激光焊接ZK60变形镁合金的组织和力学性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第2期
论文作者:严红革 赵 嫱 陈 瓶 陈吉华 苏 斌
文章页码:389 - 396
Key words:ZK60 magnesium alloy; fine grain size; laser beam welding; heat affected zone; partially melted zone
摘 要:采用激光焊接技术成功焊接了2.0 mm厚ZK60变形镁合金板材并研究了焊接参数(激光功率和焊接速度)对接头组织和力学性能的影响。在优化工艺参数下,可以获得良好的焊接接头,其抗拉强度为300 MPa,伸长率为12.0%,分别高达母材的92.5%和65%。轧制板材晶粒细小且存在很多微细的析出相,对液化开裂具有抑制作用,从而没有观察到半熔化区(PMZ)的液化开裂现象。熔化区(FZ)具有等轴晶特征,平均晶粒粒径为8 μm,与热影响区(HAZ)组织特征相似。这种组织特征有助于获得较高的焊接效率。
Abstract: Fine-grained ZK60 magnesium alloy sheets of 2.0 mm in thickness were successfully joined by laser beam welding (LBW). The effects of welding parameters including laser power and welding speed on the microstructures and mechanical properties of the joints were investigated. A sound bead, with the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 300 MPa and elongation of 12.0%, up to 92.5% and 65% of those of the base metal, respectively, is obtained with the optimized welding parameters. No liquation cracking is visible in the partially melted zone (PMZ) owing to the inhibitory action of the fine dispersed precipitates and the fine-grained microstructure in the as-rolled magnesium alloy sheets. The fusion zone (FZ) is featured with the equiaxed dendritic grains of the average grain size about 8 μm, which are similar to those in the heat affected zone (HAZ), and this contributes to the relatively high joint efficiency.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 389-396
Hong-ge YAN1,2, Qiang ZHAO1,2, Ping CHEN1,2, Ji-hua CHEN1,2, Bin SU1,2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Spray Deposition Technology and Application, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
Received 8 January 2014; accepted 5 March 2014
Abstract: Fine-grained ZK60 magnesium alloy sheets of 2.0 mm in thickness were successfully joined by laser beam welding (LBW). The effects of welding parameters including laser power and welding speed on the microstructures and mechanical properties of the joints were investigated. A sound bead, with the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 300 MPa and elongation of 12.0%, up to 92.5% and 65% of those of the base metal, respectively, is obtained with the optimized welding parameters. No liquation cracking is visible in the partially melted zone (PMZ) owing to the inhibitory action of the fine dispersed precipitates and the fine-grained microstructure in the as-rolled magnesium alloy sheets. The fusion zone (FZ) is featured with the equiaxed dendritic grains of the average grain size about 8 μm, which are similar to those in the heat affected zone (HAZ), and this contributes to the relatively high joint efficiency.
Key words: ZK60 magnesium alloy; fine grain size; laser beam welding; heat affected zone; partially melted zone
1 Introduction
Magnesium alloys have become one of the most important structure materials recently due to their low density, high specific strength, excellent castability and superior performance in insulating electromagnetic interference, absorbing vibration and etc [1,2]. Compared with AZ (Mg-Al-Zn) series and AM (Mg-Al-Mn) series magnesium alloys, the ZK (Mg-Zn-Zr) series alloys show higher strength, better stress corrosion resistance and heat-treatability [3].
ZK60 magnesium alloy has excellent mechanical properties among all commercial magnesium alloys. The absorption energy per mass in the fine-grained ZK60 is twice higher than that of high strength aluminum alloys [4]. However, ZK series alloys with a high Zn content are difficult to be welded by conventional arc welding methods because of the high cracking susceptibility caused by the wide melting range and excessive heat input of the arc [5]. Especially, the ZK60 magnesium alloy has been considered to be a material that can hardly be welded [5,6]. Therefore, this alloy is not recommended for structural applications owing to the poor weldability, and it is significant to develop a reliable joining process for widening its application. High energy beam welding can eliminate the aforementioned shortcomings with its low input energy, narrow heat-affected zone (HAZ), high welding precision and high depth-to-width ratio [7]. In order to solve hot cracking of ZK series magnesium alloys with high Zn content during welding, laser beam welding (LBW) with filler strip was adopted by YU et al [8,9]. In the process, the solidification temperature range was reduced by changing chemical compositions in the weld pool, and through this way, cracks and pits in weld can be avoided effectively. However, a good weldability depends not only on the chemical compositions but also on the initial microstructure characteristics of the base metal. Yet by far, few studies have been conducted on the welding performance of the fine-grained ZK series magnesium alloy sheets.
