Trace elements spatial distribution characteristics, risk assessment and potential source identification in surface water from Honghu Lake, China
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2018年第7期
论文作者:张敬东 刘朝阳 李飞 杨俊 仇珍珍 蔡莹 朱丽芸 肖敏思 伍紫贤
文章页码:1598 - 1611
Key words:spatial distribution characteristic; risk assessment; source identification; trace elements; Honghu Lake
Abstract: Five trace elements including Zn, Cu, Cd, Cr and As were investigated in surface water from ten typical sampling sites in Honghu Lake. The consequence indicated that all of the detected trace element levels were within the allowed standard of China’s safe water guideline. The hazard quotients (HQ) and the hazard index (HI) value levels of all the five heavy metals in all sampling sites did not exceed the acceptable risk limits of non-carcinogenic value through the selected assessment method. Pearson’s correlation analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) indicated that Zn and Cu mainly originated from the natural alluviation and non-point agricultural sources, whereas Cr and As were mainly derived from industrial effluents. Moreover, Cd mainly originated from both non-point agricultural and industrial pollution sources. In addition, cluster analysis (CA) implied that cluster 1 (including S3, S5, S6 and S10) was considered the set of high pollution sites and cluster 2 (including S4 and S9) was identified as the set of moderate pollution sites.
Cite this article as: LIU Chao-yang, ZHANG Jing-dong, LI Fei, YANG Jun, QIU Zhen-zhen, CAI Ying, ZHU Li-yun, XIAO Min-si, WU Zi-xian. Trace elements spatial distribution characteristics, risk assessment and potential source identification in surface water from Honghu Lake, China [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(7): 1598–1611. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3852-2.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2018) 25: 1598-1611
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3852-2
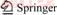
LIU Chao-yang(刘朝阳)1, ZHANG Jing-dong(张敬东)1, LI Fei(李飞)1, 2, YANG Jun(杨俊)1,QIU Zhen-zhen(仇珍珍)1, CAI Ying(蔡莹)1, ZHU Li-yun(朱丽芸)1,XIAO Min-si(肖敏思)1, WU Zi-xian(伍紫贤)1
1. Research Center for Environment and Health, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law,Wuhan 430073, China;
2. College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018
Abstract: Five trace elements including Zn, Cu, Cd, Cr and As were investigated in surface water from ten typical sampling sites in Honghu Lake. The consequence indicated that all of the detected trace element levels were within the allowed standard of China’s safe water guideline. The hazard quotients (HQ) and the hazard index (HI) value levels of all the five heavy metals in all sampling sites did not exceed the acceptable risk limits of non-carcinogenic value through the selected assessment method. Pearson’s correlation analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) indicated that Zn and Cu mainly originated from the natural alluviation and non-point agricultural sources, whereas Cr and As were mainly derived from industrial effluents. Moreover, Cd mainly originated from both non-point agricultural and industrial pollution sources. In addition, cluster analysis (CA) implied that cluster 1 (including S3, S5, S6 and S10) was considered the set of high pollution sites and cluster 2 (including S4 and S9) was identified as the set of moderate pollution sites.
Key words: spatial distribution characteristic; risk assessment; source identification; trace elements; Honghu Lake
Cite this article as: LIU Chao-yang, ZHANG Jing-dong, LI Fei, YANG Jun, QIU Zhen-zhen, CAI Ying, ZHU Li-yun, XIAO Min-si, WU Zi-xian. Trace elements spatial distribution characteristics, risk assessment and potential source identification in surface water from Honghu Lake, China [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(7): 1598–1611. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3852-2.
1 Introduction
Lakes with versatile ecosystems are thought to be one of the most vital surface water resources in the world. However, various forms of environmental pollution and human-caused destruction leave these resources vulnerable [1, 2]. With the well growth of environmental health research, trace elements are considered to be the major type of surface water pollution because of the easy accessibility of their disposal via wastewater [3]. Some trace elements have contaminated the aquatic environment [4–6]. More attention should be paid to the trace elements because of their non-degradable and toxic character as well as their persistence and tendency to accumulate in biological organisms. Trace elements could cause potential risk and hazardous effects to human health through their transportation and transformation among multiple media, for example, surface water, soil and ambient air [7, 8]. Exposure threats to trace elements on human health are as follows: chronic or acute chemical toxicity, infectious diseases, and carcinogenicity [5, 9]. Many researches have published the features of water quality, the spatial distributions and the risk effects on human health of trace elements [10–13]. Thus, it is suitable and necessary to do some researches in surface water quality assessment, heavy metals spatial distribution and possible health risks evaluation through some significant exposure ways.
Trace elements in water resources usually derive from two aspects: natural processes and human sources [14, 15]. These two pathways result in the increasing of trace elements concentrations in surface water [16]. The natural processes include flow alterations, natural corrosion, and benthic agitation. The anthropogenic sources include various types of sewage emission, industrial wastewater emission, and fertilizer from agricultural leaching. Due to the situation of regions around rivers with unusual industrial foundations and high population density, the surface waters from rivers are increasingly contaminated by the mixture of trace elements from different drainage sources [17]. Therefore, it is necessary to protect affiliated aquatic ecosystem via assessing health risk that is caused by trace elements in Honghu Lake’s surface water.
Honghu Lake is a National Nature Wetland Reserve. It is located in the Jianghan Plain between the Yangtze River and its longest tributary the Han River [18]. The region of the Honghu Lake covers 344 km2, which owns a mean depth of 1.34 m. Due to the middle of the last century extensive water conservancy policies, Honghu Lake has been altered to a semi-closed water area [19]. The continuous deterioration in the water quality of the surface water has resulted for the reasons as follows: booming local economy, limited capabilities of water treatment and ineffective measures by agricultural, industrial and local authorities [20–21]. Some recent researches have focused on surface water quality characterization and preliminary assessment [2, 22, 23]. However, few research studies, especially for the dry season of the Honghu Lake, are related to a systematic study of the trace elements in surface water, including the spatial distribution and potential health hazards through different exposure pathways and source identification.
