分段电积-SO2还原工艺分离与回收铜电解液中铜砷
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第7期
论文作者:郑雅杰 彭映林 柯 浪 陈文汨
文章页码:2166 - 2173
关键词:铜电解液;阴极铜;砷;SO2;还原;电积;结晶
Key words:copper electrolyte; copper cathode; arsenic; sulfur dioxide; reduction; electrowinning; crystallization
摘 要:通过分段电积、SO2还原、蒸发结晶使铜电解液中的铜砷得到分离与回收。当电流密度为200 A/m2、电解液温度为55 °C、电解液循环速率为10 mL/min、终点铜浓度高于25.88 g/L时,电积得到纯阴极铜。调节电流密度为100 A/m2、电解液温度为65 °C、铜离子浓度从24.69 g/L 降至0.42 g/L时,砷的去除率为18.25%。通入SO2 将脱铜电解液中的As (V)充分还原为As (III)后,蒸发浓缩还原后液,冷却结晶得到As2O3晶体,砷的回收率为59.76%。阴极极化曲线表明,铜离子浓度和As(V)均影响铜还原的极限电流密度。
Abstract: Cu and As were separated and recovered from copper electrolyte by multiple stage electrowinning, reduction with SO2 and evaporative crystallization. Experimental results showed that when the current density was 200 A/m2, the electrolyte temperature was 55 °C, the electrolyte circulation rate was about 10 mL/min and the final Cu concentration was higher than 25.88 g/L, the pure copper cathode was recovered. By adjusting the current density to 100 A/m2 and the electrolyte temperature to 65 °C, the removal rate of As was 18.25% when the Cu concentration decreased from 24.69 g/L to 0.42 g/L. After As(V) in Cu-depleted electrolyte was fully reduced to As(III) by SO2, the resultant solution was subjected to evaporative crystallization, then As2O3 was produced, and the recovery rate of As was 59.76%. The cathodic polarization curves demonstrated that both Cu2+ concentration and As(V) affect the limiting current of Cu2+ deposition.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 2166-2173
Ya-jie ZHENG1,2, Ying-lin PENG1, Lang KE1, Wen-mi CHEN1
1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Joint Research Institute of Xinjiang Nonferrous Metals Group and Central South University, Urumqi 830000, China
Received 19 November 2012; accepted 22 March 2013
Abstract: Cu and As were separated and recovered from copper electrolyte by multiple stage electrowinning, reduction with SO2 and evaporative crystallization. Experimental results showed that when the current density was 200 A/m2, the electrolyte temperature was 55 °C, the electrolyte circulation rate was about 10 mL/min and the final Cu concentration was higher than 25.88 g/L, the pure copper cathode was recovered. By adjusting the current density to 100 A/m2 and the electrolyte temperature to 65 °C, the removal rate of As was 18.25% when the Cu concentration decreased from 24.69 g/L to 0.42 g/L. After As(V) in Cu-depleted electrolyte was fully reduced to As(III) by SO2, the resultant solution was subjected to evaporative crystallization, then As2O3 was produced, and the recovery rate of As was 59.76%. The cathodic polarization curves demonstrated that both Cu2+ concentration and As(V) affect the limiting current of Cu2+ deposition.