The aim of this work is to explore the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of the laser beam welded joints in fine-grained ZK60 magnesium alloy sheets. The effects of microstructure characteristics and heat input on the quality of the joints are also analyzed.
2 Experimental
Fine-grained ZK60 (Mg-5.44Zn-0.63Zr, mass fraction, %) magnesium alloy sheets were adopted. The as-rolled ZK60 alloy plates with the dimensions of 100 mmx50 mmx2 mm were used in this work. Before welding, the surfaces of each sheet were cleaned using acetone to remove grease and residue, and then abraded using the abrasion wheel to avoid the influence of the oxides. Welding processes were conducted using a 6.0 kW continuous wave CO2 laser beam with the following features: mode, TEM01; divergence, <5 mrad; beam diameter on focusing optic, 16 mm; focused diameter, 0.25 mm. The focal length of the parabolic mirror used for focusing the laser beam was 150 mm, and the focal point of laser beam was fixed on the top surface of the workpiece. High purity argon (99.99%) was used to protect the face and the back of the weld pool with the constant flow rate of 12 and 9 L/min, respectively. During the autogenous LBW, the plates were clamped down to the fixture as a butt joint, and the variables used were laser power (p) (1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6 and 1.8 kW) and welding speed (v) (1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 and 5.0 m/min). After welding, the obtained welds were cut, polished, and etched with a solution of 5 g tartaric acid (C4H6O6)+100 mL water for microstructural examination by optical microscopy (OM, Leitz MM-6) and SEM using backscattering electrons (SEM, FEI QUANTA- 200).
The precipitate in the base metal was observed by TEM (JEM-3010). Mechanical properties were measured by the Instron 8032 tensile machine. The tensile fracture surfaces were observed by SEM (SEM, FEI QUANTA-200) using secondary electrons. The microhardness testing was conducted on a HV hardness tester (401 MV. A).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructures and mechanical properties of base metal
Our research group has prepared high-performance wrought magnesium alloy sheets by high strain rate rolling, with the average grain size less than 5 μm [10-12]. The microstructure of the base metal, produced by high strain rate rolling (HSRR) [12] at 300 °C with a reduction of 80% for one pass, is shown in Fig. 1. The grains of the base metal are uniform and the average grain size is about 4 μm. The original grain boundaries (GBs) are elongated along the rolling direction (RD), and the extent of dynamic recrystallization (DRX) is obviously enhanced since DRX is activated at almost all the GBs and twins. The volume fraction of the DRXed grains is about 90%. The engineering stress-strain curve at ambient temperature of the base metal is shown in Fig. 2. The ultimate tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of the as-rolled plate are 325 MPa, 300 MPa and 19.0%, respectively.

Fig. 1 Microstructure of base metal
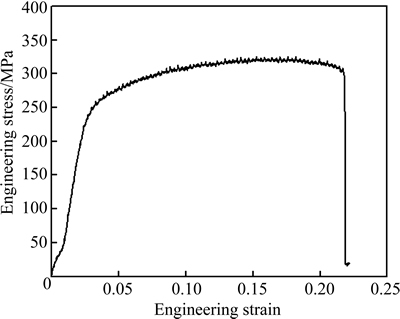
Fig. 2 Stress-strain curve of base metal
3.2 Appearance of weld
The cross-sections of the autogenously laser beam welded joints of the fine-grained ZK60 alloy under different parameters are shown in Fig. 3. The ZK60 plates were successfully joined under most conditions. It is evident that most of them are completely penetrated. The average width of the weld bead decreases with increasing the welding speed, and it also increases with increasing the laser power. Weld beads of the material are relatively wide with the welding speed of 2 m/min, and there are craters in the fusion zone caused by vaporization due to the over high heat input, especially in the welding speed of 2 m/min and the laser power of 1.8 kW. When the welding speed is 4 m/min, weld beads have a uniform width on the top, the middle, and at the bottom. The welds are not completely penetrated when the welding speed is up to 5 m/min because of the low heat input. As seen from Fig. 3, some pores are visible in the weld when the welding speed is 5 m/min. Since the solubility of the gas in liquid metal decreases upon cooling, it is released from solution in the form of bubbles. In the weld pool, buoyant bubbles formed in the liquid must overcome the surface tension of molten metal to float out if they attempt to rise. The cooling rate increases with increasing the welding speed, and thus at higher welding speed, because of rapid solidification during LBW, the bubbles have not enough time and buoyancy to float out [13,14].
