20 kA新型稀土电解槽电热场耦合数值模拟
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2020年第4期
论文作者:吕晓军 张恒星 韩泽勋 王康杰 官朝红 孙启东 王维维 韦茗仁
文章页码:1124 - 1134
关键词:稀土电解槽;极距;电解质高度;电热场;数值模拟
Key words:rare earth reduction cell; anode-cathode distance; electrolyte height; thermo-electrical field; numerical simulation
摘 要:针对传统稀土电解槽具有能耗高、效率低、使用寿命短等缺点,提出一种20 kA新型稀土电解槽。采用ANSYS探究极距和电解质高度对电热场分布的影响。结果表明:随着极距增加,电解槽欧姆压降和温度以相同的趋势增加;同时,随着电解质高度增加,电解槽温度逐渐升高,但电解槽欧姆压降下降;最终,当极距为115 mm、电解质高度为380 mm时,电解槽的欧姆压降为4.61 V,温度为1109.8 °C,此时电解槽的热场分布更加合理,槽电压较低,这有利于延长新型稀土电解槽的使用寿命,降低其能耗。
Abstract: To solve the problems of high energy consumption, low efficiency and short service life of conventional rare earth reduction cells, a 20 kA new rare earth reduction cell (NRERC) was presented. The effects of the anode-cathode distance (ACD) and electrolyte height (EH) on the thermo-electrical behavior of the NRERC were studied by ANSYS. The results illustrate that the cell voltage drop (CVD) and the temperature will rise with a similar tendency when the ACD increases. Also, the temperature rises gradually with EH, but the CVD decreases. Ultimately, when the ACD is 115 mm and the EH is 380 mm, the CVD is 4.61 V and the temperature is 1109.8 °C. Under these conditions, the thermal field distribution is more reasonable and the CVD is lower, which is beneficial to the long service life and low energy consumption of the NRERC.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 30(2020) 1124-1134
Xiao-jun Lü1, Heng-xing ZHANG1, Ze-xun HAN1, Kang-jie WANG2, Chao-hong GUAN1, Qi-dong SUN1, Wei-wei WANG1, Min-ren WEI1
1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 15 April 2019; accepted 18 March 2020
Abstract: To solve the problems of high energy consumption, low efficiency and short service life of conventional rare earth reduction cells, a 20 kA new rare earth reduction cell (NRERC) was presented. The effects of the anode-cathode distance (ACD) and electrolyte height (EH) on the thermo-electrical behavior of the NRERC were studied by ANSYS. The results illustrate that the cell voltage drop (CVD) and the temperature will rise with a similar tendency when the ACD increases. Also, the temperature rises gradually with EH, but the CVD decreases. Ultimately, when the ACD is 115 mm and the EH is 380 mm, the CVD is 4.61 V and the temperature is 1109.8 °C. Under these conditions, the thermal field distribution is more reasonable and the CVD is lower, which is beneficial to the long service life and low energy consumption of the NRERC.
Key words: rare earth reduction cell; anode-cathode distance; electrolyte height; thermo-electrical field; numerical simulation
1 Introduction
The rare earth metals (REMs) are crucial strategic resources for the development of the economy, military, science and technology, which are widely used in the aerospace, electronic information, communication technology and military hardware industries. Therefore, they are awarded as industrial vitamins [1-3]. Currently, the production of REMs (lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, etc.) generally adopts the molten salt electrolysis process in which rare earth oxides are regarded as raw materials, fluoride molten salts are electrolytes and rare earth oxides are reduced to metals at cathode [4,5].
Although the technology of rare earth production is very mature, there are still many problems in the production process, for example, the small capacity of the conventional reduction cell (with the current of 3-10 kA), the fact that removing REMs and replacing anodes has a great influence on production state (poor stability), and being entirely dependent on a worker’s manual experience to feeding (low degree of automation).
There are also some other issues needing to consider during the production process, which include consuming a lot of energy and releasing too much fluoride gas into the sky, finally causing environmental pollution [6-8]. Solutions to these problems have been restricted by the distribution of the reduction cell electrode which is fixed on a graphite crucible [9]. This distribution is not conducive to automation and makes the increase of anode-cathode distance (ACD) as the anode carbon blocks are consumed in the electrolysis process, which causes a loss of current efficiency because the partial metals reduced from cathode might be oxidized by rising carbon dioxide between cathode and anode [10,11]. Furthermore, the position of the cathode needs to be adjusted to remove REMs conveniently, resulting in the poor continuity of production [12]. Also, it is necessary to improve the existing electrode structure for realizing the large-scale, automated and green rare earth reduction cell.
