7A55铝合金热变形的速率控制机制
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第1期
论文作者:冯 迪 张新明 刘胜胆 吴泽政 谈 琦
文章页码:28 - 35
关键词:7A55铝合金;加工图;热变形;动力学分析;动态再结晶
Key words:7A55 aluminum alloy; processing maps; hot deformation; kinetic analysis; dynamic recrystallization
摘 要:利用Gleeble-3500热模拟试验机对7A55铝合金在300~450 °C温度范围和0.01~1 s-1应变速率范围内的热变形行为进行研究。建立了7A55铝合金的热加工图,对该合金的热变形行为进行了遵循幂律关系的动力学速率分析。结果表明:7A55铝合金在410~450 °C和0.05~1 s-1的热变形条件下发生了动态再结晶。热加工图的分析结果与动力学分析结果的吻合度较高。动态再结晶及动态回复变形的表观激活能分别为91.2和128.8 kJ/mol,这说明7A55合金的动态再结晶机制为晶界自扩散,而动态回复机制为位错的交滑移。
Abstract: The hot deformation behavior of 7A55 aluminum alloy was investigated at the temperature ranging from 300 °C to 450 °C and strain rate ranging from 0.01 s-1 to 1 s-1 on a Gleeble-3500 simulator. Processing maps were established in order to apprehend the kinetics of hot deformation and the rate controlling mechanism was interpreted by the kinetic rate analysis obeying power-law relation. The results indicated that one significant domain representing dynamic recrystallization (DRX) existed on the processing maps and lying in 410-450 °C and 0.05-1 s-1. The conclusions of kinetic analysis correlated well with those obtained from processing maps. The apparent activation energy values calculated in the dynamic recrystallization (DRX) domain and the stability regions except dynamic recrystallization (DRX) domain were 91.2 kJ/mol and 128.8 kJ/mol, respectively, which suggested that grain boundary self-diffusion and cross-slip were the rate controlling mechanisms.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 28-35
Di FENG1,2, Xin-ming ZHANG1,2, Sheng-dan LIU1,2, Ze-zheng WU1,2, Qi TAN1,2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. The Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Metal Materials Science and Engineering (Ministry of Education), Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 3 December 2012; accepted 16 April 2013
Abstract: The hot deformation behavior of 7A55 aluminum alloy was investigated at the temperature ranging from 300 °C to 450 °C and strain rate ranging from 0.01 s-1 to 1 s-1 on a Gleeble-3500 simulator. Processing maps were established in order to apprehend the kinetics of hot deformation and the rate controlling mechanism was interpreted by the kinetic rate analysis obeying power-law relation. The results indicated that one significant domain representing dynamic recrystallization (DRX) existed on the processing maps and lying in 410-450 °C and 0.05-1 s-1. The conclusions of kinetic analysis correlated well with those obtained from processing maps. The apparent activation energy values calculated in the dynamic recrystallization (DRX) domain and the stability regions except dynamic recrystallization (DRX) domain were 91.2 kJ/mol and 128.8 kJ/mol, respectively, which suggested that grain boundary self-diffusion and cross-slip were the rate controlling mechanisms.
