DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.11.01
2060铝锂合金的淬透性
刘 晨 1,李劲风1, 2,宁 红1,刘丹阳1,陈永来3,张绪虎3,马鹏程3,谭澄宇1
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
3. 航天材料及工艺研究所,北京 100076)
摘 要:利用新型的薄板叠层端淬法结合时效后强度变化,评价2060铝锂合金的淬透性,并采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、场发射透射电子显微镜(STEM)及能谱(EDS)对末端淬火并T8时效后的微观组织进行了分析。结果表明:以抗拉强度下降5%作为淬透深度的判断依据,则2060铝锂合金的淬透深度约为15 mm。随着距淬火端距离的增大,抗拉强度依次降低直至稳定,但在距淬火端12~18 mm的区间内,强度发生较明显变化。端淬过程中析出的富Cu相降低了固溶体过饱和程度,阻碍后续时效过程中同一位置T1相(Al2CuLi)的析出和长大,导致合金抗拉强度逐渐减小。
关键词:2060铝锂合金;淬透性;强度;微观组织
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-11-2451-08 中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
新型铝锂合金因具有高比强度、高比刚度、减重效果明显等优点,是理想的航空航天结构材料[1-3]。相比第一代和第二代铝锂合金,第三代铝锂合金具有更高的强韧性、热稳定性、耐损伤性和较好的耐蚀性,因此可作为为大型航空飞行器机身蒙皮和机翼壁板的新型结构材料[4-5]。
2060铝锂合金是2000年以后开发的第三代铝锂合金,目前已用于C919飞机蒙皮。在成分设计上,2060铝锂合金提高了Cu、Li质量比,有利于促进主要强化相T1(Al2CuLi)相的析出[6]。除此之外,合金中Mg含量(0.7%~1.1%,质量分数)显著高于其他铝锂合金,如2195、2050、2198等。研究表明[7],铝合金中合金化元素含量高,合金存在较高淬火敏感性。在Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金和Al-Cu合金中,当Mg、Zn和Mg、Cu质量比增加时,合金淬火敏感性增大[8]。在可热处理强化铝合金中,淬火敏感性与过饱和固溶体稳定性直接相关[9],从而影响可热处理强化铝合金的淬透性,并在很大程度上决定了合金在厚截面构件上的应用。
目前,针对传统2xxx系和7xxx系铝合金淬透性的研究报道较多[10-15],这些研究多采用传统Jominy端淬法,测试末端淬火并时效后距淬火端不同距离处的硬度变化。国内对铝锂合金淬透性的研究报道非常少,孙良省等[16]采用上述方法(端淬+硬度测试)对2099铝锂合金淬透性进行了简单研究。但在可热处理强化铝合金中,强度性能的工程意义远大于硬度性能;另外,由于铝锂合金厚板中心层与表层组织的差异,导致淬火并时效后中心层强度高于表层[18-19]。基于上述原因,李劲风等[17-18]设计了一种新型的薄板叠层端淬结合强度测试的淬透性研究方法。该方法在保证淬火前原始组织一致的同时,利用强度变化有效地进行淬透性的评价,并已应用于2195和2050铝锂合金的淬透性的定量评价[18]。
