文章编号:1004-0609(2014)01-0279-07
铬盐无钙焙烧工艺铬酸钠中性液铁盐除钒
杨得军1, 2,王少娜2,陈晓芳2,郑诗礼2,李世厚1
(1. 昆明理工大学 国土资源工程学院,昆明 650093;
2. 中国科学院 过程工程研究所 湿法冶金清洁生产技术国家工程实验室,北京100190)
摘 要:针对铬盐无钙焙烧工艺浸出液除钒现行钙盐沉钒法钙盐加入量大、需反复调节pH值、脱钒渣含铬酸钙等问题,提出采用铁盐作为沉钒剂进行除钒。考察铁盐加入量、pH值和温度等主要因素对钒脱除的影响,得到了最佳工艺条件,且终液钒浓度低于0.08 g/L,满足后续工艺要求。铁盐除钒可在较宽的pH值范围内操作,不需反复调节溶液pH值。渣相分析表明:脱钒渣为吸附钒酸根的氢氧化铁,其中不含铬,进一步探讨氢氧化铁对钒的吸附机理,确定钒酸根通过内层络合方式吸附在氢氧化铁表面。
关键词:铬酸钠;除钒;无钙焙烧;氢氧化铁;吸附
中图分类号:TF803.25 文献标志码:A
Removing vanadium from sodium chromate neutral liquid by non-calcium roasting technology with chromium salt
YANG De-jun1, 2, WANG Shao-na2, CHEN Xiao-fang2, ZHENG Shi-li2, LI Shi-hou1
(1. Faculty of Land and Resource, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Green Process and Engineering, Institute of Process Engineering,
Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100190, China)
Abstract: According to the current existing problem in the vanadium precipitating process in calcium salt by non-calcium roasting technology with chromium salt, such problems as large amount of calcium salt, repeatedly adjusting the pH value, slag containing calcium chromate and other issues, iron salts were used as precipitating agent to remove vanadium. The amount of iron salt added, pH value, temperature and other major factors on the impact of vanadium removal were investigated, the optimum conditions are that the vanadium concentration in final liquid is less than 0.08 g/L, which satisfies the follow-up process requirements. Utilizing iron salt to remove vanadium can be operated in wide pH range, without repeatedly adjusting the pH value. By analyzing, the slag phase is ferric hydroxide, which adsorbs vanadium, containing no chromium. And by further exploring against adsorption mechanism, vanadium is adsorbed on the surface of the iron hydroxide by inner layer complexation.
