J. Cent. South Univ. (2012) 19: 1961-1966
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-012-1232-x
Sulfur speciation transformation during bioleaching of pyrite-containing sphalerite concentrate by thermophile Sulfolobus metallicus at 65 ℃
XIA Jin-lan(夏金兰)1,2, ZHAO Xiao-juan(赵小娟)1,2, LIANG Chang-li(梁长利)1,2, YANG Yi(杨益)1,2,
NIE Zhen-yuan(聂珍媛)1,2, TANG Lu(汤露)1,2, MA Chen-yan(马陈燕)3, ZHENG Lei(郑雷)3,
ZHAO Yi-dong(赵屹东)3, QIU Guan-zhou(邱冠周)1,2
1. Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy of Ministry of Education (Central South University), Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Institute of High Energy Physics,
Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
? Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012
Abstract: Sulfur speciation transformation during bioleaching of pyrite-containing sphalerite concentrate by thermophile Sulfolobus metallicus (S. metallicus) at 65 ℃ was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and sulfur K-edge X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy (XANES). The results show that the presence of S. metallicus effectively enhances the dissolution of the mineral. The yield of zinc increases from 0.5 g/L in sterile control to 2.7 g/L in bioleaching. The pyrite in the concentrate facilitates zinc dissolution in the early stage, but has hindrance role in the late stage for the formation of jarosite. Sulfur speciation analyses show that jarosite and elemental sulfur are main products in bioleaching process, and the accumulation of jarosite is mainly responsible for the decline of leaching efficiency.
Key words: sphalerite; bioleaching; Sulfolobus metallicus; sulfur K-edge X-ray absorption near edge spectroscopy (XANES); sulfur speciation transformation
1 Introduction
As the most important source of zinc, sphalerite is a widely distributed mineral that commonly occurs in association with other sulfide minerals such as galena and pyrite. Extraction of zinc from sphalerite based on roast–leach–electro (RLE) winning technology is currently responsible for more than 85% of Zn production in the world [1]. The RLE process, however, involves highly energy-consumptive roasting and smelting and often produces a lot of sulfur dioxide that causes severe air pollution [2]. With the distinct advantages of low energy consumption and environment friendliness, biohydrometallurgical process is an effective alternative way for zinc production, and is especially efficient for the treatment of low grade zinc sulfide ore [3].
Mesophilic sulfur and ferrous-oxidizing bacteria such as Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Leptospirilum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans are most extensively investigated in sphalerite bioleaching [4-6]. However, the slow kinetics of bioleaching with mesophiles impedes their wide industrial application [7-8]. Recently, increasing attention has been focused on the application of sulfur and/or ferrous-oxidizing thermophiles, which possess a higher mineral oxidation capacity [9-10]. For instance, MOUSAVI et al [10] found that the zinc recovery in the presence of thermophile Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans was higher than that by mesophile A. ferrooxidans (87%-72% under optimum condition).
Sphalerite can be decomposed by the combined action of Fe3+ and H+ through a polysulfide pathway, during which polysulfide and elemental sulfur are suggested to be the major sulfur-containing intermediates [11]. Further findings indicated that without sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, elemental sulfur may accumulate and form a passivation layer, which hinders the further dissolution of the mineral [1, 12].
It was reported that pyrite coexisting in the mineral facilitated sphalerite decomposition, where pyrite provided extra oxidant ferric [13-14]. However, when the Fe3+ is over accumulated, it will form a less-porous iron(III) precipitates on the mineral surface and hinder the further dissolution process [15].
It was proposed that some sulfur-containing substances, e.g., elemental sulfur and jarosite on the mineral surface might lead to passivation of sphalerite. RODRIGUEZ et al [3] and da SILVA [12] suggested that the elemental sulfur would accumulate on the sphalerite surface and form a strong diffusive barrier; therefore, the elimination of the sulfur passivation layer should be the pre-requisite for optimization of the dissolution process. However, GIAVENO et al [15] considered that controlling the jarosite precipitation is more significant than the removing of the sulfur layer, which is also supported by some other studies [16-18]. Compared with the mesophiles, few studies have been conducted on sulfur speciation transformation of sphalerite with thermophiles. Thus, the passivation mechanism for sphalerite bioleaching with thermophile(s), is still unclear. Investigation of sulfur speciation transformation during sphalerite bioleaching is contributive to reveal the nature of passivation and further to understand the dissolution mechanism of sphalerite.
