高氧强化的高强高塑Ti-Zr合金
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2020年第9期
论文作者:刘咏 汤菡纯 黄千里 赵大鹏 何俊阳 曹远奎 宋旼 刘彬 欧阳思慧
文章页码:2449 - 2458
关键词:氧;Ti-Zr合金;延展性;粉末冶金
Key words:oxygen; Ti-Zr alloys; ductility; powder metallurgy
摘 要:通过粉末冶金和热加工方法制备氧含量为0.42%~0.54%(质量分数)的Ti-Zr合金。结果表明:Ti-Zr合金由具有相同α相结构的富Zr区和贫Zr区组成,富Zr区域的氧含量较高,且晶粒尺寸较小。Ti-Zr合金同时具有高强度(σs=700~900 MPa)和高的总伸长率(>20%),而氧的固溶强化是主要的强化机制。Zr由于与Ti具有高度结构相似性,对氧诱发Ti合金脆化的影响不大。因此,0.54%(质量分数)的高含量值仍处于韧性到脆性转变的临界氧含量范围内,不明显降低材料的延展性。
Abstract: Ti-Zr alloys (oxygen content 0.42-0.54 wt.%) were prepared via powder metallurgy and hot working. The results indicate that the Ti-Zr alloys exhibit Zr-rich and Zr-lean areas with the same α-phase structure, and the Zr-rich area shows a slightly higher oxygen content and a much finer grain size. The Ti-Zr alloys present a good combination of high strength (σs=700-900 MPa) and total elongation (>20%), and solid solution strengthening of oxygen plays a major role. Zr does not influence much the oxygen-induced brittleness due to its high structural similarity to Ti. Therefore, the high value of 0.54 wt.% is still within the critical oxygen content for the ductile-to-brittle transition of Ti and does not degrade the ductility.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 30(2020) 2449-2458
Yong LIU1, Han-chun TANG1, Qian-li HUANG1, Da-peng ZHAO2, Jun-yang HE3, Yuan-kui CAO1, Min SONG1, Bin LIU1, Si-hui OUYANG1
1. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. College of Biology, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
3. Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung GmbH, Düsseldorf 40237, Germany
Received 28 February 2020; accepted 6 July 2020
Abstract: Ti-Zr alloys (oxygen content 0.42-0.54 wt.%) were prepared via powder metallurgy and hot working. The results indicate that the Ti-Zr alloys exhibit Zr-rich and Zr-lean areas with the same α-phase structure, and the Zr-rich area shows a slightly higher oxygen content and a much finer grain size. The Ti-Zr alloys present a good combination of high strength (σs=700-900 MPa) and total elongation (>20%), and solid solution strengthening of oxygen plays a major role. Zr does not influence much the oxygen-induced brittleness due to its high structural similarity to Ti. Therefore, the high value of 0.54 wt.% is still within the critical oxygen content for the ductile-to-brittle transition of Ti and does not degrade the ductility.
Key words: oxygen; Ti-Zr alloys; ductility; powder metallurgy
1 Introduction
Titanium (Ti) and its alloys have been widely studied for biomedical applications, due to their high specific strength, high corrosion resistance, and good biocompatibility. Commercially pure Ti has the best ductility, but can only be used as small parts in wear and fatigue resistant areas, due to its low strength [1]. Ti alloys of high strength are usually used for high-loading large implants [2]. For example, in dental implants, pure Ti parts are not hard sufficiently, so that wear on the surface occurs to induce inflammation and mechanical instability [3]. Thus, Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-Zr alloys have been developed to satisfy the high and complex stress situations of teeth [1,4,5]. The Ti alloys can be strengthened mainly through microstructural adjustments (refining grain size and α lath thickness, increasing α/b phase ratio and dislocation density) and solid solution. The solution strengthening of Ti alloys includes alloying Ti with different metallic and interstitial elements. There are numerous compositions for commercial Ti alloys with various transition metals. However, most transition elements have a weak strengthening effect on Ti due to low interactions with dislocation gliding [6]. Except that, aluminum (Al) and tin (Sn) with high valence structures, can impede prismatic dislocation emission and reduce basal dislocation cross-slipping [7]. But, some metallic elements are not suitable for biomedical applications due to cell toxicity and insufficient biocompatibility. For example, Al, as a strong strengthening element for Ti, will induce inflammatory and proteolytic alterations in human monocytic cells [8].
