DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.09.08
铝/铜异种金属脉冲旁路耦合电弧MIG熔钎焊接头的组织与力学性能
石 玗,周相龙,朱 明,李 广,樊 丁
(兰州理工大学 省部共建有色金属先进加工与再利用国家重点实验室,兰州 730050)
摘 要:采用ER4047铝硅焊丝对5052铝合金与T2紫铜进行脉冲旁路耦合电弧MIG熔钎焊,并对接头显微组织、物相成分及力学性能进行分析。结果表明:通过控制焊接热输入可以获得成形良好的铝/铜熔钎焊搭接接头。焊接接头由铝侧熔合区、焊缝区和铜侧类钎焊区组成,其中铜侧类钎焊区可分为金属间化合物层区和Al-Cu共晶区两部分。焊缝区组织为珊瑚状Al-Cu共晶体均匀分布在α(Al)固溶体中;铜侧金属间化合物层主要由条块状Al2Cu组成。随着焊接热输入的增大,金属间化合物层的厚度在增大,而接头的抗拉强度先增大后减小;当熔化的焊丝及铝母材在铜母材上润湿良好并且焊缝与铜母材之间金属间化合物的厚度较小时,接头抗拉强度达到最大值,为167.7 MPa。
关键词:铝/铜异种金属;热输入;显微组织;金属间化合物;力学性能
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-09-1816-07 中图分类号:TG401 文献标志码:A
铜及其合金具有良好的导电、导热以及耐腐蚀性能,因此在电力电子以及空调制冷等行业得到了广泛的应用[1]。但是,我国铜储量并不丰富,需从国外大量进口,价格高。而铝及其合金储量大,产能过剩,价格低,同时也具有良好的导电和导热性能。因此,采用以铝代铜,或是部分取代铜不仅可以降低生产成本,而且有助于解决铝产能过剩的问题[2]。在电力电子和制冷构件的设计制造中采用铝/铜复合结构不仅能够节约材料、降低成本,而且可以充分发挥各自的性能优势[3]。而铝-铜异种金属的连接是铝/铜复合结构的设计和制造中的重要环节,目前铝/铜异种金属主要采用钎焊、压力焊、高能束焊等方法[4-10]来连接。钎焊和压力焊,虽然可以获得质量性能都较好的接头,但这些方法设备复杂、成本高、效率低并且焊接尺寸受到限制。熔钎焊方法的出现,能够较好的解决这一问题,现已成为异种难焊金属连接领域的研究热点。
铝铜熔钎焊过程中可以通过控制焊接热输入使低熔点的铝熔化而高熔点的铜不熔化,借助熔铝的润湿铺展来实现铝铜的连接。FENG等[11]采用AlCu5焊丝进行了1060铝合金和T2紫铜冷金属过渡(CMT)熔钎焊搭接试验,发现在铜/焊缝界面处由Al4Cu9、Al2Cu3和Al2Cu相组成的金属间化合物层,随着焊接热输入的增大,金属间化合物Al2Cu的厚度明显增大。接头最大载荷为0.983 kN,并断裂于铝板热影响区。周利等[12]采用Zn-2%Al药芯焊丝开展了铝/黄铜TIG熔钎焊搭接试验,发现在黄铜侧过渡区生成脆性的AlCu相,界面层中的金属间化合物主要由Al4Cu9和CuZn相组成。随焊接热输入的增大,界面层厚度先增大后减小,接头拉伸载荷也是先增大后减小。程东海等[13]采用Zn-5%Al钎料对LF6防锈铝和T2紫铜进行了等离子弧熔钎焊,搭接接头最大抗剪强度为175.5MPa,断裂于由Al2Cu和CuZn2组成的硬脆的金属间化合物层。董鹏等[14]采用激光深熔钎焊方法对3mm厚1060铝合金和T2紫铜进行对接,所得焊缝内含有硬脆的Al2Cu3和Al2Cu金属间化合物,接头拉伸时会断裂在铝母材或焊缝界面处。本文作者采用一种新型高效低热输入的电弧焊焊接方法,即脉冲旁路耦合电弧MIG焊[15],以ER4047铝硅焊丝为填充材料对5052铝合金和T2紫铜进行了搭接试验,并对接头显微组织和力学性能进行研究,为铝铜连接的实际应用提供参考。