本文作者采用“薄板叠层端淬”并结合强度测试,研究高Mg含量2060铝锂合金距淬火末端不同位置的强度和微观组织,并定量评价2060铝锂合金的淬透性。
1 实验
实验用2060铝锂合金为2 mm厚度冷轧薄板,其化学成分为Al-4.0Cu-0.8Li-0.7Mg-0.3Mn-0.1Zr- 0.26Ag-0.47Zn(质量分数,%)。末端淬火方法采用如图1所示的“薄板叠层端淬法”[17]。试样于盐浴中505 ℃固溶40 min后,立刻转移到末端淬火装置上进行喷水冷却,转移时间小于3 s;待试样完全冷却至室温(20 ℃)后,拆卸薄板并进行T8时效处理(5%预变形,145 ℃、30 h时效)。而后在离淬火端不同距离的位置处沿轧制方向切割拉伸试样。为方便表述,本文用“Z”表示距淬火端的距离。
拉伸性能测试在MTS810电液伺服万能材料试验机上进行,拉伸试样长度为90 mm,其中平行段长度为42 mm,平行段宽度为4 mm,拉伸应变速率为 0.01 s-1。
采用FEI Quanta200扫描电镜(SEM)进行晶界及晶界析出相观察。SEM样品表面抛光,需Keller试剂腐蚀处理,腐蚀时间为10 s。
采用Tecnai G220 ST型透射电镜(TEM)进行时效后的微观组织观察。TEM样品经机械减薄和电解双喷减薄制取,电解溶液为75%CH3OH+25%HNO3(体积分数),温度为-25 ℃以下,工作电压为40 V。部分试样采用TecnaiG2 F20 S-TWIN TMP场发射透射电镜(STEM)进行观察。

图1 “薄板叠层”法末端淬火示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of end quenching of using cold- rolled sheets
2 实验结果
2.1 淬透性曲线
图2(a)所示为2060铝锂合金末端淬火并T8时效后距淬火端不同距离处试样中心位置抗拉强度的变化曲线。由图2(a)可知,随着距淬火端距离的增加,抗拉强度呈先逐渐下降后趋于平缓的趋势。淬火端(Z=0 mm),时效后抗拉强度为524.1 MPa;距淬火端距离增加至30 mm时,抗拉强度降低至468.3 MPa。而后随距淬火端距离进一步增加,抗拉强度基本保持稳定,在远离淬火端位置(Z=66 mm)处,合金抗拉强度下降至457.7 MPa,但相比Z=30 mm位置,其降低幅度仅为10.6 MPa。
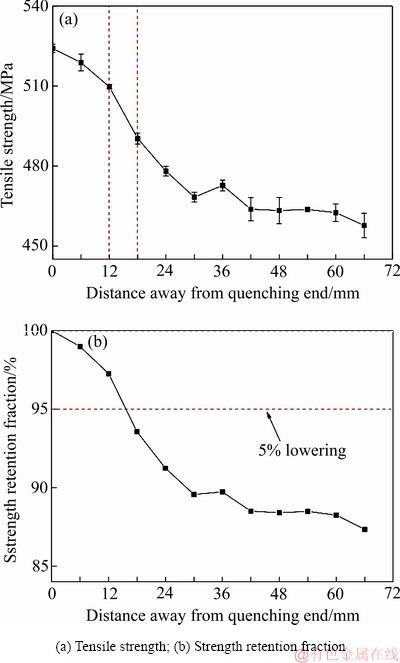
图2 抗拉强度及抗拉强度保留分数与距淬火端距离的关系
Fig. 2 Relationships between tensile strength and its strength retention fraction and distance away from quenching end
综合分析强度变化趋势,一个比较显著的特征是距淬火端Z=12 mm至Z=18 mm区间内抗拉强度下降较为迅速。相比距淬火端Z=12 mm位置,离淬火端Z=18 mm处抗拉强度下降了约19 MPa。距淬火端Z=12 mm至Z=18 mm区间内抗拉强度发生较显著变化,说明该区间内微观组织发生了明显的变化。