Interstitial elements, such as carbon (C), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N) and hydrogen (H), usually have a strong bonding with Ti atoms and occupy octahedral interstice due to small atomic size. Therefore, interstitial elements have much robust strengthening effects over transition metals due to high suppression of dislocation motions and large lattice distortion [9]. Among these impurity elements for Ti, O has gained increasing attention on its strengthening effect, because O has the highest solubility in Ti. The α-Ti can maintain a concentration of 34 at.% of O in the matrix without the formation of oxides. The high solution strengthening ability of O in Ti has been widely reported [10]. SUN et al [10] found that the yield strength of Ti can be effectively increased by the introduction of O, from about 500 MPa at 0.23 wt.% O to about 800 MPa at 0.64 wt.% O. KANG et al [11] found both the strength and the work hardening rate of Ti can be improved by raising the O content from 0.082 to 0.268 wt.%. The authors also reported the increase of hardness of Ti-Zr alloy with the increase of O contents [12]. However, high content of O will embrittle Ti by transforming Ti—Ti metallic bond to covalent bond, impeding dislocation sliding or inducing precipitation of oxides, intermetallics, and martensite phases [13,14]. The concentration limit of O in Ti not to degrade seriously the ductility is different for different alloy compositions. Generally, β-Ti alloys are much more resistant to O-induced brittleness than α-Ti alloys. For example, an O content of 0.65 wt.% totally embrittles an α-Ti (Ti-6Al-2V), while the similar O content does not degrade much the ductility of a β-Ti alloy (Ti-16V-2Al) [15]. YAN et al [14] also verified that, through careful microstructural evaluations and compositional analyses, the critical O content is about 0.33 wt.%, and does not induce much brittleness of Ti-6Al-4V. In particular, even for α-Ti alloys, the influence of O is varied with compositions. The increasing content of O from 0.06 to 0.12 wt.% decreases the tensile strain of Ti–8Al alloy from 20% to 1% [16], while this concentration range does not attack pure Ti at all [17]. It is possible that Al, with a high affinity to O, decreases the critical content of O for ductile-to-brittle transformation by a strong covalent bond. It seems that there is a strong compositional dependence of O in affecting the ductility of Ti. Zr, an active element for O, has widely been used for alloying Ti, for example, in Ti-15Zr dental alloy [18]. O can also solute- strengthen Ti-Zr alloy [19], but its influence on ductility has seldom been reported, especially at high concentrations.
In this work, Ti-Zr alloys with different contents of Zr and a high O content (0.4-0.5 wt.%) were prepared by powder metallurgy and followed by hot rolling. The mechanical behavior of various Ti-Zr alloys was evaluated, in order to show the effect of the high O content, and the underlying mechanism was discussed.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials preparation
For introducing O, Ti powder (<45 mm) of O content of 0.25 wt.% was mixed with Zr powder (<75 mm) of O content of 0.4 wt.% according to compositions of Ti-5wt.%Zr, Ti-10wt.%Zr and Ti-15wt.%Zr. The mixed powders were cold isostatically pressed at room temperature and 180 MPa into a size of d30 mm × 250 mm. The Ti-Zr compacts were sintered in a vacuum of 1×10-5 Pa, 1400 °C for 8 h. The sintered samples were cut into 10 mm-high columns, and then repeatedly hot rolled and heated in air at 750 °C, with a total reduction in thickness of 75%. For eliminating the residual stress during rolling, the plates were reheated at 600 °C for 30 min, and water quenched.
2.2 Mechanical tests
Room temperature quasi-static tensile tests were conducted on an MTS machine with a strain rate of 1×10-3 s-1. The gauge section of the standard tensile sample is 20 mm in length and 2.0 mm × 3.7 mm in cross profile.
2.3 Microstructural observation
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses were performed on a Rigaku D/max 2550VB+. X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (40 kV, 300 mA, step size of 0.02°). The XRD patterns were recorded in a 2θ range of 10°-80°. The microstructures were observed using an FEI Quanta FEG 250 scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) unit. Specimens for SEM were prepared from cross-sections of the deformed samples.
Samples for electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were electro-polished by using Struers Tenupol 5. The polishing operation was in the electrolyte of 5% perchloric acid, 60% methanol and 35% butanol (in volume fraction) at 243 K. The details of microstructures were characterized on the Helios Nanolab G3 UC dual-beam electron microscope with EBSD unit to obtain electron backscatter diffraction patterns. Data collection and post-processing analysis were performed on Aztec and Channel 5. TEM observations were conducted using an FEI Tecnai 20 transmission electron microscope (TEM).
2.4 Oxygen measurements
The O contents of Ti powder, Zr powder, and Ti-Zr alloys were measured by using a Leco TCH600 oxygen-nitrogen analyzer.
3 Results
3.1 Phase structures
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of as-sintered (Fig. 1(a)) and as-rolled (Fig. 1(b)) Ti-Zr alloys. All the Ti-Zr alloys have a single α phase structure, and as-rolled alloys show an orientation with the rolling direction (α(1000) plane is missing in the testing direction). Both the lattice parameters of a and c increase with the content of Zr (Fig. 1(c)), higher than that of pure Ti [20]. In Fig. 1(d), the c/a ratios of Ti-Zr alloys with high O contents in this work are higher than those of as-cast Ti and Ti-Zr alloys with low O contents [20,21].
