
Effect of Zn addition in Sn-rich alloys on interfacial reaction with Au foils
LIU Wei(刘 威), WANG Chun-qing(王春青), TIAN Yan-hong(田艳红), CHEN Ya-rong(陈雅容)
Department of Electronics Packaging Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 20 June 2007; accepted 9 November 2007
Abstract: To restrain the formation of AuSnx intermetallic components (IMCs) in solder joints, Zn was added into Sn-rich solders. The solder joints were fabricated by a laser reflow soldering method, and then they were aged at 125 ℃. The results show that the total thickness of AuSnx IMCs at the interface of pure Sn solder and Au foils reaches about 54 μm under the condition of 600 h aging. In Sn-1.5Zn solder joints, however, formation of AuSn4 IMCs is restrained greatly. As the content of Zn in the solder is increased to 3.5%(mass fraction), no AuSn4 IMC is observed at the interface. Au-Zn phases form beside AuSn2 and AuSn IMCs layers. As for Sn-9.0Zn solder joints, Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases and few AuSnx IMCs form at the interface. Moreover, total thickness of the phases and IMCs is far less than that of AuSnx IMCs in the pure Sn solder joints.
Key words: Zn addition; interfacial reaction; intermetallic compounds
1 Introduction
Au films have been commonly used as protective layers on pads for their excellent antioxidant ability and wettability for Sn based solder alloys[1-3]. The Au films must have certain thickness to protect other metals beneath them. Nowadays, the size of electronic devices gets smaller and smaller. As a result, content of Au in the solder joints will be increased greatly. Moreover, in some thin film circuits, micro electromechanical system (MEMS) and micro-sensors, entire pads and circuits are made of Au, where Au is used as a soldering layer, and thickness of the Au layer can reach about several microns.
Au will react with Sn in solders to form AuSnx intermetallics (IMCs) during reflow or aging processes. Moreover, growth speed of the IMCs is ultra fast. If the content of the IMCs in solder joints exceeds a certain extent, reliability of the solder joints will be degraded greatly[1, 4-5]. Therefore, it is very important to find ways to restrain formation and growth of the AuSnx IMCs.
KIM and TU[6] found that reaction speed of liquid solders and Au foils is quite different among 95Pb-5Sn, 63Sn-37Pb, pure Sn, 96Sn-4Ag, 57Bi-43Sn and 77.2Sn-20In-2.8Ag solders. Reaction kinetics between Au and Sn during aging process has been reported by YAMADA et al[7]. MITA et al[8] found that Ni addition in Sn-based solder alloys will accelerate the growth of the IMCs at the interface of alloys and Au foils. They proposed that the influence of Ni on the kinetics of the reactive diffusion is dominated by the growth behavior of the AuNiSn8 layer. Reaction kinetics between Au and Sn-x%Si (mass fraction) solder alloys has been reported by FURUTO and KAJIHARA[9]. They found that the addition of Si in the alloys can decelerate the growth of the Au-Sn IMCs. YEN et al[10] found that Cu addition in the Sn-based solder alloys will restrain the formation of the Au-Sn IMCs. The AuSn4 IMCs will disappear at the interface of alloys and Au foils with the increase of aging time and Cu concentration in the alloys. Zn in the Sn-Zn or Sn-Zn-Bi alloys, which will react with Au on the pad to form Au-Zn IMCs, has been reported widely[11-14]. However, in these studies, the Au content in the solder joints was very small, and the Au would be consumed totally during the reflow process. Little attention has been paid to the reaction process of Au and Zn in the solder joints with high Au content during the aging process. If Zn can restrain the growth of the AuSnx IMCs effectively during the aging process, the results could be helpful to improving reliability of solder joints with high Au content.
In this work, the effect of Zn addition in Sn-rich alloys on interfacial reaction between solders and Au foils during isothermal aging process was investigated. Variation of the IMCs and phase thickness at the interface of alloys and Au foils was also inspected.