In this work, we adopted X-ray diffraction (XRD), diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and sulfur K-edge X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy (XANES) to verify the surface sulfur speciation transformation of pyrite-containing sphalerite concentrate bioleaching with the thermophile Sulfolobus metallicus (S. metallicus) at 65 ℃.
2 Experimental
2.1 Minerals and reagents
The minerals used in this work were provided by School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, China. Mineral sample was analyzed by X-ray ?uorescence spectroscopy and the chemical composition is given in Table 1. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis showed the mineral was mainly composed by sphalerite and pyrite. The minerals used in this work were all ground to <75 μm. Standard minerals and other (bio)chemical reagents were of analytical or spectrographic grade.
Table 1 Chemical composition of original sphalerite concentrate (mass fraction, %)

2.2 Microorganism and culture condition
Archaeon strain S. metallicus YN 24 used in this work was isolated from an acidic hot spring associated with mine drainage in Tengchong, Yunnan Province, Southwest China and conserved by the Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy (Central South University), Ministry of Education of China. The strain used in bioleaching experiments was gradually adapted to 9K medium supplemented with 0.5% pyrite-containing sphalerite concentrate, and 0.02% yeast extraction. The cells were harvested by ?ltration (5 μm) and 30 min centrifugation (10 000 r/min). They were then washed twice with sulfuric acid (0.1 mol/L) and resuspended in sterilized fresh medium.
2.3 Bioleaching experiments
The bioleaching experiments were conducted in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, each containing 100 mL medium, supplemented with sphalerite concentrate (1%, w/φ) and yeast extraction (0.02%, w/φ). The flasks were sterilized by autoclaving (30 min, 120 ℃) and inoculated with the sphalerite-adapted S. metallicus. The initial cell concentration was 1.0×107 mL-1, and the initial pH of the cultures was adjusted to 1.5 by 0.5 mol/L H2SO4. The cell-free culture medium and sphalerite concentrate in the same condition were prepared as sterile controls. The cultures in Erlenmeyer flasks were incubated at 125 r/min and 65 ℃. The water evaporation was compensated with sterilized distilled water. In this work, triplicate identical groups were conducted in every experiment.
The progress of leaching was monitored every two days by measuring the metal concentrations (Zn and Fe), pH, redox potentials, and cell number. Zinc concentration was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS). The ferric and total iron concentrations in the solution were determined by sulfosalicylic acid spectroscopy method [19]. The concentrations of ferrous were determined by titration with potassium dichromate. The pH values were measured with pH meter (PHS-3C). Redox potentials (Eh) were measured with Pt electrode, using a calomel electrode (Hg/Hg2Cl2) as reference. The number of free cells in solution was directly counted with a Neubauer chamber counter under optical microscope. The preparation of the samples for XANES analyses were performed according to Ref. [20].
2.4 XRD and FT-IR studies
The solid samples were withdrawn every two days, prepared as described by HE et al [20] for XRD and FT-IR analysis. The FT-IR spectra of mineral samples were detected by a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (Nicolet Nexus 670) with diffusion reflectance attachment.
2.5 Sulfur K-edge XANES spectroscopy
Sphalerite, pyrite, elemental sulfur and jarosite were chosen as standard sulfur containing compounds. The sulfur K-edge XANES measurements of the samples were carried out at the beam line 4B7A of Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF), Institute of High Energy Physics (IHEP), Chinese Academy of Sciences. Sulfur K-edge spectra were obtained on a double-crystal monochromator (DCM) covering energy value of 2 460– 2 520 eV with a step size of 0.3 eV and were recorded in total electron yield (TEY) mode. Data analysis of the experimental XANES spectra was performed using the software WinXAS3.0, and the spectra were fitted with the LSFitXAFS [21].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Bioleaching of pyrite-containing sphalerite concentrate by S. metallicus
The leaching characteristics of sphalerite in bioleaching and chemical control groups are shown in Figs. 1(a) and (b), respectively. In the chemical controls, the pH increased consistently to about 3.0. However, in bioleaching group, the evolution of pH values could be divided into two stages: The pH ascended in the first two days and then consistently decreased to about 1.3. The rise of pH at the first stage of bioleaching, just like that in the chemical control, should be resulted from the acid dissolution of sphalerite through Eq. (1). However, during the second stage, S. metallicus oxidized S0 to sulfuric acid through Eq. (2), which led to the decrease of pH:
ZnS+2H++1/2O2→Zn2++H2O+S0 (1)
2S+3O2+2H2O 2SO42-+4H+ (2)
2SO42-+4H+ (2)
The redox potential in the bioleaching continuously increased from 270 mV to 640 mV (Fig. 1(b)); while in the sterile control, the redox potential decreased in the first two days and then stabilized at about 270 mV vs SCE until the end of the experiment. The obvious difference between chemical control and bioleaching group should be resulted from different abilities of Fe3+ regeneration. The Fe3+ consumed as shown in Eq. (3) cannot be effectively regenerated in the sterile chemical control group. While, in the bioleaching cases, the consumed Fe3+ can be regenerated effectively by the strain as shown in Eq. (4):
ZnS+2Fe3+→Zn2++2Fe2++S0 (3)
4Fe2++O2+4H+ 4Fe3++2H2O (4)
4Fe3++2H2O (4)
Leaching results showed that the yield of zinc in bioleaching was much higher than that in sterile control, 2.7 g/L in bioleaching and 0.5 g/L in sterile control, respectively. It is noteworthy that the leaching rate of zinc obviously decreased after the 8th day, which may come from the decrease of cell number and formation of residues on the mineral surface.
