


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2261-2267
Element distribution of high iron-bearing zinc calcine in high gradient magnetic field
LI Mi1, PENG Bing1, 2, CHAI Li-yuan1, 2, WANG Ji-ming1, PENG Ning1, YAN Huan1
1. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Control & Treatment of Heavy Metal Pollution,Changsha 410083, China
Received 24 August 2011; accepted 5 January 2012
Abstract: High gradient magnetic separation was conducted in order to separate insoluble zinc ferrite from zinc calcine before acid leaching of hydrometallurgical process. Chemical composition and structural characterization of zinc calcine were studied via inductively coupled plasma (ICP), X-ray diffraction (XRD), M?ssbauer spectra, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and laser particle analysis (LPA). The parameters of magnetic separation which affect the distribution of zinc ferrite and undesired elements, such as calcium, sulfur and lead in magnetic concentrate were investigated. The results of high gradient magnetic separation indicate that more than 85% of zinc ferrite is distributed into magnetic concentrate from the zinc calcine under the magnetic induction of 0.70 T. In addition, about 60% of calcium and 40% of sulfur distribute in non magnetic phases of tailings during magnetic separation process. Most of lead distributes uniformly along the zinc calcine in superfine particle size.
Key words: zinc calcine; zinc ferrite; magnetic separation; element distribution
1 Introduction
Zinc is an important metal required for various applications in metallurgical, chemical and textile industries [1]. At present, the roast-leach-electrowin process accounts for the greatest share of the world zinc production [2,3]. One of the major concerns related to this typical process is the zinc ferrite produced as a byproduct in the oxidative roasting of iron-bearing zinc sulfide concentrates through the reaction of zinc oxide with hematite. About 15% of zinc ferrite which is practically insoluble under dilute acidic conditions was produced in a traditional metallurgical process and became the dominant components of zinc leaching residue. The zinc leaching residue contains a variety of heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium and chromium, and is classified as a hazardous waste by environmental protection agencies.
Pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical processes are usually applied to treating such residue. An ordinary pyrometallurgical method is Waelz process, in which zinc leaching residue is heated above 1300 K with coke or powdered coal in a horizontal reducing rotary kiln, known as the Waelz furnace [4]. The zinc and other volatile non-ferrous metals in the residue are vaporized in the kiln and then reoxidized and collected as a crude zinc-bearing product which are further refined and subject to acid leaching. A major disadvantage of pyrometallurgical method is high-energy consumption, application of complicated dust collecting and gas cleaning system and difficulty for iron recovery due to the high hardness of sintering waste contributed by metallic iron generated in the reducing process.
On the contrary, hydrometallurgical process obtains more attention on account of its cost-effective and environmental-friendly advantages. Various leaching solutions including hot sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid [5,6] and alkaline [7,8] have been investigated and a considerable amount of optimum conditions have been obtained during past decades. In addition, a number of new methods with a combination of pro- hydrometallurgical process have been proposed recently. During these processes, the zinc leaching residue was roasted with one or several addition agents to make zinc ferrite transfer into soluble zinc salt and then followed by water leaching, acid leaching or alkaline leaching [9-11]. However, a major drawback of the hydrometallurgical process is that iron dissolved in undesired metal during the leaching process. Therefore, iron constitutes a serious impurity in zinc solutions and must be removed before electrolysis. To overcome this problem, several methods have been conducted to separate iron from zinc solution, such as precipitation of iron as goethite, hematite or even jarosite. Furthermore, oxidative leaching has also been employed to remove iron from solution [12].
There is no reference on separation of zinc ferrite from zinc calcine before acid leaching up to now, although many studies on zinc leaching residue to decompose zinc ferrite and recover metals have been reported. A high gradient magnetic separation was proposed to remove zinc ferrite from zinc calcine according to the weak magnetic properties of zinc ferrite, which will reduce the iron precipitation burden for traditional dilute sulfuric acid leaching and shorten the leaching flow process. However, the distribution of elements in zinc calcine is unclear. This study focused on the characteristics of zinc calcine and the behavior of impurity elements distribution during the high gradient magnetic separation process. The distribution correlation between magnetic induction and magnetic mineral phases was detected for developing magnetic separation methods to treat the high iron-bearing zinc calcine or zinc leaching residue.
2 Experimental
The sample of zinc calcine used in this study was obtained from a zinc plant in Inner Mongolia, China. It was homogenized, dried and sieved to obtain <74 μm fraction, and then prepared by dissolving in an acid admixture for the determination of metal content using inductively coupled plasma (ICP-OES, IRIS Intrepid II XSP). The phases present in zinc calcine were detected by X-ray powder diffraction (Rigaku, TTR-Ⅲ) in the pattern of monochromated Cu Kα radiation in 2θ from 10° to 80° with a scan step of 0.05° and the data were analyzed by using JADE 5.0 X-pert software. The phase composition of iron was investigated by M?ssbauer spectra on a standard spectrometer at constant acceleration and room temperature. A 70 mCi 57Co(Gr) source was used and the isomer shifts were given relatively to that of α-Fe. The spectra obtained in the experiments were analyzed using standard software based on the least-squares method. Scanning electron microscopy (JEOL.LTD, JSM-6360LV) was used to gain further information of structure, morphology and chemical composition of the zinc calcine to help commanding the distribution of elements. The particle size distribution and the average diameter of zinc calcine particles were evaluated by a laser particle size analyzer (MICRO-PLUS).
The magnetic separation was performed on the slurry of zinc calcine with the solid to liquid ratio of 1:5, using a high gradient magnetic separator under electromagnet working at a high magnetic induction from 0.1 to 1.65 T. A sample of 50 g was used in each magnetic separation experiment. The concentrates and tailings were collected, dried, weighed and analyzed for metals, respectively. The distribution rate and grade of metals in concentrates were tested to evaluate the distribution properties of main elements in zinc calcine.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization of high iron-bearing zinc calcine
ICP analysis was performed to determine the chemical content of metals in received zinc calcine. The average composition is given in Table 1. From the ICP results, the sample contains approximately 57% zinc, 12% iron, 1.27% lead and 2.44% sulfur as major elements. Besides, the zinc calcine also presents intermediate amounts of Mn, Ca, Al, Cu and trace amount of toxic element such as cadmium.
Table 1 Chemical composition of zinc calcine analyzed by ICP (mass fraction, %)