3.2 Microstructures
3.2.1 As-sintered and as-rolled states
Figure 2 shows microstructures of as-sintered and as-rolled Ti-Zr alloys. There are some residual pores in the as-sintered alloys (Figs. 2(a-c)). Since almost all the pores can be effectively eliminated by hot rolling (Figs. 2(b-d)), the density of alloys will not be paid much attention to. All the alloys consist of α laths, which precipitate during cooling from b phase. While there is a bright phase coexisting with α laths, it is also of α phase structure but rich in Zr. Such a Widmanstatten-like structure is formed by continuous and uniform precipitation, and can also be observed in Ti-Zr and other similar α-Ti alloys [22-24].
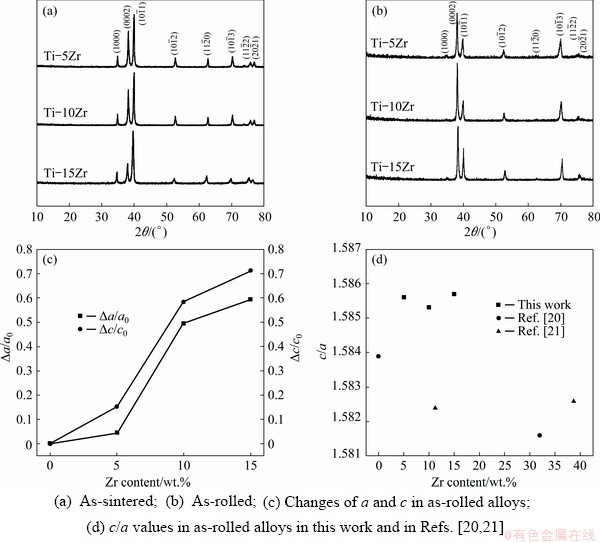
Fig. 1 XRD patterns (a, b) and lattice parameters (c, d) of various Ti-Zr alloys
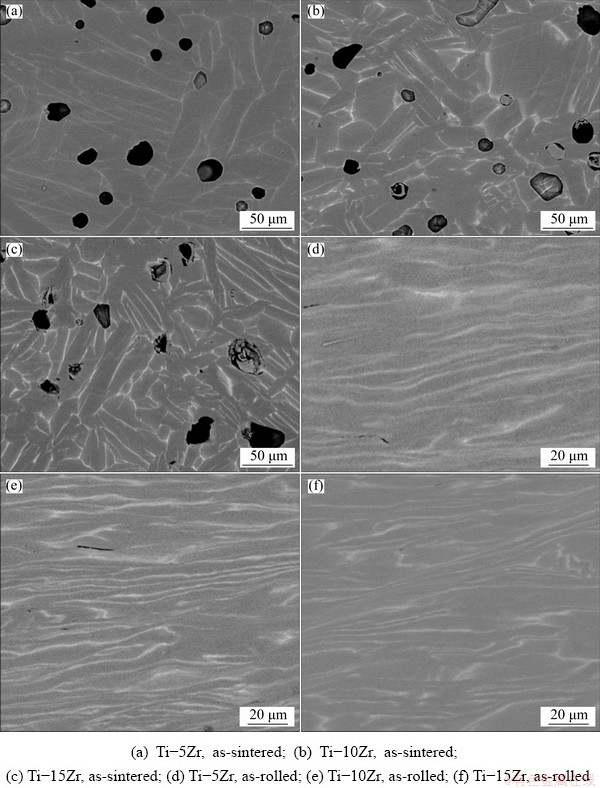
Fig. 2 Microstructures of as-sintered and as-rolled Ti-Zr alloys
After hot rolling, the grain structures are stretched along the rolling direction, and the lamellar structures are refined. For example, the spacings of Zr-rich lath for Ti-5Zr, Ti-10Zr and Ti-15Zr are 8.7, 7.4 and 5.1 μm, respectively, and the thickness is refined to about 1 μm.
3.2.2 Compositional analyses
The compositions of different laths in various Ti-Zr alloys were measured by EDX. It is shown that the contents of Zr in Zr-rich laths are 9.1, 17.8 and 20.3 wt.% for Ti-5Zr, Ti-10Zr and Ti-15Zr alloys, respectively, while those in Zr-lean laths are 4.6, 7.4 and 7.5 wt.%, respectively. Though the results are semi-quantitative, they indicate the inhomogeneous distributions of Zr in micro- structures. The O contents, measured by chemical methods, slightly increase with Zr contents increasing, and the values are 0.42, 0.47 and 0.54 wt.% for Ti-5Zr, Ti-10Zr and Ti-15Zr, respectively.
The compositional profiles of different elements in Ti-15Zr are shown in Fig. 3. Zr can still be clearly seen to be rich in dendrite-like structures, while the distribution of O has a strong overlap with that of Zr. It seems that O can distribute in the whole microstructural area, but may preferentially be close to the Zr-rich area.
