Electrochemical investigation on kinetics of potassium intercalating into graphite in KF melt
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2011年第1期
论文作者:刘东任 李旺兴 杨占红 邱仕麟 罗英涛
文章页码:166 - 172
关键词:钾插层反应;石墨;熔盐;铝电解;KF
Key words:potassium intercalation; graphite; molten salt; aluminum electrolysis; KF
摘 要:通过循环伏安法和计时安培法对1 163 K温度下钾与石墨在KF熔盐中的插层反应动力学进行研究。循环伏安研究结果表明钾与石墨在KF熔盐中的插层/脱嵌反应包括动力学因素。用可逆及准可逆理论对计时安培曲线进行分析,进一步确认钾插入石墨层间这一过程是由钾离子在石墨中的扩散和相变动力学共同控制的。用准可逆动力学方程对电流-时间瞬态曲线进行非线性拟合,求得插层反应的传递系数为0.364。通过扫描电镜对发生钾插层反应后的石墨表面进行分析,发现石墨基体被严重腐蚀。
Abstract: The kinetics of potassium intercalating into graphite in molten KF at 1 163 K was investigated by means of cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry. Cyclic voltammetry results indicate that intercalaltion/deintercalation of potassium into/from graphite involve kinetic limitations. The intercalation process of potassium was further confirmed to be governed by both the diffusion of potassium ion in graphite bulk and the phase transition kinetics through the analyses of current-time transient curves with reversible and quasi-reversible equations. The transfer coefficient of the intercalation reaction was calculated to be 0.364 according to the parameters resulting from nonlinear fitting of the current-time transient curves with a quasi-reversible equation. Analysis with scanning electron microscope shows that graphite matrix was severely eroded by intercalation of potassium.

LIU Dong-ren1,2, LI Wang-xing3, YANG Zhan-hong1, QIU Shi-lin3, LUO Ying-tao3
1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Department of Chemical and Environmental engineering, Jiaozuo University, Jiaozuo 454003, China;
3. Zhengzhou Research Institute of CHALCO, Zhengzhou 450041, China
Received 25 December 2009; accepted 22 March 2010
Abstract: The kinetics of potassium intercalating into graphite in molten KF at 1 163 K was investigated by means of cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry. Cyclic voltammetry results indicate that intercalaltion/deintercalation of potassium into/from graphite involve kinetic limitations. The intercalation process of potassium was further confirmed to be governed by both the diffusion of potassium ion in graphite bulk and the phase transition kinetics through the analyses of current-time transient curves with reversible and quasi-reversible equations. The transfer coefficient of the intercalation reaction was calculated to be 0.364 according to the parameters resulting from nonlinear fitting of the current-time transient curves with a quasi-reversible equation. Analysis with scanning electron microscope shows that graphite matrix was severely eroded by intercalation of potassium.
Key words: potassium intercalation; graphite; molten salt; aluminum electrolysis; KF
1 Introduction
Commercial primary aluminum production leads to great energy consumption because it is carried out at high temperature (around 960 °C) by electrolyzing alumina dissolved in molten cryolite. To lower the electrolysis temperature is an effective way to reduce energy consumption. Although lower temperature may decrease the electrical conductivity of the melt and subsequently increase the IR drop between cathode and anode, those disadvantages can be compensated by the application of wettable cathode (pure TiB2 or TiB2/C composite) to decrease the level of aluminum pool and then to reduce the distance between anode and cathode of aluminum reduction cell. Also, use of an appropriate low-temperature electrolyte would increase the probability of finding a suitable inert anode which can reduce the carbonous materials consumption, and more importantly, eliminate the emission of greenhouse gases. Considerable efforts have been made on low temperature aluminum electrolysis[1-4]. Works in low temperature electrolyte areas have mainly focused on the NaF-AlF3-based system, i.e. low cryolite ratio NaF/AlF3 melts[5-6]. Due to the low solubility of alumina in cryolite baths, a slurry-cell concept was proposed to keep solid alumina in suspension during electrolysis. However, the slurry-cell operation causes operational difficulties and problems with metal collection.
