文章编号:1004-0609(2011)05-0939-06
MB8镁合金CO2激光焊接工艺及接头性能
高 明, 曾晓雁, 唐海国
(华中科技大学 光电科学与工程学院,武汉 430074)
摘 要:采用高功率CO2激光器对MB8镁合金进行一系列激光焊接工艺试验,并对焊缝成形的形成规律、接头的微观组织和力学性能进行研究。结果表明:焊缝熔深基本和激光功率呈正比关系,激光功率每增加1 kW,熔深约增加2 mm。焊缝熔合区组织主要由粗大的等轴晶组成,晶粒内有连续析出的条纹状β-Mn,晶粒尺寸约为60 μm;热影响区组织为相对细小但大小不一的等轴晶,晶粒尺寸为15~40 μm。在消除焊缝表面缺陷后,焊接接头抗拉强度能达到基材的90 %左右。此外,熔合区内的粗大晶粒、晶粒内连续分布的第二相及焊缝内气孔缺陷是造成接头拉伸性能低于基材的主要原因。
关键词:MB8镁合金;激光焊接;焊缝成形;微观组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG456.9 文献标志码:A
Process characterization and joint mechanical properties of CO2 laser welding of MB8 magnesium alloy
Gao Ming, Zeng Xiao-yan, TANG Hai-guo
(School of Optoelectronics Science and Engineering,
Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China)
Abstract:A series of experiments on high power CO2 laser welding of MB8 magnesium alloy were carried out, and the forming rules of the weld seams, the microstructures and tensile strengths of the welded joints were also studied. The results show that the weld penetration depth is in the direct proportion to the laser power, when the laser power is increased by 1 kW, the penetration depth will be increased by about 2 mm. The microstructure of fusion zone center is mainly composed of coarse equiaxed grain with the size of about 60 μm and the precipitating stripe β-Mn is observed in the grains. The microstructures of heat affected zone are of equiaxed grains with different sizes from 15 to 40 μm. The tensile strength of the laser welded MB8 magnesium alloy reaches up to about 90% of that of the substrate after the surface defects are avoided. Moreover, the coarse grain of fusion zone, continuous second phase (β-Mn) and weld porosity are the main factors that result in lower tensile strength of laser welds in comparison of substrate.
Key words: MB8 magnesium alloy; laser welding; weld shape; microstructure; mechanical properties