To this end, for the first time, a 20 kA new rare earth reduction cell (NRERC) is proposed in this work. Compared with the conventional rare earth reduction cell, the NRERC has the following characteristics: the electrode structure is arranged into the upper and lower types; the ACD can be adjusted according to the electrolysis process; the selection and layout of the thermal insulation layer are more reasonable; the high thermal conductivity material is used on the side to make the cell ledge easier to form. The thermo-electrical field coupling simulation aimed at our NRERC is carried out to confirm the suitable technological parameters of electrolytic production (electrolytes height and anode-cathode distance), which is an important link for the research and development of the large, intelligent and cleaning rare earth reduction cell. All of our research is conducive to achieving a green revolution for the rare earth electrolysis industry.
2 Mathematical model
2.1 Mathematical model of electric field
The mathematical model of the electric field is based on the Maxwell’s electromagnetic field equations. Because the electrolyte in the electrostatic field is neutral, the Laplace equation in a three-dimensional reduction cell can be obtained as follows [13]:
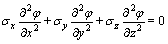 (1)
(1)
where φ is the voltage drop (V), σx, σy and σz are the electrical conductivity (S/m) in X, Y and Z directions, respectively.
2.2 Mathematical model of thermal field
The heat balance equation in reduction cell is given as
Wi-△H0-QL=0 (2)
where Wi is the energy that input to reduction cell per unit time (J/s), ΔH0 is the dissipated energy per unit time (J/s), and QL is the heat loss per unit time (J/s).
According to the principle of heat transfer, the governing equation for the thermal field is described by [14]
 (3)
(3)
where T is the temperature (K), qs is the heat source (W/m3), c is the heat capacity (J/(kg·K), t is the time (s), ρ is the density (kg/m3), and Kx, Ky and Kz are the thermal conductivities (W/(m·K), in X, Y and Z directions, respectively.
The calculation in this study is steady-state, and the temperature does not change with time. Therefore,  , Eq. (3) can be redefined as
, Eq. (3) can be redefined as
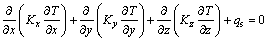 (4)
(4)
In the actual operation of the reduction cell, the electric field and thermal field interact. The electric field affects the thermal field by producing ohmic heat. Conversely, the thermal field affects the electric field because the temperature can change the conductivity of materials. Therefore, the conductivity of the materials in the electric field is expressed as a function of temperature.
A fully coupled thermo-electrical model was run to obtain the electrical potential and the temperature fields. Thermo-electrical solid elements SOLID69 was used to transmit heat and current as well as generate Joule heat, and SOLID70 thermal-only elements were used to simulate the heat transfer for thermal insulating materials. The SOLD69 and SOLD70 represent different element types. For example, SOLD70 has three-dimensional heat conduction capacity, eight nodes and only one degree of temperature freedom on each node. It can be used for three-dimensional static or transient thermal analysis. The unit can achieve uniform heat transfer. The total number of nodes is 904706. The finite element method is to discretize a continuous structure into finite elements which are combined at the nodes, simplify the load to the nodes, calculate the temperature of each node under the load, and then calculate the temperature of each element. The solution of discrete body is approximated to that of original continuum. If the element division is small enough, the result will be closer to reality, but this will be time-consuming.
3 Numerical simulation
3.1 Design of NRERC
In this study, the electrode structure of the NRERC is upper and lower arrangements (Fig. 1). The anode carbon blocks can be moved to adjust the ACD, which effectively avoids excessive cell voltage drop (CVD) in the NRERC. The NRERC side uses Z-type SiC that has good thermal conductivity, and it can release part of energy from the bath and form a cell ledge, which can then prolong the service life of the NRERC. In addition, the NRERC lining is constructed by graphite carbon blocks, castables, refractory bricks, ceramic fiberboard, etc.
The technological parameters of NRERC are shown in Table 1 (taking electrolysis of Nd2O3 as an example).
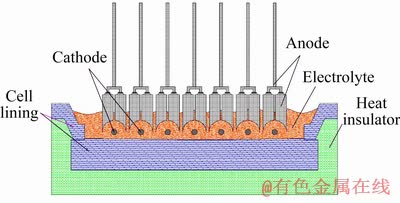
Fig. 1 Structure of new rare earth reduction cell (NRERC)
3.2 Physical properties of materials
The electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity of the NRERC materials are important parameters for the coupled thermo-electrical field simulation, and the corresponding functional forms are shown in Table 2.
Refractory bricks, castables, ceramic fiberboard and silicon carbide in the reduction cell can be regarded as insulators. The composition of the electrolyte is 85% NdF3, 15% LiF, and Nd2O3 accounts for 3% NdF3 and LiF. The solidification isotherm of the electrolyte is 1020 °C [28]. The electrolyte is not conductive in the solid state, and the conductivity increases with the increase of temperature in the melting state.