Owing to its wider range of low-temperature (<1 023 K) liquid compositions and higher alumina solubility comparing with NaF-AlF3 system, KF-AlF3 system seems to be a promising candidate as low temperature electrolyte and have attracted more and more interests in recent years[7-11]. The studies on KF-AlF3-based electrolyte system were focused mainly on its physical or chemical properties and corrosion effects on inert anode[7-11]. To our knowledge, little attention has been paid to the penetration property of the electrolyte into the cathode carbon block. However, electrolyte penetration within the carbon lining of the aluminum electrolysis cell is one of the most important problems occurring during electrolysis. Better understanding of the potassium penetration to the carbon would be of basic importance to predict the performance of cathode carbon block when KF-AlF3 system is used as low temperature electrolyte.
The process of potassium intercalates into graphite has been investigated in organic solution and at low temperature[12-15]. However, these results are not suitable to be applied to understand the mechanism of intercalation occurring between potassium and carbon in molten salt. Intercalation of alkali metal into graphite by electrolysis of molten alkali metal salts has been employed to produce nanosized carbon materials like tubes and particles[16-18]. Also, the intercalation of potassium into graphite by electrolysis in chloride melt has been investigated in order to elucidate the role of potassium intercalation in the formation process of nano-sized carbon materials[16, 19]. The electrochemical intercalation of potassium into graphite in molten KF was investigated in a previous work[20]. However, the kinetics of the reaction is still ambiguous. The present article reports a kinetics investigation on potassium intercalating into graphite in molten KF.
2 Theory
Considering that one has an electrochemical half- cell:
Molten KF︱KGICs, graphite (1)
The intercalation process of potassium into graphite may be represented by the following equation:
![]()
![]()
![]() (2)
(2)
Since molten KF is a purely ionic conductor, there is no chemical diffusion of potassium ion from the bulk melt to surface of graphite electrode. Thus the diffusion rate is determined by the diffusion of potassium in the graphite host matrix, with the concentration gradient located on the graphite side of the electrolyte/electrode interface.
Assuming one-dimensional transport, the time- dependent diffusion of potassium in graphite under semi-infinite linear transport conditions is described by Fick’s second law. The appropriate diffusion equation for potassium in graphite bulk is
![]() (3)
(3)
where t is the time, x is the distance from the electrolyte/electrode interface into the graphite, cK is the local concentration of potassium in the graphite, and DK is the chemical diffusion coefficient of potassium in graphite. The latter is assumed to be approximately concentration independent. The appropriate initial and boundary conditions are as follows:
![]() (4)
(4)
![]() (5)
(5)
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() (7)
(7)
In what follows, it is assumed that the intercalation of potassium into graphite in molten KF is either reversible or quasi-reversible process.
Case I Reversible process
Because of the assumption of a reversible electrode process, the potassium concentration in the graphite at the electrolyte/electrode interface is governed by the Nernst equation which can be expressed by the following equation[17].
![]() (8)
(8)
where cK* is the saturation concentration of potassium in graphite, γK is the Henrian activity coefficient of potassium in graphite, φ is the potential applied, φ0 is the standard potential of the half-cell reaction expressed by Eq.(2), other parameters have their universal meaning. Then a modified Cottrell equation is obtained:
![]()
![]() (9)
(9)
According to Eq.(9), the value of it-1/2 should be independent of time if the intercalation process is reversible.
Case II Quasi-reversible process
Assuming the charge transfer is not so fast as to be transparent, thus kinetic parameters influence the current responses to potential steps. As a consequence, current is governed by both mass transfer and kinetic limitations. The corresponding current may be derived as follows.
For the quasi-reversible one-step, one-electron case, the current can be described by the equation[21]:
![]() (10)
(10)
The solution of Eqs.(3) and (10) using the initial and boundary conditions (4)-(7) gives the current equation:
![]() (11)
(11)
Eq.(11) expresses the time-dependent current if the intercalation process is quasi-reversible.