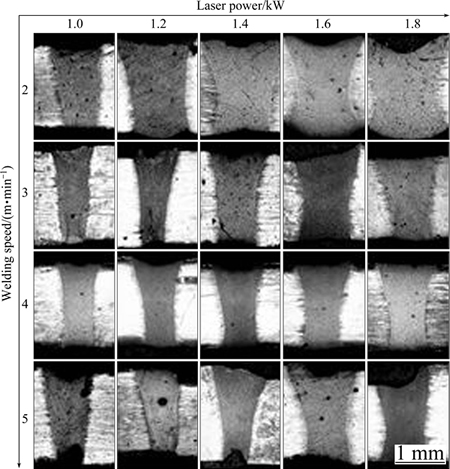
Fig. 3 Cross-sectional morphologies of autogenously laser beam welded joints under different welding parameters
3.3 Mechanical properties of welding joints
Tensile testing was conducted at room temperature to determine the strength of the joints and analyze the fracture features. Mechanical properties of the joints welded under different welding conditions are shown in Fig. 3. It is obvious that both the welding speed and the laser power have significant effects on the penetration rate of the base metal. As shown in Fig. 4(a), the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and the elongation increase when the welding speed rises from 1 to 4 m/min while decrease when the welding speed is higher than 4 m/min. Figure 4(b) shows a change trend of UTS and elongation according to laser power. As we can see, UTS and elongation increase when the laser power increases from 1.0 to 1.4 kW and then decrease when the laser power is higher than 1.4 kW. These phenomena can be explained by the results of macrostructure and microstructure observations. Firstly, craters will occur in the fusion zone if the welding speed is too low (in Fig. 3). On the contrary, a relatively high welding speed may result in a inadequate penetration and deteriorated mechanical properties of the joints. Secondly, a higher laser power will cause weld widening and other defects. These defects will lead to severe stress concentration and the grains in the fusion zone become coarser with decreasing the welding speed. It was reported that the harmful influence of stress concentration and grain coarsening on the UTS reached at least 13% and 9%, respectively [15,16]. Specially, stress concentration caused by some welding defects is fatal, and thus the as-welded samples with the laser power of 1.8 kW are characteristics of the relatively lower UTS values. As shown in Fig. 4, the optimum weld conditions can be obtained with the laser power of 1.4 kW and the welding speed of 4.0 m/min for the as-rolled fine-grained ZK60 magnesium alloy in this work. The highest UTS of the welded joint is about 300 MPa, which is up to 92.5% of that of the base metal, and the elongation of the specimen is about 12%, approximately 65% of that of the base metal. Based on the UTS, the as-welded samples in the work exhibit a higher joint efficiency than that in the Welding Handbook [5] and that reported in the literature [8]. However, the highest UTS of the AZ31B welded joint is about 212 MPa, which is up to 98.6% of that of the base metal, and the elongation of the specimen is about 12.1%, approximately 82.3% of that of the base metal [17].