为了更直观地表示抗拉强度下降趋势,绘制了不同位置处抗拉强度相对于淬火端抗拉强度的比值(抗拉强度保留分数)随距离的变化曲线。如图2(b)所示,抗拉强度保留分数随着距淬火端距离的增加而逐渐减小。距淬火端Z=6 mm位置的抗拉强度与淬火端Z=0 mm处相比,下降了仅约1%;远离淬火端Z=60 mm处抗拉强度下降了约12.7%。在可热处理强化铝合金的“淬透性”的传统评价方法中,硬度下降10%对应的深度在某些文献中定义为淬透层深度[20-21]。李劲风等[18]采用的“薄板叠层端淬法”研究2195和2050铝锂合金淬透性时,将抗拉强度下降5%的深度定义为淬透层深度。从图2(b)中还可以看出,本研究中2060铝锂合金抗拉强度下降5%对应的位置处于距离淬火端12 mm和18 mm之间,通过插值法基本可确定为距离淬火端Z=15 mm位置处。根据上述淬透性评价原则可以认为,2060铝锂合金室温水淬的淬透深度约为15 mm。而采用该方法评定2195铝锂合金淬透性,其淬透层深度为18~24 mm,而2050铝锂合金淬透层深度为36~42 mm[18],说明2060铝锂合金的淬透性低于2195和2050铝锂合金的。
2.2 显微组织
距淬火端不同位置晶界处试样的SEM像及能谱分析如图3所示。远离淬火端Z=60 mm处,沿晶界分布有许多呈白色的第二相粒子(如图3(a)中箭头所示),长度方向尺寸约为2 μm;经能谱(EDS)分析,这些白色第二相粒子为富Cu相(见图3(c))。在靠近淬火端Z=6 mm位置(见图3(b))的晶界则没有观察到类似的第二相粒子。
鉴于距淬火端12 mm至18 mm处抗拉强度变化幅度较大,因此,首先采用TEM分别进行了这两个位置的微观组织观察,如图4所示。在距淬火端Z=12 mm位置,由[112]Al晶带轴的选区衍射谱(SAED)可以观察到明锐的的T1相斑点芒线,在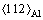 方向观察的相同位置的TEM暗场(Dark field,DF)像和明场(Bright field,BF)像中,可以发现T1相弥散分布(见图4(a)和(b))。在距离淬火端Z=18 mm处,T1相斑点芒线仍然存在,但是
方向观察的相同位置的TEM暗场(Dark field,DF)像和明场(Bright field,BF)像中,可以发现T1相弥散分布(见图4(a)和(b))。在距离淬火端Z=18 mm处,T1相斑点芒线仍然存在,但是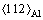 方向TEM暗场像中T1相数量略为减少,尺寸变小,而且分布不均匀,局部区域没有T1相分布(如箭头所示);而相同位置的明场像(见图4(d))中可以发现两种尺寸差异较大的第二相粒子,其中A粒子数量较多,形似“纺锤状”,长度方向尺寸约为0.1 μm;B粒子数量较少,呈粗圆棒状,长度方向尺寸约为0.2 μm。图4(e)和(f)分别为A粒子和B粒子的能谱分析,表明“纺锤状”A粒子为富Cu相,而B粒子为富Cu、Mn相。由于图4(c)和(d)为同一位置的暗场像和明场像照片,对比图4(c)和(d)分析可以发现,这两种粒子(富Cu相A粒子和富Cu、Mn相B粒子)所在的局部区域没有或缺少T1相析出(见图4(c)箭头所示处)。
方向TEM暗场像中T1相数量略为减少,尺寸变小,而且分布不均匀,局部区域没有T1相分布(如箭头所示);而相同位置的明场像(见图4(d))中可以发现两种尺寸差异较大的第二相粒子,其中A粒子数量较多,形似“纺锤状”,长度方向尺寸约为0.1 μm;B粒子数量较少,呈粗圆棒状,长度方向尺寸约为0.2 μm。图4(e)和(f)分别为A粒子和B粒子的能谱分析,表明“纺锤状”A粒子为富Cu相,而B粒子为富Cu、Mn相。由于图4(c)和(d)为同一位置的暗场像和明场像照片,对比图4(c)和(d)分析可以发现,这两种粒子(富Cu相A粒子和富Cu、Mn相B粒子)所在的局部区域没有或缺少T1相析出(见图4(c)箭头所示处)。
