DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.07.005
锰渣的理化特性及煅烧特性
闫国孟1,彭兵1,柴立元1, 2,闵小波1, 2,彭宁1,雷杰1,刘琴1,张强1,胡明1
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 国家重金属污染防治工程技术研究中心,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:分析“两矿一步法”电解MnO2酸浸中和压滤渣(简称锰渣)的理化特性,采用热重-差热分析法(TG-DTA)和X线衍射分析(XRD)确定不同温度下物相转变行为以及锰渣中锰的浸出随煅烧温度的变化。研究结果表明:锰渣为第Ⅱ类一般工业固体废物,以石英、水化硫酸钙、针铁矿和铁、铝矾矿相为主,矿相颗粒细、结晶度低。随着煅烧温度的升高,硫酸钙、针铁矿,以及铁、铝矾逐步脱水、分解,形成无水石膏、赤铁矿等,超过900 ℃时锰渣明显熔融、烧结,部分金属与硅反应形成玻璃态硅酸盐;锰渣中总锰质量分数约5%,约3%以MnSO4的形式存在。锰渣锰的浸出毒性根据煅烧温度分为3类,即低温可浸出(<300 ℃,锰离子质量浓度为0.6~1.0 g/L),中温易浸出(400~700 ℃,锰离子质量浓度为2~3 g/L);高温难浸出(>800 ℃,锰离子质量浓度为<0.01 g/L)。
关键词:锰渣;煅烧;相变行为;浸出毒性
中图分类号:X753 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)07-2419-07
Physicochemical and calcination characteristics of manganese residue
YAN Guomeng1, PENG Bing1, 2, CHAI Liyuan1, 2, MIN Xiaobo1, 2, PENG Ning1, LEI Jie1,
LIU Qin1, ZHANG Qiang1, HU Ming1
(1. School of Metallurgy & Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Control & Treatment of Heavy Metal Pollution,
Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The physicochemical characteristics of manganese residue from two ore one-step process were analyzed. The thermal phase transition behavior was detected by using TG-DTA and XRD. And manganese leaching toxicity was determined. The results show that manganese residues which belongs to general industrial solid waste in small particles contain quartz, hydrated calcium sulfate, goethite, jarosite and hydrobasaluminite. The calcium sulfate, goethite, jarosite and hydrobasaluminite are dehydrated at high temperature and decomposed to form anhydrite and hematite. Manganese residues sinter and melt obviously and silicate glass appears through reaction between some metals and silicon when the temperature is over 900 ℃. There is about 5% of Mn present in the residue and 3% of it is MnSO4. Manganese leaching toxicity appeared in three stages according to calcination temperature, that is, low-temperature stage (below 300 ℃, mass concentration of manganese ion is 0.6-1.0 g/L), middle-temperature stage (between 400 ℃ to 700 ℃, mass concentration of manganese ion is 2-3 g/L), and high-temperature stage (above 800 ℃, mass concentration of manganese ion is less than 0.01 g/L).