3.3 3D finite element model
According to the above design of NRERC, a 3D model is established, as shown in Fig. 2.
3.4 Boundary condition
The current first enters into the reduction cell through the anode, then goes through the electrolyte and finally is draws to the cell through the cathode collector bars (tungsten). In the process, the ohmic heat is generated to maintain the temperature of the reduction cell. However, in the actual operation of the reduction cell, the cell temperature will change due to the presence of bubble voltage drop, contact voltage drop and electrochemical reactions. These factors have an important impact on the thermal field. But to date, few models integrate all these phenomena in the same studies since it will take several weeks or months of CPU time to resolve a complex multiphysics simulation. To get more accurate simulation results, these factors should not be ignored. Therefore, this paper not only combines the existing research methods but also simplifies these factors as follows.
Table 1 Technological parameters of new rare earth reduction cell

Table 2 Electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity of different materials

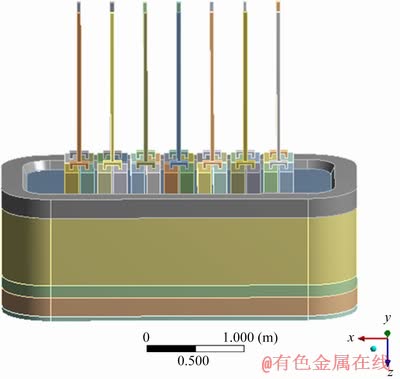
Fig. 2 3D model of NRERC
Bubble voltage drop: In the process of electrolysis production, the bubble (CO2 and CO) formed in the bottom of anode reduces the contact area of anode and electrolytes and then results in the augment of resistance, which finally causes the increase of cell voltage. Here, the increased voltage is regarded as bubble voltage drop. In order to be convenient to combining with simulation, we assumed that the bubble voltage drop is generated by the bubble layer and the bubble layer is a kind of simulated material. The bubble layer is between anodes and electrolytes. The anode reaction of rare earth reduction cell is the same as that of aluminum reduction cell, in which carbon is oxidized to CO2 and CO, and the gas evolution potential is the same. Therefore, we can calculate the conductivity of the bubble layer by referring to the method in the aluminium reduction cell simulation. From the aluminium reduction cell simulation in Ref. [29], it was mentioned that the maximum average voltage drop in the reduction cell was 24.5 mV when the size of anode carbon block was 22 mm × 50 mm × 70 mm (length × width × height) and the current density was 0.9 A/cm2. Here, we adopted 24.5 mV as the bubble voltage drop of our NRERC. So the resistivity of the bubble layer is calculated according to the bubble voltage drop using the following equation:
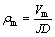 (5)
(5)
where ρm is the resistivity of bubble layer (Ω·m), Vm is the bubble voltage drop (0.0245 V), J is the anode carbon block current density (A/m2) and D is the thickness of bubble layer (m).
Contact voltage drop: In the process of actual production, contact voltage drop exists between different materials. In order to combine simulation and actual condition, we assume that the contact voltage drop between materials comes from a layer model with a given thickness. The density, thermal conductivity and specific heat of the above layer model were replaced by the paste from Ref. [30].
Electrochemical reaction: In the process of electrolysis, the anode carbon blocks are consumed and release heat. When the temperature in the cell is higher than 900 °C, carbon monoxide is the main precipitated gas [31]. Through the anode carbon blocks consumption rate and reaction enthalpy, the heat releases per unit of time can be calculated. Thus the heat generation rate can be obtained, which is 8493 kJ/h.
Considering the numerical simulation environment is an ideal state, we assume that there are not rare earth oxides and electrolyte feeding, and the current intensity is constant. The boundary conditions were applied as follows.
Electrical field: The end area of cathode collector bars was chosen as the zero potential and a constant current of 20 kA was forced with a floating constant potential on the anode carbon steel bar’s top surface. This was achieved by coupling the voltage on the surface nodes while forcing constant current on one of its other nodes [32].
Thermal field: Heat is lost to the ambient air by means of convection and radiation of the NRERC’s surfaces. The heat transfer of the NRERC’s surfaces acts as the third boundary condition. The heat convection coefficient is calculated by using the following formula [33]:
Qc=αc(t1-t0)A (6)
where Qc is the heat-transfer rate (J/s), αc is the heat convection coefficient (W/(m2·K)), t1 is the surface temperature (K), t0 is the environment temperature (K), and A is the area of convection (m2).
αc is the heat convection coefficient of the natural convection between the surface and environment; it has a different calculation formula for different directions of three surfaces [34].