3.2.3 EBSD characterization
Figure 4 shows the grain structures of Ti-15Zr after hot rolling, and the grain size and orientations can be observed. The major area, i.e., Zr-lean area, is composed of equiaxed grains with mostly high angle grain boundaries. However, in some fine- grain areas, low angle grain boundaries can be seen due to insufficient recovery and recrystallization. The mean grain size of the Zr-lean lath is roughly estimated to be 10 μm. However, the grains in the Zr-rich area are much finer. The average grain size in the Zr-rich area is about 2 mm, and many grains are of the sub-micron scale. The Zr-lean and Zr-rich areas exhibit different orientations. The Zr-rich areas have more grains in (0001) orientation, as shown in Figs. 4(b, d). According to Fig. 4(c), plenty of low-angle grain boundaries are observed in the Zr-rich areas, indicating the formation of sub-grains.
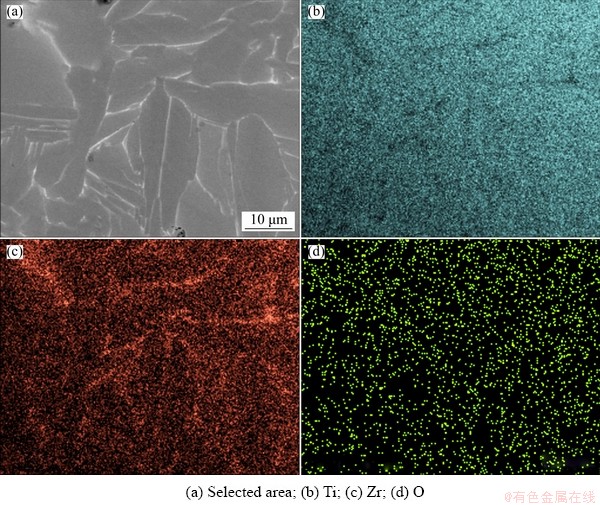
Fig. 3 Compositional profiles of elements in Ti-15Zr alloy
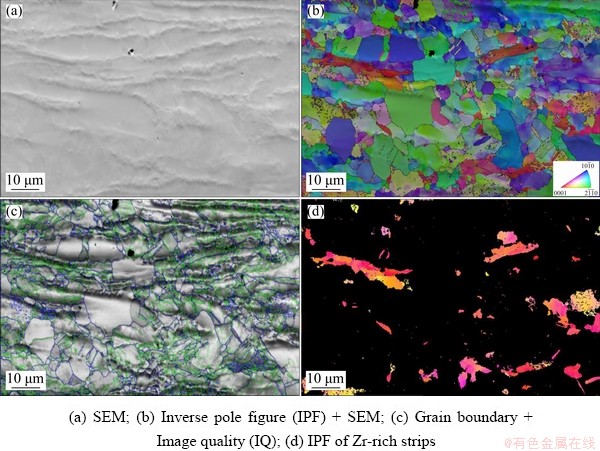
Fig. 4 Microstructures of Ti-15Zr by EBSD
3.2.4 Dislocation structures
The detailed dislocation structures in as-rolled Ti-15Zr alloy can be depicted through TEM characterization in Fig. 5. The network structures in a large grain in Figs. 5(a, b) indicate a planar gliding manner of dislocations. There are two groups of gliding, with an intersection angle of 60°. For the fine grain in Fig. 5(c), there is a strong interlocking of cellular dislocation subgrains, which is in agreement with EBSD results. Figure 5(d) indicates the hcp lattice structure of Fig. 5(a), and no other precipitate or twinning is found.
3.3 Mechanical behavior
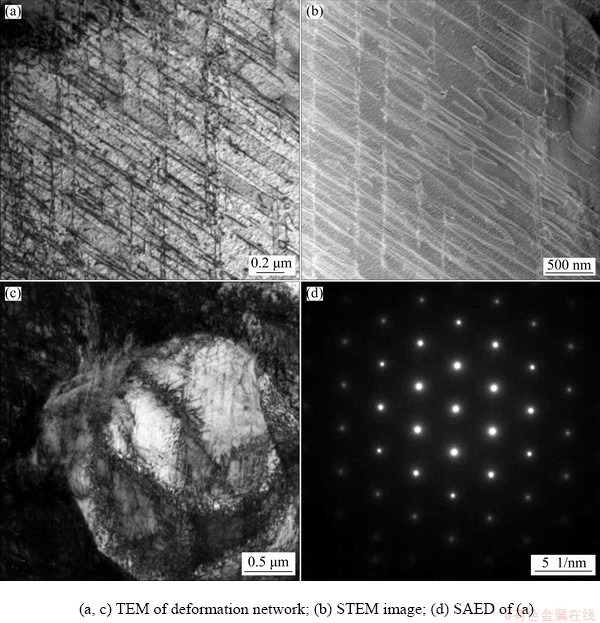
Fig. 5 TEM images of as-rolled Ti-15Zr alloy
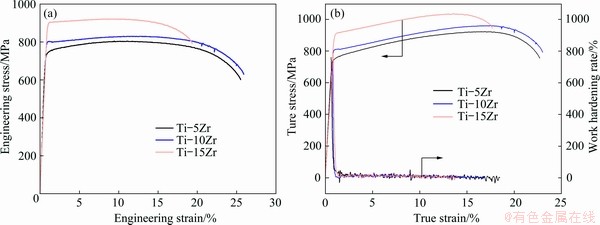
Fig. 6 Tensile engineering stress-strain curves (a) and work hardening curves (b) of various Ti-Zr alloys
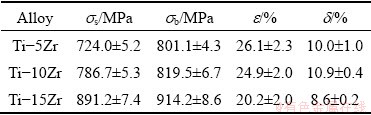
The tensile behavior of various Ti-Zr alloys is shown in Fig. 6. All the Ti-Zr alloys show high strength and good ductility. The mechanical properties of Ti-Zr alloys are described in Table 1. Both the yield strength and tensile strength increase with Zr content increasing. The uniform elongations (d) were measured from engineering stress-strain curves by cutting off the necking parts, and the elongation to failure (e) included the necking parts. The elongation to failure of Ti-Zr alloys is around 20%, and the uniform elongation is about 10%. The tensile strength increases with the content of Zr. However, Ti-15Zr alloy shows a slightly decreased uniform elongation. The work hardening rate curves of all three alloys are rather stable and are almost the same during uniform deformation, as shown in Fig. 6(b).