Key words: manganese residue; calcination; phase transition behavior; leaching toxicity
锰渣是电解MnO2生产过程中,锰矿酸浸出底液经石灰中和产生的压滤渣。中国是世界上最大的电解MnO2生产国、消费国和出口国,而我国锰矿品位较低,每产生1 t电解MnO2至少产生5~6 t锰渣,每年锰渣排放量近千万t,历年堆存量约6千万t[1]。锰渣的堆存和填埋,不仅占用了大量的土地面积,而且严重破坏了周边的生态平衡,导致严重的环境污染。锰渣中的重金属在长期的淋溶浸出作用下,随渗滤液进入土壤、地下水体和地表水,对周边的生物多样性产生致命影响,并通过农产品和食物链危害人体健康[2]。我国急需锰渣的有效资源化综合利用技术,而对锰渣的特性研究是必不可少的。Sorensen等[3]分析了4种锰矿物相组成及不同烧结气氛物相变化,指出了锰相转变规律及矿相液化温度,对于锰渣的特性研究方法及稳定化处理有很大的借鉴意义。虽然锰渣产地不同、种类多样,但其矿相成分均以二氧化硅、硫酸钙、锰盐和锰氧化物,以及其他金属化合物为主[4-6]。国内关于锰渣性质的研究重点在于其胶凝特性,主要分析煅烧锰渣中硫酸钙的晶型转变,评价其替代或部分替代石膏制备类水泥胶凝材料的缓凝和激发活性。李坦平等[7-8]研究了锰渣的基本物理性质和煅烧胶凝性能,确定其最佳胶凝性能的煅烧温度为750 ℃。张强等[9] 建立了锰渣中硫酸钙晶型-溶解度-溶解速率-激发矿渣活性作用之间的关系,确定了最佳煅烧温度为350 ℃。本文以上述研究内容和方法为基础,以锰渣的稳定化和资源化回收为出发点,分析锰渣的基本理化特性,探究锰渣中硅、铁、钙、锰主要矿物相随煅烧温度转变规律,最终确定锰渣稳定化和资源化煅烧温度。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
锰渣来自“两矿一步法”电解生产MnO2过程,黄铁矿和软锰矿的热硫酸浸出底液经石灰中和产生的2次压滤渣,其颜色呈土黄色,轻度结块,与黄土形貌相近。锰渣经烘箱105 ℃烘干24 h,机械粉磨,过孔径为150 μm筛。
1.2 分析方法
1) 含水量w:参考土壤含水量称质量法,用精确度0.01的分析天平称取10 g原渣,放入铝盒中,在105 ℃的烘箱中烘干6~8 h至恒质量m。

2) 水溶性物质质量分数。锰渣中水溶性物质主要为硫酸钙和硫酸锰,其质量分数参考FHZDZTR0070“土壤—水溶性盐分全盐量的测定—质量法”测定。
3) 真实密度ρ。采用李氏比重瓶法。向比重瓶中注入煤油至刻度0~1 mL,放入20 ℃的恒温水槽中,至温度不再变化,读取比重瓶中液面体积刻度V1。称取锰渣100 g,全部缓慢地注入比重瓶中,再次放入恒温水槽中,读取液面体积刻度V2。
 (g/cm3)
(g/cm3)
堆积密度为锰渣置于立升筒的密度测定值。
4) 煅烧特性:称取20 g锰渣置于铝盒中,在马弗炉内煅烧3 h,煅烧温度分别为150,200,300,400,500,550,800,900,1 000和1 100 ℃。用XRD (日本Rigaku D/max2550VB+型)分析不同煅烧温度下锰渣物相存在形态,结合TG-DTA(德国NETZSCH/ STA449 F3 Jupiter)分析锰渣矿相热转变温度。通过标准HJ/T 299—2007测定煅烧锰渣锰的浸出毒性,分析锰浸出稳定性。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 基本物理性质