Key words: copper electrolyte; copper cathode; arsenic; sulfur dioxide; reduction; electrowinning; crystallization
1 Introduction
During copper electrorefining, the concentrations of impurities, such as arsenic, antimony and bismuth, increase gradually in the electrolyte if no electrolyte was drawn out from the electrorefining circulatory system and to be purified. Because Bi, Sb and As are very close to Cu in the standard reduction potentials, they may deposit on the cathode and affect the cathode quality badly. Therefore, the concentrations of Bi, Sb and As in copper electrolyte should be controlled strictly. To decrease the impurity concentration in copper electrolyte, the conventional process is multistage electrolytic deposition [1], and other technologies were used as well, such as chemical precipitation [2], solvent extraction [3], absorption [4], and ion exchange [5]. The conventional process has the advantage of being mature, well-known technology, but its disadvantages are obvious especially when it is used for the removal of arsenic, the possibility of forming of toxic arsine gas in the final stage of the process and the disposal of the copper arsenide deposits formed as the end product of the process. When arsenic is removed by this process, copper also be removed simultaneously [6]. Sometimes, to increase the As removal efficiency, the product bluestone dissolves again and flows into the liberator cells, which will affect the equilibrium between copper and sulfuric acid [7]. In general, the copper arsenide deposits were recycled back into the copper smelter; however, it creates a remarkable As circulation between the smelter and the electrolysis, and seriously contaminates the environment [8]. The use of high As concentration in copper refinery electrolyte has been widely studied recently, namely, by increasing the concentration of As in the electrolyte, the concentrations of Sb and Bi depress [9-11], while the arsenic concentration increases slowly during electrorefining, till As reaches a concentration detrimental to the electrolytic production of high-purity copper, the electrolyte should be eliminated.
The aim of this work is at presenting the separation of Cu and As in copper electrolyte containing high As by multiple stage electrowinning of controlling current density, in which pure cathode copper will be recovered at the first stage electrowinning, and the Cu and As will be separated at the second stage electrowinning, then As will be recovered from the Cu-depleted electrolyte by reducing with SO2 and evaporative crystallization. Liner sweep voltammetry (LSV) is adopted to examine the effect of Cu2+ concentration and As(V) on the copper deposition during electrowinning.
2 Experimental
2.1 Separation of Cu and As by multiple stage electrowinning
Electrowinning using two Pb/Ag anodes (103 mm×96 mm) and one pure copper cathode (110 mm×100 mm) was carried out in the experimental cell with about 1.6 L electrolyte. The electrodes were separated by a distance of 4.5 cm. The electrolyte temperature was controlled at the pre-determined value by circulating it in a thermal converter. The current density was controlled at the desired value by using a direct current electric source (WYJ-0 DC). The electrolyte circulation rate was about 10 mL/min. During the first stage electrowinning process, appropriate amounts of addition agents, such as glue, thiourea and hydrochloric acid, were added into the electrolyte. Prior to the electrowinning, the electrodes were polished with ultrafine sandpaper, successively washed with 10% dilute sulfuric acid solution and deionized water, immediately dried, and weighed. After electrowinning, the cathode was washed with deionized water and then taken out from the cell, immediately dried, and weighed. The electrolyte was filtered and samples were taken out for analysis. The current efficiency of copper was calculated using the following formula:
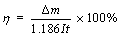 (1)
(1)
where η is the current efficiency of copper; △m is the mass difference of Cu before and after the experiment, g; I is the current, A; t is the electrowining time, h; 1.186 is the electro-chemical equivalent of Cu.
2.2 Recovery of As from Cu-depleted electrolyte
The As(V) in Cu-depleted electrolyte was reduced by SO2 at 30 °C. The reduced electrolyte was then subjected to evaporative crystallization. After filtration, As2O3 was obtained.
2.3 Electrochemical measurements
To study the effect of As(V) on the copper deposition during electrowinning, synthetic copper electrolytes were used. Electrolytes were prepared using CuSO4·5H2O, As2O5, H2SO4 (all AR grade) and 18 MΩ water. Electrolytes contained 250 g/L H2SO4. All electrolytes were deoxygenated with purified nitrogen gas before carrying out electrochemical measurements. Linear sweep voltammetry was performed at 65 °C in an H-type of electrolytic cell. Copper electrode with a diameter of 1.38 mm was used as working electrode, which was polished with ultrafine sandpaper of different grades and then washed with ethanol and 18 MΩ water before transferring into the electrochemical cell. A platinum plate and a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) were used as the counter electrode and the reference electrode, respectively. The reference electrode was positioned within a Luggin capillary. The Luggin tip was placed close to the surface of the working electrode. Electrochemical measurements including liner sweep voltammetry(LSV) technique and controlled potential electrolysis were performed using a potentiostat/ galvanostat (CHI 660 electrochemical workstation provided by Shanghai CH Instrument Company, China) and connected with a personal computer. The adopted scan rate for all the LSV was 2 mV/s.