3 Experimental
Anhydrous potassium fluoride contained in a graphite crucible was heated to 523 K and held at this temperature for 8 h under vacuum, then heated up to the working temperature of 1 163 K. The electrochemical experiments were performed using a three-terminal electrochemical cell. The crucible served as the container for the electrolyte and also as the high surface counter electrode. The working electrode (WE) was a thin sheet (with a dimension of 5.9 mm×4 mm×1.2 mm exposed to molten salt) machined from a spectral pure graphite rod. Due to the difficulty of finding a suitable reference electrode in molten KF, platinum wire of 1.0 mm diameter was employed as the quasi-reference electrode. In the following, all potentials are expressed with respect to the platinum reference electrode. The graphite crucible was positioned inside a sintered corundum tube within a programmable vertical furnace. The electrochemical cell was under a continuous nitrogen circulation during the experiment. The electrochemical measurements were performed using a PAR Model 263A Potentiostat/ Galvanostat monitored by a computer using commercial PowerSuit software.
The WE was characterized by means of cyclic voltammetry with various scan rates firstly. Then it was subjected to a series of potential steps. During the potential step experiments, the WE was held at a negative potential initially for 10 s to ensure no intercalation or reduction reaction occurred at zero time. Whereafter the potential was stepped to a selected negative potential and held for 80 s. Around 70% of the measured solution resistance between working and reference electrodes was compensated using PowerCV and PowerStep software for all cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry measurements. Then, galvanostatic electrolysis was conducted to allow potassium intercalate into graphite. After the galvanostatic electrolysis, the electrode was removed from the melt and cooled down naturally in nitrogen atmosphere. The electrode was washed with distilled water to get rid of the solidified electrolyte on the electrode surface. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) performed on JSM-6360LV (JEOM) was utilized to investigate the surface morphology of the electrode.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Cyclic voltammetry
Figure 1 shows cyclic voltammograms obtained on platinum wire and graphite sheet electrode with a scanning rate of 100 mV/s in molten KF at 1 163 K. It can be seen that potassium deposition occurs at a relatively positive potential of around -1.1 V on platinum electrode. Because the working temperature (1 163 K) is higher than the boiling point of potassium (1 032 K), none of oxidation peak is observed during the reverse potential scanning on platinum electrode due to the fast evaporation of potassium. However, a reduction wave starts from around -0.8 V, which can be seen from position of the abrupt increase of the cathodic current, and an oxidation wave appears in the reverse sweep on graphite electrode. The coupled cathodic and anodic waves recorded on graphite electrode are ascribed to the intercalation/deintercalation of potassium into/from graphite layers. In the middle potential range from the onset to -0.8 V in the negative direction sweep, relatively high reduction current is observed on graphite electrode. It has been demonstrated in the previous study that this current does not result from the intercalation of the potassium but electro-endosmosis of molten electrolyte into the interior of graphite bulk[20]. It should be noted that the anodic current density is much lower than cathodic current density. This behavior can be attributed in part to the decomposition of KGICs and also may be indicative of kinetic limitations. The occurrence of kinetic limitations is further hinted by the unsymmetrical shape with extra broad width of anodic wave of cyclic voltammogram recorded on graphite electrode.
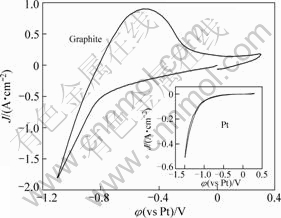
Fig.1 Cyclic voltammograms recorded at graphite and platinum electrode in molten KF at sweep rate of 100 mV/s and temperature of 1 163 K
Typical voltammograms at various scanning rates for the intercalation and deintercalation of potassium on the graphite electrode in KF melt are presented in Fig.2. Analysis of Fig.2 shows that the value of φp,a-φp,a/2 (φp,a, φp,a/2 are the anodic peak and the half-peak potentials) is considerably larger than that of the expected for reversible processes. The positive shift in anodic peak potential with increasing scanning rate also indicates the lack of reversibility of anodic reaction. Figure 3 shows the dependence of anodic peak current (Jp,a) against the square root of scanning rate (v1/2) for the potassium extraction process. It is indicated that during the anodic process a kinetic current contributes to the peak current as it can be seen that the plot of Jp,a vs v1/2 does not pass through the origin as expected for a simple linear diffusion controlled process. The dependence of Jp,a against v1/2 (Fig.3) shows good linearity at low scanning rates. The deviation from linearity at high scanning rates is attributed to the kinetic limitations rather than uncompensated solution resistance. Due to the difficulty of determining the exact value of the cathodic peak current (Jp,c), the relationship of Jp,c vs v1/2 can not be precisely exposed. For a rough approximation, the maximum cathodic current density (Jmax,c) vs v1/2 is plotted in Fig.3. Surprisingly, the dependence of the maximum cathodic current density against v1/2 is found to be similar to that of anodic peak current density. In order to get a clearer insight to the cathodic process, potential step chronoamperometry was carried out.