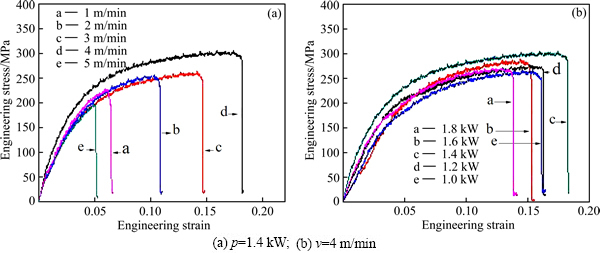
Fig. 4 Stress-strain curves of laser welded wrought fine-grained ZK60 alloy sheets under different welding conditions
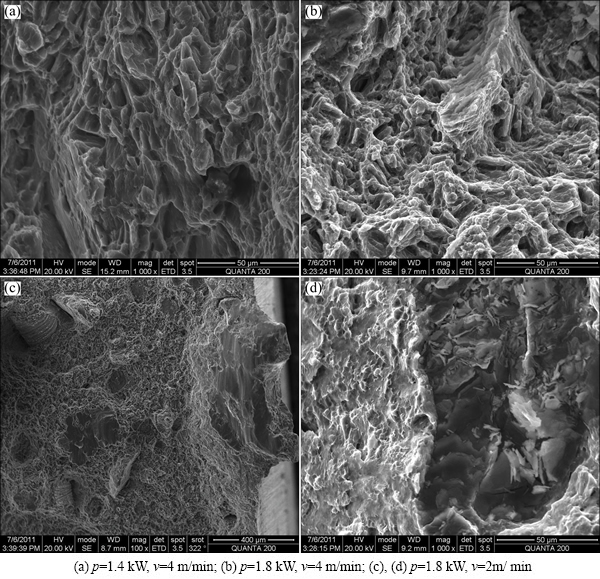
Fig. 5 SEM fractographs of joints
The fracture generally occurs in the fusion zone of the joint. The typical secondary electron images of the tensile fracture are shown in Fig. 5. As seen from Fig. 5(a), a large number of dimples can be seen in ZK60 with the laser power and the welding speed of 1.4 kW and 4 m/min, respectively, indicating that the fracture is characteristic of ductility. As shown in Fig. 5(b), the fracture of ZK60 is characteristic of quasi-cleavage with the laser power of 1.8 kW and the welding speed of 4 m/min. There are several tearing ridges in the local positions, and some dimples can also be clearly observed. Therefore, it can be concluded that there is a mixed fracture mode for the ZK60 under this condition. As seen from Figs. 5(c) and (d), the ZK60 alloy exhibits cleavage fracture when the laser power is 1.8 kW and the welding speed is 2 m/min. As shown in Fig. 5(c), some scallops are visible in the upper part of the weld under the high heat input. A fairly high temperature occurs on the surface of molten pool due to the high power density of the focused laser beam. Consequently, the high vapour pressure elements in the weld pool of ZK60, such as Mg and Zn, suffer heavy losses by evaporation during LBW, and thus, scallops occur because of filler insufficient [8]. The scallops increase when the welding speed decreases. As seen from Fig. 3, although scallops appear almost in all welds, it can be effectively reduced under proper welding processes. Mechanical properties of the welding joints can be improved under the optimized parameters. It can be concluded that the heat input can not be too high for welding of the ZK60 magnesium alloy. Microhardness was measured on the cross-section of the welded joint.
The hardness distribution in the middle of the penetration is presented in Fig. 6 (p=1.4 kW, v=4 m/min). The hardness near the fusion boundary appears to be the maximum value, and the hardness in the partially melted zone (PMZ) decreases with the increase of distance from fusion line. Besides, the hardness in HAZ and fusion center is slightly lower than that in base metal.
3.4 Microstructures of welding joint
According to the results of tensile testing, the welded samples with the welding speed of 4 m/min and the laser power of 1.4 kW were selected for microstructural examination. The microstructure evolutions of the welding joint are shown in Figs. 7-9. As seen from Fig. 8(a), the microstructure of the fusion boundary consists of three kinds of grains, i.e., cellular, columnar dendritic and equiaxed dendritic. The cellular and columnar dendritic grains only locate at a very narrow zone adjacent to the fusion boundary, while the equiaxed dendritic grains are dominant in the fusion zone. According to the theory of welding metallurgy [18], the G/R value (where G is the temperature gradient and R is the growth rate) decreases from the fusion line toward the center line of the fusion zone. In fact, G and R are determined by heat input and the welding speed during the welding process. Under the optimum welding condition, the average grain size in the FZ is about (8±0.5) μm.