The X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) pattern of the zinc calcine is shown in Fig. 1. Based on the peaks detected and their respective intensities, it can conclude that the zinc calcine consists of the major phases of zincite (ZnO), zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4), willemite (Zn2SiO4), zinc sulfide (ZnS) and magnetite (Fe3O4). However, the signals from zinc ferrite and magnetite exhibit overlapping in all peaks, as shown in Fig. 1. Such overlapping was also observed by other researchers [13,14]. Hence, the presence of these phases cannot be assured. In order to improve the phase identification of zinc calcine samples, it is necessary to use other techniques like M?ssbauer spectra, scanning electron microscopy and X-ray mapping analysis.

Fig. 1 X-ray diffraction pattern of zinc calcine
The M?ssbauer spectrum for zinc calcine is displayed in Fig. 2. The hyperfine field (Heff), isomer shift (IS), quadrupole splitting (QS), line width (Г/2) and area (%) obtained from best fitted M?ssbauer spectrum line are presented in Table 2. As can be seen from Fig. 2, only one bimodal line was observed by M?ssbauer spectra fitted by least-square method. This indicates that zinc ferrite is the unique form of iron in the zinc calcine according to M?ssbauer parameters listed in Table 2. We can conclude that the magnetite phase (Fe3O4) detected by XRD in overlapped peaks does not exist in zinc calcine or the content of Fe3O4 is below the detection limit of the M?ssbauer equipment, so it could be neglected during the next magnetic separation experiments. Thus, the iron grade of magnetic concentrates mainly exists in the form of zinc ferrite and could be applied to analyze the zinc ferrite distribution.