2 Experimental
Cylinders (1.5 mm in diameter, 0.5 mm in thickness) of Sn-x%Zn (x=0, 1.5, 3.5 and 9.0) solders and commercial Au foils with a dimension of 2 mm×2 mm×0.1 mm were used. The solder cylinders and the Au foils were ultrasonically cleaned by acetone first, and then the solder cylinders were dipped into a soluble flux and placed on the Au foils.
In order to reduce the formation of IMCs in the reflow soldering process, a continuous wave (CW) Nd: YAG laser was utilized to fabricate the solder joints. The laser beam was 0.38 mm in diameter. Because melting point of pure Sn is higher than that of the Sn-x%Zn alloys, longer reflow time was utilized to fabricate the pure Sn solder joints. The laser reflow parameters for pure Sn and Sn-x%Zn solder joints were chosen as 11 W, 590 ms and 11 W, 500 ms, respectively. The laser reflow soldered samples were then aged at 125 ℃ for 96, 216, 384 or 600 h.
The samples were sectioned and mounted in epoxy resin, then they were ground, polished and etched in a solution of 0.3 mL concentrated HCl, 2.9 mL concentrated HNO3, 84.5 mL C2H5OH and 12.3 mL H2O. Scanning Electron Microscopy(SEM) was used to analyze microstructures of the solder joints. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometer(EDX) was utilized to determine element composition of the IMCs or phases.
To obtain the average thickness of the IMCs or phases, firstly the total area of the IMCs or phases near the interface of the solder and Au foil was calculated by an image processing software, then it was divided by total length of the interface. In this process, three samples from each aging condition were measured.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Interfacial microstructure
Evolution of AuSnx IMCs in the pure Sn solder joints is shown in Fig.1. In the laser reflowed solder joints, a layer of AuSn4 and Au-rich IMCs formed at the interface of the solder and Au foil. Besides the IMCs layer, many platelet-type AuSn4 IMCs were observed. Areas of the IMCs were summed up, and then divided by length of the interface. Corresponding thickness of the IMCs was about 9 μm (Fig.1(a)). As the pure Sn solder joints were aged for 96 h, layers of AuSn4, AuSn2 and AuSn IMCs were observed at the interface, and thickness of the IMCs layers was about 28, 4 and 3 μm, respectively. Moreover, the AuSn4 IMCs inside the solder changed from platelet-type to nubby morphology (Fig.1(b)). As the aging time was extended further, thickness of the IMCs layers was increased greatly (Figs.1(c), (d) and (e)). On the condition of 600 h aging, thickness of AuSn4 IMCs layer and total thickness of the IMCs layers reached about 40 and 54 μm, respectively.
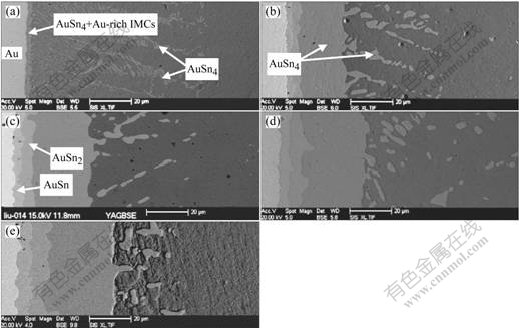
Fig.1 Evolution of AuSnx IMCs in pure Sn solder joints aged for different time at 125 ℃: (a) Without aging; (b) 96 h; (c) 216 h; (d) 384 h; (e) 600 h
Fig.2 shows the formation of IMCs and phases at the interface of the Sn-1.5%Zn solder and Au foils. Besides the thin AuSn4 and Au-rich IMCs layers, many platelet-type AuSn4 IMCs and a few Au-Zn phases were observed at the interface (Figs.2(a) and(b)). On the condition of 96 h aging, AuSn4, AuSn2 and AuSn IMCs layers formed at the interface. The AuSn4 IMCs layer was about 30 μm in thickness. In addition, within the AuSn4 IMCs layer, Au-Zn phases in nubby morphology were observed (Figs.2(c) and (d)). As the aging time was increased to 600 h, the AuSn4 IMCs layer decreased to 24 μm in thickness, and the AuSn2 and AuSn IMCs layers reached about 10 and 8 μm in thickness, respectively, which were thicker than those in the pure Sn solder joints aged for 600 h (7 and 6 μm).