3.2 XRD of mineral sample and leaching residues
The XRD spectra of original mineral and leaching residues are shown in Figs. 2(a), (b), and (c), respectively. It can be seen from Figs. 2(a) and (b) that the solid leaching residues in the sterile chemical control were mainly un-reacted sphalerite and pyrite, along with small amount of elemental sulfur and jarosite, which indicated that the leaching of mineral was minor. Compared with that, jarosite and elemental sulfur were obviously found as the main compounds in bioleached residues.

Fig. 1 Leaching behaviors of sphalerite concentrate in sterile chemical control (a) and with S. metallicus (b), and comparison of variations in concentrations of Fe2+ and total iron in presence of S. metallicus and without bacteria (c)
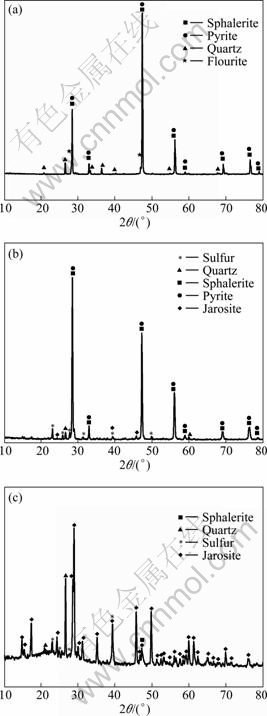
Fig. 2 XRD spectra of original sphalerite concentrate (a), leached residues in sterile control (b), and bioleached residues with S. metallicus (c)
3.3 FT-IR spectroscopic analysis
To further identify the species accumulated on the mineral surface during leaching process, the leaching residues were analyzed by FT-IR and the spectra are shown in Fig. 3, where the spectra of the original sphalerite concentrate, potassium jarosite and ammonium jarosite are presented as the references. Three peaks appearing at the wavelength domain of 1 000- 1 200 cm-1 could be assigned to S—O bending vibration of SO42-, and they are similar in potassium jarosite and ammonium jarosite; while the peak appearing at 1 430 cm-1 could be assigned to N—H vibration, because it similarly appeared on the spectra of ammonium jarosite. The spectra of chemical and bioleaching residues confirmed the formation of potassium jarosite and ammonium jarosite, and this result is consistent with that of KONISHI et al [22].
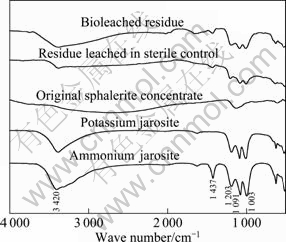
Fig. 3 FT-IR spectra of leached residues of sterile control and bioleached experiment (Spectra of original sphalerite concentrate, potassium jarosite and ammonium jarosite present as references)
3.4 XANES analysis
To further understand the sulfur speciation transformation of sphalerite concentrate leached by S. metallicus, sulfur K-edge XANES spectroscopy was applied. Zinc sulfide, pyrite, elemental sulfur and jarosite that may appear in bioleaching process were chosen as the reference compounds, and the sulfur K-edge XANES spectra of these compounds are shown in Fig. 4(a). The spectra of the sphalerite concentrate bioleached with time and the fitted results for that at the 6th day are shown in Figs. 4(b) and (c), respectively. The fitted results of the XANES spectra for other sampling points are given in Table 2.