2.4 Analysis
The total content of the elements was determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Intrepid II XSP). The valence of the elements was determined by standard chemical methods. The X-ray diffraction(XRD) patterns were recorded on a Rigaku Miniflex diffractometer with Cu Kα X-ray radiation at 40 kV and 250 mA.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 First stage electrowinning
It is well known that Cu2+ concentration plays an important role in deciding the quality of cathode copper. The effect of final Cu concentration on the recovery of cathode copper was investigated. The compositions of initial copper electrolyte are listed in Table 1. According to the above experimental procedure, when the current density is 200 A/m2, the electrolyte temperature is 55 °C, the effect of final Cu concentration on the removal rates of As, Sb and Bi in the copper electrolyte is shown in Fig. 1. The chemical compositions of copper electrolyte with final Cu of 30.16 g/L (1# electrolyte) and 25.88 g/L(2# electrolyte) are presented in Table 1.
From Fig. 1 it can be seen that the removal rates of As and Sb do not show any significant change in the range of Cu concentration studied, and the removal rates of As and Sb are lower than 4% and 10% respectively, whereas the removal rate of Bi increases obviously when the Cu concentration is lower than 25.88 g/L.
Table 1 Compositions of copper electrolyte
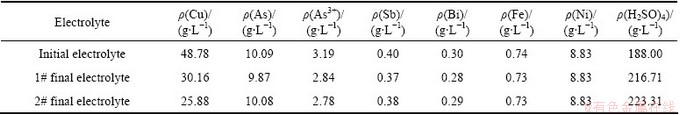
Table 2 Impurities in copper cathodes with final Cu concentration of 30.16 g/L and 25.88 g/L


Fig. 1 Effect of final Cu concentration on removal rates of As, Sb and Bi
When the final Cu concentrations are 30.16 g/L and 25.88 g/L in the electrolyte, respectively, the copper cathodes obtained are smooth and bright, the impurities in the copper cathodes are shown in Table 2. The total impurity content of 0.0022% is achieved when the final Cu is 30.16 g/L, the impurity level easily meets the London Metal Exchange (LME) Grade A standard (Cu-CATH -1). The total impurity content of 0.0066% is achieved when the final Cu content is 25.88 g/L, the quality of cathode copper meets the standard of Cu-CATH -2 except Bi and Pb. The Pb in the cathode copper comes from Pb-Ag anodes corrosion.
Table 1 shows that the concentrations of As, Sb and Bi in the 2# electrolyte are slightly higher than those in the 1# electrolyte, which may be due to the fact that the filtrate temperature of 2# electrolyte is higher than that of 1# electrolyte, as the higher the temperature is, the higher the solubilities of As, Sb and Bi are. In 1# and 2# electrolytes, when H2SO4 contents are 216.71 g/L (pH=-0.34) and 223.31 g/L(pH=-0.36) respectively, As(III) is in the form of AsO+ and HAsO2, As(V) is in the form of undissociated arsenic acid H3AsO4 [12], Sb is mostly in the form of trivalent state SbO+ [13], and Bi usually exists in the form of BiO+. From Table 1 and Table 2, it can be found that the As, Sb and Bi in electrolyte are mainly removed as precipitate, and the reactions can be expressed as follows [14,15]:
aH3AsO4+bH[Sb(OH)6]+cMeO+→MecAsaSbbO(3a+5b+c/2+1)H(a+5b-2c+2)·xH2O+cH++(a+b+c/2-1-x)H2O
(Me=As(III), Sb(III), Bi(III); a≥1; b≥1; c≤3a+b) (2)
26H++6HAsO2+4SbO++8HSb(OH)6=3H2O+H30(As2O3)3·(Sb2O3)2·(Sb2O5)4·26H2O (3)
The standard and equilibrium potentials for various possible cathode deposition reactions are listed in Table 3 when final Cu contents are 30.16 g/L and 25.88 g/L, respectively [16-18]. The equilibrium potentials for the cathode deposition reactions at 55 °C are close to those at 25 °C. From Table 3, it can be seen that when Cu2+ is reduced to Cu, As(V) is already reduced to AsO+ and HAsO2. During the electrowinning, O2 is produced in the anode, and it can oxidize As(III) into As(V); since the rate of As(III) oxidation is higher than the reduction rate of As(V), the As(III) concentration decreases gradually. Generally, the reactions (IV) and (V) cannot take place during the copper electrowinning. The φe of reaction (VII) is close to that of reaction (I). As the Cu concentration decreases, the deposition potential decreases gradually, and copper arsenide may form. According to reactions (IX) and (X), the deposition potentials of Sb and Bi in 2# electrolyte are slightly higher than those in 1# electrolyte, hence, the lower the Cu concentration is, the more the possibility of the deposition of Bi and Sb is. By controlling appropriate Cu concentration, pure cathode copper can be obtained.
