contact angles (CA) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Though the electrochemical and XPS findings substantiate the structural changes of the polymeric nanofilm, the directional alignment of the nanofilm in each stage has not been clarified with firsthand evidence. Thus, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and the contact angles (as the insets) of the samples are performed in Fig. 9. Peaks at around 1580 cm-1 are observed on the TESPA-treated copper surfaces and can be attributed to C=N bonds inside the triazine ring of TESPA, indicative of successful deposition of TESPA nanfilm [37,38]. The bare copper with a 62.8° contact angle turns to 72.5° as TESPA is galvanostatically deposited. The surface is more hydrophobic than the reference, indicating that the nanofilm is directionally arranged with hydrophobic SiOCH2CH3 groups atop the nanofilm. Naturally, the disulfide units are underlying as the interface between copper surface and the nanofilms, because of the chemical interactions between copper atoms and thiol groups as expected and confirmed by S 2p XPS. The outer SiOCH2CH3 groups transform into Si—OH groups after hydrolysis, and the hydrophobic surface absolutely evolves into a hydrophilic one (60.7°). The vacuum curing treatment prompts the formation of Si—O—Si network and accordingly decreases the Si—OH groups, thus the surface exhibits a slight increase, but it is still hydrophilic with a contact angle of 66.2 due to the residual Si—OH groups. These chemical reactions can also be testified by the change of hydroxyl groups atop each surface. In the magnified inset of the associated hydroxyl group (around 3300 cm-1) [39], the peak on the hydrolyzed Cu-TESPA surface is greater than those of the other three surfaces, demonstrating that SiOCH2CH3 groups turn into Si—OH groups. As the hydrolyzed Cu-TESPA sample was heated, the peak of associated hydroxyl group becomes smaller, revealing that Si—OH groups condense with each other. The contact angle evolution and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy interpretation confirm the procedure proposed in Fig. 1(b).
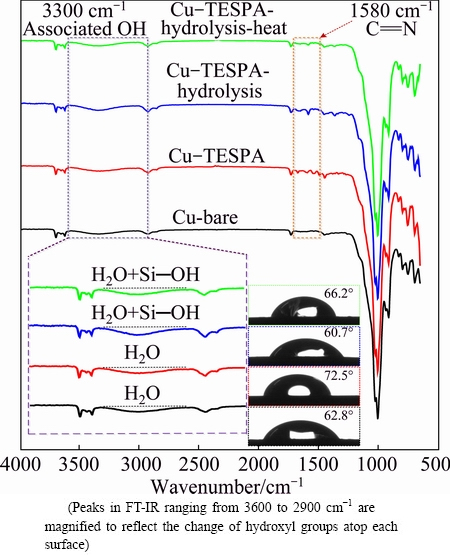
Fig. 9 FT-IR and contact angles (insets) of surfaces from bare copper, TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT, hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT, and hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper prepared by GT along with heating
In order to entirely understand the surface morphology of the investigated surfaces, scanning electron microscopy was performed with 5 μm scanning scale. Figure 10 illustrates the SEM images of the bare copper (a), the TESPA-deposited copper (b), the hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper (c), and the hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper along with following heating (d), respectively. Figure 10(a) shows the initial surface state of the polished bare substrate. The surface is considerably rough, some fine steaks resulting from the polishing process are visible, and plenty of white spots are obvious which originate from naked copper. As TESPA is deposited on the bare substrate (Fig. 10(b)), certain white spots disappear because the naked copper is covered with TESPA monomers. Nevertheless, a number of black spots emerge owing to the electrochemical damage to copper, because some tiny bubbles are observed on the working electrode during the preparation process. The hydrolyzed TESPA-treated copper surface (Fig. 10(c)) is totally different from the former two. The black spots disappear, and the substrate seems to be covered by another type of rougher film. These changes demonstrate that a new interface has developed originating from the hydrolysis of silane moiety in TESPA. No apparent changes can be observed when the Cu-TESPA-hydrolysis is heated, i.e., the surface is till rougher and inhomogeneously covered, as shown in Fig. 10(d). In short, the hydrolyzed Cu-TESPA surfaces with/without heating can be effortlessly differentiated from the Cu-TESPA; a new “interface phase” seems to shape. Water molecules just gather atop the new phase/interface and cannot penetrate into the nanofilm. As a result, water uptake in the coatings declines; the Qfilm values of hydrolyzed and condensed Cu-TESPA decrease.