It is clear that in the 2nd day, two peaks appeared at 2.470 2 and 2.480 4 keV, respectively, which showed the appearance of elemental sulfur and jarosite on the mineral surface, and the fitted results confirmed that about 5.1% jarosite and 37.5% elemental sulfur were accumulated in the solid phase (Table 2). This indicated that in the first stage the chemical dissolution of pyrite and sphalerite was processed, which resulted in accumulation of elemental sulfur. It was noteworthy that the amount of elemental sulfur decreased with time, while the tendency of jarosite was just reversed. The results suggested that the strain played an important role in this stage, which effectively eliminated elemental sulfur and regenerated Fe3+, and further led to the formation of jarosite.
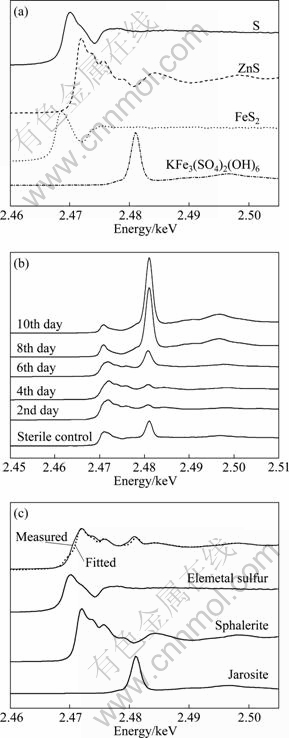
Fig. 4 Sulfur K-edge spectra of different sulfur-containing reference compounds (a) and bioleached sphalerite concentrate at different time and sterile control (b), and fitted XANES spectra of sphalerite concentrate bioleached residues after 6 days (c)
Table 2 Fitted results of sulfur K-edge XANES spectra of sphalerite concentrate bioleached at different time and spectrum of acid leached residue in sterile control
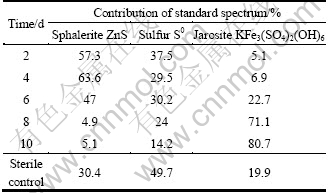
The fitted results confirmed that sphalerite, elemental sulfur and jarosite are the main components of the sterilized residues, among which elemental sulfur is most abundant. In the bioleached residues, jarosite rather than elemental sulfur was found to be the most abundant substance. The results confirmed that S. metallicus can effectively eliminate the elemental sulfur produced during the oxidative dissolution of pyrite and sphalerite. Meanwhile, pyrite was not detected in both the chemical and bioleached residues by XRD and sulfur K-edge XANES spectroscopy indicated that the dissolution of pyrite was prior to the sphalerite. The dissolution of pyrite in the first stage provided Fe2+, which could be oxidized to Fe3+ by S. metallicus to enhance the dissolution of sphalerite.
The decline of bioleaching rate occurred after the 8th day, and at the same time the amount of jarosite in the residues reached approximately 71%, which indicated that the accumulation of jarosite should account for the decline of the bioleaching rate. The result is not consistent with some studies of sphalerite concentrate bioleached with mesophilic A. ferrooxidans, in which elemental sulfur was suggested to be responsible for the passivation [23]. We think that the difference might come from the different sulfur oxidation activities of the strains applied, because thermophiles possess higher sulfur oxidation activity, thus they can more effectively eliminate the passivation of elemental sulfur [3].
It seems that in bioleaching of sphalerite with thermophilic microorganisms, iron contained in sphalerite can promote dissolution of zinc at the early stage, but may hinder the progress at the late stage due to the formation of iron precipitate jarosite. It is suggested that the control of passivation from ferric precipitate jarosite is the key step to maintain high bio-oxidation efficiency in thermo-bioleaching of pyrite-containing sphalerite concentrate.
4 Conclusions
1) The presence of S. metallicus can effectively enhance the zinc dissolution. The yield of zinc is 2.7 g/L in bioleaching and 0.5 g/L in sterile control, respectively.
2) The pyrite in the concentrate facilitates the zinc dissolution in the early stage, but hinders the zinc dissolution in the late stage for the accumulation of jarosite.
3) Jarosite and elemental sulfur are the main compositions of the bioleached residues, and the accmulation of jarosite is mainly responsible for the decline of the dissolution rate.
References
[1] de SOUZA A D, PINA P S, LEAO V A. Bioleaching and chemical leaching as an integrated process in the zinc industry [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(6): 591-599.
[2] HOANG J, REUTER M A, MATUSEWICZ R, HUGHES S, PIRET N. Top submerged lance direct zinc smelting [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2009, 22 (9/10) :742-751.
[3] RODRIGUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BLAZQUEZ M, GONZALEZ F, MUNOZ J. New information on the sphalerite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71(1/2): 57-66.
[4] FOWLER T, CRUNDWELL F. Leaching of zinc sulfide by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: Experiments with a controlled redox potential indicate no direct bacterial mechanism [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(10): 3570-3575.