Fig.2 Cyclic voltammograms of graphite electrode with various scanning rates in molten KF at 1 163 K

Fig.3 Plot of maximum cathodic current density and anodic peak current density versus square root of scanning rate in molten KF at 1 163 K
4.2 Potential step chronoamperometry
In the potential step experiments, the step potential was carefully selected so as to minimize the interference caused by metallic potassium deposition on electrode with intercalation process. Typical current-time transients resulting from potential step experiments on graphite electrode in molten KF at 1 163 K are shown in Fig.4. According to Eq.(9), the it1/2 values measured during potential step periods should be independent of time if the intercalation process is solely governed by mass transfer. At the initial stage of potential step, the charge of electric double-layer and the uncompensated ohmic resistance between the working electrode and reference electrode would interfere with the effective potential imposed on working electrode to a significant extent and cause the measured currents to deviate from expected value[17]. But the capacitance of electric double-layer and ohmic resistance in the circuit should be independent of the applied potential and time, so the variation of the current with time caused by the two factors should become relatively small or constant in the long time domain of the potential steps. Then the current-time transients should display a Cottrellian behavior after the initial stage of the potential step if the reaction is ruled by diffusion of active species. However, it is found from Fig.5 that it1/2 values of all the potential steps are kept rising with time not only at the initial stage of
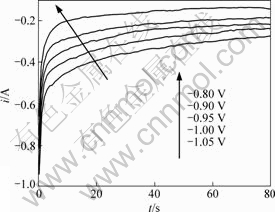
Fig.4 Current-time transient curves resulting from various potential steps in molten KF at 1 163 K
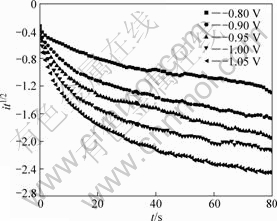
Fig.5 Plot of it1/2 vs t from current-time transient curves for graphite electrode in molten KF at 1 163 K
the potential step but the whole period, and this effect is more pronounced when larger potential steps are applied. This deviation of current-time transient from Cottrellian behavior at the whole time domain of potential step indicates that the intercalation of potassium into graphite in molten KF is not controlled solely by the diffusion process. Also, kinetic limitations should be taken into consideration.
If potassium intercalation into graphite in molten KF is considered a quasi-reversible process, the dependence of current against time should be described using Eq.(11). Unfortunately, error function and exponential function are involved in this equation. So it is not easy to determine directly whether the current-time transients accord with the equation. Nonlinear fitting is a common method used for modelling of electrochemical transients and calculating parameters in some kinetic investigations[22-23]. The overall goodness of the fit is usually expressed by statistics like the standard deviation (σ), the chi-square (χ2) and the adjusted coefficient of determination (![]() ) accompanied by analysis of the behavior of the residuals of the model[24]. For the sake of testing the appropriateness of the model expressed by Eq.(11) to the experimental current-time transient, the nonlinear fitting method was applied using commercial OriginPro8 software (OriginLab). Then the statistics of the fitting results were analyzed to check the goodness of the fit. The fitting results of the parameters involved in Eq.(11) as well as the statistics data are listed in Table 1. It should be mentioned that only those experimental data obtained during the period from 10 s to 80 s were fitted in view of preventing the disturbance of ohmic resistance and charge of electric double-layer at the initial stage of potential step. From Table 1, it can be seen that the χ2 value of all the fittings are less than 1×10-5, indicating the deviations between the fitted and experimental data is quite small. And the value of adjusted coefficient of determination (
) accompanied by analysis of the behavior of the residuals of the model[24]. For the sake of testing the appropriateness of the model expressed by Eq.(11) to the experimental current-time transient, the nonlinear fitting method was applied using commercial OriginPro8 software (OriginLab). Then the statistics of the fitting results were analyzed to check the goodness of the fit. The fitting results of the parameters involved in Eq.(11) as well as the statistics data are listed in Table 1. It should be mentioned that only those experimental data obtained during the period from 10 s to 80 s were fitted in view of preventing the disturbance of ohmic resistance and charge of electric double-layer at the initial stage of potential step. From Table 1, it can be seen that the χ2 value of all the fittings are less than 1×10-5, indicating the deviations between the fitted and experimental data is quite small. And the value of adjusted coefficient of determination (![]() ) is close to 1, denoting the fittings are satisfactory and reasonable. Analyses of plot of the residual vs independent (not be presented) of all the fittings reveal that residuals are randomly distributed around zero, showing the experimental data are well fitted with the equation. The statistics analyses indicate the experimental current-time transient curves accord well with Eq.(11). The fitted curves are shown in Fig.6. Comparing the experimental curves with the fitted curves, the two sets of curves are nearly overlapped to each other except the initial stage of the step. Based on the results of nonlinear fitting of the experimental current-time transient curves, it is reasonable to conclude that the intercalation of potassium into graphite in molten KF is a quasi-reversible process. Namely, the reaction is governed by both the mass transfer and the kinetic limitations.