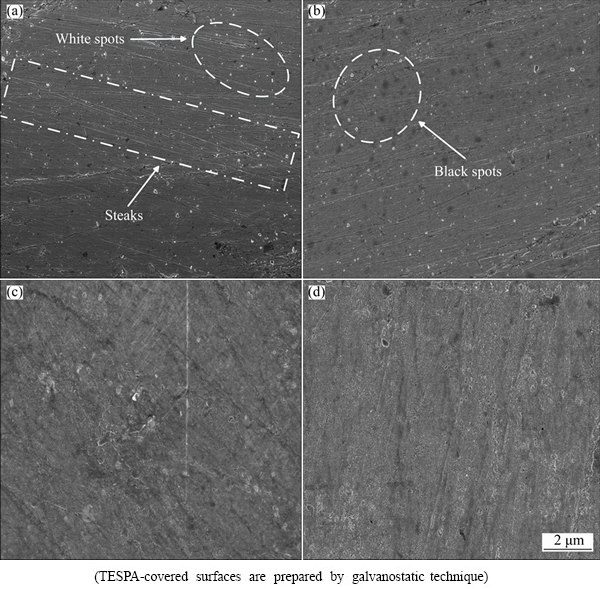
Fig. 10 SEM images of bare copper (a), TESPA-deposited copper (b), hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper (c), and hydrolyzed TESPA-deposited copper plus following heating under vacuum (d)
3.7 Prospects
Detailed conditions of improving the performance of TESPA polymeric nanofilm need to be discussed. For protective capability, the electrochemical polymerization degree of triazinedithiol groups [4] depends on current density, galvanostatic time, temperature, etc. In the case of the activation ability, factors influencing the kinetics and equilibrium of hydrolysis for SiOC2H5 groups [40] into silanol groups include the pH, catalyst, solvent and hydrolysis time, by which the wetting properties of the latter two surfaces are directly determined. The subsequent curing time and temperature also have influence on the formation of the Si—O—Si network.
The significant point of this investigation lies in enlightening us to fabricate a similar multifunctional interface on other metal surfaces, such as iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg) and aluminum (Al). Because TESPA (or rather, the active —SH groups form triazinedithiol part of TESPA) cannot self-assemble onto these metal surfaces; however, —SNa and —SH groups form triazinedithiol entity of TESPA can be electrochemically polymerized onto Fe [4], Mg [14] and Al [41] in previous studies, which offers the possibility for TESPA to be deposited and functionalize these metal’s surfaces with this novel polymeric nanofilm.
4 Conclusions
1) Through electrochemical and the following hydrolysis-condensation approaches, the designed fabrication process of TESPA polymeric nanofilm as a multifunctional interface for copper is practical and effectual.
2) The polymeric nanofilm not only resists copper corrosion, but also activates the surface. The corrosion resistance stems from the underlying disulfide units between copper and the nanofilm, as well as the Si—O—Si structure atop the nanofilm; the activation comes from the outer Si—OH groups.
3) This multifunctional interface (the polymeric nanofilm on copper surface) opens up the possibilities for other OH-containing reagents to be anchored onto copper surface in demanding researches or industrial applications, such as catalysis, coloring and paint processes that need a protective and activated medium for higher performances.
4) The preparing method is expected to construct the alike polymeric nanofilms on other metal surfaces, such as iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg) and aluminum (Al).
References
[1] WANG Ya-bin, LIU Zhong, LI De-yu, DONG Ya-ping, LI Wu, LI Ning. The polymeric nanofilm of triazinedithiolsilane fabricated by self-assembled technique on copper surface. Part 1: Design route and corrosion resistance [J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 98: 382-390.
[2] WANG Ya-bin, LIU Zhong, HUANG Yu-dong, QI Yu-tai. The polymeric nanofilm of triazinedithiolsilane fabricated by self-assembled technique on copper surface. Part 2: Characterization of composition and morphology [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 356: 191-202.
[3] MORI K, OISHI Y, MIYASHITA T, MATSUDA M. Polymerization of monomer films of triazine dithiols on a copper surface [J]. Polymer International, 1992, 28: 193-199.
[4] MORI K, SASAKI Y, SAI S, KANEDA S, HIRAHARA H, OISHI Y. Electrochemical polymerization of 2-(dioctylamino)-1, 3, 5-triazine-4, 6-dithiol on iron plates [J]. Langmuir, 1995, 11: 1431-1434.
[5] ZHU Dan-qing, OOIJ W J. Enhanced corrosion resistance of AA 2024-T3 and hot-dip galvanized steel using a mixture of bis-[triethoxysilylpropyl] tetrasulfide and bis-[trimethoxysilylpropyl] amine [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 49: 1113-1125.
[6] WANG Fang, LI Yan-ni, WANG Ya-bin, CAO Zhuo. Self-assembled monolayer of designed and synthesized triazinedithiolsilane molecule as interfacial adhesion enhancer for integrated circuit [J]. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2011, 6: 483-488.
[7] ZHOU Kun, WANG Bin, ZHAO Yu, LIU Jie. Corrosion and electrochemical behaviors of 7A09 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy in chloride aqueous solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 2509-2515.