Key words: 7A55 aluminum alloy; processing maps; hot deformation; kinetic analysis; dynamic recrystallization
1 Introduction
Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy is one of the important aeronautical materials owing to the excellent combination properties of high strength, high toughness and good corrosion resistance. Study on the hot deformation behavior is significant in optimizing its workability as well as in avoiding microstructural damage during processing [1]. Evaluation of the stress- strain curves, calculation of stress activation energy and processing maps have been the traditional approaches to analyze the deformation mechanisms of aluminum alloy. Kinetics of Al-5Si alloy [2], Al-4Mg alloy [3], Al-10% SiC (volume fraction) [4] alloy and Al-Cu-Mg alloy [5] were studied by RAO and PRASAD et al using the stress-strain curves together with processing maps. The “safe” windows for metal processing were identified; the rate controlling and the damage mechanisms at certain processing conditions were also discussed. Based on the hot deformation behavior of Al-5.7Mg alloy with erbium, it was found that two dynamic recovery domains existed in the processing map [6], and the activation energies estimated in these two domains were 180 kJ/mol and 163 kJ/mol respectively, which suggested that cross-slip of dislocation and lattice self-diffusion were the deformation mechanisms. High-temperature deformation behaviors of Al-5.9Cu-0.5 Mg alloy and Al-5.9Cu-0.5 Mg alloy containing 0.06Sn by hot compression tests were researched [7], and the generated flow stress data were used to develop processing maps to delineate the process domains for safe metal working. YAN et al [8,9] investigated the hot deformation behavior and microstructures of 7055 commercial alloy. They concluded that dynamic recrystallization behavior occurred at 375-425 °C and 0.001 s-1 and dynamic recovery was the main softening mechanism during hot deformation. The hot deformation activation energy of the alloy was given as 146 kJ/mol.
However, in the bulk of industrial Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy, which contains a large number of dispersion particles precipitated during slow cooling from the high temperature of homogenization, the pinning effect of the second phase on the motion of dislocations at different temperatures may not be ignored, since those effects can alter the flow stress and result in different rate controlling mechanisms. Besides, the bulk materials (thick plates) with large cross section under severe plastic deformations would show various thermal deformation behaviors in different layers. Therefore, the flow softening mechanism of bulk industrial 7A55 alloy remained debatable, and the rate controlling mechanism of hot deformation has not been evaluated in details. The aim of the present work is applying the processing map to reveal the dynamics of hot deformation behavior for bulk of industrial 7A55 alloy and correlating with the results on the rate controlling mechanism evaluated from the kinetic analysis.
2 Experimental
The material used in this study was 7A55 aluminum alloy, which was provided by the China Aluminum Group Co. LTO (CHALCO). This material was industrially homogenized and air cooled. The microstructure of the initial temper was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). For hot compression testing, cylindrical specimens of 10 mm in diameter and 15 mm in height were machined. A 0.8 mm-diameter hole was drilled to a depth of 5 mm at half the height of the specimen for insertion of a thermocouple. Hot compression tests were conducted in the temperature range of 300-450 °C and true strain rate range of 0.01-10 s-1. Constant true strain rate with strain was achieved by the Gleeble-3500 simulator. The adiabatic temperature rise was measured and the flow stress was corrected for the adiabatic temperature rise by assuming a linear relation of log (flow stress) with inverse of temperature over intervals of 50 °C [1,10]. The maximum adiabatic temperature rise was 42.1 °C at 300 °C and 10 s-1 and it decreased with increasing temperature and decreasing strain rate to become zero at 450 °C and below 0.1 s-1. After each compression test, the deformed specimens were quenched into water quickly, sectioned parallel to the compression axis for microstructural examination. Metallographic samples were anodized (5 mL HBF4, 200 mL H2O) at 20 V for 3 min. Grain structures were observed by OM under polarized light. The average grain size was determined by the mean liner intercept technique (grain size=mean liner intercept×1.78) [11].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure of initial temper
The original microstructure and the distribution of the second phase particles precipitated during air cooling after industrial homogenization are shown in Fig. 1. Coarse precipitates at the grain boundary (GBPs) and relative fine particles in the matrix (MPs) were observed. As mentioned above, the bulk of aluminum alloy billet after industrial homogenization was all cooled in air at room temperature, and the cooling time may be 20 h or more for thick plates. Therefore, a large number of the second phase particles precipitated and even coarsened during this course. EDS revealed that the GBPs were S(A), coarsened η phases (B) and Al7Cu2Fe (C), and the relative finer η phase also precipitated in the matrix (D). The average particle size at the grain boundary was 10 μm, while that precipitated in the grain interior was 1-1.5 μm. Some of these pre-precipitated particles provided with high dissolution temperature cannot re-dissolve during thermal processing in solution treatment. The reciprocity between even the second phase particles and dislocations would affect the thermal deformation behavior of 7A55 aluminum alloy.