3.2 Second stage electrowinning
Some published data showed that As will be co-deposited with Cu when the Cu concentration drops to about 10 g/L in the electrolyte [19]. In the following section, the separation of Cu and As in electrolyte with Cu concentration below 10 g/L is investigated. The compositions of copper electrolyte are listed in Table 4.
Table 3 Standard (φ0) and equilibrium (φe) potentials for various possible cathode deposition reactions at 25 °C

Table 4 Compositions of copper electrolyte (g/L)

3.2.1 Effect of current density
Electrowinning was first conducted by varying the current density from 60 A/m2 to 235 A/m2 at a temperature of 55 °C, electrolyte circulation rate of 10 mL/min and a total input electric quantity of 6.75 C. The result is shown in Fig. 2. Clearly, both the removal rate and the current efficiency of Cu increase with decreasing current density, and conversely the removal rates of As, Sb and Bi decrease with decreasing current density. When the current density decreases from 235 A/m2 to 60 A/m2, the removal rate of As decreases from 5.78 % to 0, and the current efficiency of Cu rises from 79.2 % to 95.8 %. At the same time, the quality of the deposit also changes, the deposit is loose and non-adherent at high current density. This may be due to exceeding of the critical current density, but as the current density decreases from 235 A/m2 to 60 A/m2, the deposit is more adherent.

Fig. 2 Effect of current density on removal rates of Cu, As, Sb and Bi in copper electrolyte and current efficiency of Cu
Metal deposition occurs at faster rates with higher current densities. However, if the current density is too high, the solution surrounding the cathodes can become depleting of copper and the cathode potential will decrease, which limits the copper deposition rate and results in the co-deposition of impurities As, Sb and Bi. Obviously, the lower the current density is, the better the separation of Cu and As is. However, the lower current density requires an increase in the electrowinning time. Considering all these factors, 100 A/m2 is considered the optimal current density.
3.2.2 Effect of electrolyte temperature
The effect of electrolyte temperature on the removal rates of Cu, As, Sb and Bi in copper electrolyte and the current efficiency of Cu was conducted by varying the temperature from 35 °C to 75 °C at a current density of 100 A/m2. Figure 3 indicates that the removal rate of Cu increases with temperature up to 65 °C, beyond which it decreases slowly. It can also be seen that the removal rates of Bi and As decrease with increasing temperature, while the removal rate of Sb decreases with increasing temperature till 55 °C, then it increases with temperature. Furthermore, the copper deposit formed at temperature below 45 °C is non-uniform and non-adherent, whilst higher temperature improves both the quality and adherence. When the electrolyte temperature is 65 °C, the removal rates of Cu, As, Sb and Bi are 46.37%, 1.67%, 13.13% and 27.18%, respectively, and the current efficiency of Cu is 93.49%.
Increasing temperature can increase the ionic mobility, and the rapid availability of Cu2+ ions at the cathode can decrease concentration polarization and increase deposition potential. So, as the temperature increases, the removal rate and current efficiency of Cu increase, and the removal rates of As and Bi decrease. However, the increased temperature also results in the cathode copper’s dissolving again into the electrolyte and the decrease of current efficiency. Furthermore, a too high temperature leads to excessive evaporation and energy consumption. Hence, 65 °C is chosen as the optimal temperature.