[8] XIANG Nan, SONG Ren-guo, ZHUANG Jun-jie, SONG Ruo-xi, LU Xiao-ya, SU Xu-ping. Effects of current density on microstructure and properties of plasma electrolytic oxidation ceramic coatings formed on 6063 aluminum alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 806-813.
[9] ALEXANDER M R, THOMPSON G E, ZHOU X, BEAMSON G, FAIRLEY N. Quantification of oxide film thickness at the surface of aluminium using XPS [J]. Surface and Interface Analysis, 2002, 34: 485-489.
[10] PERRUCHOT C, CHEHIMI M M, DELAMAR M, CABET- DELIRY E, MIKSA B, SLOMKOWSKI S, KHAN M A, ARMES S P. Chemical deposition and characterization of thin polypyrrole films on glass plates: Role of organosilane treatment [J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 2000, 278: 1139-1154.
[11] YE Qi, KANG Zhi-xin, LI Yuan-yuan. Electrochemical performance of organic film on copper surface by polymer plating of 6-mercapto-1, 3, 5-triazine-2, 4-dithiol monosodium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: s747-s751.
[12] SINAPI F, JULIEN S, AUGUSTE D, HEVESI L, DELHALLE J, MEKHALIF Z. Monolayers and mixed-layers on copper towards corrosion protection [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53: 4228-4238.
[13] BABA H, KODAMA T, MORI K, HIRAHARA H. The corrosion inhibition of copper by potentiostatic anodization in triazinedithiol solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 1997, 39: 555-564.
[14] KANG Zhi-xin, YE Qi, SANG Jing, LI Yuan-yuan. Fabrication of super-hydrophobic surface on copper surface by polymer plating [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209: 4543-4547.
[15] KEAR G, BARKER B D, WALSH F C. Electrochemical corrosion of unalloyed copper in chloride media—A critical review [J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46: 109-135.
[16] SUDHEER, QURAISHI M A. Electrochemical and theoretical investigation of triazole derivatives on corrosion inhibition behavior of copper in hydrochloric acid medium [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 70: 161-169.
[17] FENG Y, TEO W K, SIOW K S, TAN K L. The corrosion behaviour of copper in neutral tap water. Part I: Corrosion mechanisms [J]. Corrosion Science, 1996, 38: 369-385.
[18] LI S L, WANG Y G, CHEN S H, YU R, LEI S B, MA H Y, LIU D X. Some aspects of quantum chemical calculations for the study of Schiff base corrosion inhibitors on copper in NaCl solutions [J]. Corrosion Science, 1999, 41: 1769-1782.
[19] SUN Wei, SUN Chen, LIU Run-qing, CAO Xue-feng, TAO Hong-biao. Electrochemical behavior of galena and jamesonite flotation in high alkaline pulp [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 551-556.
[20] CABRINI M, LORENZI S, PASTORE T. Cyclic voltammetry evaluation of inhibitors for localised corrosion in alkaline solutions [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 124: 156-164.
[21] MANDEL M, KRGER L, DECKER S. Electrochemical corrosion studies of spark plasma sintered zirconia particle-reinforced high-alloy steel at different temperatures [J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 90: 323-330.
[22] KANG Zhi-xin, SANG Jing, SHAO Ming, LI Yuan-yuan. Polymer plating on AZ31 magnesium alloy surface and film evaluation of corrosion property [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209: 4590-4594.
[23] KANG Zhi-xin, LAI Xiao-ming, SANG Jing, LI Yuan-yuan. Fabrication of hydrophobic/super-hydrophobic nanofilms on magnesium alloys by polymer plating [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 520: 800-806.
[24] WANG Dan, XIANG Bin, LIANG Yuan-peng, SONG Shan, LIU Chao. Corrosion control of copper in 3.5wt% NaCl solution by domperidone: Experimental and theoretical study [J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 85: 77-86.
[25] HONG Song, CHEN Wen, ZHANG Yu, LUO Hong-qun, LI Ming, LI Nian-bing. Investigation of the inhibition effect of trithiocyanuric acid on corrosion of copper in 3.0wt% NaCl [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 66: 308-314.
[26] CHEN Zhen-yu, HUANG Ling, ZHANG Guo-an, QIU Yu-bing, GUO Xing-peng. Benzotriazole as a volatile corrosion inhibitor during the early stage of copper corrosion under adsorbed thin electrolyte layers [J]. Corrosion Science, 2012, 65: 214-222.
[27] PENG Shu-sen, ZENG Zhi-xiang, ZHAO Wen-jie, LI He, CHEN Jian-min, HAN Jin, WU Xue-dong. Novel functional hybrid silica sol-gel coating for copper protection via in situ thiol-ene click reaction [J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4: 15776-15781.
[28] DESTRERI M D G, VOGELSANG J, FEDRIZZI L, DEFLORIAN F. Water up-take evaluation of new waterborne and high solid epoxy coatings. Part II: Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy [J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 1999, 37: 69-81.