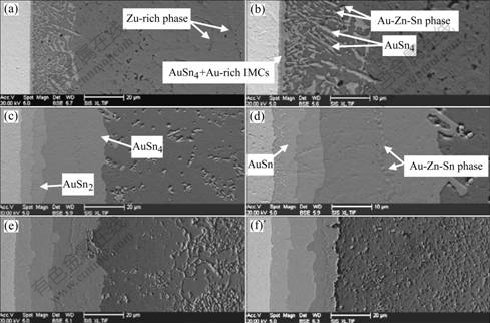
Fig.2 Evolution of AuSnx IMCs, Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases in Sn-1.5%Zn solder joints aged for different time at 125 ℃: (a) Without aging; (b) Enlarged SEM image of (a); (c) 96 h; (d) Enlarged SEM image of (c); (e) 384 h; (f) 600 h
Fig.3 shows the formation of IMCs and phases at the interface of the Sn-3.5%Zn solder and Au foils. In the laser reflowed solder joints, more Au-Zn phases were observed at the interface as compared with those in the Sn-1.5%Zn solder joints (Fig.3(a)). As the solder joints were aged for 96 h, a AuSn4 IMCs layer, which was embedded with many Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases, was observed at the interface (Fig.3(b)). The thickness of AuSn2 and AuSn IMCs layers was about 8 and 11 μm, respectively. On the condition of 600 h aging, Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases formed at the interface instead of AuSn4 IMCs layer. Moreover, AuSn2 IMCs became discontinuous at the interface (Fig.3(d)). The AuSn2 IMCs layer experienced the following change: it grew in the earlier aging period, and then was consumed in the subsequent aging period.
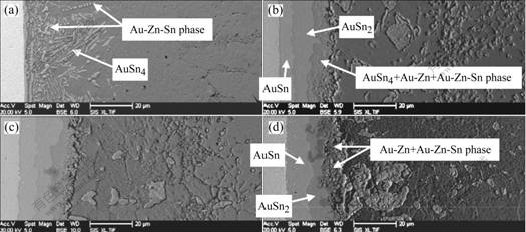
Fig.3 Evolution of AuSnx IMCs, Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases in Sn-3.5%Zn solder joints aged for different time at 125 ℃: (a) Without aging; (b) 96 h; (c) 384 h; (d) 600 h
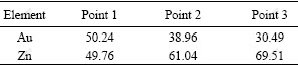
Fig.4 shows the formation of IMCs and phases at the interface of the Sn-9.0%Zn solder and Au foils. In the laser reflowed solder joints, Au-Zn phases and AuSn4 IMCs formed at the interface, where the content of the phases was comparable with that of the AuSn4 IMCs (Fig.4(a)). When the solder joints were aged for 96 h, Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phase layer, discontinuous AuSn2 IMCs, and AuSn IMCs layer were observed at the interface. However, no AuSn4 IMCs formed at the interface (Fig.4(b)). When the aging time was extended to 600 h, thickness of the AuSn IMCs layer decreased, and parts of the AuSn IMCs layer were consumed at the interface. In addition, Au-Zn phases with different ratios of Au to Zn formed at the interface. The contents of Zn at three points were 49.76, 61.04 and 69.51 (molar fraction), respectively (Table 1).

Fig.4 Evolution of AuSnx IMCs, Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases in Sn-9.0%Zn solder joints aged for different time at 125 ℃: (a) Without aging; (b) 96 h; (c) 384 h; (d) 600 h
Table 1 EDX results of three points indicated in Fig.4 (molar fraction, %)
3.2 Effect of Zn on interfacial reaction
The results shown above indicate that the pure Sn solder will react with Au foils to form AuSnx IMCs in the reflow and aging processes. However, when Zn was introduced into the solders, Zn and Au will react and form Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases. Moreover, in the solders with high content of Zn, when the solder joints were aged for long time, the AuSnx IMCs, such as AuSn4, AuSn2 and AuSn will be consumed in sequence, and Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases will form at the interface instead. By comparing the results of the present and previous studies[11-14], it can be inferred that the Au-Zn phases have higher driving force for formation than AuSnx IMCs, and the phases are more stable than AuSnx IMCs on the aging condition. That is to say, introduction of the Zn in solder will restrain the formation of AuSnx IMCs effectively.