Fig. 1 Optical micrographs showing initial microstructure and second phase particles observation
3.2 Stress–strain curves
True stress-true strain curves obtained at 300, 350, 400 and 450 °C and at different strain rates are shown in Fig. 2. Referring to Fig. 2, the flow curves exhibited almost no decline after the stress peak reached during deformation. Only at temperature of 400-450 °C and strain rate of 0.1 s-1, a small single peak has occurred before a steady state is reached, and the wave characteristic could be considered the occurrence of DRX [12]. At all the strain rates, the first stress peak has been reached at a low strain in the high temperature range than the corresponding curve in the low temperature range. The strain to the peak stress increases with increasing strain rate (Fig. 2). The above temperature and strain rate effects on the strain to peak stress suggest that this parameter is thermally activated, but the flow softening mechanism remained debatable and must be confirmed by further microstructure examination correlating with processing maps and kinetic analysis.
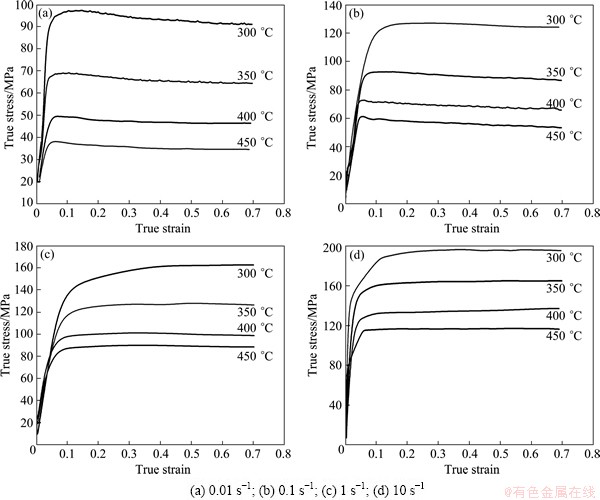
Fig. 2 True stress-strain curves at different strain rates
3.3 Microstructure after deformation
The hot expressed microstructures under different deformation conditions are shown in Fig. 3. Large particles at the grain boundaries and fine precipitates in the grain interior are similar to those of the starting material in the temperature range of 300-350 °C (Figs. 3(a) and (b)). After processing at 400 °C, the number of particles and precipitates decreased (Figs. 3(c), (d)). At temperature higher than 400 °C, a large number of dispersion particles were dissolving, and fine grains nucleation occurred preferentially at grain boundaries (Figs. 3(e), (f)), which could be considered the evidence of DRX [12].
3.4 Processing maps
3.4.1 Approach
The basis for the processing maps is the dynamic materials model [13-18]. The efficiency of power dissipation occurring through microstructural changes during deformation is given as
 (1)
(1)
where m is the strain rate sensitivity of flow stress given by 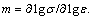 The extremum principles of irreversible thermodynamics as applied to continuum mechanics of large plastic flow are explored to define a criterion for the onset of flow instability given by the equation for the instability parameter ξ:
The extremum principles of irreversible thermodynamics as applied to continuum mechanics of large plastic flow are explored to define a criterion for the onset of flow instability given by the equation for the instability parameter ξ:
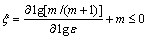 (2)
(2)
The three-dimensional variation of the efficiency of power and dissipation instability parameter as a function of temperature and strain rate represents a processing map. Processing map reveals the deterministic domains where individual microstructural processes occur and the limiting conditions for the regimes of flow instability. By processing under conditions of the highest efficiency in the “safe” domains and by avoiding the regimes of flow instabilities, the intrinsic workability of the material may be optimized and microstructural control may be achieved.