Fig. 3 Effect of electrolyte temperature on removal rates of Cu, As, Sb and Bi in copper electrolyte and current efficiency of Cu
3.2.3 Confirmation experiment
Based on the above studies, the appropriate conditions for the separation of Cu and As in copper electrolyte in the second stage electrowinning are as follows: current density 100 A/m2, temperature 65 °C, electrolyte circulation rate about 10 mL/min, electrode distance 4.5 cm. These conditions were then applied to a confirmation experiment to separate Cu and As from copper electrolyte. The compositions of copper electrolyte before and after electrowinning are listed in Table 5. During electrowinning, the electrolyte sample was taken out in a certain interval, at the same time, the cell voltage was recorded. The variation in the cell voltage as a function of Cu2+ concentration is shown in Fig. 4. In the final stage of the process, black sludge was produced. The compositions of cathode copper are listed in Table 6. Table 7 and Fig. 5 give the compositions and XRD pattern of the black sludge. The black sludge was first washed with water, and then dried at 105 °C till its mass was constant.
It can be calculated from Table 5 that the removal rates of Cu, As, Sb and Bi are 98.18%, 18.25%, 68.74% and 88.69%, respectively. The current efficiency of Cu is 71.46%. The removal rates of Sb and Bi are similar to those of the conventional continuous decopperization and dearsenication by electrowinning, i.e., 70%-90% [19], while the removal rate of As is much lower than that of conventional method, i.e., 70%-85%. Table 6 shows that the cathode copper includes 86.37% Cu. It is demonstrated that Cu and As could be separated by electrowinning through controlling current density.
Figure 4 reveals that the cell voltage increases with decrease of Cu concentration. The cell voltage rises sharply from 1.84 V to 2.25 V as the Cu concentration decreases from 3.04 g/L to 0.45 g/L, which is lower than that of conventional method, i.e., 2.4 V [19].
From Table 7, it can be seen that the main elements in black sludge are Cu, As and O. Figure 5 shows that the black sludge contains Cu3As, Cu5As2 and Cu2O. The presence of the Cu3As and Cu5As2 in the deposit can be explained by the reactions shown in Table 3. The reduction of Cu2+ is a two-consecutive one-electron steps, with Cu+ as an intermediate [20], some of the dissolved cuprous ions precipitate as Cu2O, and the reaction can be expressed as follows [21]:
2Cu2++H2O+2e=Cu2O+2H+ (4)
3.3 Recovery of As from Cu-depleted electrolyte
As can be found from Table 5, there is 7.68 g/L As in the Cu-depleted electrolyte, and the As exists mostly in the form of As(V). According to the above experimental procedure, after the As(V) in the electrolyte is reduced to As(III) completely, the reduced electrolyte is concentrated, then the concentrated solution is cooled to 30 °C and crystallized product is obtained after filtration. The compositions of electrolyte after reducing and crystallizing are listed in Table 8. The compositions and XRD pattern of the crystallized product are shown in Table 9 and Fig. 6.
It can be calculated from Tables 5 and 8 that the recovery rate of As in copper electrolyte is as high as 59.76%. The concentrations of As and Ni in the mother liquor are high. After the As and Ni are recovered by crystallization at lower temperature, the solution can be used as H2SO4 solution and turned into the electrolysis system.