作为密度最小的金属结构材料,镁合金适合应用在汽车、航空航天和船舶制造等行业,以满足减轻结构质量、降低能耗及提高产品性能的需求。然而,镁合金较差的变形能力限制了其应用范围,尤其是难以直接通过成形工艺制备复杂零部件。通过连接工艺实现镁合金复杂零部件的制备是扩大镁合金应用领域的有效方法。镁合金的低熔点、高蒸气压及易氧化等物化特性使其焊接存在一定困难。因此,如何提高其焊接性能是当前镁合金研究的重点[1-2]。目前,已经有多种焊接工艺,如电弧焊接[3-5]、电子束焊[6]、搅拌摩擦焊[7-8]及激光焊接[9-14]等应用于镁合金并取得了一定进展。其中,激光焊接具有焊接速度快、热输入低、焊缝变形小、热影响区窄及接头性能优良等优 点[9, 15-16],逐渐成为镁合金焊接研究关注的焦点。
现阶段,有关镁合金焊接的大部分研究主要采用AZ或AM系列镁合金,且大多在薄板上进行实验。对耐腐蚀性能良好且在航空航天中常用的MB8镁合金来说,其焊接研究还很少,仅邢丽等[17]开展了3 mm厚MB8镁合金薄板的搅拌摩擦焊研究,并取得了重要的试验数据。但是,该研究得到的最大焊接速度仅为0.3 m/min,接头拉伸性能最高也仅为母材的73%,显然难以满足现代工业高质高效的焊接需求。利用激光焊接的优点,MB8镁合金的焊接效率和接头质量有望进一步提高。因此,MB8镁合金激光焊接研究对镁工业发展具有积极意义。为此,本文作者采用高功率CO2激光器对10 mm MB8镁合金厚板的焊接工艺进行研究,并对其焊缝成形规律、接头微观组织和力学性能进行探讨。
1 实验
采用Rofin Sinar TR050 5kW CO2激光器,光束模式为TEM01,激光束用铜镜反射聚焦,焦距为286 mm,聚焦直径为0.6 mm。实验材料为10 mm厚的MB8镁合金板,试板尺寸为100 mm×50 mm,其成分(质量分数)为:1.8% Mn-0.18%Ce-98.02%Mg。实验中激光功率(P)和焊接速度(v)的变化范围分别为1.0~4.0 kW和0.5~2.0 m/min,负离焦为1 mm。
采用气流量为10 L/min的旁轴He气流来抑制激光光致等离子体效应,旁轴喷嘴内径为8 mm,吹气方向和工件移动方向相同,同时采用气流量为10 L/min的尾随Ar气流来防止焊缝氧化,其实验装置如图1所示。其中,焊缝成形工艺试验采用平板堆焊,拉伸试样采用平板对接焊,试样尺寸如图2所示。

图1 MB8镁合金激光焊接装置示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of laser welding of MB8 magnesium alloy

图2 拉伸测试试样尺寸
Fig.2 Dimensions of tensile test specimens (mm)
焊接完成后,试样都从焊道中间切断并采用标准程序制作金相试样,用苦味酸-乙醇溶液(4.2 g苦味酸-10 mL醋酸-20 mL水-100 mL乙醇)腐蚀。随后,采用金相显微镜测量焊缝成形参数,扫描电镜观测焊缝显微组织和断口形貌,显微硬度计测量焊缝显微硬度,测试点位于焊缝中部,测量参数为HV0.1,加载时间为15 s。
2 结果
2.1 焊缝成形
图3所示为实验所得激光焊接MB8镁合金焊缝截面的形貌。由图3可知,MB8镁合金激光焊缝呈指状形貌,表现出典型的激光深熔焊特征。实验发现,因镁合金的密度较低,沸点低和蒸气压较高,焊接熔池内容易形成气泡,且存在气泡浮力小、难以逸出的现象,从而导致焊缝内容易形成气孔,如图3 (g)所示。但是,通过降低焊接速度、提高焊接热输入和增加气泡逸出时间,焊缝气孔能够得到有效抑制。在完全熔透的情况下,焊缝根部因为形成凸出部分会消耗部分母材,因此,焊缝表面因为缺乏材料补充会形成如图3(d)所示的未填满缺陷,且只能通过衬垫防止液态金属流出、减少焊缝部分金属消耗来得到改善,或通过填充金属材料来彻底消除。
图4所示为激光功率对焊接熔深的影响规律。由图4可知,随着激光功率的增加,焊接熔深逐渐增加,两者基本保持正比例关系:激光功率每增加1 kW,焊接熔深约增加2 mm。当激光功率为4 kW、焊接速度为1 m/min时,10 mm厚镁合金板完全熔透,如图3(d)所示。在焊缝未熔透时,焊缝宽度随激光功率增加而增加,但焊缝熔透后,焊缝宽度反而降低。这是因为随着焊缝的熔透,熔池内液态金属向下流淌的阻力减小,更多的焊接热量通过熔池向下流动进入焊缝底部,减少了其在焊缝上半部分的积聚,最终使焊缝宽度 降低。

图3 MB8镁合金在不同激光功率和焊接速度下焊缝截面的形貌