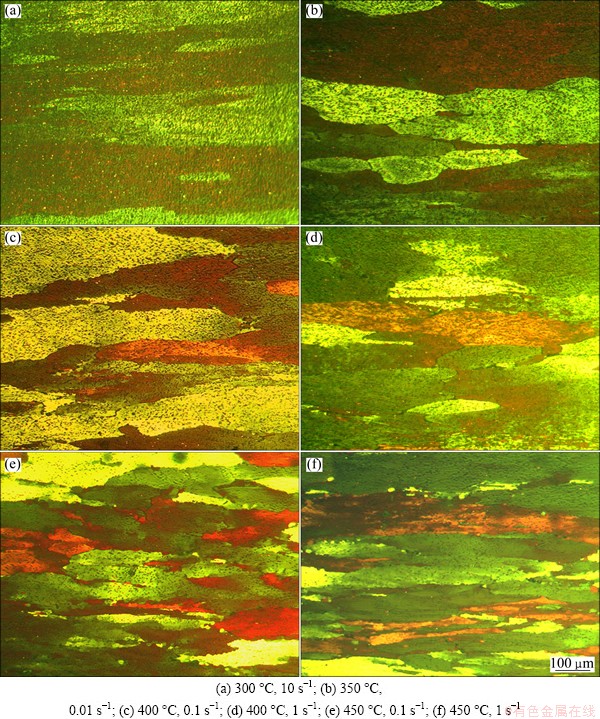
Fig. 3 Optical micrographs of deformed specimens conducted at different temperatures and strain rates
3.4.2 Processing maps
Processing maps obtained at strain ranging from 0.1 to 0.9 are shown in Figs. 4. The numbers against each contour represent the efficiency of power dissipation as percent and the dot lines represent regimes of flow instability as delineated using the criterion given in Eq. (1). The microstructural evolution of the system with hot deformation may be tracked by following the changes in the processing maps as a function of strain [1]. At the start of the plastic deformation, the different temperature and strain rate combinations generate a spectrum of dissipative energy states. With strain increasing, the dissipative energy states will self-organize into microstructural trajectories that go through transients to form domains within which the efficiency of power dissipation reaches a peak.
Referring to Fig. 4(a), the map obtained at a strain of 0.1 exhibits an instantaneous state, and the highest efficiency domain of 35.3% lies in the temperature range of 430-450 °C and the strain rate range of 0.01-0.1 s-1. As the strain increased to 0.5, this domain has changed to a wide temperature and high strain rate range domain 1 in Fig. 4(b) at 410-450 °C and 0.05-1 s-1 with a peak efficiency of 35.2%.
In higher strains, the profile continued to self- organize into a steady state, and the peak efficiency values increased to 37.7 % and 38% at strain of 0.5 and 0.9 respectively, while the instability area lied in high strain rate range(>1 s-1) in the entire temperature range.
In high metallic materials, the maximum efficiency of power dissipation for DRX is about 50% while it is 35% in stacking fault material [6]. Therefore, it is seemed that the deformation behavior in domain 1 might represent DRX. However, the addition of solution atoms reduced the stacking fault energy of 7A55 aluminum alloy so effectively that DRX could occur in certain conditions, as observed in true stress-strain curves (Fig. 2(b)) and microstructure after deformation (Fig. 3).
3.5 Kinetic analysis
The kinetic analysis that is generally used for steady state flow at large strains has been applied to the flow stress data at lower plastic strains with a view to correlate the changes with the dynamics revealed by processing maps as described above [1,12]. The power law type kinetic rate equation for strain rate is given by
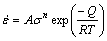 (3)
(3)
where A is the constant, σ is the flow stress, n is the stress exponent, Q is the activation energy, R is the mole gas constant and T is the thermodynamic temperature.