Table 1 Tensile properties of Ti-Zr alloys
3.4 Fractography
The microstructures of the fracture surface of Ti-Zr alloys after tensile tests are shown in Fig. 7. It is indicated that most fracture occurs in a transgranular manner, showing good ductility of the grain structures. For Ti-15Zr, more microcracks can be found in the former Zr-rich area.
4 Discussion
4.1 Evolution of microstructures
The introduction of O to Ti-Zr alloys was mainly through raw Ti and Zr powders with high O content. O may be in the form of the solid solution inside Ti and Zr particle and surface oxide layer on Ti and Zr particle. Then, the powder metallurgical process, including handling, cold pressing, and sintering, may increase the content of O by about 0.1-0.15 wt.%. Therefore, the O content of Ti-Zr alloy after sintering can be estimated to be in the range of 0.4-0.5 wt.%, and the experimental values are reasonable. Since O has a high solubility in Ti, during sintering at 1400 °C, all the O will dissolve in β-Ti as the calculated equilibrium O content could be around 2.7 wt.% [14]. During cooling, β-phase transforms to α phase at about 882 °C [25]. Due to the continuous and uniform precipitation, Zr-rich metastable area is formed, leading to the formation of the Widmanstatten-like structure. This structure shares the same hcp crystal structure but slightly different chemical compositions, as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 3. The Widmanstatten-like structure of Ti-Zr alloy can be deformed and refined during hot rolling. After hot rolling, the structure is transformed into a large number of fine grains and sub-grains through dynamic recrystallization. These grains and sub-grains formed by hot rolling can also prevent crack and contribute to the high strength [24].
As shown in Fig. 3(d), different O distributions in the Zr-rich and Zr-lean areas should be attributed to the higher affinity of O to Zr than that of O to Ti. The significantly higher bonding energy of Zr—O (53.1 eV) compared with that of Ti—O (37.5 eV) indicates that O atoms tend to bond with Zr instead of Ti [26,27].
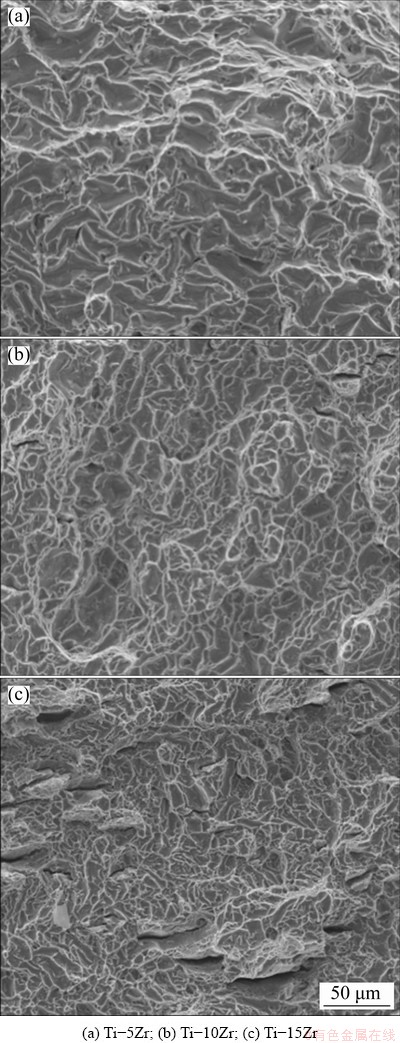
Fig. 7 Fracture morphologies of Ti-Zr alloys after tensile tests
4.2 Effects of oxygen on strength and ductility
For O-containing Ti-Zr alloys, solid solutions of both O and Zr will bring about strengthening effect. However, the extents of strengthening of O and Zr are different in Ti. Therefore, MEDVEDEV et al [18] indicated that Ti-15wt.%Zr alloy will have a strength gain of 50 MPa over pure Ti. While, SUN et al [10] and KANG et al [11] established empirical relationships of strength increment with O concentrations as 769.8 MPa/(wt.%[O]) and 0.43 GPa/(at.%[O]1/2) , respectively. When the O content increases by 0.4 wt.%, the strength gain will be as high as 300 MPa. Moreover, compared with a fine-grained (grain size of 1-2 μm) Ti-15Zr reported by KANG et al [11], the Ti-Zr alloy of the same composition in this work, but with coarser grain size and higher content of O, is in almost the similar strength level. The robust strengthening of O may come from the strong bonding of Ti—O that hinders the nucleation of basal and prismatic dislocations and blocks the emission of almost all the slip modes [7,9]. For example, a one-sixth monolayer of O will increase the Peierls stress by 4 times [28]. Therefore, O has a much higher strengthening effect than Zr in Ti alloys and can harden Ti alloys in no need of severe refinement on microstructures.