Table 5 Compositions of copper electrolyte before and after electrowinning

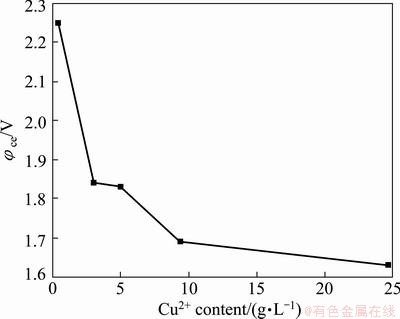
Fig. 4 Cell voltage variation as a function of Cu2+ content
Table 6 Compositions of cathode copper produced at second stage electrowinning (mass fraction,%)
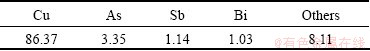
Table 7 Compositions of black sludge (mass fraction,%)


Fig. 5 XRD pattern of black sludge
Table 8 Compositions of copper electrolyte after reducing and crystallizing
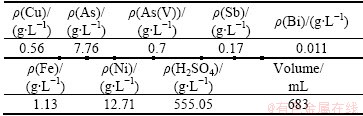
Table 9 Compositions of crystallized product (mass fraction, %)

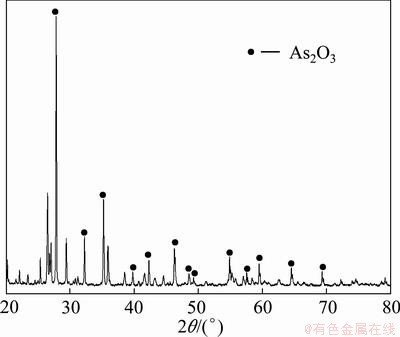
Fig. 6 XRD pattern of crystallized product
Table 9 and Fig. 6 show that the crystallized product is As2O3, and the content of As2O3 is about 58.74%. H2SO4 concentration in copper electrolyte increases gradually in the process of concentration, when H2SO4 concentration increases from 0 to 800 g/L, the solubility of trivalent arsenic decreases gradually, and trivalent arsenic deposits in the form of arsenic trioxide. The reactions are shown as follows [22,23]:
SO2(g)+H2O=H2SO3(aq) (5)
H2SO3+H3AsO4=HAsO2+H2SO4+H2O (6)
H2SO3+H3AsO4=AsO++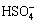 +2H2O (7)
+2H2O (7)
2HAsO2=As2O3↓+H2O (8)
2AsO++H2O= As2O3↓+2H+ (9)
3.4 Electrochemical measurements
The cathodic polarization curves ranging from open circuit potential to -0.65 V (vs SCE) recorded for acidified CuSO4 aqueous solutions containing different Cu concentrations in the absence and presence of 10 g/L As(V) are shown in Fig. 7.
Figure 7(a) shows that reduction peak A in region I is associated with the copper deposition. Though the charge transfer at the Cu/Cu2+ electrode occurs in two- consecutive one-electron steps, with Cu+ as an intermediate, but Cu+ is much more easily reduced than Cu2+ in CuSO4-H2SO4 solution, only one peak is observed [24]. After the presence of peak A, the curves reach a limiting current, which increases with Cu2+ concentration. The cathodic behavior in region II is associated with hydrogen evolution.
Compared with Fig. 7(a), from Fig. 7(b) it can be seen that the current density of peak A in electrolyte containing As(V) is slightly higher than that without As(V). The addition of As(V) in electrolyte causes an acceleration of the Cu deposition process. When Cu2+ content is 2.5g/L, the peak current density increases from 10.1 mA/cm2 to 15.7 mA/cm2. The cathodic behavior in region II is associated with H2 evolution and AsH3 evolution.
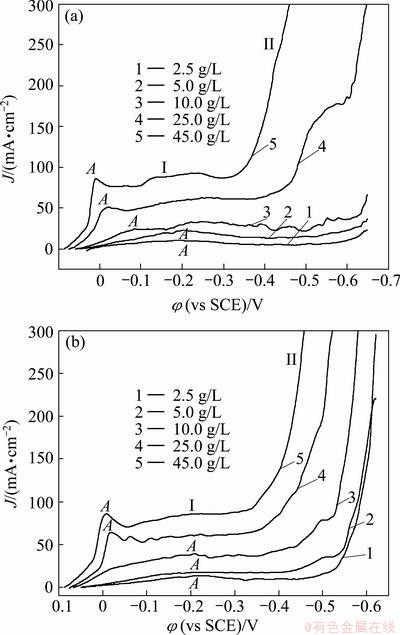
Fig. 7 Effect of copper concentration on cathodic polarization curves of copper in the absence(a) and in the presence (b) of 10 g/L As(V)
In order to determine the composition of compounds, which are produced as a result of the reduction of Cu when Cu2+ was 2.5 g/L in the presence of 10 g/L As(V), electrodeposition experiments were performed at a controlled potential, and the deposit was analyzed by XRD. The controlled-potential electrodeposition reactions were carried out at potential of -0.2 V and -0.43 V (vs SCE) respectively. The deposits formed at -0.2 V (vs SCE) are observed to be in the metal copper color, and the XRD shows that the deposit contains Cu and Cu2O; while the deposits formed at -0.43 V (vs SCE) are observed to be in a brownish black color and of a powdery nature; the deposit contains Cu3As, Cu2O and Cu5As2.