Key words: sodium chromate; vanadium removal; non-calcium roasting; ferric hydroxide; adsorption
铬盐是重要的无机化工原料,产品主要应用于冶金、颜料、制革、染料、金属表面处理、催化剂、医药等工业,与国民经济15%的商品品种相关。我国铬盐行业长期采用的传统有钙焙烧法资源能源利用率低,且排放大量的含高毒性铬酸钙的铬渣,严重污染环境,被列为我国污染行业之首[1]。国家高度重视有钙焙烧工艺产生的严重环境污染问题,工业和信息化部发布的《铬盐行业清洁生产实施计划》要求2013年底前,我国全面淘汰有钙焙烧落后生产工艺,在全行业推广无钙焙烧[2]、钾系亚熔盐液相氧化法[3]等清洁生产技术。
铬盐无钙焙烧技术[4]核心是在铬铁矿焙烧过程中不使用钙质填料,而是以返渣作为填料避免炉窑结圈问题。与传统有钙焙烧工艺相比,无钙焙烧工艺因不采用钙质填料,可将铬渣产生量由2.5~3 t降低至0.8 t每吨铬盐产品,特别是能消除铬渣中致癌物铬酸钙的产生。在所有的铬铁矿中均伴生有钒元素,一般铬铁矿中钒的含量(以V2O5计,下同)不高于0.1%。南非铬铁矿是含钒较高的矿种,钒含量约为0.3%~0.5%之间。在有钙焙烧工艺中,铬铁矿中的钒会与钙质填料生成不溶于水的钒酸钙,铬酸钠浸出液中的钒含量极低,不存在浸出液脱钒问题。而在无钙焙烧工艺中,铬铁矿中的钒会生成钒酸钠,在熟料浸出时随铬酸钠进入溶液,造成铬酸钠浸出液中钒浓度达到1~2 g/L,而工业要求钒含量不高于0.08 g/L。若不对浸出液除钒,将导致铬盐产品使用性能(如电镀、催化剂等)明显恶化,因此,除钒已成为无钙焙烧工艺的必需工序之一[5-6]。
目前,钙盐沉钒是无钙焙烧工艺的常规除钒方法[7],通过添加氧化钙生成钒酸钙实现钒的脱除,其操作简便,处理成本相对较低。但铬酸钠浸出液中铬浓度高达200 g/L以上(以Na2Cr2O7·2H2O计)、且溶液含有CO32-、SO42-、CrO42-、VO43-等多种组分,因钒酸钙溶度积相对较大,加入氧化钙会生成碳酸钙、硫酸钙、铬酸钙、钒酸钙等多种物质的混合物,不能实现钒的选择性脱除,致使钙盐加入量需理论量的十倍以上。更为严重的是,钙盐沉钒法仍会有致癌物铬酸钙生成,且沉淀物中六价铬(以重铬酸钠计)含量高达20%。如果采用加钙除钒,新产生的含钒及六价铬的含钙渣不仅会造成严重的环境污染,而且因钒价值较高,也会造成有价资源的浪费。因此,探索高效、无污染并能合理回收利用钒的非钙沉钒法已成为铬盐无钙焙烧工艺技术升级的必然趋势。
铁盐沉淀法作为一种溶液中脱除钒的方法已有很多文献报道。欧阳玉祝等[8]采用铁屑微电解—共沉淀法处理石煤矿空白焙烧法生产V2O5时的含钒废水,废水中钒的脱除率可达97%。陈亮等[9]和LIANG等[10]以硫酸铁为沉淀剂,以钒浸出液(钒摩尔浓度为0.57 mol/L)为研究对象,钒沉淀率可达97%以上。但文献[8-10]中报道的铁盐沉淀都是针对无铬溶液的除钒研究,在钒铬共存条件下特别是高浓度铬酸钠溶液条件下采用铁盐沉淀法脱除钒的研究尚未见报道。
本文作者基于铬盐清洁生产的要求,提出在无钙焙烧工艺铬酸钠中性液除钒过程引入硫酸铁进行钒的脱除,通过实验研究了硫酸铁加入量、反应时间、反应温度、pH值等因素对钒脱除的影响,确定了铁盐沉钒的可行性。
1 实验
1.1 实验原料与仪器
实验用主要试剂见表1。实验用主要设备见表2和图1,图1所示为主要反应设备装置图。
表1 实验用主要试剂
Table 1 Main reagents in experiment

表2 实验用主要设备
Table 2 Main equipments in experiment

图1 实验装置图
Fig. 1 Experimental device figure
1.2 实验方法