Top surface:
αT=1.31(t1-t0)1/3 (7)
Vertical surface:
αV=1.52(t1-t0)1/3 (8)
Bottom surface:
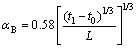 (9)
(9)
where αT, αV and αB are the top surface convection coefficient (W/(m2·K)), the vertical surface convection coefficient and the bottom surface convection coefficient, respectively, and L is the length of the shorter side on the surface (m).
The radiation heat loss QR (J/s) of the reduction cell surface is given as [35,36]
QR=εφ[(t1+273)4(t0+273)4]A (10)
where ε is the emissivity, φ is the Stefan- Boltzmann constant, and A is the area of radiation (m2).
4 Results and discussion
For the NRERC, the different effects of ACD and EH on the electrical and thermal fields were investigated. The ACDs are 85, 95, 105, 115, 125, 135 mm and the EHs are 320, 340, 360, 380, 400, 420 mm.
4.1 Effects of ACD on electric field and thermal field
The CVD is composed of cathode voltage drop, anode voltage drop, electrolyte voltage drop and bus voltage drop of the reduction cell (bus voltage drop is not considered in this study). This is defined as [37]
V=V1+V2+V3 (11)
where V1 is the cathode voltage drop, V2 is the anode voltage drop, and V3 is the electrolyte voltage drop.
The CVD distributions are shown in Fig. 3. As can be seen from Fig. 3, the maximum potential of the reduction cell is distributed at the anode aluminum guide rod and the minimum potential is distributed at the cathode collector bar, which is consistent with the current flow from the anode to the cathode. Besides, the CVD is mainly distributed in the electrolyte, anode and cathode. The electrolyte voltage drop is the largest. The CVD increases with the ACD. This is because the electrical current pathway flowing into electrolyte is longer than before when the ACD increases, resulting in an increase of path resistance.
The CVD varies with ACD as shown in Fig. 4. The tendency of CVD is linear with the augment of ACD from 85 to 115 mm, and then nonlinear from 115 to 135 mm. To sum up, the CVD increases from 4.05 to 5.41 V. For different ACD, the thickness of electrolyte between the anode and the cathode has a distinct variation, so the electrolyte voltage drop in the NRERC is different. The percentage of electrolyte voltage drop with the CVD is shown in Table 3. It can be seen from Table 3 that the electrolyte voltage drop accounts for a large proportion of the CVD, and the increase of ACD enhances the percentage of the electrolyte voltage drop.
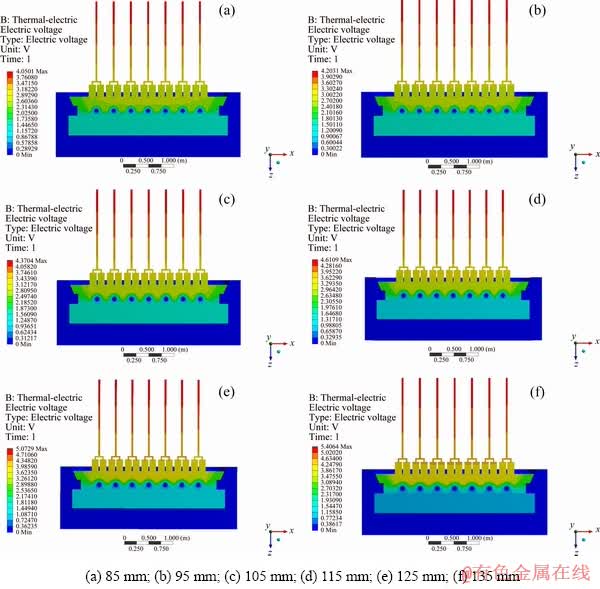
Fig. 3 Cell voltage drop (CVD) distribution with different anode-cathode distances

Fig. 4 CVD as function of ACD
In the NRERC, the heat will be consumed by convection and radiation between the reduction cell and air. During operation, electrical current enters the cell through the anode beams and is distributed among all operating anodes. The current flow creates an electrical network consisting of parallel circuits with a structure determined by the anode arrangement. Path resistances in those parallel circuits are responsible for the ohmic heat generation within the cell. Finally, when the rate of heat dissipation is equal to the rate of heat formation, a steady-state thermal balance was formed.