It is well known that to increase the density is necessary to increase the cathodic voltage which will result in the co-deposition of As. During electrowinning, in order to avoid the co-deposition of arsenic, the current density should be adjusted according to the Cu2+ concentration in electrolyte.
4 Conclusions
1) Under the conditions that the current density is 200 A/m2, the electrolyte temperature is 55 °C, the electrolyte circulation rate is about 10 mL/min, and the final Cu is higher than 25.88 g/L, the pure copper cathode is recovered.
2) The appropriate conditions for the separation of Cu and As in electrolyte in the second stage electrowinning are current density of 100 A/m2, temperature of 65 °C and electrolyte circulation rate of 10 mL/min. Under the above conditions, when the Cu concentration decreases from 24.69 g/L to 0.42 g/L, the removal rates of Cu and As are 98.18% and 18.25%, respectively.
3) When the As concentration in the Cu-depleted electrolyte is 7.68 g/L, the recovery rate of As reaches 59.76% after the As(V) in Cu-depleted electrolyte was reduced and H2SO4 concentration reached 555.05 g/L. The crystallized product is As2O3.
4) The cathodic polarization curves demonstrate that the limiting current of Cu2+ deposition increases with Cu2+ concentration, and the presence of As(V) in copper electrolyte increases the peak current density of Cu deposition.
References
[1] NAVARRO P, ALGUACIL F J. Adsorption of antimony and arsenic from a copper electrorefining solution onto activated carbon [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2002, 66(1-3): 101-105.
[2] TOMITA M, HIAI H, ISHII T. Method of purifying copper electrolyteic solution: American, US 5783057[P]. 1998-07-21.
[3] NAVARRO P, ALGUACIL F J. Removal of arsenic from copper electrolytes by solvent extraction with tributylphosphate [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1996, 35(2): 133-141.
[4] WANG Xue-wen, CHEN Qi-yuan, LONG Zi-ping, SU Zhong-fu, YIN Zhou-lan, ZHANG Ping-min. Application of antimony in purification of copper electrolyte [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(6): 1277-1280. (in Chinese).
[5] RIVEROS P A. The removal of antimony from copper electrolytes using amino-phosphonic resins: Improving the elution of pentavalent antimony[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 105(1-2): 110-114.
[6] LINDROOS L, VIRTANEN H. Method for the removal of arsenic from sulfuric acid solution: American, US6495024 B1 [P]. 2002-12-17.
[7] QIU Yong-hai, CHEN Bai-zhen. Comparison of different electrowinning processes for purification of copper electrolyte [J]. Nonferrous Smelting, 2002(3): 30-33. (in Chinese)
[8] BASHA C A, SELVI S J, RAMASAMY E, CHELLAMMAL S. Removal of arsenic and sulphate from the copper smelting industrial effluent [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 141(1-3): 89-98.
[9] HOFFMANN J E. The purification of copper refinery electrolyte [J]. Jom-Us, 2004, 56(7): 30-33.
[10] WANG S J. Impurity control and removal in copper tankhouse operations [J]. Jom-Us, 2004, 56(7): 34-37.
[11] ZHENG Ya-jie, XIAO Fa-xin, WANG Yong, LI Chun-hua, XU Wei, JIAN Hong-sheng, MA Yu-tian. Industrial experiment of copper electrolyte purification by copper arsenite [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15(2): 204-208.