The aims of this research are (1) to detect heavy metal concentrations in the surface water and find out its spatial distribution in Honghu Lake; (2) to evaluate the human environmental health risk through the hazard quotients (HQ) of each heavy metal and the hazard index (HI) of the mixed heavy metals via different exposure ways, like dermal and ingestion absorption; (3) to identify different heavy metals sources by utilizing multivariate statistical analysis methods.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Research zone
Honghu Lake is located in Hubei Province, China (113°22′18′′E, 29°51′35′′N). It is the seventh largest fresh water lake in China, which lies between Honghu City and Jianli City (Figure 1).
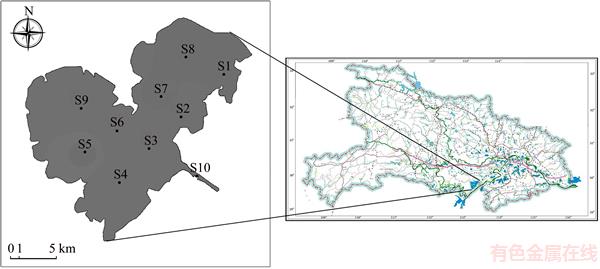
Figure 1 Map of sampling site locations in Honghu Lake
This region is in the northern edge of the temperate and subtropical zone, and its average temperature and precipitation are in the ranges of 15.9–16.6 °C and 1000–1300 mm, respectively. Due to the development of the economy and increasing levels of human activities, Honghu Lake has suffered from a variety of environmental issues over the past few years, with the shrinking of the water region and the deterioration of water quality [24, 25].
2.2 Collection of samples
Water samples were collected from surface water of Honghu Lake in November 2015. The sites were chosen based upon the use of Montana650 GPS. The locations and designations of the sampling sites were numbered from 1 to 10 (hereafter called S1 to S10) (Figure 1). All the samples were filtered through filter membrane whose aperture was 0.45 μm and then stored in polyethylene containers which were washed by hydrogen nitrate. Subsequently, these samples were acidified with concentrated nitric acid and then kept in ice boxes for transportation to the laboratory. In addition, the pH and water temperatures were measured at the scene. Individual demographic information, such as weight, age, exposure frequency and exposure time, was obtained through the questionnaire.
2.3 Determination of trace element concentrations
The contents of zinc, copper, cadmium and chromium in samples were detected by atomic absorption spectroscopy, while arsenic was detected by atomic fluorescence spectrometry under appropriate conditions. Each calibration curve was calculated before, during and after the analyses of samples according to the analyses of quality control standards. The sampling bottles were washed three times with freshwater before gathering surface water samples. In order to control and ensure the quality of results, blank samples and 10% parallel samples were selected throughout the process. The matrix interference (Blank) was less than 2% for all trace elements. Analysis of triplicate samples exceeded no more than 5% relative differences. A new calibration curve would be used to re-analyze the samples when their recovery rate yielded the recommended range (90%–110%).
2.4 Health risk assessment
The main process of health risk assessment is exposure evaluation, risk characterization, and hazard discrimination [26]. There are three ways in which human beings are exposed to heavy metals: direct ingestion, dermal absorption via exposures skin, and inhalation via mouth and nose [12, 27]. In addition, ingestion and dermal absorption play vital roles in the water environmental exposure for the purpose of daily drinking and daily showering of the residents, respectively [28]. In this study, the exposure dose through those two patterns were calculated by Eqs. (1) and (2), according to the risk assessment guidance of the USEPA [29]. Based on the questionnaires, some of the residents around Honghu Lake rely on the surface water for domestic and potable use in their daily life. These residents were divided into two groups: children under the age of 12 and adults over 12 years of age.
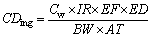 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
where CDing (mg/(kg·d)) represents the mean daily exposure doses via ingestion, and CDderm (mg/(kg·d)) is the mean daily exposure doses via skin; Cw represents average levels of heavy metals in water samples (μg/L); IR represents the daily intake of water (L/d), for this study and water intake for adult is 2.2 L/d and 1.5 L/d for child; EF represents exposure frequency (d/year) 350 d/year, and the residents are assumed to leave the residence for 15 d/year; ED represents the exposure duration (year), for this research 70 years; BW represents body weight (kg), weight of adult is 65 kg and 22 kg of child; AT represents average time (d) and average of adult is 10950 d and 2190 d of children in this study; SA is exposed area of skin (cm2), 18000 cm2 for adult and 6660 cm2 for child in this study; Kp represents the dermal permeability coefficient in surface water, in this study, the values of As, Cd, and Cu are 1×10–3 cm/h, 2×10–3 cm/h of Cr, and 6×10–4 of Zn; ET represents exposure time (h/d), 0.6 h/d in this study. These exposure variables were set according to the investigation results of the structured questionnaire, the relative research studies, and the standards of the USEPA [11, 29–31].
Risk characterization is divided into two aspects: non-carcinogenic risk and carcinogenic risk [32]. To study potential hazards of non-carcinogenic risks, HQs were calculated from the exposure pathways by ratio of daily exposure doses and corresponding reference dose (RfD) through the following formulas. When HQ>1, there can be considered that it exists non-carcinogenic risk. HI refers to the non-carcinogenic risks of a variety of heavy metals through all the exposure ways as presented in Eqs. (5). HI>1 indicates potential negative impact on human health [33].
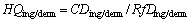 (3)
(3)
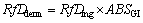 (4)
(4)
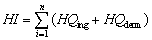 (5)
(5)
where HQing/derm (a unitless quantity) represents the risk quotient via ingestion or dermal absorption of water; HI (also a unitless quantity) represents the risk index, which is the summation of the HQs from the exposure pathways, including the dermal absorption and ingestion ways; i represents the specific heavy metal; RfD represents reference dose of each trace element (μg/(kg·d)); RfDing represents the reference dose via ingestion, obtained from the database of USEPA [34] and WHO [35], and RfDderm represents the dermal reference dose; ABSGI represents gastrointestinal absorption factor.
2.5 Geostatistical methods and statistical data analyses
Geographic information system (GIS) and inverse distance weighted (IDW) were used to study the spatial distribution of heavy metals and health risk. IDW applies a specific number of closest sites based on their spatial distance from the interpolated site. Ten sampling sites were chosen to specifically reveal spatial patterns and the spatial variation of the health hazard for studied metals.