) is close to 1, denoting the fittings are satisfactory and reasonable. Analyses of plot of the residual vs independent (not be presented) of all the fittings reveal that residuals are randomly distributed around zero, showing the experimental data are well fitted with the equation. The statistics analyses indicate the experimental current-time transient curves accord well with Eq.(11). The fitted curves are shown in Fig.6. Comparing the experimental curves with the fitted curves, the two sets of curves are nearly overlapped to each other except the initial stage of the step. Based on the results of nonlinear fitting of the experimental current-time transient curves, it is reasonable to conclude that the intercalation of potassium into graphite in molten KF is a quasi-reversible process. Namely, the reaction is governed by both the mass transfer and the kinetic limitations.
Table 1 Fitting results of current-time transient resulting from potential step in Fig.4 with quasi-reversible Eq.(11)

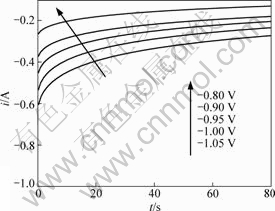
Fig.6 Current-time transient curves of various potential steps fitted with Eq.(11)
Intercalation of guest species into graphite lattice leads to a phase transition converting from graphite to intercalation compounds. Forming such a new phase is generally by way of guest species nucleating in host material, then the boundary of the new phase moves to the interior of the host material. A typical example is the intensively studied intercalation of lithium into graphite in Li-ion battery[25-26]. Also, structural change of the host material such as lattice expanding occurred in the intercalation process could induce lattice strain in the host material[27]. This kind of structural change is more strengthened in the case of potassium intercalation due to its relative larger ionic radius compared with lithium and sodium. Indeed, strong volume swelling of the graphite electrode was observed during the cathodic polarization process in molten KF. Thus electrochemical intercalation process of potassium may be hindered to some extent by the phase transition kinetics such as the lattice strain and nucleation. Consequently, the reaction is ruled by both the phase transition kinetics and the diffusion of potassium in graphite.
If the assumption that transfer coefficient α is independent of potential is met, the value of α calculated according the series of fitted![]() parameters by the formula of
parameters by the formula of ![]() is 0.364, which is another evidence for quasi-reversible process.
is 0.364, which is another evidence for quasi-reversible process.
4.3 SEM characterization
The surface morphology images of the graphite electrode before and after electrolysis are presented in Fig.7. The graphite owns a scalelike surface (Fig.7(a)). After electrolysis, the electrode is severely eroded as many irregular crystal facets and concaves can readily be observed (Fig.7(b)). The crystal facets and concaves are believed to be caused by the exfoliation of graphite layers and particles from the graphite matrix. In the process of potassium intercalation, potassium atoms entered into the interlayer of graphite and led to strong lattice expansion due to the large ionic radius of potassium, whereafter resulted in some of graphite layers and particles stripping from the graphite bulk. The stripping process was facilitated by the weakened interaction between adjacent graphite layers under high temperature.