首先配制铬酸钠中性液,浓度如下:Na2Cr2O7·2H2O 200 g/L,V2O5 0.4~1 g/L。待水浴升至指定温度后,将配制好的溶液装入三口瓶中,开通搅拌器,使体系温度稳定。待水浴升至指定温度时,加入一定量的铁盐,开始计时。定时取样,样品经过滤后分析溶液中V2O5和Fe2O3的浓度变化。根据铬盐无钙焙烧工艺要求,终液中钒浓度(以V2O5计)需低于0.08 g/L、铁浓度(以Fe2O3计)低于0.1 g/L才能保证最终产品的质量。
实验所得固相用水洗涤后,在80 ℃下烘干。
1.3 分析方法
溶液及所得固相中钒浓度(以V2O5计)及铁浓度(以Fe2O3计)采用美国Pekin Elmer公司生产的Optima 5300DV型电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES)分析。固相渣的物相分析采用Panalytical公司生产的X’Pert PRO MPD 型X射线衍射仪(XRD)和德国NETZSCH仪器公司生产的Spectrum GX型傅里叶转换红外光谱仪进行分析,X射线衍射仪为铜靶,管电压40 kV,管电流40 MA。
2 结果与分析
2.1 正交实验
本文作者选用Fe2(SO4)3作为铁盐进行钒的脱除,一是因为硫酸铁在酸性和近中性溶液中会水解生成氢氧化铁,氢氧化铁是本研究所需的除钒剂,新生成的氢氧化铁活性高,有利于钒的脱除;二是因为铬酸钠中性液在后续工艺调pH值时采用的是硫酸,硫酸铁中的硫酸根进入溶液不仅有利于后续pH值的调节,而且不会增加溶液引入新的阴离子的负担,避免了杂质干扰。
实验中以钒脱除率(终液V2O5浓度)、终液Fe2O3浓度为主要考察指标。影响钒脱除率的主要因素有铁盐加入量、pH值、反应温度等,为探究各因素对考察指标影响的重要性,首先进行了三因素三水平正交实验,其中初始溶液pH值分别为3、5、7;硫酸铁加入量以硫酸铁n(Fe)/n(V)计(硫酸铁中铁以Fe计;无论溶液中的钒以何种形式存在,钒的量均以单质V计,分别为n(Fe)/n(V)为3、9、15);反应初始温度分别为30、50和80 ℃。正交实验结果见表3~4。
表3所列为以终液钒浓度与钒脱除率作为指标的正交分析。从表3的极差可以看出,Fe2(SO4)3的加入量对钒的脱除影响最大,在n(Fe)/n(V)=15条件下溶液中的钒均可以达标。从均值可以看出,各水平较好的条件为pH值为5,n(Fe)/n(V)为15,温度为80 ℃。
溶液中铁含量高会影响铬酸钠溶液的后续处理,铁若进入铬盐后续生产工艺,也可能对铬盐产品质量造成影响。因此,在实验过程中要将Fe浓度保持在0.10 g/L以下。表4所列为以溶液中以铁浓度作为指标的正交分析。
从表4可以看出,pH值对溶液中铁浓度影响最大。通过文献查阅,氢氧化铁大约在pH值为2时开始沉淀,在pH值为3.7时就沉淀完全。从表4实验数据上看,pH值为7时溶液中铁含量均可达标,而pH值低的情况下溶液中会有部分铁的进入。
综合考虑溶液中钒的浓度及铁的浓度,选取pH值为7、n(Fe)/n(V)为15、温度为80 ℃为最佳反应条件。
2.2 单因素条件实验
为了进一步确定铬酸钠浸出液中铁盐除钒的最佳工艺条件,进行了Fe2(SO4)3加入量、pH值和时间对沉钒影响的单因素实验。
2.2.1 硫酸铁加入量的影响
在反应时间3 h、pH值7、温度80 ℃实验条件下,探究不同Fe2(SO4)3加入量对钒脱除率的影响,实验结果见图2。
从图2中可看出,钒的脱除率随着Fe2(SO4)3、加入量的增加而上升,在n(Fe)/n(V)=15时,脱除率接近90%,终液中钒浓度达标。
表3 正交实验设计与结果(终液钒浓度与钒脱除率)
Table 3 Orthogonal experimental design and results (Final solution concentration of vanadium and vanadium removal rate)
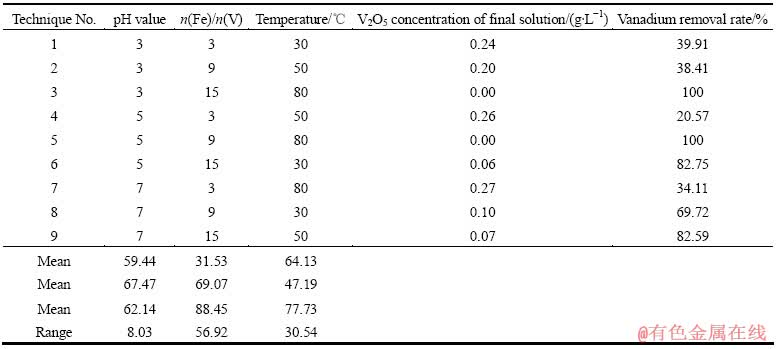
表4 正交实验设计与结果(终液铁浓度)
Table 4 Orthogonal experimental design and results (Final iron concentration)