Pearson’s correlation analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), and cluster analysis (CA) techniques were used to calculate the concentration data of heavy metals through SPSS version 16.0 for Windows. Correlativity among the heavy metals studied in this study was measured via Pearson’s coefficient, and when P is less than 0.05, it has the statistical significance. Hierarchical agglomerative CA was applied to showing the system of organizing variables according to their similarity [36–38]. The normalized variables of principal component analysis (PCA) were used to extract important principal components (PCs) with Bartlett’s sphericity and Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) tests to examine the suitability of the data.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Mean heavy metals levels of surface water
Tables 1 and 2 revealed the total and individual heavy metal levels of the study area. Firstly, the detected heavy metals levels of the surface water were observed between 0.1 μg/L (S7 and S10) and 22.96 μg/L (S10), with a mean value of 6.33 μg/L. Secondly, the mean concentration level of Cr (12.43 μg/L) was the highest, followed by Zn (10.53 μg/L) and Cu (7.92 μg/L). These three heavy metals accounted for 97.57% of the total concentrations. Cr, Zn, and Cu were the main pollutants of Honghu Lake surface water that occupied 97.57% in total, and comparatively Cd (0.15 μg/L) was the lowest. Different sample sites’ heavy metals contents were extremely different. In particular, Cr and Zn exhibited higher standard deviations compared with the other heavy metals. As shown in Table 2, S4 (52.95 μg/L) has the highest total mixed heavy metals contents, followed by S9 (45.59 μg/L) and S10 (41.94 μg/L); the lowest concentration is observed at S8 (8.42 μg/L). The west side of Honghu Lake had higher content of Zn, Cu and Cr than the east side.
The mean levels of the entire heavy metals were below the allowed values of WHO drinking water guidelines [35], the USEPA [39] and the Chinese standards [40] (Table 1). Following the average background concentrations, the heavy metals average levels of Honghu Lake surface water were found to be higher than its blank background levels (Table 1) [41]. Cd was 15 times higher than the average background level [41], and Cr was 12.43 times higher.
Compared to other lakes’ entire heavy metal data from some reliable published articles, the total heavy metals contents of Honghu Lake are comparatively in the middle content level. Due to the rapid development of economic with deficient regulation policies, concentrations of the mean levels of the entire heavy metal from lakes and rivers in China were found to be higher than those in the other countries [42, 43]. In addition,comparing the native lakes, the average concentrations of Zn and Cu in the surface water from Honghu Lake were higher than from Poyang Lake [44], and the concentrations of Cd and Cr were higher than that from Dongting Lake [45], but the concentrations of Zn, Cu and As were much lower. Furthermore, the average levels of the entire heavy metal from Honghu Lake were lower than that from Taihu Lake [46].
Table 1 Analysis of maximum, minimum, mean and standard deviation (SD) values of concentrations of heavy metals and comparison to guidelines and previous researches
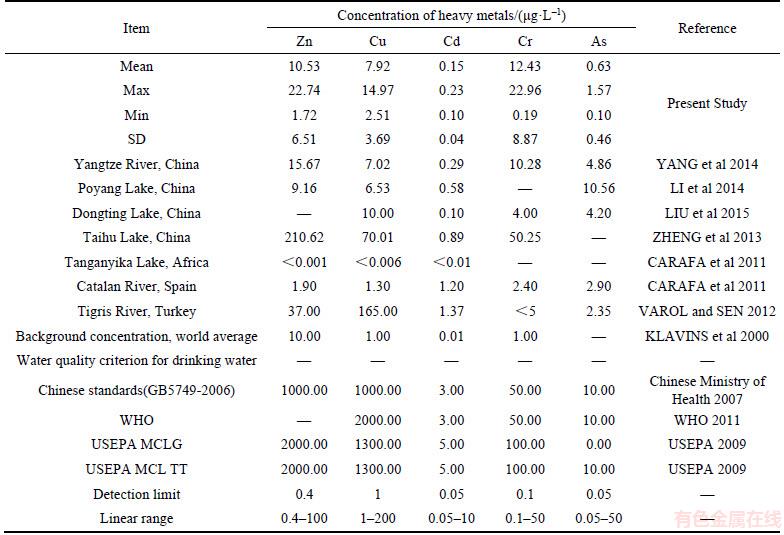
Table 2 Concentration of heavy metals in each sampling site
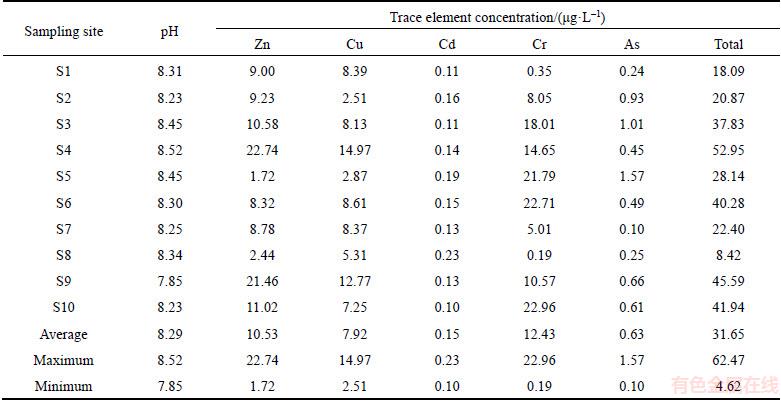
3.2 Spatial distributions of trace elements in surface water
The heavy metal distributions of surface water from Honghu Lake, applying contour maps upon IDW method, are shown in Figures 2(a) to (e). These maps indicated the distinct regions with higher or lower concentration values in Honghu Lake. To characterize the trace elements’ spatial distributions in surface water efficiently, Honghu Lake was segmented into three parts: East Honghu Lake (S1, S2, S7 and S8), West Honghu Lake (S3, S4, S5, S6 and S9) and the outlet of Honghu Lake (S10).