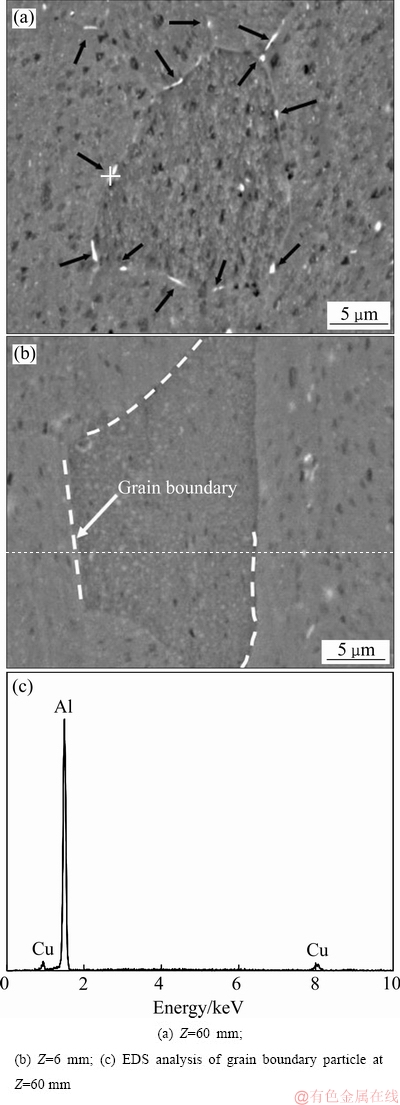
图3 离淬火端不同距离处试样的SEM像及能谱分析
Fig. 3 SEM images and EDS analysis of aged specimens at different distances away from quenching end
图5所示为距淬火端Z=60 mm处的[112]Al晶带轴SAED谱和TEM明场像照片及相应粒子能谱分析。[112]Al晶带轴SAED谱中T1相的斑点非常微弱(见图5(a)),但暗场像中很难观察到T1相,说明该位置析出T1相非常少。明场像中则可观察到大量显著粗化的“纺锤形”的粒子(见图5(b))。能谱分析(见图5(c))表明这些“纺锤形”第二相粒子仍然主要为富Cu相。
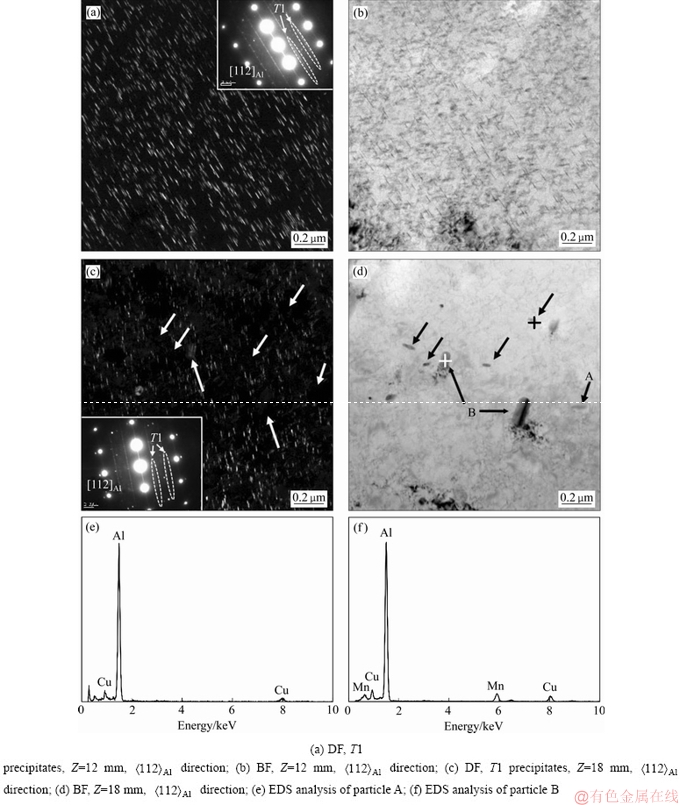
图4 距淬火端Z=12 mm和Z=18 mm处试样的TEM像及能谱分析
Fig. 4 TEM images and EDS analysis of aged specimens at distances of 12 mm and 18 mm away from quenching end
为确认远离淬火端位置析出T1相特征,进一步采用STEM观察了远离淬火端的微观组织,如图6所示。远离淬火端形成了大量粗大密集的第二相粒子(见图6(a))。而仔细观察粗大粒子的间隙区域,仍可发现一些细小T1相析出(见图6(b)箭头所示处)。
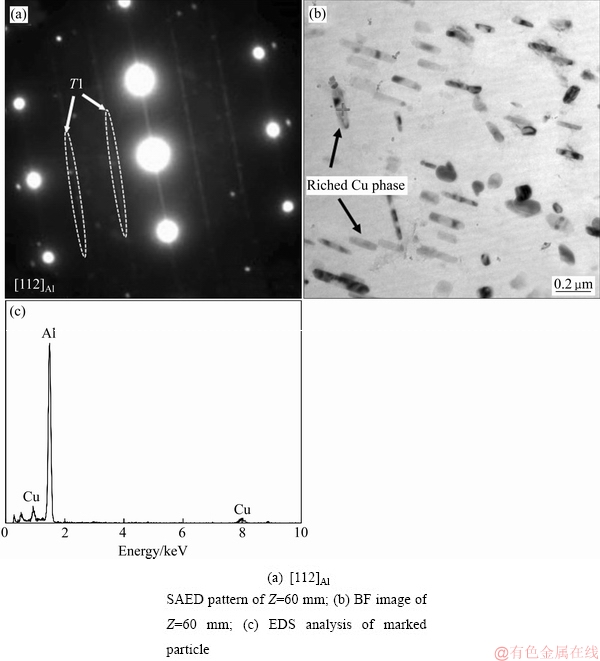
图5 远离淬火端Z=60 mm处试样SAED谱、TEM像及能谱分析
Fig. 5 SAED pattern, TEM image and EDS analysis of samples at distance of 60 mm away from quenching end
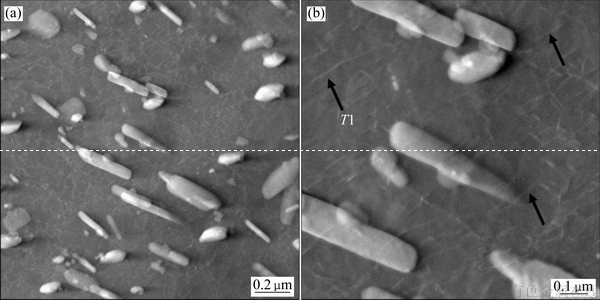
图6 远离淬火端Z=60 mm处试样的STEM像
Fig. 6 STEM images of samples at distance of 60 mm away from quenching end
3 分析与讨论
根据上述组织观察,合金远离淬火端发现有同时含Cu、Mn的第二相粒子,这些第二相应为Al20Cu2Mn3相,主要形成于退火过程。且这种粒子在所有含Cu、Mn的铝锂合金中均有发现[22],实际上在淬火端也同样发现这种粒子存在。另外,一个重要现象是距淬火端一定距离,晶界处及晶内均形成了富Cu的第二相粒子;而且随该距离增加,晶内“纺锤状”富Cu相粒子数量增加,尺寸变大。基于其变化趋势,可以确定这些富Cu相粒子是由于冷却速率较低,在端淬过程中从固溶体中析出。