Fig.3 Cross-section morphologies of laser welded MB8 magnesium alloy at different laser powers (P) and weld velocities (v): (a) P=1 kW, v=1 m/min; (b) P=2 kW, v=1 m/min; (c) P=3 kW, v=1 m/min; (d) P=4 kW, v=1 m/min; (e) P=1 kW, v=2 m/min; (f) P= 2 kW, v=2 m/min; (g) P=3 kW, v=2 m/min; (h) P=4 kW, v=2 m/min

图4 激光功率对焊缝形状的影响
Fig.4 Effects of laser power on weld shape
2.2 组织和性能分析
为了研究MB8镁合金激光焊接接头的微观组织和力学性能,采用全熔透平板对接焊缝进行分析,其工艺参数和形貌与图3(d)所示的焊缝相同。
2.2.1 微观组织
图5所示为典型焊缝不同区域的的微观组织。如图5(a)所示,MB8镁合金基材组织表现为等轴晶,晶粒大小为10 μm左右。如图5(b)所示,热影响区(Heat affected zone, HAZ)和熔合区(Fusion zone, FZ)之间存在明显的熔合线,热影响区组织表现为等轴晶,但晶粒大小不一,尺寸为15~40 μm。这是因为热影响区内的变形晶粒在焊接加热后发生再结晶,并在变形储能的驱动下重新形核长大形成等轴晶。在焊接加热过程中,一旦热影响区温度过高,其中的部分晶粒会发生二次再结晶,并通过晶界迁移,吞并周围其他晶粒,形成粗大晶粒,这种现象造成该区域晶粒分布极不均匀。从图5(b)和(c)可以发现,相对于基材和热影响区,熔合区的晶粒明显粗化。这是因为要实现10 mm厚板的全熔透,必须采用高功率激光。在较高的热输入下,熔合区凝固速度较慢,容易形成粗大晶粒。此外,熔合区主要由晶粒粗大的等轴晶组成,晶粒大小约为60 μm,晶粒内呈条纹状分布的析出物质为β-Mn。在熔合区外围,即熔合线附近的组织为垂直熔合线外延生长的粗大柱状晶。
2.2.2 显微硬度
图6所示为典型焊缝的显微硬度分布图。由图6可知,熔合区的显微硬度明显低于基材的,热影响区的显微硬度稍高于基材的,其宽度仅为0.4 mm。显然,熔合区的低显微硬度取决于其内部的粗大晶粒。对于热影响区来说,晶粒尺寸存在较大差异,区域内存在部分明显粗化的晶粒,但是仍然存在大量和母材相差不大的晶粒(尤其是靠近熔合线一侧),避免了该区域显微硬度的迅速降低;另一方面,在再结晶过程中,硬度更高的第二相(β-Mn)的沉淀析出有利于该区域显微硬度的增加。在两者的综合作用下,热影响区的显微硬度反而略高于基材的。总体上来说,激光焊缝的显微硬度和图5所示的微观组织具有较好的对应关系。
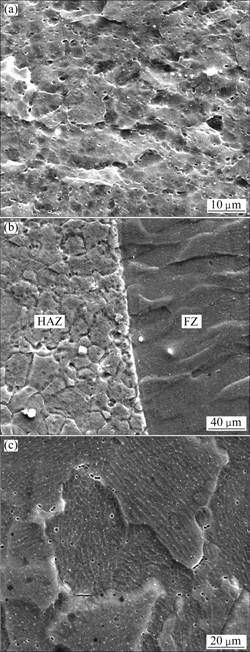
图5 典型激光焊缝的微观组织
Fig.5 Microstructures of typical laser weld seam: (a) Substrate; (b) Near fusion line; (c) Center of fusion zone

图6 典型激光焊缝的显微硬度分布
Fig.6 Microhardness distribution of typical laser weld seam
2.2.3 拉伸性能
因为镁合金在焊接过程中烧损严重,激光焊接,尤其是厚板焊接中极易出现如图3(d)所示的未填满缺陷(Incompletely filled groove, IFG)。这种过渡不连续的成形缺陷在焊件使用过程中容易形成应力集中,引发工程事故。对此,本文作者对其影响进行了测试,具体方法为分别采用带有IFG缺陷和机加工消除IFG缺陷的两种拉伸试样进行测试。此外,还采用能够填充材料的激光填丝焊工艺获得了如图7所示成形饱满的焊缝,同时测量了其接头的抗拉强度以验证通过工艺方法消除IFG缺陷后,接头抗拉强度的实际提升程度。

图7 激光填丝焊缝表面及截面形貌
Fig.7 Surface (a) and transverse (b) morphologies of laser filling weld of MB8 magnesium alloy at P=4 kW and v=0.8 m/min