Fig. 2 M?ssbauer spectrum of zinc calcine
Table 2 M?ssbauer parameters of zinc calcine at room temperature

Figure 3 shows a secondary electron image of zinc calcine and the X-ray mapping for the elements of Zn, Ca, Fe, Pb, Si and S present in the calcine. There are mainly four phases present in zinc calcine according to the BSE image. Figure 3 demonstrates that oxygen is distributed all over the sample, which suggests the existence of metal oxide structural forms. The dark gray area A rich in S and Ca may suggest the existence of CaSO4. The high light region B in which the presence of a significant amount for iron, zinc and oxygen should be the zinc ferrite phase (ZnFe2O4). The grey area C rich in zinc and silicate suggests the presence of Zn2SiO4 that was also detected by XRD. The area D rich in zinc with a lower content of iron suggests the presence of zinc oxide. However, the lead is scattered along all the samples but no obvious phase is observed. This distribution can illustrate that the lead is attached to other phases such as zinc oxide, zinc ferrite and calcium sulfide in a very fine particle size. We can predict the difficulty in separating this metal from zinc calcine by traditional separation methods.
The particle distribution of zinc calcine is shown in Fig. 4. It shows that 80% of the particles are smaller than 74 μm and the median particle size (d50) is around 25 μm. This fine size distribution suggests that the zinc calcine used in this study is not necessary to be milled and can be used for magnetic separation test directly.
3.2 Effects of magnetic induction on element distribution
Table 3 gives the concentrate yield of zinc calcine as a function of magnetic induction during magnetic separation. Increasing the magnetic induction significantly improves the concentrate yield. This means that magnetic induction has a great influence on particle inclusion. Non magnetic phases such as zinc oxide, zinc sulfide, zinc silicate attaching to zinc ferrite will be taken into concentrate, which makes the separation of zinc and iron difficult. The effect of magnetic induction from 0.20 to 1.50 T on elements distribution (see Fig. 5 to Fig. 9) illustrates that the iron, zinc, calcium, sulfur and lead grades of the concentrates were obtained in the magnetic separation experiments.
It can be seen from Fig. 5 that the iron grade of the magnetic products after one step separation with the magnetic induction of 0.21 T is 21.4% with the recovery of 35%. Iron distribution rate increases up to about 85% under magnetic induction of 0.70 T and then remains almost constant at high magnetic induction from 1.10 to 1.50 T. However, the grade of iron concentrate keeps constant about 16% in the magnetic induction range of 0.7-1.5 T. The drastic increase in iron distribution rate in concentrate is related to the magnetic induction in the case of the presence of weak magnetic minerals, such as zinc ferrite which is difficult to be recovered at a low magnetic induction but easy to be recycled at a high magnetic induction level. On the other hand, the grade of iron concentrates keeping at a lower-level is attributed to the fine non-magnetic grains, such as zinc oxide, silicate and sulfide with the particle size of 5-8 μm, which are entrained in the magnetic products according to the particle size distribution analysis in Fig. 4.
Figure 6 shows the correlation between distribution rate and grade of zinc in concentrate and magnetic induction. It is seen that the distribution of zinc in magnetic products under different magnetic inductions exhibits the uniform behavior with the iron. It is concluded that the zinc-containing phases mainly attach to the magnetic zinc ferrite. Various studies have been carried out on the formation of zinc ferrite generated simultaneously with zinc oxide [15,16]. Thus, a certain pretreatment should be employed to separate the zinc ferrite from zinc oxide in order to obtain a high iron recovery and reduce the zinc content in the concentrates.

Fig. 3 Secondary electron images of element distribution: (a) BSE; (b) O; (c) Zn; (d) Ca; (e) Fe; (f) Pb; (g) Si; (h) S
The effect of magnetic induction on calcium distribution is shown in Fig. 7. Clearly, the magnetic induction has a significant impact on the calcium distribution rate in the concentrate. Increasing the magnetic induction from 0.21 to 1.50 T increases the calcium distribution rate in the concentrate from 10% to 45% but reduces the grade obviously. The grade of calcium in concentrate decreases drastically from 1.25% to 1.05% when magnetic induction is over 0.7 T. The results indicate that most of calcium exists in non-magnetic phases and most of non-calcium- containing minerals distribute to the concentrate when a high magnetic induction (over 0.7 T) is applied to the zinc calcine. This is illustrated by X-ray mapping analysis in Fig. 3. The calcium mainly exists in CaSO4 entrapped by zinc ferrite and zinc oxide. The increase of magnetic induction improves the distribution rate of zinc ferrite in concentrate and about 45% of calcium attached to zinc ferrite is distributed to magnetic concentrate simultaneously.