锰渣的基本物理性质参数如表1和图1所示。由表1可知:原渣自由水质量分数较高,约35%,仍需进一步的烘干脱水处理,便于运输和填埋。105 ℃烘干的锰渣水溶性物质的质量分数约20%,主要为硫酸钙和硫酸锰,因此,洗涤处理可作为锰渣的一种重要的资源回收和减量、无害化方法。锰渣经105 ℃烘干和粉磨的真实密度与岩石的相近(2~3 g/cm3),堆积密度与水的相近,具有较高的体积压缩比,约70%。从图1还可知:锰渣颗粒粒度小,均在10.5 μm以下,集中分布于2.5~6.5 μm之间。因此,锰渣粉磨细化能耗相对较低,在资源化利用方面具有优势。
2.2 浸出毒性分析
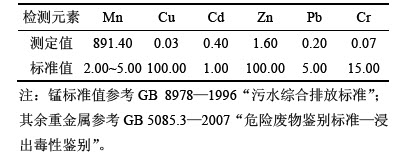
采用HJ/T 299—2007“固体废物—毒性浸出方 法—硫酸硝酸法”规定方法,测得锰渣浸出毒性如表2所示。由表2可知:锰渣中主要重金属浸出毒性均小于GB 5085.3—2007“危险废物鉴别标准—浸出毒性鉴别”中的鉴别标准值,而锰的浸出质量浓度为891.40 mg/L,严重超出了GB 8978—1996“污水综合排放标准”中的标准值,因此,锰渣属于第Ⅱ类一般工业固体废物。
表1 锰渣的基本物理参数
Table 1 Basic physical parameter of manganese residue


图1 锰渣的粒径分布
Fig. 1 Particle size distribution of manganese residue
表2 锰渣主要重金属浸出毒性
Table 2 Main heavy metal leaching toxicity of manganese residue mg/L
2.3 矿相成分分析
锰渣XRF分析结果如表3所示,其氧化态成分如表4所示。综合表3和表4可知:锰渣为高硅、铁和钙硫的废渣,硅和铁氧化态质量分数在50%以上,钙硫氧化态质量分数在30%以上。锰渣XRD分析结果如图2所示。从图2可见:锰渣主要矿相为石英[SiO2],水化硫酸钙[CaSO4·0.67H2O],黄钾铁矾[KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6],针铁矿[FeOOH]和水基性矾[Al4SO4(OH)10·(H2O)7]。石英相晶体结构最为完整,主峰为在26.6°(2θ)处最强衍射峰,峰型尖锐;其他矿物相结晶度较低,衍射峰强度低,峰型弥散。由锰渣产生工艺推断,黄钾铁矾和水性基矾为酸浸过程产物[10-11],针铁矿和水化硫酸钙为浸出底液中和沉淀产物。
表3 锰渣主要元素XRF分析结果(质量分数)
Table 3 XRF analytic result of main elements in manganese residue %

表4 锰渣主要氧化态组成(质量分数)
Table 4 Main oxidation composition of manganese residue %


图2 锰渣的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 X-ray diffraction spectra of manganese residue
2.4 TG-DTA分析
对105 ℃烘干和粉磨的锰渣进行热重-差热分析(样品质量为30 mg;温度范围为25~1 200 ℃;气氛为Ar惰性气氛;升温速率为10 ℃/min)。锰渣的TG,DTG和DTA曲线如图3所示。从图3(a)可知:锰渣在25~1 200 ℃范围内总质量损失率约26%,其中吸附水、结晶水、羟基脱水约11%,主要发生在400 ℃以下;铁、铝和锰的硫酸盐分解约15%,主要发生在500~1 000 ℃之间。