端淬过程中由于不同位置冷却速度的差异,导致相应区域在端淬过程中形成不同数量及尺寸的富Cu相,从而影响后续时效过程中T1相的析出。在紧邻淬火端,冷却速度高,淬火过程中固溶体未发生脱溶,淬火后的固溶体过饱和程度高,时效后T1相数量多,尺寸(直径)较大,因而具有较高强度。在距淬火端一定距离位置,端淬过程中在晶内和晶界形成富Cu的第二相粒子,消耗了基体中的一部分固溶Cu原子,使淬火后固溶体过饱和程度降低,这一方面阻碍了在富Cu相同一局部位置T1相的析出,如图4(c)和(d)所示。同时也导致T1相尺寸(直径)有所降低,相应地合金强度有所降低。特别是在远离淬火端位置(Z=60 mm),端淬过程中晶内析出的粗大富Cu相粒子数量更多、尺寸更大(见图5),后续时效过程中对T1相的析出阻碍作用更加强烈,导致T1相的析出和长大更为困难,合金的强度下降幅度更大。
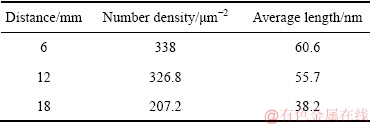
为尽量精确表征距淬火端不同距离处时效析出相T1相的分布特征,分别进行了不同位置T1相的密度及尺寸统计。析出相尺寸及数密度的统计是通过手动计数完成,从每个位置 方向观察的TEM暗场像中选取3~5张照片,最终计算其平均值。而在Z=60 mm位置处,[112]Al晶带轴SAED谱中T1相的斑点非常微弱(见图5(a)),TEM暗场像中很难观察到T1相,因此未统计Z=60 mm位置处的相关信息。Z=6 mm、Z=12 mm和Z=18 mm位置的统计结果如表1所示。距淬火端距离Z=6 mm及Z=12 mm位置处T1相差别不大。而在距淬火端Z=18 mm处,T1相数密度和尺寸明显降低,导致该处强度有明显下降。因此,基于强度和析出相的变化,可将2060铝锂合金的淬透层深度评定为15 mm左右。
方向观察的TEM暗场像中选取3~5张照片,最终计算其平均值。而在Z=60 mm位置处,[112]Al晶带轴SAED谱中T1相的斑点非常微弱(见图5(a)),TEM暗场像中很难观察到T1相,因此未统计Z=60 mm位置处的相关信息。Z=6 mm、Z=12 mm和Z=18 mm位置的统计结果如表1所示。距淬火端距离Z=6 mm及Z=12 mm位置处T1相差别不大。而在距淬火端Z=18 mm处,T1相数密度和尺寸明显降低,导致该处强度有明显下降。因此,基于强度和析出相的变化,可将2060铝锂合金的淬透层深度评定为15 mm左右。
表1 距离淬火端不同位置处T1相的数密度及尺寸
Table 1 Number density and size of T1 precipitates at location with different distance away from quenching end
4 结论
1) 采用新型薄板叠层端淬法,结合后续T8时效强度变化,进行了2060铝锂合金的淬透性评价。
2) 随距淬火端距离增加,T8时效后合金强度降低。以强度降低5%作为淬透性评价依据,则2060铝锂合金淬透性深度约为15 mm,明显低于2195和2050铝锂合金的。
3) 端淬过程中,距淬火端一定距离的位置(12~18 mm)开始析出明显的富Cu相,降低了固溶体过饱和程度,阻碍后续时效过程中同一位置T1相的析出,并减小T1相尺寸,导致时效后合金强度较明显降低。
REFERENCES
[1] ZOU Cheng-lu, GENG Gui-hong, CHEN Wei-ye. Development and application of aluminium-lithium alloy[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 599/601: 12-17.