Fig. 4 Processing maps at different true strains
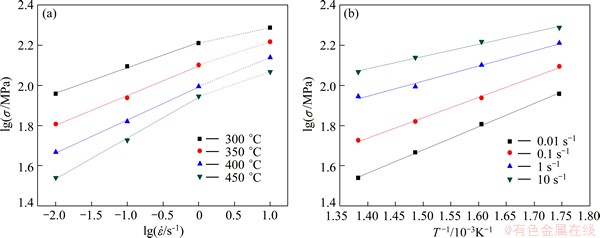
Fig. 5 Variation of lg σ and  at different test temperatures (a) and variation of lg σ and 1000/T at different strain rates (b)
at different test temperatures (a) and variation of lg σ and 1000/T at different strain rates (b)
Plot of lg σ versus  is shown in Fig. 5(a), where flow stress values corresponding to a strain of 0.5 have been used. As lg σ versus
is shown in Fig. 5(a), where flow stress values corresponding to a strain of 0.5 have been used. As lg σ versus 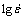 does not obey the linear relationship at the highest strain rate (10 s-1), the data at lower strain rates are taken for linear fit to calculate the activation energy and stress exponent. From this plot, the values of stress exponent (n) have been estimated to be 4.94 and 6.95 in domain 1 and flow stability regime respectively. These values are found to be nearly independent of strain. The Arrhenius plot of lg σ versus 1/T is shown in Fig. 5(b) for the same strain of 0.7 (steady state). The apparent activation energy values in domain 1 and flow stability regime except domain 1 were estimated to be 91.2 kJ/mol and 128.8 kJ/mol respectively. These two activation values matched with the grain boundary self-diffusion (84 kJ/mol for pure aluminum) and cross-slip (117 kJ/mol for pure aluminum) respectively [12,19,20].
does not obey the linear relationship at the highest strain rate (10 s-1), the data at lower strain rates are taken for linear fit to calculate the activation energy and stress exponent. From this plot, the values of stress exponent (n) have been estimated to be 4.94 and 6.95 in domain 1 and flow stability regime respectively. These values are found to be nearly independent of strain. The Arrhenius plot of lg σ versus 1/T is shown in Fig. 5(b) for the same strain of 0.7 (steady state). The apparent activation energy values in domain 1 and flow stability regime except domain 1 were estimated to be 91.2 kJ/mol and 128.8 kJ/mol respectively. These two activation values matched with the grain boundary self-diffusion (84 kJ/mol for pure aluminum) and cross-slip (117 kJ/mol for pure aluminum) respectively [12,19,20].
However, the above activation energy values were higher than those for grain boundary self-diffusion and cross-slip. It is possible that there was a significant contribution from the lager back stress caused by the presence of a large number of dispersion particles precipitated during slow cooling from the high temperature of homogenization, which might retard the process of dynamic recovery and dynamic recrystallization [21,22].
Equation (3) is not based on any theoretical model or atomistic rate-controlling mechanism and the constants A and n do not have simple physical interpretations. A more rigorous equation has been found very useful, and an important conception called activation volume was defined as [3]
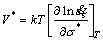 (4)
(4)
where  is the steady-state strain rate, V* is the activation volume, σ* is the effective stress, k is Boltzman constant and T is the thermodynamic temperature.
is the steady-state strain rate, V* is the activation volume, σ* is the effective stress, k is Boltzman constant and T is the thermodynamic temperature.
To a first approximation, the magnitude of back-stress (σ0) may be estimated by assuming that grain boundary self-diffusion is the rate-controlling in domain 1 (Q=135 kJ/mol) and cross-slip is rate-controlling in the flow stability regime except domain 1. The effective stress (σ*) given by (σ-σ0) may then be obtained for 7A55 aluminum alloy.