从图3(b)和3(c)可知:TG曲线在131,256,355,515,754和1 006 ℃附近存在明显的质量损失峰,并伴有吸热发生;DTA曲线整体呈现下凹形状,吸热过程伴随较多的放热,为锰渣矿物相变重结晶的结果,当温度为105 ℃左右时,主要为锰渣颗粒间吸附水脱附;当温度为131 ℃左右时出现较明显吸热峰,为水化硫酸钙脱除结晶水;当温度为256 ℃和355 ℃左右时,水基性矾[Al4SO4(OH)10·7H2O]脱除结晶水和羟基水,生成无定形的铝硫氧化物[12];在350~450 ℃之间,黄钾铁矾[KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6]脱除羟基水,K2SO4和Fe2(SO4)3析出[13-14];当温度为515 ℃左右时,硫酸铁分解生成赤铁矿;当温度为754 ℃左右时,铝硫氧化物分解;当温度为1 006 ℃左右时,硫酸锰分解。

图3 在25~1 200 ℃之间锰渣TG-DTA曲线
Fig. 3 TG-DTA curve of manganese residue between 25 to 1 200 ℃
2.5 煅烧特性分析
2.5.1 相变过程分析
不同煅烧温度锰渣XRD物相分析结果如图4所示。
1) 石英相分析。由图4可知:煅烧温度在800~ 1 100 ℃之间,锰渣中石英相衍射峰强度逐渐减弱,至1 100 ℃时衍射峰基本消失,说明该温度范围石英晶相逐步无定形化[15],并与其他金属元素熔融向玻璃态硅酸盐转变。煅烧温度为1 000 ℃时,在22°处出现低温方石英[Cristobalite low, PDF-771316]主衍射峰,说明有部分石英重结晶为方石英。相比前人研究[16-17],通过石英在1 500~1 600 ℃下烧制方石英,温度降低了500~600 ℃。
2) 硫酸钙相分析。结合图3和图4可知:在200 ℃以下,硫酸钙已脱除全部结晶水,随着温度升高,依次转变为Ⅱ型慢溶性无水石膏、Ⅱ型不溶性无水石膏、浇注地板石膏[18]。从图3可知:在131 ℃左右时出现吸热-质量损失峰,在400 ℃左右时出现放热谷,在550 ℃左右时出现放热谷,在1 100 ℃左右时出现放热峰。从图4可知:当温度高于200 ℃时,在14.7°,25.7°,29.7°和31.9°处衍射峰消失,为水化硫酸钙脱水;当温度低于900 ℃时,在25.5°,31.4°和40.9°处衍射峰逐渐增强,为无水石膏[Anhydrite, PDF-742421]析晶;当温度高于900 ℃时,无水石膏衍射峰逐渐减弱,至1 100 ℃时完全消失,这与锰渣中熔融相和玻璃态石英相的包裹相关[19]。
3) 铁相分析。结合图3和图4可知:在300 ℃以下,针铁矿已完全脱水,重结晶为赤铁矿。从图4可知:当温度低于300 ℃时,在21.2°处衍射峰逐渐消失,为针铁矿脱水分解;当温度高于300 ℃时,伴随33.2°和35.6°处出现赤铁矿的衍射峰[20-21];在400 ℃以下时,黄钾铁矾脱水重结晶为硫酸铁;在800 ℃以下时,硫酸铁分解重结晶为赤铁矿。从图3可知:在515 ℃附近出现质量损失-吸热峰。对应图4可知:当温度低于400 ℃时,在17.4°,28.7°和29.0°处衍射峰逐渐消失,为黄钾铁矾脱水;在400~550 ℃之间,在24.7°处出现硫酸铁主衍射峰;当温度高于400 ℃时,24.2°,33.2°和35.6°处出现赤铁矿衍射峰,在400~900 ℃之间,赤铁矿衍射峰逐渐增强,赤铁矿相结晶度逐步增大。因此,锰渣在800~900 ℃下煅烧,能够促进铁相向赤铁矿相转化,便于铁的资源化回收利用。
4) 铝相分析。结合图3和图4可知:在400 ℃以下,水基性矾先后脱除结晶水和羟基水,转化为无定形的铝硫氧化物2Al2O3·SO3;在600~800 ℃之间,铝硫氧化物分解为无定形氧化铝;当温度高于800 ℃时,无定形氧化铝与硅相反应生成铝硅酸盐。结合图3可知:在256 ℃和355 ℃附近出现2个质量损失-吸热峰;在754 ℃附近出现质量损失和吸热谷。结合图4可知:当温度低于400 ℃时,在17.6°,29.5°和29.8°衍射峰逐渐消失,为水基性矾脱水;在900~1 000 ℃之间,在28°处出现铝硅酸盐衍射峰。