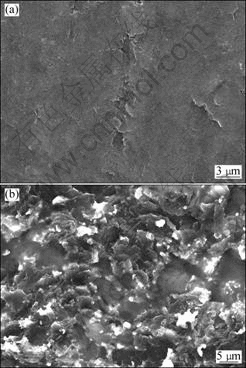
Fig.7 SEM images of graphite electrodes surface: (a) Before electrolysis; (b) After electrolysis
5 Conclusions
1) Kinetic limitations are certainly involved in the intercalation/deintercalation process of the potassium into/from graphite in molten KF.
2) The current-time transient curves resulting from a series of potential step were found to deviate from Cottrellian behavior at the whole time domain but be well fitted with the quasi-reversible equation. The analyses of current-time transient indicate that the intercalation of potassium into graphite is not controlled solely by potassium ion diffusion in graphite bulk but by both the diffusion and phase transition kinetics.
3) The transfer coefficient of quasi-reversible intercalation reaction was calculated to be 0.364.
4) Severe erosion of the graphite was observed after potassium intercalation.
References
[1] SLEEP W C, KENSIGNTON N, COCHRAN C N. Bench scale electrolysis of alumina in sodium fluoride-aluminium fluoride melts below 900 °C [J]. Aluminium, 1979, 55: 604-608.
[2] VECCHIO A M, DORIN R, FRAZER E J. Evaluation of low-temperature cryolite-based electrolytes for aluminium smelting [J]. J of Appl Electrochem, 1995, 25: 1098-1104.
[3] LU Hui-min, QIU Zhu-xian, FANG Ke-ming, HONG Yan-ruo. Low temperature aluminum electrolysis in Na3AlF6-AlF3-CaF2-LiF-Al2O3 bath system [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 1999, 21(4): 324-326. (in Chinese)
[4] BALARAJU J N, ANANTH V, SEN U. Studies on low temperature Al electrolysis using composite anodes in NaF-KCl bath electrolyte [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1995, 142: 439-441.
[5] BROWN C. Next generation vertical electrode cells [J]. JOM, 2001, 53: 39-42.
[6] KAN H, WANG Z, BAN Y, SHI Z, QIU Z. Electrical conductivity of Na3AlF6-AlF3-Al2O3-CaF2-LiF(NaCl) system electrolyte [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: 181-186.
[7] ZHOU Chuang-hua, MA Shu-lan, LI Guo-xun, SHEN Jian-yun. Study on the novel low temperature electrolyte system for aluminum electrolysis—The solubility and dissolution rate of alumina [J]. Nonferrous Metals, 1998, 50(2): 81-84. (in Chinese)
[8] H?VE? J, THONSTAD J. Electrical conductivity of low-melting electrolytes for aluminum smelting [J]. Electrochim Acta, 2004, 49: 5111-5114.
[9] ROBERT E, OLSEN J E, DANEK V, TIXHON E, ?STVOLD T, GILBERT B. Structure and thermodynamics of alkali fluoride- aluminum fluoride-alumina melts, vapour pressure, solubility, and Raman spectroscopic studies [J]. J Phys Chem B, 1997, 101: 9447-9457.
[10] YANG Jian-hong, HRYNL J N, DAVIS B R, ROY A, KRUMDICK G K, POMYKALA J A. New opportunities for aluminum electrolysis with metal anodes in a low temperature electrolyte system [C]//Light Metals 2004. Warrendale: TMS, 2004: 321-326.
[11] ZAIKOV Y, KHARAMOV A, KOVROV V, KRYUKOVSKY V, APISAROV A, TKACHEVA O, CHEMESOV O, SHUROV N. Electrolysis of aluminum in the low melting electrolytes based on potassium cryolite [C]//Light Metals 2008. Warrendale: TMS, 2008: 505-508.
[12] KYOTANI T, SUZUKI K-Y, SONOBE N, TOMITAP A. Potassium-graphite intercalation compounds from thin carbon films prepared between montmorillonite lamellae [J]. Carbon, 1993, 31: 149-153.
[13] NIXON D E, PARRY G S. Formation and structure of the potassium graphites[J]. J Appl Phys, 1968, 1: 291-298.
[14] MIZUTANI Y, ABE T, IKBDA K, IHARA E, ASANO M, HARADA T, INANA M, OGUMI Z. Graphite intercalation compounds prepared in solutions of alkali metals in 2-methyltetrahydrofuran and 2,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran [J]. Carbon, 1997, 35: 61-65.