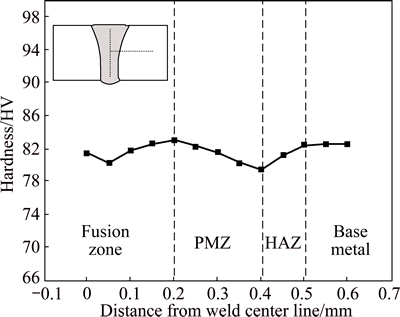
Fig. 6 Hardness profile of joint
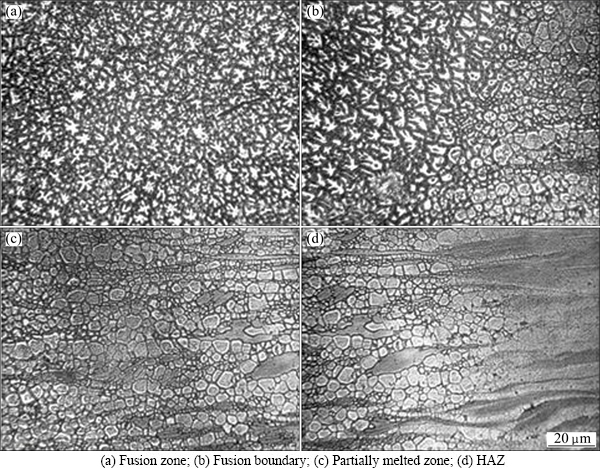

Fig. 7 Microstructure evolutions of welded joint
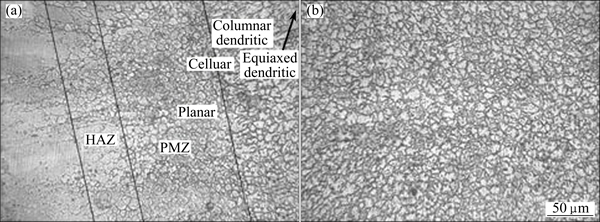
Fig. 8 Grain morphology in fusion boundary (a) and in fusion zone center (b) of welded joint
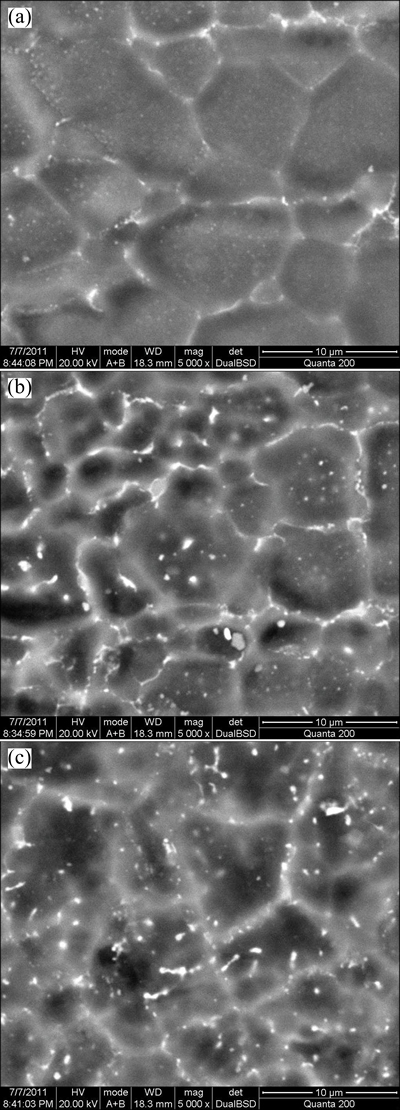
Fig. 9 SEM images in HAZ (a), PMZ (b) and fusion zone (c)
The PMZ is the area immediately outside the weld metal where liquation can occur during welding [18]. According to the Mg-Zn phase diagram, the liquid-solid dual-phase temperature range of ZK60 is very wide [9].