Table 3 Percentage of electrolyte voltage drop in new rare earth reduction cell
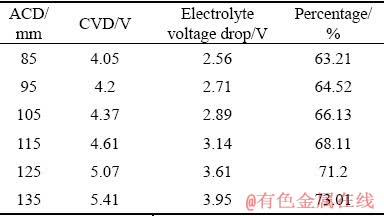
Figure 5 shows the thermal field distribution with different ACD. It can be seen from that the maximum temperature of the NRERC distributed in the electrolyte, which increases with the ACD, and the minimum temperature on the outer surface of the NRERC is 42 °C. On the outer surface of NRERC, the temperature of the SiC structure is higher than that of others. This is mainly due to the good thermal conductivity of SiC, which transfers the heat from the electrolyte to the outer surface of silicon carbide, resulting in the high temperature of outer surface of silicon carbide. The good thermal conductivity of SiC is conducive to forming the cell ledge where the electrolyte freezing occurs in the bath side. The red region boundary line represents electrolyte solidification temperature of 1020 °C, and the red region in the picture is a high temperature above 1020 °C, in which the electrolytes are in a melting state. From Fig. 5, it can be seen that the NRERC temperature slowly increases, and the electrolyte solidification isotherm expands gradually outward with the ACD. When ACD is 115 mm, the solidification temperature line has a reasonable distribution, the cell ledge thickness is appropriate for NRERC.
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the cell temperature and the ACD. It is found that when the ACD increases from 85 to 115 mm, the cell temperature increases linearly from 1087.5 to 1109.8 °C. Then, it presents a non-linear change. When compared to Fig. 4, we find that the NRERC temperature and voltage drop have the same trend. This mainly is due to the Joule heat generated by the current, which flows through the electrolyte to provide a heat source.
4.2 Effect of EH on electric field and thermal field
The EH is a very important parameter for the NRERC. If the electrolyte is too high, the NRERC will generate a thicker crust, which makes it difficult to feed, resulting in reduced oxide solubility, easy precipitations and poor thermal stability. Hence, it is necessary to find a suitable electrolyte height before the NRERC is baked and started.
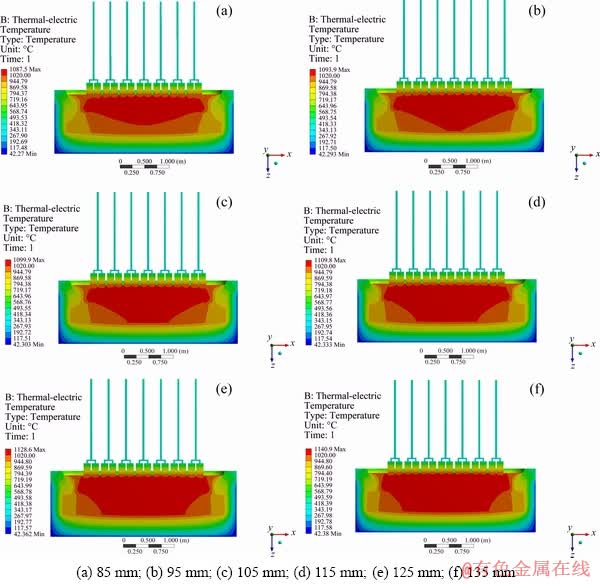
Fig. 5 Cell temperature contours and distribution with different ACD

Fig. 6 Relationship between cell temperature and ACD for NRERC
Figure 7 shows the variation of the CVD with the EH. The maximum potential of the reduction cell is distributed at the anode aluminum guide rod and the minimum potential is distributed at the cathode collector bar. The side of the reduction cell is an insulator and there is no current through it, causing that potential is zero. It can be seen from the figure that the CVD decreases when the EH increases. Compared to the change of ACD, the EH has less influence on the CVD. From Fig. 8, it can be seen that when the EH rises from 320 to 380 mm, the CVD decreases. From 380 to 400 mm, the CVD has a sharp drop and then returns to a normal decline. The change of EH has little effect on cell voltage (only 0.076 V).