[29] MCCAFFERTY E, HACKERMAN N. Double layer capacitance of iron and corrosion inhibition with polymethylene diamines [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1972, 119: 146-154.
[30] CASTNER D G, HINDS K, GRAINGER D W. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy sulfur 2p study of organic thiol and disulfide binding interactions with gold surfaces [J]. Langmuir, 1996, 12: 5083-5086.
[31] NEAL A L, TECHKARNJANARUK S, DOHNALKOVA A, MCCREADY D, PEYTON B, GEESEY G G. Iron sulfides and sulfur species produced at hematite surfaces in the presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65: 223-235.
[32] DENG Sheng-yuan, ZHANG Ting-ting, ZHANG Yuan, SHAN Dan, ZHANG Xue-ji. Chronopotentiometric synthesis of quantum dots with efficient surface-derived near-infrared electrochemiluminescence for ultrasensitive microchip-based ion-selective sensing [J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4: 29239-29248.
[33] ONISAWA K, ABE Y, TAMURA K, NAKAYAMA T, HANAZONO M, ONO Y A. Oxygen in SrS phosphor powder and its effects on performance of thin film electroluminescent devices [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1991, 138: 599-601.
[34] CASTANO J G, ARROYAVE C, MORCILLO M. Characterization of atmospheric corrosion products of zinc exposed to SO2 and NO2 using XPS and GIXD [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42: 9654-9662.
[35] ISHIDA T, CHOI N, MIZUTANI W, TOKUMOTO H, KOJIMA I, AZEHARA H, HOKARI H, AKIBA U, FUJIHIRA M. High-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectra of organosulfur monolayers on Au (111): S (2p) spectral dependence on molecular species [J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15: 6799-6806.
[36] HEISTER K, ALLARA D L, BAHNCK K, FREY S, ZHARNIKOV M, GRUNZE M. Deviations from 1:1 compositions in self-assembled monolayers formed from adsorption of asymmetric dialkyl disulfides on gold [J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15: 5440-5443.
[37] WANG Fang, WANG Ya-bin, LI Yan-ni, WANG Qian. Preparation of triazinedithiol polymeric nanofilm by two-step potentiostatic polymerization technique on aluminum surface [J]. Materials Letters, 2010, 65: 621-623.
[38] WANG Fang, WANG Ya-bin, LI Yan-ni, WANG Qian. Fabrication of triazinedithiol functional polymeric nanofilm by potentiostatic polymerization on aluminum surface [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 257: 2423-2427.
[39] ZENG Rong-chang, LIU Zhen-guo, ZHANG Fen, LI Shuo-qi, HE Qing-kun, CUI Hong-zhi, HAN En-hou. Corrosion resistance of in-situ Mg-Al hydrotalcite conversion film on AZ31 magnesium alloy by one-step formation [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 1917-1925.
[40] SHI Xiang-ke, GRAIVER D, NARAYAN R. Hydrolysis and condensation of hydrophilic alkoxysilanes under acidic conditions [J]. Silicon, 2012, 4: 109-119.
[41] WANG Fang, LIU Jun-jun, LI Yan-ni, WANG Ya-bin. Novel composite nanofilm of electropolymerization and self-ssembling on AA5052 surface as anticorrosion coating [J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012, 123: 2906-2910.
王亚斌1,2,黄玉东1,亓玉台1
1. 哈尔滨工业大学 化工与化学学院,哈尔滨 150001;
2. 中国科学院 青海盐湖研究所,西宁 810008
摘 要:通过恒电流技术和水解-缩合方法,在铜表面制备均三嗪二硫醇硅烷单钠盐多功能聚合纳米薄膜,该纳米薄膜能够防腐蚀和活化铜表面。采用电化学测试来评价该薄膜的防腐蚀性能;用傅里叶变换红外光谱学(FT-IR)和接触角技术监测纳米薄膜表面功能团的变化;用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)及扫描电子显微镜(SEM)分别研究聚合纳米薄膜的化学组成和形貌特征。结果表明:在整个制备过程,电化学聚合形成的二硫单元优先保护铜表面;紧接的水解(缩合)作用使得该薄膜形成新的、具有防腐蚀和活化铜的多功能聚合纳米薄膜。该界面(聚合纳米薄膜)使得其他含有羟基的化合物可能在铜表面键合,且能够应用在高要求的研究和工业中。
关键词:铜;均三嗪二硫醇硅烷;恒电流技术;多功能聚合纳米薄膜;功能化界面
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (2013DFR40700) supported by International S&T Cooperation Program of China; Projects (21174034, 51003019, 51302280) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Yu-dong HUANG ; Tel: +86-451-86414806; E-mail: ydhuang.hit1@aliyun.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64425-4