Fig.5 shows the element distribution of the Sn-9.0%Zn solder joints, which were aged at 125 ℃ for different time. With the increase of aging time, the content of Zn near the interface was obviously larger than that in the laser reflowed solder joints. In the earlier aging process, some of the Zn elements added in the solder, which was far away form the Au foil, diffused to the interface, and reacted with Au and Sn to form Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases. However, Zn content was relatively small as compared with the Au and Sn near the interface. In consequence, besides the Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases, AuSnx IMCs, such as AuSn2 and AuSn IMCs also grew in the aging process. As the aging time was extended further, more Zn elements diffused to the interface. Because the Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases have higher driving force for formation than AuSnx IMCs, moreover, the Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases are more stable than AuSnx IMCs, the AuSn4, AuSn2 and AuSn IMCs could be consumed in sequence, and transformed to Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases.
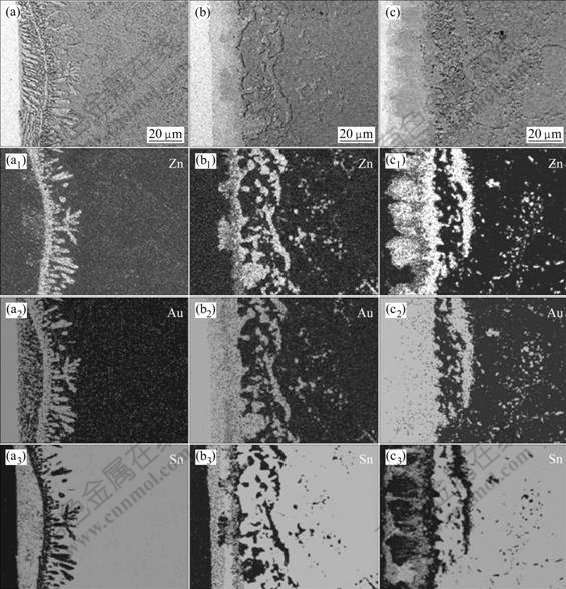
Fig.5 Element distribution of Sn-9.0%Zn solder joints aged for different time at 125 ℃: (a) Without aging; (b) 96 h; (c) 384 h; (d) 600 h
3.3 Effect of Zn on IMCs and phase thickness
The variation of the IMCs and total phase thickness at the solder/Au foil interface is shown in Fig. 6. As for the four kinds of laser reflowed solder joints, difference of the IMCs and phase thickness was smaller than 4.5 μm. In the pure Sn solder joints, the thickness of IMCs increased continuously during the aging process. However, as for the solder joints with Zn addition, the thickness of the IMCs and phases increased till 216 h aging. As the aging time was extended further, more Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases formed at the interface. When the solder joints were aged for 600 h, total thicknesses of the IMCs and phases in the pure Sn, Sn-1.5%Zn, Sn-3.5%Zn and Sn-9.0%Zn solder joints were about 54.0, 43.0, 25.9 and 26.3 μm, respectively. The thickness of the IMCs and phases in the Sn-3.5%Zn and Sn-9.0%Zn solder joints was less than one half of that of AuSnx IMCs in the pure Sn solder joints. The results indicated that Zn addition in the solders could both restrain the formation of the AuSnx IMCs and restrain the fast increase of the IMCs and phase thickness greatly. As we know, reliability of the solder joints will be affected by thickness of IMCs layers at the interface of the solder and pad[15-16]. Therefore, the thin IMCs and phases achieved by Zn addition in solder alloys could be beneficial to improving the long-term reliability of the solder joints.