[12] PENG Ying-lin, ZHENG Ya-jie, ZHOU Wen-ke, CHEN Wen-mi. Separation and recovery of Cu and As during purification of copper electrolyte [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(9): 2268-2273.
[13] RIVEROS P A, DUTRIZAC J E, LASTRA R. A study of the ion exchange removal of antimony(III) and antimony(V) from copper electrolytes [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2008, 47(3): 307-315.
[14] WANG X W, CHEN Q Y, YIN Z L, WANG M Y, TANG F. The role of arsenic in the homogeneous precipitation of As, Sb and Bi impurities in copper electrolyte [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108(3-4): 199-204.
[15] ZHENG Ya-jie,ZHOU Wen-ke, PENG Ying-lin, MA Yu-tian. Effect of valences of arsenic, antimony on removal rates of arsenic, antimony and bismuth in copper electrolyte [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2012, 43(3): 821-826. (in Chinese)
[16] NANSEU-NJIKI C P, ALONZO V, BARTAK D, NGAMWNI E, DARCHEN A. Electrolytic arsenic removal for recycling of washing solutions in a remediation process of CCA-treated wood [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 384(1-3): 48-54.
[17] SPEIGHT J G. Lange's handbook of chemistry [M]. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional, 2005.
[18] HISKEY J B, MAEDA Y. A study of copper deposition in the presence of group-15 elements by cyclic voltammetry and auger-electron spectroscopy [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2003, 33(5): 393-401.
[19] CHEN Bai-zhen, QIU Yong-hai, MEI Xian-zhi, ZHANG Xiang-yuan, ZHONG Sheng-tao, LIU Hong-tao, LIU Hui-quan. Current situation and development of decopperization and dearsenication by electrowinning [J]. Nonferrous Metals: Smelting, 1998(3): 29-31. (in Chinese)
[20] BARRADAS R G, GIRGIS M. Cathodic copper deposition at 65 °C in the absence and presence of Bi3+ and Sb3+ additives in acidified CuSO4 aqueous solutions [J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1991, 22B(5): 575-581.
[21] PIROGOV B Y, ZELINSKY A G. Numerical simulation of electrode process in Cu/CuSO4 + H2SO4 system [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 49(20): 3283-3292.
[22] ZHOU Wen-ke, PENG Ying-lin, ZHENG Ya-jie, MA Yu-tian, CUI Tao. Reduction and deposition of arsenic in copper electrolyte [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(12): 2772-2777.
[23] DALEWSKI F. Removing arsenic from copper smelter gases [J]. Journal of the Minerals and Materials Society, 1999, 51(9): 24-26.
[24] HINATSU J T, FOULKES F R. Electrochemical kinetic parameters for the cathodic deposition of copper from dilute aqueous acid sulfate solutions [J]. The Canadian Jornal of Chemical Engineering, 1991, 69(2): 571-577.
郑雅杰1,2,彭映林1,柯 浪1,陈文汨1
1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院, 长沙 410083;
2. 新疆有色中南大学联合研究院,乌鲁木齐 830000
摘 要:通过分段电积、SO2还原、蒸发结晶使铜电解液中的铜砷得到分离与回收。当电流密度为200 A/m2、电解液温度为55 °C、电解液循环速率为10 mL/min、终点铜浓度高于25.88 g/L时,电积得到纯阴极铜。调节电流密度为100 A/m2、电解液温度为65 °C、铜离子浓度从24.69 g/L 降至0.42 g/L时,砷的去除率为18.25%。通入SO2 将脱铜电解液中的As (V)充分还原为As (III)后,蒸发浓缩还原后液,冷却结晶得到As2O3晶体,砷的回收率为59.76%。阴极极化曲线表明,铜离子浓度和As(V)均影响铜还原的极限电流密度。
关键词:铜电解液;阴极铜;砷;SO2;还原;电积;结晶
(Edited by Hua YANG)
Foundation item: Project (2011B0508000033) supported by the Special Project on the Integration of Industry, Education and Research of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, China
Corresponding author: Ya-jie ZHENG; Tel: +86-731-88836285; E-mail: zzyyjj01@qq.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62713-2