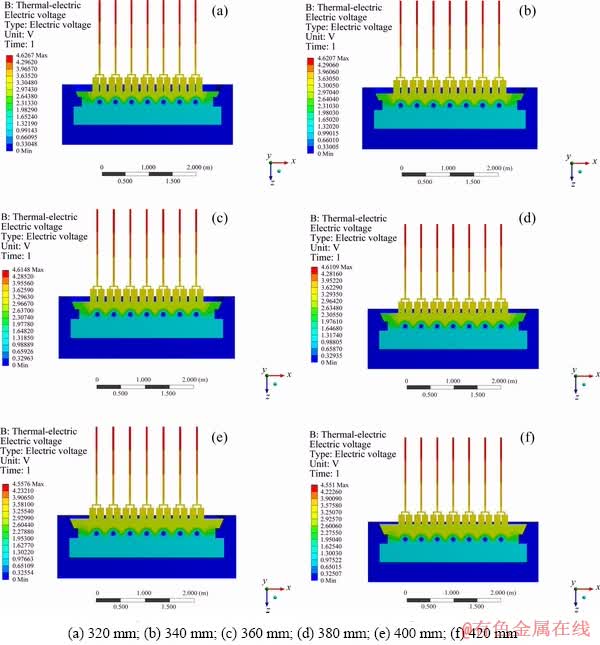
Fig. 7 CVD distribution with different EH
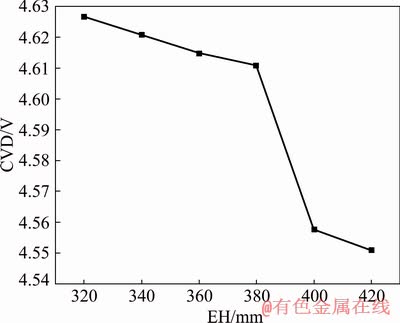
Fig. 8 Relationship between CVD and EH for NRERC
Figure 9 shows the cell temperature distribution with different EH, and the minimum temperature on the outer surface of the NRERC is 42 °C. The cell temperature increases with EH and the solidification isotherm moves outward, meaning that the high-temperature zone of the reduction cell diffuses outward. The thickness of the NRERC’ crust will increase and the thermal insulation of NRERC is strengthened with the increase of EH. As shown in Fig. 10, the cell temperature increases linearly with the EH and the cell temperature increases from 1100.9 to 1116.7 °C. At the same time, the higher the cell temperature is, the lower the CVD is, which can be ascribed to the reason why the increase of cell temperature leads to the decrease of electrolyte resistivity. The results are in agreement with Fig. 8, in which the cell voltage decreases with the EH. Especially, when the EH is 380 mm, the cell temperature distribution is more reasonable.
In this work, taking electrolysis of neodymium oxide as an example, combined with numerical simulation of a coupled thermo-electrical field, we can get the applicable ACD and EH of the new rare earth reduction cell. This cell is still suitable for the production of other rare earth metals using molten salt electrolysis process. But for different rare earth electrolysis, their electrolytes and temperatures are different and the insulation structure of the rare earth reduction cell needs to be redesigned. For the production process of rare earth metals with lower electrolysis temperature, the thickness of insulation materials should be reduced, and on the contrary, the insulation should be strengthened.
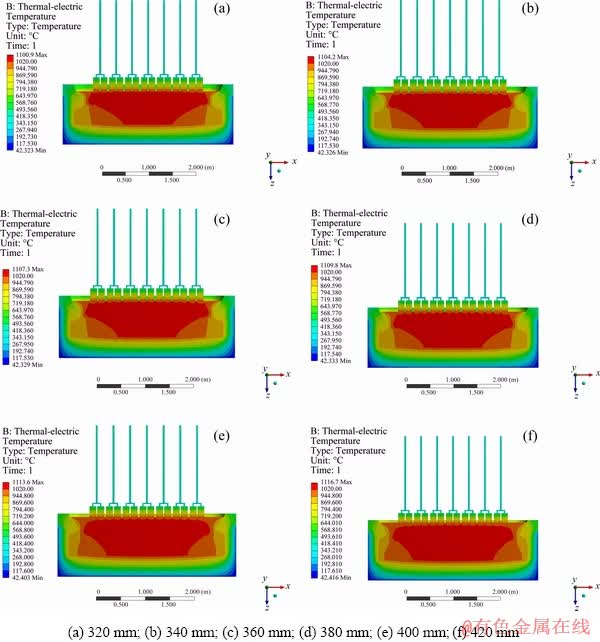
Fig. 9 Cell temperature distribution with different EH: (a) 320 mm
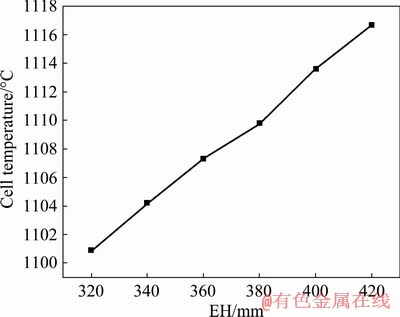
Fig. 10 Relationship between cell temperature and EH for NRERC
5 Conclusions
(1) As the ACD increases, the CVD increases from 4.05 to 5.41 V. This is because the electrolyte between anodes and cathodes becomes thicker and the resistance of the current path increases with the increase of the ACD. Also, the cell temperature increases with the ACD. The main reason is that with the increase of ACD, the resistance of current path increases, which leads to an increase of Joule heat and cell temperature. The CVD and cell temperature have a similar trend with the ACD.
(2) As the EH rises, the CVD increases. When the EH increases from 320 to 380 mm, the CVD decreases evenly and then the descend becomes sharply, and finally a uniform decline occurs. The cell temperature keeps a linear increase with the EH. Compared with the change of ACD, the EH has less influence on the reduction cell.