图2 硫酸铁加入量对钒浓度和钒脱除率的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of addition amount of sulfur ferric on vanadium concentration (a) and vanadium removal rate (b)
2.2.2 pH值的影响
在反应时间3 h、n(Fe)/n(V)=15、温度80 ℃实验条件下,探究不同pH值条件下铁盐沉钒效果以及终液铁含量是否达标,其实验结果如图3所示。

图3 不同pH值终液钒和铁的浓度
Fig. 3 Concentrations of vanadium (a) and iron (b) in final solution at different pH values
由图3可知,随着pH值的升高,终液V2O5浓度逐渐降低,且中性与酸性条件变化明显,接近弱酸性与中性时终液钒沉淀基本完全。说明pH值是铬酸钠溶液中实现钒脱除较为重要的因素,在pH值5以上可实现钒的高效脱除。由图3可知,在pH值2~3条件下,终液铁浓度高于1 g/L,在pH值大于5条件下,溶液铁含量低于0.10 g/L,满足要求。
2.2.3 反应时间的影响
在pH值7、n(Fe)/n(V)=15、温度80 ℃实验条件下,不同时间点取样,最长反应时间30 min,实验结果见图4。
从图4中可以看出,铁盐除钒的反应在1 min内即可完成,随着时间的变化,钒脱除率并无明显变化。据文献[11-12]报道,氢氧化铁的吸附过程瞬间即可完成,因此推断铁盐除钒的机理为吸附,且在1 min之内,氢氧化铁对钒的吸附已完成。

图4 时间对终液中钒浓度和钒脱除率的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of time on vanadium concentration (a) and vanadium removal rate (b) in final solution
2.3 机理探讨
为探讨反应过程铁盐对钒的脱除机制,对生成固相简单水洗后进行了分析。采用AXIOS型X射线荧光光谱分析仪(荷兰PANalytical公司生产)对固相进行了化学成分分析,确定主要元素及含量如表5所列。
表5 反应后固相主要化学成分
Table 5 Main chemical components of solid phase after reaction (mass fraction, %)

采用X射线衍射仪(Panalytical公司生产)和傅里叶转换红外光谱(德国NETZSCH仪器公司生产)对反应生成的固相渣进行了进一步光谱分析,分别见图5。
从图5中可以看出,n(Fe)/n(V)为3、9、15时,生成的物相基本一致,结合红外光谱分析,确定生成物为吸附钒酸根的氢氧化铁。
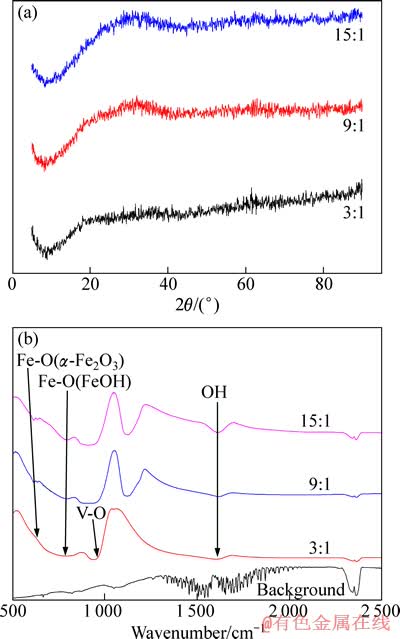
图5 反应后固相的XRD和红外光谱
Fig. 5 XRD spectra (a) and infrared graphs (b) of solid phase after reaction
将Fe2(SO4)3加入溶液后,铁盐即水解成红褐色的氢氧化铁胶体,此过程不涉及铁盐与钒酸根的化学反应。
铁的氢氧化物具有良好的吸附阴阳离子的能力,以铁元素为主要吸附成分的吸附剂的开发、研制和应用已经得到了国内外的关注[13]。已有研究表明:铁氧体表面对钒酸根离子有吸附作用,PEACOCK等[14]探究了pH值从1.5~12时针铁矿(α-FeOOH)对钒的吸附机制,即在较低pH值条件下,形成表面络合物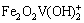 ;
;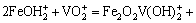
 ;较高pH条件下,则形成表面络合物Fe2O2VO(OH):
;较高pH条件下,则形成表面络合物Fe2O2VO(OH):
 ,钒吸附量随pH值升高而下降。陈亮[15]对产物中钒的可能存在形态做了分析,即1) 通过内层络合的方式吸附在水和氢氧化铁表面;2) 形成钒酸铁进入沉淀物;3) 同时存在以上两种形式。罗南等[16]研究认为活性氢氧化铁胶体表面以胶团离子存在,且有如下电离形式:
,钒吸附量随pH值升高而下降。陈亮[15]对产物中钒的可能存在形态做了分析,即1) 通过内层络合的方式吸附在水和氢氧化铁表面;2) 形成钒酸铁进入沉淀物;3) 同时存在以上两种形式。罗南等[16]研究认为活性氢氧化铁胶体表面以胶团离子存在,且有如下电离形式:
Fe(OH)3=Fe(OH)2++OH-
Fe(OH)2+=Fe(OH)2++OH-
Fe(OH)2+=Fe3++OH-
综合以上研究,得出氢氧化铁对钒的吸附行为可表示为
[Fe(OH)3]m·Fe3+·yOH-}(3x-y)+y/nAn-=[Fe(OH)3]m·xFe3+·y/nAn-}(3x-y)++yOH-
式中:A代表钒酸根;x、y、m、n分别代表不同数值。
钒在溶液中的聚集状态与其浓度及溶液的pH值有关。图6所示为不同pH值及钒浓度下的钒酸根和钒氧根离子所呈状态区域图[17]。

图6 不同pH值与浓度下钒酸根存在形态
Fig. 6 Vanadate existing forms at different pH values and concentrations
根据图6,由于实验中钒浓度(以V2O5计)约为1 g/L,不同pH值时,氢氧化铁所吸附的钒酸根可能为VO43-、 HVO42- 、 VO3- 、 V3O9- 、V10O286-、HV10O255-、H2V10O284-、VO2+,若仅考虑正负电荷吸附,应在pH值为3.8~6.8之间,即钒酸根为V10O286-、HV10O255-时吸附能力最强。
吸附过程有OH-离子释放,因此H+浓度越大,吸附效果越好,但pH值接近2,V以VO2+存在,正电荷相斥,不利于吸附。
考虑到Fe(OH)3沉淀在pH值2.7~3.7之间完全形成,因此,pH值大于3.7有利于溶液除铁,所以理论上确定脱钒的最佳pH值范围为3.7~7,这个也在实验部分得到了验证。因此,铁盐除钒可在较宽的pH值范围内操作,不需反复调节溶液pH值。
铁盐除钒后得到的含钒氢氧化铁可直接用于钒铁冶炼,或经脱附钒处理后循环用于钒的脱除,这将在今后作进一步的研究。
3 结论
1) 采用铁盐对无钙焙烧所得铬酸钠浸出液除钒,实现钒的选择性脱除,未产生铬酸钙、碳酸钙等物质,钒浓度可脱除到要求值以下。
2) 硫酸铁除钒的最佳工艺条件如下:pH值为7、n(Fe)/n(V)=15、温度为80 ℃、反应时间在5 min内,5 min时钒浓度降至0.06 g/L。
3) 氢氧化铁对钒的吸附机理为钒酸根通过内层络合方式吸附在氢氧化铁表面。
REFERENCES
[1] 石玉敏, 李俊杰, 都兴红, 隋智通. 采用固相还原法利用工业废渣治理铬渣[J].中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(5): 3542-3547.
SHI Yu-min, LI Jun-jie, DU Xing-hong, SUI Zhi-tong. Detoxified treatment of chromium slag with industrial waste by solid reduction[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(5): 3542-3547.
[2] 李小斌, 齐天贵, 彭志宏, 刘桂华, 周秋生. 铬铁矿氧化焙烧动力学[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(9): 1822-1828.
LI Xiao-bin, QI Tian-gui, PENG Zhi-hong, LIU Gui-hua, ZHOU Qiu-sheng. Kinetics of chromite ore in oxidation roasting process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(9): 1822-1828.
[3] 张 懿, 陈家镛, 刘会洲. 新一代资源回收·循环集成技术与生态化产业体系[J]. 化工进展, 2000, 19(12): 10-12.