It is interesting that the high O-content Ti-Zr alloy exhibits not only higher strength, but also rather good ductility. In comparison with the same Ti-15Zr alloy made by KANG et al [11], which has a uniform elongation of only 6%, in this work, the uniform elongation is about 8% for Ti-15Zr and is higher than 10% for both Ti-5Zr and Ti-10Zr alloys. The ductility of Ti alloys highly depends on the screw dislocations. It has been reported that O may interact with the core structure of screw dislocations, and influence the mobility of dislocations of different gliding modes [17,29]. On the other hand, as shown in Fig. 1(d), the higher c/a ratios of the Ti-Zr alloys in the present work compared with those of the ones reported in Refs. [20,21] should be mainly attributed to the higher O content. The addition of substitutional Zr atom into Ti matrix usually results in lattice expansion due to the larger atomic size of Zr, and a lower c/a is usually obtained [30]. The octahedral O interstitial in hcp Ti may also lead to lattice expansion but a higher c/a ratio [21]. Such a strong effect of O on the c/a ratio influences the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) of different gliding systems [9,17]. For example, O can change the type glide system to 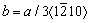 along
along 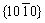 prismatic planes, as also indicated in this work. All these factors support the enhancement of the ductility of O for Ti. However, the interaction of O with dislocation structures strongly varies with its occupancy and concentrations [7]. O has a strong bonding with Ti and varies the Ti—Ti metallic bond to covalent bond, which is tighter but leads to brittleness. At a high concentration of O, dislocations are much highly possible to be pinned by O-rich obstacles rather than more glissile [17]. Therefore, it is widely believed that there should be a critical value of O for the ductile-to-brittle transition. Usually, for Al-containing alloys, the critical value for O is low, because Al itself is a strong bonding element to Ti and may introduce covalent bonds at high concentrations, for example, the formation of Ti3Al and TiAl intermetallics [31]. On one hand, the introduction of O in Ti-Al alloy can enhance the covalent bond. And on the other hand, it can induce the precipitation of α2 intermetallics phase [14]. However, in this work, Ti-Zr alloy has a much larger tolerance for O. Zr is very close to Ti in both structures and physical properties and forms an unlimited solid solution with Ti. The weak solute strengthening effect of Zr in Ti also indicates that Zr does not change much the metallic bond and dislocation structures. Moreover, the homogeneous stress distribution in the ‘dual-structure’ in this work shows that Zr-rich α phase actually is similar to Ti-rich α phase. Therefore, Ti-Zr alloy can be taken as pure Ti in structure. Although O can distribute more closely to the Zr-rich area, it does not change much the intrinsic metallic bonds of Ti—Ti and Ti—Zr. Since pure Ti with an O content as high as 0.64 wt.% has a good elongation of 26% [10], it is reasonable to believe that the introduction of 0.4-0.5 wt.% O will not degrade the ductility of Ti-Zr alloys.