图8所示为不同激光焊缝的抗拉强度测试结果。其中,带有IFG缺陷和机加工消除IFG缺陷的激光焊接接头拉伸试样分别用1#和2#表示,激光填丝焊接拉伸试样用3#表示。如图8所示,所有试样均断裂于焊缝。当有IFG缺陷时,焊缝的抗拉强度为177 MPa,仅为基材(235 MPa)的75%;但是,机加工去除IFG缺陷后,抗拉强度升至214 MPa,达到基材的91%。与此同时,通过填充材料消除IFG缺陷的激光填丝焊接头的抗拉强度也达到205 MPa,为基材的87%。显然,IFG缺陷处形成的应力集中是1#接头抗拉强度急剧降低的主要原因。但是,消除IFG缺陷的影响后,2#接头的抗拉强度仍然低于基材的。通过焊缝微观组织和图9(a)所示的拉伸断口形貌可以发现,主要原因有两点:首先,熔合区内的粗大晶粒造成接头强度的降低。根据Hall-Petch关系,接头强度和晶粒尺寸有如下 关系:
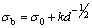 (1)
(1)
式中:σb为接头的抗拉强度;d为晶粒直径;σ0和k为与材料晶体类型有关的常数。从式(1)可以看到,接头抗拉强度与晶粒直径的平方成反比。显然,熔合区晶粒的粗化能显著降低接头的抗拉强度。其次,焊缝内存在的一定数量的气孔将降低接头强度。在拉伸过程中,气孔会在拉伸力作用下因应力集中发展成为裂纹扩展源,同时减少接头受力截面的面积,造成接头强度的降低。

图8 不同激光焊缝的抗拉强度
Fig.8 Tensile strength of different laser weld seams
图9为典型激光焊缝(2#)的拉伸断口形貌。由图9可知,MB8镁合金激光焊缝拉伸断口呈现明显的层状撕裂形貌,表现为脆性解理断口。造成这种形貌的主要原因是熔合区内的粗大晶粒和连续分布的第二相(β-Mn)。一方面,粗大晶粒降低了接头的断裂应力,提高了其脆性程度;另一方面,在晶粒和晶界上连续析出的脆性β-Mn破坏了晶界的连续性,在拉伸过程中,因为位错塞积作用,裂纹容易在这些位置形成并扩展,造成接头断裂,降低接头抗拉强度。

图9 激光焊缝(2#)的拉伸断口形貌
Fig.9 Tensile fracture surface morphologies of typical laser weld (2#)
通过上述试验研究可以认为,相比已有的MB8镁合金摩擦搅拌焊方法[17],激光焊接能够在一定程度上提高其焊接性能和焊接效率,并提高焊接接头的抗拉强度(由基材的73 %增加至90 %左右)。但是,对厚板的激光焊接来说,采用辅助方法,如采用激光填丝焊方法来消除表面未填满缺陷,并通过减小热输入来减小焊缝熔合区晶粒大小才能获得抗拉强度更高的MB8镁合金焊接接头。
3 结论
1) MB8镁合金激光焊缝呈典型指状形貌,焊接熔深与激光功率基本呈正比关系:在本实验条件下,激光功率每增加1 kW,熔深增加约2 mm。当激光功率为4 kW、焊接速度为1 m/min时,10 mm厚镁合金板完全熔透。
2) 焊缝熔合区组织主要由粗大的等轴晶组成,晶粒大小约为60 μm,晶内有连续析出的条纹状β-Mn。熔合区内靠近熔合线区域的组织为垂直熔合线外延生长的粗大柱状晶;热影响区微观组织为晶粒大小不一的等轴晶,晶粒尺寸为15~40 μm。
3) 在消除表面未填满缺陷的情况下,MB8镁合金接头的抗拉强度可达到母材的90%左右。熔合区的粗大晶粒、晶粒内连续分布的第二相及焊缝内气孔缺陷是造成MB8镁合金激光焊接接头力学性能低于基材力学性能的主要原因。
REFERENCES
[1] FRIEDRICH H E, MORDIKE B L. Magnesium technology[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 336-348.
[2] 冯吉才, 王亚荣, 张忠典. 镁合金焊接技术的研究现状及应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(2): 165-178.
Feng Ji-cai, Wang Ya-rong, ZHANG Zhong-dian. Status and expectation of research on welding of magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(2): 165-178.
[3] BEN-HAMU G, ELIEZER D, CROSS C E, BOLLINGAUS T. The relation between microstructure and corrosion behaviorof GTA welded AZ31B magnesium sheet[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 452/453: 210-218.