ZHANG Yi, CHEN Jia-yong, LIU Hui-zhou. A new generation of integration technology of resource recovery recycling and the ecological industry[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2000, 19(12): 10-12.
[4] 王少娜, 郑诗礼, 张 懿. 铬盐清洁生产工艺中铝硅的脱除[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(7): 1188-1194.
WANG Shao-na, ZHENG Shi-li, ZHANG Yi. Separation of aluminum and silicon in clean production process for potassium dichromate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(7): 1188-1194.
[5] BLOCK H, HALSTENBERG J, LONHOFF N, ROSENOW B, SPRECKELMEYER B, WEBER R. Process for the production of sodium dichromate[P]. US: 5250274, 1993-10-05.
[6] WEBER R, BLOCK H D, BATZ M, HALSTENBERG J, LUMM M, ROTH R, MERRE D. Process for the utilization of vanadium from chromium ore as vanadium (V) oxide[P]. US: 7157063B2, 2007-01-02.
[7] 丁瑞峰. 铬酸钠溶液中加石灰除钒的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2011.
DING Rui-feng. Vanadate removal from the sodium chromate solution by adding lime[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2011.
[8] 欧阳玉祝, 王继徵. 铁屑微电解-共沉淀法处理含钒废水[J]. 化工环保, 2002, 22(3): 165-166.
OYANG Yu-zhu, WANG Ji-hui. Treatment of vanadium-containing wastewater by iron filings microelectrolysis-coprecipitation process[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2002, 22(3): 165-166.
[9] 陈 亮. 从钒浸出液中沉淀结晶型钒酸铁试验研究[J].湿法冶金, 2010, 29(3): 171-175.
CHEN Liang. Study on precipitation of crystal-forming fervanite from vanadium leaching solution[J]. Hydrometallurgical, 2010, 29(3): 171-175.
[10] LIANG C, LIU F, LI D. Precipitation of crystallized hydrated iron(Ⅲ) vanadate from industry Al vanadium[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 105: 229-233.
[11] AVOTINS P V. Adsorption and coprecipitation studies of mercury on hydrous iron oxide[D]. Stanford: Stomforde Stanford University, 1975.
[12] BENJAMIN M M, HAYES K F, LECKIE J O. Removal of toxic metals from power generation waste streams by adsorption and co-precipitation[J]. Water Poll Control Fed J, 1982, 54: 1472-1481.
[13] TOKUNAGA S, WASAY S A, PARK S W. Removal of arsenic(V) ion from aqueous solutions by lanthanum compounds[J]. Water Sci Tech, 1997, 35(7): 71-78.
[14] PEACOCK C L, SHERMAN D M. Vanadium (V) adsorption onto goethite (α-FeO -OH) at pH 1.5 to12: A surface complexation model based on ab initio molecular geometries and EXAF spectroscopy[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(8): 1723-1733.
[15] 陈 亮. 从提钒浸出液中沉淀结晶型钒酸铁工艺研究[C]//第19届全国铁合金学术研讨会论文集. 吉林: 《铁合金》编辑部, 2010: 137-143.
CHEN Liang. Study on precipitation of crystal-forming fervanite from vanadium leaching solution[C]//The 19th National ferroalloy Symposium. Jilin: “Ferroalloy” Editorial, 2010: 137-143.
[16] 罗 南, 刘 波, 李国良, 何晋秋. 活性氢氧化铁处理含钒(V )废水的研究[J]. 四川环境, 1989, 8(1): 39-48.
LUO Nan, LIU Bo, LI Guo-liang, HE Jin-qiu. Study on handling vanadium (V) containing wastewater with active ferric hydroxide[J]. Sichuan Environmental, 1989, 8(1): 39-48.
[17] GREENWOOD, N N, EARNSHAW A. Chemistry of the Elements[M]. 2nd ed. Oxford: Butterworth -Heinemann, 1997.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51274178);国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2011AA060702)
收稿日期:2013-03-20;修订日期:2013-10-17
通信作者:王少娜,副研究员,博士;电话:010-82544856,E-mail:shnwang@home.ipe.ac.cn