1 实验
采用脉冲旁路耦合电弧MIG熔钎焊的方法,其原理如图1所示,在焊丝与工件的主路电弧中间并入TIG旁路电弧,从而对流入母材的电流进行分流。流经焊丝的焊接电流I是两部分电流之和,一部分是旁路电流Ibp,另一部分是流经母材电流Ibm,即I=Ibp+Ibm,焊接电流I可以保证焊丝能加热到较高的温度,同时通过调节旁路电流值又可以改变母材热输入,在母材输入电流很小的情况下仍能保持稳定的熔滴过渡。此外,利用该方法焊接铝铜异种金属时,铜板在阴极位置,阴极发热量小,也能减少热输入,并且铜的导热性极好,焊接过程中热量很难集中,这也保证了铜板在焊接过程中不被熔化。
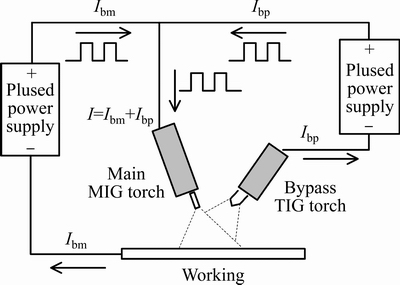
图1 脉冲旁路耦合电弧MIG熔钎焊电弧形态
Fig. 1 Shape of coupling arc of pulsed DE-GMAW
试验材料为150 mm×50 mm×1 mm 尺寸的5052铝合金和150 mm×50 mm×2 mm 尺寸的T2紫铜,填充材料为直径1.2 mm的ER4047 AlSi12焊丝。本试验采用铝板在上、铜板在下的搭接形式,搭接宽度为10 mm。
焊前,用钢丝刷对两种母材的表面进行打磨,去掉氧化膜,用丙酮擦拭待焊区域,去除灰尘、油污。焊接时,令主路焊枪和旁路焊枪之前的夹角为45°,钨极高度为5 mm,采用氩气作为保护气,主路氩气流量为20 L/min,旁路氩气流量为 5 L/min。焊接工艺参数:旁路、主路采用同步脉冲,脉冲频率 80 Hz,占空比为15%,焊接速度0.5 m/min,旁路电流固定为25 A,主路电流在15~65 A范围内调节,即焊接电流I为40~90 A。焊后,对在不同焊接电流下得到的搭接接头进行打磨处理,并沿垂直于焊接方向截取试样进行标准金相试样制备。
采用WDW-300J型电子拉伸试验机对接头力学性能进行测试,其加载速率为1 mm/min,并且每组数据测试3次,然后取平均值,拉伸试样尺寸如图2所示。采用JSM-5600LV低真空扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和能谱分析仪(EDS)对接头的显微组织和元素组成以及断口形貌进行观察和分析,并采用X射线衍射(XRD)仪对界面断口处物相进行分析。
图2 拉伸试样尺寸
Fig. 2 Dimension of tensile specimen (Unit: mm)
2 结果与及分析
2.1 铝/铜焊接接头成形
图3所示为不同焊接电流下所得接头表面形貌。当焊接电流为40 A时,由于焊接接头热输入较小,熔化的焊丝及铝母材没有完全铺展开来,局部出现未熔合现象,难以获得成形良好的接头。当焊接电流为50~70 A时,随着焊接电流的增大,熔化的焊丝及铝母材在铜母材表面的润湿性越来越好,所得焊缝表面越来越平整规则。当焊接电流为80~90 A时,由于焊接接头热输入较大,形成的焊缝较宽,气孔明显增多,局部出现咬边现象,甚至会产生热裂纹,这对焊缝强度产生不利的影响。
2.2 显微组织及物相分析
图4所示为典型的铝/铜Pulsed DE-MIG熔钎焊搭接接头截面的SEM像。图4(a)所示为焊接接头的整体形貌图,由图4(a)可知,焊接接头成形良好,无明显的裂纹,焊缝顶端存在少量的气孔,当热输入过低时铝和铜未熔合会出现黑色带状区域,如图4(a)中红色区域所示。由接头截面形貌可以看出,接头主要由3个区域组成:铝侧熔合区、焊缝区以及铜侧类钎焊区。图4(b)所示为铝侧熔合区组织。由图4(b)可知,铝侧熔合区界面清晰,柱状晶组织比较明显。由于焊接时电弧的作用,铜母材表面会出现局部熔化,并且铜在焊接不平衡结晶条件下极易向铝中的扩散,因此在焊缝中很容易生成铝铜共晶组织[16]。由图4(c)可知,焊缝区组织为灰色珊瑚状物质均匀分布于黑色的基体组织中。