Fig. 4 Particle size distribution of zinc calcine
Table 3 Concentrate yield of zinc calcine during magnetic separation

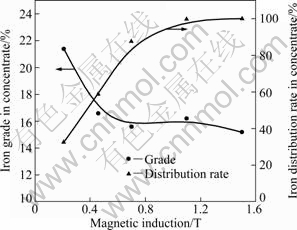
Fig. 5 Iron distribution during high gradient magnetic separation

Fig. 6 Zinc distribution during high gradient magnetic separation

Fig. 7 Calcium distribution during high gradient magnetic separation
Figure 8 illustrates the sulfur distribution of zinc calcine in magnetic field. An overall distribution rate of sulfur increases from 35% to 60% when magnetic induction increases from 0.21 to 0.70 T. But there is no significant improvement with further increase of magnetic induction. The grade of sulfur decreases significantly at a low magnetic induction and then keeps at constant about 1.5% at a high magnetic induction. The grade of sulfur in concentrate is lower than that in zinc calcine (about 2.44%), which demonstrates that sulfur mainly presents in non-magnetic mineral phases, such as CaSO4 (detected by X-ray mapping analysis), ZnS (observed by XRD) and PbS which may be present in zinc calcine but were not detected due to their trace contents. The sharp decrease of sulfur grade in concentrate is due to the function of ZnS entrapped by zinc ferrite. During the magnetic separation process, zinc ferrite is primarily extracted to concentrate with a considerable amount of sulfide and thus contributes to a higher sulfur grade than the zinc calcine sample. It can be predicted that the sulfur could be easily separated from zinc calcine during magnetic separation process and mainly remains in tailings.
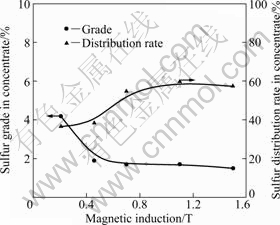
Fig. 8 Sulfur distribution in high gradient magnetic separation
The effect of magnetic induction on lead distribution in zinc calcine under magnetic induction ranging from 0.21 to 1.50 T is given in Fig. 9. The lead distribution in magnetic concentrate increases from 25% to 90% when the magnetic induction increases from 0.21 to 1.1 T, while the grade of lead in concentrate decreases slightly from 1.6% to 1.3% and then no significant change is observed with further increase of magnetic induction. The grade of lead keeps at a constant level, which indicates that lead mainly exists in non-magnetic phases distributing uniformly along all the zinc calcine. This is also demonstrated by X-ray mapping analysis shown in Fig. 3. The distribution characteristic of lead in zinc calcine makes the separation of lead from these materials difficult and special pretreatment should be applied to lead enrichment before magnetic separation.