As seen from Fig. 7(c) and Fig. 8(a), it can be seen that there are a few dark-etching particles distributed within grains in the PMZ, demonstrating that liquation occurs in the grain interior, but not at the GBs, and no liquation cracking is visible in the PMZ during welding, which indicates that cracks in the weld can be avoided by LBW. Continuous coarse precipitates distributing along GBs and among dendritic arms would weaken the anticracking ability of the weld metal [8]. As seen from Fig. 9(b), lots of precipitates can be observed within grains and along GBs in the PMZ, and the quantity decreases as the distance from the fusion line increases, so does the hardness. As seen from Fig. 9(a), only a few precipitates distribute along the GBs in HAZ and no obvious precipitates are visible within the grains. The grain size in both HAZ (Fig. 7(d)) and the fusion center (Fig. 7(a)) is larger than that in the base metal. However, the grain size in HAZ increases as the distance from the base metal increases and coarse grains have a bad effect on the hardness. Most fractures mentioned in this work occur in the fusion zone of the joint since the weld has a typical cast structure, which indicates that the HAZ is no longer the weakest location. It is reflected by the narrow width of the HAZ shown in Fig. 8(a). As seen from Fig. 10, the size of the precipitates which are dispersive in the fine-grained ZK60 magnesium alloy sheets is about 25.0-50.0 nm. Although precipitates liquation will happen in the PMZ, liquation cracking will not appear because there is no obvious liquid film formed at the GBs owing to the small size and discontinuity of precipitates. Furthermore, the finer the grains are, more the GB area is and hence the less concentrated the impurities or low-melting-point segregates are at the GB. Consequently, a base metal with finer grains is expected to be less susceptible to liquation cracking in the PMZ.
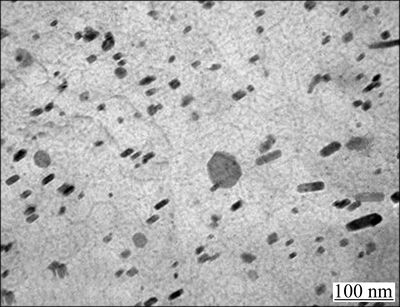
Fig. 10 TEM images in base metal
The presented experimental results demonstrate that refining precipitates and grains in the ZK60 magnesium alloys is an effective way to inhibit liquation cracking.
As shown in Fig. 7(d) and Fig. 8(a), the width of the HAZ is about 50 μm. The grain size is nonuniform without obvious grain coarsening. Some fine grains distribute around the large grains due to the recrystallization during thermal cycles of laser welding. The largest grain in the HAZ is only about 8.0 μm in size, and almost all the grains have the same size in the fusion center. No obvious difference in the grain size is detected from the fusion center to the HAZ and the joint exhibits a high joint efficiency. The research on the mechanism of microstructural stability is still under work. The reasons may be as follows: Firstly, the DRX is activated at nearly all the GBs and twins of the fine-grained magnesium alloy sheets. The stored strain energy is released during rolling. In the low-energy state, the plate has a good microstructural stability. Secondly, because of the low heat input and the high cooling rate in LBW, there is no enough time for grain coarsening. Thirdly, as the stored strain energy in the unannealed sheets is released along with the activating of DRX in the HAZ, the grain coarsening in the HAZ is not obvious. This is also the reason why the HAZ width is narrow. So, refining grains and using as-rolled microstructure are effective measures for inhibiting grain growth in the HAZ during welding.
4 Conclusions
1) The fine-grained ZK60 alloy sheets of 2 mm in thickness can be autogenously laser welded. The optimum welding can be obtained with the laser power of 1.4 kW and the welding speed of 4.0 m/min. The joints are characteristics of the highest UTS of 300 MPa and good elongation of 12%, which are up to 92.5% and 65% of the base metal, respectively.
2) Fine dispersed precipitates and fine grains of the as-rolled magnesium alloy sheets can inhibit the generation of liquation cracking in the PMZ. The complete dynamic recrystallization microstructures in the base metal contribute to the good heat stability in the HAZ.
3) The fusion zone is characteristic of equiaxed dendritic grains of about 8 μm in size, and no severe grain coarsening occurs in the zone adjacent to the fusion boundary. Under the optimum welding condition, the grain size in the HAZ grows from 4 to 8 μm. A high joint efficiency is obtained for there is no obvious difference in the grain size detected from the fusion center to the HAZ.
References
[1] CAO X, JAHAZI M, IMMARIGEON J P, WALLACE W. A review of laser welding techniques for magnesium alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 171 (2): 188-204.
[2] YANG Z, LI J P, ZHANG J X. Review on research and development of magnesium alloys [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008, 21(5): 313-328.
[3] WANG C Y, WANG X J, CHANG H, WU K, ZHENG M Y. Processing maps for hot working of ZK60 magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 464: 52-58.