图3 不同焊接电流下所得接头表面形貌
Fig. 3 Weld appearance of Al/Cu lap joint at various weld parameters
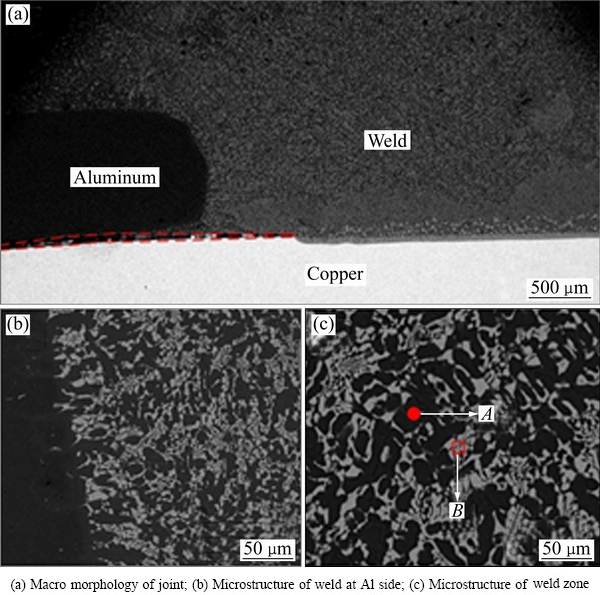
图4 典型焊接接头的SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of welding joint
黑色基体组织中Al、Cu、Si含量分别为92%、2.2%和5.8%(摩尔分数),由Al-Cu、Al-Si二元相图并结合文献[17]可知,该基体物质可能由α(Al)固溶体及一些Al-Si共晶体组成。灰色物质中Al、Cu含量分别为74.5%和24.2%(摩尔分数),可以推测出该物质为α(Al)和Al2Cu形成的共晶组织。
图5所示为不同焊接电流下所得接头中铜侧类钎焊区微观组织,其中又可以细分为:金属间化合物层区(Ⅰ)、Al-Cu共晶区(Ⅱ)、和焊缝区(Ⅲ) 3个区域。焊接过程中,铜母材吸收了金属液传递的能量,会向焊缝金属中溶解和扩散,同时可能存在铜母材少量熔化进入焊缝中;液态焊缝金属中的Al原子会向铜母材中扩散,从而形成以Al和Cu为主的条块状金属间化合物[13]。焊接电流为50 A时,金属间化合物层厚度在26 μm左右;焊接电流为60 A时,金属间化合物层厚度在32 μm左右;焊接电流为70 A时,金属间化合物层厚度在42 μm左右;焊接电流为80 A时,块状金属间化合物成倍增加,分布更广,尺寸大小不一。随焊接热输入的增大,金属间化合物层厚度明显增加,并且块状金属间化合物数量明显增多、尺寸明显增大,这可能是由于随着焊接热输入的提高导致铜母材部分熔化,在熔池内部形核并长大。在块状金属间化合物或Al-Cu共晶体之间可观察到黑色的块状析出物(图5(d)的C点所示)。经EDS分析表明,这些块状物可能为在焊缝凝固中从Al2Cu析出的Si。图6是图5(c)显微组织的局部放大图,可以观察到靠近铜侧还有一层平滑生长的反应层,厚度在2 μm左右。
为了进一步了解焊缝区各物质的组成,对其进行EDS分析,其结果如表1所列。根据D点EDS分析结果可以推断出条块状的金属间化合物为Al2Cu,其中固溶了一定量的Si原子。由E点和F点EDS分析结果可知,反应层中的成分复杂,主要由Al2Cu3和Al4Cu9两种金属间化合物相组成。
2.3 接头力学性能
图7所示为不同焊接电流下接头的抗拉强度。由图7可知,抗拉强度随着焊接电流的增大先增大后减小。焊接电流为40 A时,此时熔化的焊丝及铝母材在铜母材上没有完全润湿,其结合欠佳,接头的抗拉强度仅为130 MPa。焊接电流为50 A时,此时熔化的焊丝及铝母材在铜母材上润湿铺展较好,使得抗拉强度迅速增大。焊接电流为60 A时,此时熔化的焊丝及铝母材在铜母材上润湿铺展良好,使得接头抗拉强度达到最大值,为167.7 MPa。焊接电流为70 A时,此时熔化的焊丝及铝母材在铜母材上完全润湿铺展,形成较宽的焊缝,冶金结合较为牢固,另一方面,焊缝与铜母材之间金属间化合物层厚度明显增大,脆硬相的Al2Cu使得接头抗拉强度有所降低。焊接电流为80 A时,由于热输入过大,一方面,铜母材的熔化量增大,生成脆硬的Al2Cu相更多、更广;另一方面,局部区域可能会产生热裂纹,这些因素都使得接头抗拉强度急剧下降。