Zn and Cu in the surface water are two micronutrients for aquatic life, but they could become toxic when enriched to high concentrations [47]. As shown in Figure 2(a) and Table 2, the concentrations of Zn of each sampling sites were in the descending order of S4>S9>S10>S3>S2>S1> S7>S6>S8>S5. On the basis of the average concentrations of the world background,40% of the sampling sites’ content surpassed the background levels. The West Honghu Lake and the outlet of the Honghu Lake were the regions of highest enrichment area. As for the concentrations of Cu, shown in Figure 2(b), the sampling sites were in the descending order of S4>S9>S6>S1>S7>S3>S10> S8>S5>S2. The concentration of Cu in each sampling sites exceeded the average concentration of the world background, with most of the enrichment in the West Honghu Lake. The similarity of the spatial distribution patterns of the above two trace heavy metal levels indicated that they may originate from the same source and lead to similar damage.
Cd is a toxic trace element with a relatively low concentration in natural water [48]. According to Figure 2(c) and Table 2, the spatial distribution pattern of Cd is not the same as the other trace elements from two ways: firstly, the concentration of Cd was descending in order of the East Honghu Lake > the West Honghu Lake > the outlet of the Honghu Lake. Secondly, the mean concentrations from each sampling site for Cd was in the descending order of S8>S5>S2>S6>S4>S7> S9>S1>S3>S10. Similar to the trace element Zn and Cu, all the sampling sites were found to exceed the average concentration of world background.
According to a survey result of the environmental protection agency of USA (USEPA), Cr and As are proved to be of high risk to the ecological environment and human beings.Figure 2(d), Figure 2(e) and Table 2 indicate that the Cr concentration decreases in order of the West Honghu Lake > the outlet of the Honghu Lake > the East Honghu Lake, and the As concentration is in the descending order of the West Honghu Lake > the East Honghu Lake > the outlet of the Honghu Lake. The average levels of Cr and As content were decreased in the orders of S10>S6>S5>S3>S4>S9> S2>S7>S1>S8 and S5>S3>S2>S9>S10>S6>S4> S8>S1>S7, respectively. Furthermore, 80% sampling sites were found to surpass the average concentration of world background for Cr.
3.3 Health risk assessment of heavy metals and risk mapping
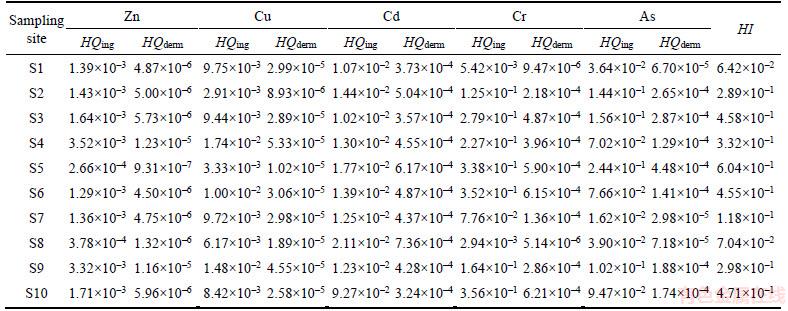
Health risk assessment was used to evaluate the surface water heavy metal pollutant hazard levels. Both HQ values of individual elements and HI values of mixed elements were calculated based on the above formulas; the consequences were presented in Tables 3 and 4 for adults and children, respectively.
The mean degrees of HQs were in the descending order of Cr>As>Cd>Cu>Zn. The risk level for adults was lower than that for children, demonstrating that adults were more vulnerable to endure the hazards of the non-carcinogenic influence. The local residents could be in direct contact with the heavy metals through absorption of the heavy metals across the gastrointestinal tract [49, 50]. As shown in Tables 3 and 4, the results are consistent with this exposure pathway because all the HQing (hazard quotients of ingestion) were higher than HQderm (hazard quotients of derm) in the sampling sites. Moreover, none of the HQing and HQderm exceeded the safety limit for adults or children. This phenomenon suggested that the trace elements detected in this study posed little or no potential non-carcinogenic risks for whether it was an adult or a child.
For the total value of HQing in adults and children, site S5 had the highest level, whereas S1 had the smallest; these results were similar for the total value of HQderm. The heavy metal Cr possessed the highest HQing and HQderm values compared with the other four trace elements. The largest value of HQing of 0.356 corresponds to the value for Cr in children at S10. The largest value of HQderm of 0.211 corresponds to Cr for adults at S10. As a consequence, Cr in surface water had a higher risk than the other trace elements. From the overall viewpoint of pollution level in all the sampling sites, the highest risk rank of heavy metal HQ for adults and children were S4 for Zn, S4 for Cu, S8 for Cd, S10 for Cr and S5 for As (Tables 3 and 4).
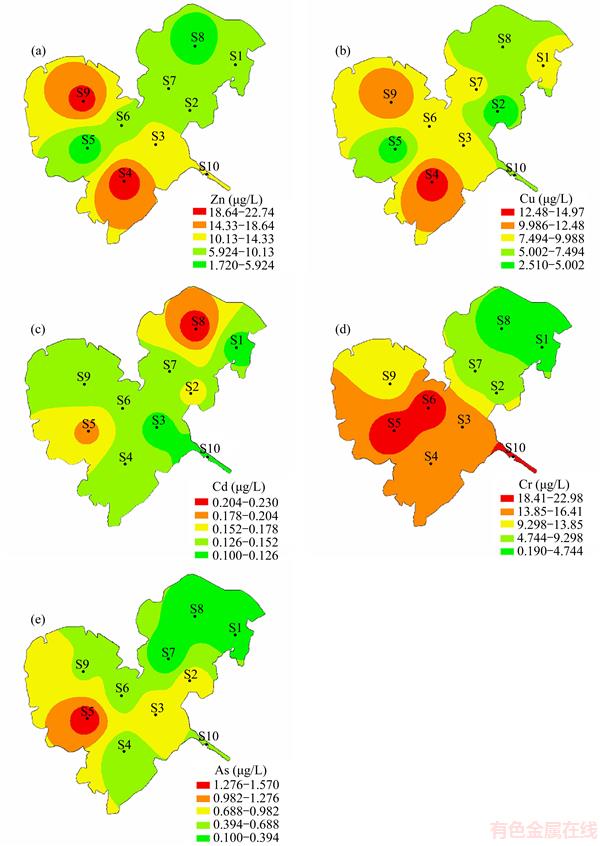
Figure 2 Spatial distributions of Zn (a), Cu (b), Cd (c), Cr (d) and As (e) in surface water from Honghu Lake
The hazard index (HI) values calculated by the levels of mixed heavy metals in sampling sites, both for adults and children, descended in order of S5, S10, S3, S6, S4, S9, S2, S7, S8 and S1 (Tables 3 and 4). Regarding adults around the Honghu area, the HI values of S1, S7 and S8 are at the relatively small risk rank, the HI values of S2, S4 and S9 are in the middle risk rank, and the calculated HI values of S3, S5, S6 and S10 are in relatively large risk rank (Figure 3(a)). Regarding children around the Honghu area, the calculated HI values of S1, S7 and S8 are in the low risk level, the HI values of S2, S3, S4, S6, S9 and S10 are in the middle risk rank, and the calculated HI values of S5 is in high risk level (Figure 3(b)). More detailed HI values among the different sampling sites are specifically presented in Figure 3. In short, HI values in all the sampling sites, for adults and children, were not found to exceed the acceptable risk limits of non- carcinogenic impurities (the mixed heavy metals).