prismatic planes, as also indicated in this work. All these factors support the enhancement of the ductility of O for Ti. However, the interaction of O with dislocation structures strongly varies with its occupancy and concentrations [7]. O has a strong bonding with Ti and varies the Ti—Ti metallic bond to covalent bond, which is tighter but leads to brittleness. At a high concentration of O, dislocations are much highly possible to be pinned by O-rich obstacles rather than more glissile [17]. Therefore, it is widely believed that there should be a critical value of O for the ductile-to-brittle transition. Usually, for Al-containing alloys, the critical value for O is low, because Al itself is a strong bonding element to Ti and may introduce covalent bonds at high concentrations, for example, the formation of Ti3Al and TiAl intermetallics [31]. On one hand, the introduction of O in Ti-Al alloy can enhance the covalent bond. And on the other hand, it can induce the precipitation of α2 intermetallics phase [14]. However, in this work, Ti-Zr alloy has a much larger tolerance for O. Zr is very close to Ti in both structures and physical properties and forms an unlimited solid solution with Ti. The weak solute strengthening effect of Zr in Ti also indicates that Zr does not change much the metallic bond and dislocation structures. Moreover, the homogeneous stress distribution in the ‘dual-structure’ in this work shows that Zr-rich α phase actually is similar to Ti-rich α phase. Therefore, Ti-Zr alloy can be taken as pure Ti in structure. Although O can distribute more closely to the Zr-rich area, it does not change much the intrinsic metallic bonds of Ti—Ti and Ti—Zr. Since pure Ti with an O content as high as 0.64 wt.% has a good elongation of 26% [10], it is reasonable to believe that the introduction of 0.4-0.5 wt.% O will not degrade the ductility of Ti-Zr alloys.
5 Conclusions
(1) The high O-containing Ti-Zr alloys have a single α-phase structure but show Zr-rich and Zr-lean ‘dual-phase’ microstructures. The increase of Zr induces more formation of Zr-rich structures, and decreases the spacing between the two areas. O is in a state of solid solution in Ti-Zr alloys, and preferentially distributes close to the Zr-rich area.
(2) The strength of Ti-Zr alloys is enhanced slightly with the content of Zr increasing, but the major strengthening effect comes from O solid solution. The ductility of Ti-Zr alloys is rather good and not largely degraded by the high content of O, because Zr has a high similarity to Ti and does not influence much the O-effect on the metallic bond.
(3) O solution strengthening is a very effective way to improve the mechanical properties of Ti-Zr alloys without the sacrifice of the ductility.
References
[1] CORDEIRO J M, BARAO V A R. Is there scientific evidence favoring the substitution of commercially pure titanium with titanium alloys for the manufacture of dental implants? [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 71: 1201-1215.
[2] IBRAHIM M K, HAMZAH E, SAUD S, NAZIM E M, BAHADOR A. Parameter optimization of microwave sintering porous Ti-23%Nb shape memory alloys for biomedical applications [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 700-710.
[3] SAGHIRI M A, ASATOURIAN A, KAZERANI H, GUTMANN J L, MORGANO S M. Effect of thermocycling on the surface texture and release of titanium particles from titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) plates and dental implants: An invitro study [J]. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.11. 013.
[4] CORREA D R N, ROCHA L A, DONATO T A G, SOUSA K S J, GRANDINI C R, AFONSO C R M, DOI H, TSUTSUMI Y, HANAWA T. On the mechanical biocompatibility of Ti-15Zr-based alloys for potential use as load-bearing implants [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9: 1241-1250.
[5] BARTOLOMEU F, BUCIUMEANU M, PINTO E, ALVES N, SILVA F S, CARVALHO O, MIRANDA G. Wear behavior of Ti6Al4V biomedical alloys processed by selective laser melting, hot pressing and conventional casting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 829-838.
[6] CONRAD H. Effect of interstitial solutes on the strength and ductility of titanium [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 1981, 26: 123-403.
[7] KWASNIAK P, GARBACZ H, KURZYDLOWSKI K J. Solid solution strengthening of hexagonal titanium alloys: Restoring forces and stacking faults calculated from first principles [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 102: 304-314.
[8] LIGI D, SANTI M, CROCE L, MANNELLO F. Aluminum induces inflammatory and proteolytic alterations in human monocytic cell line [J]. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 2015, 152: 190-198.
[9] REN J Q, WANG Q, LU X F, LIU W F, ZHANG P L, ZHANG X B. Effect of oxygen content on active deformation systems in pure titanium polycrystals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 731: 530-538.
[10] SUN B, LI S, IMAI H, MIMOTO T, UMEDA J, KONDOH K. Fabrication of high-strength Ti materials by in-process solid solution strengthening of oxygen via P/M methods [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 563: 95-100.
[11] KANG D S, LEE K J, KWON E P, TSUCHIYAMA T, TAKAKI S. Variation of work hardening rate by oxygen contents in pure titanium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 632: 120-126.
[12] TANG Han-chun, LIU Yong, ZHAO Da-peng, CHENG Wen-juan. Influence of oxygen on grindability of Ti-15Zr-based alloy as dental material [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29: 2285-2291. (in Chinese)
[13] KWASNIAK P, MUZYK M, GARBACZ H, KURZYDLOWSKI K J. Influence of oxygen content on the mechanical properties of hexagonal Ti—First principles calculations [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 590: 74-79.
[14] YAN M, DARGUSCH M S, EBEL T, QIAN M. A transmission electron microscopy and three-dimensional atom probe study of the oxygen-induced fine microstructural features in as-sintered Ti-6Al-4V and their impacts on ductility [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 68: 196-206.