[2] WANHILL R J H, BRAY G H. Aerostructural design and its application to aluminum-lithium alloys[M]. Aluminum- Lithium Alloys, 2014: 27-58.
[3] RIOJA R J, LIU J. The evolution of Al-Li base products for aerospace and space applications[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012, 43(9): 3325-3337.
[4] ALEXOPOULOUS N D, MIGKLIS E, STYLIANOS A, MYRIOUNIS D P. Fatigue behavior of the aeronautical Al-Li (2198) aluminum alloy under constant amplitude loading[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2013, 56(11): 95-105.
[5] RIOJA R J. Fabrication methods to manufacture isotropic Al-Li alloys and products for space and aerospace applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 257(1): 100-107.
[6] 郑子樵, 李劲风, 陈志国, 李红英, 李世晨, 谭澄宇. 铝锂合金的合金化与微观组织演化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10):2337-2351.
ZHENG Zi-qiao, LI Jin-feng, CHEN Zhi-guo, LI Hong-ying, LI Shi-chen, TAN Cheng-yu. Alloying and microstructural evolution of Al-Li alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2337-2351.
[7] LIU Sheng-dan, ZHONG Qi-min, ZHONG Yong, LIU Wen-jun, ZHANG Xin-ming, DENG Yun-lai. Investigation of quench sensitivity of high strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys by time-temperature-properties diagrams[J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31(6): 3116-3120.
[8] 刘文军. Al-Zn-Mg-Cu铝合金淬火析出行为及淬火敏感性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2011.
LIU Wen-jun. The research about the quench induced precipitation and quenching sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2011.
[9] ZHANG Zhi-hui, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHU Bao-hong, ZUO Yu-ting. Stability of supersaturated solid solution of quenched Al-X(X=Zn, Mg, Cu)binary alloys[J]. Rare Metals, 2014, 33(2): 139-143.
[10] NEWKIRK J W, MACKENZIE D S. The Jominy end quench for light-weight alloy development[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2000, 9(4): 408-415.
[11] 张新明, 刘胜胆, 游江海, 张 翀, 张小艳. 时效对7055铝合金淬火敏感效应的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(2): 260-264.
ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan, YOU Jiang-hai, ZHANG Chong, ZHANG Xiao-yan. Influence of aging on quench sensitivity effect of 7055 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(2): 260-264.
[12] 刘君城, 张永安, 刘红伟, 李锡武, 李志辉, 朱宝宏, 熊柏青. 基于末端淬火试验2124铝合金的淬透性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(11): 2118-2123.
LIUJun-cheng, ZHANGYong-an, LIUHong-wei, LIXi-wu, LI Zhi-hui, ZHU Bao-hong, XIONG Bai-qing. Hardenability of 2124 aluminum alloy based on Jominy end quench test[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(11): 2118-2123.
[13] 刘胜胆, 李承波, 李璐璐, 邓运来, 张新明. 7055铝合金厚板的淬透性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(6): 1564-1569.
LIU Sheng-dan, LI Cheng-bo, LI Lu-lu, DENG Yun-lai, ZHANG Xin-ming. Hardenability of 7055 aluminum alloy plate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(6): 1564-1569.
[14] 李承波, 张新明, 韩素琦, 刘胜胆, 邓运来. 时效对7085铝合金厚板淬火引起的不均匀性影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(9): 1823-1831.
LI Cheng-bo, ZHANG Xin-ming, HAN Su-qi, LIU Sheng-dan, DENG Yun-lai. Effect of aging on quench-induced in homogeneity of 7085 aluminum alloy thick plate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(9): 1823-1831.