[15] MIZUTANI Y, IHAYA E, ABE T, ASANO M, HARADA T, OGUMI Z, INABAT M. Preparation of alkali metal graphite intercalation compounds in organic solvents [J]. J Phys Chem Solids, 1996, l57: 799-803.
[16] CHEN G Z, FAN X, LUGET A, SHAFFER M P, FRAY D J, WINDLE A H. Electrolytic conversion of graphite to carbon nanotubes in fused salts [J]. J Electroanal Chem, 1998, 446: 1-6.
[17] XU Q, SCHWANDT C, CHEN G Z, FRAY D J. Electrochemical investigation of lithium intercalation into graphite from molten lithium chloride [J]. J Electroanal Chem, 2002, 530: 16-22.
[18] XU Q, SCHWANDT C, FRAY D J. Electrochemical investigation of lithium and tin reduction at a graphite cathode in molten chlorides [J]. J Electroanal Chem, 2004, 562: 15-21.
[19] CHEN G Z, KINLOCH I, SHAFFER M P, FRAY D J, WINDLE A H. Electrochemical investigation of the formation of carbon nanotubes in molten salts [J]. High Temp Mater Processes, 1998, 2: 459-469.
[20] LIU D R, YANG Z H, LI W X, QIU S L, LUO Y T. Electrochemical intercalation of potassium into graphite in KF melt [J]. Electrochim Acta, 2010, 55: 1013-1018.
[21] BARD A J, FAULKNER L R. Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications [M]. 2nd Edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2001: 119-120.
[22] BIENIASZ L K, SPEISER B. Use of sensitivity analysis methods in the modelling of electrochemical transients. Part 1. Gaining more insight into the behaviour of kinetic models [J]. J Electroanal Chem, 1998, 441: 271-258.
[23] BIENIASZ L K, SPEISER B. Use of sensitivity analysis methods in the modelling of electrochemical transients. Part 3. Statistical error: uncertainty propagation in simulation and in nonlinear least-squares parameter estimation [J]. J Electroanal Chem, 1998, 458: 209-229.
[24] WISNIAK J, POLISHUK A. Analysis of residuals—A useful tool for phase equilibrium data analysis [J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1999, 164: 61-82.
[25] LEVI M D, MARKEVICH E, AURBACH D. Comparison between Cottrell diffusion and moving boundary models for determination of the chemical diffusion coefficients in ion-insertion electrodes [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 51: 98-110.
[26] LEVI M D, MARKEVICH E, AURBACH D. The effect of slow interfacial kinetics on the chronoamperometric response of composite lithiated graphite electrodes and on the calculation of the chemical diffusion coefficient of Li ions in graphite [J]. J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109: 7420-7427.
[27] DRESSELHAUS M S, DRESSELHAUS G. Intercalation compounds of graphite [J]. Advances in Phys, 2002, 51: 1-186.
刘东任1, 2,李旺兴3,杨占红1,邱仕麟3,罗英涛3
1. 中南大学 化学化工学院, 长沙 410083;
2. 焦作大学 化学与环境工程系,焦作 454003;
3. 中国铝业公司郑州轻金属研究院,郑州 450041
摘 要:通过循环伏安法和计时安培法对1 163 K温度下钾与石墨在KF熔盐中的插层反应动力学进行研究。循环伏安研究结果表明钾与石墨在KF熔盐中的插层/脱嵌反应包括动力学因素。用可逆及准可逆理论对计时安培曲线进行分析,进一步确认钾插入石墨层间这一过程是由钾离子在石墨中的扩散和相变动力学共同控制的。用准可逆动力学方程对电流-时间瞬态曲线进行非线性拟合,求得插层反应的传递系数为0.364。通过扫描电镜对发生钾插层反应后的石墨表面进行分析,发现石墨基体被严重腐蚀。
关键词:钾插层反应;石墨;熔盐;铝电解;KF
(Edited by LAI Hai-hui)
Foundation item: Project(1343-74236000004) supported by the Hunan Province Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate
Corresponding author: YANG Zhan-hong; Tel: +86-731-88830886; E-mail: zhyang@mail.csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60694-8