Table 3 Hazard quotient (HQ) and hazard index (HI) of heavy metals for adults
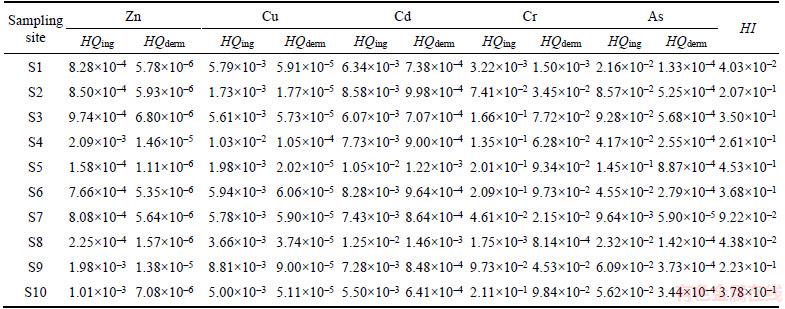
Table 4 Hazard quotient (HQ) and hazard index (HI) of heavy metals for children
4 Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals
4.1 Pearson’s correlation analysis of heavy metals
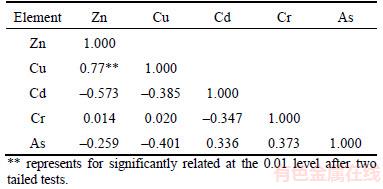
The Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to calculate correlation matrix of data. Table 5 shows that there is obvious positive correlation between zinc and copper, which has an important positive correlation at significant level of < 0.01, whereas no significant correlations were identified among the other trace elements. As the published studies indicated, if trace element factors have positive correlation coefficient, then these factors may have the same source, mutual dependence and similar behavior [28, 51].

Figure 3 Spatial risk mapping based on HI of trace elements in surface water from Honghu Lake
Table 5 Correlation coefficients of heavy metals in surface water of Honghu Lake
4.2 Principal component analysis (PCA)
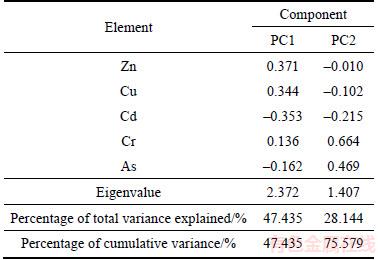
Before principal component analysis (PCA), Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) and Bartlett’s sphericity tests were utilized to test the suitability of the data. Next, the data sets of the selected elemental concentrations were analyzed by PCA. These data were derived individually from the 10 sampling sites and used to identify similarities in their behavior and their common source via varimax rotation with Kaiser Normalization, which was a measure of sampling adequacy, indicating variance proportions. As shown in Table 6, the PCA of the dataset shows that eigenvalues of PC1 and PC2 were larger than 1, explaining 75.58% of the total variance in the trace elements concentrations data set. The first component, contributing up to 47.44% of total square deviation, illustrated high loadings of Zn as well as Cu. The second component (PC2), Cr and As prevail over other heavy metals, explains 28.14% of total square deviation. Therefore, the results of the PCA were in accordance with the outcomes of the Pearson correlation analysis.
Table 6 Rotating component matrix of heavy metals in surface water from Honghu Lake
4.3 Cluster analysis (CA)
CA was applied to determining the spatial variability of the concentrations of heavy metals in data set. After standardization of the data, the Euclidean distances of the similarities among variables were computed. Next, hierarchical clustering was conducted to standardize the data using Ward’s method. Dendrogram of the five trace elements was rendered by CA (Figure 4). Three statistically significant clusters were identified: 1) the first cluster was Cr, classified as the high pollution level; 2) the second cluster was Cu, identified as the moderate pollution level, and 3) the third cluster was Cd, As and Zn, grouped as the relatively low contamination level.
Likewise, CA was performed for sampling sites, and another dendrogram was shown to discern the groups of spatial geochemistry (Figure 5). It reveals that three statistically analyzed important clusters: 1) Cluster 1 is probably the relatively high pollution sites, which includes S3, S5, S6 and S10;2) Cluster 2 could be the moderate pollution sites, which includes S4 and S9; 3) Cluster 3 might be the relatively low concentration level sites, which includes S1, S2, S7 and S8.
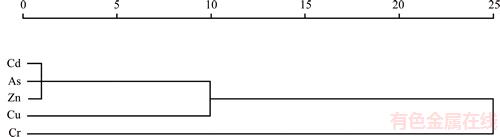
Figure 4 Dendrogram of trace elemental concentrations in surface water from Honghu Lake

Figure 5 Dendrogram of sampling sites at surface of Honghu Lake
4.4 Source identification of heavy metals
On the basis of spatial distribution, Pearson’s correlation coefficient analysis, PCA and CA, the three main identified sources of the detected heavy metals in samples from Honghu Lake are as follows: 1) Zn and Cu primarily originating from natural alluviation and non-point agricultural sources; 2) Cr and As mainly derived from industrial effluents; 3) Cd mainly originating from anthropogenic activities and non-point agricultural sources.