(3) When the ACD is 115 mm and the EH is 380 mm, the cell voltage drop is 4.61 V and the temperature is 1109.8 °C. Under the condition, the thermal field distribution of the NRERC and the structure of the cell side ledge are more reasonable, which is more conducive to enhancing the service life of the reduction cell.
References
[1] ZHANG Lu, GUO Qing, ZHANG Jun-biao, HUANG Yong, XIONG Tao. Did China’s rare earth export policies work?—Empirical evidence from USA and Japan [J]. Resources Policy, 2015, 43: 82-90.
[2] Meenashisundaram G K, Ong T H D, Parande G, Manakari V, xiang Shu-lin, Gupta M. Using lanthanum to enhance the overall ignition, hardness, tensile and compressive strengths of Mg-0.5Zr alloy [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2017, 35(7): 723-732.
[3] HAN Bao-jun, GU Dong-dong, HE Qiong, ZHANG Xiao-lian, PENG Guang-huai, YANG Chu-bin. Fabrication of a novel Mg-RE (Nd, Ce) intermetallic compound coating by molten salt diffusion and its effect on corrosion resistance of magnesium alloys [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2016, 34(7):731-735.
[4] LIANG Yong, LI Yong-kang, XUE Li-yan, ZOU Yu. Extraction of rare earth elements from fluoride molten salt electrolytic slag by mineral phase reconstruction [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 177: 567-572.
[5] Osen K S, Martinez A M, Gudbrandsen H, Store A, Sommerseth C, Kjos O, Aarhaug T A, Gaertner H, Chamelot P, Gibilaro M, Massot L. Perfluorocarbon formation during rare earth electrolysis [C]//TMS Annual Meeting & Exhibition. Berlin: Springer, Cham, 2018: 1443-1448.
[6] Vogel H, Flerus B, Stoffner F, Friedrich B. Reducing greenhouse gas emission from the neodymium oxide electrolysis. Part I: Analysis of the anodic gas formation [J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2017, 3(1): 99-107.
[7] WANG Jun, SUN Shu-chen, ZHANG Zuo-liang, TU Gan-feng, WU Wen-yuan. Simulation of the temperature field in 10 kA bottom-cathode-structure rare earth electrolytic cell [J]. Chinese Rare Earth, 2013, 6: 35-38. (in Chinese)
[8] Hurst C. China's rare earth elements industry: What can the west learn? [R]. Institute for the Analysis of Global Security Washington DC, 2010.
[9] Vogel H, Friedrich B. Reducing greenhouse gas emission from the neodymium oxide electrolysis. Part II: Basics of a process control avoiding PFC emission [J]. International Journal of Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2017, 6(3): 27-46.
[10] Bourbos E, Giannopoulou I, Karantonis A, Paspaliaris I, Panias D. Reduction of light rare earths and a proposed process for Nd electrorecovery based on ionic liquids [J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2018, 4(3): 395-406.
[11] ZHU Wei-wei, WANG Jin-liang, YANG Yi-qing. Analysis of the temperature field in rare earth molten salt electrolytic cell based on Comsol [J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 18: 038.
[12] Lee G G, Jo S K, Lee C K, Ryu H Y, Lee J H. Study on electrolysis for neodymium metal production [C]//Rare Metal Technology 2015. Berlin: Springer, Cham, 2015: 249-252.
[13] Dupuis M. Thermo-electrical design of a 400 kA cell using mathematical models: a tutorial [C]//Light Metals. Berlin: Springer, Cham, 2000: 303-308.
[14] Moreno-Navarro P, Ibrahimbegovic A, PErez- Aparicio J L. Plasticity coupled with thermo-electrical fields: Thermodynamics framework and finite element method computations [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 315: 50-72.
[15] HU Xian-wei, WANG Zhao-wen, GAO Bing-liang, SHI Zhong-ning, LIU Feng-guo, BAO M G. Identification of structural entities in NdF3-LiF melts with cryoscopic method [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(12): 2387-2391.
[16] HU Xian-wei, WANG Zhao-wen, GAO Bing-liang, SHI Zhong-ning, LIU Feng-guo, CAO Xiao-zhou. Density and ionic structure of NdF3-LiF melts[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28(4): 587-590.
[17] ASSOCIATION A. Aluminum: Properties and physical metallurgy [M]. USA: ASM International, 1984.
[18] DRESSELHAUS G, DRESSELHAUS M S, RIICHIRO S. Physical properties of carbon nanotubes [M]. London: Imperial College Press, 1998.
[19] YILMAZ O, CELIK H. Electrical and thermal properties of the interface at diffusion-bonded and soldered 304 stainless steel and copper bimetal [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 141(1): 67-76.