[15] KANG Lei, ZHAO Gang, TIAN Ni, ZHANG Hai-tao. Computation of synthetic surface heat transfer coefficient of7B50 ultra-high-strength aluminum alloy during spray quenching[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(5): 989-997.
[16] 孙良省, 许晓静, 张振强, 吴 瑶, 邓平安. 2099铝锂合金的淬透性研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2013, 42(22): 156-158.
SUN Liang-sheng, XU Xiao-jing, ZHANG Zhen-qiang, WU Yao, DENG Ping-an. Study on hardenability of 2099 Al-Li alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2013, 42(22): 156-158.
[17] 李劲风, 刘丹阳, 郑子樵. 一种测试金属材料淬透性的方法: 中国, ZL201710225016.6[P]. 2018-06-15.
LI Jin-feng, LIU Dan-yang, ZHENG Zi-qiao. A method for testing hardenability of metallic materials: China, ZL201710225016.6[P]. 2018-06-15.
[18] LI Jin-feng, LIU Dan-yang, NING Hong, LIU Chen, MA Peng-cheng, CHEN Yong-lai. Experimental quantification of “hardenability” of 2195 and 2050 Al-Li alloys by using cold-rolled sheets[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 137: 180-188.
[19] 王海金, 郑子樵, 范雪松. 2297-T87铝合金厚板力学性能的各向异性与厚向不均匀性[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(5): 1196-1203.
WANG Hai-jin, ZHENG Zi-qiao, FAN Xun-song. Mechanical anisotropy and inhomogeneity through thickness of 2297-T87 aluminum alloy thick plate[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(5): 1196-1203.
[20] DENG Yun-lai, WAN Li, ZHANG Yu-ya, ZHANG Xin-ming. Influence of Mg content on quench sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(13):4636-4642.
[21] LIM S T, YUN S J, NAM S W. Improved quench sensitivity in modified aluminum alloy 7175 for thick forging applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 371(1): 82-90.
[22] ZHU Ri-hua, LIU Qing, LI Jin-feng, XIANG Sheng, CHEN Yong-lai, ZHANG Xu-hu. Dynamic restoration mechanism and physically based constitutive model of 2050 Al-Li alloy during hot compression[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 650: 75-85.
[23] HUANG J C, ARDELL A J. Crystal structure and stability of T1 precipitates in aged Al-Li-Cu alloys[J].Metal Science Journal, 2013, 3(3): 176-188.
Hardenability of 2060 Al-Li alloy
LIU Chen1, LI Jin-feng1, 2, NING Hong1, LIU Dan-yang1, CHEN Yong-lai3, ZHANG Xu-hu3, MA Peng-cheng3, TAN Cheng-yu1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Mental Materials Science and Engineering, Ministry of Education, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Aerospace Research Institute of Materials and Processing Technology, Beijing 100076, China)
Abstract: The harden ability of 2060 Al-Li alloy was experimentally evaluated by using cold-rolled thin sheets, which combined end-quenching with strength change after aging. The scanning electron microscopy(SEM), transmission electron microscopy(TEM), scanning transmission electron microscopy(STEM) and energy dispersive spectrometer(EDS) were used to analyze the microstructure of samples with T8-aging following end-quenching. The results show that the quenching depth of 2060 Al-Li alloy is 15 mm, the tensile strength is reduced by 5% is defined as the quenching depth. With the distance away from the quenching end increasing, the tensile strength gradually decreases to a stable level. Moreover, there is a significant decreasing in the tensile strength at the location from 12 mm to 18 mm. During the end-quenching process, the Cu-rich phase which reduces the supersaturation of the solid solution precipitates and hinders the precipitation and growth of T1 phase(Al2CuLi) in the same region during the subsequent aging process. The tensile strength is therefore decreased gradually.
Key words: 2060 Al-Li alloy; hardenability; strength; microstructure
Foundation item: Project(2013AA032401) supported by Key National High-tech Research and Development Program of China
Received date: 2018-10-29; Accepted date: 2019-03-27
Corresponding author: LI Jin-feng; Tel: +86-13278861206; E-mail: lijinfeng@csu.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2013AA032401)
收稿日期:2018-10-29;修订日期:2019-03-27
通信作者:李劲风,教授,博士;电话:13278861206;E-mail:lijinfeng@csu.edu.cn