[4] WOHLFAHRT H, RETHMEIER M, BOUAIFI B, SCHUTZ M. Metal-inert gas welding of magnesium alloy[J]. Weld Cut, 2003, 55: 80-84.
[5] 刘黎明, 张兆栋, 沈 勇, 王 来. 活性剂对镁合金TIG焊接熔深的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2006, 42(4): 399-404.
Liu Li-ming, Zhang Zhao-dong, Shen Yong, WANG Lai. Effects of activating fluxes on TIG welding penetration of magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2006, 42(4): 399-404.
[6] CHI C T, CHAO C G, LIU T F, WANG C C. A study of weldability and fracture modes in electron beam weldments of AZ series magnesium alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 435/436: 672-680.
[7] LEE W B, YEON Y M, JUNG S B. Joing properties of friction stir welded AZ31B-H24 magnesium alloy[J]. Mater Sci Tech, 2003, 19: 785-790.
[8] WANG X H, WANG K S. Microstructure and properties of friction stir butt-welded AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 431: 114-117.
[9] CAO X, JAHAZI M, IMMARIGEON J P, WALLACE W. A review of laser welding techniques for magnesium alloys[J]. J Mater Process Tech, 2006, 171: 188-204.
[10] PAN L K, WANG C C, HSIAO Y C, HO K C. Optimization of Nd: YAG laser welding onto magnesium alloy via Taguchi analysis[J]. Opt Laser Tech, 2004, 37: 33-42.
[11] 全亚杰, 陈振华, 黎 梅, 俞照辉, 龚晓叁. AM60变形镁合金薄板激光焊接接头的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(4): 525-529.
QUAN Ya-jie, CHEN Zhen-hua, LI Mei, YU Zhao-hui, GONG Xiao-san. Microstructure and properties of joints of wrought magnesium alloy AM60 plates welded by laser beam welding[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous metals, 2007, 17(4): 525-529.
[12] 王红英, 李志军. AZ61 镁合金激光焊接接头的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(8): 1388-1393.
WANG Hong-ying, LI Zhi-jun. Microstructure and properties of AZ61 magnesium alloy joints produced by laser welding method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(8): 1388-1393.
[13] 刘黎明, 王继锋, 宋 刚. 激光电弧复合焊接AZ31B镁合金[J]. 中国激光, 2004, 31: 1523-1526.
Liu Li-ming, Wang Ji-feng, Song Gang. Hybrid laser-arc welding of AZ31B Mg alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of lasers, 2004, 31: 1523-1526.
[14] 高 明, 谭 兵, 冯杰才, 曾晓雁, 严 军. 工艺参数对AZ31镁合金激光-MIG复合焊缝成形的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(2): 222-227.
GAO Ming, TAN Bing, FENG Jie-cai, ZENG Xiao-yan, YAN Jun. Effects of welding parameters on weld shape of laser-MIG hybrid welding of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(2): 222-227.
[15] 王红英, 莫守形, 李志军. AZ31镁合金CO2激光填丝焊工艺[J]. 焊接学报, 2007, 28(4): 93-96.
WANG Hong-ying, MO Shou-xing, LI Zhi-jun. CO2 laser welding of AZ31 magnesium alloys with filler wire[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2006, 28(6): 93-96.
[16] 肖荣诗, 吴世凯. 激光-电弧复合焊接的研究进展[J]. 中国激光, 2008, 35: 1680-1685.
XIAO Rong-shi, WU Shi-kai. Progress on laser-arc hybrid welding[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2008, 35: 1680-1685.
[17] 邢 丽, 柯黎明, 孙德超, 周细应. 镁合金薄板的搅拌摩擦焊工艺[J]. 焊接学报, 2006, 22(6): 18-21.
XING Li, KE Li-ming, SUN De-chao, ZHOU Xi-ying. Friction stir welding of MB8 magnesium alloy sheet[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2006, 22(6): 18-21.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2008AA030116); 教育部博士点新教师基金资助项目(200804871013)
收稿日期:2010-05-25;修订日期:2010-11-05
通信作者:高 明,副教授,博士;电话:027-87792404; E-mail:mgao@mail.hust.edu.cn