5) 锰相分析。锰渣中锰相结晶度极低,主要以硫酸锰和锰氧化物的形式存在;煅烧温度在1 000 ℃附近,硫酸锰分解为锰氧化物,并且部分锰相与硅相反应生成硅酸盐;在800~1 050 ℃之间,锰氧化物重结晶为四氧化三锰。从图3可知:在800~1 000 ℃之间出现质量损失和放热谷,其原因是部分锰氧化物失氧结晶生成四氧化三锰;在1 000 ℃附近出现质量损失和吸热峰和在1 000~1 050 ℃之间出现放热谷,为硫酸锰分解并转化为四氧化三锰。从图4可知:当温度高于800 ℃时,在30.0°和35.3°处出现四氧化三锰衍射峰;在28.0°处出现锰镁硅酸盐衍射峰[22]。因此,控制煅烧温度为900 ℃左右,能够实现锰渣中锰相转变为四氧化三锰,便于锰的资源化回收。
2.5.2 表观形貌分析
不同煅烧温度下锰渣表观形貌变化如图5所示。从图5可知:随着煅烧温度的增加,在150~300 ℃之间,锰渣颜色呈现土黄色加深,逐步显现红色,主要为针铁矿颜色;在400~550 ℃之间,淡红色转变为赤红色,颜色明显加深,为赤铁矿颜色;煅烧至800 ℃时,锰渣呈现暗棕色,开始出现轻度烧结团聚,至1 100 ℃时呈现出熔融态,转变为黑色,为四氧化三锰颜色。

图4 不同煅烧温度下的锰渣XRD图谱
Fig. 4 X-ray diffraction spectra of calcination manganese residue
2.5.3 锰浸出稳定性分析
锰渣中锰的浸出毒性随着煅烧温度变化如图6所示。由图6可知:随着煅烧温度的升高,锰渣中锰的浸出毒性有3种变化:当温度低于300 ℃时为低温可浸出温度段,浸出毒性质量浓度为0.6~1.0 g/L;在400~700 ℃之间为中温易浸出温度段,浸出毒性质量浓度2~3 g/L;当温度高于800 ℃为高温难浸出温度段,浸出毒性质量浓度为1~10 mg/L。这与锰渣矿物相成分密切相关。温度在300 ℃以下,锰渣含有较多黄钾铁矾和水基性矾,对锰离子有较强的吸附作用[23-24],仅部分硫酸锰浸出,约占全部硫酸锰的1/3;在400~700 ℃之间,黄钾铁矾和水基性矾脱水、分解,吸附作用消失,全部硫酸锰浸出;在800 ℃以上,由于固溶体的包裹和锰硅酸盐的形成,致使锰浸出毒性急剧减少;在1 000 ℃左右,硫酸锰分解析出四氧化三锰,锰的浸出毒性略微上升。因此,仅以锰渣的稳定化处理为目的,热处理温度应低于300 ℃或者高于800 ℃;若通过酸浸出实现锰的资源化回收,热处理温度以400~700 ℃为宜。

图5 煅烧锰渣表观形貌对比照片
Fig. 5 Surface morphology photos comparison of calcination manganese residue

图6 不同煅烧温度下锰渣锰的浸出毒性
Fig. 6 Mn leaching toxicity of manganese residue under different calcination temperatures
3 结论
1) 锰渣中水溶性物质的质量分数较高,且矿物种类多、结晶度低,主要矿相为石英、水化硫酸钙、针铁矿等,而硅、铁和钙的氧化物质量分数在63%以上,因此,锰渣具有较高的资源化利用价值。
2) 锰渣经800~900 ℃煅烧,能够实现其中铁矿相转变为赤铁矿、锰矿相转变为四氧化三锰,为磁选方法资源化回收铁锰提供可能。
3) 锰的浸出毒性随着煅烧温度出现3个阶段变化。经400~700 ℃煅烧处理,锰渣中的锰转变为易浸出形态,适于酸浸资源化回收锰;高于800 ℃煅烧处理,易浸出锰形成四氧化三锰并与硅酸盐反应,转变为稳定形态,能够实现锰渣稳定化。
参考文献:
[1] 吴伟金. 电解锰浸渣的综合利用研究进展[J]. 大众科技, 2013, 15(6): 92-95, 22.