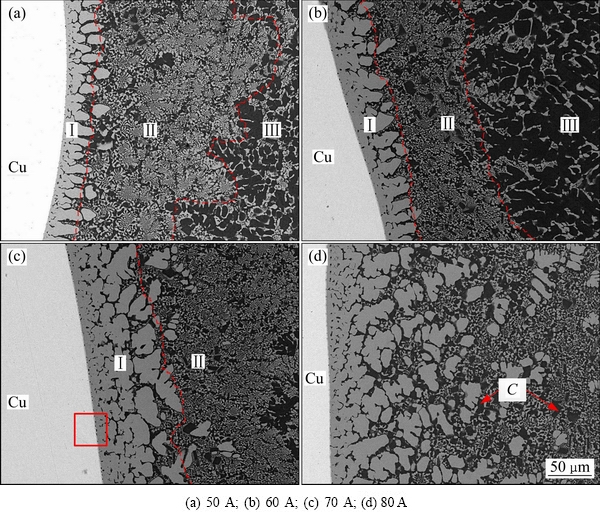
图5 不同焊接电流下所得接头铜侧类钎焊区的显微组织
Fig. 5 Microstructures of brazing area of Cu side in joints obtained at various welding currents

图6 图5(c)中显微组织局部放大图
Fig. 6 High magnification of microstructures in Fig. 5(c)
表1 图4~6所示位置的EDS分析结果
Table 1 EDS results of selected zone from Figs. 4-6

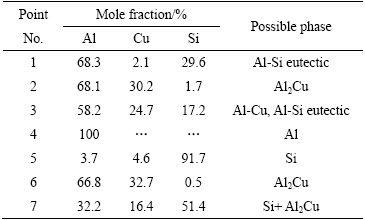
图8所示为焊接电流为50 A、70 A、80 A的铝/铜熔钎焊接头拉伸断口形貌。由图8(a)可知,断裂位置随着焊接热输入的增加而改变。当焊接电流为50 A时,接头断裂于铝侧熔合线附近,断口比较整齐。通过SEM观察,发现断口分布着许多夹杂和气孔,如图8(b)所示;并且断口由解离面和少量撕裂脊组成(见图8(c))。当焊接电流为70 A时,接头断裂于铝母材热影响区,并且有明显的颈缩现象。断口由滑移区和韧窝组成(见图8(d)),韧窝呈轴状,窝内存在更小的韧窝(见图8(e))。当焊接电流为80 A时,接头断裂于焊缝/铜界面处,由图8(f)可知,断口较为平整,分布着裂纹,从放大图可以看出断面为解理,并且断面上分布着黑色块状物质,对比图5(d)的显微组织,可以确定黑色物为析出的Si相。由于Si的存在,在外载作用下,应力容易集中,从而强度低。对不同断口位置进行EDS分析,结果如表2所列。为了进一步确认断口表面处的物相,对其进行了X射线衍射分析(见图9)。结果表明,由于金属间化合物层中块状Si的数量较少,且较分散,故未检测到Si相,仅为Cu和Al2Cu相。由此可以得出结论,接头断裂发生在Al2Cu相。
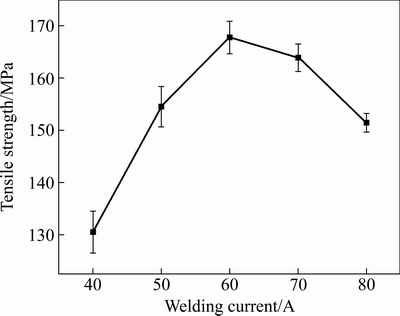
图7 不同焊接电流下接头的抗拉强度
Fig. 7 Tensile strength of joints at different welding currents
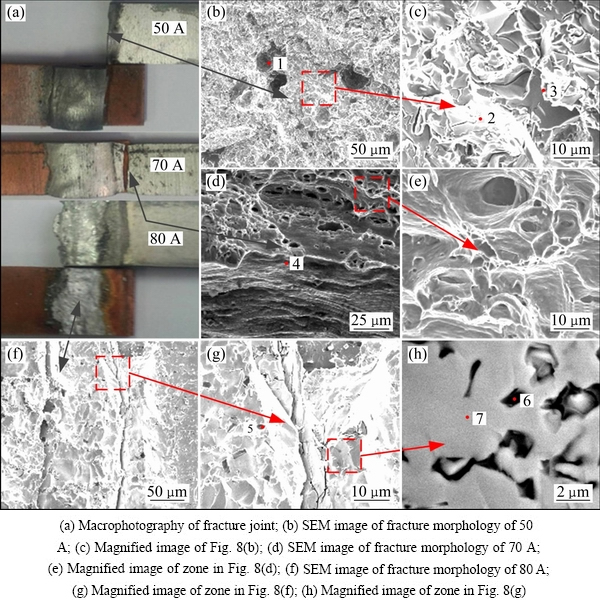
图8 典型试样的铝/铜熔钎焊接头拉伸断口形貌
Fig. 8 Fracture morphologies of joint in case
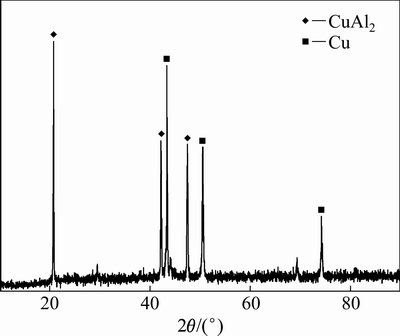
图9 界面断口处XRD谱
Fig. 9 XRD pattern of fractured surface at current of 80 A
表2 图8 中断口表面不同位置EDS分析结果
Table 2 EDS results of selected position at fracture surface shown in Fig. 8
3 结论
1) 采用脉冲旁路耦合电弧MIG熔钎焊方法可以实现Al/Cu异种金属连接,焊接电流为60~80 A时,搭接接头成形良好,焊缝平整规则。
2) Al/Cu异种金属熔钎焊接头可分为3个区域:铝侧熔合区、焊缝区以及铜侧类钎焊区。其中铜侧类钎焊区可分为金属间化合物层和Al-Cu共晶区两部分。焊缝区组织为珊瑚状Al-Cu共晶体,均匀分布在α(Al)固溶体中;铜侧金属间化合物层主要由条块状Al2Cu组成。随着焊接热输入的增大,金属间化合物层厚度明显增加。