[4] MUKAI T, YAMSNOI M, WATANABE H, ISHIKAWA K, HIGASHI K. Effect of grain refinement on tensile ductility in ZK60 magnesium alloy under dynamic loading [J]. Materials Transactions, 2001, 42(7): 1176-1181.
[5] KEARNS W H. Metals and their weldability in welding handbook [M]. Miami: American Welding Society, 1982: 396-398.
[6] OATES W R. Welding handbook [M]. Florida: American Welding Society, 1996: 121-162.
[7] DRAUGELATES U, SCHRAM A, BOUAIFI B, KETTLER C. Jointing technologies for magnesium alloys [C]//MORDIKE B, KAISER K U. Magnesium Alloys and their Applications. Wolfsburg: Werkstoff-Informations Gesellschaft, 1998: 29-35.
[8] YU Z H, YAN H G, CHEN S J, CHEN J H, ZENG P L. Method for welding highly crack susceptible magnesium alloy ZK60 [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2010, 15(5): 354-360.
[9] YU Z H, YAN H G, CHEN J H, WU Y Z. Effect of Zn content on the microstructures and mechanical properties of laser beam-welded ZK series magnesium alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2010, 45(14): 3797-3803.
[10] ZHU S Q, YAN H G, CHEN J H, WU Y Z, LIZ J Z, SU B, DU Y G, LIAO X Z. Feasibility of high strain-rate rolling of a magnesium alloy across a wide temperature range [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 67: 404-407.
[11] ZHU S Q, YAN H G, LIU J Z, CHEN J H, CHEN J H, WU Y Z, DU Y G, LIAO X Z. Fabrication of Mg-Al-Zn-Mn alloy sheets with homogeneous fine-grained structures using high strain-rate rolling in a wide temperature range [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 559(1): 766-772.
[12] ZHU S Q, YAN H G, CHEN J H, WU Y Z, LIU J Z, TIAN J. Effect of twinning and dynamic recrystallization on the high strain rate rolling process [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 63(10): 985-988.
[13] ZHAO H, DEBROY T. Pore formation during laser beam welding of die-cast magnesium alloy AM60B-Mechanism and remedy [J]. Welding Journal, 2001, 80(8): 204-210.
[14] ROBERT W, MESSLER J. Principles of welding [M]. New York: Wiley, 1999: 326-327.
[15] CHI C T, CHAO C G, LIU T F, LEE C H. Aluminum element effect for electron beam welding of similar and dissimilar magnesium– aluminum–zinc alloys [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56: 733-736.
[16] CHI C T, CHAO C G, LIU T F. Optimal parameters for low and high voltage electron beam welding of AZ series magnesium alloys and mechanism of weld shape and pore formation [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2008, 13(2): 199-211.
[17] PADMANABAN G, BALASUBRAMANIAN V. Effects of laser beam welding parameters on mechanical properties and microstructure of AZ31B magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(9): 1917-1924.
[18] KOU S. Welding metallurgy [M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2002: 263-430.
严红革1,2,赵 嫱1,2,陈 瓶1,2,陈吉华1,2,苏 斌1,2
1. 湖南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410082;
2. 湖南大学 喷射沉积技术及应用湖南省重点实验室,长沙 410082
摘 要:采用激光焊接技术成功焊接了2.0 mm厚ZK60变形镁合金板材并研究了焊接参数(激光功率和焊接速度)对接头组织和力学性能的影响。在优化工艺参数下,可以获得良好的焊接接头,其抗拉强度为300 MPa,伸长率为12.0%,分别高达母材的92.5%和65%。轧制板材晶粒细小且存在很多微细的析出相,对液化开裂具有抑制作用,从而没有观察到半熔化区(PMZ)的液化开裂现象。熔化区(FZ)具有等轴晶特征,平均晶粒粒径为8 μm,与热影响区(HAZ)组织特征相似。这种组织特征有助于获得较高的焊接效率。
关键词:ZK60镁合金;细晶;激光焊接;热影响区;半熔化区
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (51274092) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (20120161110040) supported by the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China
Corresponding author: Qiang ZHAO; Tel: +86-731-88664005; E-mail: yanhg68@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63615-9