Fig. 6 Dependence of flow stress (ε=0.5) on strain rate at different temperatures (a) and variation of apparent activation volume V with flow stress (b)
Table 1 Activation energy and activation volume obtained for 7A55 aluminum alloy (b is Burger’s vector)
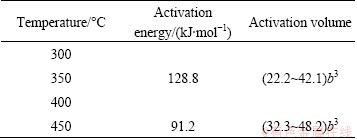
The activation parameters and the apparent activation volume could be then estimated from Eq.(4) as a function of effective stress and the variation is shown in Fig. 6 and Table 1. The estimated V* values in stability domain and domain 1 falling in the range of (22.2~42.1)b3 and (32.3~48.2)b3 decreased with increasing flow stress respectively. The activation area decreases with the effective stress in an exponential fashion which is well established in other materials [3,21]. Also the data corresponding to the domains falling in different activation volumes ranges suggested that the mechanism of dynamic recrystallization involving grain boundary self-diffusion was the rate-controlling mechanism in the temperature range of 410-450 °C and strain rate of 0.05-1 s-1, while the mechanism of dynamic recovery involving dislocation cross-slip was the rate-controlling mechanism in stability domain [3,12,19,20].
The variation of the apparent activation volume V* with effective stress also took the deformation conditions of high strain rate (>1 s-1) into account, and scattered data points appeared (arrows in Fig. 6(b)). The reason was that the shear deformation occurred at higher strain rate (10 s-1) in the instability domain (Fig. 7) [7].

Fig. 7 Optical micrograph showing shear band formation when deformed at 450 °C and 10 s-1
4 Conclusions
1) The processing maps revealed the existence of a high efficiency of power dissipation domain in the temperature range of 410-450 °C and strain rate of 0.05-1 s-1 with a peak efficiency of 38%. The instability domain lied in the high strain rate (>1 s-1) and entire temperature range, and shear deformation was the major irreversible changes in the microstructure.
2) The apparent activation energy values were 91.2 kJ/mol and 128.8 J/mol in the high efficiency domain and stability domain respectively.
3) The apparent activation area values estimated after making a correction for the back-stress were (22.2~42.1)b3 in the temperature range of 300-400 °C. The activation volume decreased with increase in effective stress.
4) The mechanism of dynamic recrystallization involving grain boundary self-diffusion was suggested to be the rate-controlling mechanism in the temperature range of 410-450 °C and strain rate of 0.05-1 s-1, while the mechanism of dynamic recovery involving dislocation cross-slip was the rate-controlling mechanism in stability domain.
References
[1] PRASAD Y V R K, RAO K P. Processing maps and rate controlling mechanisms of hot deformation of electrolytic tough pitch copper in the temperature range 300-950 °C [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 391(1-2): 141-150.
[2] RAO K P, DORAIVELU S M, ROSHAN H M, PRASAD Y V R K. Deformation processing of an aluminum alloy containing particles: Studies on Al-5 pct Si alloy 4043 [J]. Metallurgical Transaction A, 1983, 14(8): 1671-1679.
[3] RAO K P, PRASAD Y V R K. High temperature deformation kinetics of Al-4Mg alloy [J]. Journal of Mechanical Working Technology, 1986, 13(1): 83-95.
[4] RADHAKRISHNA B B V, MAHAJAN Y R, ROSHAN H M, PRASAD Y V R K. Processing maps for hot-working of powder metallurgy 1100 Al-10 vol% SiC-particulate metal-matrix composite [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1992, 28(8): 2141-2147.
[5] SARKAR J, PRASAD Y V R K, SURAPPA M K. Optimization of hot workability of an Al-Mg-Si alloy using processing maps [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1995, 30(11): 2843-2848.
[6] MENG G, LI B L, LI H M, HUANG H, NIE Z R. Hot deformation and processing maps of an Al-5.7 wt.% Mg alloy with erbium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 517(1-2): 132-137.
[7] BANERJEE S, ROBI P S, SRINIVASAN A. Deformation processing maps for control of microstructure in Al-Cu-Mg alloys microalloyed with Sn [J]. Metallurgical Transaction A, 2012, 43(10): 3834-3849.