3) 接头的抗拉强度随焊接热输入增大先增大后减小。当热输入较时,接头的抗拉强度随填充材料在铜母材上润湿铺展而增大;当热输入较大时,接头的抗拉强度随焊缝与铜母材之间金属间化合物层厚度增大而减小。
4) 当焊接电流为60 A时,所得接头抗拉强度最大,为167.7 MPa。接头拉伸时,在铝侧熔合线附近、铝母材热影响区及焊缝/铜界面处均有可能发生断裂,并且热输入对断裂有较大影响。
REFERENCES
[1] MAI T A, SPOWAGE A C. Characterisation of dissimilar joints in laser welding of steel-kovar, copper-steel and copper-aluminium[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 374(1): 224-233.
[2] 黄伯云. 我国有色金属材料现状及发展战略[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(5): 122-127.
HUANG Bai-yun. Status and developing strategy for China nonferrous metal materials industry[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(5): 122-127.
[3] 夏春智, 李亚江, 王 娟. Cu/Al异种金属连接的研究现状[J].焊接, 2008, 19(1): 17-20.
XIA Chun-zhi, LI Ya-jiang, WANG Juan. Research status of joining of Cu/Al dissimilar metals[J]. Welding & Joining, 2008, 19(1): 17-20.
[4] FENG J, XUE S. Growth behaviors of intermetallic compound layers in Cu/Al joints brazed with Zn-22Al and Zn-22Al-0.05 Ce filler metals[J]. Materials & Design, 2013(51): 907-915.
[5] JI Feng, XUE Song-bai, LOU Ji-yuan, LOU Yin-bin, WANG Shui-qing. Microstructure and properties of Cu/Al joints brazed with Zn-Al filler metals[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(2): 281-287.
[6] LEE W B, BANG K S, JUNG S B. Effects of intermetallic compound on the electrical and mechanical properties of friction welded Cu/Al bimetallic joints during annealing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 390(1): 212-219.