WU Weijin. Research of using electrolytic manganese slag[J]. Journal of Popular Science and Technology, 2013, 15(6): 92-95, 22.
[2] 周长波, 孟俊利. 电解锰废渣的污染现状及综合利用进展[C]// 中国环境科学学会. 中国环境科学学会学术年会议论文集. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2009: 516-519.
ZHOU Changbo, MENG Junli. Current pollution situation and comprehensive utilization progress of electrolytic manganese residue[C]// Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences. China Environmental Science Society Academic Essays. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2009: 516-519.
[3] Sorensen B, Gaal S, Ringdalen E, et al. Phase compositions of manganese ores and their change in the process of calcination[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2010, 94(3): 101-110.
[4] 邓跃全, 彭碧辉, 戴亚堂, 等. 锰渣成份分析[J]. 西南工学院学报, 2000, 15(4): 23-25.
DENG Yuequan, PENG Bihui, DAI Yatang, et al. The analysis of manganous slag[J]. Journal of Southwest Institute of Technology, 2000, 15(4): 23-25.
[5] 王星敏, 徐龙君, 胥江河, 等. 电解锰渣中锰的浸出条件及特征[J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(10): 3757-3761.
WANG Xingmin, XU Longjun, XU Jianghe, et al. Leaching conditions and characteristics of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012, 6(10): 3757-3761.
[6] WANG Jia, PENG Bing, CHAI Liyuan, et al. Preparation of electrolytic manganese residue-ground granulated blastfurnace slag cement[J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 241: 12-18.
[7] 李坦平, 周学忠, 曾利群, 等. 电解锰渣的理化特征及其开发应用的研究[J]. 中国锰业, 2006, 24(2): 13-16.
LI Tanping, ZHOU Xuezhong, ZENG Liqun, et al. Research on physicochemical characteristics of electrolytic manganese residue and its development and application[J]. China’s Manganese Industry, 2006, 24(2): 13-16.
[8] 柯国军, 耿鸿芝. 煅烧锰渣的胶凝性和水化机理[J]. 硅酸盐建筑制品, 1995(5): 20-24.
KE Guojun, GENG Hongzhi. Gelling property and hydration mechanism of calcined manganese residue[J]. Silicate Building Products, 1995(5): 20-24.
[9] 张强, 彭兵, 柴立元, 等. 电解锰渣体系中硫酸钙特性的研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2010, 30(5): 70-73, 78.
ZHANG Qiang, PENG Bing, CHAI Liyuan, et al. Study on characteristics of calcium sulfate in electrolytic manganese residue [J]. Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, 2010, 30(5): 70-73, 78.
[10] 王长秋, 马生凤, 鲁安怀, 等. 黄钾铁矾的形成条件研究及其环境意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2005, 24(6): 607-611.
WANG Changqiu, MA Shengfeng, LU Anhuai, et al. The formation conditions of jarosite and its environmental significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 2005, 24(6): 607-611.
[11]  J, Yusta I, Diez-Ercilla M. Schwertmannite and hydrobasaluminite: A re-evaluation of their solubility and control on the iron and aluminium concentration in acidic pit lakes[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(9): 1752-1774.
J, Yusta I, Diez-Ercilla M. Schwertmannite and hydrobasaluminite: A re-evaluation of their solubility and control on the iron and aluminium concentration in acidic pit lakes[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(9): 1752-1774.
[12] Clayton T. Hydrobasaluminite and basaluminite from Chickerell, Dorset[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1980, 43: 931-937.
[13] 吴文伟, 李姝姝, 廖森, 等. 黄钾铵铁矾的热分解过程及其产物[J]. 有色金属, 2009, 61(3): 71-75.