Fig. 9 Lead distribution during high gradient magnetic separation
4 Conclusions
1) The zinc calcine contains about 12% iron and the major phases detected by XRD are zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4), zinc oxide (ZnO), willemite (Zn2SiO4) and zinc sulfide (ZnS).
2) The distribution rate of zinc ferrite is affected significantly by magnetic induction and more than 85% is recycled from zinc calcine to magnetic concentrate at a suitable magnetic induction over 0.7 T.
3) Undesired elements for zinc production such as Ca, S and Pb mainly present in non-magnetic phases and could be easily enriched to magnetic concentrate which makes the separation of theses impurities from concentrates difficult.
4) Significant amount of impurities are brought into concentrate although most of zinc ferrite is enriched by high gradient magnetic separation. Further study should be carried out to understand the process mineralogy of impurities during magnetic separation.
References
[1] JHA M K, KUMAR V, SINGH R J. Review of the hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from industrial wastes [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2001, 33(1): 1-22.
[2] FILIPPOU D, DEMOPOULOS G P. Steady-state modeling of zinc-ferrite hot-acid leaching [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1997, 28(4): 701-711.
[3] XU Dong, ZHU Jun, WANG Zheng-min. The research progress of fluidized roasting technology in aqueous method of zinc production [J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 23(6): 20-22. (in Chinese)
[4] ?OPUR M, PEKDEMIR T, ?OLAK S, K?NK?L A. Industrial symbiosis: High purity recovery of metals from Waelz sintering waste by aqueous SO2 solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 149(2): 303-309.
[5] VILDAN B A, NURCAN B, MEHMET ?, SABRI ?, NURI A O. Optimization of dissolution of metals from Waelz sintering waste (WSW) by hydrochloric acid solutions [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 162(2): 718-722.
[6] LANGOVA S, LESKO J, MATYSEK D. Selective leaching of zinc from zinc ferrite with hydrochloric acid [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 95(3-4): 179-182.
[7] TURAN M D, ALTUNDOGAN H S, T?MEN F. Recovery of zinc and lead from zinc plant residue [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 75(1-4): 169-176.
[8] DUTRA A, PAIVA P, TAVARES L. Alkaline leaching of zinc from electric arc furnace steel dust [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2006, 19(5): 478-485.
[9] HOLLOWAY P C, ETSELL T H. Recovery of zinc, gallium and indium from La Oroya zinc ferrite using Na2CO3 roasting [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2008, 117(3): 137-146.
[10] ZHAO Y C, STANFORTH R. Extraction of zinc from zinc ferrites by fusion with caustic soda [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2000, 13(13): 1417-1421.
[11] GUO Ting, HU Xiao-jun, SHU Qi-feng, ZHOU Guo-zhi. Removal of zinc from ZnFe2O4 by selective chlorination and evaporation [J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2008, 26: 849-853. (in Chinese)
[12] ALIZADEH R, RASHCHI F, VAHIDI E. Recovery of zinc from leach residues with minimum iron dissolution using oxidative leaching [J]. Waste Management & Research, 2010, 29(2): 165-171.
[13] MACHADO J, BREHM F A, MORAES C A. Chemical, physical, structural and morphological characterization of the electric arc furnace dust [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 136(3): 953-960.
[14] MACHADO J, BREHM F A, MORAES C A. Characterization study of electric arc furnace dust phases [J]. Materials Research, 2006, 9(1): 41-45.
[15] CHEN T T, DUTRIZAC J E. Mineralogical changes occurring during the fluid-bed roasting of zinc sulfide concentrates [J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2004, 56(12): 46-51.
[16] GRAYDON J W, KIRK D W. The mechanism of ferrite formation from iron sulfides during zinc roasting [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1988, 19: 777-785.
高铁锌焙砂在高梯度磁场中的元素分布行为
李 密1,彭 兵1, 2,柴立元1, 2,王纪明1,彭 宁1,闫 缓1
1. 中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 国家金属污染防治工程技术研究中心,长沙 410083
摘 要:采用高梯度磁选将难溶铁酸锌从锌焙砂中分离,并利用ICP、XRD、穆斯堡尔、SEM及激光粒度仪分析锌焙砂中的元素组成及物相结构。考察磁感应强度对铁酸锌及杂质元素如钙、硫和铅在磁选过程中的分布行为的影响。结果表明,85%以上的铁酸锌在0.70 T的磁感应强度下能分布到精矿中,60%的钙和40%的硫主要分布在非磁性物相中,并在磁选过程中富集于尾矿中,大部分的铅以超细颗粒均匀分散在锌焙砂中。
关键词:锌焙砂;铁酸锌;磁选;元素分布
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (2011AA061001) supported by the High-tech Research and Development Program of China; Project (50830301) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (50925417) supported by National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scientists, China; Project (2012BAC12102) supported by the National “Twelfth Five-year” Plan for Science and Technology Support, China
Corresponding author: PENG Bing; Tel: +86-731-88830577; Fax: +86-731-88710171; E-mail: pb@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61458-1