[7] LI Xia-wei, ZHANG Da-tong, CHENG Qiu, ZHANG Wen. Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar pure copper/1350 aluminum alloy butt joints by friction stir welding[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(6): 1298-1306.
[8] KUANG B B, SHEN Y F, CHEN W H, YAO X, XU H S, GAO J C, ZHANG J Q. The dissimilar friction stir lap welding of 1A99 Al to pure Cu using Zn as filler metal with “pinless” tool configuration[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 68(5): 54-62.
[9] ABBASI M, TAHERI A K, SALEHI M T. Growth rate of intermetallic compounds in Al/Cu bimetal produced by cold roll welding process[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2001, 319(1): 233-241.
[10] KRAETZSCH M, STANDFUSS J, KLOTZBACH A, KASPAR J, BRENNER B, BEYER E. Laser beam welding with high-frequency beam oscillation: Welding of dissimilar materials with brilliant fiber lasers[J]. Physics Procedia, 2011, 12:142-149.
[11] FENG J, LIU Y, SUN Q, LIU J, WU L. Microstructures and properties of aluminum-copper lap-welded joints by cold metal transfer technology[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2015, 17(10): 1480-1485.
[12] 周 利, 李志勇, 赵洪运, 谢 宇, 黄永宪, 冯吉才. 铝/黄铜异种金属TIG熔钎焊接头显微组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(9): 2389-2395.
ZHOU Li, LI Zhi-yong, ZHAO Hong-yun, XIE Yu, HUANG Yong-xian, FENG Ji-cai. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/brass dissimilar metals TIG welding-brazing joint[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(9): 2389-2395.