The first group of trace elements, which included Zn and Cu, had an analogous spatial distribution in the lake, primarily located in the western part of Honghu Lake. Furthermore, Zn and Cu had importantly positive correlations in Pearson’s correlation analysis and PCA (Tables 5 and 6). These trace elements were probably derived from a combination of natural alluviation and non-point agricultural sources. The main reasons for this phenomenon were as follows: Firstly, the emission load of the wastewater to Honghu Lake, according to the statistical data from Honghu environmental protection bureau, decreased in the order of upstream river input, fish breeding ponds and purse seine aquaculture, which accounted for 66.52%, 14.62% and 5.15%, respectively. Downstream of the Jianghan Plain, large quantities of wastewater from non-point agricultural pollution, such as cultivated land, aquaculture and livestock breeding, was emitted to Honghu Lake through the Dongjing River, the Neijing River and the Hansha River. Secondly, due to the rapid development of the local aquatic economy, the rise of purse seine aquaculture had occurred in Honghu Lake, especially around the sampling sites S1 and S9 (which was the site nearest to the upstream rivers). As reported in previously published studies [52, 53], the fertilizer used in farmland and aquaculture feed applied in the aquaculture in Jianghan Plain contains heavy metals, such as Zn and Cu, which exceeded the limit of the Chinese National Standards (GB 18877–2002). This was considered as the origin of the enhanced concentration of Zn and Cu in Honghu Lake. Furthermore, being an area of alluvial lacustrine plain, the background level of Zn was high [54], indicating that the source of Zn could originate from natural and anthropogenic factors.
The second group of trace elements, including Cr and As, indicated associations in PCA with a homologous spatial distribution (Table 6). The statistical data from the Honghu environmental protection bureau showed that there were several enterprises present around Honghu Lake, including chemical, pharmaceutical, apparel, textile and aquatic product enterprises. According to published researches [55, 56], some trace elements come from the wastewater of the above-mentioned multitudinous industrial enterprises. Cr was abundant in the effluent of the textile and pharmaceutical industries, and As was present in an abnormally high level in the dyestuff from apparel companies. Most of these enterprises are close to the west and southeast of the Honghu Lake, which could be regarded as the primary sources of heavy metals Cr and As discharged to the surface water. In addition, the spatial distributions show that sites S3, S5, S6 and S10 were found to own the higher values of Cr and As (Figure 2). In addition, these sites were near to sources of pollution such as the enterprises of Honghu Odd Fish Co., Ltd., Hubei Dahua Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Honghu Xinglin Chemical Co., Ltd.,
The third group of trace elements was Cd, which had a mixed source of non-point agricultural and industrial waste water. The spatial distribution of Cd is shown in Figure 2, and the highest concentrations are located at S5 and S8. According to previous research, the Cd in the surface 30 cm of sediment from Honghu Lake might be derived from the anthropogenic activities around the lake because of the fast growth of industrial development and urbanization [57, 58]. Further, agricultural runoff and industry sources in soils which were heavily polluted from dense land use of phosphate fertilizer probably result in the pollution of Cd in Honghu Lake.
5 Conclusions
It was concluded that the surface water from Honghu Lake was safe to use. The main reason was all the five trace elements’average contents within the scope of drinking water requirement by WHO,USEPA and Chinese standards. Based on the geostatistical methods, the spatial distribution of the five studied trace elements in all sampling sites indicated higher concentrations in West Honghu Lake. West Honghu Lake was considered as a priority area for management by the local government. Regarding the health risk assessment,the mean HQs increased in the following order:Zn
References
[1] FORGHANI G, MOORE F, LEE S, QISHLAQI A. Geochemistry and speciation of metals in sediments of the Maharlu Saline Lake, Shiraz, SW Iran [J]. Environmental Earth Science, 2009, 59(1): 173–184.
[2] HU Ying, QI Shi-hua, WU Chen-xi, KE Yan-ping, CHEN Jing, CHEN Wei. Preliminary assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments from Honghu Lake, East Central China [J]. Frontiers Earth Science, 2012, 6(1): 39–47.
[3] ZHANG G Z, LIU H, JIA D W. River basin management based on themechanisms of water rights trading [J]. Procedia Environmental Science, 2010, 6(2): 665–673.
[4] SUN Yue-bing, ZHOU Qi-xing, XIE Xiao-kui, LIU Rui. Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contaminationof urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174: 455–462.
[5] LI Fei, HUANG Jin-hui, ZENG Guang-ming, YUAN Xing-zhong, LI Xiao-dong, LIANG Jie. Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 132: 75–83.
[6] SMITH T B, OWENS P N. Individual and cumulative effects of agriculture, forestry and metalmining activitieson the metal and phosphorus content of fluvial fine-grained sediment; Quesnel River Basin, BritishColumbia, Canada [J]. Science of the Total Environmental, 2014, 496: 435–442.
[7] IP CCM, LI X D, ZHANG G, WAI OWH, LI Y S. Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China [J]. Environmental PollutIon, 2007, 147: 311–323.
[8] LI Fei, ZHANG Jing-dong, YANG Jun, LIU Chao-yang, ZENG Guang-ming. Site-specific risk assessment and integrated management decision-making: A case study of a typical heavy metal contaminated site, Middle China [J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 2016, 22(5): 1224–1241.
[9] YUAN He-zhong, SHEN Ji, LIU En-feng WANG Jian-jun, MENG Xiang-hua. Assessment of nutrients and heavy metals enrichment in surface sediments from Taihu Lake, a eutrophic shallow lake in China [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2011, 33(1): 67–81.
[10] DE-MIGUEL E, IRIBARREN I, CHACON E, ORDONEZ A, CHARLESWORTH S. Risk-based evaluation of the exposure of children to trace elementsin playgrounds in Madrid (Spain) [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 66(3): 505–513.
[11] IQBAL J, SHAH M H, AKHTER G. Characterization, source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace metals in freshwater Rawal Lake, Pakistan [J]. Journal of Geochemitry Exploration, 2013, 125(125): 94–101.
[12] LI Fei, HUANG Jin-hui, ZENG Guang-ming, HUANG Xiao-long, LI Xiao-dong, LIANG Jie. Integrated source apportionment, screening risk assessment and risk mapping of heavy metals in surface sediments: A case study of the Dongting Lake, Middle China [J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 2014, 20(5): 1213–1230.