[20] LIU Zhan-jun, GUO Quan-gui, SHI Jing-li, ZHAI Geng-tai, LIU Lang. Graphite blocks with high thermal conductivity derived from natural graphite flake [J]. Carbon, 2008, 46(3): 414-421.
[21] ZAWRAH M F M, KHALIL N M. Effect of mullite formation on properties of refractory castables [J]. Ceramics International, 2001, 27(6): 689-694.
[22] AL-AMAIREH M. Improving the physical and thermal properties of the fire clay refractory bricks produced from bauxite [J]. Journal of Applied Sciences, 2006, 6(12): 2605-2610.
[23] ZHANG Qi-sheng, ZHAO Qin-sheng. Tungsten molybdenum metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005. (in Chinese)
[24] ROBERTS L, NORDGARD-HANSEN E, MIKKELSEN O, HALVORSEN S A, VANGORDER R A. A heat and mass transfer study of carbon paste baking [J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 88: 9-19.
[25] KAN Hong-yuan. High strength ceramic board used for industrial furnace [J]. Industrial Furnace, 2008, 30(2): 45-46. (in Chinese)
[26] CAPANO M A, TREW R J. Silicon carbide electronic materials and devices[J]. MRS bulletin, 1997, 22(3): 19-23.
[27] CHEN Lin-yun. Research on physical and chemical properties of LiF-NdF3-Nd2O3 molten salt system [D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2015. (in Chinese)
[28] HU Xian-wei, WANG Zhao-wen, SHI Zhong-ning, GAO Bing-liang. Nd2O3 solubility in NdF3-LiF-Nd2O3 melts [C]// Proceedings of Non-grid-connected Wind Power Systems. Shanghai: Global Wind Energy Council, 2007: 284-286.
[29] ZHAO Zhi-bin, WANG Zhao-wen, GAO Bing-liang, FENG Yu-qing, SHI Zhong-ning, HU Xian-wei. Anodic bubble behavior and voltage drop in a laboratory transparent aluminum electrolytic cell [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2016, 47(3): 1962-1975.
[30] Allard B, Tawfik M, Kumar A. Performances of green and eco-friendly ramming pastes in EGA pots [J]. Metals, 2016, 6(5): 112.
[31] Dewing E W. The chemistry of the alumina reduction cell [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1974, 13(4): 607-618.
[32] Richard D, Fafard M, Lacroix R, ClEry P, Maltais Y. Aluminum reduction cell anode stub hole design using weakly coupled thermo-electro-mechanical finite element models [J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and design, 2001, 37(4): 287-304.
[33] Dupuis M. Computation of aluminum reduction cell energy balance using ANSYS finite element models [C]// Light Metals. American: TMS, 1998: 409-417.
finite element models [C]// Light Metals. American: TMS, 1998: 409-417.
[34] TAO Wen-ju, WANG Zhao-wen, GAO Bing-liang, SHI Zhong-ning, HU Xian-wei, CUI Jian-zhong. Numerical simulation electric distribution in aluminum reduction cell with vertical collector bars [J]. Metalurgija, 2014, 53(1): 17-20.
[35] DUPUIS M, BOJAREVICS V. Weakly coupled thermo- electric and MHD mathematical models of an aluminium electrolysis cell [C]//Light Metals. American: TMS, 2005: 449-454.
[36] LIU Yan-ting, YANG Tian-zu, CHEN Zhuo, ZHU Zhen-yu, ZHANG Ling, HUANG Qing. Experiment and numerical simulation of two-phase flow in oxygen enriched side-blown furnace [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China. 2020, 30(1): 249-258.
[37] Cheung C Y, Menictas C, Bao J, SKYLLAS- KAZACOS M, wELch b J. Spatial temperature profiles in an aluminum reduction cell under different anode current distributions [J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(5): 1544-1556.
吕晓军1,张恒星1,韩泽勋1,王康杰2,官朝红1,孙启东1,王维维1,韦茗仁1
1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 化学与化工学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:针对传统稀土电解槽具有能耗高、效率低、使用寿命短等缺点,提出一种20 kA新型稀土电解槽。采用ANSYS探究极距和电解质高度对电热场分布的影响。结果表明:随着极距增加,电解槽欧姆压降和温度以相同的趋势增加;同时,随着电解质高度增加,电解槽温度逐渐升高,但电解槽欧姆压降下降;最终,当极距为115 mm、电解质高度为380 mm时,电解槽的欧姆压降为4.61 V,温度为1109.8 °C,此时电解槽的热场分布更加合理,槽电压较低,这有利于延长新型稀土电解槽的使用寿命,降低其能耗。
关键词:稀土电解槽;极距;电解质高度;电热场;数值模拟
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (51674302) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Xiao-jun Lü; Tel: +86-18684680039; E-mail: lvxiaojun@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65283-9