[15] LIU Z, WELSCH G. Effects of oxygen and heat treatment on the mechanical properties of alpha and beta titanium alloys [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1988, 19: 527-542.
[16] LIM J Y, MCMAHON C J, POPE D P, WILLIAMS J C. The effect of oxygen on the structure and mechanical behavior of Aged Ti-8wt.%Al [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1976, 7: 139-144.
[17] BARKIA B, COUZINIE J P, LARTIGUE-KORINEK S, GUILLOT I, DOQUET V. In situ TEM observations of dislocation dynamics in α titanium: Effect of the oxygen content [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 703: 331-339.
[18] MEDVEDEV A E, MOLOTNIKOV A, LAPOVOK R, ZELLER R, BERNER S, HABERSETZER P, TORRE F D. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-15Zr alloy used as dental implant material [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2016, 62: 384-398.
[19] MUSIL J, ZENKIN S, CERSTVY R, HAVIAR S, CIPEROVA Z. (Zr,Ti,O) alloy films with enhanced hardness and resistance to cracking prepared by magnetron sputtering [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 322: 86-91.
[20] ZHOU Y K, JING R, MA M Z, LIU R P. Tensile strength of Zr-Ti binary alloy [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2013, 30: 116201.
[21] ZHOU W, SAHARA R, TSUCHIYA K. First-principles study of the phase stability and elastic properties of Ti-X alloys (X=Mo, Nb, Al, Sn, Zr, Fe, Co, and O) [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 727: 579-595.
[22] HAN Mi-kyung, HWANG Moon-jin, YANG Min-soo, YANG Hong-so, SONG Ho-jun, PARK Yeong-joon. Effect of zirconium content on the microstructure, physical properties and corrosion behavior of Ti alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 616, 268-274.
[23] VICENTE F, CORREA D R N, DONATO T A G, ARANA-CHAVEZ V E, BUZALAF M A R, GRANDINI C R. The influence of small quantities of oxygen in the structure, microstructure, hardness, elasticity modulus and cytocompatibility of Ti-Zr alloys for dental applications [J]. Materials, 2014, 7: 542-553.
[24] DING Chao, SHI Qi, LIU Xin, ZHENG Li, LI Run-xia, HANG Zheng-xiang, YU Bao-yi, WU Wei. Microstructure and mechanical properties of PM Ti600 alloy after hot extrusion and subsequent annealing treatment [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019, 748: 434-440.
[25] OKAMOTO H. Phase diagrams for binary alloys [M]. Materials Park: ASM International, 2010.
[26] RIGA J, TENRETNOEL C, PIREAUX J J, CAUDANO R, VERBIST J J, GOBILLON Y. Electronic structure of rutile oxides TiO2, RuO2 and IrO2 studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy [J]. Physica Scripta, 1977, 16: 351-354.
[27] SARMA D D, RAO C N R. XPES studies of oxides of second- and third-row transition metals including rare earths [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 1980, 20: 25-45.
[28] BHATIA M A, ZHANG X, AZARNOUSH M, LU G, SOLANKI K N. Effects of oxygen on prismatic faults in α-Ti: A combined quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics study [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 98: 32-35.
[29] YU Q, QI L, TSURU T, TRAYLOR R, RUGG D, MORRIS J W, ASTA M, CHRZAN D C, MINOR A M. Origin of dramatic oxygen solute strengthening effect in titanium [J]. Science, 2015, 347: 635-639.
[30] SHIRAISHI T, YUBUTA K, SHISHIDO T, SHINOZAKI N. Elastic properties of as-solidified Ti-Zr binary alloys for biomedical applications [J]. MaterialsTransactions, 2016, 57: 1986-1992.
[31] APPEL F, PAUL J D H, OEHRING M. Gamma titanium aluminide alloys (Science and Technology) [M]. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2011.
刘 咏1,汤菡纯1,黄千里1,赵大鹏2,何俊阳3,曹远奎1,宋 旼1,刘 彬1,欧阳思慧1
1. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 湖南大学 生物学院,长沙 410082;
3. Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung GmbH, Düsseldorf 40237, Germany
摘 要:通过粉末冶金和热加工方法制备氧含量为0.42%~0.54%(质量分数)的Ti-Zr合金。结果表明:Ti-Zr合金由具有相同α相结构的富Zr区和贫Zr区组成,富Zr区域的氧含量较高,且晶粒尺寸较小。Ti-Zr合金同时具有高强度(σs=700~900 MPa)和高的总伸长率(>20%),而氧的固溶强化是主要的强化机制。Zr由于与Ti具有高度结构相似性,对氧诱发Ti合金脆化的影响不大。因此,0.54%(质量分数)的高含量值仍处于韧性到脆性转变的临界氧含量范围内,不明显降低材料的延展性。
关键词:氧;Ti-Zr合金;延展性;粉末冶金
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (51625404) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholar of China
Corresponding author: Yong LIU; Tel: +86-731-88836939; E-mail: yonliu@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65391-2