[13] CHEN Hong-wei, AN Jing, WEI Shu-he, GU Jian. Spatial patterns and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils in a resource-exhausted city, northeast China [J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(9): e0137694.
[14] LALAH J O, OCHIENG E Z, WANDIGA S O. Sources of heavy metal input into Winam Fulf, Kenya [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 81(3): 277–284.
[15] BANERJEE K, SENTHILKUMAR B, PURVAJA R, RAMESH R. Sedimentationand trace metal distribution in selected locations of Sundarbansmangroves and Hooghly estuary, Northeast coast of India [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2012, 34(1): 27–42.
[16] LI Fei, ZHANG Jing-dong, HUANG Jin-hui, HUANG Da-wei, YANG Jun, SONG Yong-wei, ZENG Guang-ming. Heavy metals in road dust from Xiandao District, Changsha city, China: Characteristics, health risk assessment and integrated source identification [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23: 13100–13113.
[17] LI Fei, ZHANG Jing-dong, LIU Chao-yang, XIAO Min-si, WU Zi-xian. Distribution, bioavailability and probabilistic integrated ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Honghu Lake, China [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2018, 116: 169–179.
[18] LIU Hui, LIANG He-cheng, LIANG Ying, ZHANG Dan, WANG Cheng, CAI He-sheng. Distribution of phthalate esters in alluvial sediment: A case study at Jianghan Plain, Central China [J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(4): 382–388.
[19] YUAN Lin-xi, QI Shi-hua, WU Xiao-guo, WU Chen-xi, XING Xin-li, GONG Xiang-yi. Spatial and temporal variations of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water and sediments from Honghu Lake, China [J]. Journal of Geochemistry Exploration, 2013, 132(3): 181–187.
[20] CHENG Xiao-ying, LI Shi-jie. An analysis on the evolvement processes of lakeeutrophication and their characteristics of the typical lakes in themiddle and lower reaches of Yangtze River [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(13): 1603–1613.
[21] GUI Feng, YU Ge. Numerical simulations of nutrient transport changesin Honghu Lake Basin, Jianghan Plain [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(13): 2353–2363.
[22] BIANRONG C. Quantitative impacts of climate change and human activities on water-surface area variations from the 1990s to 2013 in Honghu Lake, China [J]. Researchgate, 2015, 7: 2881–2899.
[23] YANG Yu-yi, CAO Xin-hua, ZHANG Miao-miao, WANG Jun. Occurrence and distribution of endocrine-disrupting compoundsin the Honghu Lake and East Dongting Lake along the Central Yangtze River, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(22): 17644–17652.
[24] BAN Xun, WU Qiu-zhen, PAN Bao-zhu, DU Yun, FENG Qi. Application of composite water quality identification index on the water quality evaluation in spatial and temporal variations: A case study in Honghu Lake, China [J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2014, 186(7): 4237–4247.
[25] MO Ming-hao, WANG Xue-lei, WU Hou-jian, CAI Shun-ming, ZHANG Xiao-yang, WANG Hui-liang. Ecosystem health assessment of Honghu Lake wetland of China using artificial neural network approach [J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 2009, 19: 349.
[26] MEZA-MONTENEGRO M M, GANDOLFI A J, SANTANA-ALCANTAR M E, KLIMECKIW T, AGUILAR-APODACA M G, DEL RIO-SALAS R. Metals in residential soils and cumulative risk assessment in Yaqui and Mayo agricultural valleys, northern Mexico [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 433: 472–481.
[27] LI Fei, ZHANG Jing-dong, JIANG Wei, LIU Chao-yang, ZHANG Zhong-min, ZHANG Cheng-de, ZENG Guang-ming. Spatial health risk assessment and hierarchical risk management for mercury in soils from a typical contaminated site, China [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2017, 39(4): 923–934. DOI: 10.1007/s10653- 016-9864-7.
[28] ZENG Xiao-xia, LIU Yun-guo, YOU Shao-hong, ZENG Guang-ming, TAN Xiao-fei, HU Xin-jiang. Spatial distribution, health risk assessment and statisticalsource identification of the trace elements in surface waterfrom the Xiangjiang River, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(12): 9400–9412.
[29] United States Environmental Protection Agency. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume 1 Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment [R]. Washington D.C.: US Environmental Protection, EPA 540-R-99-005, 2004.
[30] LI Fei, HUANG Jin-hui, ZENG Guang-ming, YUAN Xin-zhong, LIANG Jie, WANG Xiao-yu. Multimedia health risk assessment: a case study of scenario-uncertainty [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(10): 2901–2909.
[31] PHAN K, PHAN S, HUOY L, SUY B, WONG M H, HASHIM J H. Assessing mixed trace elements in groundwater and their health risk of residents living in the Mekong River basin of Cambodia [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 182: 111–119.
[32] HUANG Jin-hui, LI Fei, ZENG Guang-ming, LIU Wen-chu, HUANG Xiao-long, XIAO Zhi-hua, WU Hai-peng, GU Yan-ling, LI Xue, HE Xiao-xiao, HE Yan. Integrating hierarchical bioavailability and population distribution into potential eco-risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust: A case study in Xiandao District, Changsha city, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 541: 969–976.
[33] LI Fei, MAO Wen-juan, LI Xue, WANG Xiao-yu, XIAO Zhi-hua, ZHOU Yao-yu. Characterization of Microcystis Aeruginosa immobilized in complex of PVA and sodium alginate and its application on phosphorous removal in wastewater [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(1): 95–102.
[34] United States Environmental Protection Agency. Risk-based concentration table [R]. 2013.
[35] World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking-water quality, recommendations incorporating 1st and 2nd addenda,13th ed [R]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2008.
[36] LI Si-yue, ZHANG Quan-fa. Risk assessment and seasonal variations of dissolvedtrace elements and heavy metals in the Upper Han River, China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1–3): 1051–1058.
[37] RODRIGUEZ-PROTERU R, GRANT R L. Toxicity evaluation and humanhealth risk assessment of surface and ground water contaminated byrecycled hazardous waste materials [J]. Water Pollution, 2005, 2: 133–189.