[5] XIA Le-xian, LIU Jian-she, XIAO Li, ZENG Jia, LI Ban-mei, GENG Mei-mei, QIU Guan-zhou. Single and cooperative bioleaching of sphalerite by two kinds of bacteria-Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans [J]. Transactions of the Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(1): 190-195.
[6] CHEN Song, QIU Guan-zhou, QIN Wen-qing, LAN Zhuo-yue. Bioleaching of sphalerite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans cultured in 9K medium modified with pyrrhotite [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15(4): 503-507.
[7] DEVECI H, JORDAN M, POWELL N, ALP I. Effect of salinity and acidity on bioleaching activity of mesophilic and extremely thermophilic bacteria [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(3): 714-721.
[8] PINA P, LEAO V, SILVA C, DAMAN D, FRENAY J. The effect of ferrous and ferric iron on sphalerite bioleaching with Acidithiobacillus sp [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18(5): 549-551.
[9] MOUSAVI S, JAFARI A, YAGHMAEI S, VOSSOUGHI M, ROOSTAAZAD R. Bioleaching of low-grade sphalerite using a column reactor [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 82(1/2): 75-82.
[10] MOUSAVI S, YAGHMAEI S, VOSSOUGHI M, JAFARI A, ROOSTAAZAD R. Zinc extraction from Iranian low-grade complex zinc-lead ore by two native microorganisms: Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and sulfobacillus [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2006, 80(2/3/4): 238-243.
[11] ROHWERDER T, GEHRKE T, KINZLER K, SAND W. Bioleaching review part A [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2003, 63(3): 239-248.
[12] da SILVA G. Relative importance of diffusion and reaction control during the bacterial and ferric sulphate leaching of zinc sulphide [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 73(3/4): 313-324.
[13] SHI Shao-yuan, FANG Zhao-heng, NI Jin-ren. Comparative study on the bioleaching of zinc sulphides [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2006, 41(2): 438-446.
[14] CRUNDWELL F K. Physical chemistry of bacterial leaching [M]// RAWLINGS D E ed. Biomining: Theory, microbes and industrial processes. New York: Springer, 1997: 177-200.
[15] GIAVENO A, LAVALLE L, CHIACCHIARINI P, DONATI E. Bioleaching of zinc from low-grade complex sulfide ores in an airlift by isolated Leptospirillum ferrooxidans [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 89(1/2): 117-126.
[16] CORDOBA E M, MUNOZ J A, BLAZQUEZ M L, GONZALEZ F, BALLESTER A. Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion. Part IV: The role of redox potential in the presence of mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93(3/4): 106-115.
[17] HIROYOSHI N, ARAI M, MIKI H, TSUNEKAWA M, HIRAJIMA T. A new reaction model for the catalytic effect of silver ions on chalcopyrite leaching in sulfuric acid solutions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2002, 63(3): 257-267.
[18] VILCOEZ J, INOUE C. Mathematical modeling of thermophilic bioleaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2009, 22(11): 951-960.
[19] KARAMANEV D, NIKOLOV L, MAMATARKOVA V. Rapid simultaneous quantitative determination of ferric and ferrous ions in drainage waters and similar solutions [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2002, 15(5): 341-346.
[20] HE Huan, XIA Jin-lan, YANG Yi, JIANG Hong-chen, XIAO Chun-qiao, ZHENG Lei, MA Chen-yan, ZHAO Yi-dong, QIU Guan-zhou. Sulfur speciation on the surface of chalcopyrite leached by Acidianus manzaensis [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 99(1/2): 45-50.
[21] PAKTUNC D, FOSTER A, HEALD S, LAFLAMME G. Speciation and characterization of arsenic in gold ores and cyanidation tailings using X-ray absorption spectroscopy [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(5): 969-983.
[22] KONISHI Y, NISHIMURA H, ASAI S. Bioleaching of sphalerite by the acidophilic thermophile Acidianus brierleyi [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1998, 47(2/3): 339-352.
[23] FOWLER T, CRUNDWELL F. Leaching of zinc sulfide by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: Bacterial oxidation of the sulfur product layer increases the rate of zinc sulfide dissolution at high concentrations of ferrous ions [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(12): 5285-5292.
(Edited by YANG Bing)
Foundation item: Project(50974140) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(VR-09157) supported by Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF) Public User Program, China
Received date: 2011-04-2; Accepted date: 2011-06-22
Corresponding author: XIA Jin-lan, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-731-88836944; E-mail: jlxia@csu.edu.cn