[8] YAN Liang-ming, SHEN Jian, LI Zhou-bing, LI Jun-ping, YAN Xiao-dong, MAO Bai-ping. Modelling for flow stress and processing map of 7055 aluminum alloy based on artificial neural networks [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(7): 1296-1301. (in Chinese)
[9] YAN Liang-ming, SHEN Jian, LI Zhou-bing, LI Jun-ping, YAN Xiao-dong. Microstructure evolution of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy during hot deformation [J]. Rare Metals, 2010, 29(4): 426-432.
[10] PRASAD Y V R K, RAO K P. Mechanisms of high temperature deformation in electrolytic copper in extended ranges of temperature and strain rate [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 374(1-2): 335-341.
[11] LIU F C, MA Z Y. Influence of tool dimension and welding parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction-stir-welded 6061-T651 aluminum alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2008, 39(10): 2377-2388.
[12] JONAS J J, SELLARS C M, TEGAR W J. Strength and structure under hot working conditions [J]. Metallurgical Reviews, 1969, 14: 1-24.
[13] RAO K P, PRASAD Y V R K, SURESH K. Materials modeling and simulation of isothermal forging of rolled AZ31B magnesium alloy: Anisotropy of flow [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32(5): 2545-2553.
[14] RAO K P, PRASAD Y V R K, DHARMENDRAA C, HORTC N, KAINERC K U. Compressive strength and hot deformation behavior of TX32 magnesium alloy with 0.4% Al and 0.4% Si additions [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(22-23): 6964-6970.
[15] PRASAD Y V R K, RAO K P, HORTB N, KAINERB K U. Optimum parameters and rate-controlling mechanisms for hot working of extruded Mg–3Sn–1Ca alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 502(1-2): 25-31.
[16] PRASAD Y V R K, RAO K P, HORTB N, KAINERB K U. Hot working parameters and mechanisms in as-cast Mg–3Sn–1Ca alloy [J]. Materials Letters, 2008, 62(26): 4207-4209.
[17] SRINIVASAN N, PRASAD Y V R K, RAO P R. Hot deformation behaviour of Mg-3Al alloy—A study using processing map [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 476(1-2): 146-156.
[18] PRASAD Y V R K, RAO K P. Mechanisms of high temperature deformation in electrolytic copper in extended ranges of temperature and strain rate [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 374(1-2): 335-341.
[19] FORST H J, ASHBY M F. Deformation mechanism maps: The plasticity and creep of metals and ceramics [M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1982.
[20] ASHBY M F. A first report on deformation mechanism maps [J]. Acta Metallurgical, 1972, 20(7): 887-897.
[21] SASTRY D H. Impression creep technique—An overview [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 409(1-2): 67-75.
[22] RAO K P, PRASADA Y V R K, HORTB N, KAINERB K U. Hot workability characteristics of cast and homogenized Mg–3Sn–1Ca alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 201(1-3): 359-363.
冯 迪1,2,张新明1,2,刘胜胆1,2,吴泽政1,2,谈 琦1,2
1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:利用Gleeble-3500热模拟试验机对7A55铝合金在300~450 °C温度范围和0.01~1 s-1应变速率范围内的热变形行为进行研究。建立了7A55铝合金的热加工图,对该合金的热变形行为进行了遵循幂律关系的动力学速率分析。结果表明:7A55铝合金在410~450 °C和0.05~1 s-1的热变形条件下发生了动态再结晶。热加工图的分析结果与动力学分析结果的吻合度较高。动态再结晶及动态回复变形的表观激活能分别为91.2和128.8 kJ/mol,这说明7A55合金的动态再结晶机制为晶界自扩散,而动态回复机制为位错的交滑移。
关键词:7A55铝合金;加工图;热变形;动力学分析;动态再结晶
(Edited by Hua YANG)
Foundation item: Project (2012CB619505) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Xin-ming ZHANG; Tel: +86-731-88830265; E-mail: xmzhang_cn@yahoo.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63024-7