[38] LI Fei, HUANG Jin-hui, ZENG Guang-ming, LIU Wen-chu, HUANG Xiao-long, HUANG Bin, GU Yan-ling, SHI Li-xiu, HE Xiao-xiao, HE Yan. Toxic metals in topsoil under different land uses from Xiandao District, middle China: Distribution, relationship with soil characteristics and health risk assessment [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22: 12261–12275.
[39] United States Environmental Protection Agency. Drinking water standards and health advisories. EPA 822-R-09-011 Office of Water [R]. US Environmental Protection Agency, 2009.
[40] GB5749–2006. Chinese State Standards (CSS) for drinking water quality, 2007 [S]. (in Chinese)
[41] KLAVINS M, BRIEDE A, RODINVO V, KOKORITE I, PARELE E. Heavy metals in rivers of Latvia [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2000, 262(1, 2): 175.
[42] CARAFA R, FAGGIANO L, REAL M, MUNNE A, GINEBRADE A. Water toxicity assessment and spatial pollution patterns identification in a mediterranean river basin district [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2011,409(20): 4269–4279.
[43] VAROL M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the tigris river (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,195(1): 355–364.
[44] LI Wen-ming, YANG Zhong-fang, ZHOU Lei, TANG Man, YUAN Guo-li. Geochemical characteristic and fluxes of heavy metals in water system of the poyang lake [J]. Geoscience,2014, 28(3): 512–522.
[45] LIU Jia-yu, LIANG Jie, YUAN Xing-zhong, ZENG Guang-ming, YUAN Yu-jie, WU Hai-peng, HUANG Xiao-long, LIU Jun-feng, HUA Shan-shan, LI Fei, LI Xiao-dong. An integrated model for assessing heavy exposure risk to migratory birds in wetland ecosystem: A case study in Dongting Lake Wetland, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 135: 14–19.
[46] ZHENG Sha-sha, WANG Pei-fang, WANG Chao, HOU Jun, QIAN Jin. Distribution of metals in water and suspended particulate matter during the resuspension processes in Taihu Lake sediment, China [J]. Quaternary International, 2013, 286(3): 94–102.
[47] HALL LWJ, SCOTT M C, KILLEN W D. A screening level probabilistic ecological risk assessment of copper and cadmium in the Chesapeake Bay watershed [R]. Annapoils: Environmental Protection Agency, 1997.
[48] FARKAS A, ERRATICO C, VIGANO L. Assessment of the environmental significance of heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments of the River Po [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 68(4): 761–768.
[49] WU Bing, ZHAO D, JIA H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X X, CHENG S P. Preliminary risk assessment of trace metal pollution in surface water from Yangtze River in Nanjing Section, China [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2009, 82(4): 405–409.
[50] SURESH G, SUTHARSAN P, RAMASAMY V, VENKATACHALAPATHY R. Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India [J]. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 2012, 84(10): 117–124.
[51] LU Xin-wei, WANG Li-jun, LI L Y, LEI Kai, HUANG Li, KANH Dan. Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Material, 2010, 173(1–3): 744–749.
[52] CHEN Lin-hua, NI Wu-zhong, LI Xue-lian, SUN Jian-bing. Investigation of heavy metal concentration in commercial fertilizers commonly-used [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2009, 26(2): 223–227. (in Chinese)
[53] ZHANG Tao, CHEN Jian-wu, HE Li. Heavy metal residues in the muscle of Monopterus albus from Jianghan Plain [J]. Chinese Fishery Quality & Standards, 2015, 5(1): 19–27. (in Chinese)
[54] ZENG Zhao-hua. Background feature and formation of Zn element in the groundwater in the lower-middle reachesarea of the yangtse river [J]. Chongqing Environmental Science. 1997, 19(2): 36–39. (in Chinese)
[55] ZHAO Da-shun, CHEN Hhui-min. Arsenic pollution situation and poison in water [J]. Liaoning Urban Rural Environmental Science Technology, 2005(4): 55–56. (in Chinese)
[56] LIU Yang, FU Qiang, GAO Jun, XU Wang-gu, YIN Bo, CAO Ya-qiao. Concentrations and safety evaluation of heavy metals in aquatic products of Yancheng, Jiangsu Province [J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(10): 4081–4089.
[57] LI Fei, CAI Ying, ZHANG Jing-dong. Spatial characteristics, health risk assessment and sustainable management of heavy metals and metalloids in soils from central China [J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(1): 91.
[58] QIU Yao-wen, LIN Duan, LIU Jing-liu, ZENG Eddy Y. Bioaccumulation of trace metals in farmed fish from South China and potential risk assessment [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2010, 74(3): 284–293.
(Edited by HE Yun-bin)
中文导读
洪湖水体中微量元素的空间分布特征、风险评价及潜在来源识别
摘要:本文对洪湖10个代表性采样点表层水中的锌(Zn)、铜(Cu)、镉(Cd)、铬(Cr)和砷(As)5种微量元素进行研究。研究结果表明,洪湖水体中该5种微量元素的浓度均未超过中国的水质安全标准。各个采样点中5种微量元素的单独非致癌风险及综合非致癌风险水平均未超过相应评价方法的可接受风险限值。皮尔森相关分析和主成分分析结果表明洪湖水体中的Zn和Cu主要来源于天然冲击作用和农业面源污染,Cr和As主要来源于工业废水,而Cd同时来源于农业面源污染和工业污染。此外,各个采样点的聚类分析结果表明采样点S3、S5、S6和S10被判定为重度污染区域,而S4和S9为中度污染区域。
关键词:空间分布特征;风险评价;来源识别;微量元素;洪湖
Foundation item: Projects(51578222, 51178172) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects(17Z017, 17G025) supported by the Humanities and Social Science Project of Hubei Provincial Education Department, China; Project(1718WT15) supported by the Hubei College Student Affairs Research Institute, China; Projects(2016J1410, 2016J1411) supported by the Graduate Innovative Education Program of Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, China
Received date: 2017-01-22; Accepted date: 2017-04-01
Corresponding author: ZHANG Jing-dong, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86–27–88385099; E-mail: jdzhang@zuel.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0003- 4791-3264