[13] 彭 迟, 程东海, 陈益平. 铝/铜异种材料填丝钨极氩弧焊对接接头的组织和性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(4): 975-981.
PENG Chi, CHENG Dong-hai, CHEN Yi-ping. Microstructure and properties of Al/Cu dissimilar materials TIG butt joints with filler wire[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(4): 975-981.
[14] 董 鹏, 陈凯华, 肖荣诗. 铝-铜异种金属激光深熔钎焊接头力学性能[J]. 中国激光, 2011, 38(6): 129-133.
DONG Peng, CHEN Kai-hua, XIAO Rong-shi. Mechanical properties of aluminum-copper joint by laser penetration brazing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2011, 38(6): 129-133.
[15] 石 玗, 温俊霞, 黄健康, 卢立晖, 樊 丁, 张裕明. 基于旁路耦合电弧的铝钢MIG熔钎焊研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2011, 47(16): 25-29.
SHI Yu, WEN Jun-xia, HUANG Jian-kang, LU Li-hui, FAN Ding, ZHANG Yu-ming. Study on DE-GMAW MIG-brazing method for bonding steel with aluminum[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 47(16): 25-29.
[16] CAI Z P, AI B Q, CAO R, LIN Q, CHEN J H. Microstructure and properties of aluminum AA6061-T6 to copper (Cu)-T2 joints by cold metal transfer jointing technology[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2016, 31(18): 2876-2887.
[17] LIU Y B, SUN Q J, WANG H,ZHANG H M, CAI S J, FENG J C. Effect of the axial external magnetic field on copper/aluminium arc weld joining[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2016, 21(6): 1-6.
Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/Cu dissimilar metals pulsed DE-MIG welding-brazing joint
SHI Yu, ZHOU Xiang-long, ZHU Ming, LI Guang, FAN Ding
(State Key Laboratory of Advanced Processing and Recycling of Nonferrous Metals, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou 730050, China)
Abstract: 5052 aluminum alloy and T2 copper dissimilar metals were welded using 4047 AlSi12 wire by pulsed DE-MIG welding-brazing. The microstructure, elements composition and mechanical properties of joint were studied. The results show that it is feasible to obtain a favorable welding-brazing joint of Al-Cu by controlling the welding heat input. The welding joint is composed of fusion zone of the aluminum side, the weld zone and brazing zone of the copper side which is divided into two parts, Al-Cu eutectic zone and Al-Cu IMC layer zone. The microstructure of the weld zone is coral Al-Cu eutectic distributed in α(Al) solid solution, and IMC layer of Cu side mainly consists of strip Al2Cu. The tensile strength of joint firstly increases, and then decreases with the increase of welding heat input. When the wettability of wire and aluminum on the copper is good, and the thickness of IMC layer between the welding seam and the Cu base metal is relatively small, the tensile strength of joint can reach up to 167.7 MPa.
Key words: Al/Cu dissimilar metal; heat input; microstructure; intermetallic compound; mechanical property
Foundation item: Project(51675256) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (SKLAB 020114208) supported by the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Advanced Processing and Recycling of Non-ferrous Metals, China; Project (J201201) supported by the Hong Liu Outstanding Talent Training Plan of Lanzhou University of Technology, China; Project (175R5RA107) supported by the Basic Research Innovation Group Plan of Gansu Province, China
Received date: 2016-07-21; Accepted date: 2017-01-02
Corresponding author: SHI Yu; Tel: +86-931-2972765; E-mail: shiyu@lut.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51675256);省部共建有色金属先进加工与再利用国家重点实验室开放基金课题(SKLAB 020114208);兰州理工大学红柳杰出人才培养计划项目(J201201);甘肃省基础研究创新群体计划(17JR5RA107)
收稿日期:2016-07-21;修订日期:2017-01-02
通信作者:石 玗,教授,博士;电话:0931-2972765;E-mail:shiyu@lut.cn