WU Wenwei, LI Shushu, LIAO Sen, et al. Products and kinetics of potassium ammonium jarosite thermal decomposition[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 61(3): 71-75.
[14] 薛佩毅, 巨少华, 张亦飞, 等. 焙烧-浸出黄钾铁矾渣中多种有价金属[J]. 过程工程学报, 2011, 11(1): 56-60.
XUE Peiyi, JU Shaohua, ZHANG Yifei, et al. Recovery of valuable metals by leaching of roasted jarosite residue[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2011, 11(1): 56-60.
[15] 徐常明, 王士维, 黄校先, 等. 方石英的析晶与无定形化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(4): 577-582.
XU Changming, WANG Shiwei, HUANG Xiaoxian, et al. Crystallization and amorphization of cristobalite[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(4): 577-582.
[16] 雷芸, 姚建云, 张科, 等. 方石英的制备及表征[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2011, 30(2): 304-307.
LEI Yun, YAO Jianyun, ZHANG Ke, et al. Preparation and characterization of cristobalite from quartz [J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2011, 30(2): 304-307.
[17] 申柯娅, 王睿, 曾群, 等. 方石英的制备及其热性能测试[J]. 铸造技术, 2013, 34(3): 324-326.
SHEN Keya, WANG Rui, ZENG Qun, et al. Preparation of cristobalite and testing of its thermal characteristics[J]. Foundry Technology, 2013, 34(3): 324-326.
[18] 石庆忠. 磷石膏为原料制硬石膏的初步研究[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2006, 21(1): 65-66.
SHI Qingzhong. Preliminary study on manufacture of anhydrite from phosphogypsum[J]. Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer, 2006, 21(1): 65-66.
[19] 高福烨, 李帆. 煤的高温灰在加热过程中的行为研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 1989, 17(2): 175-182.
GAO Fuye, LI Fan. Study on the behavior of coal ash at high temperature [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 1989, 17(2): 175-182.
[20] 邹雪华, 陈天虎, 刘海波, 等. 热处理针铁矿的色度与结构演化[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2013, 41(5): 669- 673.
ZOU Xuehua, CHEN Tianhu, LIU Haibo, et al. The structural and chromatic evolution of goethite by thermal treatment[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 41(5): 669- 673.
[21] 张建良, 毛瑞, 黄冬华, 等. 红土镍矿脱水机理及还原过程动力学[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(3): 843-851.
ZHANG Jianliang, MAO Rui, HUANG Donghua, et al. Dehydration mechanism and reduction process dynamics of laterite nickel ore[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(3): 843-851.
[22] Gnos E, Armbruster T, Nyfeler D. Kanoite, donpeacorite and tirodite: Mn-Mg-silicates from a manganiferous quartzite in the United Arab Emirates[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 1996, 8(2): 251-262.
[23] 王长秋, 马生凤, 鲁安怀. 黄钾铁矾类矿物沉淀去除Cr(Ⅵ)的初步研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 25(4): 335-338.
WANG Changqiu, MA Shengfeng, LU Anhuai. A Preliminary Study on the Cr(Ⅳ) Removing from Waste water by precipitation of Jarosite Group Minerals [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2006, 25(4): 335-338.
[24] Dutrizac J E, Kaiman S. Synthesis and properties of jarosite-type compounds[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 1976, 14(2): 151-158.
(编辑 罗金花)
收稿日期:2014-10-18;修回日期:2014-12-20
基金项目(Foundation item):高科技研究发展计划(863计划)项目(2011AA061000);国家“十二五”科技支撑计划项目(2012BAC12B02);湖南省科技重大专项(2012FJ1010) (Project(2011AA061000) supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program); Project(2012BAC12B02) supported by the National Science and Technology Pillar Program during the 12th Five-Year Plan Period; Project(2012FJ1010) supported by Major Science and Technology Projects of Hunan Province)
通信作者:彭兵,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事冶金环境工程研究;E-mail: pb@csu.edu.cn