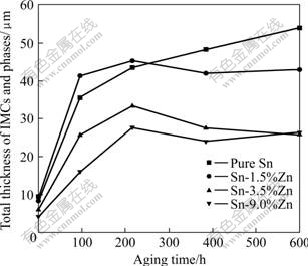
Fig.6 Variation of total thickness of IMCs and phases at interface of solder and Au foils during aging process
4 Conclusions
1) As compared with the solder/Au foil interface in the pure Sn solder joints, Zn addition in the Sn-rich solder alloys will restrain the formation of AuSnx IMCs greatly.
2) With the increase of aging time and the amount of Zn addition in the solder alloys, more Au-Zn and Au-Zn-Sn phases will form at the interface. The AuSn4, AuSn2 and AuSn IMCs will be consumed in sequence.
3) The Zn addition in Sn-rich solder alloys will also restrain the increase of the IMCs and phase thickness at the solder/Au foil interface.
References
[1] JACOBSON D M, JUMPSTON G. Gold coatings for fluxless soldering [J]. Gold Bull, 1989, 22(1): 9-18.
[2] ZENG K, TU K N. Six cases of reliability study of Pb-free solder joints in electronic packaging technology [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2002, 38: 55-105.
[3] KIM P G, TU K N. Morphology of wetting reaction of eutectic SnPb solder on Au foils [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1996, 80(7): 3822-3827.
[4] MEI Ze-qun, KAUFMANN M, JOHNSON P. Brittle interfacial fracture of PBGA packages soldered on electroless nickel/immersion [C]// Proceedings of the 48th Electronic Components and Technology Conference. Washington, 1998: 952-961.
[5] HUNG S C, ZHENG P J, HO S H, LEE S C, CHEN H N, WU J D. Board level reliability of PBGA using flex substrate [J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2001, 41: 677-687.
[6] KIM P G, TU K N. Fast dissolution and soldering reactions on Au foils [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 1998, 53: 165-171.
[7] YAMADA T, MIURA K, KAJIHARA M, KUROKAWA N, SAKAMOTO K. Kinetics of reactive diffusion between Au and Sn during annealing at solid-state temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 390: 118-126.
[8] MITA M, MIURA K, TAKENAKA T, KAJIHARA M, KUROKAWA N, SAKAMOTO K. Effect of Ni on reactive diffusion between Au and Sn at solid-state temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2006, 126: 37-43.
[9] FURUTO A, KAJIHARA M. Influence of Si on reactive diffusion between Au and Sn at solid-state temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 445/446: 604-610.
[10] YEN Y W, JAO C C, HSIAO H M, LIN C Y, LEE C Y. Investigation of the phase equilibria of Sn-Cu-Au ternary and Ag-Sn-Cu-Au quaternary systems and interfacial reactions in Sn-Cu/Au couples [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2007, 36(2): 147-158.
[11] CHANG S C, LIN S C, HSIEH K C. Phase reaction in Sn–9Zn solder with Ni/Au surface finish bond-pad at 175 ℃ageing [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 428: 179-184.
[12] YU C H, KIM K S, KIM H I, JEON H I. Influence of interfacial reaction layer on reliability of chip-scale package joint from using Sn-37Pb and Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2005, 34(2): 161-167.
[13] LEE C Y, YOON J W, KIM Y J, JUN S B. Interfacial reactions and joint reliability of Sn-9Zn solder on Cu or electrolytic Au/Ni/Cu BGA substrate [J]. Microelectronic Engineering, 2005, 82: 561-568.
[14] SHARIF A, CHAN Y C. Retardation of spalling by the addition of Ag in Sn-Zn-Bi solder with the Au/Ni metallization [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 445/446: 686-690.
[15] HUANG Wei, LOMAN J M, SENER B. Study of the effect of reflow time and temperature on Cu-Sn intermetallic compound layer reliability [J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2002, 42: 1229-1234.
[16] PANG. J H L, LOW T H, XIONG B S, LUHUA X, NEO C C. Thermal cycling aging effects on Sn-Ag-Cu solder joint microstructure, IMC and strength [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2004, 462/463: 370-375.
Foundation item: Project(50675047) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: LIU Wei; Tel: +86-451-86418359; E-mail: wangcq@hit.edu.cn; w_liu@hit.edu.cn
(Edited by YANG Bing)